Construction of a Mathematical Model of the Irregular Plantar and Complex Morphology of Mallard Foot and the Bionic Design of a High-Traction Wheel Grouser
Abstract
1. Introduction
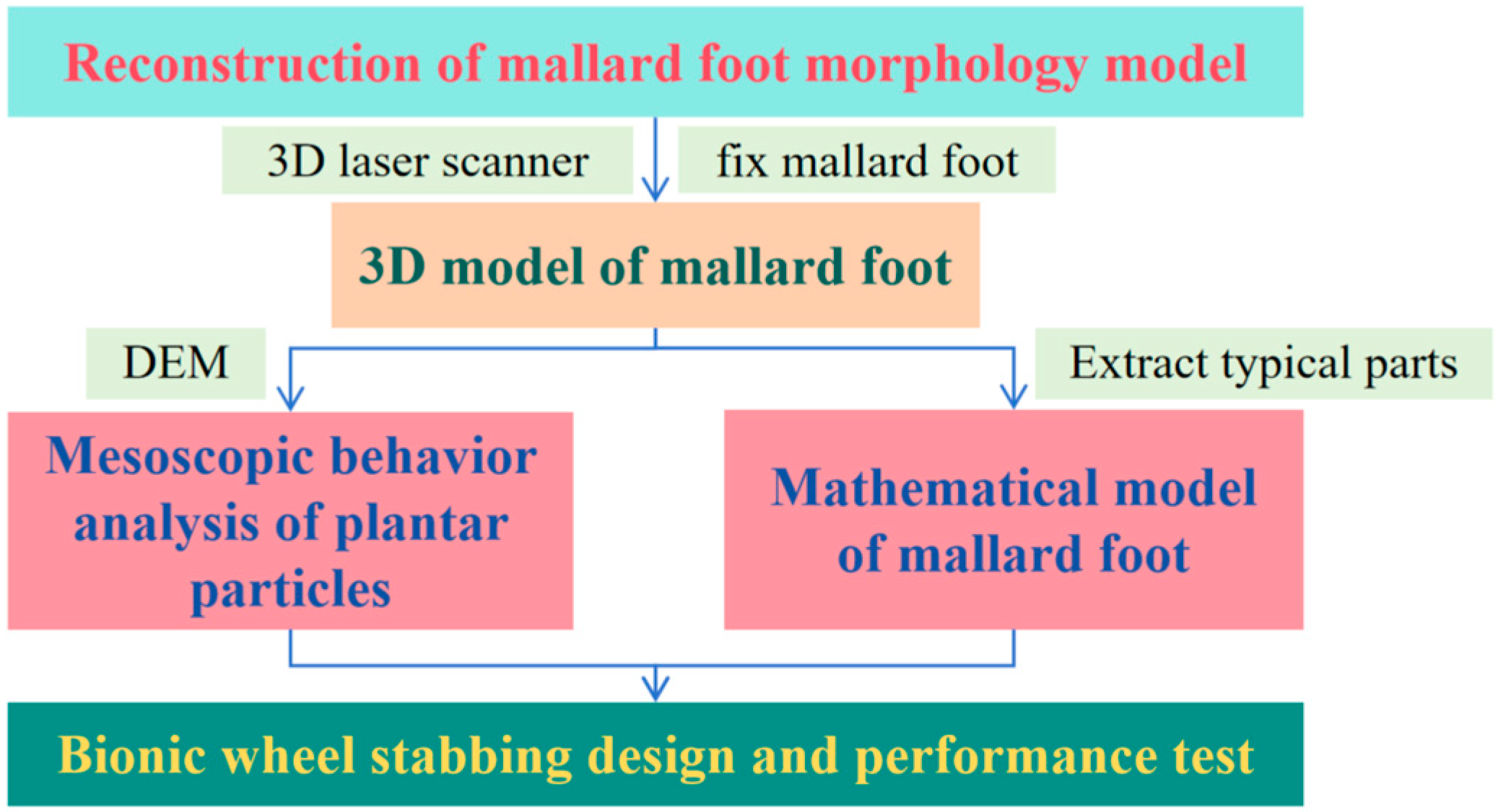
2. A 3D Model of the Plantar of Mallards
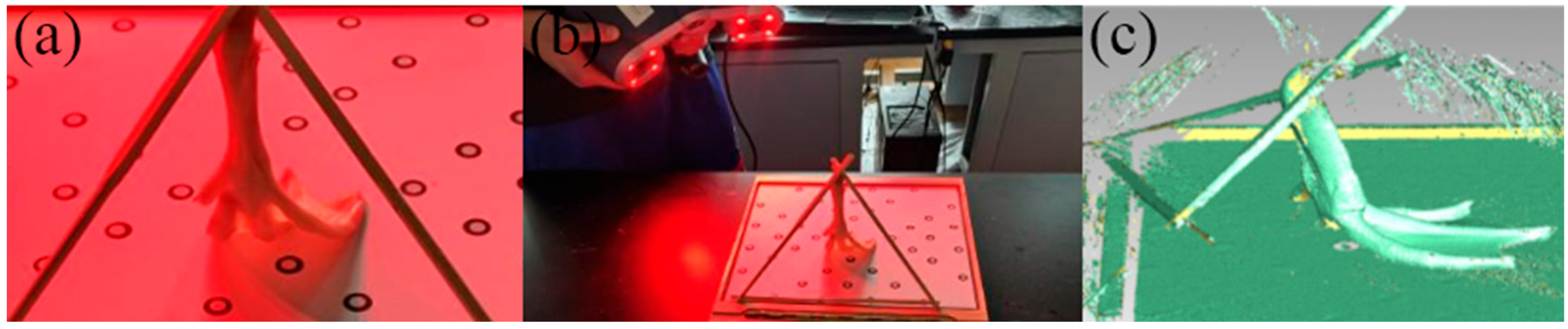
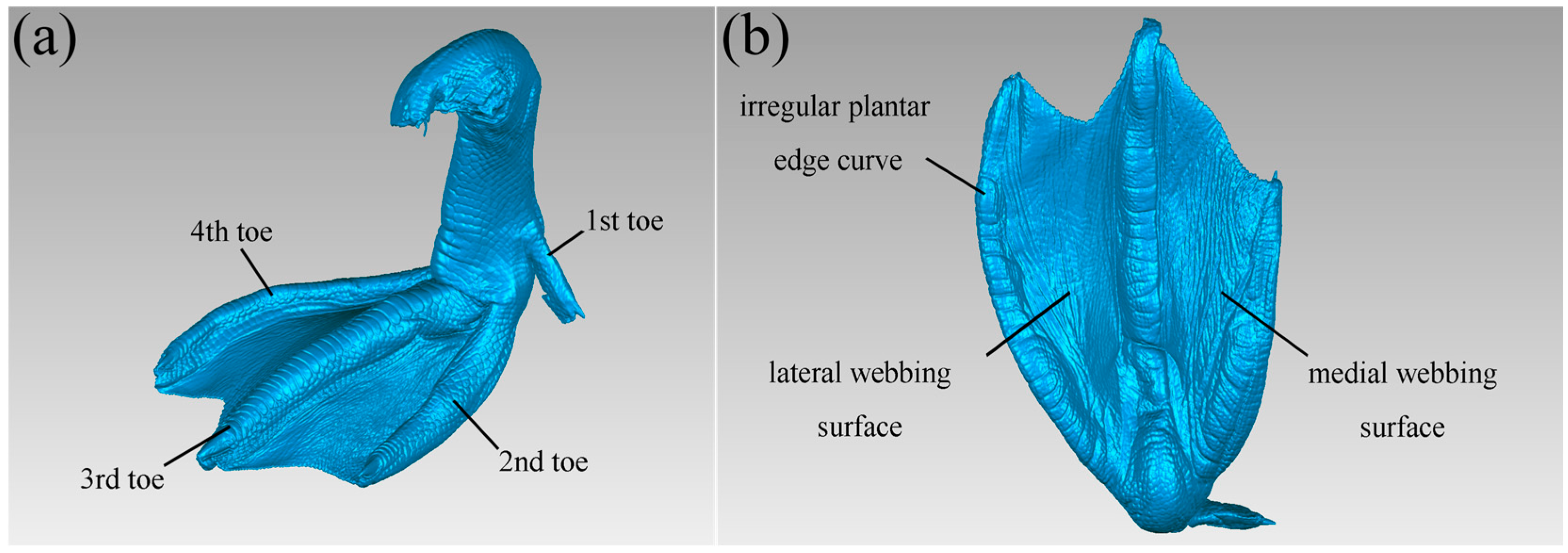
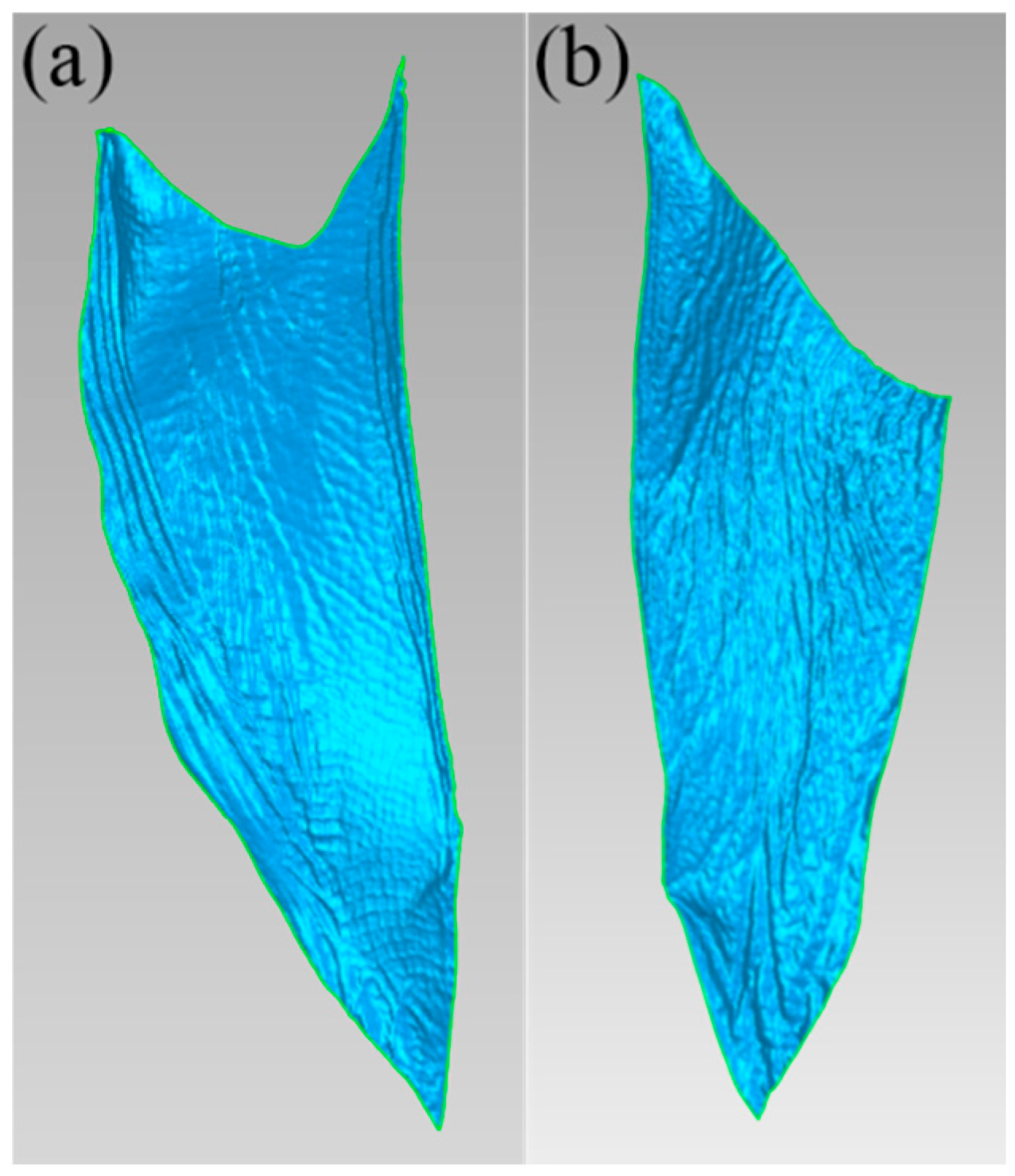
2.1. Reconstruction of a Mallard Foot Morphology Model
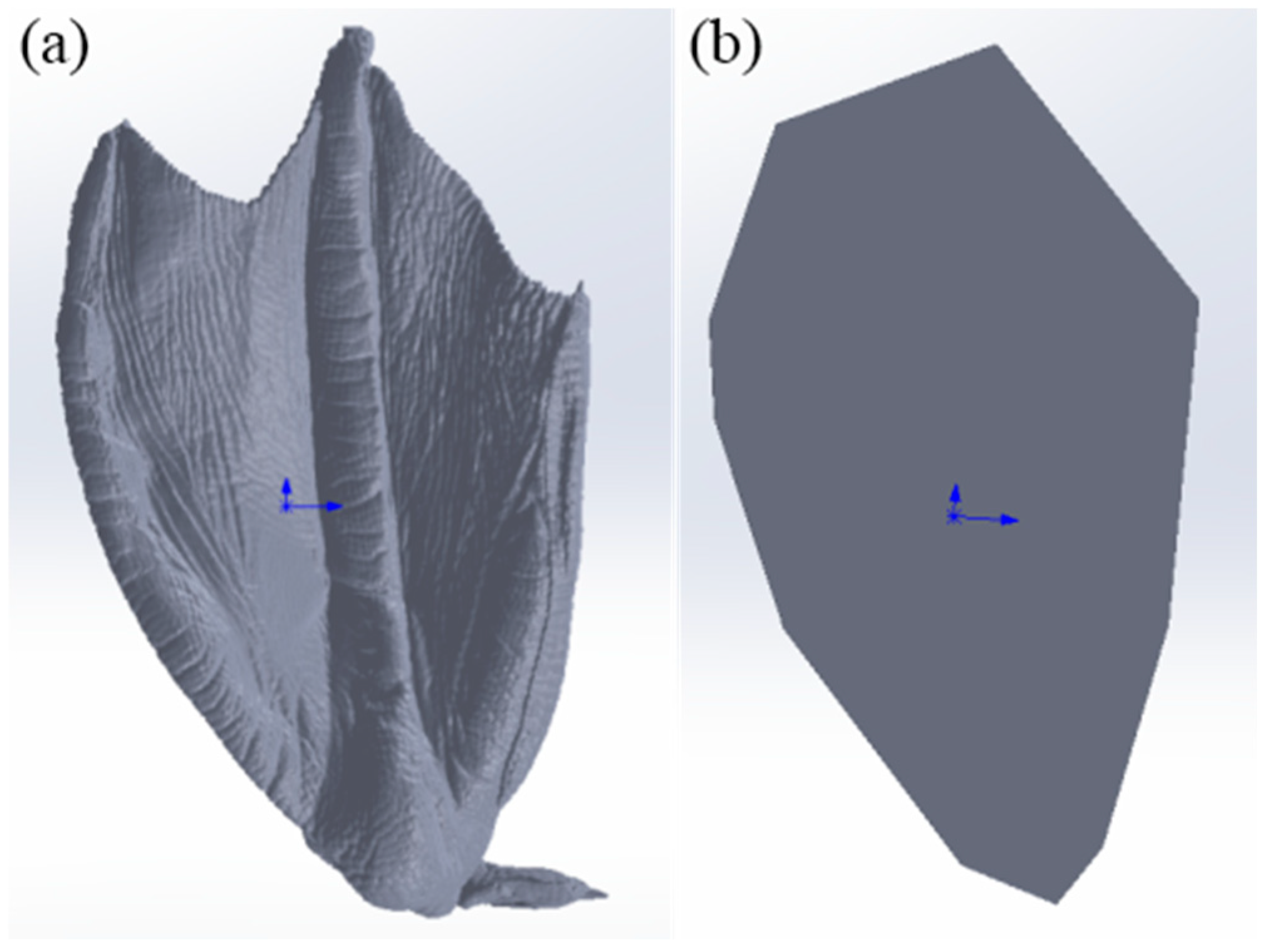
2.2. Mathematical Model of Mallard Soles
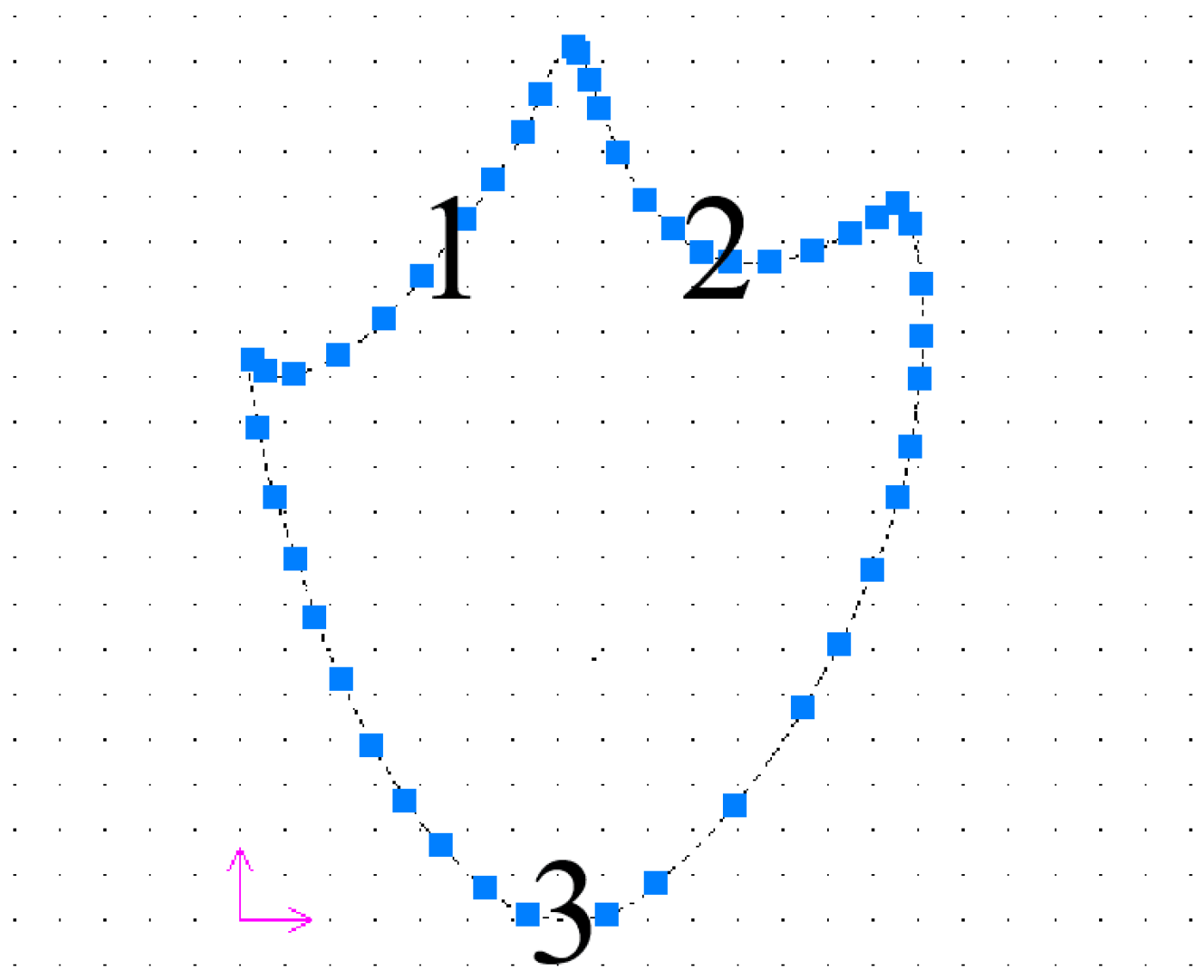
2.2.1. Mathematical Model of Mallard Plantar Irregular Edge Curve
2.2.2. Mathematical Modeling of the Lateral and Medial Webbed Surfaces of Mallards
3. Mesoscopic Behavior Analysis of Mallard Plantar Particles
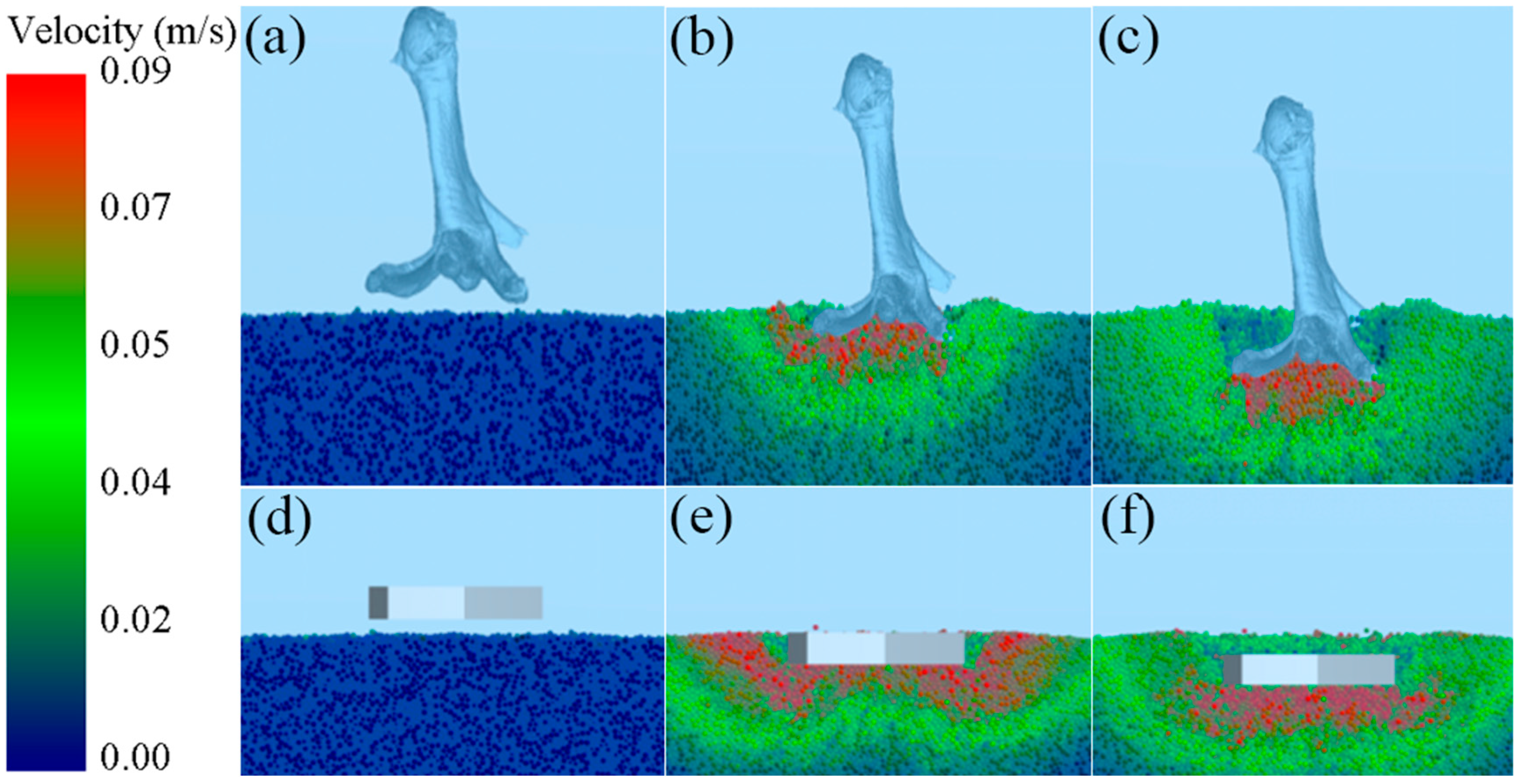
3.1. Discrete Element Simulation Intrusion Test
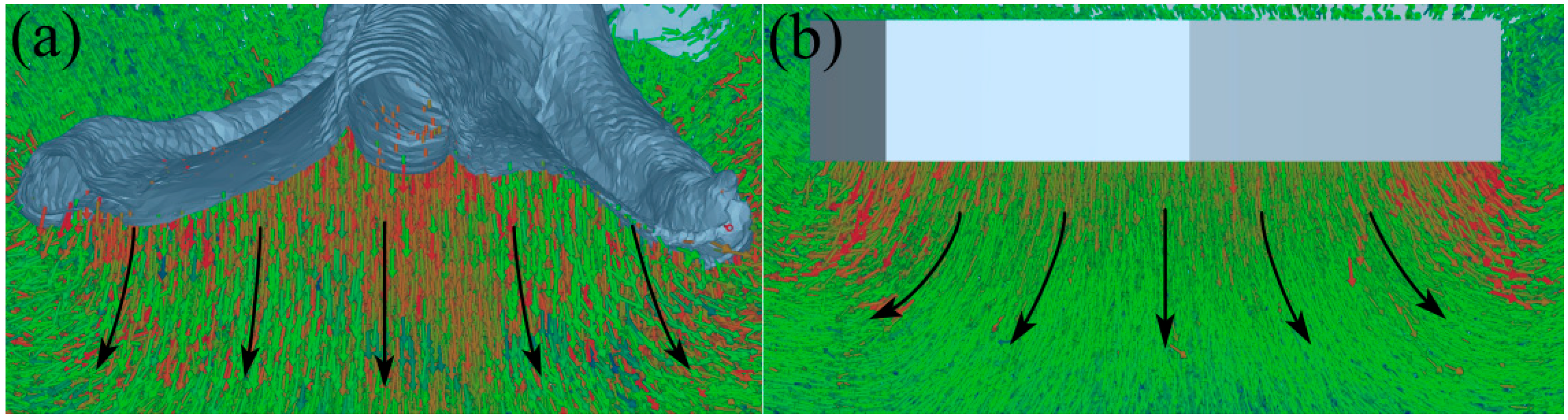
3.2. Behavior Analysis of Sand Particles
4. Bionic Wheel Stabbing Design and Performance Test
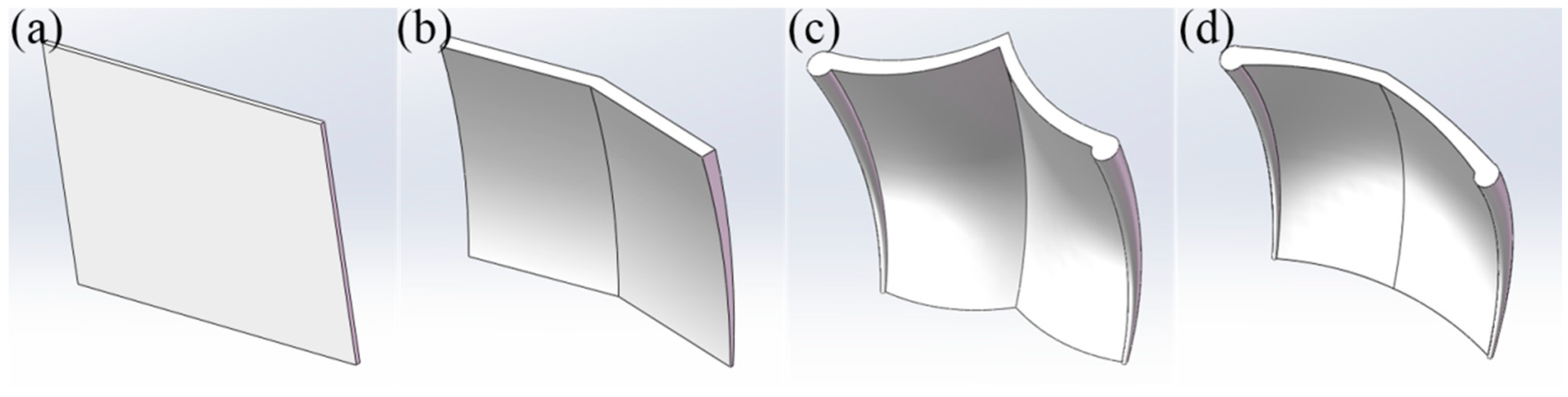
4.1. Bionic Wheel Grouser Design
4.2. Discrete Element Simulation Experimental Design
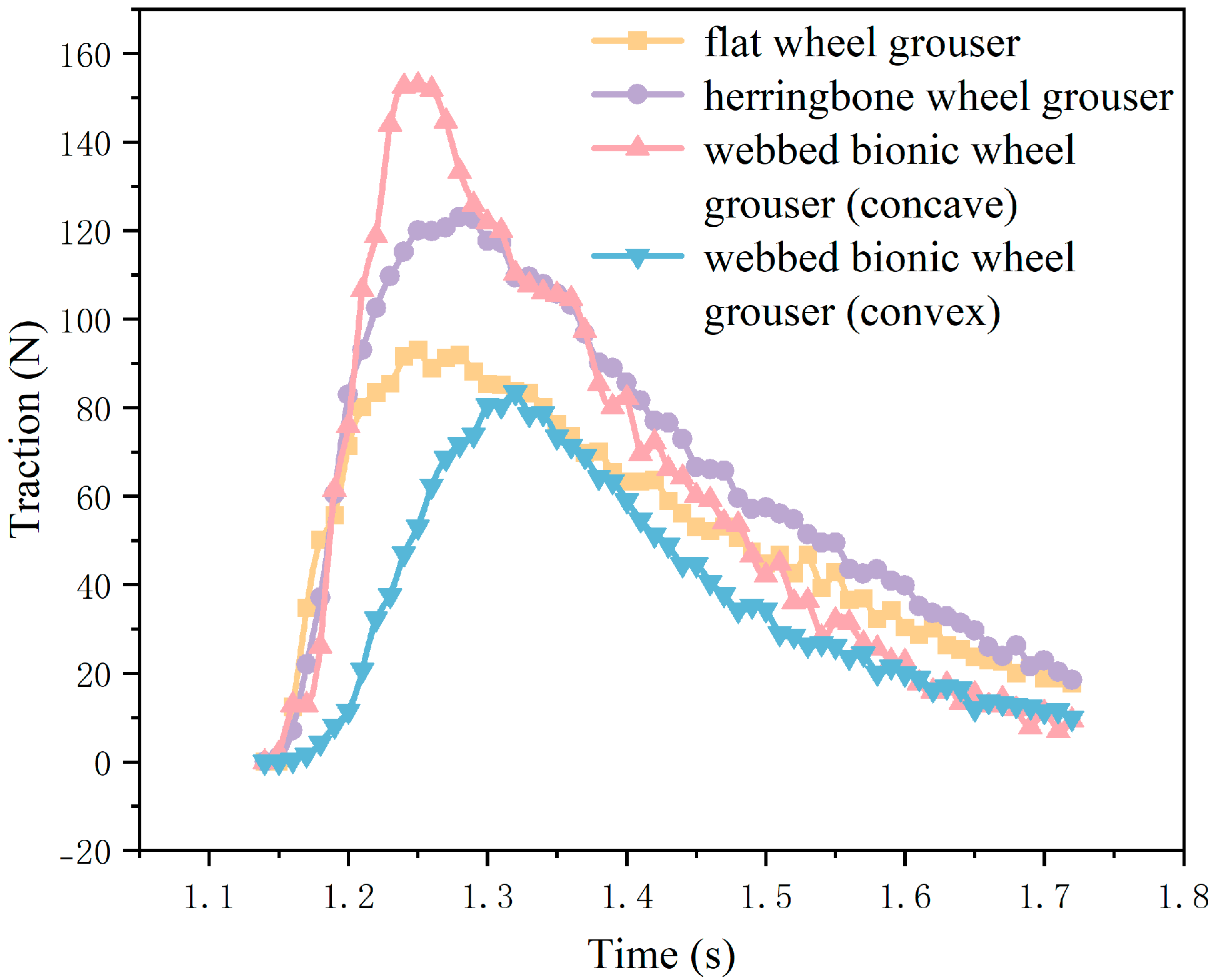
4.3. Comparative Analysis of Wheel Stabbing Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Shang, Z.; Li, R.; Cui, B. Adaptive sliding mode path tracking control of unmanned rice transplanter. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Z.; Sun, H. Design and experimental investigation of a transplanting mechanism for super rice pot seedlings. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.Q.; Liang, Y.H. Preliminary studies on the basic factors of bionics. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2014, 57, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Qiu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, P.; Luo, J. Primary Study on the Ability for Camel to Travel on Sand. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1991, 7, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Ding, X.L.; Xu, K.; Chen, H. Design and kinematics analysis of a bionic mechanical goat hoof. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 461, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazouchova, N.; Gravish, N.; Savu, A.; Goldman, D.I. Utilization of granular solidification during terrestrial locomotion of hatchling sea turtles. Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, A.C.; Lieb, J.; Seleb, B.; Thatcher, M.; Kim, S.; Asberry, A.T.; Nadler, J.H.; Hu, D.L. Enhanced wet grip with North American river otter paws. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2024, 1542, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.H. Surface ultrastructure and evolution of tarsal attachment structures in Plecoptera (Arthropoda: Hexapoda). Aquatic Insects 2009, 31 (Suppl. S1), 523–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. Significance and Progress of Bionics. J. Bionics Eng. 2004, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Teng, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, Z.; Xu, R. Design of bionic goat quadruped robot mechanism and walking gait planning. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, K.; Qian, M. An octopus-inspired bionic flexible gripper forapple grasping. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Fu, J.; Xu, L.; Cui, Z.; Jiang, X.; Wang, S. Study on the reduction of soil adhesion and tillage force of bionic cutter teeth in secondary soil crushing. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 213, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ma, Z.; Li, Y. Test and analyses of the reciprocal friction properties between the rapeseeds threshing mixture and non-smooth bionic surface. J. Agric. Mech. Asia Afr. Lat. Am. 2016, 47, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Tonia, H.; Goldman, D.I. Multi-functional foot use during running in the zebra-tailed lizard (Callisaurus draconoides). J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 215 Pt 18, 3293–3308. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Yang, M.; Pan, R.; Liu, H. Mathematical model establishment of irregular plantar surface of ostrich didactyl foot. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Qiao, Y.; Ji, Q.; Li, J. Mathematical model establishment and validation of irregular characteristic morphology for reindeer foot bottom. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Ma, T.; Wang, J.; Xu, R.; Guo, Z. Mathematical model establishment and validation of bionic irregular plantar surface of goat’s hoof. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Qiu, Y.; Teng, S.; Cui, X.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Ali, S.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Fu, S. Design and test of tread-pattern structure of biomimetic goat-sole tires. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.F.; Ma, S.S.; Zhang, R. Structural Design and Numerical Analysis of Bionic Wheel. In Proceedings of the 2nd Annual International Conference on Advanced Material Engineering (AME 2016), Wuhan, China, 15–17 April 2016; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 889–894. [Google Scholar]
- Godon, S.; Ristolainen, A.; Kruusmaa, M. Robotic feet modeled after ungulates improve locomotion on soft wet grounds. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2024, 19, 066009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnani, V.; Delap, D.; Creager, C. The development of wheels for the Lunar Roving Vehicle. J. Terramech. 2009, 46, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Tiwary, S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, H.N.S.; Murthy, K.A.K. Systematic design and development of a flexible wheel for low mass lunar rover. J. Terramech. 2018, 76, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, M.A. Design of a special rigid wheel for traversing loose soil. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Gao, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y. Numerical analysis on tractive performance of off-road wheel steering on sand using discrete element method. J. Terramech. 2017, 71, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, R.; Jia, Y.; Yang, L.; Guo, L. Design of a high performance suspension for lunar rover based on evolution. Acta Astronaut. 2009, 64, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, R.; Du, Y.; Zhou, G.; Wen, L.; Zhang, H. Research in innovative mesh wheel with bionic wheel surfaces and lugs for superior lunar rover performance. Acta Astronaut. 2025, 228, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, J.B. Kinematic state estimation for a Mars rover. Robotica 2000, 18, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvidson, R.E.; Bell, J.F., III; Bellutta, P.; Cabrol, N.A.; Catalano, J.G.; Cohen, J.; Crumpler, L.S.; Marais, D.J.D.; Estlin, T.A.; Farrand, W.H.; et al. Spirit Mars Rover Mission: Overview and selected results from the northern Home Plate Winter Haven to the side of Scamander crater. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2010, 115, E00F03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, K.; Nakashima, H.; Yoshida, T.; Ono, T.; Miyasaka, J.; Ohdoi, K.; Shimizu, H. 2D FE–DEM analysis of tractive performance of an elastic wheel for planetary rovers. J. Terramech. 2016, 64, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpman, E.; Kövecses, J.; Holz, D.; Skonieczny, K. Discrete element modelling for wheel-soil interaction and the analysis of the effect of gravity. J. Terramech. 2020, 91, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, J.; Chen, B.; Wu, B.; Zou, M. Performance evaluation of a wire mesh wheel on deformable terrains. J. Terramech. 2016, 68, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Tang, Z.; Liu, S.; Ding, Z.; Wang, T. Design for Copying Grouser and Bionic Convex Hull Patterns on Track Surfaces of Crawler Combine Harvesters. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Mao, H.; Guan, X. Numerical simulation and experimental verification of the deposition concentration of an unmanned aerial vehicle. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2019, 35, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, R. Research status and prospects on plant canopy structure measurement using visual sensors based on three-dimensional reconstruction. Agriculture 2020, 10, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Hu, J.; Liu, H.; Ren, L.; Zhou, M.; Yang, Q.; Li, B.; Chen, X. Parameter calibration and experiment of the discrete element contact model of water-containing sandy soil particles. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2025, 41, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Shi, L.; Shi, A.; He, M.; Zhao, X.; Addy, M.; Zhang, L. Determination of key soil characteristic parameters using angle of repose and direct shear stress test. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2023, 16, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Li, P.; Xu, R.; Chen, B.; Chen, C.; Yuan, S.; Wang, J. Numerical simulation of particle motion at cucumber straw grinding process based on EDEM. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Qiu, B.; Ding, Q.; Ding, W.; Khan, Z.M.; Chandio, F.A.; Rehim, A.; Khaliq, A.; Shoaib, M. Discrete element method simulation of disc type furrow openers in paddy soil. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | xy | x2y | xy2 | x2y2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum of squares of residuals (SSE) | 401,610 | 115,310 | 376,440 | 21,471 |
| Mean square deviation (RMSE) | 2.0103 | 1.0772 | 1.9463 | 0.4648 |
| Coefficient of determination (R2) | 0.7309 | 0.9227 | 0.7478 | 0.9856 |
| Parameter | xy | x2y | xy2 | x2y2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum of squares of residuals (SSE) | 65,957 | 38,158 | 56,770 | 30,640 |
| Mean square deviation (RMSE) | 0.8669 | 0.6594 | 0.8043 | 0.5909 |
| Coefficient of determination (R2) | 0.9046 | 0.9448 | 0.9179 | 0.9557 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Han, D.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Ren, L.; Pang, H. Construction of a Mathematical Model of the Irregular Plantar and Complex Morphology of Mallard Foot and the Bionic Design of a High-Traction Wheel Grouser. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060390
Hu J, Han D, Li C, Liu H, Ren L, Pang H. Construction of a Mathematical Model of the Irregular Plantar and Complex Morphology of Mallard Foot and the Bionic Design of a High-Traction Wheel Grouser. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(6):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060390
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jinrui, Dianlei Han, Changwei Li, Hairui Liu, Lizhi Ren, and Hao Pang. 2025. "Construction of a Mathematical Model of the Irregular Plantar and Complex Morphology of Mallard Foot and the Bionic Design of a High-Traction Wheel Grouser" Biomimetics 10, no. 6: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060390
APA StyleHu, J., Han, D., Li, C., Liu, H., Ren, L., & Pang, H. (2025). Construction of a Mathematical Model of the Irregular Plantar and Complex Morphology of Mallard Foot and the Bionic Design of a High-Traction Wheel Grouser. Biomimetics, 10(6), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060390







