Abstract
The ever-growing interest in wearable electronic devices has unleashed a strong demand for sustainable and flexible power sources that are represented by the combination of flexible energy harvesting with storage devices/technologies. Triboelectric nanogenerators (TENG), which harvest mechanical energy and charge their matching supercapacitors (SCs), may form a distributed power system with flexibility to tap their potential applications in powering wearable electronic devices. This review aims to cover the recent progress in the integration of TENG with flexible SC in terms of operation principle, material selection, device configuration and power management, with an accent on the application scenario in flexible wearable electronics. Further, the current shortcomings, challenges and new prospects for future developments in the emerging field of integrated flexible TENG-SCs for self-powered wearable electronics are discussed.
1. Introduction
The fast advancement in wearable electronics is generating a variety of integrated and miniaturized circuits that are revolutionizing our lives in the forms of artificial electronic skin, on-body sensors and wearable displays, with important examples in medical diagnostics and the healthcare industry [1,2,3,4,5]. While the energy usage of these individual devices may be low, their long-term operation requires frequent charging, which makes the need for sustainable, high-performance and biocompatible power supplies even more urgent.
Electrochemical energy storage devices, such as batteries and supercapacitors (SCs), are the most conventional technology to store and supply energy, even with limited lifetime and capacity [6,7,8]. Consequently, the frequent charging or replacement of these devices can cause great inconvenience and high maintenance costs, as well as difficulties with recycling and environmental pollution [9,10,11]. These problems may be solved by enhancing the energy density of the energy storage devices or integrating them with energy-converting devices into self-charging power systems (SCPSs) [12].
Harvesting micro-energy (characterized by low frequency and low amplitude) from our living environment to provide power for portable electronics is considered a suitable approach because it provides long-lasting, maintenance-free, self-driven energy. At present, collecting energy from thermal, solar and biochemical sources is still affected by many factors such as weather and even seasons. In such cases, harvesting mechanical energy from the body and environment and converting it into electricity by triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) is an ideal candidate solution [13,14,15,16,17]. On one hand, the TENG is low cost, highly efficient, environmentally friendly, and can be made from a wide variety of raw materials, making it very useful for various self-powered sensors [18,19,20,21]. On the other hand, the power outputs are typically irregularly sized pulses, determined by the strength of the mechanical trigger, and cannot be directly employed to power the majority of electronic devices [22,23,24]. SCs are outstanding in energy storage devices because of their high-power density, long life cycles, and environmental benignancy. Additionally, considering the characteristics of the pulse energy produced by a TENG operating at a low frequency, supercapacitors are excellent candidates to store energy harvested by TENGs due to the advantages of SCs, such as higher peak current, small leakage currents, low cost, and good reversibility.
In the past few years, there has been a notable endeavor to integrate SCs with TENGs to create SCPSs [25,26], as depicted schematically in Figure 1. Herein, this review focuses on the recent progress of flexible SCPSs by integrating TENG with SCs (TENG-SCs). The operation principle, material selection, and device configuration are introduced. Additionally, the TENG-SCs applied in flexible wearable electronics are also presented. Further, the power management circuits that enhance energy storage efficiency are reviewed. Finally, future perspectives and challenges for the development of TENG-SC-based SCPSs are discussed.
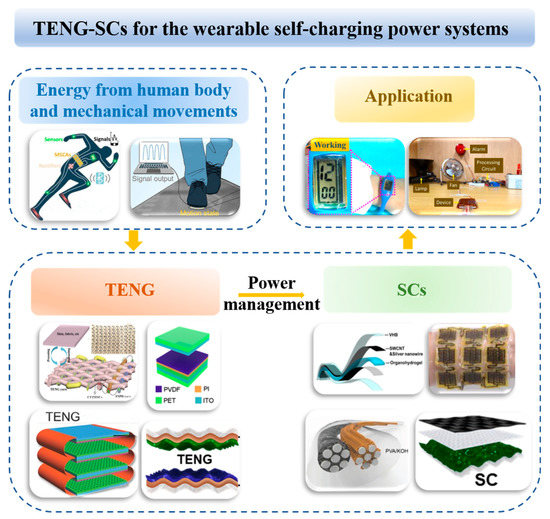
Figure 1.
Illustration of the wearable self-charging power systems that are based on the integration of TENG-SCs.
2. Integration of the TENG with SCs
2.1. The Working Principle of TENG
In 2012, Wang and colleagues developed the TENG, a technology that converts mechanical energy into electricity. It works by utilizing a combination of triboelectric and electrostatic induction based on mechanical interface micro-/nano-energy technology [27]. When two materials come into contact with each other, the contacting surfaces generate equal amounts of charges with opposite polarities [28]. Because materials with strong triboelectric effects are typically insulators or have low conductivity, the charges can remain static on the surface for extended periods [29]. The mobile charges can be induced by attaching electrodes to the backside of electrified materials. Therefore, when the two materials are separated, positive and negative electrostatic charges are separated spatially, and the induced potential difference is generated on the corresponding surface electrodes of the material. This potential difference can drive electron flow between the electrodes, generating electricity when connected to an external circuit load or a short circuit [30].
Up to now, varieties of TENGs have been widely reported and studied, and generally, they can be categorized into four basic working modes, vertical contact–separation mode, sliding mode, single-electrode mode and independent mode [31]. Based on the above modes, TENGs with different kinds of structures are utilized to harvest different types of mechanical energy such as human motion from pressing, sliding and bending, running, heart beating, vibration, wind, water drops or flows, and so on [32,33,34,35,36,37]. On the one hand, TENGs are ideal for self-powered active sensing as they can directly convert mechanical stimuli to electrical signals without the need for additional transducers [38]. On the other hand, TENGs made from flexible and lightweight triboelectric materials (mainly dielectric polymer materials), which have a strong triboelectric effect, can be used for wearable electronics since they are feasible and easy to fabricate. However, the mechanical energy input is typically unstable, and TENGs cannot be directly used to drive most electronic devices due to their pulsed alternative output characteristic. Therefore, an energy storage component is indispensable to store TENG-generated electrical energy to provide a steady, regulated and uninterrupted power output for wearable devices.
2.2. Integration Strategy of TENG-SCs
A supercapacitor, also known as electrochemical capacitor, is a promising energy storage technology that can offer higher power density and longer cycling stability compared to batteries [39,40,41]. In particular, in order to accommodate the need for portable and wearable electronic devices, flexible solid-state SCs have been designed, offering superior portability and security while operating under bending and folding without degrading performance [42,43,44]. Considering that the alternative current (AC) output of the TENG cannot be directly employed to charge the SC, it is necessary to convert it into direct current (DC) using a bridge rectifier before charging SCs, which means that the TENG and SC are connected together with rectifying circuits to build up a sustainable self-charging power system (SCPS). Although it is difficult for the TENG and SC to share electrodes, the triboelectric layer of the TENG can be used as a substrate/package for the SC or designed in a way that the TENG and SC share the package or substrate [45]. The detailed discussion will be presented in the next section.
3. TENG-SC-Based Flexible Self-Charging Power Systems
In this section, recent advances containing supercapacitors with various configurations and the novel and functional materials in the SCPSs are briefly reviewed.
3.1. Textile-/Fiber-Based SCPSs
Wearable electronics can benefit greatly from the use of textile or fiber materials, as people wear clothes on a daily basis. The first wearable electronic prototype was proposed by Wang’ s group, which consisted of a fiber-based TENG and fiber-based SC [46]. The RuO2 xH2O@carbon fibers served as two symmetric electrodes of the SC, and received an impressive specific capacitance of 83.5 F cm−3. Meanwhile, the TENG was created using carbon wire electrodes coated in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Further, the SC and the TENG were weaved on a coat to harvest the motion energy while jogging. After being charged by the rectified output of the TENG, the SC obtained an average charging current of 1.28 µA within 10 s, which demonstrates the effectiveness of SCPSs. To achieve a higher specific capacitance, solid-state asymmetric supercapacitor devices (SASD) were developed; Ren et al. [47] prepared an all-yarn SCPS cloth that incorporates a knitted TENG textile with SASD yarns for wearable application. To fabricate the SCPS, a single-electrode mode was employed to design the TENG, which involved sealing the conductive liquid inside a silicone rubber tube modified with trichloro (1H, 1H, 2H, 2H-perfluorooctyl) silane (FOTS) and utilizing a copper wire for electrical connectivity. Additionally, the TENG fabric can work under deformations such as twisting, stretching and bending, as shown in Figure 2a,b. For the SC yarn, Co3O4 nanosheet arrays grown on carbon fiber bundles were used as the positive electrode and activated carbon (AC) was the negative electrode material, and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/KOH was used as the gel electrolyte (Figure 2c). Then, the TENG and SCs were connected in series, and an AC–DC converter bridge rectifier was employed. Then, the external load was connected in parallel to the SC yarns (Figure 2d). The three supercapacitor yarns in series were charged to 2 V in 28 s and successfully drove a temperature–humidity meter (Figure 2e,f). Using the same knitting strategy, Hu et al. [48] developed a PDMS/MnO2NW hybrid elastomer sheathed with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) yarn as a TENG device and wearable textile. MnO2 NW on carbon cloth (CC) was the positive electrode, and AC on CC was the negative electrode for the SC. Recently, Guo et al. [49] designed a SASD based on dual redox active sites Ni2P/NiSe2 heterostructure inlaid on N-doped carbon nanowires (N-C@Ni2P/NiSe2) (Figure 2g), achieving a high energy density of 60.4 Wh kg–1 at 1598.8 W kg–1. This SASD can be charged by a designed rotational TENG to 4 V after 50 s by hand-held rotation at a rotation speed of 200 rpm. The power of the SCPS is enough to drive a watch for 70 s with the potential dropping to 1 V, after which it could be charged back to 4 V within 25 s and repeatedly power the watch (Figure 2h,i). This work presents broad application prospects in next-generation SCPSs.
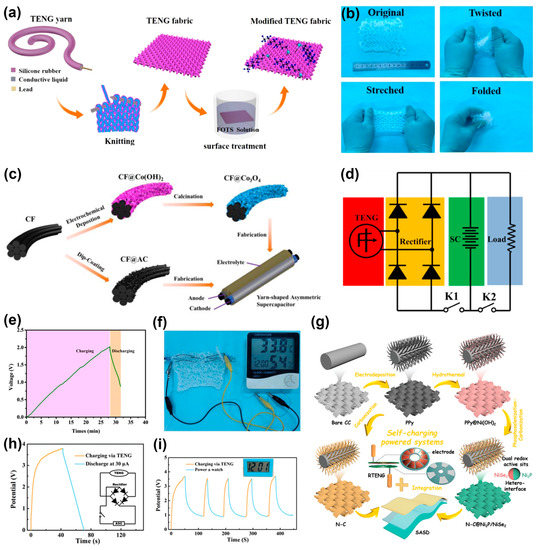
Figure 2.
(a,b) Fabrication of the TENG textile, which can be operated under various deformations. (c) Fabrication of the supercapacitor yarn. (d–f) Circuit diagram of the SCPS to power a temperature–humidity meter. Reproduced with permission [47]. Copyright 2021. IOPscience. (g) Schematic illustration for the fabricated of N-C@Ni2P/NiSe2 and N-C; the construction of SASD, RTENG and SCPS. (h,i) The charge–discharge curves of the SCPS and a charged watch for 5 cycles. Reproduced with permission [49]. Copyright 2022. Wiley-VCH.
To simplify the structure of the SCPS, Sun et al. [50] proposed a versatile coaxial fiber-based SCPS that utilizes carbon fiber bundles as both the electrode material for the TENG and the active electrode material for the SC. Additionally, they employed silicone rubber as the triboelectric material for the TENG, as well as the separator between the SC and TENG, as well as the encapsulation material for the entire fiber (Figure 3a). Recently, Han et al. [51] developed an all-fiber shaped SCPS, including the TENG and SC and a pressure sensor, assembled in a coaxial geometry. As shown in Figure 3b, the inner core is an SC based on two twisted carbon fibers for energy storage, and is covered by a PDMS layer and an Ag electrode. The outer sheath consists of a TENG in single-electrode mode, with a layer of PDMS supported by a metallic spring. Simultaneously, another coaxial TENG in contact–separation mode is created by the outer PDMS friction layer and the inner PDMS layer coated with Ag. The structure of this SCPS is extremely simple and realizes multiple functions, leading the potable textile wearable electronics in a more intelligent, more accessible direction. Pu et al. [52] also designed an SCPS in which the TENG and SC can be interlaced into a single tissue for real-time energy collection and storage. They initially manufactured polyester yarns coated with Ni and Cu films as substrates for the TENG and SC. As shown in Figure 3c, for the SC, the negative yarn electrode was coated with hydrothermally self-assembled rGO/CNT, and the positive electrode was the electroplated Ni-Co bimetallic oxyhydroxide (NiCo BOH) coating. The SASD exhibited an area energy density of 78.1 µWh cm−2, a power density of 14 mW cm−2, and a retention rate of 82.7% after 5000 cycles. For the TENG, PDMS was coated on the Cu-plated polyester yarn as an electrification layer, as shown in Figure 3d. Park et al. [53] presented an SCPS based on woven carbon fiber (WCF), and P-doped Cu0.5Mn0.5Se2 nanowires were coated on its surface, which can simultaneously act as the active materials of SC and the positive triboelectric layer of the TENG. Then, PDMS grown on the nanowires was used as the negative triboelectric material. This TENG can generate a maximum VOC (open-circuit voltage) and current at 443.2 V and 132.5 μA. The specific capacitance of the SC was 47.34 F g−1, and the energy density and power density were 97.21 Wh kg−1 and 54.25 W kg−1, respectively. Later, they reported an SCPS based on WCF with the same structure, but with a N-doped ZnCuSe2 nanoporous material used to enhance the storage capacity. Compared with the above results, a higher performance of the 636.5 VOC and 165.4 µA current was obtained [54]. Wang et al. [55] fabricated a Zn–ion hybrid SC by utilizing AC coated on CNT film (AC/CNT) as a cathode and electrodeposited Zn nanosheet arrays on MOF-derived carbon with a functional group scaffold as an anode, while the PVA/Zn (CF3SO3)2 was used as the gel electrolyte (Figure 3e). As a result, this SC device shows a high volumetric specific capacitance of 128.06 F cm−3 and capacitance retention, as well as outstanding mechanical flexibility performance (Figure 3f,g). Further, they developed an integrated SCPS textile using the SC, a TENG, a heater, a temperature sensor, and a Bluetooth device (Figure 3h,i). This system is capable of powering the heater and temperature sensor, as well as detecting temperature changes in the human body (Figure 3j,k). This work provides a promising direction that the SCPS can take in not only charging wearable electronics, but also monitoring and sensing body conditions.

Figure 3.
(a) Schematic illustration of the coaxial TENG and SC fiber. Reproduced with permission [50]. Copyright 2018. American Chemical Society. (b) Schematic structure diagrams of the fiber-based TENG, SC and sensor. Additionally, the energy fiber can be operated under different mechanical deformations. Reproduced with permission [51]. Copyright 2021. American Chemical Society. (c) Schematic illustration of the fabrication of yarn ASC. (d) Schematic illustration of a TENG textile. The insets are cross-sectional SEM images and EDS elementary mapping of the yarn. Reproduced with permission [52]. Copyright 2019. Wiley-VCH. (e) The cross-sectional view of the SC device and the wrapping 3DFAC/CNT film cathode. (f) Specific capacitance and capacitance retention of the SC device at a scan rate of 25 mV s−1. (g) Capacity and capacitance retention of the SC device evaluated after 5000 cycles at various bending angles. (h) Schematic illustration and photograph of a textile-based SCPS. (i) Schematic illustration to depict the incorporation of a temperature sensor and Bluetooth module into the textile-based device. (j) Temperature monitoring at various motion states. (k) Response signals of the detected temperature. Reproduced with permission [55]. Copyright 2022. Elsevier Ltd.
As a conclusion, the CC yarns and carbon fiber are always used as current collectors for both wearable TENGs and SCs because of their good conductivity, flexibility and wearability. Textile/fiber materials, such as nylon, polyester, silk, etc., can be woven into fabrics and textiles to harvest energy from motion, making them suitable platforms for fabricating flexible TENGs due to their wearability and excellent electrification. Moreover, numerous microfibers can provide large surface areas for triboelectrification. At the same time, the lightweight/comfortability are also maintained.
3.2. Film-Based SCPSs
For wearable SCPSs, being lightweight and convenient is one of the future trends. Lu et al. [56] prepared an SCPS composed of cellulose-organohydrogel-based TENG and SC with an impressive anti-freezing property down to −54.3 °C. Firstly, the cellulose was dispersed in BzMe3NOH aqueous with poly (ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (PEGDE) as a crosslinking agent. After the crosslinking process, the hydrogel was soaked in NaCl/EG/H2O solution to obtain organohydrogel, where the EG acted as anti-freezing agent. As shown in Figure 4a, the organohydrogel displayed remarkable optical transparency and could endure twisting without any harm, both at room temperature and −40.0 °C. For the SC, as depicted in Figure 4b, a flexible SWCNT paper coated with Ag nanowires served as the electrodes, while organo-hydrogels acting as both the separator and the electrolyte. For the TENG, latex and VHB were used as the friction layers, and the organohydrogels embedded in the VHB were the electrodes. The SCPS was demonstrated via charging the SC by the rectified output of TENG, and then driving an electronic calculator. This work shows the potential of cellulose-based SCPS with flexibility and low-temperature tolerance for harsh conditions. Ni and coworkers [57] also developed an SCPS based on organohydrogel, which was designed with a triple network composed of PVA, sodium alginate (SA) and cellulose nanofibrils. To enhance the conductivity, the MXene nanosheets were functionalized by graphene oxide (MX-GO) and added to the organohydrogel. Furthermore, by incorporating MX-GO, conductive pathways were established, which enabled the hydrogel to possess direction recognition and tensile strain sensing, as well as sensitive pressure- and temperature-sensing capabilities. This work shows the multifunctionality of a flexible SCPS. Jeong et al. [58] investigated the characterization and modulation of the DC voltage produced by the SCPS utilizing an ion gel/WO3 electrochromic supercapacitor. The multilayer film structure of the TENG was composed of polyvinylidene fluoride/polyimide/poly(ethylene terephthalate)/Indium tin oxide (PVDF/PI/PET/ITO) and ITO/PET film, which acted as the negative and positive triboelectric layer, respectively (Figure 4c). The SC was composed of multilayers (ITO/ion gel/WO3/ITO). Compared to the SC without WO3, the capacitance increased from 0.08 μF < C < 0.63 μF to 0.11 μF < C < 2.15 μF (Figure 4d,e). Figure 4f,g show the scheme of the SCPS and the camera image of the integrated SCPS. When placed in hand, the SCPS was in a deformed state, but its output voltage remained the same as that produced on a flat, rigid substrate. Furthermore, the author also investigated how factors such as contact frequency, contact area, capacitor area and the type of capacitor connection influenced the average DC voltage. Caironi et al. [59] proposed a novel approach to fabricating TENGs using edible composites. They developed a bilayer film consisting of ethylcellulose (EC) and AC, with the top layer acting as an insulator and the bottom layer as a conductive electrode that can serve as the positive triboelectric layer of the TENG. Additionally, the edible AC/EC composite (90:10 wt%) can also be applied as the electrode of the SC. This innovative technology holds great potential for the development of edible electronics, which can be used for a variety of applications, including drug release monitoring through intra-body communication.
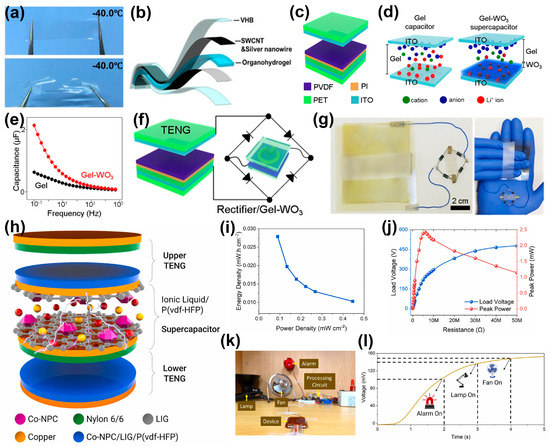
Figure 4.
(a) Photograph of the cellulose organohydrogel at −40.0 °C. (b) Schematic for supercapacitor assembly with cellulose organohydrogel. Reproduced with permission [56]. Copyright 2021. Elsevier Ltd. (c) Scheme of TENG. (d) Structures of the Gel capacitor and the Gel-WO3 supercapacitor. (e) The capacitance of both the Gel and Gel-WO3 was measured as a function of frequency. (f) Scheme of the SCPS. (g) Camera images of the power unit (left) and the measurement on hand (right). Reproduced with permission [58]. Copyright 2020. American Chemical Society. (h) Illustration of the layer-by-layer structure of the self-charging SCPS. (i) The relationship between energy density and power density of the SC. (j) Load voltage and peak power of the TENG. (k) Photograph of the experimental setup. (l) Charging curve of turning on smart home appliances. Reproduced with permission [60]. Copyright 2022. Elsevier Ltd.
Park et al. [60] designed an SCPS that can be used without the need for power management or rectifier circuits due to its “tribo-electrochemical mechanism”. The layer–by-layer structure of the SCPS is illustrated in Figure 4h, which comprises an upper and lower TENG with a solid polymer electrolyte (SPC) sandwiched between them. The solid polymer electrolyte is composed of a poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) (P(vdf-HFP)) separator infused with an ionic liquid (1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide [TFSI]). The electrode is made up of a MOF-derived cobalt nanoporous carbon/laser-induced graphene/copper (Co-NPC/LIG/Cu). The triboelectric materials of the TENG consist of a Nylon 66 and Co-NPC/LIG/P(vdf-HFP) layer, while the Cu layer serves as the electrodes. When a compressive force is applied, the upper and lower TENGs come into contact with the SC, generating an electric field. This electric field drives the ions in the SC electrolyte towards the electrode layer, forming an electrical double layer near the interface of the electrolyte and electrode, which charges the SC. This is the first SCPS prototype that does not use any external circuitry, and the SC can deliver an energy density of 0.0278 mW.h.cm−2, and the power density is 0.089 mW cm−2 (Figure 4i). Additionally, the TENG can generate a power of 2.5 mW in a single integrated device, which can successfully charge the SC (Figure 4j). Further, the SCPS can serve as smart switches for activating intelligent appliances (Figure 4k,l). This research highlights the process of converting energy into self-charging supercapacitors in a simpler and more effective way.
Paper, a common commodity in daily life, is a great candidate as a flexible substrate due to its biocompatibility, cost effectiveness and integrability. Sun et al. [61] prepared an all-electrospun paper SCPS in which the TENG was composed of non-conductive polyacrylonitrile (PAN) paper as a triboelectric layer and carbon paper as electrodes. The carbon paper was obtained by thermally treating PAN paper at 700 °C in an inert atmosphere (Figure 5a). For the SC, the carbon paper was utilized as both the electrode and active material. Then, the TENG was integrated with three SCs connected in series to form an SCPS, and the PAN paper was the separator, as shown in Figure 5b,c. This work shows the outstanding advantages of simple operation and low cost for large-scale production. Recently, Kim et al. [62] designed an SCPS using wrinkled polystyrene (PS) and electro-spun materials. As shown in Figure 5d, the Cu deposited wrinkled PS material was covered with PAN/Nylon 66, which was used as the triboelectric material. The polyaniline (PANI)-coated wrinkled PAN/PS substrate acted as the positive electrode, while the carbon cloth acted as a negative electrode for the SC (Figure 5e). With a rectifying circuit, the SCPS was capable of driving a commercial thermo-hygrometer. Lu and co-worker [63] proposed an air-laid paper-based SCPS. Air-laid paper is a nonwoven material made from a blend of cellulose fibers and/or other materials that are formed using air instead of water to create a web of fibers. The heterogeneous structure of air-laid paper allows for the felt side and wire side to be utilized as the positive and negative triboelectric layers, respectively. This is due to the presence of coarse cellulose fibers on the felt side and fine polyester fibers on the wire side. As shown in Figure 5f, MWCNTs and waterborne polyurethanes were spray-coated on either the felt or wire side of the papers to act as paper electrodes of the TENG. For the SCs, two paper electrodes were assembled with a PVA/H3PO4 film as the separator membrane. In addition, the SC utilizing a gel electrolyte exhibited significantly lower leakage current compared to the ISC (short-circuit current) produced by the TENGs, suggesting that the TENGs can effectively charge the SCs.
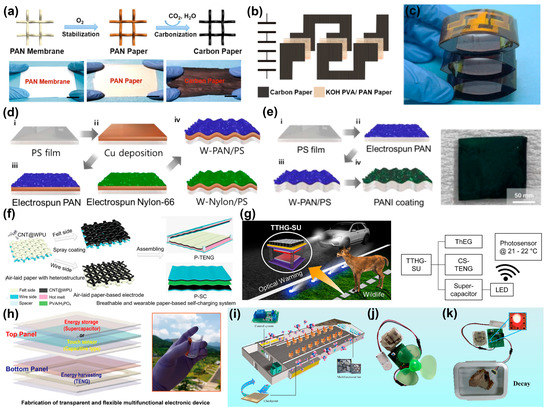
Figure 5.
(a) Synthesis process of the flexible electrospun papers. (b) Diagram depicting the structure of series-connected integrated SCs. (c) Photograph of an as-fabricated SCPS. Reproduced with permission [61]. Copyright 2017. Elsevier Ltd. (d) Fabrication of W-PAN/PS and W-Nylon/PS materials. (e) Fabrication of wrinkled substrate for the SC (left), and a photograph of W-PAN/PS@PAN (right). Reproduced with permission [62]. Copyright 2022. MDPI. (f) Preparation of a TENG and an SC based on air-laid paper. Reproduced with permission [63]. Copyright 2019. Wiley-VCH. (g) The light stimulating process (left), and the flow chart of the process (right). Reproduced with permission [64]. Copyright 2021. Wiley-VCH. (h) Schematic illustration of transparent and multifunctional electronic devices. Reproduced with permission [65]. Copyright 2019. American Chemical Society. (i) Alarm diagram of chicken farm. (j) The SCPS used to power fans. (k) Real picture of alarm systems to monitor food corruption. Reproduced with permission [64]. Copyright 2021. Elsevier Ltd.
Kim et al. [64] designed an all-in-one energy harvesting system with triboelectric and thermoelectric hybrid generator and Au nanoflower supercapacitor. As depicted in Figure 5g, the energy stored in the SC can drive an external photo-sensing system stimulated by an LED light that provides an optical warning signal. When animals see bright lights, they become alert to vehicles and avoid being hit. This research sheds light on the potential for harvesting energy from wildlife and opens up a new frontier in ecologically friendly technology. Choi et al. [65] proposed a transparent and flexible multifunctional SCPS with a touch-sensing system (Figure 5h). An adaptive single-layer graphene (SLG) film was selected as an electrode for the supercapacitor, a touch sensor, and a TENG. The upper portion comprises two symmetrical SLG electrodes on transparent polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) substrates, which are separated and coated with an intermediate PAN mat soaked in PVA−LiCl serving as the electrolyte and separator. The bottom part is a TENG made of PTFE and PEN as the triboelectric layers, which can harvest a significant amount of electric power, up to 1.45 mW/cm2, within the pressure range detectable by human touch, around 17 kPa. In another study, Sun et al. [66] developed a hybrid nanogenerator comprised of a nylon- and PTFE-based TENG and an electromagnetic generator (EMG). A button supercapacitor was assembled, featuring PANI/MXene as the positive electrode, active carbon as the negative electrode and H2SO4/PVA gel as the electrolyte. Furthermore, the PANI/MXene can also be used as a NH3 sensor. Then, a self-powered gas detection network was constructed and realized the display of test data on a computer and APP. As shown in Figure 5i–k, the multifunctional SCPS designed in this study has the potential to be implemented across various aspects of industrial production and social life, including but not limited to alarm systems and ensuring food safety with the aid of a mobile APP.
Overall, gel film, flexible cellulose paper, electrospun paper or some transparent film, such as PTFE, PVDF, PET, ITO, etc., are often used as flexible substrates due to their versatility, low cost, lightweight, and high energy conversion efficiency. These characteristics make them an attractive solution for a wide range of applications, from wearable sensors to outdoor activities and emergency situations.
3.3. Other Materials-Based SCPS
For wearable electronics, stretchability is a crucial factor in ensuring resistance against mechanical deformations. Park et al. [67] fabricated a fully stretchable SCPS using micro-SC and TENG by employing stretchable oxidized single-walled carbon nanotubes (Ox-SWCNT)/polymer electrodes. As shown in Figure 6a, the stretchable current collector for the micro-SC and TENG was made of a composite using Ag flakes, Ag nanoparticle-Ox-SWCNTs and PDMS. The SCs were fabricated using the Ox-SWCNT/PVA/H3PO4 as stretchable electrodes and PVA/H3PO4 as stretchable hydrogel electrolytes. After being integrated together, the SC was charged by the TENG from 0 to 2.2 V within 1200 s and was capable of powering a commercial digital clock for 10 s (Figure 6b,c). Xu et al. [68] reported a stretchable, self-powered wireless sensing platform based on LIG (laser-induced graphene) foams, which can provide an efficient flow in TENGs, and by applying a coating or a second laser irradiation process, the platform is capable of enhancing the energy density in micro-SC arrays (MSCAs). Figure 6d–f illustrate that the sensors in the SCPS sensing platform are powered directly by the integration of TENG with MSCAs, which continuously harnesses mechanical energy from human movements. Tian et al. [69] built a compressible SCPS comprising a TENG with polyurethane (PU) sponges serving as structural frameworks, Ag NWs as electrodes and PTFE and PI coated on the sponges as the negative and positive dielectric layers, respectively (Figure 6g). PANI-rGO-sponges were used as the electrode materials of the SC. Then, by combining the TENG and four SCs in series with a rectifier, the SCPS was created to drive electronic equipment such as an electronic calculator, a watch and a hygro-thermograph (Figure 6h–j).
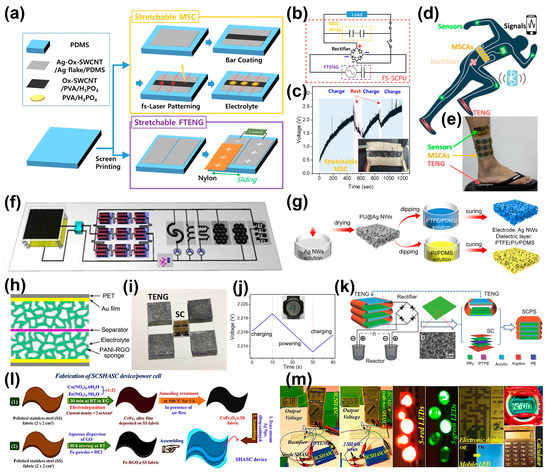
Figure 6.
(a) Schematic of the fabrication process for the SCPS. (b) Circuit diagram of SCPS. (c) Charging curve of the SC component of SCPS. Inset image is stretchable SC array. Reproduced with permission [67]. Copyright 2021. Elsevier Ltd. (d–f) Schematic illustration and optical images of the LIG-based wearable sensing platform. Reproduced with permission [68]. Copyright 2022. AIP Publishing. (g) The preparation of 3D electrode pairs for the TENG. (h) Structure of an all-solid-state compressible supercapacitor. (i) Photograph of the SCPS consisting of four TENGs and four serial SCs. (j) Charging curves of electronic watch driven by the SCPS. Reproduced with permission [69]. Copyright 2022. Elsevier Ltd. (k) Schedule of the SCPS. Reproduced with permission [70]. Copyright 2016. Wiley-VCH. (l) Fabrication of the CoFe2O4@SS and Fe-RGO@SS electrodes. (m) Demonstration of the application. Reproduced with permission [71]. Copyright 2019. American Chemical Society.
To guarantee a long durability and environmental benignancy, Wang et al. [70] prepared an all-plastic-materials-based SCPS, with PPy serving as the electrode material for the TENG and being synthesized using the pulse output of the TENG. By connecting the TENGs in series through a full-wave rectifier, several reactors are prepared to produce PPy with a horn-like morphology (hPPy) (Figure 6k). The as-prepared hPPy can also be used as the active material of both anode and cathode in the SC. This work verifies that TENG, as a natural and effective pulse generator, can be used not only as a power source, but also as a technique for synthesizing electrochemical materials. Khatua et al. [71] fabricated an SCPS on a stainless steel (SS) fabric. Figure 6l shows that the positive electrode of the SC was made of CoFe2O4 grown on SS, while the negative electrode was Fe-RGO@SS, which consisted of iron-oxide-decorated RGO grown on SS. The separator was an Fe3+-PAA/KOH hydrogel electrolyte with self-healing ability. For the TENG, the positive and negative triboelectric friction layers were SS fabric and PVDF-HFP/SS-impregnated PDMS, respectively. The SCPS was constructed by sandwiching a single SC unit between two TENGs connected in parallel. The SCPS was capable of immediately powering small electronic devices such as a digital display, wristwatch, mobile LED screen and commercial digital calculator (Figure 6m). Wang et al. [72] introduced the concept of an e-textile microgrid by demonstrating a bioenergy microgrid system consisting of multiple textile-based modules. These modules were powered by complementary and synergistic energy harvesters and matched energy storage components. Moreover, this system was capable of harvesting biomechanical energy through sweat-based biofuel cells and TENG and regulating the harvested energy via SCs to produce a high-power output.
Overall, the materials selected to construct TENGs and SCs depend on the service conditions, power requirements, structure design, etc. Additionally, more materials with high performance, flexibility, wear resistance and the ability to adapt to various environments are in urgent need of development.
3.4. The Device Configuration of SCPSs
Flexible SCs and TENGs are two types of energy-harvesting devices that have garnered significant interest due to their potential for powering wearable and flexible electronics. The integration of these devices can lead to a self-powered system that is both lightweight and flexible. Typically, SCPS devices can be classified based on the arrangement of the TENG and the SC, the type of SC and the integration with other components. One common configuration is the parallel-plate TENG [60,73], where the TENG and the SC are arranged in a parallel-plate structure. The TENG can be placed on top of the SC, and the contact between the TENG and the SC can generate charges that are stored in the SC. The SC usually consists of two layers of conductive material separated by a layer of electrolyte. In this situation, the SC can be fabricated on the same substrate as the TENG, and the functional materials that improve energy conversion efficiency can be used for both TENGs and SCs, thus simplifying the experimental procedure and setup.
Another configuration is the “all-in-one” configuration, where the TENG and the SC are arranged in one coaxial fiber or one fabric structure [50,51]. In the coaxial fiber, the inner core is commonly an SC used for energy storage, and the outer sheath is a TENG in single-electrode mode used for energy harvesting. In the one-fabric form, the SC and TENG are always knitted as cloth with the desired style, and they can share the same current collector. The current collectors (electrodes) are usually conductive carbon fibers, silver or copper, and can be added using a variety of deposition techniques, such as sputtering, evaporation or printing. This configuration can provide a high flexibility and conformability with a high energy conversion efficiency, and it is usually used for harvesting energy from body motion or environmental vibration.
The aforementioned SCPSs combine TENGs and SCs into a single device, but the rectifying circuit is typically independent. The packaged SCPS configuration consists of a package that contains the TENG, SC and rectifier, all sealed in silicone rubber or other elastomers [74,75]. The shape-adaptive, waterproof performance and the outstanding mechanical durability of this configuration make it suitable for use in humid environments and inclement weather. The SCPS can also incorporate other components, such as sensors, to improve energy utilization and functionality.
Overall, the selection of the device configuration should consider the requirements of the application, such as the power density, energy conversion efficiency, flexibility, operating conditions, working environment and easiness to integrate in SCPSs, which are of the prior concerns. In addition, the type of SC used in TENG-SCPSs can also vary depending on the specific application requirements. Carbon-based SCs, metal-oxide-based SCs and polymer-based SCs are some of the commonly used SC types, with each type offering unique properties and advantages. Carbon-based SCs, such as activated carbon and carbon nanotubes, are commonly used due to their high surface area and low cost. Metal-oxide-based SCs, such as manganese oxide and nickel oxide, can provide a remarkable capacitance and energy density. Polymer-based SCs, such as poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-based SCs, can provide high flexibility and conductivity. Therefore, by integrating flexible SCs with TENGs, more self-powered devices are created and expand the scope of their application such as in wearable sensors, flexible displays and smart textiles, but not limited to these.
4. Power Management
TENG is a device that can generate electricity from mechanical motion by utilizing the triboelectric effect. Typically, TENG exhibits high voltage and low current/charge transfer along with large internal impedance, which results in low energy transfer efficiency for powering electronics or charging a supercapacitor/battery, as these devices usually possess relatively low impedance. Achieving maximum power utilization in TENGs requires an external loading impedance of around 105–107 Ω, which is significantly higher than that of batteries and supercapacitors (10−2–102 Ω) [8,24,61,76]. To address the issue of limited energy storage efficiency in SCPSs caused by the impedance mismatch between TENG and energy storage units, traditional approaches have involved a direct connection between the two components through a rectifier. However, this method may not be efficient enough for practical applications. To improve energy storage efficiency, proper power management circuits are necessary to maximize efficiency.
Recently, Liu et al. [77] designed a passive power management switch (PMS) composed of a simple-circuit topology that can track the maximum internal capacitance point of TENG, which is driven by the TENG. The schematic diagram of the PMS can be seen in Figure 7a, which is primarily composed of a rectifier, a temporary capacitor, a switch and a Buck converter. Numerous studies have shown that the switching time plays a crucial role in energy transfer. Early in 2015, Zi et al. [78] proposed an explanation for this phenomenon based on the V-Q (open-circuit voltage–transfer charge amount) relationship diagram of TENG. Later, they proposed an energy management design that utilizes switches to alternate between serial-connected and parallel-connected capacitors, which could be triggered automatically by TENG movement [79]. As shown in Figure 7b,c, the TENG was designed as a sliding freestanding-triboelectric-layer (SFT) mode, achieving a 5× supercapacitor charge rate compared to the charge directly through the rectifier. Additionally, Xi et al. [80] reported a comprehensive power management for TENG, including steps to maximize energy transfer, DC buck conversion and self-management mechanisms (Figure 7d). The first step is to maximize the energy transfer from the TENG to the back-end circuit (Figure 7e). By using a power management module (PMM), up to 85% of the energy generated by the TENG can be autonomously released and output as a steady and continuous DC voltage on a load resistance, thus improving energy transfer efficiency. Zhang et al. [81] employed an LC oscillating model to maximize the transferred energy from the TENG to the energy storage unit (Figure 7f); then, a PMM was assembled to regulate and manage the electric outputs from TENG, achieving a power conversion × efficiency of over 70%. In 2020, Zhang et al. [82] designed a self-sustained and automatic hysteresis plasma switch, which was fabricated through silicon micromachining and incorporated TENGs into a two-stage efficient conditioning circuit to power low-voltage devices. This switch ensures electrical isolation between the TENG and the storage circuit before closing, and its threshold is determined by the breakdown voltage of the electrode gap (Figure 7f). Harmon et al. [83] discovered that the internal capacitor of the TENG can generate additional energy. The TENG functions as a capacitor in parallel with the temporary storage capacitor, contributing an extra amount of energy proportional to its capacitance, while the buck converter transfers the energy stored in a temporary capacitor to the output.
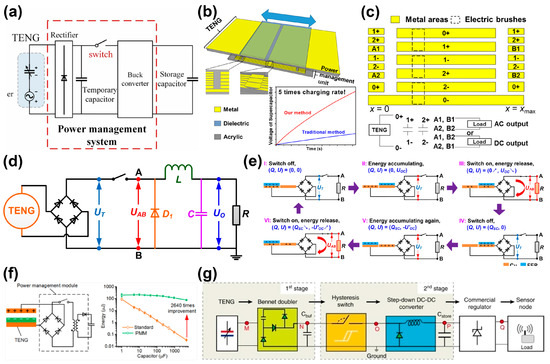
Figure 7.
(a) The structure of PMS. Reproduced with permission [77]. Copyright 2023. Elsevier Ltd. (b) The illustration of the power management unit. (c) The designed metal areas in the board and the electric brushes of the power management unit. Reproduced with permission [79]. Copyright 2017. Elsevier Ltd. (d) The circuit diagram of AC–DC buck conversion. (e) Operating process in one cycle to release max energy from TENG. Reproduced with permission [80]. Copyright 2017. Elsevier Ltd. (f) The power management based on LC oscillating triggered by a TENG enables a 2640-fold enhancement in stored energy through the use of PMM. Reproduced with permission [81]. Copyright 2017. Elsevier Ltd. (g) Diagram of the conditioning system. Reproduced with permission [82]. Copyright 2020. Nature Publishing Group.
5. Conclusions and Perspective
In summary, we have provided an overview of the recent advances in SCPSs that integrate energy-harvesting devices (TENGs) and energy storage devices (SCs). Wearable electronics have benefited greatly from this technology, as they often rely on energy harvested from human body motion or activities. A variety of integration prototypes have been developed with common types of mechanical resources and energies. The in situ storage of energy collected with SCs, making it a competitive method for sustainably powering wearable/portable electronics or sensors that pick up environmental energy.
5.1. Application Scenario
Recent studies have suggested more potential applications of SCPSs, and in the future, the research on wearable devices will be more concentrated on personal healthcare, such as such as smart watches, fitness trackers, cardiac pacemaker and implantable sensors/electronics. Here are some application scenarios:
- Smart clothing, such as jackets, shirts and pants, can incorporate SPCSs to power built-in sensors, lighting and other electronics. This allows the device to operate continuously without the need for external power sources. Furthermore, the TENG in the smart clothing can be used as a self-powered sensor to monitor body signals, such as the sleep status of snoring and breathing.
- Electronic skin, a type of flexible and stretchable sensor that can be attached to the skin to monitor various physiological signals, such as heart rate, sweat or blood pressure. Additionally, it is better with environmental sensing ability.
- Body sensors and medical devices, such as glucose monitors, heart rate monitors and prosthetics, require a constant power supply to function properly. TENG-based SPCSs can be used to provide a continuous and reliable source of power for these devices, reducing the need for frequent battery replacements and minimizing downtime.
- Flexible electronics for sports and outdoor activities, such as hiking or camping. The TENG and SCs can be integrated into a backpack strap or a hiking shoe that can harvest energy during movement and charge a portable electronic device, such as a GPS or a flashlight.
- Safety devices, such as GPS trackers, personal alarms and emergency lights, in case of an emergency. Additionally, the SCPS can be integrated into wearable accessories, such as bracelets or keychains, to provide a reliable and self-powered source of energy in a critical situation.
Overall, TENG-SCs-based SPCSs can be used in a variety of flexible wearable electronics to provide a reliable and self-sustaining power supply. With continued research and development, along with innovative designs and new materials, we believe that TENG-SCs-based SCPSs will achieve the widespread adoption of TENG-SCs for a variety of applications with a great impact and can be applied to the practical future in the near future.
5.2. Challenges
TENG-SCs-based SCPSs are still in the research and development stage, and most of these reported are proof-of-concept prototypes. There are many challenges that need to be overcome before they can be widely used in commercial applications and achieve their widespread adoption.
One of the main challenges is to improve the efficiency and reliability of TENG-SCs. The efficiency of TENG-SCs is still relatively low compared to traditional energy harvesting methods, and the output voltage and current are often unstable, which limits their practical applications. The key performance parameters of the SCPSs are energy density, charging time and charging voltage. More efficient energy management circuits need to be developed and appropriate supercapacitors need to be designed (including electrode materials, current collectors, electrolytes, separators, etc.).
Another challenge is to integrate TENG-based SCPSs with wearable electronics in a seamless and effective way. This requires developing new fabrication methods and designs that can ensure a reliable and durable connection between the TENG and the electronic device. Additionally, it is urgent to design novel structures to expand the application scope. It would be better to collect multiple types of mechanical energy or other environmental energy sources, for example, thermal and solar energy could be gathered simultaneously.
In addition, the durability, flexibility and reliability of TENG-SCs needs to be improved, especially when they are subjected to frequent bending and stretching. Wearable electronics are often exposed to harsh and dynamic environments, such as exposure to varying temperature and humidity atmospheres, which can cause mechanical fatigue and wear on the TENG and other components. Therefore, developing materials and designs that are durable and can withstand these conditions is crucial for ensuring the long-term performance of SCPSs.
Last but not least, to enable the mass production of SCPSs, it is important to develop scalable and cost-effective fabrication methods that can ensure consistent performance and quality of the devices. Furthermore, with the increasing use of wearable electronics, there is a growing need for standardization and regulation of TENG-based SCSs to ensure their safety and performance.
Author Contributions
Y.L.: Investigation, Writing—original draft and editing. Conceptualization. T.W.: Writing—original draft and editing. Z.M.: Investigation, Conceptualization. Y.M.: Investigation, Conceptualization. Z.Z.: Investigation, Conceptualization. F.L.: Investigation, Conceptualization. X.C.: Resources, Supervision, Conceptualization, Validation. N.W.: Resources, Supervision, Conceptualization, Validation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by [the National Natural Science Foundation of China] grant number [51873020] and [the University Basic Scientific Research Business Fee] grant number [FRF-MP-20-38].
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC No. 51873020) and the University Basic Scientific Research Business Fee (FRF-MP-20-38).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhu, M.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, B. Superstable and Intrinsically Self-Healing Fibrous Membrane with Bionic Confined Protective Structure for Breathable Electronic Skin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202200226. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Li, J.; Xiao, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J. Topographic design in wearable MXene sensors with in-sensor machine learning for full-body avatar reconstruction. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, J.; Lopez, G.; Shuzo, M.; Yamada, I. Collaborative Processing of Wearable and Ambient Sensor System for Blood Pressure Monitoring. Sensors 2011, 11, 6760–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Xianyu, Y. Gold Nanomaterials-Implemented Wearable Sensors for Healthcare Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2113012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Hua, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guo, P.; Hao, D.; Gao, Y.; Huang, J. Recent advancements in flexible and wearable sensors for biomedical and healthcare applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2022, 55, 134001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Q.; Park, H. Perspective on High-Energy Carbon-Based Supercapacitors. Energy Environ. Mater. 2020, 3, 286–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Garg, A.; Gupta, A.; Madan, A.; Jain, P. Comprehensive review on latest advances on rechargeable batteries. J. Energy Storage 2023, 57, 106204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedajova, V.; Bakandritsos, A.; Blonski, P.; Medved, M.; Langer, R.; Zaoralova, D.; Ugolotti, J.; Dzibelova, J.; Jakubec, P.; Kupka, V. Nitrogen doped graphene with diamond-like bonds achieves unprecedented energy density at high power in a symmetric sustainable supercapacitor. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Lu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Feng, X.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Ouyang, M. A review on the key issues of the lithium-ion battery degradation among the whole life cycle. eTransportation 2019, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xie, Y.; You, Y.; Yuan, J.; Xu, Q.; Xie, H.; Chen, Y. Rational Design of Electrode Materials for Advanced Supercapacitors: From Lab Research to Commercialization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, K. Aging state prediction for supercapacitors based on heuristic kalman filter optimization extreme learning machine. Energy 2022, 250, 123773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, X.; Wang, N. From Triboelectric Nanogenerator to Uninterrupted Power Supply System: The Key Role of Electrochemical Batteries and Supercapacitors. Batteries 2022, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xu, Z.; Li, L.; Wei, J.; Wang, W.; Yan, Z.; Chen, T. Breakage-resistant hydrogel electrode enables ultrahigh mechanical reliability for triboelectric nanogenerators. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, M.; Murillo, G. Tapping-Actuated Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Surface Charge Density Optimization for Human Motion Energy Harvesting. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, F.; Jie, Y.; Cao, X.; Li, T.; Wang, N. Natural triboelectric nanogenerator based on soles for harvesting low frequency walking energy. Nano Energy 2017, 42, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qian, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, K.; Wang, J.; Meng, Z.; Li, F.; Zhu, C.; Chen, P. Highly Adaptive Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Nanogenerator for Scavenging Flow Energy and Self-Powered Marine Wireless Sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhen, G.; Liu, G.; Bu, T.; Liu, W.; Fu, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Remarkable merits of triboelectric nanogenerator than electromagnetic generator for harvesting small-amplitude mechanical energy. Nano Energy 2019, 61, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Mi, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qin, Q.; Wang, X.; Meng, J.; Liu, F.; Cao, X.; Wang, N. Weaved piezoresistive triboelectric nanogenerator for human motion monitoring and gesture recognition. Nano Energy 2022, 96, 107135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh Le, T.; Jianing, A.; Huang, Y.; Vo, Q.; Boonruangkan, J.; Tran, T.; Kim, S.; Sun, G.; Kim, Y. Ultrasensitive Anti-Interference Voice Recognition by Bio-Inspired Skin-Attachable Self-Cleaning Acoustic Sensors. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13293–13303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Zhu, C.; Shi, J.; Morikawa, H. Stretchable, Adhesive, Self-Healable, and Conductive Hydrogel-Based Deformable Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting and Human Motion Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 9126–9137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Hu, G.; Min, H.; Qiu, Y.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M. Respiration-mediated self-switched triboelectric nanogenerator for wearable point-of-care prevention and alarm of asthma. Nano Energy 2023, 106, 108058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kitchamsetti, N.; Cho, H.; Kim, D. Microwave-Assisted Hierarchically Grown Flake-like NiCo Layered Double Hydroxide Nanosheets on Transitioned Polystyrene towards Triboelectricity-Driven Self-Charging Hybrid Supercapacitors. Polymer (Basel) 2023, 15, 454. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Zhou, L.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, J.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Qiao, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J. Achieving High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerator by DC Pump Strategy. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 2201957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Yang, J.; Cao, X.; Wang, N. Flexible and highly sensitive triboelectric nanogenerator with magnetic nanocomposites for cultural heritage conservation and human motion monitoring. Nano Energy 2022, 101, 107570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, Z.L. Recent advances in triboelectric nanogenerator based self-charging power systems. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 23, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhu, M.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Z.; He, T.; Lee, C. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Enabled Wearable Sensors and Electronics for Sustainable Internet of Things Integrated Green Earth. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2203040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Pan, C.; Guo, W.; Chen, C.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, R.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric-generator-driven pulse electrodeposition for micropatterning. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4960–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Mo, J.L.; Fu, Q.; Lu, Y.X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.F.; Nie, S.X. Enhancement of Triboelectric Charge Density by Chemical Functionalization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, M.; Kim, S.; Cho, Y.; Byun, K.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Shin, H.; Park, S. Triboelectric Series of 2D Layered Materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.R.; Lin, L.; Zhu, G.; Wu, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.L. Transparent triboelectric nanogenerators and self-powered pressure sensors based on micropatterned plastic films. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Bai, P.; Chen, J.; Jing, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerators as a new energy technology: From Fundamentals, Devices, to applications. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Cao, X.; Wang, N. Triboelectric Nanogenerators in Sustainable Chemical Sensors. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Kang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, F.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Development, applications, and future directions of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 2951–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Yang, O.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. A Dual-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wind Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Wind Speed Monitoring. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6244–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, M.; Shu, M.; An, J.; Ding, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, H. Underwater wireless communication via TENG-generated Maxwell’s displacement current. Nat Commun. 2022, 13, 3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, C.; Kottapalli, A. Bioinspired designs and biomimetic applications of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, M.; Sun, J.; Jiang, D.; Xu, M.; Wu, Z.; Xu, B.; Algadi, H.; Huang, M. Waterwheel-inspired high-performance hybrid electromagnetic-triboelectric nanogenerators based on fluid pipeline energy harvesting for power supply systems and data monitoring. Nanotechnology 2023, 34, 025401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Mi, Y.; Wu, T.; Cao, X.; Wang, N. From Triboelectric Nanogenerator to Polymer-Based Biosensor: A Review. Biosensors 2022, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehan, P.; Ensafi, A.; Andikaey, Z.; Rezaei, B. H-CoNiSe2/NC dodecahedral hollow structures for high-performance supercapacitors. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, M.; Subramani, K.; Sathish, M.; Dhanuskodi, S. NiTe Nanorods as Electrode Material for High Performance Supercapacitor Applications. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 9034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Park, S. Highly Porous Carbon Aerogels for High-Performance Supercapacitor Electrodes. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Jiang, C.; Wu, W. Toward fiber-, paper-, and foam-based flexible solid-state supercapacitors: Electrode materials and device designs. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 7041–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Yuan, W.; Liu, X.; Xie, P.; Yang, F.; Zhao, H.; Lu, D.; Yin, Y.; Wu, Z. All-in-one integration of polyaniline-polyvinyl alcohol electrode/electrolyte interface for tailorable solid-state supercapacitors. J. Energy Storage 2023, 61, 106761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ji, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, P.; Huang, Y. Flexible and stretchable polyaniline supercapacitor with a high-rate capability. Polym. Int. 2021, 70, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Toward Wearable Self-Charging Power Systems: The Integration of Energy-Harvesting and Storage Devices. Small 2018, 14, 1702817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zi, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yi, F.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.L. A Flexible Fiber-Based Supercapacitor–Triboelectric-Nanogenerator Power System for Wearable Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4830–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Xiang, X.; Yin, H.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, H. All-yarn triboelectric nanogenerator and supercapacitor based self-charging power cloth for wearable applications. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 315404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, J.; Liu, H.; Guo, C.; Hu, W. Triboelectric nanogenerator/supercapacitor in-one self-powered textile based on PTFE yarn wrapped PDMS/MnO2NW hybrid elastomer. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, S.; Mao, Y.; Gui, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, C.; Guo, S. Dual Redox Active Sites N-C@Ni2P/NiSe2 Heterostructure Supercapacitor Integrated with Triboelectric Nanogenerator toward Efficient Energy Harvesting and Storage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, L.; Wen, Z.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Wei, A.; Cheng, P.; Xie, X.; Sun, X. Coaxial Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Supercapacitor Fiber-Based Self-Charging Power Fabric. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 42356–42362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, N.; Xiong, Y.; Cao, X.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Sun, J.; Zhai, J.; et al. Multifunctional coaxial energy fiber toward energy harvesting, storage, and utilization. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Cong, Z.; Pu, X.; Guo, W.; Liu, T.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z.L. High-energy asymmetric supercapacitor yarns for self-charging power textiles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, B.; Hazarika, A.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.; Park, Y.; Park, H. Triboelectric-nanogenerator-integrated structural supercapacitor based on highly active P-doped branched Cu–Mn selenide nanowires for efficient energy harvesting and storage. Nano Energy 2020, 73, 104754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, B.; Hazarika, A.; Kwak, M.; Kim, D.; Jaiswal, A.; Lee, H.; Seo, J.; Jeong, C.; Jang, J.; Park, Y.; et al. Triboelectric nanogenerator-integrated structural supercapacitor with in situ MXene-dispersed N-doped Zn–Cu selenide nanostructured woven carbon fiber for energy harvesting and storage. Nano Energy 2021, 43, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cong, Z.; Hu, J.; Lu, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Malyi, O.; Pu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, H.; et al. Regulating zinc electroplating chemistry to achieve high energy coaxial fiber Zn ion supercapacitor for self-powered textile-based monitoring system. Nano Energy 2022, 93, 106893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Lu, A. Flexible, anti-freezing self-charging power system composed of cellulose-based supercapacitor and triboelectric nanogenerator. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 274, 118667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, K.; Wu, H.; Huang, L.; Chen, L.; Ni, Y. A tough organohydrogel-based multiresponsive sensor for a triboelectric nanogenerator and supercapacitor toward wearable intelligent devices. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 12092–12103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, K.-W.; Kim, J.; Jeong, U. DC Voltage Modulation for Integrated Self-Charging Power Systems of Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Ion Gel/WO3 Supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 2550–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamanna, L.; Pace, G.; Ilic, I.; Cataldi, P.; Viola, F.; Friuli, M.; Galli, V.; Demitri, C.; Caironi, M. Edible cellulose-based conductive composites for triboelectric nanogenerators and supercapacitors. Nano Energy 2023, 108, 108168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, K.; Sharma, S.; Pradhan, G.B.; Bhatta, T.; Rana, S.M.S.; Lee, S.; Seonu, S.; Shin, Y.; Park, J.Y. A triboelectric driven rectification free self-charging supercapacitor for smart IoT applications. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Wen, Z.; Zhao, F.; Yang, Y.; Shao, H.; Zhou, C.; Shen, Q.; Feng, K.; Peng, M.; Li, Y. All flexible electrospun papers based self-charging power system. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jo, S.; Kim, Y.; Zaman, S.; Kim, D. Electrospun Nanofiber Covered Polystyrene Micro-Nano Hybrid Structures for Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Supercapacitor. Micromachines 2022, 13, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Lu, X. Triboelectric Power Generation from Heterostructured Air-Laid Paper for Breathable and Wearable Self-Charging Power System. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Yun, J.; Jo, S.; Kim, Y.; Roh, H.; Kim, D. All-in-one energy harvesting system with triboelectric and thermoelectric hybrid generator and Au nanoflower supercapacitor for a light stimulation to the wildlife. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.; Son, W.; Lee, G.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Kim, S.; Pang, C.; Choi, C. Single-Layer Graphene-Based Transparent and Flexible Multifunctional Electronics for Self-Charging Power and Touch Sensing Systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 9301–9308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Gong, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yu, S.; Yin, Y.; Sun, D. In situ polymerized polyaniline/MXene (V2C) as building blocks of supercapacitor and ammonia sensor self-powered by electromagnetic-triboelectric hybrid generator. Nano Energy 2021, 88, 106242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lee, J.-W.; Seo, S.; Jeong, B.; Lee, B.; Do, W.; Kim, J.; Cho, J.; Jo, A.; Jeong, H.; et al. Fully stretchable self-charging power unit with micro-supercapacitor and triboelectric nanogenerator based on oxidized single-walled carbon nanotube/polymer electrodes. Nano Energy 2021, 86, 106083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, H.; Ding, X.; Lorestani, F.; Huang, C.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, B.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H.; Xu, Y. Human motion-driven self-powered stretchable sensing platform based on laser-induced graphene foams. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2022, 9, 011413. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Huang, S.; Luo, J.; Zhao, J.; Fan, F.; Tian, Z. Supercapacitor-Inspired Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Electrostatic Double Layer. Nano Energy 2022, 95, 106971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wen, Z.; Zi, Y.; Lin, L.; Wu, C.; Guo, H.; Xi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Electrochemical Synthesis of Polypyrrole from the Pulsed Output of a Triboelectric Nanogenerator as a Sustainable Energy System. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 3542–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, A.; Paria, S.; Karan, S.; Bera, R.; Bera, A.; Das, A.; Si, S.; Halder, L.; De, A.; Khatua, B. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Driven Self-Charging and Self-Healing Flexible Asymmetric Supercapacitor Power Cell for Direct Power Generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5022–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Kim, K.N.; Lv, J.; Tehrani, F.; Lin, M.; Lin, Z.; Moon, J.M.; Ma, J.; Yu, J.; Xu, S.; et al. A self-sustainable wearable multi-modular E-textile bioenergy microgrid system. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Zhang, M.; Huang, J.; Bian, J.; Jie, Y.; Willander, M.; Cao, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.L. Coupled Supercapacitor and Triboelectric Nanogenerator Boost Biomimetic Pressure Sensor. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, H.; Cheng, X.; Li, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Miao, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. High-efficiency self-charging smart bracelet for portable electronics. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yin, Y.; Yi, F.; Dai, K.; Niu, S.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; You, Z. Bioinspired stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator as energy-harvesting skin for self-powered electronics. Nano Energy 2017, 39, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical systems of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 161–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liufu, Y.; Dai, D.; Liu, Z. Triple-MOSFETs switch for adaptive maximum capacitance point tracking of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2023, 106, 108042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Y.; Niu, S.; Wang, J.; Wen, Z.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Standards and figure-of-merits for quantifying the performance of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nat Commun. 2015, 4, 8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; Wen, Z.; Li, S.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. An inductor-free auto-power-management design built-in triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2017, 31, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, F.; Pang, Y.; Li, W.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, L.; Guo, T.; Liu, G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Universal power management strategy for triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2017, 37, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Miao, L.; Song, Y.; Su, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. High efficiency power management and charge boosting strategy for a triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Marty, F.; Xia, X.; Zi, Y.; Bourouina, T.; Galayko, D.; Basset, P. Employing a MEMS plasma switch for conditioning high-voltage kinetic energy harvesters. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, W.; Guo, H.; Bamgboje, D.; Hu, T.; Wang, Z.L. Timing strategy for boosting energy extraction from triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 105956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).