Abstract
This study aimed to develop the eco-friendly production of bioactive 1-hydroxyphenazine (HP) through fermentation using an industrial processing by-product of cassava as the main carbon/nitrogen source. Cassava starch processing by-product (CSPB) was screened as a suitable substrate for fermentation to produce HP with a high yield. Mixing CSPB with a minor amount of tryptic soy broth (TSB) at a ratio of 8/2 and with 0.05% K2HPO4 and 0.05% FeSO4 was effective in HP production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa TUN03. HP was also further scaled up through production on a bioreactor system, which achieved a higher level yield (36.5 µg/mL) in a shorter fermentation time (10 h) compared to its production in the flask (20.23 µg/mL after 3 days). In anti-fungal activity tests against various Fusarium phytopathogens, HP exhibited the most significant effect on Fusarium oxysporum F10. It could inhibit the mycelial growth of this fungus, with an inhibition rate of 68.7% and anti-spore germination activity of up to 98.4%. The results of the docking study indicate that HP effectively interacted with the protein 1TRY targeting anti-F. oxysporum, with all obtained docking parameters in the accepted range. This study supports the novel use of CSPB as the carbon/nitrogen source for P. aeruginosa fermentation to produce HP, a F. oxysporum anti-fungal agent reported here for the first time.
1. Introduction
Cassava (Manihot esculenta C.), a drought-tolerant crop, may be grown in unfavorable conditions such as in soils with poor nutrients and unpredictable rainfall (FAO 2013). Cassava is one of the major staple crops in sub-Saharan Africa and is a high-value crop in industrialized Asian countries [1]. Cassava is also cultivated widely in Vietnam, being a top cassava cultivator and ranking seventh among the top cassava-producing countries in the world [2]. This plant has been long used as human food and feed for animals, as well as for starch extraction, bioethanol production, and in other products, such as cosmetics, medicine, and biopolymers [3]. Cassava starch processing by-product (CSPB) is generated in a significant amount after the extraction of starch from cassava and is still rich in nutrients that can cause environmental pollution if not well managed [4]. CSPB is mainly reused as animal feed and fertilizer [5,6,7]. It has been widely investigated as a material for producing organic acids, volatile fatty acids, biofuels, aroma compounds, biosurfactants, and biogases [4,8,9,10]. In Vietnam, CSPB is produced annually in large amounts and stable quantities. Thus, this by-product source is abundant and holds promise in research and application. Thus, in this work, we utilized CSPB for the production of a bioactive phenazine compound (1-hydroxyphenazine) through fermentation.
Phenazine, a nitrogenous and heterocyclic compound, has the formula of (C6H4)2N2. Approximately 100 natural phenazines are formed from the basic chemical structure of phenazine [11]. Natural phenazines are mainly produced by microbial strains. Pseudomonas species were found to produce more than 50 phenazines [12], of which P. aeruginosa has been used as a major phenazine compound-producing bacterial strain. In previous reports, commercial culture broths were used as a C/N source for the fermentation of phenazine production, and the fermentation processes were mainly conducted at minor scales in flasks. Given its environmental issues and cost production, this study aims to use CSPB as the main substrate for fermentation. In addition, most earlier reports focus on the investigation of production and bioactivity testing for a major phenazine pyocyanin, while only very few evaluated the production and bioactivities of hemi-pyocyanin (also known as 1-hydroxyphenazine) [13,14,15].
In our earlier work, P. aeruginosa TUN03 was newly found as a potent 1-hydroxyphenazine-producing strain [16]. In the current work, 1-hydroxyphenazine was produced at low cost using CSPB for fermentation by P. aeruginosa TUN03. This bacterial strain can use diverse nutrient sources from various by-products and wastes [17]; thus, CSPB can be a novel ideal substrate for its fermentation to produce this valuable metabolite. The effect of purified 1-hydroxyphenazine against various plant pathogen fungal strains was tested, and the possible mechanism of action concerning the anti-fungal effect was also investigated using molecular docking.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Nutrient Ingredient Content of Cassava Starch Processing By-Product
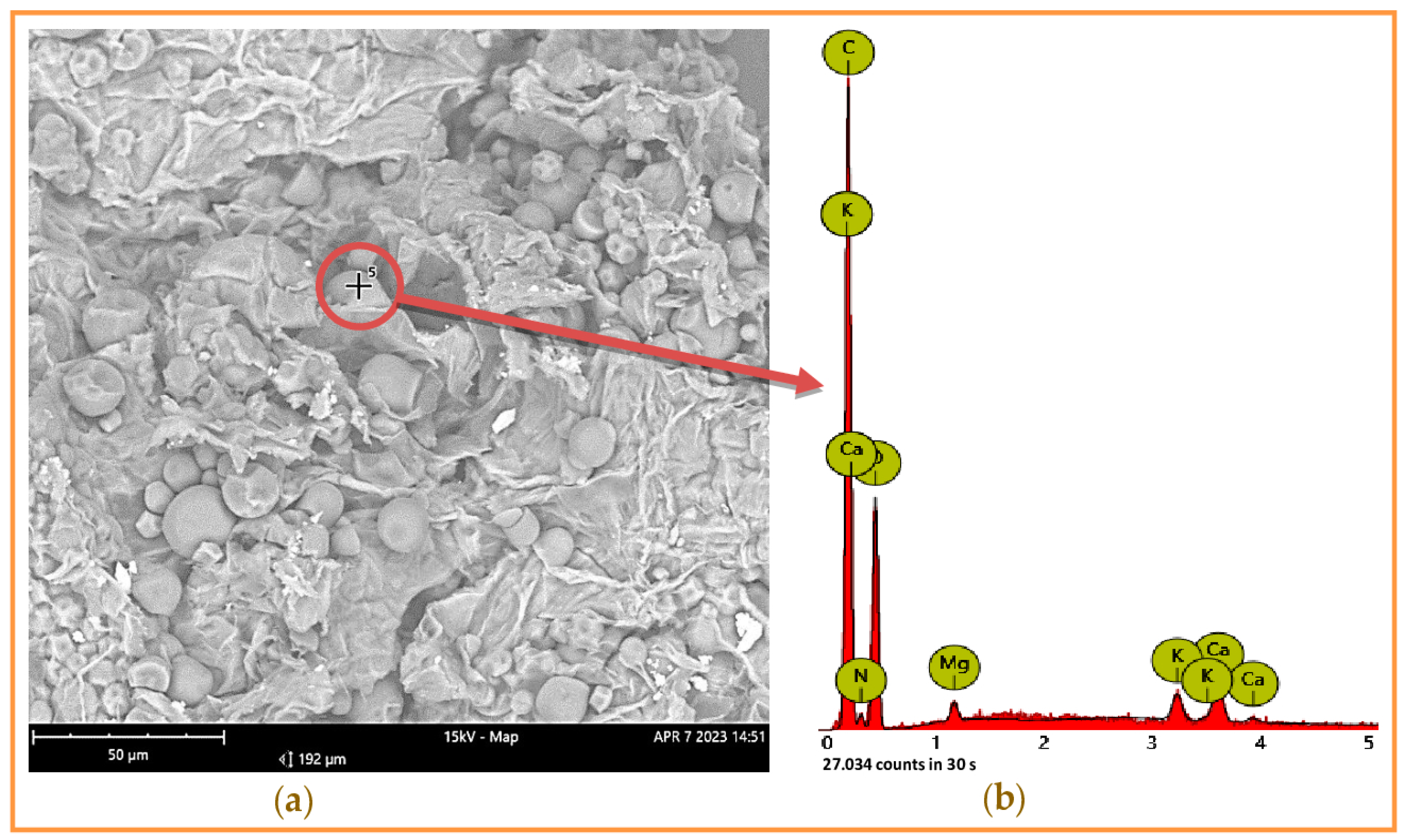
Some essential nutrient contents such as protein, lipids, ash, and glucids in the input material CSPB were determined. As per the data summarized in Table 1, CSPB has a significant amount of starch and crude fiber, at 9.954% and 16.61%, respectively, and a moderate content of protein (1.83%), lipids (0.87%), and total sugar (0.61%). In addition, this by-product is also rich in ash at 6.73%, along with diverse mineral elements. The amount of some specific minerals was also determined, including Ca, Mg, K, and P in the range of 0.023–0.149%. Further, mineral elements presented in CSPB ash were also further detected by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (Figure 1), and data recorded the presence of C, K, Ca, and Mg. Based on the analysis results, CSPB still contains a nutrient composition that may be suitable for bacterial fermentation. In previous studies, P. aeruginosa produced various enzymes such as amylase, protease, lipase, and cellulase [18,19]. Thus, CSPB may be a suitable nutrient source for P. aeruginosa TUN03 fermentation in this study. This information would be helpful for designing necessary supplements for the cultural medium to achieve an effective fermentation process. However, the substrate composition did not reach 100%, as other components such as pectin and lignin were not quantified in this work.

Table 1.
The content of nutrient ingredients in cassava starch processing by-product.
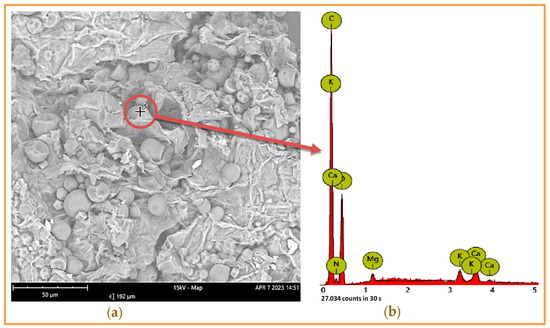
Figure 1.
Application of scanning electron microscopy for analysis of mineral elements contained in cassava starch processing by-product (CSPB) ash. The analyzed point on the surface of CSPB ash (a) and the mineral elements were detected by energy dispersive X-ray (b).
2.2. Production of 1-Hydroxyphenazine via Fermentation
2.2.1. Establishing 1-Hydroxyphenazine Biosynthesis in Small Flasks
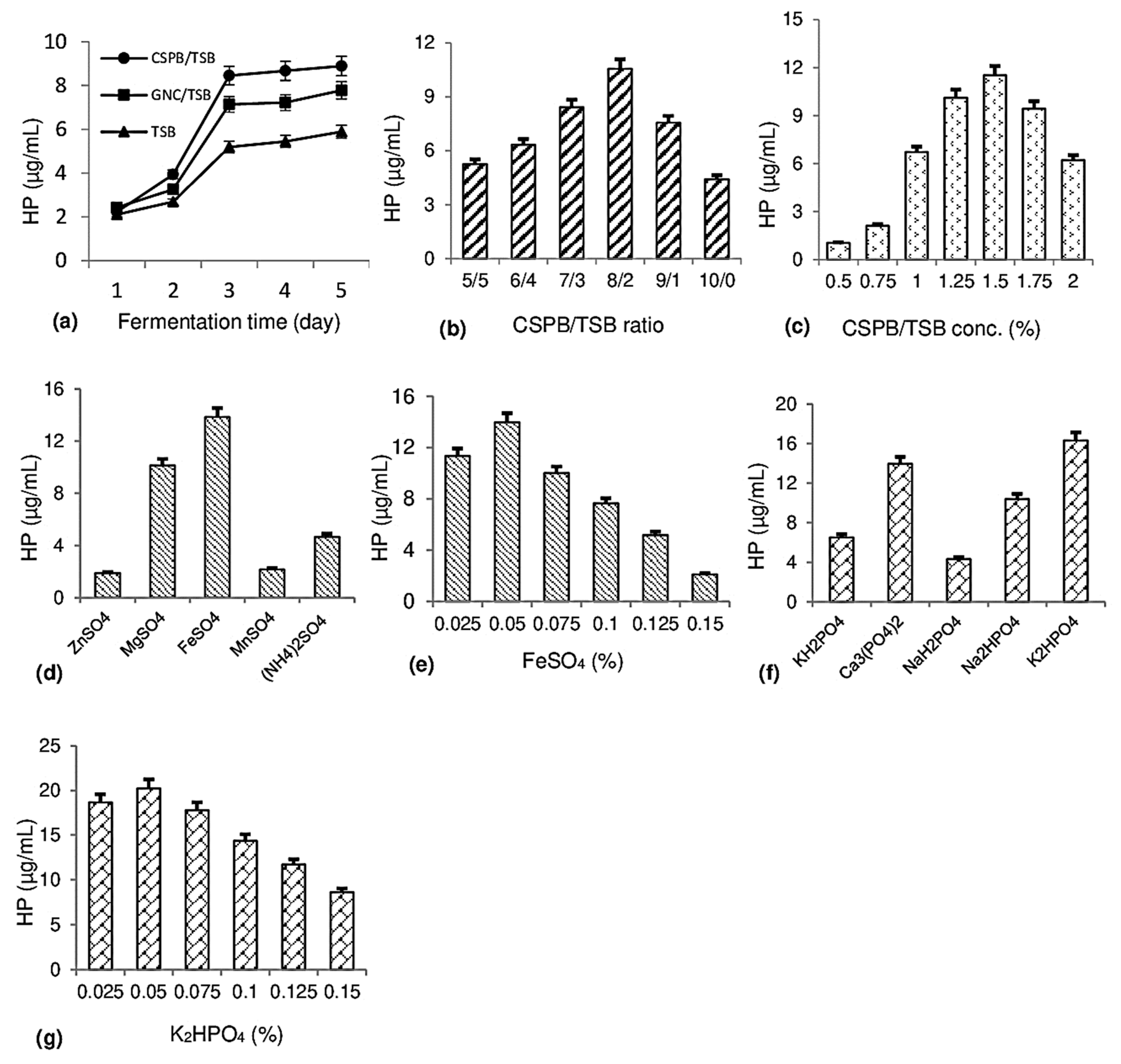
Fermentation in a small flask was designed to evaluate the effect of certain factors including carbon/nitrogen (C/N) sources, CSPB/tryptic soy broth (TSB) ratios, substrate concentration, and mineral salts on HP biosynthesis by P. aeruginosa TUN03. The results are summarized in Figure 2.
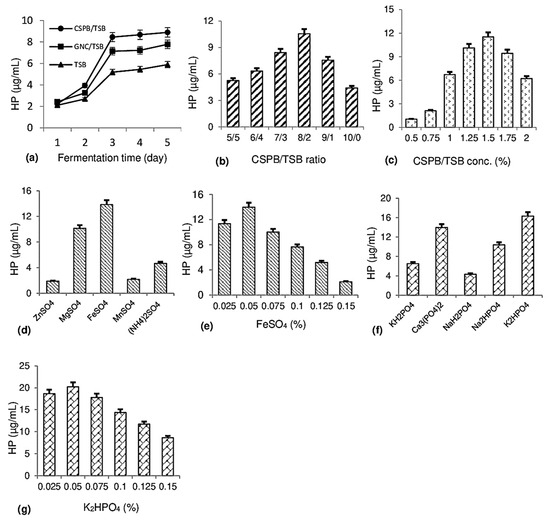
Figure 2.
Establishing biosynthesis of 1-hydroxyphenazine (HP) in small flasks. The effect of C/N source (a), cassava starch processing by-product (CSPB)/tryptic soy broth (TSB) ratio (b), CSPB/TSB concentration (c), sulfate salt (d), FeSO4 concentration (e), phosphate salt (f), and K2HPO4 concentration (g) on HP production by P. aeruginosa TUN03.
The effect of C/N sources on HP production: Organic by-products (CSPB, groundnut cake (GNC)) and a commercial medium (TSB) were used as C/N sources for fermentation by P. aeruginosa TUN03. In a previous report [20], groundnut cake was found to be suitable as a C/N source for fermentation to produce HP. Therefore, this potential substrate and CSPB were utilized for fermentation under similar conditions for comparison of HP production by P. aeruginosa TUN03. As shown in Figure 2a, most media reached the highest yield after 3 days out of a total of 5 days of fermentation. Of those, the medium with only TSB showed weakly supported HP biosynthesis with a yield of 5.19 µg/mL, while the medium comprising TSB with organic waste materials demonstrated better ability for HP production; for instance, the HP yield of the GNC/TSB medium reached 7.14 µg/mL and the CSPB/TSB medium yielded 8.45 µg/mL. Hence, CSPB was used as a substrate for HP biosynthesis in further experiments.
The effect of mixing ratios and the added concentration of CSPB/TSB on HP production: Given that the main fermentation substrate CSPB has a relatively low protein content, this experiment was designed to add free protein (TSB) into the culture medium to support effective fermentation. Several CSPB/TSB ratios were examined at a concentration of 1.25% to determine the suitable ratio for HP production. As shown in Figure 2b, the CSPB/TSB ratio of 8/2 was the most effective ratio for HP biosynthesis, with the yield reaching 10.56 µg/mL. Next, several substrate concentrations of CSPB/TSB (8/2) were tested in a range of 0.5–2% to choose an effective concentration for HP production. As shown in Figure 2c, the HP yield increased from 1.04 to 11.52 µg/mL at CSPB/TSB concentrations of 0.5–1.5% but continued increases in CSPB/TSB concentration over 1.5% reduced the HP yield. Hence, the concentration of CSPB/TSB (8/2) at 1.5% was chosen for further experiments.
The effect of sulfate salts on HP production: Several sulfate salts such as ZnSO4, MgSO4, FeSO4, MnSO4, and (NH4)2SO4 were added into the culture medium to assess their effects on HP production. The culture medium contained 1.5% CSPB/TSB (8/2), 0.1% Ca3(PO4)2, and 0.05% assayed sulfate salt. As shown in Figure 2d, the highest HP yield (13.85 µg/mL) was obtained from a medium containing FeSO4 salt, a relative HP yield (10.13 µg/mL) was recorded for the medium with MgSO4, and a small HP yield was detected from the medium of the remaining sulfate salts (1.89–4.67 µg/mL). Several concentrations of FeSO4 salt were evaluated and the most effective concentration for HP biosynthesis was 0.05%, yielding 13.89 µg/mL (Figure 2e).
The effect of phosphate salts on HP production: The effect of phosphate salts, such as KH2PO4, Ca3(PO4)2, NaH2PO4, Na2HPO4, and K2HPO4, on HP biosynthesis was evaluated. As shown in Figure 2f, the medium containing K2HPO4 gave the highest HP yield of 16.32 µg/mL, followed by the medium containing Ca3(PO4)2, with an HP yield of 13.98 µg/mL. The medium containing other phosphates recorded lower HP content in the range of 4.32–10.38 µg/mL. Subsequently, K2HPO4 was added in different concentrations from 0.025 to 0.15% to find a suitable concentration for HP production. As shown in Figure 2g, 0.05% K2HPO4 resulted in the most effective HP biosynthesis (20.23 µg/mL).
Finally, the newly formulated culture medium for effective HP biosynthesis by P. aeruginosa TUN03 included 1.5% C/N source (CSPB/TSB ratio of 8/2), 0.05% K2HPO4, and 0.05% FeSO4 to obtain a high yield of HP at 20.23 µg/mL. Until now, most reports have focused on pyocyanin research—a main phenazine widely investigated for its bioactivities [13,14,15,21]—while very few studies have evaluated the production of hemi-pyocyanin [16,20]. Our previous studies used by-products such as shrimp heads and groundnut cake for HP production [16,21]. A groundnut oil processing by-product was also indicated as a potential substrate for HP biosynthesis with the medium containing 1.25% groundnut cake, 0.075% MgSO4, and 0.0.075% K2HPO4, giving a high HP yield of 19.5 μg/mL [20]. In this study, cassava processing by-product is also elucidated as a promising substrate for HP production in a small flask with a high yield of 20.23 µg/mL. Subsequently, HP was trial produced at a large scale in an automatic liquid 14 L fermented system—a bioreactor.
2.2.2. Scaling Up of 1-Hydroxyphenazine Production Using a 14 L Bioreactor System
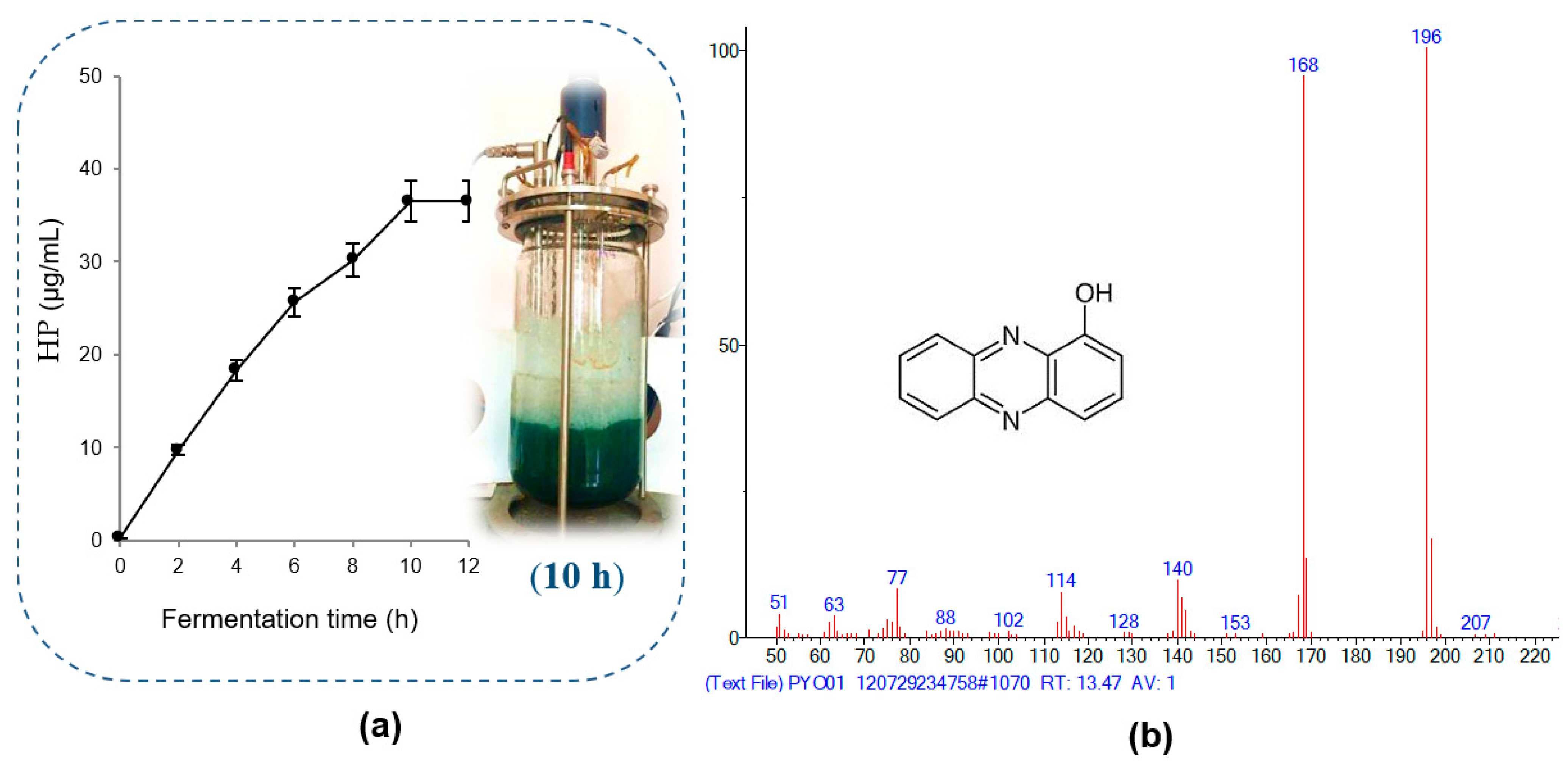
For large-scale HP production by P. aeruginosa TUN03, a bioreactor system was used for fermentation at the total fermented volume of 6 L (mixture of 5.4 L of cultural medium with 0.6 L of bacterial inoculum). The fermentation was conducted at 30 °C at a shaking speed of 250 rpm and 1.2 vvm for 12 h of cultivation. The HP content was recorded every 2 h, and the results are presented in Figure 3a. HP was effectively produced in the bioreactor system using CSPB as the main substrate for fermentation by P. aeruginosa TUN03. The highest HP yield reached 36.5 µg/mL after 10 h of fermentation. The yield was enhanced compared to that in the small flask, from 20.23 µg/mL to 36.5 µg/mL, while the cultivation time was also shortened from 3 days to 10 h. Thus, CSPB as a substrate showed potential for large-scale HP production with a high yield and short fermentation time. In our previous report, HP was also produced successfully in a bioreactor system using GNC [20]. HP was produced at the highest yield of 35.1 μg/mL after 8 h of fermentation in 6 L of liquid medium using groundnut cake as the fermentation substrate [20].
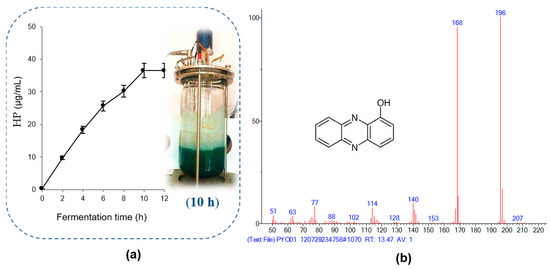
Figure 3.
The efficiency of 1-hydroxyphenazine (HP) production in a bioreactor system (a) and mass spectrum of HP isolated from the fermented broth tested in this study (b).
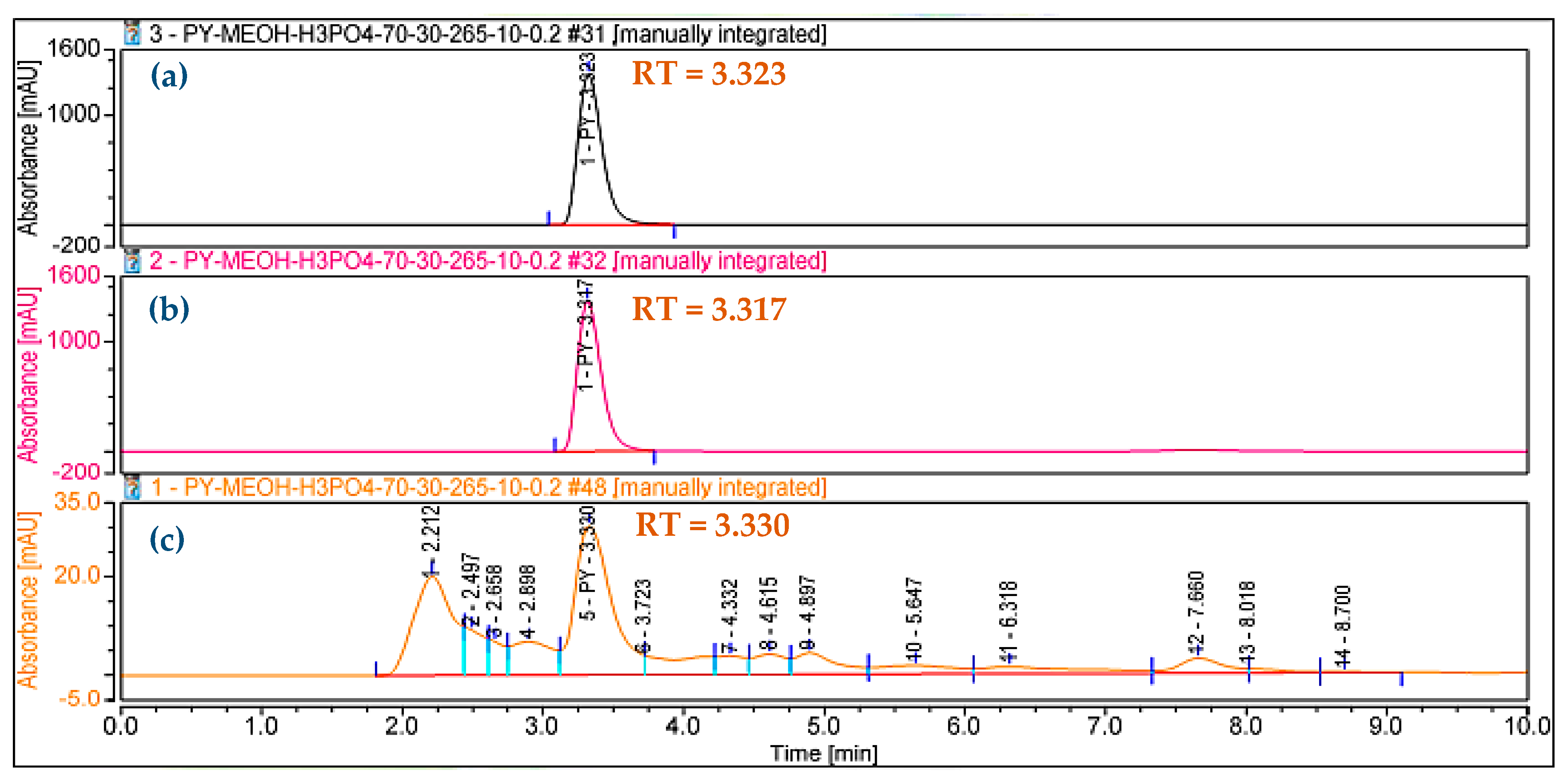
In our previous report, HP was confirmed to be harvested from sub-fraction 1 at a gradient solvent of 100/0 [16]. For precise analysis, the HP purified in this work was also reconfirmed as 1-hydroxyphenazine using the GCMS spectrum (Figure 3b) and HPLC (Figure 4). The purity grade of the HP isolated in this work compared to standard HP was also determined by employing HPLC analysis. As shown in Figure 4, the RT value of the HP isolated in this study (RT= 3.323 min) appearing as a sole peak is similar to standard HP (RT = 3.317 min), and the HP in this study also appeared at an RT of 3.330 min in the crude sample. The HPLC analysis confirmed that the HP compound isolated in this work had high purity and could be used in further bioactivity tests.
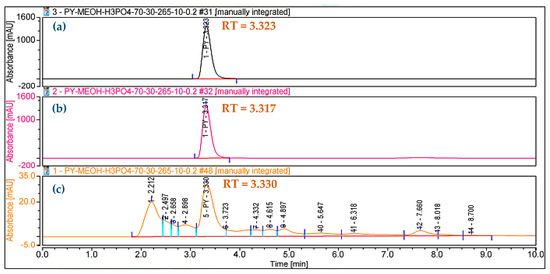
Figure 4.
The HPLC chromatograms of isolated 1-hydroxyphenazine (HP) in this study (a), standard HP (b), and HP in the crude sample (c).
2.3. Evaluation of the Novel Bio-Effect of 1-Hydroxyphenazine against Phytopathogen Fungi
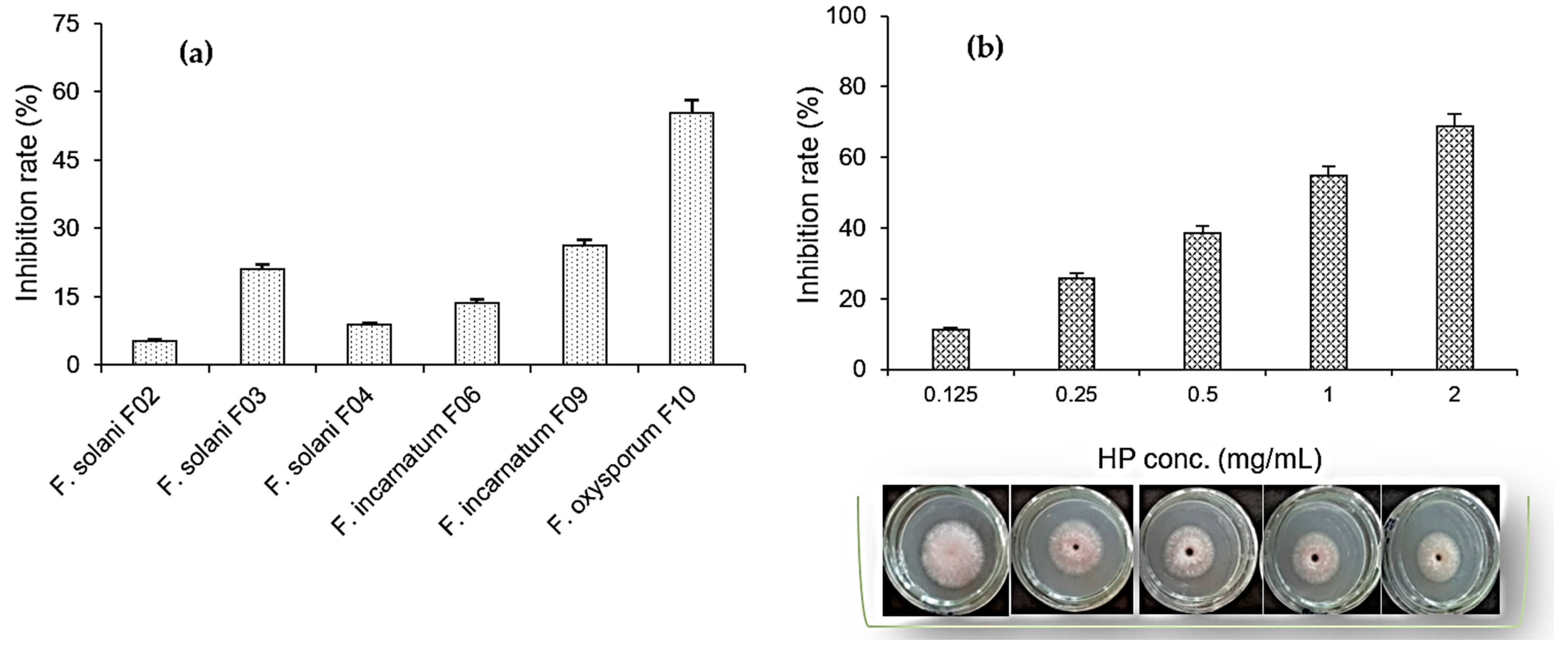
For screening purposes, several Fusarium strains isolated from the roots of some crops including F. solani F02 (durian roots), F. solani F03 (pepper roots), F. solani F04 (coffee roots), F. incarnatum F06 (citrus roots), F. incarnatum F09 (dragon fruit roots), and F. oxysporum F10 (pepper roots) were used to assess the ability of HP to inhibit mycelial growth. Based on the results shown in Figure 5a, HP at 1 mg/mL showed the maximum inhibition on F. oxysporum F10, with an inhibition rate of 55.4%. It mildly inhibited another Fusarium fungus isolated from pepper roots as the F03 strain (21.1% inhibition rate) and the inhibition rate on other Fusarium fungi was in the range of 5.3–26.2%. The most inhibited strain (F. oxysporum F10) was used for further tests at various concentrations of HP.
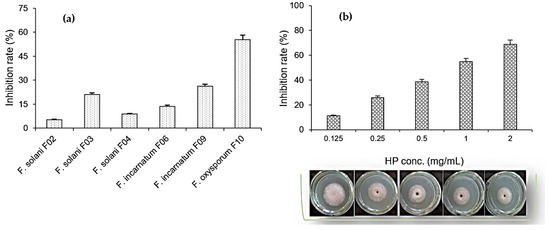
Figure 5.
Screening the inhibitory effects of 1-hydroxyphenazine (HP) on Fusarium strains (a) and the capacity for mycelial growth inhibition of Fusarium oxysporum F10 fungus of HP at various concentrations (b).
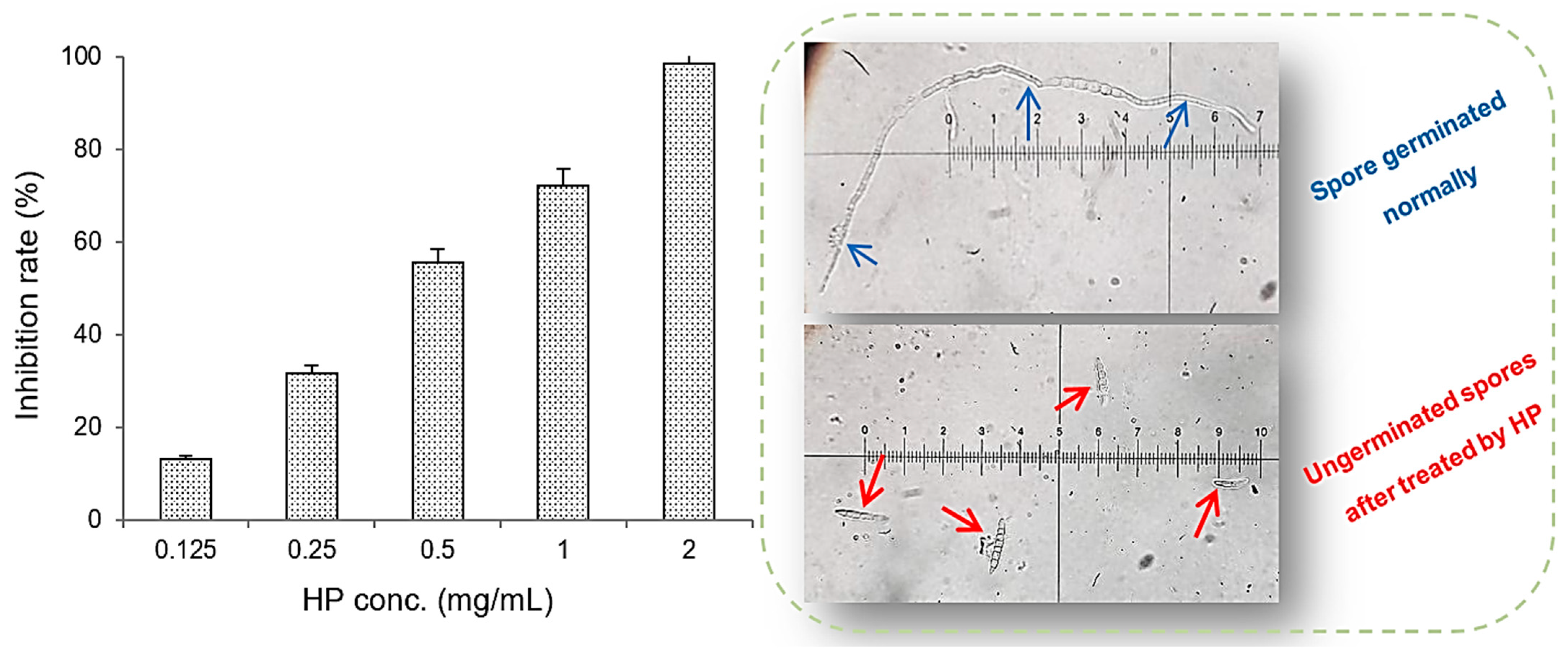
In terms of the capacity of mycelial growth inhibition (Figure 5b), the maximum inhibition reached 68.7% at an HP concentration of 2 mg/mL and the inhibition rates of 11.2–54.7% were achieved at lower HP concentrations of 0.025–1 mg/mL. The spore germination inhibition by HP against F. oxysporum F10 was also tested at various concentrations, and the results after 16 h of treatment are summarized in Figure 6. HP showed better inhibition capacity for spore germination over mycelial growth. The maximal inhibition rate reached 98.4% at 2 mg/mL of HP and this value was above 55% at 0.5–1 mg/mL.
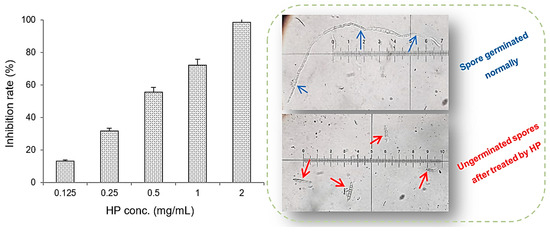
Figure 6.
The ability of different concentrations of 1-hydroxyphenazine (HP) to inhibit spore germination of Fusarium oxysporum F10 fungus at 16 h. Blue arrows indicate the spores germinate normally. Red arrows indicate the spores did not germinate after being treated by HP.
Until now, few reports have evaluated the effects of hemi-pyocyanin, especially its bioactivities related to agricultural phytopathogens [22]. Similar to our result, Dharni et al. [23] reported that HP isolated from P. aeruginosa SD12 also demonstrated a moderate effect on the mycelial growth inhibition of F. oxysporum (no clear isolated source), with an inhibition zone of 10 mm. Further, HP from Streptomyces griseoluteus P510 is also indicated as an effective anti-fungal agent for F. oxysporium (no clear isolated source), with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value of 2 μg/mL [24]. However, the antagonistic activity of this fungal spore germination remains to be clarified. The fungal spores play a vital role in the pathogenesis of fungi, and this is also the most sensitive stage to inhibition [25]. Thus, assessing the inhibition of both mycelial growth and spore germination is an effective strategy for the management of phytopathogenic fungi. Phytopathogenic fungi reduce the global crop productivity by 20% and destroy 10% of crops after harvesting [26]. Of these, F. oxysporium ranks fifth in the top ten phytopathogens and it can infect more than 100 plant species. For the first time, we report HP as a potent agent for the inhibition of spore germination, with a moderate mycelial inhibitory effect on F. oxysporum, which causes disease in pepper plants. In addition, the effect of HP on other phytopathogenic Fusarium species, such as F. solani and F. incarnatum, is also a new discovery in this work.
2.4. The Anti-Fungal Activity of 1-Hydroxyphenazine via Docking Simulation
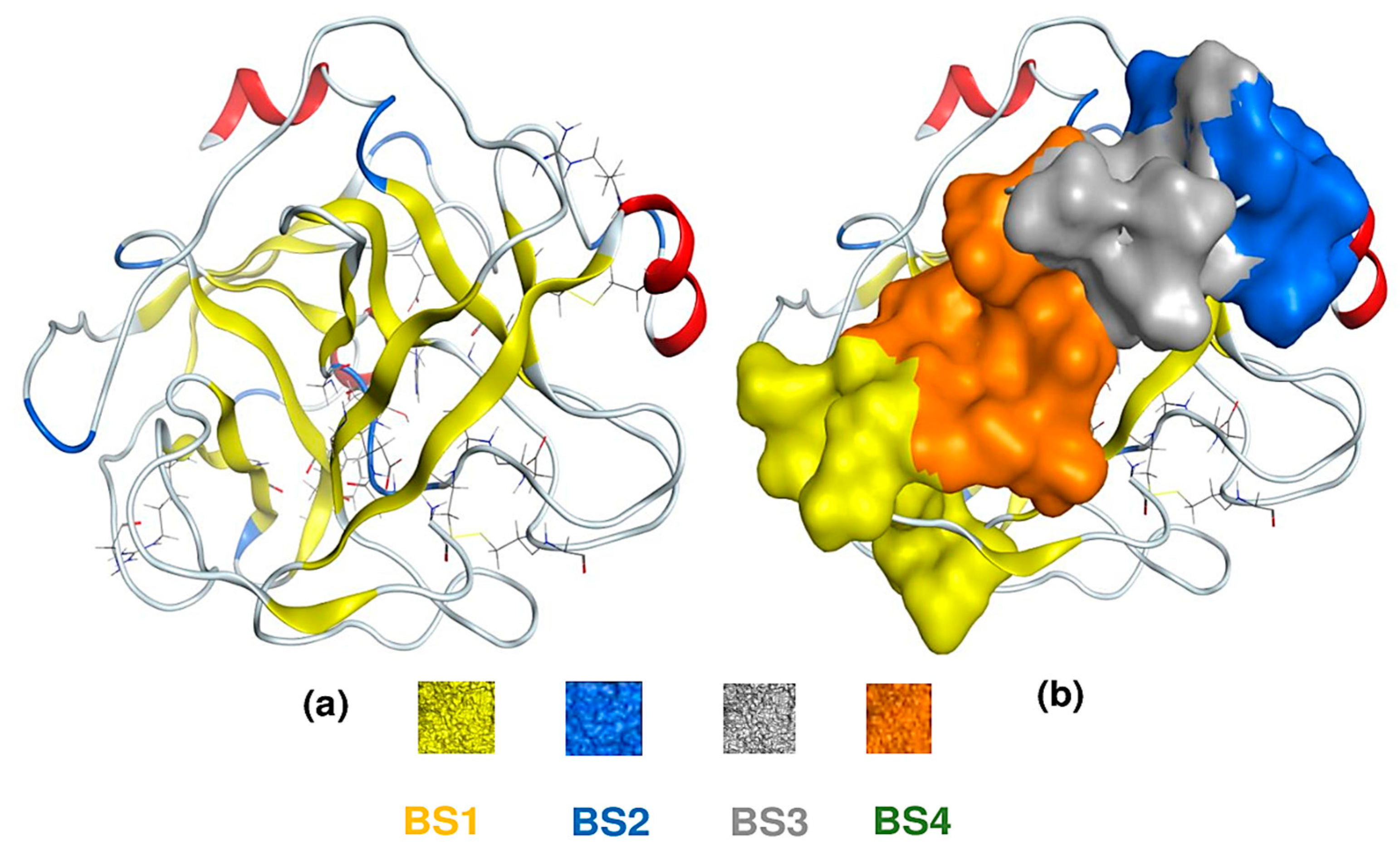
Until now, the possible action mechanism of HP on F. oxysporium is still not known; thus, in this work, we assess this lacuna through a molecular docking simulation of HP with 1TRY—a target protein responsible for F. oxysporium inhibition [27]. For comparison, asparagine—a reported anti-fungal compound—was also examined simultaneously. The 3D structure of the protein 1TRY was constructed using the MOE-2015.10 software (Figure 7a); its four binding sites were also pointed out through the site finder using the same software (Figure 7b). In a docking simulation, ligands (inhibitors) can interact with protein at various binding sites (BS); however, only the one BS possessing the lowest biding energy is chosen for description in detail. Among four BS, both HP and asparagine ligands showed the best interaction with 1TRY protein at BS1. Both ligands documented good docking scores (DS) in the accepted range of less than −3.20 kcal/mol. Further, the DS value reached −9.8 kcal/mol for HP and −9.4 kcal/mol for asparagine. Furthermore, their RMDS values were also qualified under 2.0 Å, reaching 1.66 Å for HP and 1.81 Å for asparagine.
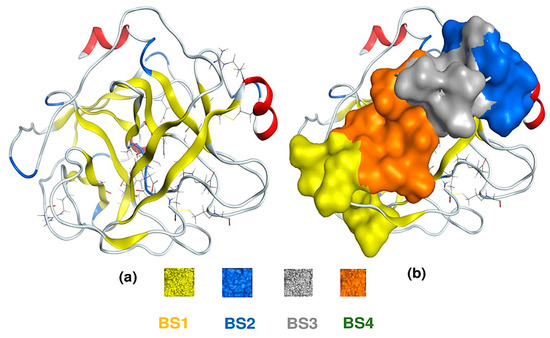
Figure 7.
The 3D structure of 1TRY protein (a) and four binding sites (BS) on protein 1TRY (b). The sizes/residues of BS on protein 1TRY including BS1—27/1:(Ala24 Gly25 Asp26 Phe27 Pro28 Ser70 Leu71 Ser72 Gly116 Asn117 Asn154), BS2—24/1:(Asp129 Pro130 Val131 Ala132 Ile162 Val163 Ser164 Arg165 Cys168 Met180 Phe181 Cys182), BS3—16/1:(Pro130 Val131 Ser134 Ser135 Ala136 Ile162 Asp201 Ser201a Ile210), and BS4—15/1:(Asp26 Phe27 Pro28 Phe29 Thr137 Lys157 Val200 Asp201 Asn203).
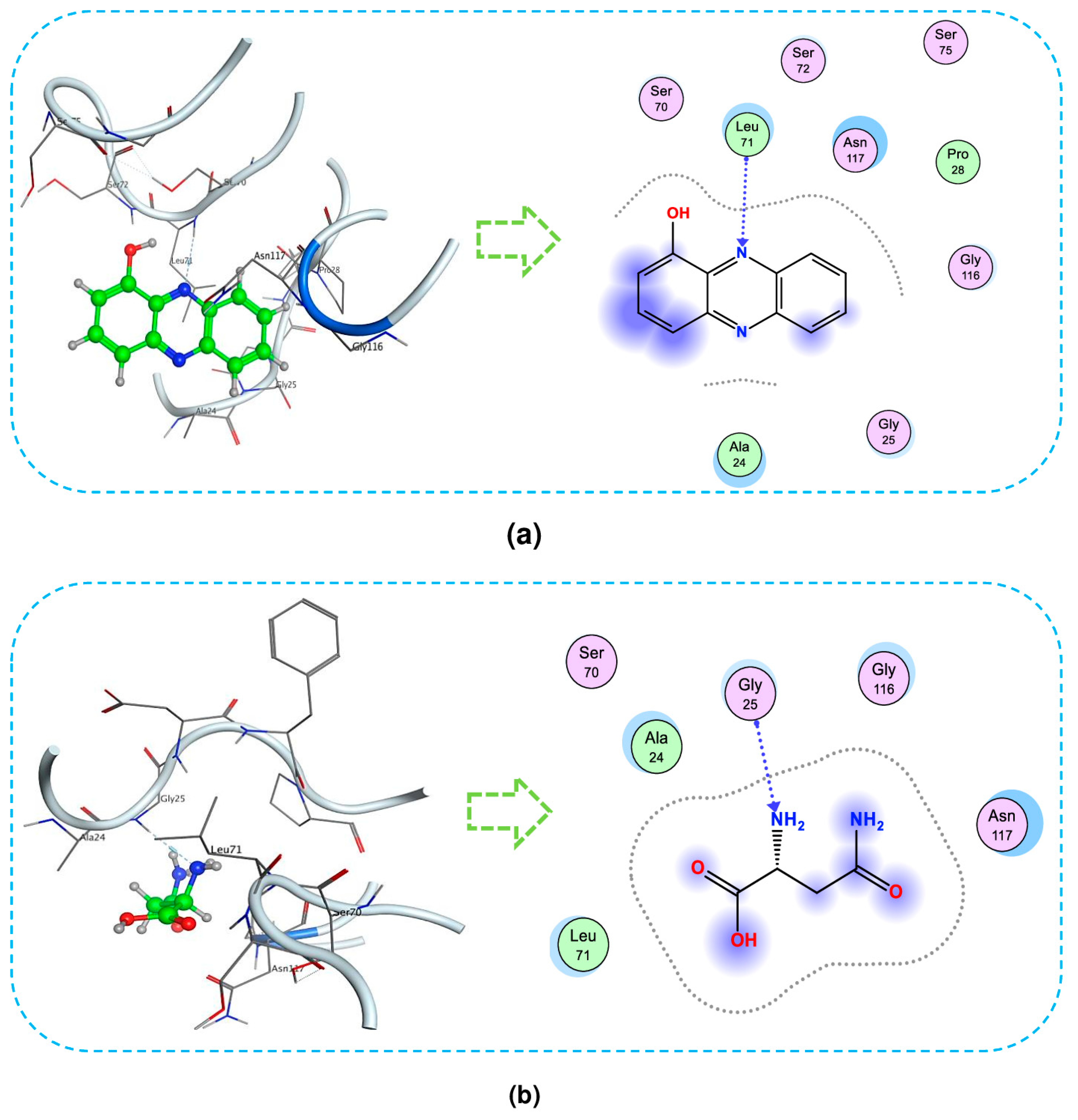
For a deeper understanding of the interactions, the detailed interaction of ligands with the target protein is also presented using the type–distance of linkages and amino acid composition. The 3D and 2D presentation of the interaction between ligands with the 1TRY protein is described in Figure 8. As shown in Figure 8a, HP bonds with 1TRY at Leu71 through H-acceptor linkage with a distance of 3.64 Å and an energy binding value of −0.9 kcal/mol. In Figure 8b, asparagine also forms one H-acceptor linkage with 1TRY at Gly25, with an energy binding of −1.9 kcal/mol and a distance of 3.15 Å.
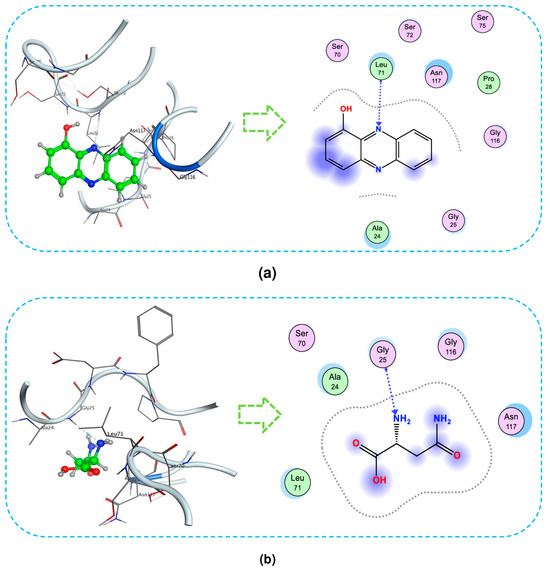
Figure 8.
The interaction of 1-hydroxyphenazine (HP) (a) and asparagine (b) with protein 1TRY at BS1 targeting Fusarium oxysporum F10 inhibition. The 3D and 2D presentation of the interaction between ligands with protein (Section 2.1).
Based on the experimental data and docking simulation, HP is indicated as an effective and novel fungicide for anti-F. oxysporium that damages the pepper plant. It possesses the inhibition capacity for both mycelial growth and spore germination of this fungus. In addition, a good interaction is also recorded with the 1TRY protein that mediates F. oxysporium inhibition.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
CSPB in this work was purchased from a local factory (DAKTASCO company, Dak Lak, Vietnam) in a dry form with a moisture content of 12%. It was stored at room temperature for further experimentation. P. aeruginosa TUN03 (an HP-producing bacteria strain) was isolated from the soil of Dak Lak province of Vietnam in the previous work [16]. The pathogenic fungal strains were those isolated and identified in our earlier study [28]. Silica gel (Geduran® Si 60, size: 0.040–0.063 mm) was obtained from Merck Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis City, MO, USA), and all of the common chemical agents and solvents used were of the highest grade.
3.2. Determination of Nutrient Ingredients of Cassava Starch Processing By-Product
Some major nutrient components of CSPB, including starch, fiber, protein, lipids, reducing sugar, and total dissolved sugar, were determined based on the assays in the previous reports [29,30,31,32,33,34], respectively. The total mineral content (ash) was determined using the approach in the previous report [31]. The mineral elements were detected using the Generation 5 Phenom Pro and proX SEMs machine. The content of potassium, magnesium, and calcium was determined using an atomic absorption spectrophotometer (AA-7000). The phosphorus content was also determined using spectrophotometric methods [35].
3.3. Biosynthesis of 1-Hydroxyphenazine from Cassava Starch Processing By-Product via Fermentation
The effect of C/N sources on HP production: Several organic wastes (cassava residue; groundnut cake) and a commercial medium TSB were used as C/N sources for fermentation by P. aeruginosa TUN03. The culture broth containing 1.25% C/N source (organic by-product/TSB ratio of 7/3), 0.05% MgSO4, and 0.1% Ca3(PO4)2 with an initial pH of 7 was fermented at 30 °C, at 150 rpm (shaking speed), for 5 days. The culture broth liquid was centrifuged at a rotation speed of 10,000× g for 10 min to obtain the supernatant which was further used for determination of HP content.
The effect of CSPB/TSB ratios and their concentration on HP production: CSPB and TSB were mixed at various ratios (CSPB/TSB) of 10/0, 9/1, 8/2, 7/3, 6/4, and 5/5 and used as C/N sources at a concentration of 1.25% for fermentation to produce HP. The CSPB/TSB ratio of 8/2 was the most suitable for fermentation. Thus, this mixture was further investigated for fermentation at various concentrations (0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.25, 1.5, 1.75, and 2%). The medium contained respective C/N sources, 0.05% MgSO4, and 0.1% Ca3(PO4)2. The medium was used for culturing at 30 °C, at a shaking speed of 150 rpm, for 3 days, and this fermentation condition was noted as (*).
The effect of sulfate salts on HP production: Several sulfate salts, such asZnSO4, MgSO4, FeSO4, MnSO4, and (NH4)2SO4, were added individually into the cultural medium to check their effects. The medium containing 1.5% C/N source (CSPB/TSB ratio of 8/2), 0.075% K2HPO4, and 0.075% sulfate salt with an initial pH of 7 was fermented by P. aeruginosa TUN03 using the above (*) fermentation condition. The produced HP content in the culture broth was measured after 3 days of fermentation. FeSO4 was found to be the most suitable sulfate salt source to add into the medium; therefore, this salt was further added into the culture medium at different concentrations (0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1, 0.125, and 0.15%) to investigate the suitable concentration for HP production.
The effect of phosphate salts on HP production: Five kinds of phosphate salts, such as KH2PO4, Ca3(PO4)2, NaH2PO4, Na2HPO4, and K2HPO4, were added individually into the culture medium to check their effects. The culture medium containing 1.5% C/N source (CSPB/TSB ratio of 8/2), 0.075% phosphate salt, and 0.05% FeSO4 with an initial pH of 7 was fermented by P. aeruginosa TUN03 using the (*) fermentation condition, and the HP content was measured after 3 days of fermentation. K2HPO4 was found to be the most suitable phosphate source to add into the medium; as such, this salt was further added into the culture medium at various concentrations (0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1, 0.125, and 0.15%) to observe its optimal concentration.
Scaling up of HP production in a 14 L bioreactor system: The TUN03 strain was pre-cultivated in culture broth TSB in several 500 mL flasks at a fermentation temperature of 30 °C for 1.5 days. A total of 600 mL of fermented medium (bacterial inoculum) was added to the reactor containing 5.4 L of the newly investigated culture medium containing 1.5% C/N source (CSPB/TSB ratio of 8/2), 0.05% K2HPO4, and 0.05% FeSO4 with an initial pH of 7. Fermentation was performed at 30 °C, 250 rpm, and 1.2 vvm for 12 h of cultivation, and the HP content was determined every 2 h.
3.4. Yield Quantification, Extraction, Purification, and Identification of 1-Hydroxyphenazine
The yield of HP was determined by HPLC analysis using the protocol reported in our previous work [20]. The supernatant was collected by removing the cultural medium and P. aeruginosa TUN03 biomass by centrifuging for 10 min at 8000 rpm. Then, 5 μL of the supernatant was injected into the HPLC equipment for analysis. The C18 column was used to separate the compound using a solvent system of methanol/H3PO4 at a ratio of 70/30 (v/v). The analysis condition was set at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min and a detecting wavelength of 265 nm. The HP yield in the culture medium was calculated using the standard HP equation reported in our previous work [20].
HP was extracted and purified according to the detailed method presented in our earlier report [16]. The fermented broth was extracted from the bioreactor system using the liquid–liquid method. The chloroform layer was aspirated and mixed with 70% ethanol to remove protein residue. The supernatant was vaporized at 50 °C to harvest the crude sample powder. The crude sample was further separated using a silica column with a solvent system of chloroform/methanol (the gradient changed from 100/0 to 80/20). HP was confirmed to be extracted from sub-fraction 1 at a gradient solvent of 100/0 and was further reconfirmed as 1-hydroxyphenazine using GCMS and HPLC, and its purity grade was also determined using HPLC analysis [16].
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GCMS) was conducted to identify the presence of HP. Helium gas (99.999%) was used as a carrier gas at a constant flow rate of 1 mL/min, and an injection volume of 2 μL was employed (a split ratio of 10:1). The injector temperature was maintained at 250 °C, the ion-source temperature was 250 °C, and the column temperature was programmed T 65 °C (isothermal for 1 min), with an increase of 15 °C/min to 200 °C, ending with a 2 min isothermal at 200 °C. MS data were acquired at 70 eV, a scanning interval of 0.5 s, and fragments from 34 to 450 Da. HP was detected using data comparison in mass spectra libraries (NIST 17 and Wiley).
3.5. Determination of the Anti-Fungal Effect of 1-Hydroxyphenazine
For screening purposes, six Fusarium strains were used to test the mycelial growth inhibition of HP at 1 mg/mL and the most inhibited strain was chosen for further experiments. The fungi were isolated and identified in our former work [28]. The anti-fungal effect on the most inhibited strain was assessed in detail using the the assays of the mycelial growth inhibition and the fungal spore germination inhibition with various concentrations of HP.
The mycelial growth inhibition effect: This effect was determined using the methods presented in previous reports [28,36], with modifications. A mycelial plug of growing pathogen fungal strain was placed on potato D-glucose agar medium in the center of the Petri dish. Subsequently, 25 µL of compound solution was sprayed onto this plug of fungal mycelia and 25 µL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was used as the control group. Then, the Petri dishes were maintained at 28 °C for 3 to 7 days. The diameter of fungal mycelium growth in the experiment group (DE, mm) and in the control group (DC, mm) was measured to calculate the anti-fungal effect using the following equation: inhibition rate (%) = [DC − DE]/DC × 100%.
Fungal spore germination inhibition: A total of 50 µL of sterile distilled water containing around 105 fungal spores and 25 µL of the compound solution were mixed in a 200 µL microfuge tube and then incubated at 28 °C. The control group containing 50 µL of fungal spores and 25 µL of sterile distilled water was also incubated under the same conditions. The number of germinated spores were counted every 8 h. A fungal spore was considered as germinated when the length of its germinal tube reached one-half of the spore diameter [37]. The number of germinated spores in the control group (GSC) and experiment group (GSE) were counted to calculate the inhibition effect using the following equation: inhibition rate (%) = [GSC − GSE]/GSC × 100%.
3.6. Molecular Docking Protocol
The docking study was performed following the protocol previously presented in earlier works [38,39,40]. The structural data of 1TRY protein target for the anti-Fusarium oxysporum activity assessment were obtained from the Worldwide Protein Data Bank to construct a 3D protein structure using MOE-2015.10 software. The 3D structures of ligands such as 1-hydroxyphenazine and asparagine (a reported anti-fungal compound) were also prepared and optimized using the same software. These ligands were docked into the most active binding site on 1TRY. Then, the docking score (DS), root mean square deviation (RMSD), interaction kinds, amino acid composition, and the distances of linkages were obtained as output data for analysis.
4. Conclusions
We report a novel culture medium for effective HP biosynthesis by P. aeruginosa TUN03 comprising 1.5% C/N source (CSPB/TSB ratio of 8/2), 0.05% K2HPO4, and 0.05% FeSO4 to obtain a high HP yield of 20.23 µg/mL in a small flask. Furthermore, this is the first report to detail the use of CSPB for successful HP production in a bioreactor system achieving a higher yield (36.5 µg/mL) within a short duration (10 h) compared to fermenting at a small scale. The purified HP was evaluated for its anti-fungal activity against several phytopathogenic Fusarium strains isolated from various plant roots. Among these, HP showed the most effective inhibition against F. oxysporum F10 from pepper roots. It could also moderately inhibit the mycelial growth of this strain, with a maximal inhibition rate of 68.7%. This phenazine also recorded a high anti-spore germination capacity against this fungus, with a 98.4% inhibition rate. Moreover, we also propose a possible mechanism of HP action against F. oxysporum F10 through molecular simulation; the assessment showed good interaction with the 1TRY protein which was the target of fungal inhibition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.B.N.; methodology, T.H.N. (Thi Hanh Nguyen), T.Q.P., S.-L.W., and V.B.N.; software and validation, T.Q.P., T.H.N. (Thi Hanh Nguyen), and V.B.N.; formal analysis, S.-L.W., A.D.N., T.H.T.P., T.H.T.T., V.A.N., and V.B.N.; investigation, T.H.N. (Thi Hanh Nguyen), T.Q.P., T.H.N. (Thi Huyen Nguyen), M.D.D., and V.B.N.; resources, V.B.N.; data curation, S.-L.W., A.D.N., and V.B.N.; writing—original draft preparation, T.H.N. (Thi Hanh Nguyen); writing—review and editing, S.-L.W., T.Q.P., and V.B.N.; supervision, S.-L.W. and V.B.N.; visualization and project administration, V.B.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the project of Tay Nguyen University, Vietnam (T2023-44CBTĐ), and the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan (NSTC 112-2320-B-032-001).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Le, D.P.; Labarta, R.A.; Haan, S.; Maredia, M.; Becerra, L.A.; Nhu, L.; Ovalle, T.; Nguyen, V.; Pham, N.; Nguyen, H.; et al. Characterization of cassava production systems in Vietnam. Work. Paper CIAT 2019, 480, 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- WorldAtlas, Top Cassava Producing Countries in the World. Available online: https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/top-cassava-producing-countries-in-the-world.html (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Li, S.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, M. The industrial applications of cassava: Current status, opportunities and prospects. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2282–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xie, L.; Yin, Z.; Khanal, S.K.; Zhou, Q. Biorefinery approach for cassava-based industrial wastes: Current status and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 215, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, M.P.D.; Padmaja, G.; Moorthy, S.N. Biodegradation of cassava starch factory residue using a combination of cellulases, xylanases and hemicellulases. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xue, S.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S. Effect of cassava residue substituting for crushed maize on in vitro ruminal fermentation characteristics of dairy cows at mid-lactation. Animals 2020, 10, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Cheng, J.; Cao, L.; Mu, D.; Luo, S.; Zheng, Z.; Jiang, S.; et al. Fermentation process and metabolic flux of ethanol production from the detoxified hydrolyzate of cassava residue. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 290853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.G.; Zhou, Q. pH-adjustment strategy for volatile fatty acid production from high-strength wastewater for biological nutrient removal. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 2043–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Y.; Ren, H.; Liu, D.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, N.; Ying, H. Economically enhanced succinic acid fermentation from cassava bagasse hydrolysate using Corynebacterium glutamicum immobilized in porous polyurethane filler. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 174, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andin, V.A.; Fidia, F.; Talitha, W.; Risa, D.H. Bioconversion and valorization of cassava-based industrial wastes to bioethanol gel and its potential application as a clean cooking fuel. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 35, 102093. [Google Scholar]
- Cimmino, A.; Evidente, A.; Mathieu, V.; Andolfi, A.; Lefranc, F.; Kornienko, A.; Kiss, A. Phenazines and cancer. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; He, Y.; Jiang, H.; Peng, H.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Linda, S.T.; Xu, Y. Characterization of a phenazine-producing strain Pseudomonas chlororaphis GP72 with broad-spectrum antifungal activity from green pepper rhizosphere. Curr. Microbiol. 2007, 54, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaus, G.; Wulf, B.; Rolf, B. Recent developments in the isolation, biological function, biosynthesis, and synthesis of phenazine natural products. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 6149–6166. [Google Scholar]
- Alka, R.; Wamik, A. An overview on biosynthesis and applications of extracellular pyocyanin pigment and its role in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis. Ann. Phytomed. 2019, 8, 28–42. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.T.; Ye, F.C.; Pang, C.P.; Yong, T.Q.; Tang, W.D.; Xiao, J.; Shang, C.H.; Lu, Z.L. Isolation and identification of bioactive substance 1-hydroxyphenazine from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its antimicrobial activity. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Wang, S.-L.; Nguyen, A.D.; Doan, M.D.; Tran, T.N.; Doan, C.T.; Nguyen, V.B. Novel α-amylase inhibitor hemi-pyocyanin produced by microbial conversion of chitinous discards. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Wang, S.L.; Nguyen, T.H.; Doan, M.D.; Tran, T.H.T.; Ngo, V.A.; Ho, N.D.; Tran, T.N.; Doan, C.T.; Do, V.C.; et al. Utilization of fishery-processing by-product squid pens for scale-up production of phenazines via microbial conversion and its novel potential antinematode effect. Fishes 2022, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqel, H.; Sannan, N.; Foudah, R.; Al-Hunaiti, A. enzyme production and inhibitory potential of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Contrasting clinical and environmental isolates. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, E.V.N.; Divakar, G. Production of amylase by using Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from garden soil. IJAPBC 2013, 2, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Wang, S.-L.; Nguyen, A.D. Bioconversion of a peanut oil processing by-product into a novel α-glucosidase inhibitor: Hemi-pyocyanin. Processes 2023, 11, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, A.A.; Kamer, A.M.A.; Monofy, K.B.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa’s greenish-blue pigment pyocyanin: Its production and biological activities. Microb. Cell Fact. 2023, 22, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafim, B.; Bernardino, A.R.; Freitas, F.; Torres, C.A.V. Recent Developments in the Biological Activities, Bioproduction, and Applications of Pseudomonas spp. Phenazines. Molecules 2023, 28, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharni, S.; Alam, A.; Kalani, K.; Abdul, K.; Samad, A.; Srivastava, S.K.; Patra, D.D. Production, purification, and characterization of antifungal metabolite from Pseudomonas aeruginosa SD12, a new strain obtained from tannery waste polluted soil. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Hu, H.; Peng, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W. Isolation and structural identification of two bioactive phenazines from Streptomyces griseoluteus P510. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slawecki, R.A.; Ryan, E.P.; Young, D.H. Novel fungitoxicity assays for inhibition of germination-associated adhesion of Botrytis cinerea and Puccinia recondita spores. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Ghany, M.N.; Hamdi, S.A.; Korany, S.M.; Elbaz, R.M.; Farahat, M.G. Biosynthesis of Novel Tellurium Nanorods by Gayadomonas sp. TNPM15 Isolated from Mangrove Sediments and Assessment of Their Impact on Spore Germination and Ultrastructure of Phytopathogenic Fungi. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rypniewski, W.R.; Dambmann, C.; Von, C.D.O.; Dauter, M.; Wilson, K.S. Structure of inhibited trypsin from Fusarium oxysporum at 1.55 Å. Acta Cryst. 1995, D51, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.N.; Wang, S.-L.; Nguyen, A.D.; Doan, M.D.; Tran, D.M.; Nguyen, T.H.; Ngo, V.A.; Doan, C.T.; Tran, T.N.; Do, V.C.; et al. Potential Application of rhizobacteria isolated from the Central Highland of Vietnam as an effective biocontrol agent of robusta coffee nematodes and as a bio-fertilizer. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.G.P.; Fernandes, F.E.P.; Pires, A.J.V. Determination of starch and pectin in animal feed. Electron. J. Vet. Med. 2006, 8, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz, W.; Latimer, G.W., Jr. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 22nd ed.; AOAC: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Oko, J.O.; Abriba, C.; Audu, J.A.; Kutman, N.A.; Okeh, Q. Bacteriological and nutritional analysis of groundnut cake sold in an open market in Samaru, Zaria-Kaduna state. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2015, 4, 225–228. [Google Scholar]
- Señoráns, F.J.; Luna, P. Sample preparation techniques for the determination of fats in food. Compr. Sampl. Sample Preparat. 2012, 4, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibli, S.; Siddique, F.; Raza, S.; Ahsan, Z.; Raza, I. Chemical composition and sensory analysis of peanut butter from indigenous peanut cultivars of Pakistan. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 32, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.; Omar, D.; Cheng, G.L.E.; Nasehi, A.; Wong, M.Y. Characterization of phenazine and phenazine-1-carboxylic acid isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa UPMP3 and their antifungal activities against ganoderma boninense. Pertanika J. Trop. Agri. Sc. 2018, 41, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; He, Z.; Shen, Q.; Fan, W.; Tan, G.; Zou, Y.; Mei, Q.; Qian, Z. Rapid screening alpha-glucosidase inhibitors from polygoni vivipari rhizoma by multi-step matrix solid-phase dispersion, ultrafiltration and HPLC. Molecules 2021, 26, 6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamadalieva, N.Z.; Youssef, F.S.; Hussain, H.; Zengin, G.; Mollica, A.; Al Musayeib, N.M.; Ashour, M.L.; Westermann, B.; Wessjohann, L.A. Validation of the antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory potential of selected triterpenes using in vitro and in silico studies, and the evaluation of their ADMET properties. Molecules 2021, 26, 6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Wang, S.-L.; Nguyen, T.H.; Phan, T.Q.; Nguyen, T.H.; Tran, T.H.T.; Doan, M.D.; Ngo, V.A.; Nguyen, A.D. Recycling fish heads for the production of prodigiosin, a novel fungicide via experimental and molecular docking characterization. Fishes 2023, 8, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollica, A.; Zengin, G.; Durdagi, S.; Ekhteiari, S.R.; Macedonio, G.; Stefanucci, A.; Dimmito, M.P.; Novellino, E. Combinatorial peptide library screening for discovery of diverse α-glucosidase inhibitors using molecular dynamics simulations and binary QSAR models. J. Biomol. Str. Dynam. 2019, 37, 726–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).