Multi-Modal Medical Image Registration with Full or Partial Data: A Manifold Learning Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Mono-Modality Medical Image Registration
1.2. Multi-Modality Medical Image Registration
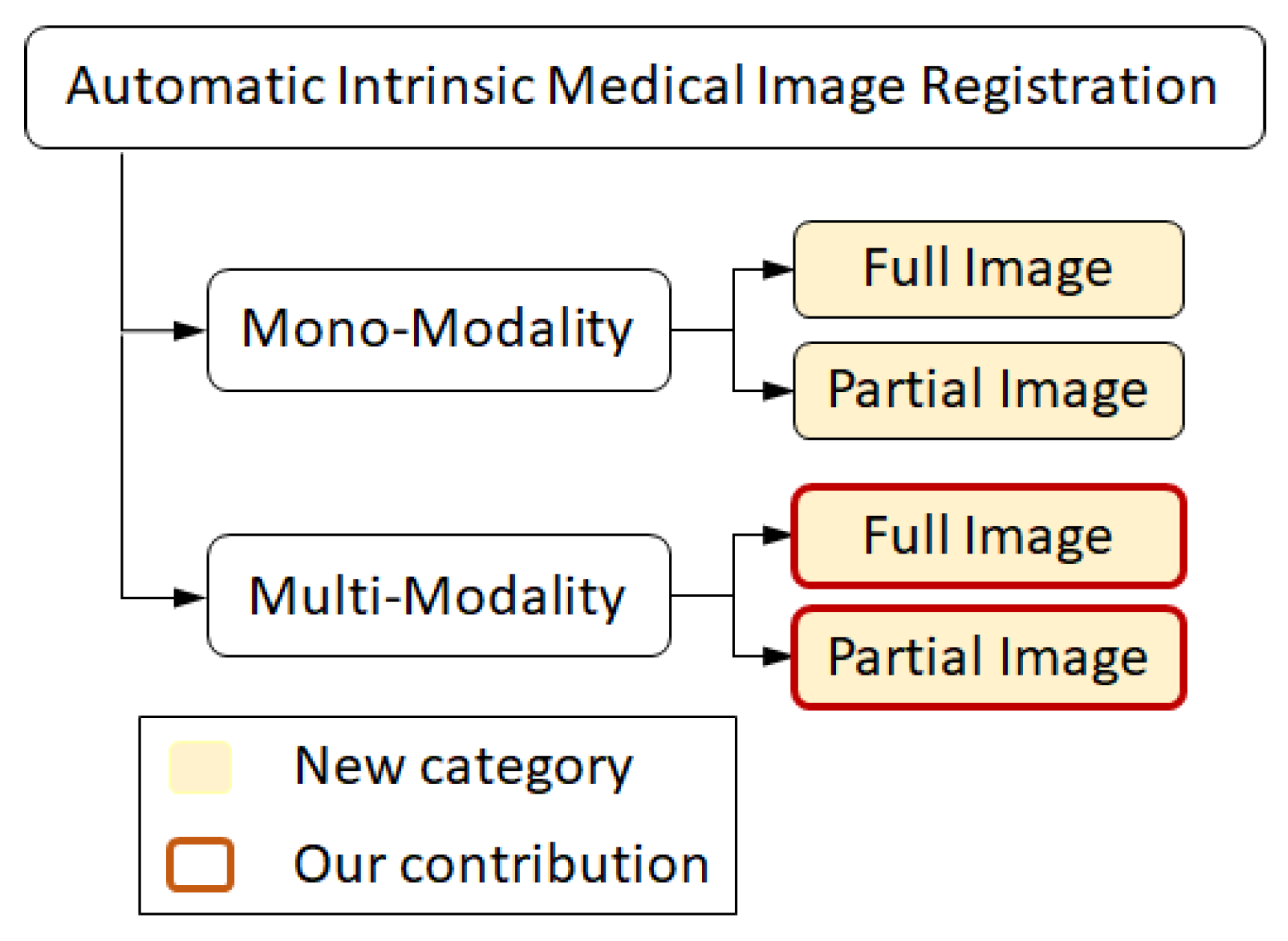
1.3. Motivations and Main Contributions
- We improve the technique presented in [37] and implement a multi-modal to mono-modal transformation. The proposed transformation facilitates a direct application of well-founded mono-modal registration techniques on multi-modal medical images as well as recovering strong scales, rotations, and translations. The current contribution falls into the group of multi-modality registration techniques (taxonomy presented in Figure 1). The method is novel in terms of its applicability for both types of images with full and partial overlap.
- Furthermore, we propose a fast and easy-to-use alignment technique that compensates random sign ambiguities caused by reflection of a principal vector. The alignment technique facilitates application of more complex optimization algorithms as well as intensity-based metrics. The proposed intensity transformation addresses the problem of registering multi-modal medical images with partial overlap. We qualitatively examine the performance of the proposed method, where commonly used MI-based multi-modal registration methods fail.
- From the experimental perspective, we present a set of qualitative and quantitative analysis to examine the performance and accuracy of the proposed system in which, a clinical input image was subject to multiple degree of freedom (translation, rotation, and/or scale at the same time). Using multiple datasets, including synthetic and real patients’ human brain images, we obtained a lower mean absolute error across different multi-modality registrations.
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Notations
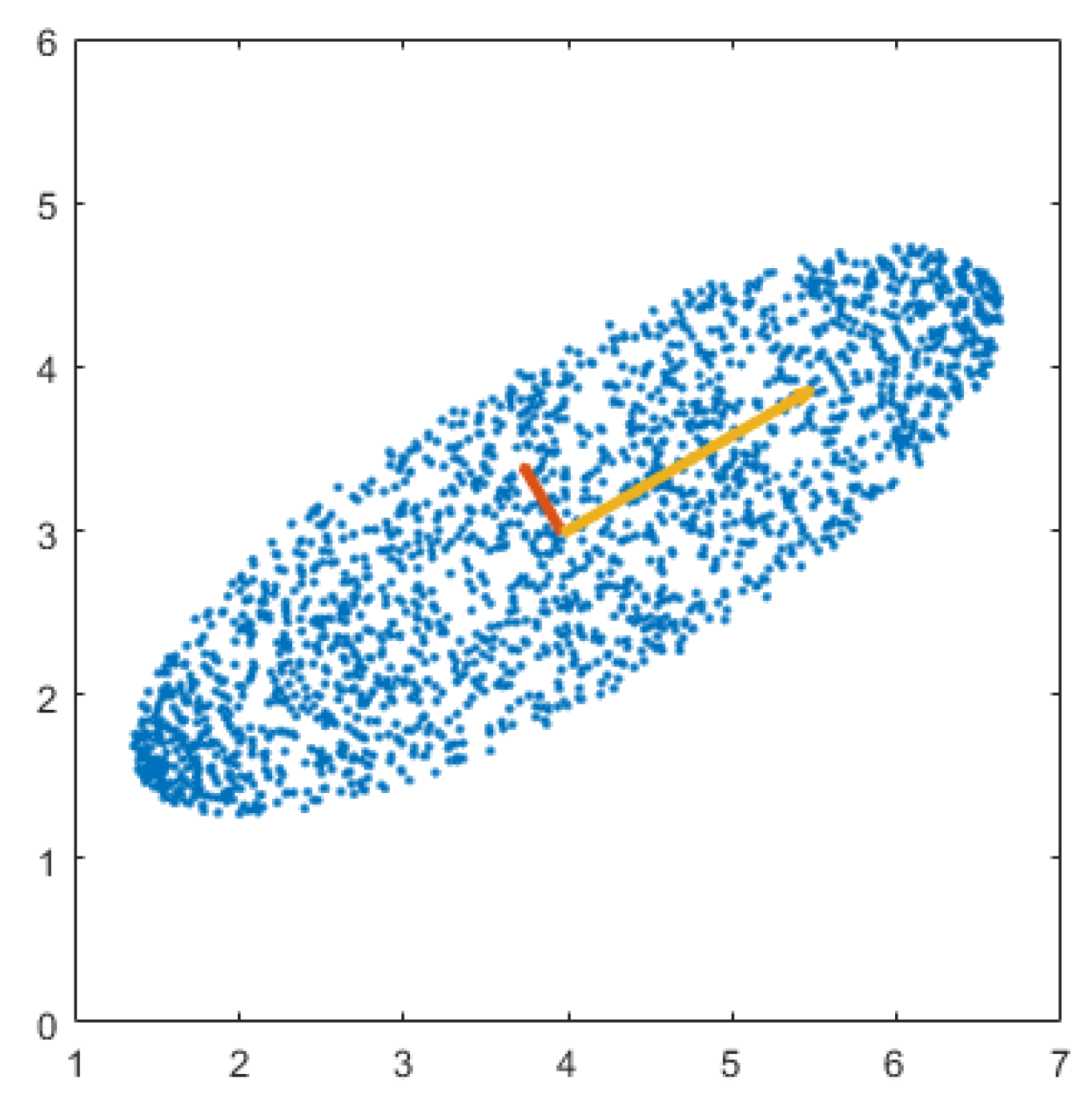
2.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.3. Laplacian Eigenmap
3. Methods
3.1. Constructing High-Dimensional Space
3.2. Manifold Learning
| Algorithm 1: Summary of dimensionality reduction (structural representation) with Laplacian Eigenmap. |
| Input: A set of N points in high-dimensional space Output: A set of N points in low-dimensional space 1 Compute the distance between every two data points; 2 Construct the adjacency graph by considering k-nearest neighbor with the choice of k and symmetric kNN graph; 3 Define bandwidth for ; 4 Assign weight to each edge between every two neighbors using heat kernel weighting scheme; 5 Construct the sparse, real, and symmetric matrices , , and ; 6 Find the number of connected components () from ; 7 Solve the generalized eigenvalue problem for eigenvalues and the corresponding eigenvectors; 8 Sort eigenvectors to represent the eigenvalues in increasing order; 9 Leave out the first eigenvectors; 10 Return the remaining d-eigenvectors; |
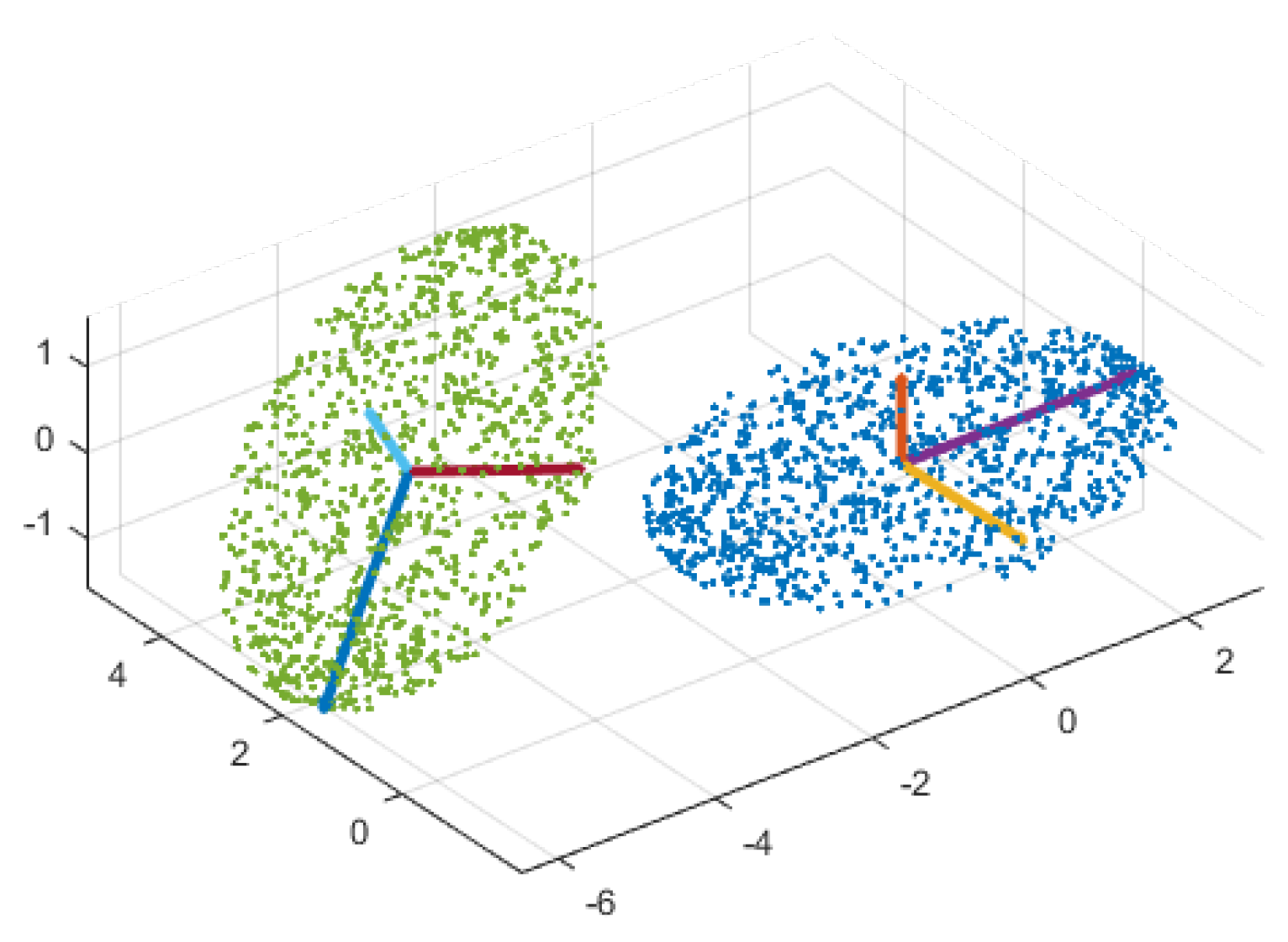
3.3. Manifold Alignment
3.4. Registration
4. Experimental Validation
4.1. Experimental Setup
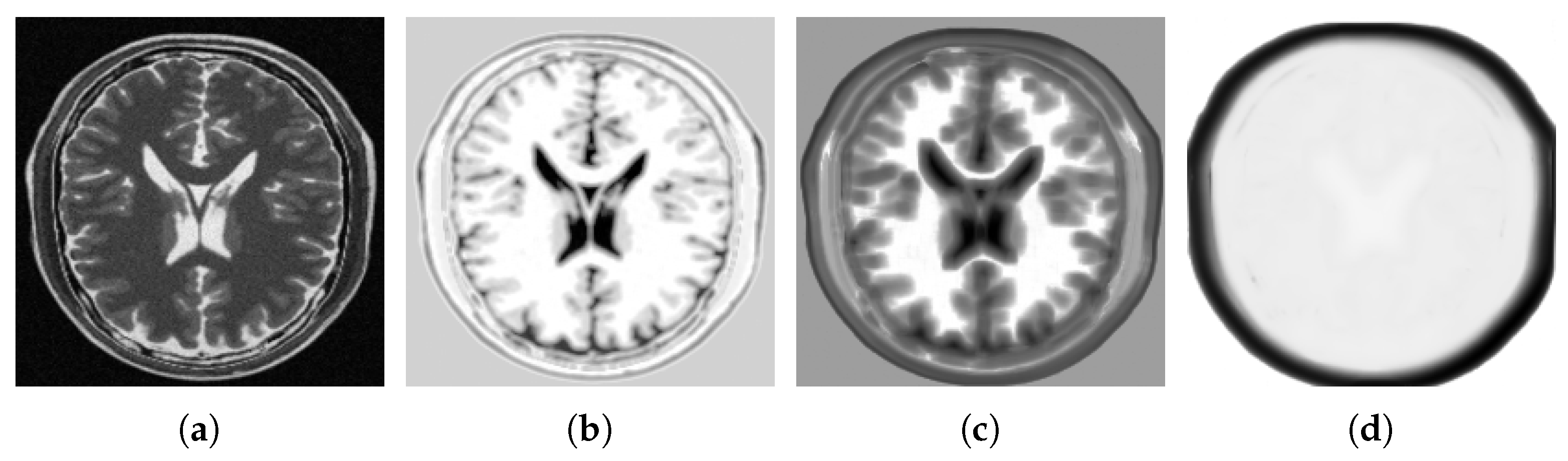
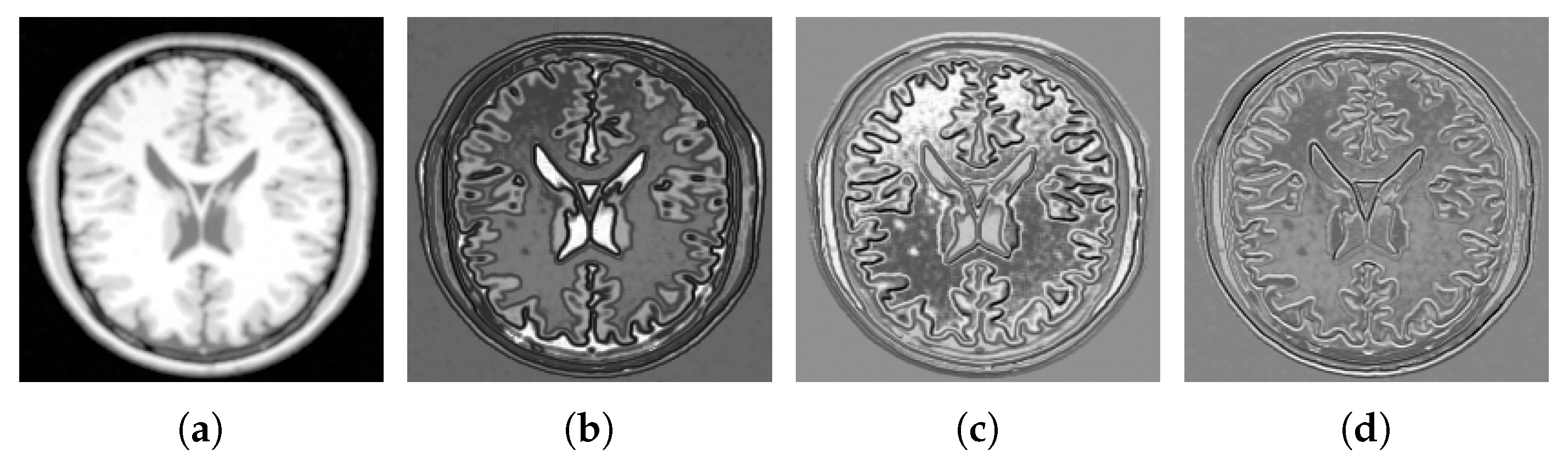
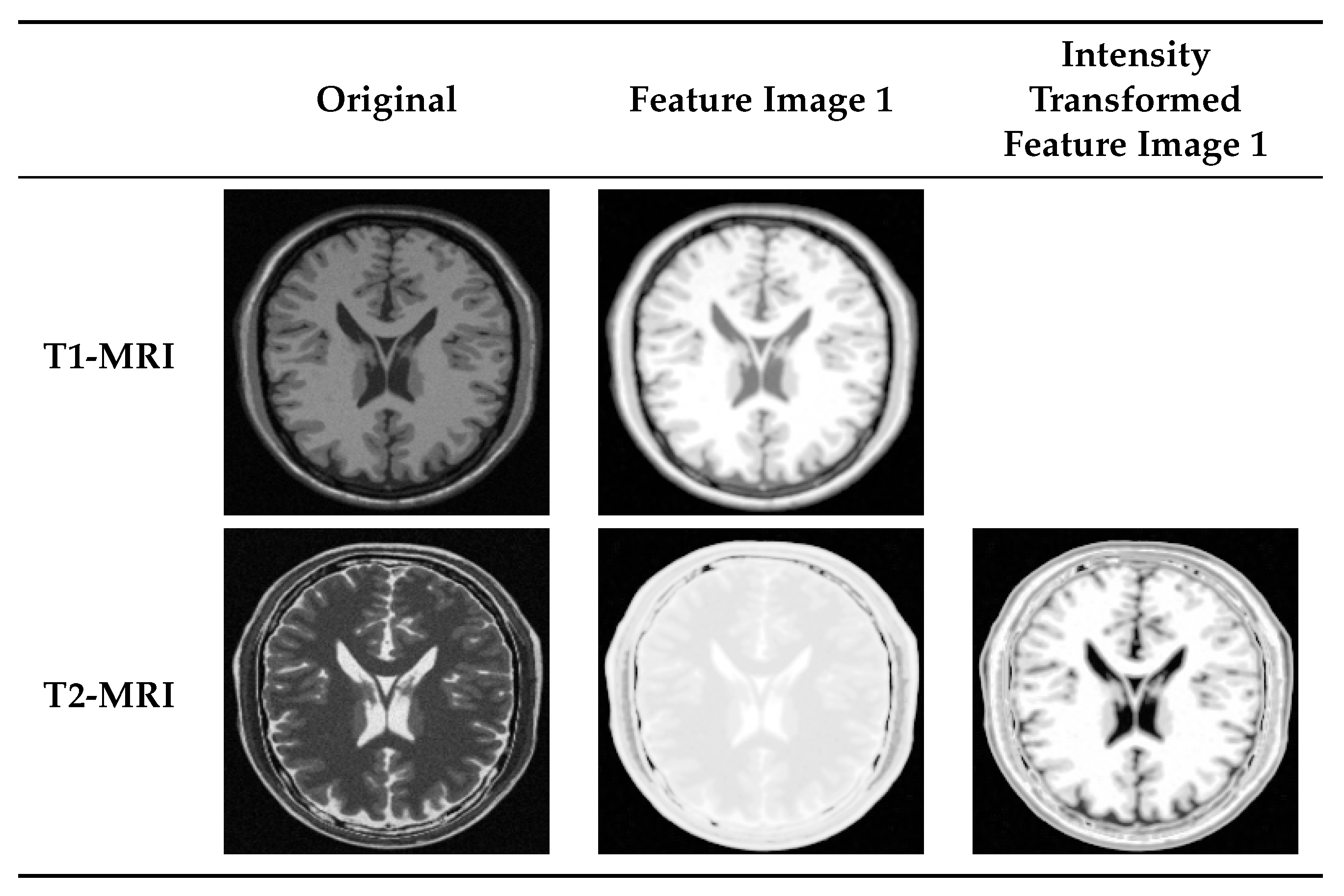
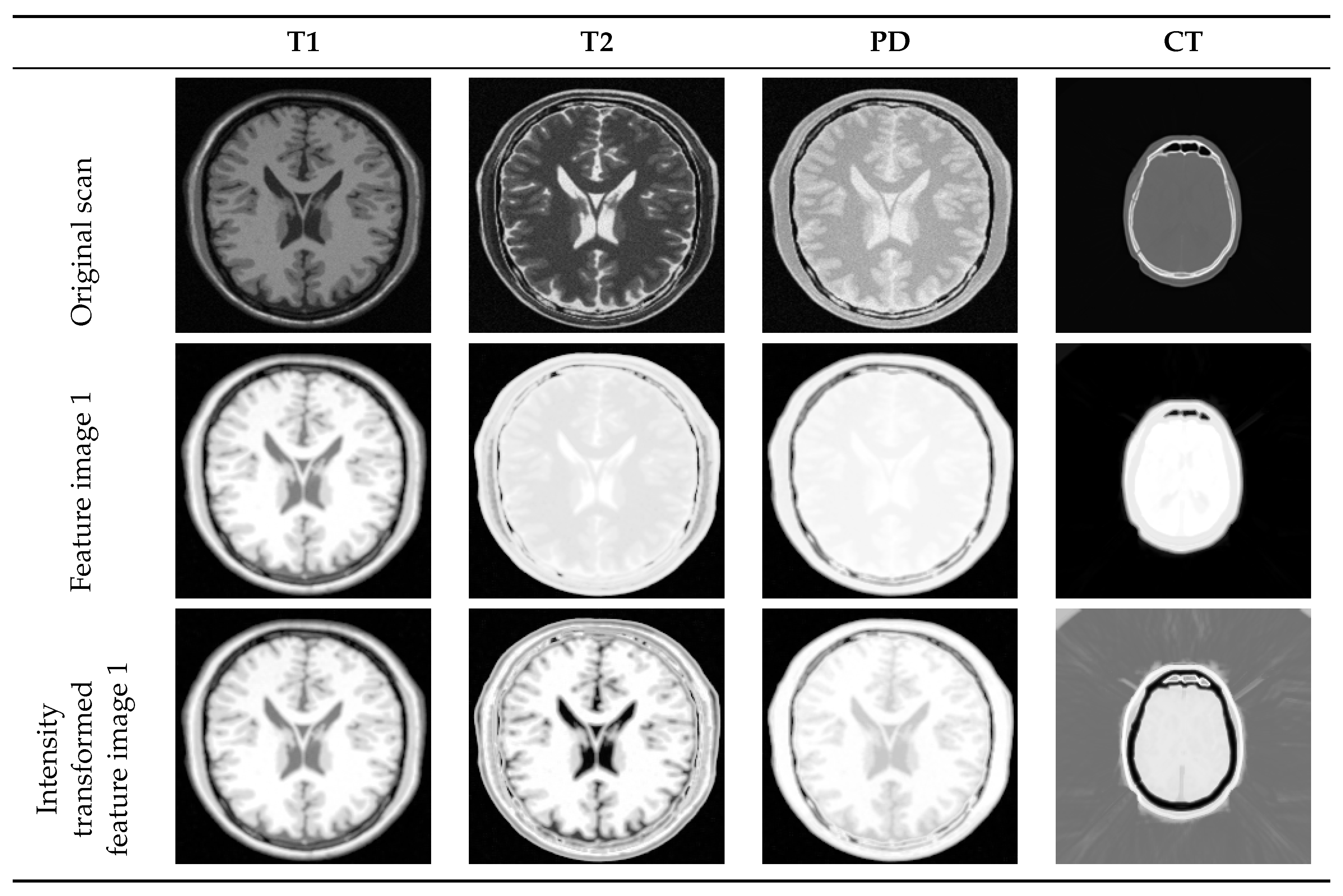
4.2. Multi-Modal to Mono-Modal Transformation
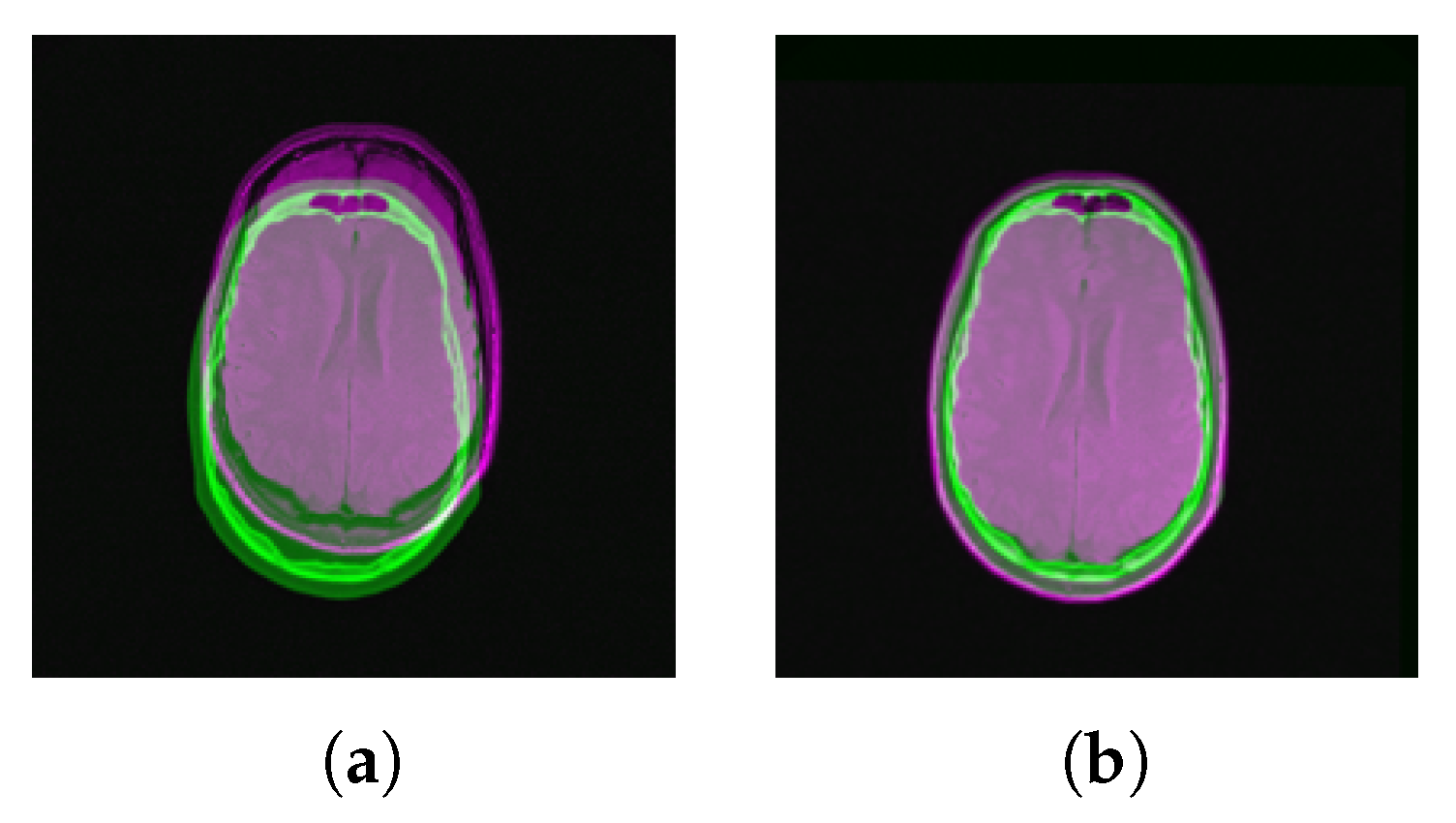
4.3. Multi-Modal Registration with Full Data
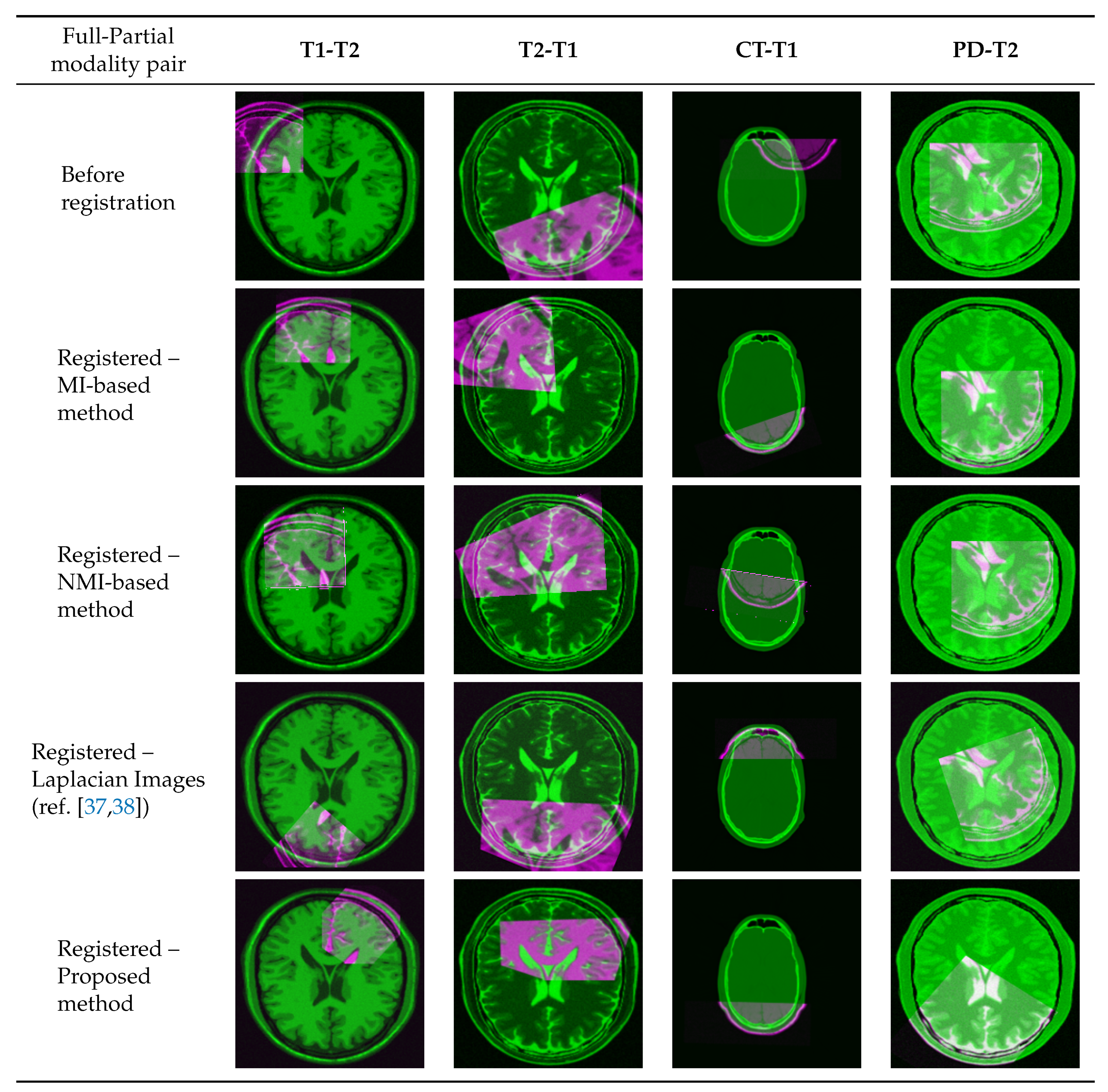
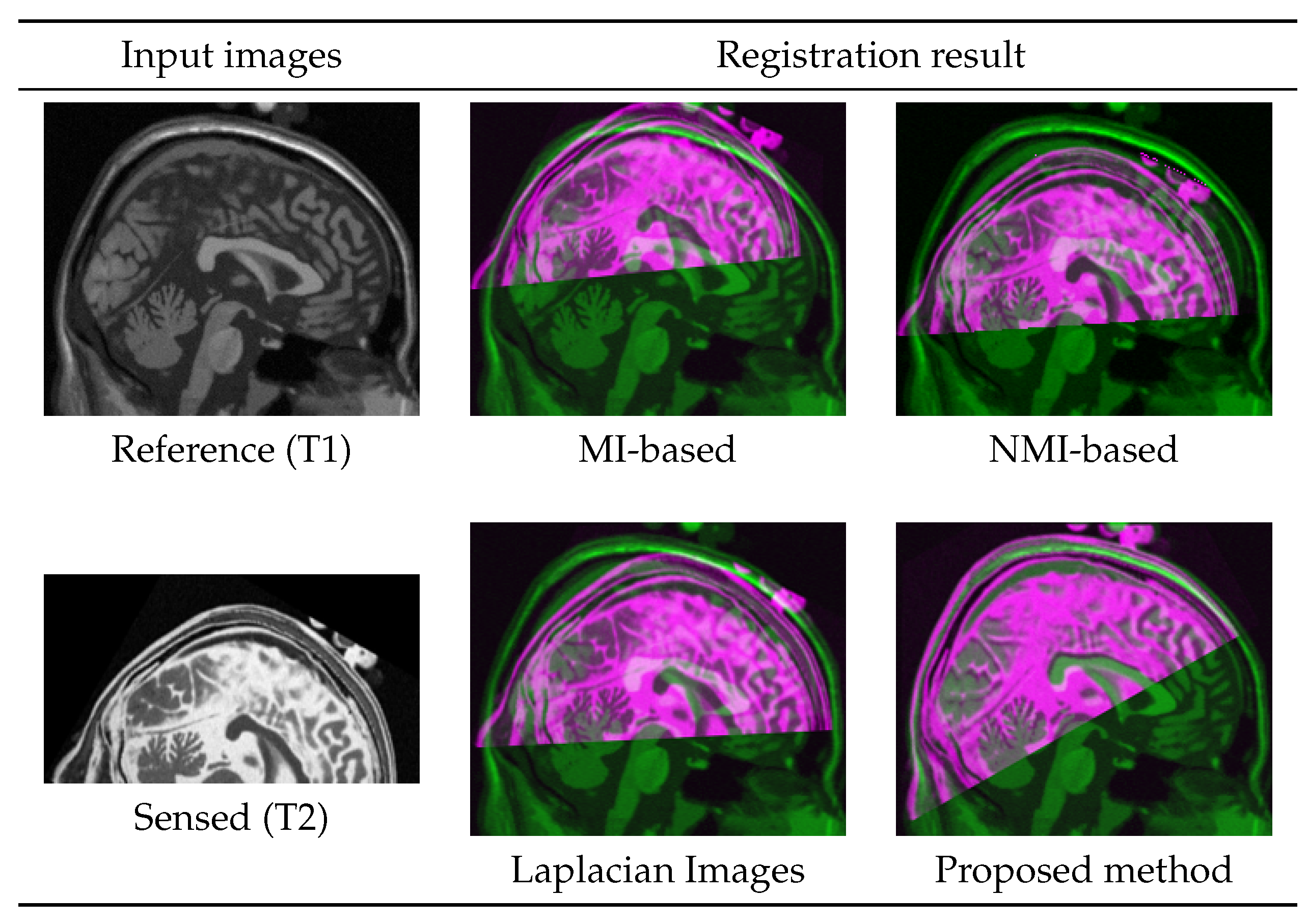
4.4. Multi-Modal Registration with Partial Data
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Havaei, M.; Davy, A.; Warde-Farley, D.; Biard, A.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y.; Pal, C.; Jodoin, P.M.; Larochelle, H. Brain tumor segmentation with deep neural networks. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 35, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Hou, Y.; Lam, F.; Guo, D.; Zhong, J.; Chen, Z. Magnetic resonance image reconstruction from undersampled measurements using a patch-based nonlocal operator. Med. Image Anal. 2014, 18, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedini, M.; Codella, N.C.; Connell, J.H.; Garnavi, R.; Merler, M.; Pankanti, S.; Smith, J.R.; Syeda-Mahmood, T. A generalized framework for medical image classification and recognition. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2015, 59, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H. Medical image classification via multiscale representation learning. Artif. Intell. Med. 2017, 79, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, A.; Khan, E.; Beg, M.S. Improved edge detection algorithm for brain tumor segmentation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 58, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshtasby, A.A. Image Registration: Principles, Tools and Methods; Advances in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Springer Science & Business Media: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sarvaiya, J.N.; Patnaik, S.; Kothari, K. Image registration using log polar transform and phase correlation to recover higher scale. J. Pattern Recognit. Res. 2012, 7, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Arivazhagan, S. Survey of medical image registration. J. Biomed. Eng. Technol. 2013, 1, 8–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sotiras, A.; Davatzikos, C.; Paragios, N. Deformable medical image registration: A survey. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 1153–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periaswamy, S.; Farid, H. Medical image registration with partial data. Med. Image Anal. 2006, 10, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gamal, F.E.Z.A.; Elmogy, M.; Atwan, A. Current trends in medical image registration and fusion. Egypt. Inform. J. 2016, 17, 99–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitova, B.; Flusser, J. Image registration methods: A survey. Image Vis. Comput. 2003, 21, 977–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, H.; Arridge, S.R. A survey of hierarchical non-linear medical image registration. Pattern Recognit. 1999, 32, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maintz, J.A.; Viergever, M.A. A survey of medical image registration. Med. Image Anal. 1998, 2, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.G. A survey of image registration techniques. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 1992, 24, 325–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Elsen, P.A.; Pol, E.J.; Viergever, M.A. Medical image matching—A review with classification. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 1993, 12, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohr, K. Elastic registration of multimodal medical images: A survey. Künstliche Intelligenz 2000, 14, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, D.L.; Batchelor, P.G.; Holden, M.; Hawkes, D.J. Medical image registration. Phys. Med. Biol. 2001, 46, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, F.P.; Tavares, J.M.R. Medical image registration: A review. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 17, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebara, N.V.; Meltzer, D.E. Extraspinal findings on lumbar spine MR imaging. J. Radiol. Case Rep. 2009, 3, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, B.S.; Chatterji, B.N. An FFT-based technique for translation, rotation, and scale-invariant image registration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1996, 5, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Pang, Y. An application of Fourier–Mellin transform in image registration. In Proceedings of the Fifth IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (CIT 2005), Shanghai, China, 21–23 September 2005; pp. 619–623. [Google Scholar]
- Pace, D.F.; Enquobahrie, A.; Yang, H.; Aylward, S.R.; Niethammer, M. Deformable image registration of sliding organs using anisotropic diffusive regularization. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Chicago, IL, USA, 30 March–2 April 2011; pp. 407–413. [Google Scholar]
- Pace, D.F.; Aylward, S.R.; Niethammer, M. A locally adaptive regularization based on anisotropic diffusion for deformable image registration of sliding organs. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 2114–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, C.; Klein, S.; Schaap, M.; van Walsum, T.; Niessen, W.J. Nonrigid registration of dynamic medical imaging data using nD+ t B-splines and a groupwise optimization approach. Med. Image Anal. 2011, 15, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Staring, M.; Andersson, P.; Pluim, J.P. Preconditioned stochastic gradient descent optimisation for monomodal image registration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Toronto, ON, Canada, 18–22 September 2011; pp. 549–556. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Azzawi, N.; Abdullah, W.A.K.W. MRI monomodal feature-based registration based on the efficiency of multiresolution representation and mutual information. Am. J. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 2, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, A.; Fatemizadeh, E. Sparse-induced similarity measure: Mono-modal image registration via sparse-induced similarity measure. IET Image Process. 2014, 8, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumchoba, N.; Jewpraserta, S.; Chantrapornchaib, C. Multigrid solution of the nonlinear PDEs arising in elastic image registration with application to a group of monomodal images. SCIENCEASIA 2016, 42, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, A.; Fatemizadeh, E. Image Registration based on Low Rank Matrix: Rank-Regularized SSD. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, F.; Collignon, A.; Vandermeulen, D.; Marchal, G.; Suetens, P. Multimodality image registration by maximization of mutual information. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1997, 16, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viola, P.; Wells III, W.M. Alignment by maximization of mutual information. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1997, 24, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studholme, C.; Hill, D.L.; Hawkes, D.J. An overlap invariant entropy measure of 3D medical image alignment. Pattern Recognit. 1999, 32, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronache, A.; von Siebenthal, M.; Székely, G.; Cattin, P. Non-rigid registration of multi-modal images using both mutual information and cross-correlation. Med. Image Anal. 2008, 12, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, S.; Su, H.; Chen, Y. Mutual information-based multimodal image registration using a novel joint histogram estimation. Comput. Med. Imaging Gr. 2008, 32, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, N.D.; Schnabel, J.A.; Noble, J.A.; Hawkes, D.J. Overlap invariance of cumulative residual entropy measures for multimodal image alignment. Proc. SPIE 2009, 7259, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Wachinger, C.; Navab, N. Manifold Learning for Multi-Modal Image Registration. In Proceedings of the 11st British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Aberystwyth, UK, 31 August–3 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wachinger, C.; Navab, N. Entropy and Laplacian images: Structural representations for multi-modal registration. Med. Image Anal. 2012, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, M.P.; Jenkinson, M.; Bhushan, M.; Matin, T.; Gleeson, F.V.; Brady, M.; Schnabel, J.A. MIND: Modality independent neighbourhood descriptor for multi-modal deformable registration. Med. Image Anal. 2012, 16, 1423–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktar, M.N.; Alam, M.J.; Pickering, M. A non-rigid 3D multi-modal registration algorithm using partial volume interpolation and the sum of conditional variance. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Digital lmage Computing: Techniques and Applications (DlCTA), Wollongong, Australia, 25–27 November 2014; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schuh, A.; Rajchl, M.; Keraudren, K.; Gomez, A.; Heinrich, M.P.; Penney, G.; Rueckert, D. Structured decision forests for multi-modal ultrasound image registration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 363–371. [Google Scholar]
- Simonovsky, M.; Gutiérrez-Becker, B.; Mateus, D.; Navab, N.; Komodakis, N. A deep metric for multimodal registration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2016; pp. 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Yang, J.; Gao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wu, G.; Shen, D. Dual-core steered non-rigid registration for multi-modal images via bi-directional image synthesis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 41, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceranka, J.; Polfliet, M.; Lecouvet, F.; Michoux, N.; de Mey, J.; Vandemeulebroucke, J. Registration strategies for multi-modal whole-body MRI mosaicing. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 1684–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, F.; Zhang, J.; Dashtbozorg, B.; Abbasi-Sureshjani, S.; Sun, Y.; Long, X.; Yu, Q.; ter Haar Romeny, B.; Tan, T. Multi-modal and multi-vendor retina image registration. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljabar, P.; Wolz, R.; Rueckert, D. Manifold learning for medical image registration, segmentation, and classification. In Machine Learning in Computer-Aided Diagnosis: Medical Imaging Intelligence and Analysis: Medical Imaging Intelligence and Analysis; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2012; p. 351. [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez, C.; Plassard, A.J.; Davis, L.T.; Newton, A.T.; Resnick, S.M.; Landman, B.A. Learning Implicit Brain MRI Manifolds with Deep Learning. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1801.01847. [Google Scholar]
- Mateus, D.; Wachinger, C.; Atasoy, S.; Schwarz, L.; Navab, N. Learning manifolds: Design analysis for medical applications. In Machine Learning in Computer-Aided Diagnosis: Medical Imaging Intelligence and Analysis; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 374–402. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, K. LIII. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, M.; Niyogi, P. Laplacian Eigenmaps for Dimensionality Reduction and Data Representation. Neural Comput. 2003, 15, 1373–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hao, P. Finding representative landmarks of data on manifolds. Pattern Recognit. 2009, 42, 2335–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Zhang, P.; Wang, D.; Zhang, B. An explicit nonlinear mapping for manifold learning. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Maaten, L.; Postma, E.; Van den Herik, J. Dimensionality reduction: A comparative. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2009, 10, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Cayton, L. Algorithms for Manifold Learning; Technical Report; University of California at San Diego: San Diego, CA, USA, 2005; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Fu, Y. Manifold Learning Theory and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bellekens, B.; Spruyt, V.; Berkvens, R.; Weyn, M. A survey of rigid 3D pointcloud registration algorithms. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Ambient Computing, Applications, Services and Technologies, Rome, Italy, 24–28 August 2014; pp. 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Belkin, M.; Niyogi, P. Laplacian Eigenmaps and Spectral Techniques for Embedding and Clustering. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–8 December 2001; pp. 585–591. [Google Scholar]
- Blockeel, H.; Kersting, K.; Nijssen, S.; Zelezny, F. Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kafieh, R.; Rabbani, H.; Abramoff, M.D.; Sonka, M. Intra-retinal layer segmentation of 3D optical coherence tomography using coarse grained diffusion map. Med. Image Anal. 2013, 17, 907–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, A.; Erban, R.; Kevrekidis, I.G.; Coifman, R.R. Detecting intrinsic slow variables in stochastic dynamical systems by anisotropic diffusion maps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16090–16095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, F.R. Spectral Graph Theory; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 1997; Volume 92. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A. Representation, Segmentation and Matching of 3D Visual Shapes Using Graph Laplacian and Heat-Kernel. Ph.D. Thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Grenoble-INPG, Grenoble, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, R. Elementary Linear Algebra; Nelson Education: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Buser, P. Geometry and Spectra of Compact Riemann Surfaces; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Householder, A.S.; Bauer, F.L. On certain methods for expanding the characteristic polynomial. Numer. Math. 1959, 1, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.H.; Wilkinson, J.H. The Algebraic Eigenvalue Problem; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1965; Volume 87. [Google Scholar]
- Bathe, K.; Wilson, E.L. Large eigenvalue problems in dynamic analysis. J. Eng. Mech. Div. 1972, 98, 1471–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Bathe, K.; Saunders, H. Finite Element Procedures in Engineering Analysis; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, P. The truncated Lanczos algorithm for partial solution of the symmetric eigenproblem. Comput. Struct. 1976, 6, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehoucq, R.B.; Sorensen, D.C.; Yang, C. ARPACK Users’ Guide: Solution of Large-Scale Eigenvalue Problems with Implicitly Restarted Arnoldi Methods; Siam: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1998; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Wang, M.; Song, Z. Manifold-based feature point matching for multi-modal image registration. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2013, 9, e10–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Mahadevan, S. Manifold alignment using procrustes analysis. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning, Helsinki, Finland, 5–9 July 2008; pp. 1120–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Mahadevan, S. Heterogeneous Domain Adaptation Using Manifold Alignment. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Second International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI’11), Barcelona, Spain, 16–22 July 2011; Volume 22, pp. 1541–1546. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, Y.; Kim, T.K.; Zha, H. Unsupervised random forest manifold alignment for lipreading. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Tuia, D.; Volpi, M.; Trolliet, M.; Camps-Valls, G. Semisupervised manifold alignment of multimodal remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 7708–7720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Staring, M.; Murphy, K.; Viergever, M.A.; Pluim, J.P. Elastix: A toolbox for intensity-based medical image registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamonin, D.P.; Bron, E.E.; Lelieveldt, B.P.; Smits, M.; Klein, S.; Staring, M. Fast parallel image registration on CPU and GPU for diagnostic classification of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocosco, C.A.; Kollokian, V.; Kwan, R.K.S.; Pike, G.B.; Evans, A.C. Brainweb: Online interface to a 3D MRI simulated brain database. NeuroImage 1997, 5, S425. [Google Scholar]
- Kwan, R.S.; Evans, A.C.; Pike, G.B. MRI simulation-based evaluation of image-processing and classification methods. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1999, 18, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, R.K.S.; Evans, A.C.; Pike, G.B. An extensible MRI simulator for post-processing evaluation. In Proceedings of the Visualization in biomedical computing, Hamburg, Germamy, 22–25 September 1996; pp. 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, D.L.; Zijdenbos, A.P.; Kollokian, V.; Sled, J.G.; Kabani, N.J.; Holmes, C.J.; Evans, A.C. Design and construction of a realistic digital brain phantom. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1998, 17, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.B.; Fitzpatrick, J.M.; Wang, M.Y.; Dawant, B.M.; Maurer, C.R.; Kessler, R.M.; Maciunas, R.J.; Barillot, C.; Lemoine, D.; Collignon, A.M.; et al. Comparison and evaluation of retrospective intermodality image registration techniques. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 1996: Image Processing, Newport Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 February 1996; Volume 2710, pp. 332–348. [Google Scholar]
- West, J.; Fitzpatrick, J.M.; Wang, M.Y.; Dawant, B.M.; Maurer, C.R., Jr.; Kessler, R.M.; Maciunas, R.J.; Barillot, C.; Lemoine, D.; Collignon, A.; et al. Comparison and evaluation of retrospective intermodality brain image registration techniques. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1997, 21, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, J.M.; West, J.B.; Maurer, C.R. Predicting error in rigid-body point-based registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1998, 17, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Fitzpatrick, J.M. A technique for accurate magnetic resonance imaging in the presence of field inhomogeneities. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1992, 11, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattes, D.; Haynor, D.R.; Vesselle, H.; Lewellyn, T.K.; Eubank, W. Nonrigid multimodality image registration. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2001: Image Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 17–22 February 2001; Volume 4322, pp. 1609–1621. [Google Scholar]
- Styner, M.; Gerig, G. Evaluation of 2D/3D Bias Correction with 1+1 ES-Optimization; Technical Report 179; Image Science Lab, ETH: Zürich, Switzerland, 1997; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]


| Modality Pair | Before Registration | After Registration |
|---|---|---|
| CT-PD | 0.8752 ± 0.15 | 1.2084 ± 0.22 |
| CT-T1 | 0.8685 ± 0.15 | 1.1863 ± 0.23 |
| CT-T2 | 0.8151 ± 0.10 | 1.0800 ± 0.20 |
| CT-PD Rectified | 0.7846 ± 0.08 | 1.1132 ± 0.09 |
| CT-T1 Rectified | 0.7759 ± 0.06 | 1.0958 ± 0.08 |
| CT-T2 Rectified | 0.7736 ± 0.06 | 1.0450 ± 0.06 |
| Modality Pair | Laplacian Images (ref. [37,38]) | MI-Based Reg. w/o Intensity Trans. | Mono-Modal Reg. w/ Proposed Trans. |
|---|---|---|---|
| CT-PD | 3.5622 ± 0.05 | 2.0239 ± 0.14 | 1.3740 ± 0.09 |
| CT-T1 | 2.9912 ± 0.11 | 1.3873 ± 0.18 | 1.0042 ± 0.11 |
| CT-T2 | 1.9467 ± 0.15 | 1.7335 ± 0.12 | 1.4137 ± 0.09 |
| CT-PD Rectified | 2.3318 ± 0.12 | 1.3260 ± 0.21 | 1.1462 ± 0.11 |
| CT-T1 Rectified | 2.0075 ± 0.07 | 0.9727 ± 0.39 | 0.7424 ± 0.22 * |
| CT-T2 Rectified | 1.9447 ± 0.33 | 0.9294 ± 0.23 | 0.9922 ± 0.16 ** |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bashiri, F.S.; Baghaie, A.; Rostami, R.; Yu, Z.; D’Souza, R.M. Multi-Modal Medical Image Registration with Full or Partial Data: A Manifold Learning Approach. J. Imaging 2019, 5, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging5010005
Bashiri FS, Baghaie A, Rostami R, Yu Z, D’Souza RM. Multi-Modal Medical Image Registration with Full or Partial Data: A Manifold Learning Approach. Journal of Imaging. 2019; 5(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging5010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleBashiri, Fereshteh S., Ahmadreza Baghaie, Reihaneh Rostami, Zeyun Yu, and Roshan M. D’Souza. 2019. "Multi-Modal Medical Image Registration with Full or Partial Data: A Manifold Learning Approach" Journal of Imaging 5, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging5010005
APA StyleBashiri, F. S., Baghaie, A., Rostami, R., Yu, Z., & D’Souza, R. M. (2019). Multi-Modal Medical Image Registration with Full or Partial Data: A Manifold Learning Approach. Journal of Imaging, 5(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging5010005





