RIOK1/2 Negatively Regulates the Antiviral Response by Targeting TBK1 in Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Fish, Cell Lines, and Viral Strains
2.2. Plasmids
2.3. Subcellular Localization Assays
2.4. Transfection, Luciferase Activity Assay, and RT-PCR
2.5. Antiviral Activity Analysis
2.6. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) and Western Blot (WB)
2.7. Data Collection and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. PfRIOK1/2 Negatively Regulates the IFN Response by Targeting the RLR Pathway
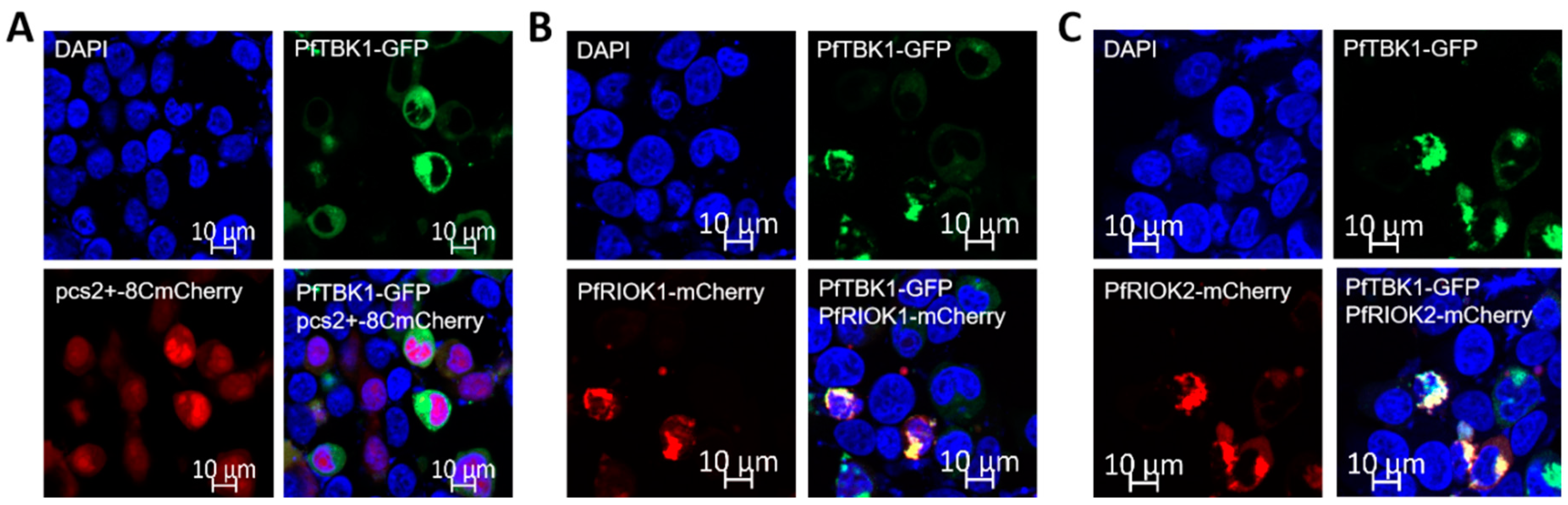
3.2. Co-Localization of PfRIOK1/2 with PfTBK1
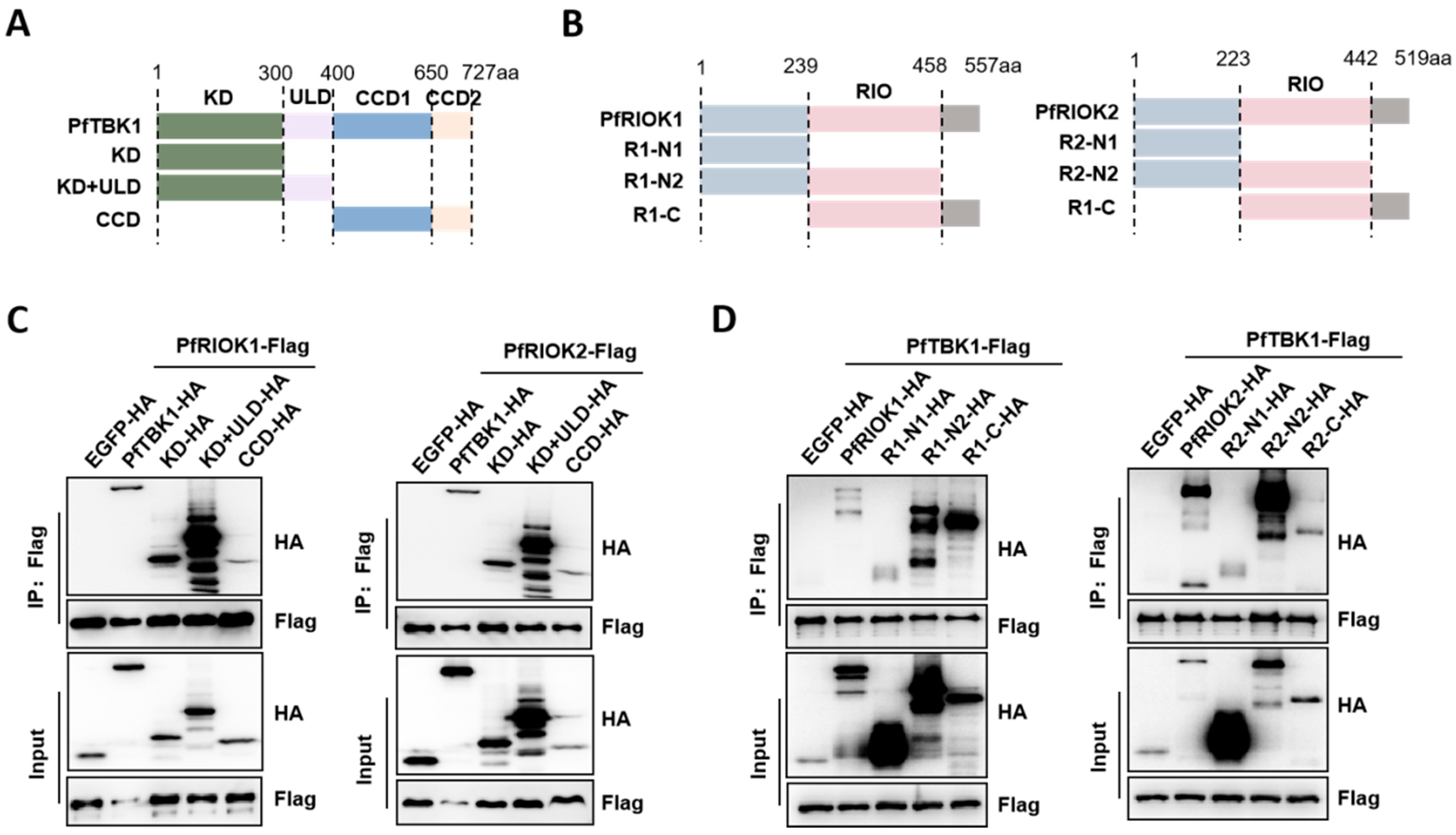
3.3. Interaction of PfRIOK1/2 with PfTBK1
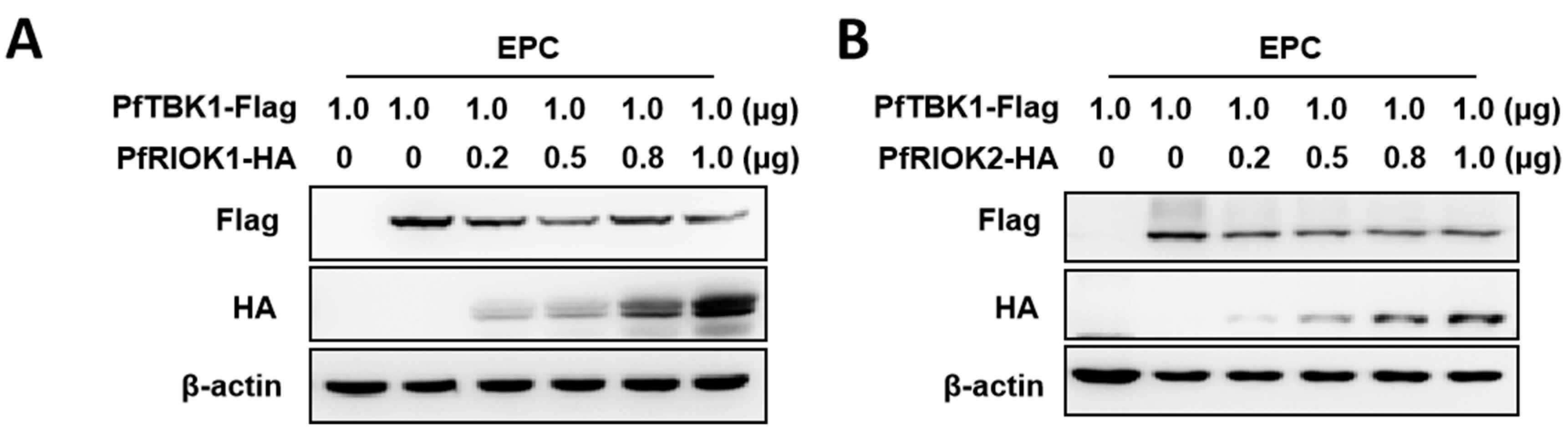
3.4. PfRIOK1/2 Degrade PfTBK1 Protein
3.5. PfRIOK1/2 Inhibits PFTBK1-Mediated Antiviral Response
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diamond, M.S.; Kanneganti, T.-D. Innate immunity: The first line of defense against SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platanias, L.C. Mechanisms of type-I- and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onomoto, K.; Onoguchi, K.; Yoneyama, M. Regulation of RIG-I-like receptor-mediated signaling: Interaction between host and viral factors. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chathuranga, K.; Weerawardhana, A.; Dodantenna, N.; Lee, J.-S. Regulation of antiviral innate immune signaling and viral evasion following viral genome sensing. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1647–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Shi, W.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; Qi, A.; Yang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Yang, D.; Song, N.; Song, B.; et al. Chapter One—RIG-I-like receptors: Molecular mechanism of activation and signaling. In Advances in Immunology; Alt, F.W., Murphy, K.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; Volume 158, pp. 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Bakshi, S.; Taylor, J.; Strickson, S.; McCartney, T.; Cohen, P. Identification of TBK1 complexes required for the phosphorylation of IRF3 and the production of interferon β. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lei, X.; Jiang, Z.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Cellular nucleic acid-binding protein is essential for type I interferon-mediated immunity to RNA virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2100383118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhol, N.K.; Bhanjadeo, M.M.; Singh, A.K.; Dash, U.C.; Ojha, R.R.; Majhi, S.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. The interplay between cytokines, inflammation, and antioxidants: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic potentials of various antioxidants and anti-cytokine compounds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanks, S.K.; Quinn, A.M.; Hunter, T. The protein kinase family: Conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science 1988, 241, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.B.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damizia, M.; Moretta, G.M.; De Wulf, P. The RioK1 network determines p53 activity at multiple levels. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messling, J.E.; Peña-Rømer, I.; Moroni, A.S.; Bruestl, S.; Helin, K. RIO-kinase 2 is essential for hematopoiesis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0300623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xie, L.; Pan, J.; He, Y.; Wang, E.; Wu, H.; Xiao, J.; Feng, H. Black carp RIOK3 suppresses MDA5-mediated IFN signaling in the antiviral innate immunity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2023, 149, 105059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Ko, W.C.; Chen, C.S.; Chen, P.L. RIOK-1 Is a Suppressor of the p38 MAPK Innate Immune Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandadi, M.; Dobi, A.; Malhotra, S.V. A role for RIO kinases in the crosshair of cancer research and therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.Q.; Lok, J.B.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Stoltzfus, J.D.; Gasser, R.B.; He, S.Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, J.L.; et al. Structural and developmental expression of Ss-riok-2, an RIO protein kinase encoding gene of Strongyloides stercoralis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; De Jesus, P.D.; Su, V.; Han, S.; Gong, D.; Wu, N.C.; Tian, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, T.T.; Chanda, S.K.; et al. RIOK3 is an adaptor protein required for IRF3-mediated antiviral type I interferon production. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7987–7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Dan, C.; Gong, X.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Qu, Z.L.; Sun, H.Y.; An, L.L.; Guo, W.H.; Mei, J.; Gui, J.F.; et al. Yellow catfish RIO kinases (RIOKs) negatively regulate fish interferon-mediated antiviral response. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2023, 142, 104656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Zhang, Q.-M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Gui, J.-F. Zebrafish IRF1 Regulates IFN Antiviral Response through Binding to IFNϕ1 and IFNϕ3 Promoters Downstream of MyD88 Signaling. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gong, X.-Y.; Li, Y.-L.; Dan, C.; Gui, J.-F.; Zhang, Y.-B. Characterization of DNA Binding and Nuclear Retention Identifies Zebrafish IRF11 as a Positive Regulator of IFN Antiviral Response. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Zhao, X.; Gong, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Gui, J.-F.; Zhang, Y.-B. FTRCA1, a Species-Specific Member of finTRIM Family, Negatively Regulates Fish IFN Response through Autophage-Lysosomal Degradation of TBK1. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 2407–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-M.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.-L.; Qu, Z.-L.; Li, Z.; Dan, C.; Gui, J.-F.; Zhang, Y.-B. LGP2 is essential for zebrafish survival through dual regulation of IFN antiviral response. iScience 2022, 25, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsili, G.; Perrotti, E.; Remoli, A.L.; Acchioni, C.; Sgarbanti, M.; Battistini, A. IFN Regulatory Factors and Antiviral Innate Immunity: How Viruses Can Get Better. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016, 36, 414–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Dan, C.; Gong, X.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Qu, Z.L.; Sun, H.Y.; An, L.L.; Guo, W.H.; Gui, J.F.; Zhang, Y.B. Zebrafish MARCH8 downregulates fish IFN response by targeting MITA and TBK1 for protein degradation. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 135, 104485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wu, M. Pattern recognition receptors in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.M.; Zhang, L.; Long, Z.; Zhao, X.; Ying, Y.R.; Xiao, T.Y.; Xiong, S.T. TBK1 upregulates the interferon response against virus by the TBK1-IRF3/7 axis in yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 144, 109272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, C.; Jia, S.; Deng, H.; Tang, J.; Sun, X.; Zeng, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; et al. Dual modifying of MAVS at lysine 7 by SIRT3-catalyzed deacetylation and SIRT5-catalyzed desuccinylation orchestrates antiviral innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2314201121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRonde-LeBlanc, N.; Wlodawer, A. The RIO kinases: An atypical protein kinase family required for ribosome biogenesis and cell cycle progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1754, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handle, F.; Puhr, M.; Gruber, M.; Andolfi, C.; Schäfer, G.; Klocker, H.; Haybaeck, J.; De Wulf, P.; Culig, Z. The Oncogenic Protein Kinase/ATPase RIOK1 Is Up-Regulated via the c-myc/E2F Transcription Factor Axis in Prostate Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 193, 1284–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, K.J.; Selfors, L.M.; Bui, J.; Reynolds, A.; Leake, D.; Khvorova, A.; Brugge, J.S. Identification of genes that regulate epithelial cell migration using an siRNA screening approach. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Primer Name | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| EPC-β-actin-RT-F | CAGATCATGTTTGAGACC |
| EPC-β-actin-RT-R | ATTGCCAATGGTGATGAC |
| EPC-mx-F | GGCTGGAGCAGGTGTTGGTATC |
| EPC-mx-R | TCCACCAGGTCCGGCTTTGTTAA |
| EPC-ifn-F | ATGAAAACTCAAATGTGGACGTA |
| EPC-ifn-R | GATAGTTTCCACCCATTTCCTTAA |
| EPC-viperin-F | AGCGAGGCTTACGACTTCTG |
| EPC-viperin-R | GCACCAACTCTCCCAGAAAA |
| SVCV-N-F | GGTGCGAGTAGAAGACATCCCCG |
| SVCV-N-R | GTAATTCCCATCATTGCCCCAGAC |
| SVCV-L-F | CAAGTTCACAATCGGGAAGACGC |
| SVCV-L-R | CCAGTTGCTTGTTGGCTTATCCG |
| SVCV-G-F | CCATTCTGTTCATTTGGAGCCGTA |
| SVCV-G-R | AATTTCATTCGACAAGACCCCC |
| Pfriok2-RT-F | GGAAACCAAATGGGTGTCGGC |
| Pfriok2-RT-R | GTCCACTGGCTTTGGAACAGG |
| Pfriok1-RT-F | CTAAACGCTACGCTGCGATGC |
| Pfriok1-RT-R | CCACCGTCGCTCTATCAGAC |
| PfRIOK1-EcoRV-F | GTGGAATTCTGCAGATATGTCTCAGATTGTCCTGGG |
| PfRIOK1-EcoRV-R | GCCACTGTGCTGGATTCTTCCTTTCTTCATCTTGGC |
| PfRIOK2-EcoRV-F | GTGGAATTCTGCAGATATGGGGAAGTTAAACGTCGTT |
| PfRIOK2-EcoRV-R | GCCACTGTGCTGGATTCCCCAGAACTGGGCTGC |
| PfTBK1-F | GTGGAATTCTGCAGATATGCAGAGTACGGCCAATTA |
| PfTBK1-R | CGCCACTGTGCTGGATTCACATCCGCTCCACTGTCC |
| PfRIOK1-BamHI-F | CTTGTTCTTTTTGCAGATGTCTCAGATTGTCCTGGG |
| PfRIOK1-BamHI-R | GCGCCACTAGTGGATCCTCTTCCTTTCTTCATCTTGGC |
| PfRIOK2-BamHI-F | CTTGTTCTTTTTGCAGATGGGGAAGTTAAACGTCGTTG |
| PfRIOK2-BamHI-R | GCGCCACTAGTGGATCCTCCCCAGAACTGGGCTGCTTC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, K.; Huang, J.; Gui, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, S. RIOK1/2 Negatively Regulates the Antiviral Response by Targeting TBK1 in Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Fishes 2025, 10, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10010006
Liu K, Huang J, Gui Y, Li Q, Zhang L, Xiong S. RIOK1/2 Negatively Regulates the Antiviral Response by Targeting TBK1 in Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Fishes. 2025; 10(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Kejun, Jiayang Huang, Yuting Gui, Qian Li, Lei Zhang, and Shuting Xiong. 2025. "RIOK1/2 Negatively Regulates the Antiviral Response by Targeting TBK1 in Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco)" Fishes 10, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10010006
APA StyleLiu, K., Huang, J., Gui, Y., Li, Q., Zhang, L., & Xiong, S. (2025). RIOK1/2 Negatively Regulates the Antiviral Response by Targeting TBK1 in Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Fishes, 10(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10010006





