Coordinated Locomotion Control for a Quadruped Robot with Bionic Parallel Torso
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bionic Active Torso Modeling
2.1. Overview of the Active Torso Model
2.2. Inverse Kinematics Analysis
3. Bionic Active Torso Quadruped Robot
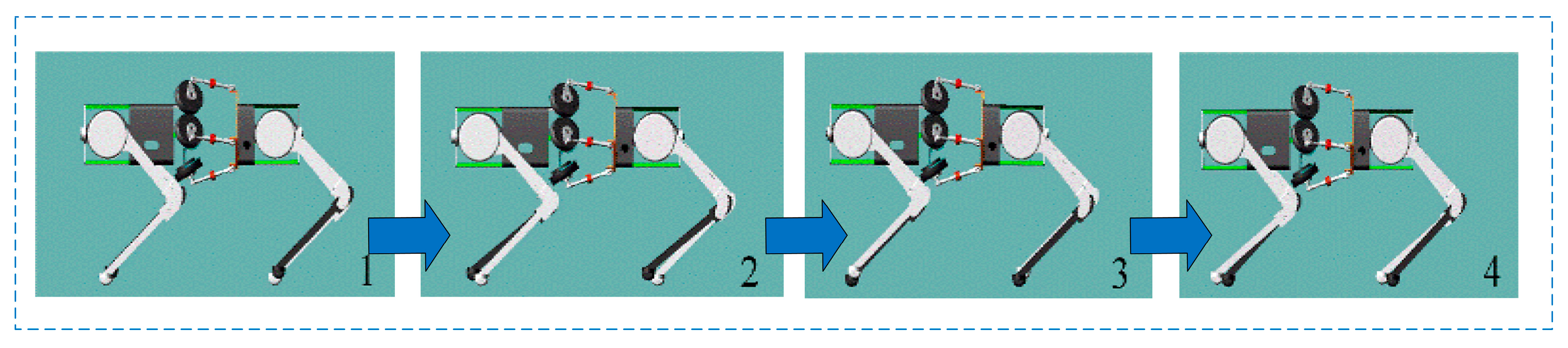
3.1. Bionic Quadruped Robot Structure
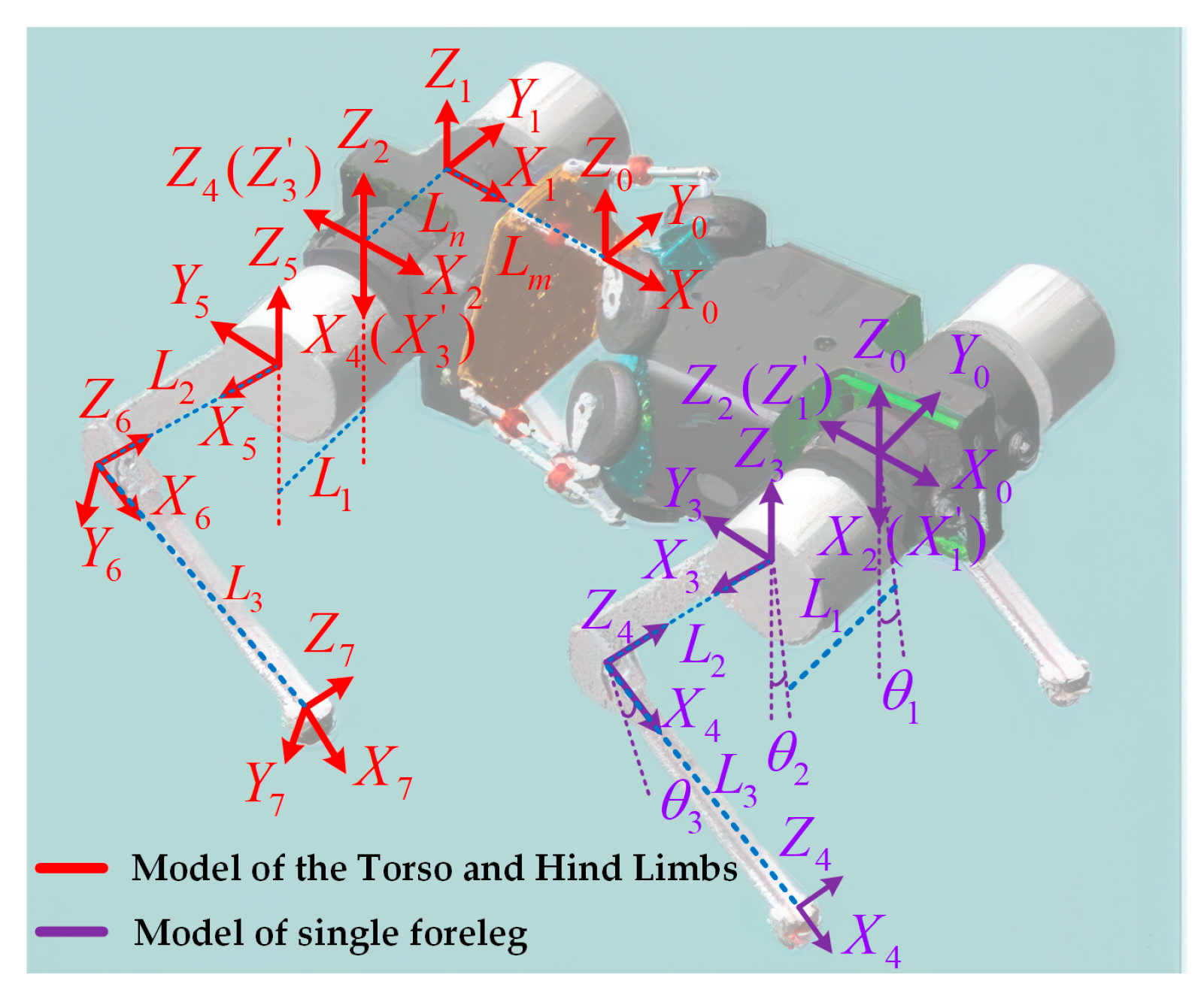
3.2. Single-Leg Kinematics
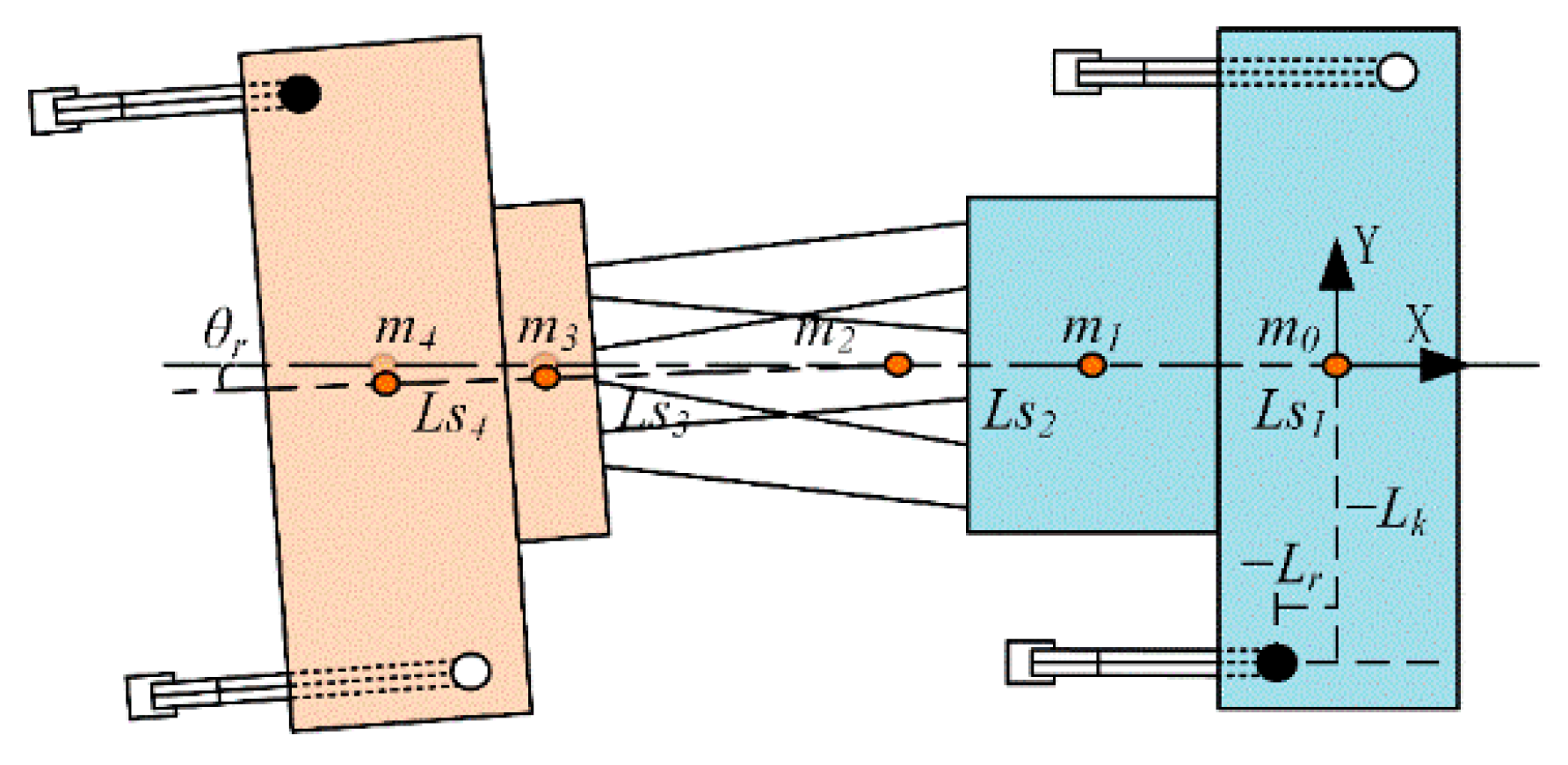
3.3. Kinematics of the Torso and Hind Limbs
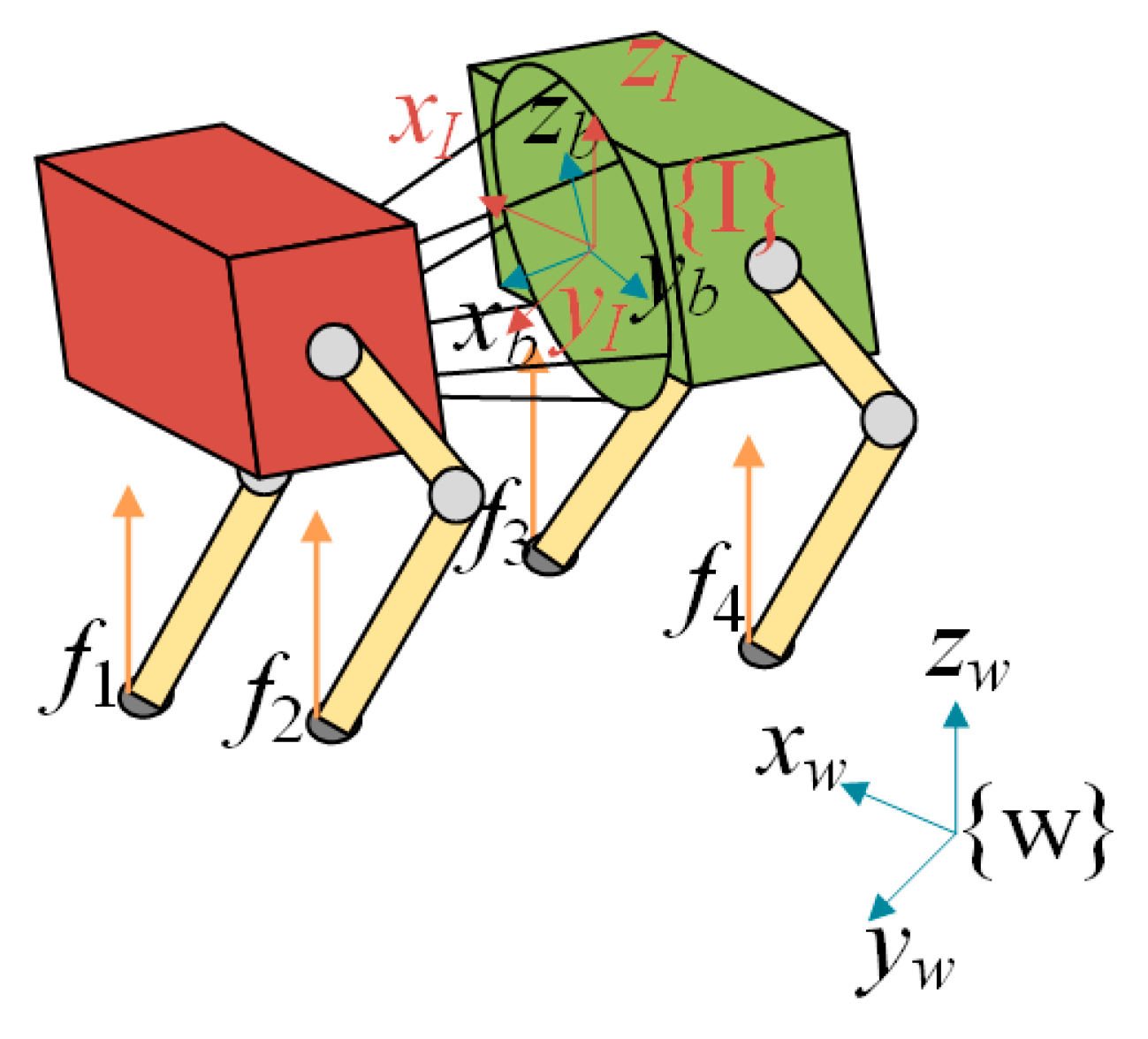
3.4. Model Predictive Controller Based on Shifted Center of Mass Position
3.4.1. Simplified Dynamic Model
3.4.2. Construction of the Model Predictive Controller (MPC)
3.4.3. Overall Motion Control
4. Torso–Leg Coordinated Locomotion
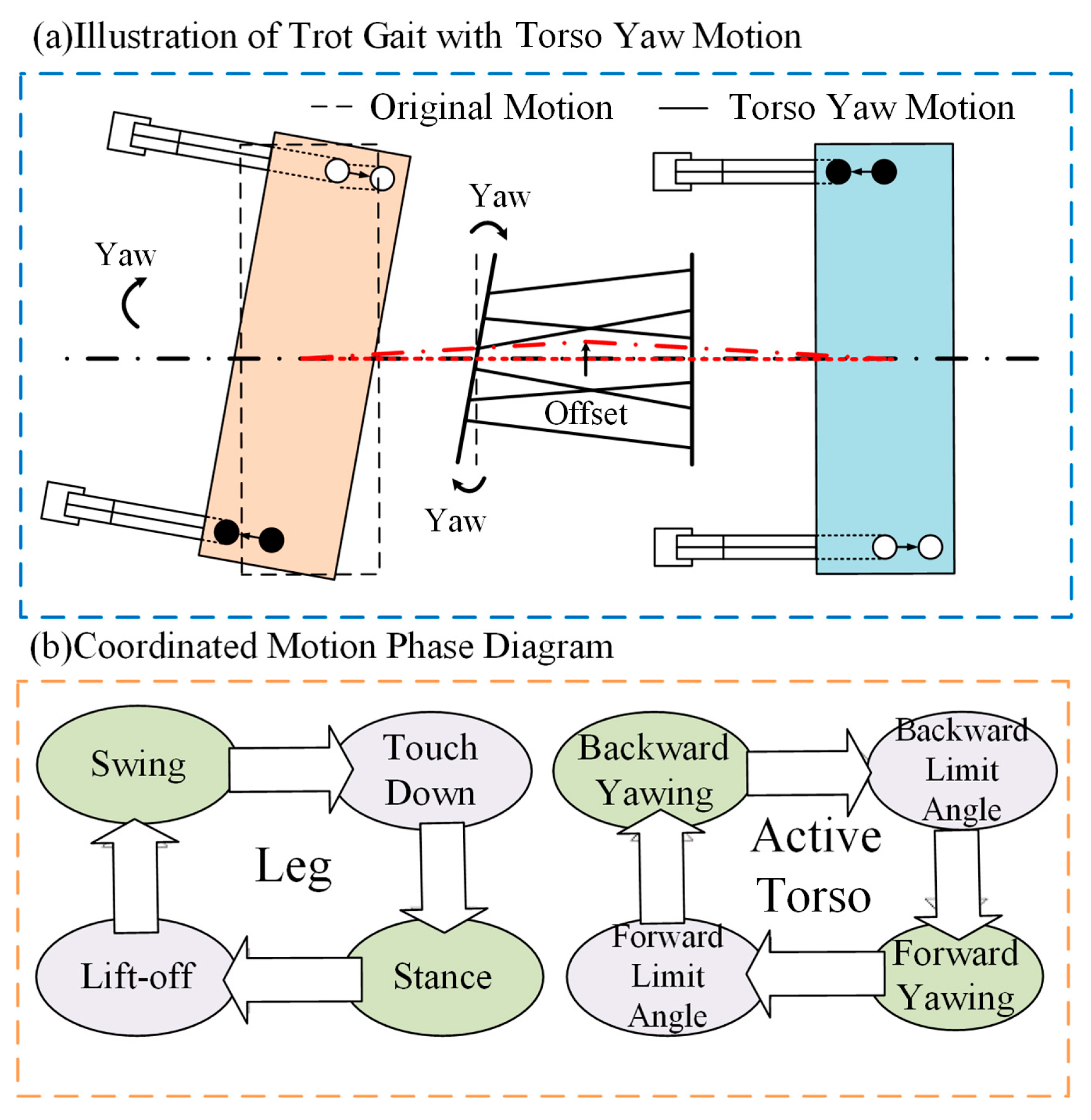
4.1. Torso–Leg Coordinated Locomotion Mechanism
4.2. CPG-Based Torso Motion Trajectory
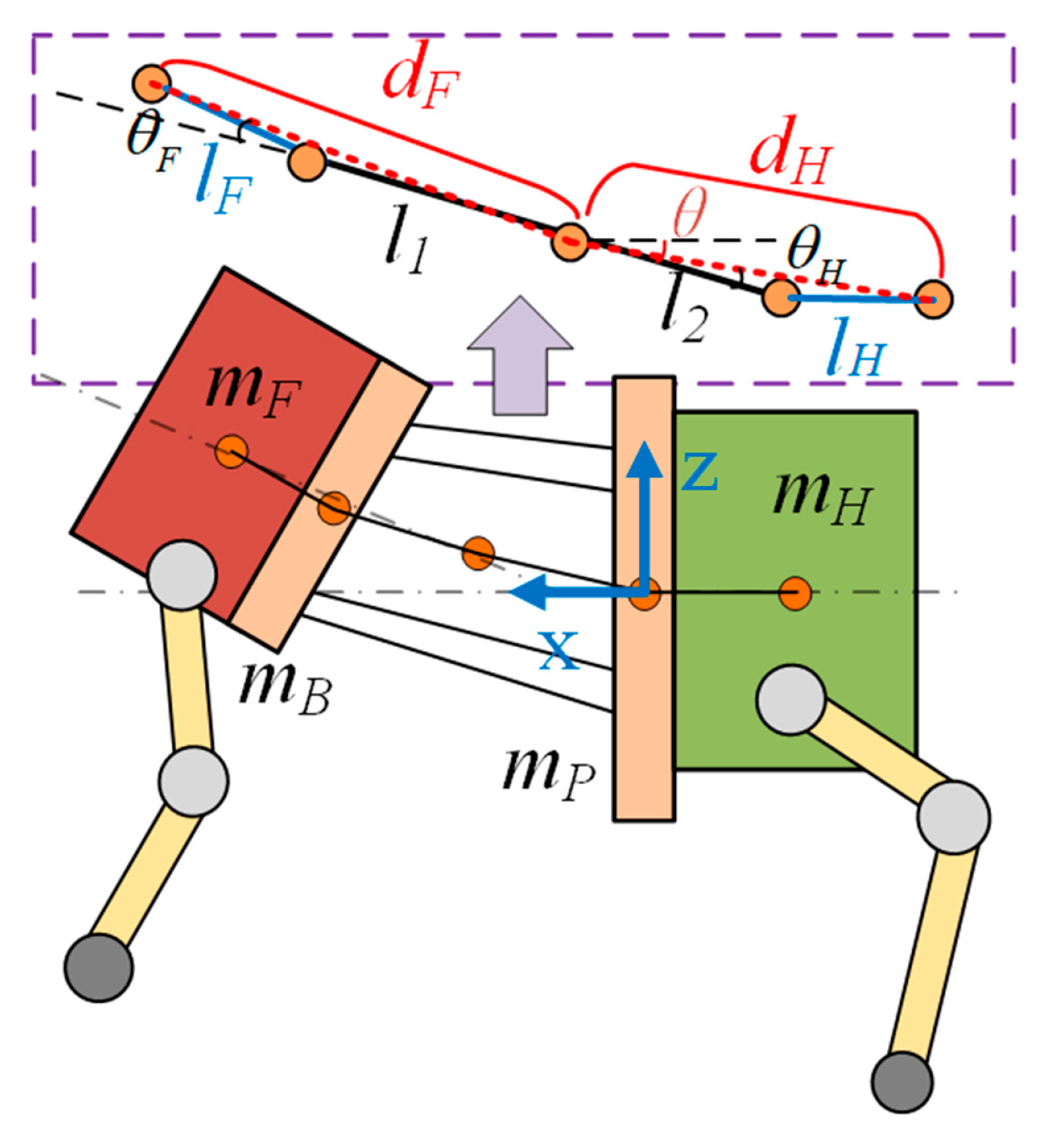
4.3. Torso Trajectory Based on the Center of Mass
4.4. Torso Motion Trajectory Based on Zero Moment Point
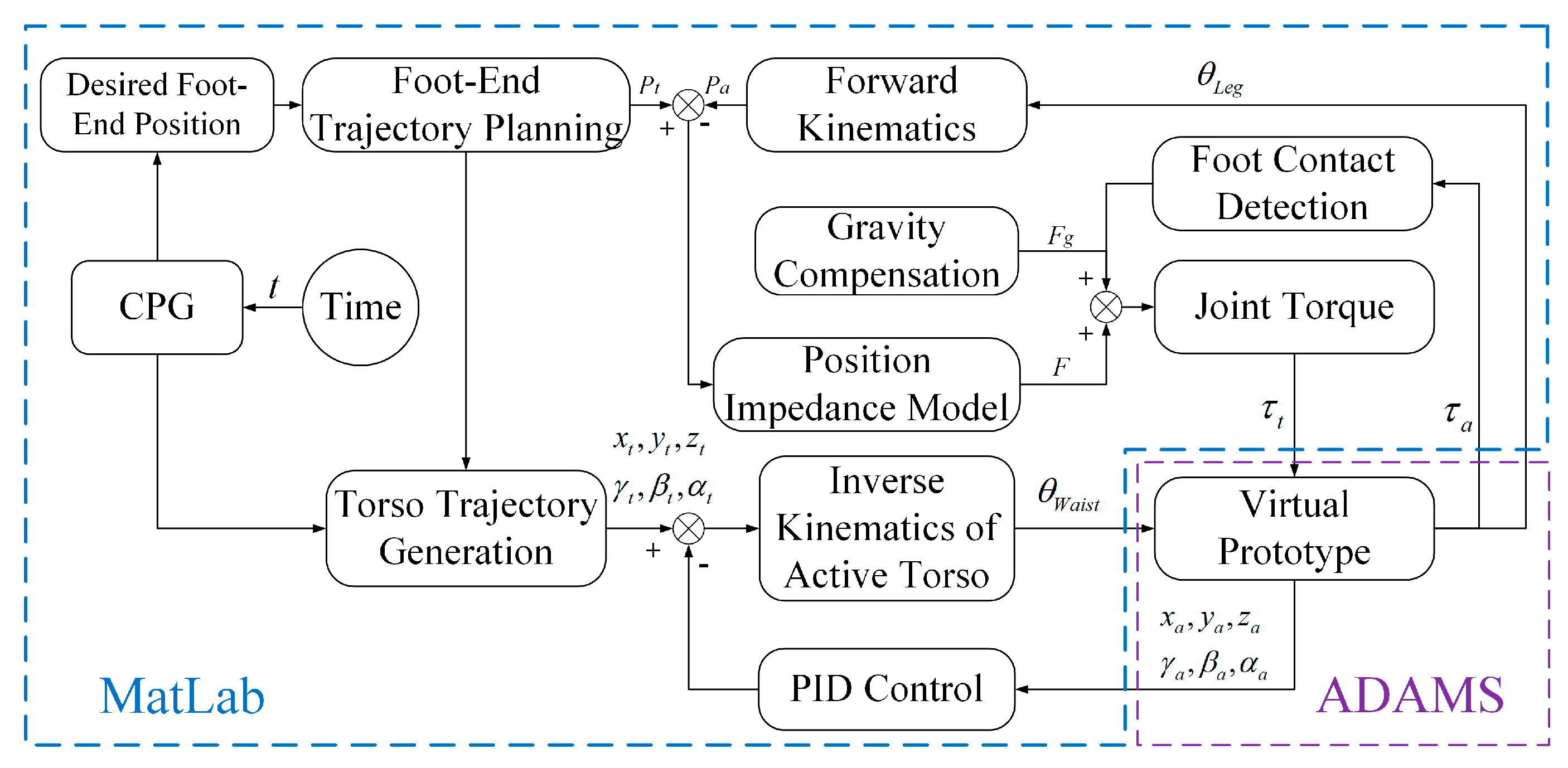
4.5. Algorithm Verification Framework for Bionic Active Torso Quadruped Robot
5. Simulation and Analysis
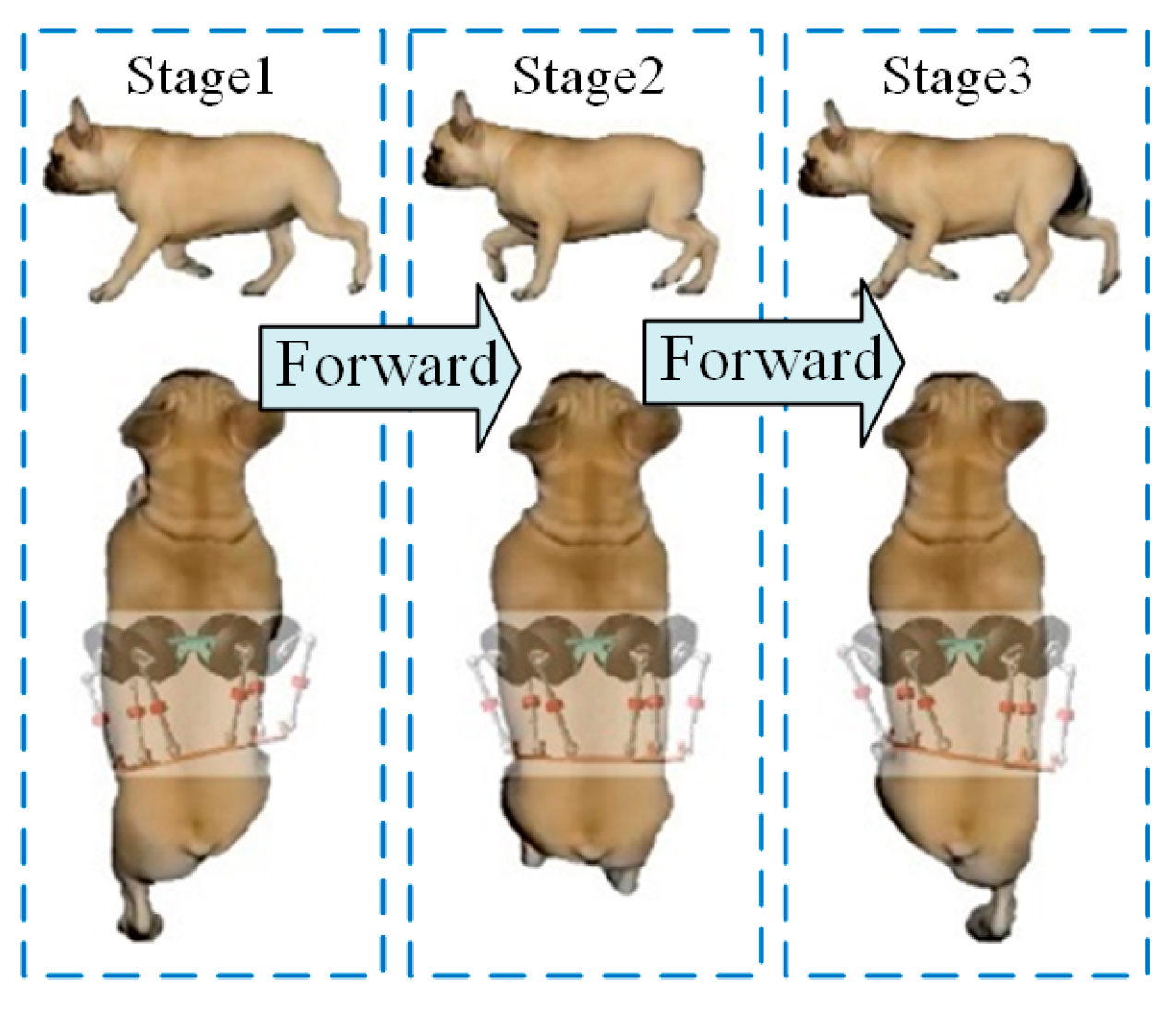
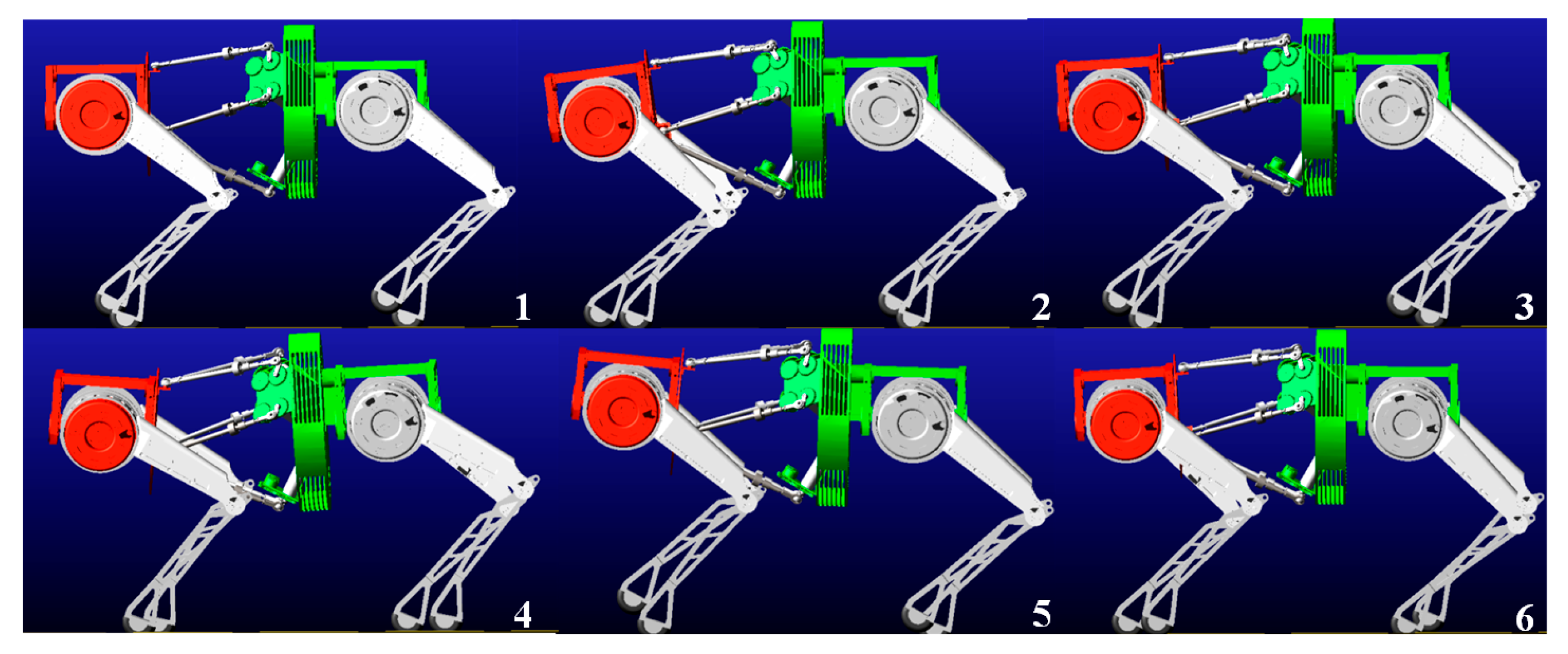
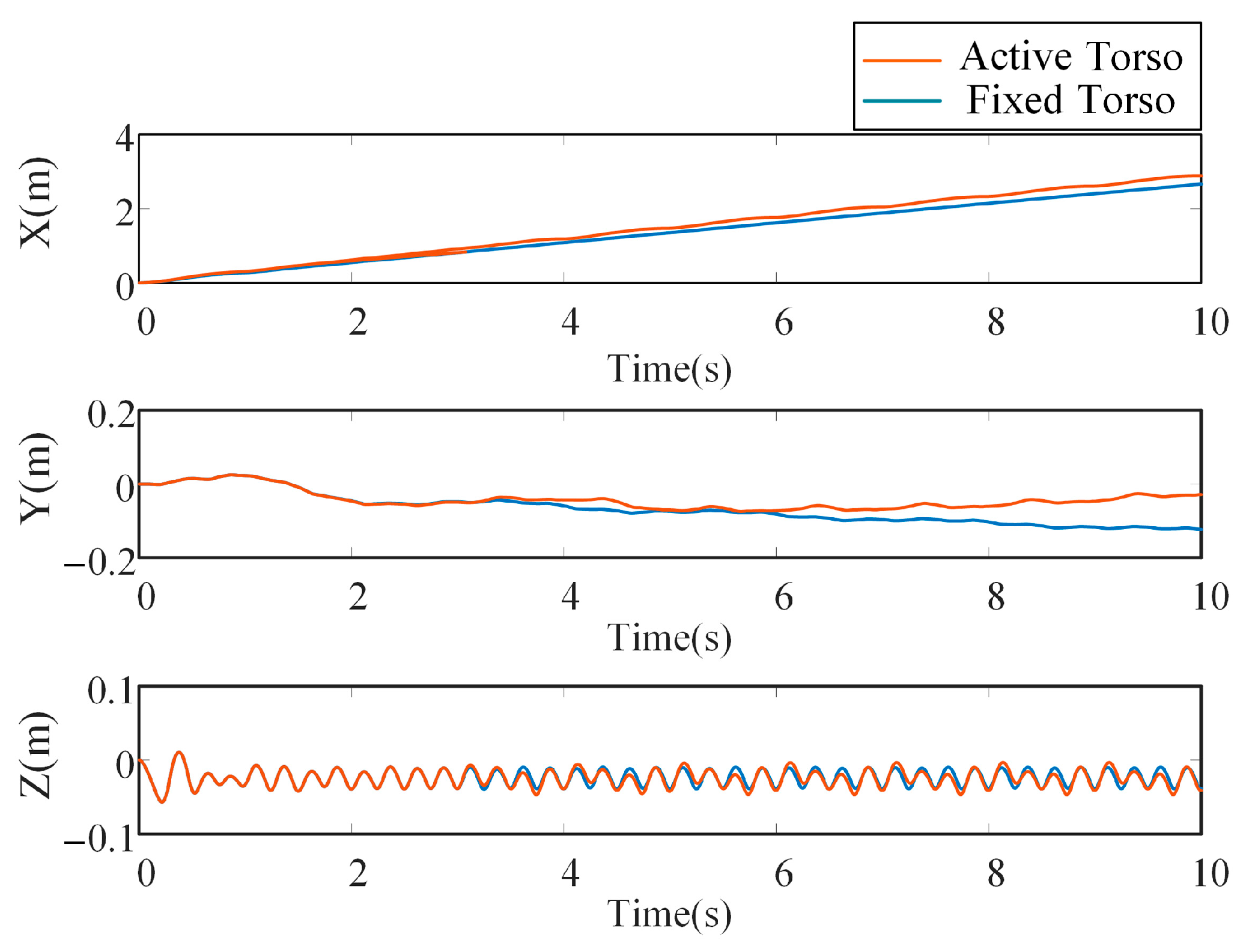
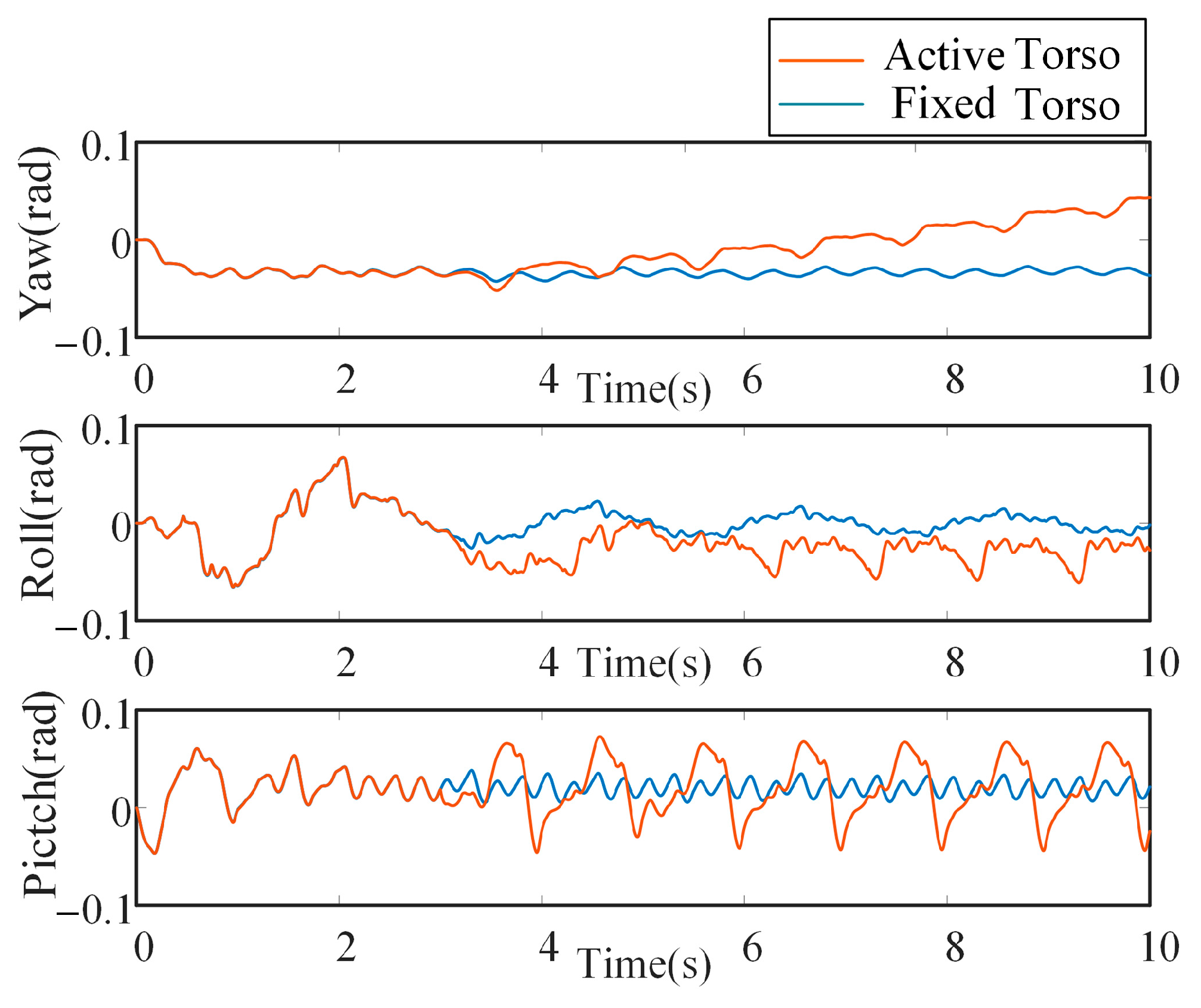
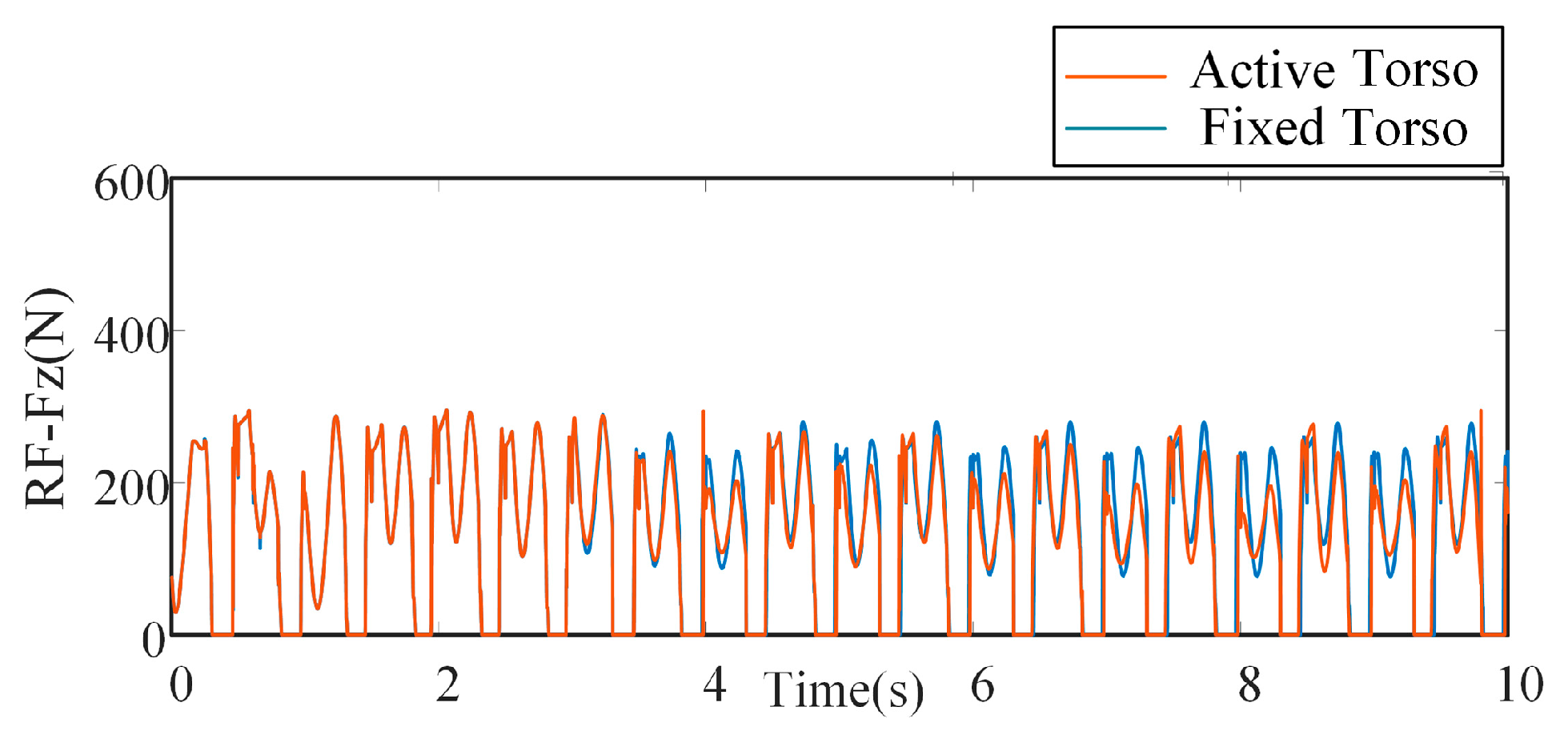
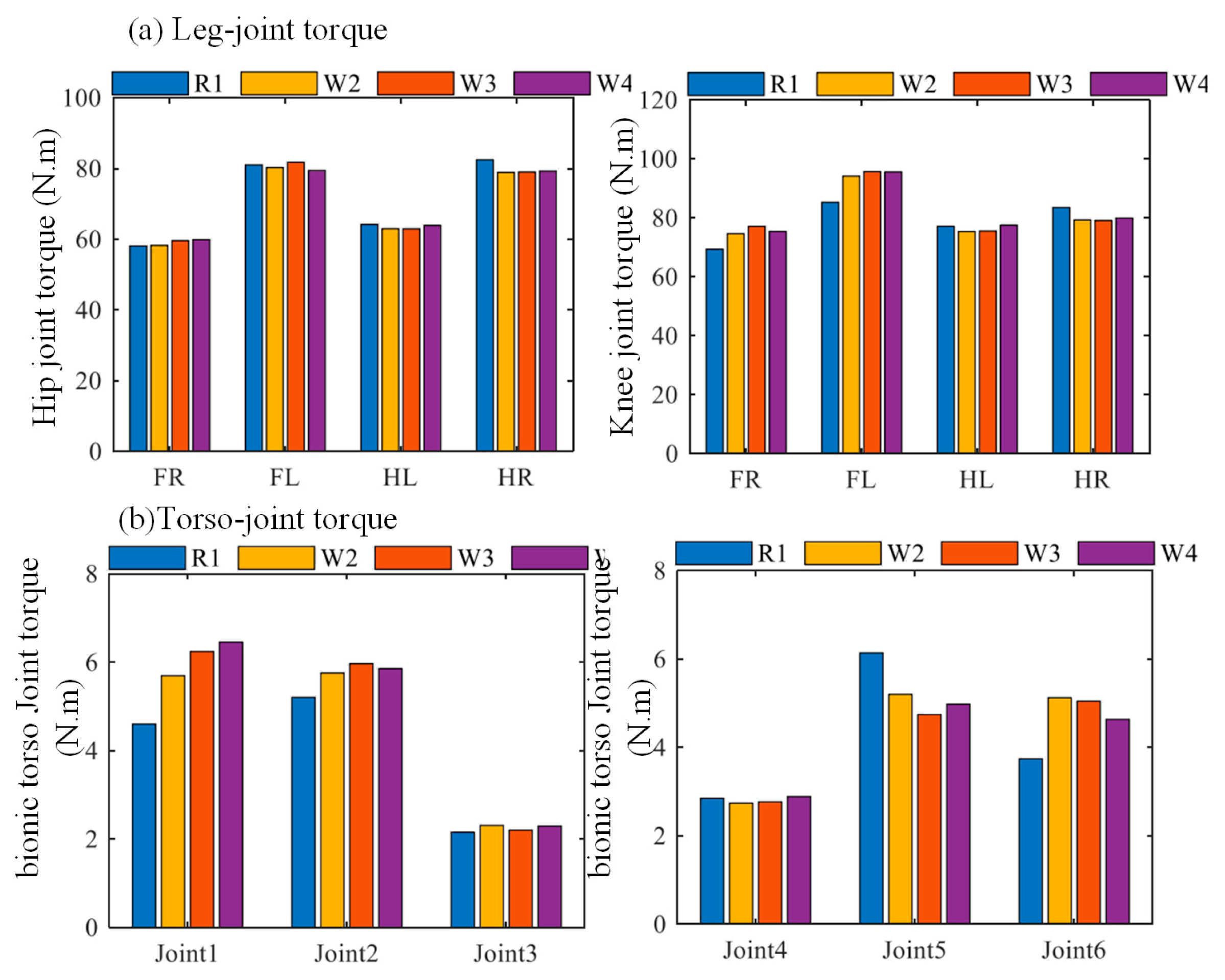
5.1. Motion Performance of the Bionic Parallel Torso Quadruped Robot
5.2. Coordinated Motion of the Bionic Parallel Torso Quadruped Robot
6. Results
7. Discussions and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gracovetsky, S.A.; Iacono, S. Energy transfers in the spinal engine. J. Biomed. Eng. 1987, 9, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boszczyk, B.M.; Boszczyk, A.A.; Putz, R. Comparative and functional anatomy of the mammalian lumbar spine. Anat. Rec. 2001, 264, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, M.A.; Bunting, M.R.; Salemi, B.; Hoffmann, H. Toward Ultra High Speed Locomotors: Design and test of a cheetah robot hind limb. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 1990–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kani, M.H.H.; Derafshian, M.; Bidgoly, H.J.; Ahmadabadi, M.N. Effect of flexible spine on stability of a passive quadruped robot: Experimental results. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Karon Beach, Thailand, 7–11 December 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, B.; Aydin, Y.O.; Gong, C.; Sartoretti, G.; Wu, Y.; Rieser, J.; Xing, H.; Rankin, J.; Michel, K.; Nicieza, A.; et al. Coordination of back bending and leg movements for quadrupedal locomotion. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 26–30 June 2018; Volume 20. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.-H.; Kim, D.-S.; Lee, Y.-J. Discontinuous spinning gait of a quadruped walking robot with torso-joint. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2–6 August 2005; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Takuma, T.; Ikeda, M.; Masuda, T. Facilitating multi-modal locomotion in a quadruped robot utilizing passive oscillation of the spine structure. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, M.; Ikuo, M. Analysis of the energy loss on quadruped robot having a flexible trunk joint. J. Robot. Mechatron. 2017, 29, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Liu, B.; Gu, X. A bionic quadruped robot with a global compliant spine. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Shenzhen, China, 12–14 December 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; Wei, X.; Long, Y.; Wang, S. Bionic control strategy study for the quadruped robot with a segmented spine. Ind. Robot. Int. J. 2017, 44, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkertsma, G.A.; Kim, S.; Stramigioli, S. Parallel stiffness in a bounding quadruped with flexible spine. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sabelhaus, A.P.; van Vuuren, L.J.; Joshi, A.; Zhu, E.; Garnier, H.J.; Sover, K.A.; Navarro, J.; Agogino, A.K.; Agogino, A.M. Design, Simulation, and Testing of Laika, a Quadruped Robot with a Flexible Actuated Spine. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.06527v2. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, H.; Nishikawa, S.; Niiyama, R.; Kuniyoshi, Y. Dynamic locomotion of quadruped with laterally parallel leaf spring spine. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Climbing and Walking Robots and the Support Technologies for Mobile Machines, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 26–28 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.K.; Seol, W.; Park, J. Biomimetic quadruped robot with a spinal joint and optimal spinal motion via reinforcement learning. J. Bionic Eng. 2021, 18, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, R.; Sato, R.; Kazama, E.; Ming, A.; Shimojo, M. Development of a flexible coupled spine mechanism for a small quadruped robot. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Qingdao, China, 3–7 December 2016; pp. 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, T. Dynamic bending of bionic flexible body driven by pneumatic artificial muscles(PAMs) for spinning gait of quadruped robot. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2016, 29, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Wang, Z.; Su, B.; Dang, R.; Liao, J.; Liu, S.; Guo, Z. Design of a continuous bionic spine with variable stiffness for quadruped robots. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2023, 54, 3112–3121. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, L.; Huang, S.; Yao, Y. A cheetah-inspired quadruped running robot with a 2-DOF articulated torso. Robot 2022, 44, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dai, J. Trot Gait with Twisting Trunk of a Metamorphic Quadruped Robot. J. Bionic Eng. 2018, 15, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J. Research on Dynamic Modeling Method and Flying Gait Characteristics of Quadruped Robots with Flexible Spines. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Shuangjie, Z.; Poramate, M.; Li, R. Design, analysis, and neural control of a bionic parallel mechanism. Front. Mech. Eng. 2021, 16, 468–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, Z.; Zhou, M. An Active and Dexterous Bionic Torso for a Quadruped Robot. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Abu Dhabi, UAE, 14–18 October 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, S.; He, Z.; Sun, J.; Liu, S. Modeling and control system design of 6-DOF bionic parallel mechanism with compliant modules. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2023, 46, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Gao, W.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, S. Predictive Control of a Spined Quadrupedal Robot Based on a Dual Rigid-Body Model. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Bangkok, Thailand, 10–14 December 2024; pp. 292–298. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.; Yin, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y. Adaptive control algorithm for quadruped robots in unknown high-slope terrain. J. Eng. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, T.; Du, Q. Motion Control of Quadruped Robot Based on Improved CPG Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 7th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 15–17 March 2024; pp. 1527–1533. [Google Scholar]
- Mirletz, B.T.; Bhandal, P.; Adams, R.D.; Agogino, A.K.; Quinn, R.D.; SunSpiral, V. Goal-Directed CPG-Based Control for Tensegrity Spines with Many Degrees of Freedom Traversing Irregular Terrain. Soft Robot. 2015, 2, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, Z.; Cheng, L.; Chen, G.; Röhrbein, F.; Huang, K.; Knoll, A. Towards autonomous locomotion: CPG-based control of smooth 3D slithering gait transition of a snake-like robot. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2017, 12, 035001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Gao, D.; Liu, Q. Synchronization of Non-linear Oscillators for Neurobiologically Inspired Control on a Bionic Parallel Torso of Legged Robot. Front. Neurorobot. 2019, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Manoonpong, P. Generic Mechanism for Waveform Regulation and Synchronization of Oscillators: An Application for Robot Behavior Diversity Generation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 4495–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z. Research on the Motion Mechanism and Control Method of a Spine-Type Wheel-Leg Hybrid Robot. Ph.D. Thesis, Southeast University, Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, A.W.; Farshidian, F.; Neunert, M.; Pardo, D.; Buchli, J. Online walking motion and foothold optimization for quadruped locomotion. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 5308–5313. [Google Scholar]
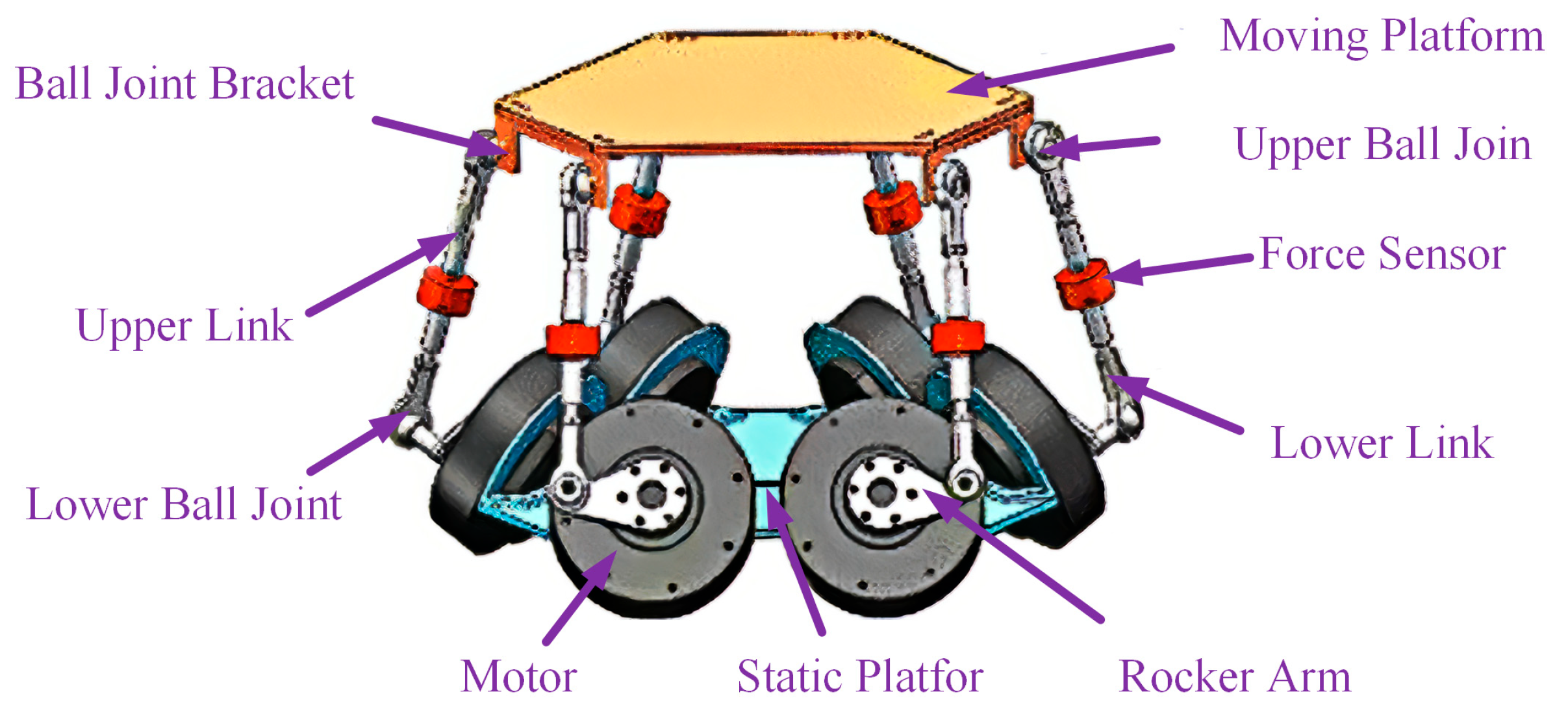
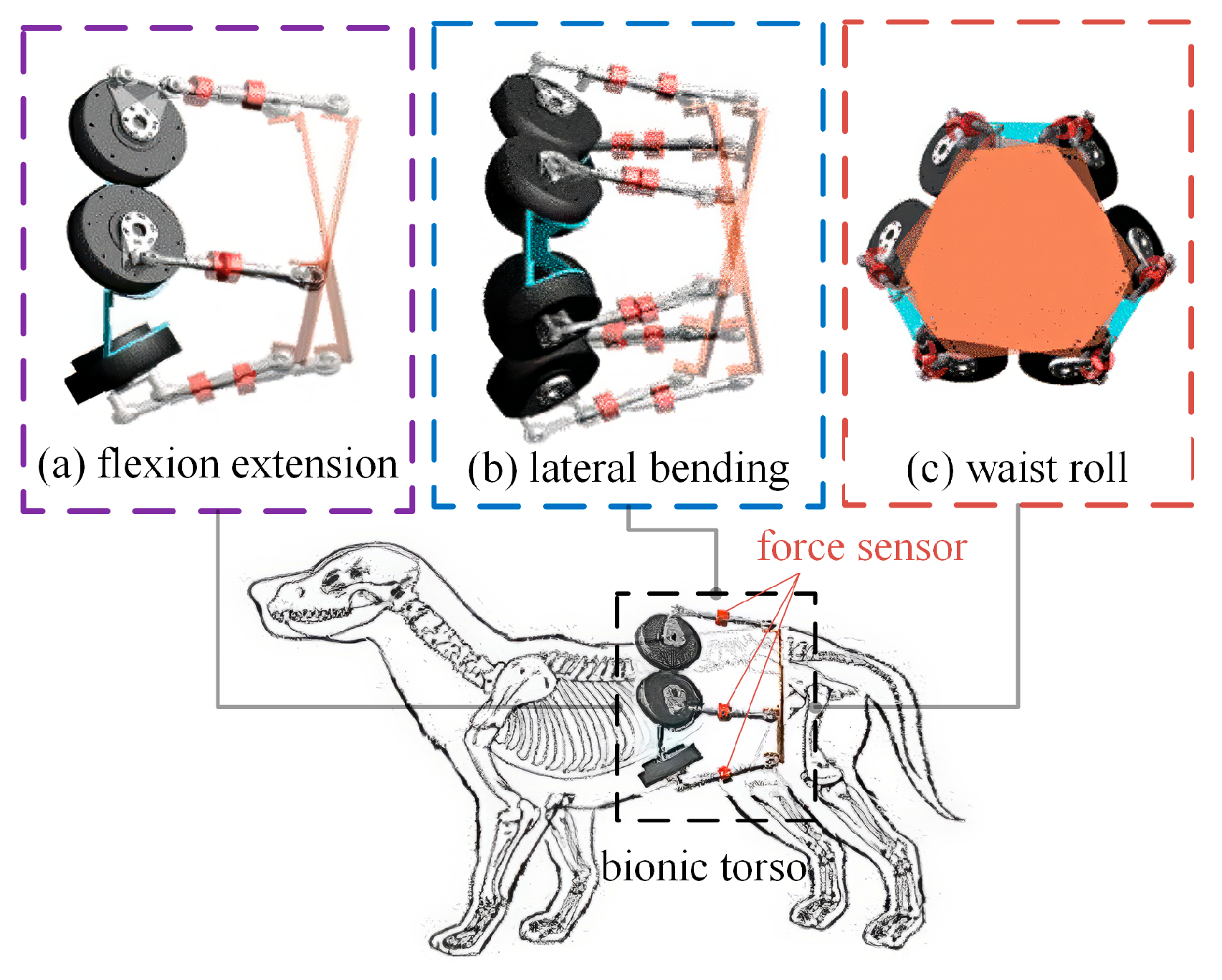
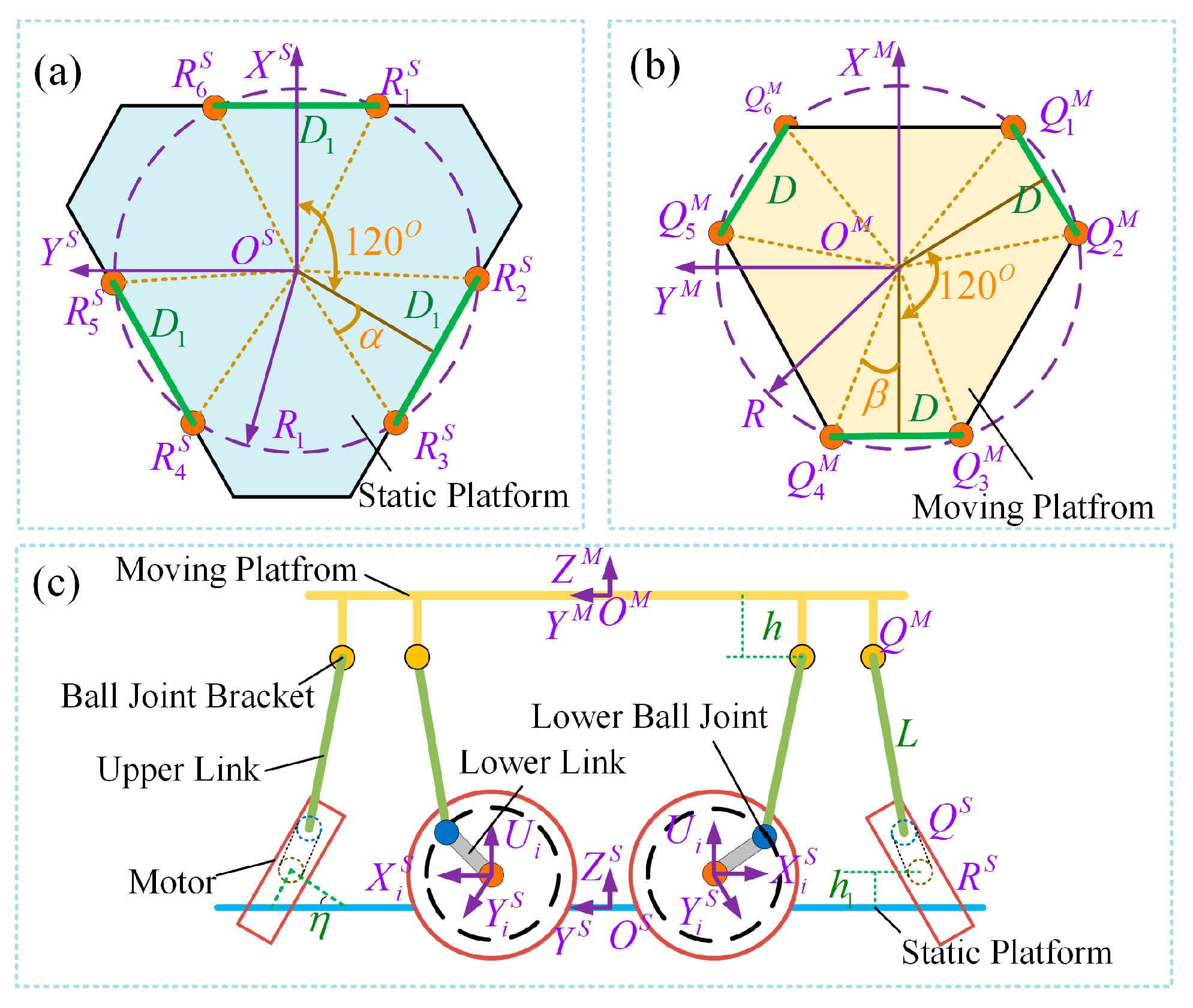
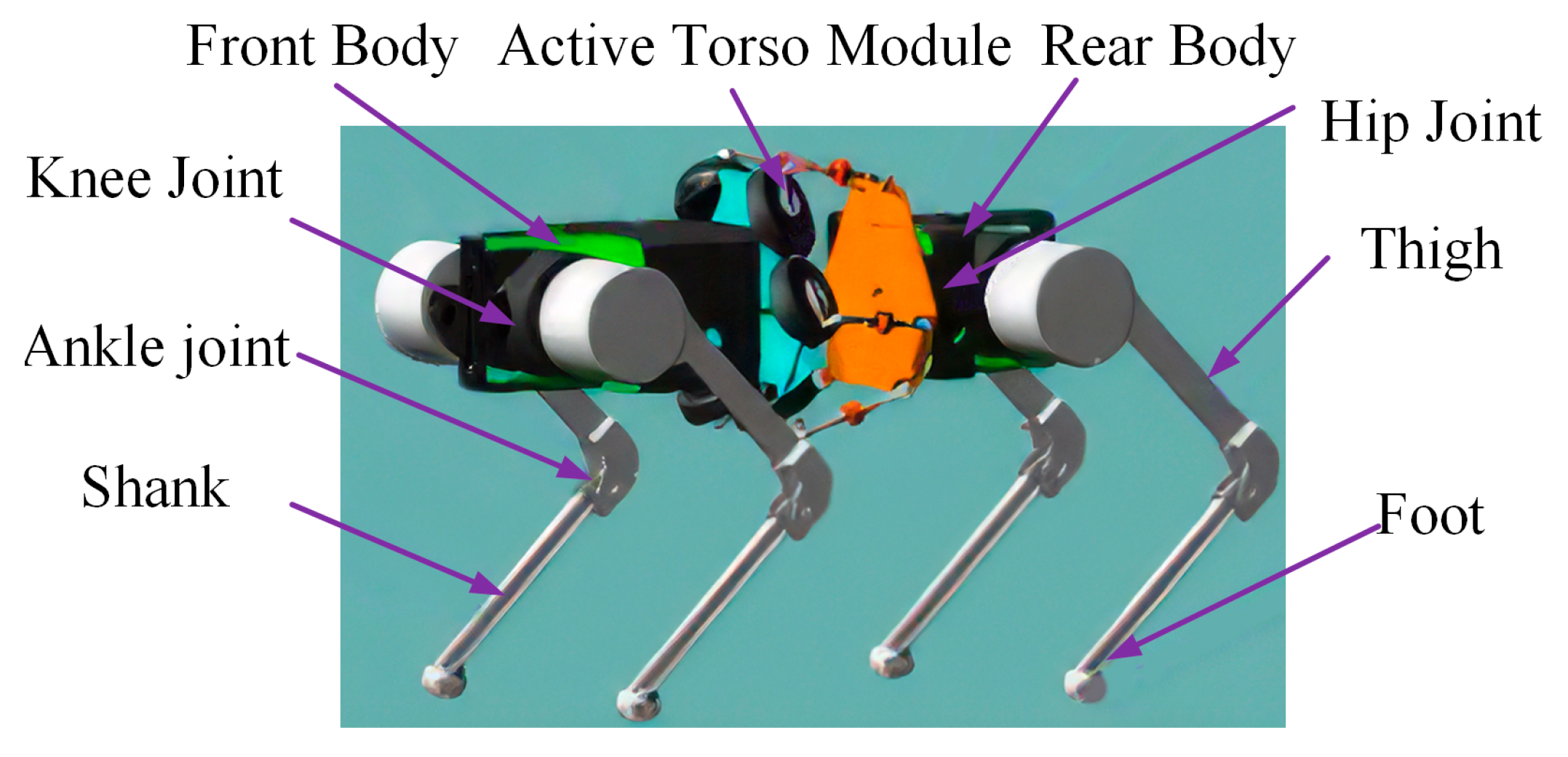




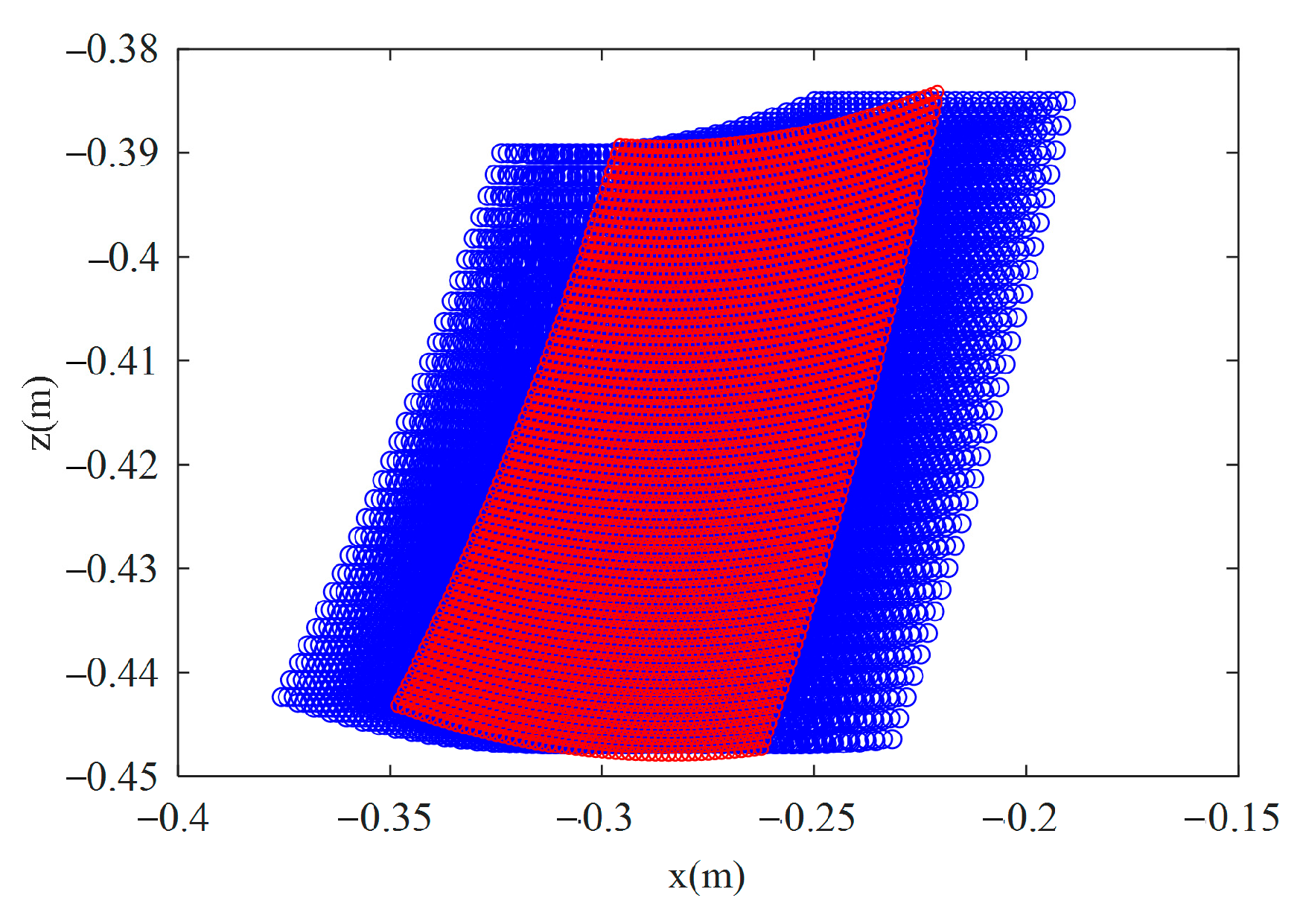

| Symbol | Structural Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Motor inclination angle | π/6 rad | |
| Radius of the | 0.136 m | |
| Radius of the | 0.132 m | |
| Distance between | 0.110 m | |
| Distance between | 0.088 m | |
| Rocker length | 0.040 m | |
| Link length | 0.140 m | |
| Height of from the moving platform | 0.015 m | |
| Height of from the static platform | 0.0235 m |
| Symbol | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Distance from the torso CoM to the front/rear hip joint | 0.286 m | |
| Distance from the longitudinal midline of The body to the hip joint | 0.058 m | |
| Distance between the Hip joint and the knee joint | 0.155 m | |
| Length of the thigh | 0.323 m | |
| Length of the shank | 0.304 m | |
| Vertical distance from the CoM to the foot end | 0.450 m |
| i | α° | a (m) | θ° | d (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0 | 0 | θ1 | 0 |
| 3 | 90° | 0 | θ2 | −L1 |
| 4 | 0 | L2 | θ3 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | L3 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Cao, A.; He, Z.; Zhou, M.; Li, R. Coordinated Locomotion Control for a Quadruped Robot with Bionic Parallel Torso. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050335
Zhu Y, Cao A, He Z, Zhou M, Li R. Coordinated Locomotion Control for a Quadruped Robot with Bionic Parallel Torso. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(5):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050335
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yaguang, Ao Cao, Zhimin He, Mengnan Zhou, and Ruyue Li. 2025. "Coordinated Locomotion Control for a Quadruped Robot with Bionic Parallel Torso" Biomimetics 10, no. 5: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050335
APA StyleZhu, Y., Cao, A., He, Z., Zhou, M., & Li, R. (2025). Coordinated Locomotion Control for a Quadruped Robot with Bionic Parallel Torso. Biomimetics, 10(5), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050335






