Chemo-Mechanical Coupling Measurement of LiMn2O4 Composite Electrode during Electrochemical Cycling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Method
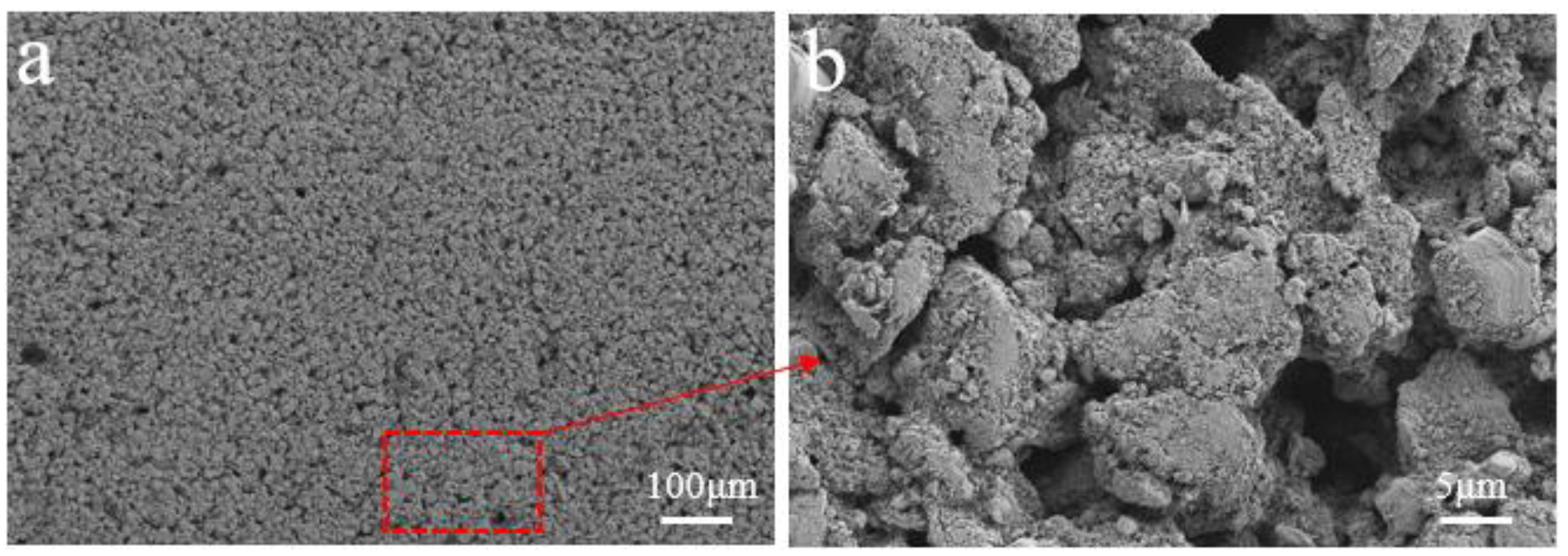
2.1. Electrode Preparation
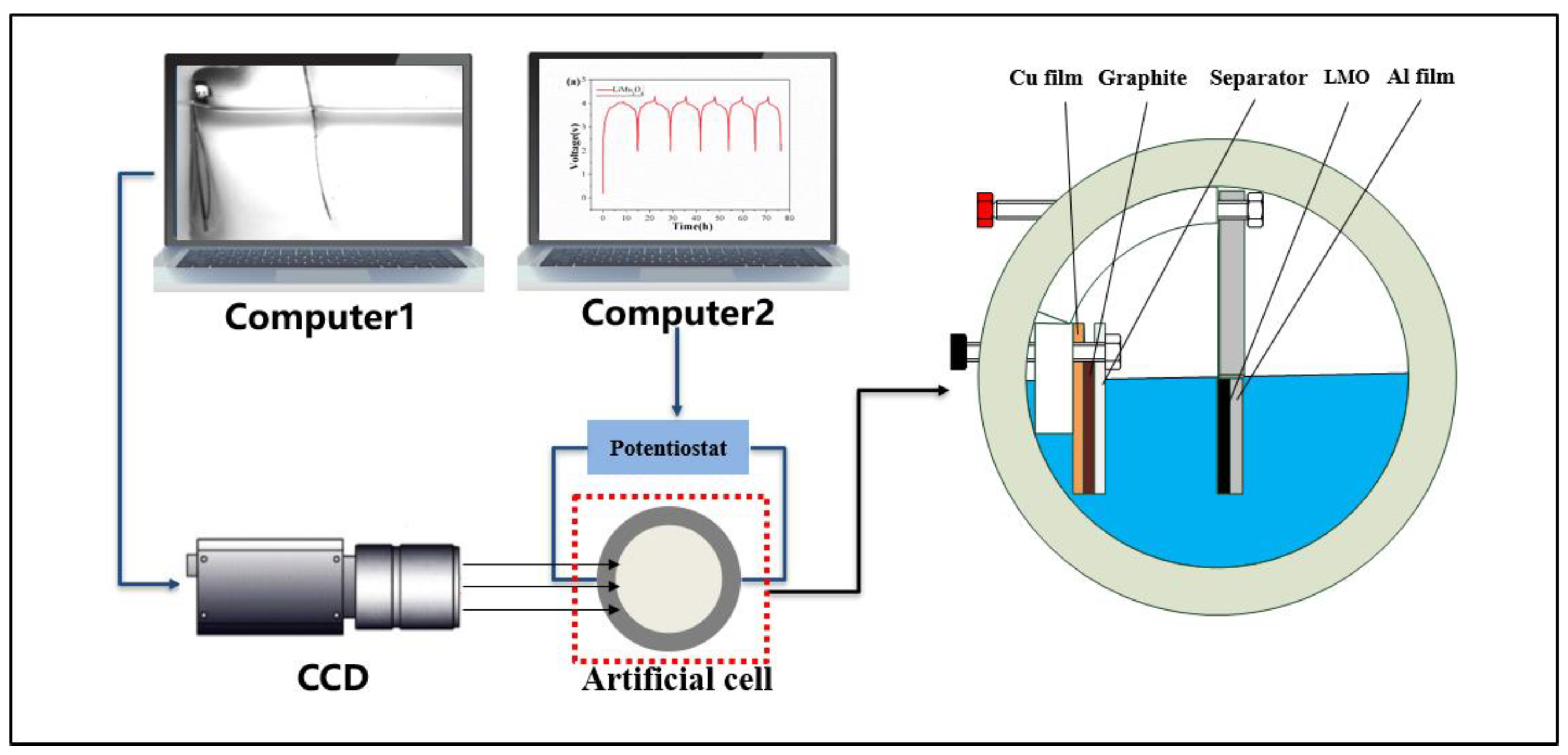
2.2. Chemo-Mechanical Measurement System
2.3. The Electrochemical Test
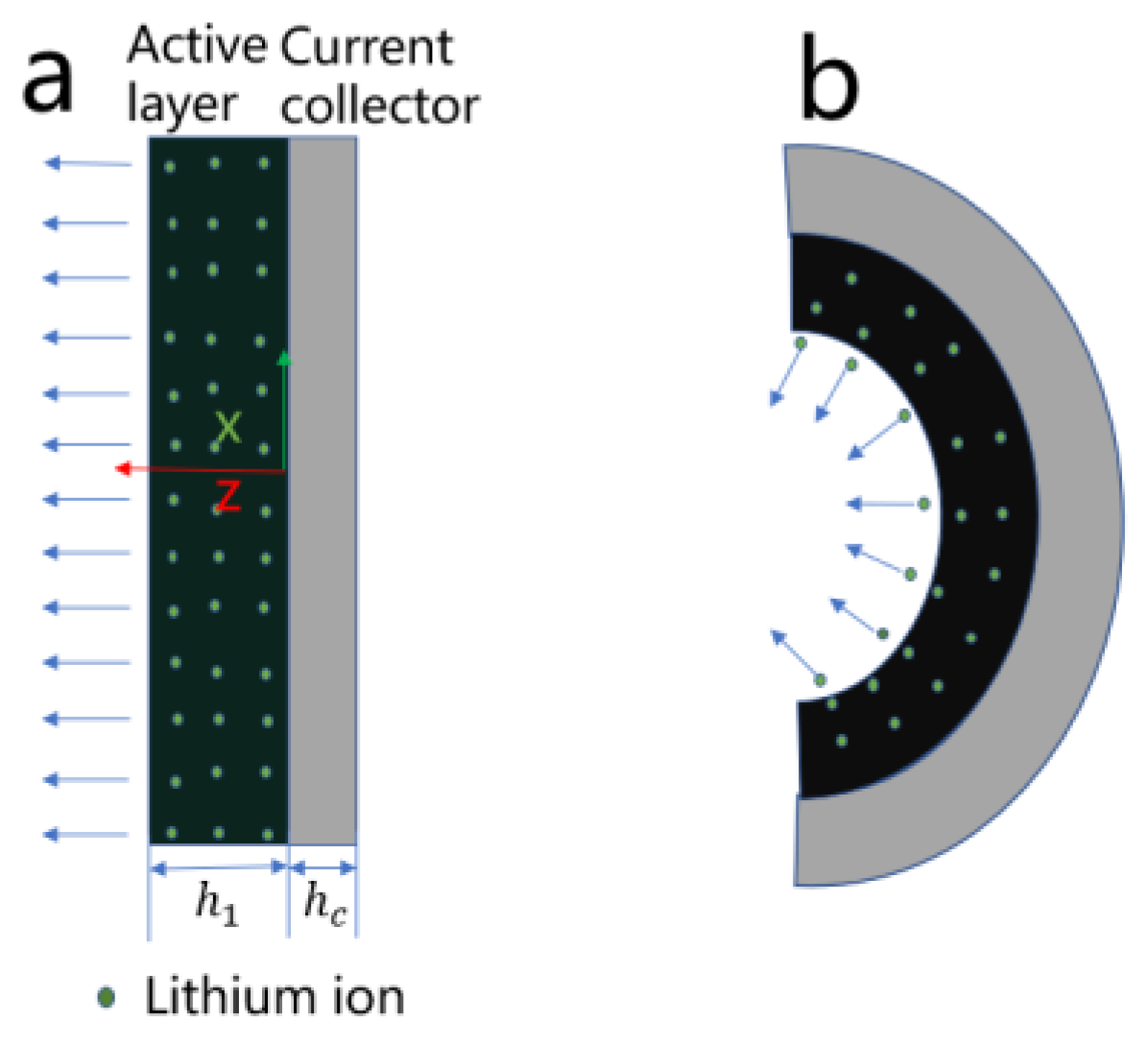
2.4. Mechanical Mode of LiMn2O4 Composite Electrode
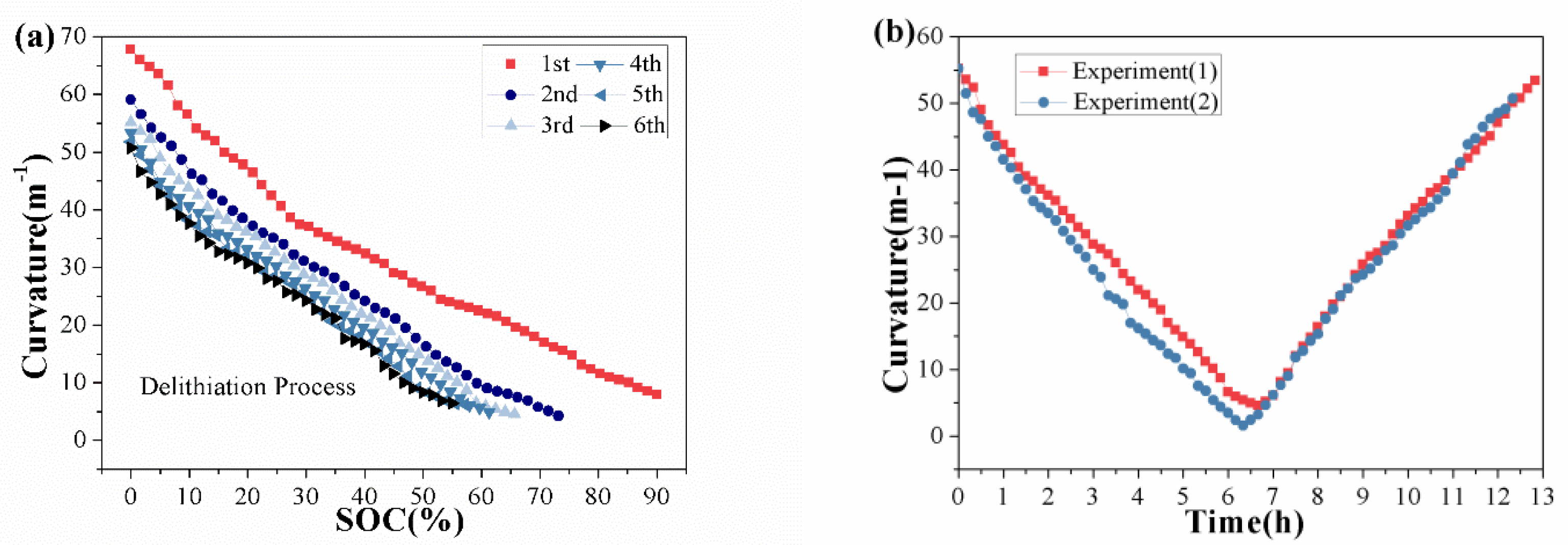
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, J.; Liang, Z.; Lu, Y.C. Molecular crowding electrolytes for high-voltage aqueous batteries. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Qin, P.; Li, Z.; Wei, Z.; Jin, K.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Q. Analysis of gas release during the process of thermal runaway of lithium-ion batteries with three different cathode materials. J. Energy Storage 2022, 50, 104302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Sheldon, B.W. Deformation and stress in electrode materials for Li-ion batteries. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 63, 58–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Danilov, D.L.; Eichel, R.A.; Notten, P.H.L. Porous Electrode Modeling and its Applications to Li-Ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2201506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Lu, B.; Zhang, J. Real-time measurements of electro-mechanical coupled deformation and mechanical properties of commercial graphite electrodes. Carbon 2020, 169, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, I.; Vostrov, N.; Mirolo, M.; Colalongo, M.; Kúš, P.; Richard, M.-I.; Wang, L.; Zhu, X.; Schülli, T.U.; Drnec, J. Revisiting Phase Transformation Mechanisms in LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 High Voltage Cathodes with Operando Microdiffraction. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 2528–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikin, D.; Slautin, B.; Kholkin, A. Revealing Lithiation Kinetics and Battery Degradation Pathway in LiMn2O4-Based Commercial Cathodes via Electrochemical Strain Microscopy. Batteries 2022, 8, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, E.J.; Ashby, D.S.; Polop, C.; Salagre, E.; Bhargava, B.; Song, Y.; Vasco, E.; Sugar, J.D.; Albertus, P.; Mentes, T.O.; et al. Imaging Phase Segregation in Nanoscale Li(x)CoO(2) Single Particles. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 16363–16371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Kim, S.; Huang, H.-Y.S. Exploration of the dislocation-electrochemistry relation in LiFePO4 cathode materials. Acta Mater. 2022, 237, 118158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, N.; Shen, M.; Hu, B.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhao, W.; et al. Sb@Ni6 superstructure units stabilize Li-rich layered cathode in the wide voltage window. J. Power Sources 2022, 551, 232148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kang, S.; Gyu Park, H.; Park, K.; Min, K. Maximizing the energy density and stability of Ni-rich layered cathode materials with multivalent dopants via machine learning. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Na, S.; Kim, J.; Jun, T.H.; Oh, M.H.; Min, K.; Park, K. Multifunctional surface modification with Co-free spinel structure on Ni-rich cathode material for improved electrochemical performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 918, 165454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, C. Strain Engineering of Ni-Rich Cathode Enables Exceptional Cyclability in Pouch-Type Full Cells. Adv. Mater. 2022, 35, 2209357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, D.A.; Rezaei, S.; Zhang, D.; Luo, Y.; Lin, B.; Balakrishna, A.R.; Xu, B.-X.; Banerjee, S. Chemistry–mechanics–geometry coupling in positive electrode materials: A scale-bridging perspective for mitigating degradation in lithium-ion batteries through materials design. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 458–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokko, K.; Nishizawa, M.; Horikoshi, S.; Itoh, T.; Mohamedi, M.; Uchida, I. In situ observation of LiNiO2 single-particle fracture during Li-ion extraction and insertion. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2000, 3, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Jang, Y.I.; Huang, B.Y.; Sadoway, D.R.; Chiang, Y.T. TEM study of electrochemical cycling-induced damage and disorder in LiCoO2 cathodes for rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 146, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.J.; Proff, C.; Wen, J.G.; Abraham, D.P.; Bareño, J. Observation of Microstructural Evolution in Li Battery Cathode Oxide Particles by In Situ Electron Microscopy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2013, 3, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Cui, G.; Chen, L. Strategies for improving the cyclability and thermo-stability of LiMn2O4-based batteries at elevated temperatures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 4092–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Hu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, C. Synergistic Enhancement Effect of Al Doping and Highly Active Facets of LiMn2O4 Cathode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 3800–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahifar, M.; Huang, S.-S.; Lin, Y.-H.; Sheu, H.-S.; Lee, J.-F.; Lu, M.-L.; Liao, Y.-F.; Wu, N.-L. Tetragonal LiMn2O4 as dual-functional pseudocapacitor-battery electrode in aqueous Li-ion electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2019, 412, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Yuan, A.; Zhao, H.; Xu, J. High-performance LiMn2O4 with enwrapped segmented carbon nanotubes as cathode material for energy storage. J. Power Sources 2013, 235, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, D.; Nanba, Y.; Makinose, Y.; Matsuda, H.; Hosono, E. Investigation of the relationship between the cycle performance and the electronic structure in LiAl(x)Mn(2−x)O(4) (x = 0 and 0.2) using soft X-ray spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 16507–16511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Zhang, P.; Lv, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Sui, Y.; Ye, Y.; Qin, C. Spinel LiMn2O4 nanoparticles fabricated by the flexible soft template/Pichini method as cathode materials for aqueous lithium-ion capacitors with high energy and power density. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 14891–14898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Su, Z.; Wang, L. Pyrometallurgically regenerated LiMn2O4 cathode scrap material and its electrochemical properties. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-L.; Gu, Y.-J.; Huo, Y.-L.; Ma, X.-Y.; Wu, F.-Z. Enhanced electrochemical performance of manganese-based metal organic frameworks-derived spinel LiMn2O4 cathode materials by improving the Mn3+ content and oxygen vacancies. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 917, 165485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Lin, X.; Lu, W.; Bartlett, B.M. Oxygen vacancies lead to loss of domain order, particle fracture, and rapid capacity fade in lithium manganospinel LiMn2O4 batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 10849–10857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanieu, H.-Y.; Rosato, D.; Sebastiani, M.; Massimi, F.; Lupascu, D.C. Mechanical property measurements of heterogeneous materials by selective nanoindentation: Application to LiMn2O4 cathode. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 593, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Bi, Z.; Shang, Y.; Chen, K.; Liang, Y.; Li, X.; Shang, G. Bimodal AFM-Based Nanocharacterization of Cycling-Induced Topographic and Mechanical Evolutions of LiMn2O4 Cathode Films. Langmuir 2021, 37, 6406–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, J.; Karan, N.K.; Abraham, D.P.; Nguyen, C.C.; Lucht, B.L.; Sheldon, B.W.; Guduru, P.R. In Situ Stress Evolution in Li1+xMn2O4Thin Films during Electrochemical Cycling in Li-Ion Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A2524–A2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Warburton, R.E.; Mane, A.U.; Greeley, J.; Elam, J.W. Modification of LiMn2O4 surfaces by controlling the Acid–Base surface chemistry of atomic layer deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Bi, Z.; Wang, X.; Shang, G. A novel design for the combination of electrochemical atomic force microscopy and Raman spectroscopy in reflection mode for in situ study of battery materials. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2022, 93, 073707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, K.; Raza, H.A.; Malik, M.I.; Ibn Shamsah, S.; Amna, R.; Sarfraz, A. To Study the Effect of LiMn2O4, Nanofibers of LiMn2O4, and Graphene/Polyaniline/Carbon Nanotube as Electrode Materials in the Fuel Cell. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 2020, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, B.; Song, Y.; Ji, X. Diffusion induced stress in layered Li-ion battery electrode plates. J. Power Sources 2012, 209, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, Q.T.N.; Kawamura, J.; Kurihara, K. Effect of vinylene carbonate on SEI formation on LiMn2O4 in carbonate-based electrolytes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 25611–25619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, D.H.; Shin, Y.J.; Oh, S.M. Dissolution of spinel oxides and capacity losses in 4 V Li/LixMn2O4 cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 2204–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Taeye, L.L.; Vereecken, P.M. Chemo-mechanical effect of chlorine modified TiO2 coatings on LMO. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 24398–24409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.R.; Holzapfel, M.; Novak, P.; Johnson, C.S.; Kang, S.-H.; Thackeray, M.M.; Bruce, P.G. Demonstrating oxygen loss and associated structural reorganization in the lithium battery cathode Li[Ni0.2Li0.2Mn0.6O]2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8694–8698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.Y.; Shu, D.; Kim, K.B. Determination of the potential range responsible for the replacement of surface film on LiMn2O4. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thackeray, M.M. Spinel Electrodes for Lithium Batteries. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 82, 3347–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


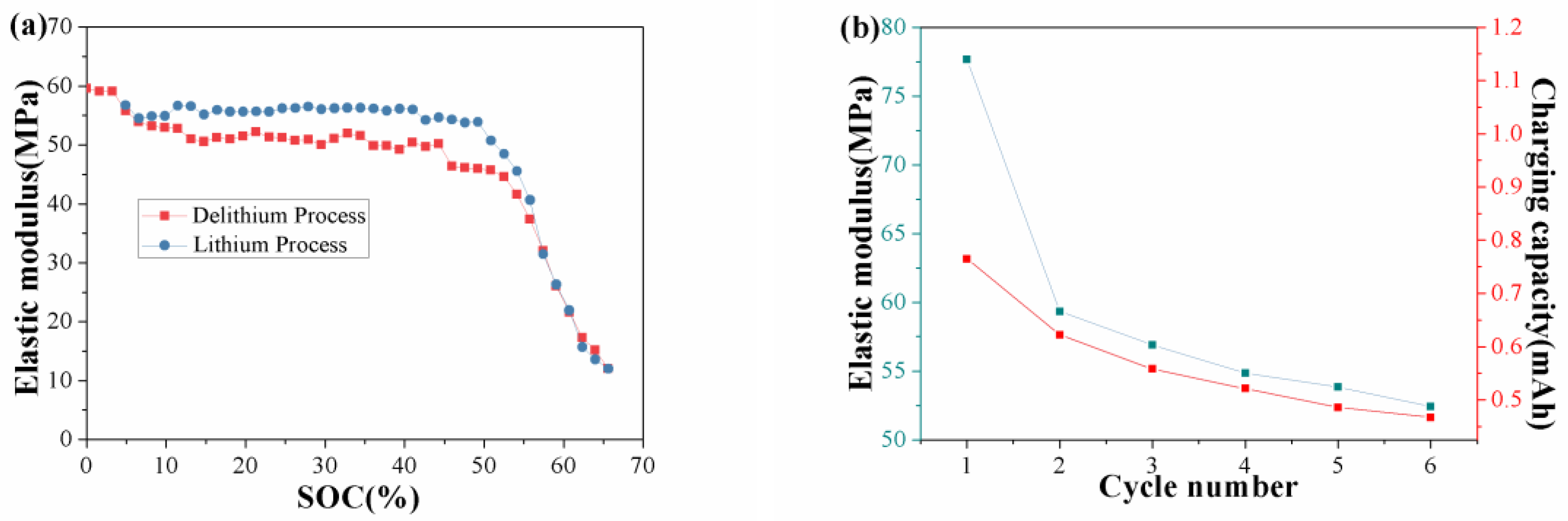
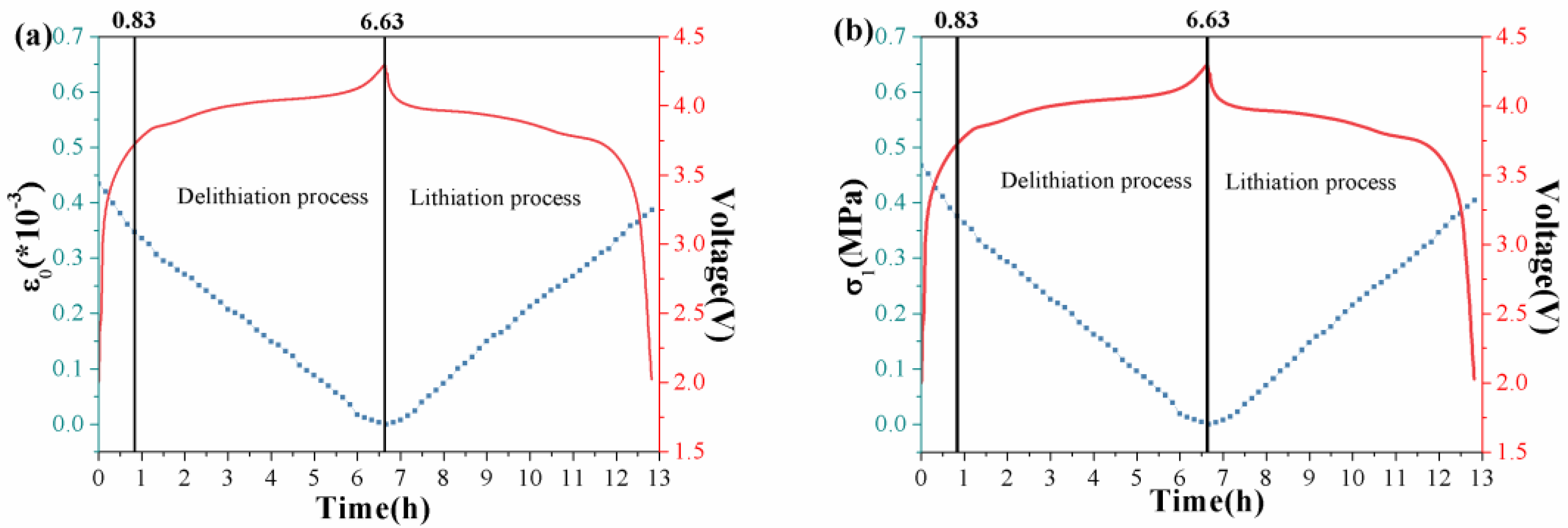
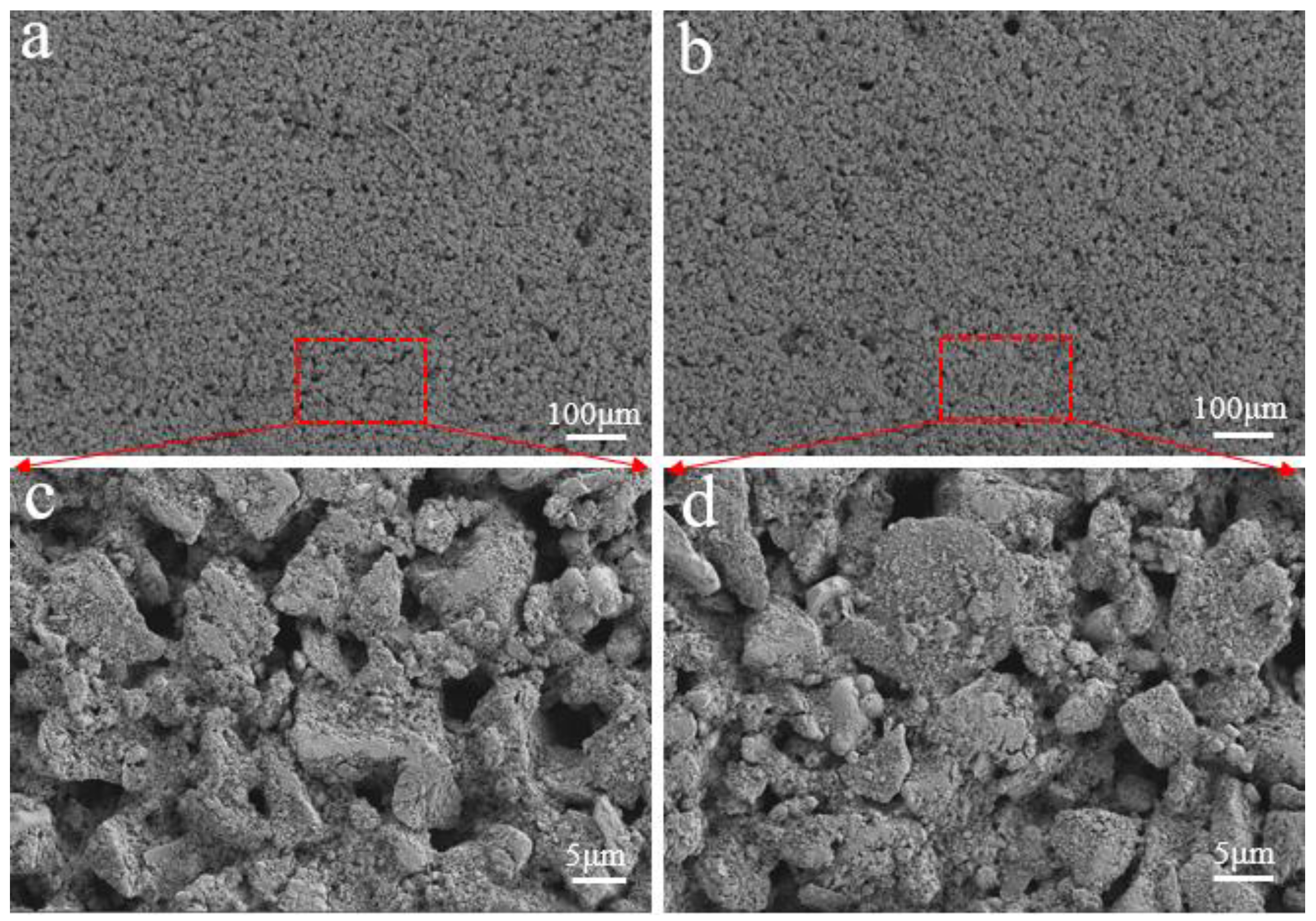
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Li, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, W.; Li, G.; Li, D. Chemo-Mechanical Coupling Measurement of LiMn2O4 Composite Electrode during Electrochemical Cycling. Batteries 2023, 9, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9040209
Yu H, Li J, Jiang H, Li W, Li G, Li D. Chemo-Mechanical Coupling Measurement of LiMn2O4 Composite Electrode during Electrochemical Cycling. Batteries. 2023; 9(4):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9040209
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Huijie, Jiangtao Li, Hainan Jiang, Wei Li, Guorui Li, and Dawei Li. 2023. "Chemo-Mechanical Coupling Measurement of LiMn2O4 Composite Electrode during Electrochemical Cycling" Batteries 9, no. 4: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9040209
APA StyleYu, H., Li, J., Jiang, H., Li, W., Li, G., & Li, D. (2023). Chemo-Mechanical Coupling Measurement of LiMn2O4 Composite Electrode during Electrochemical Cycling. Batteries, 9(4), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9040209





