Effect of Cr3+ Doping on Magnetic Properties of Zn-Mg Ferrite Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
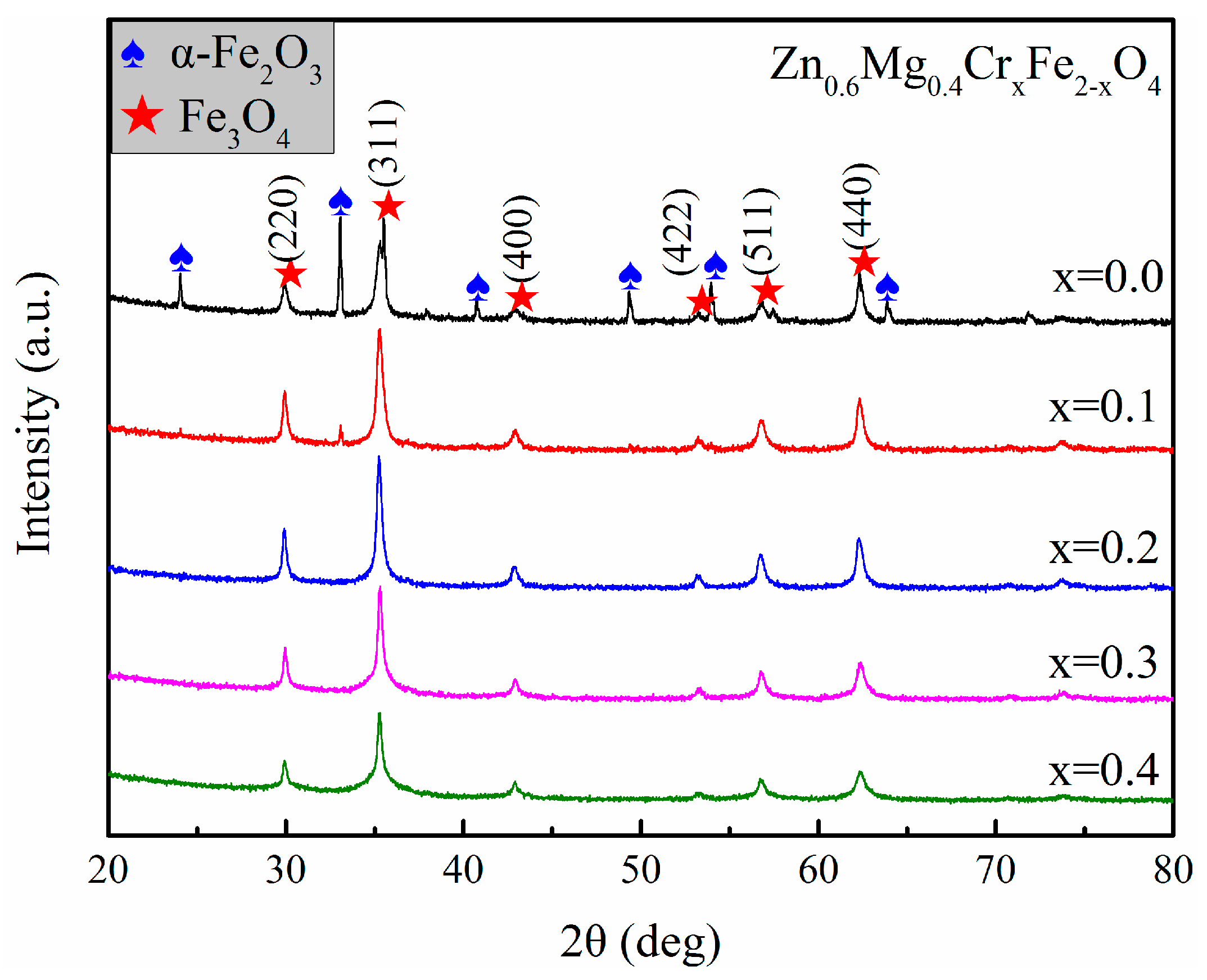
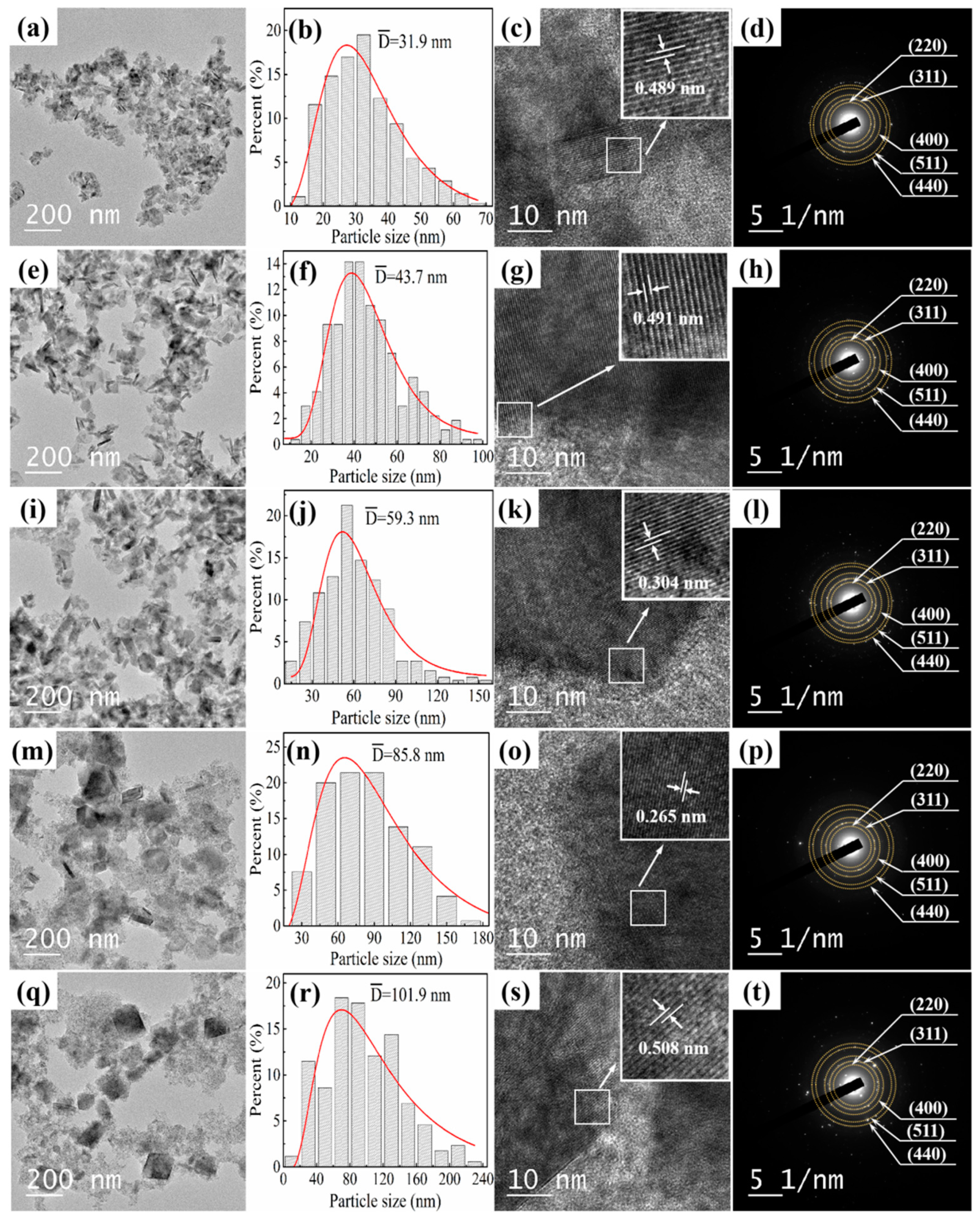
3.1. Crystalline Structure and Morphology Analysis
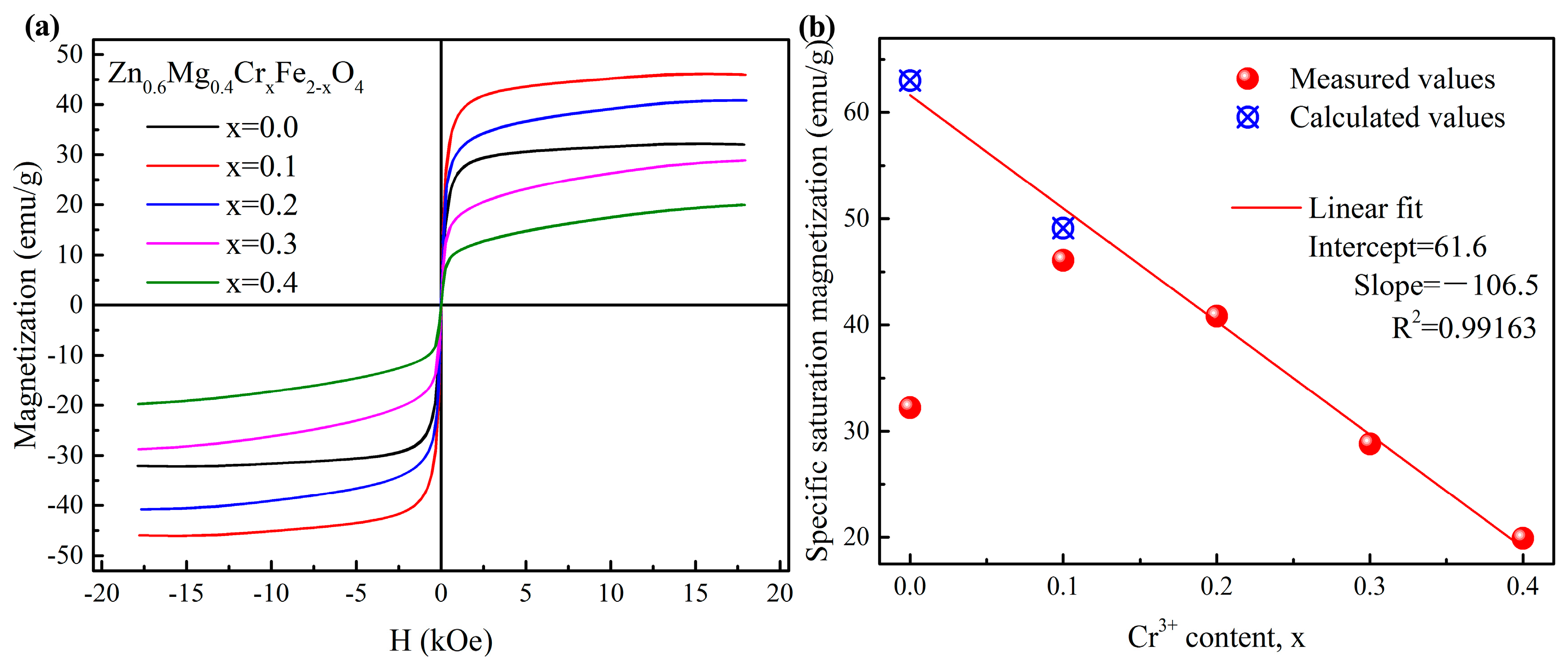
3.2. Magnetic Properties
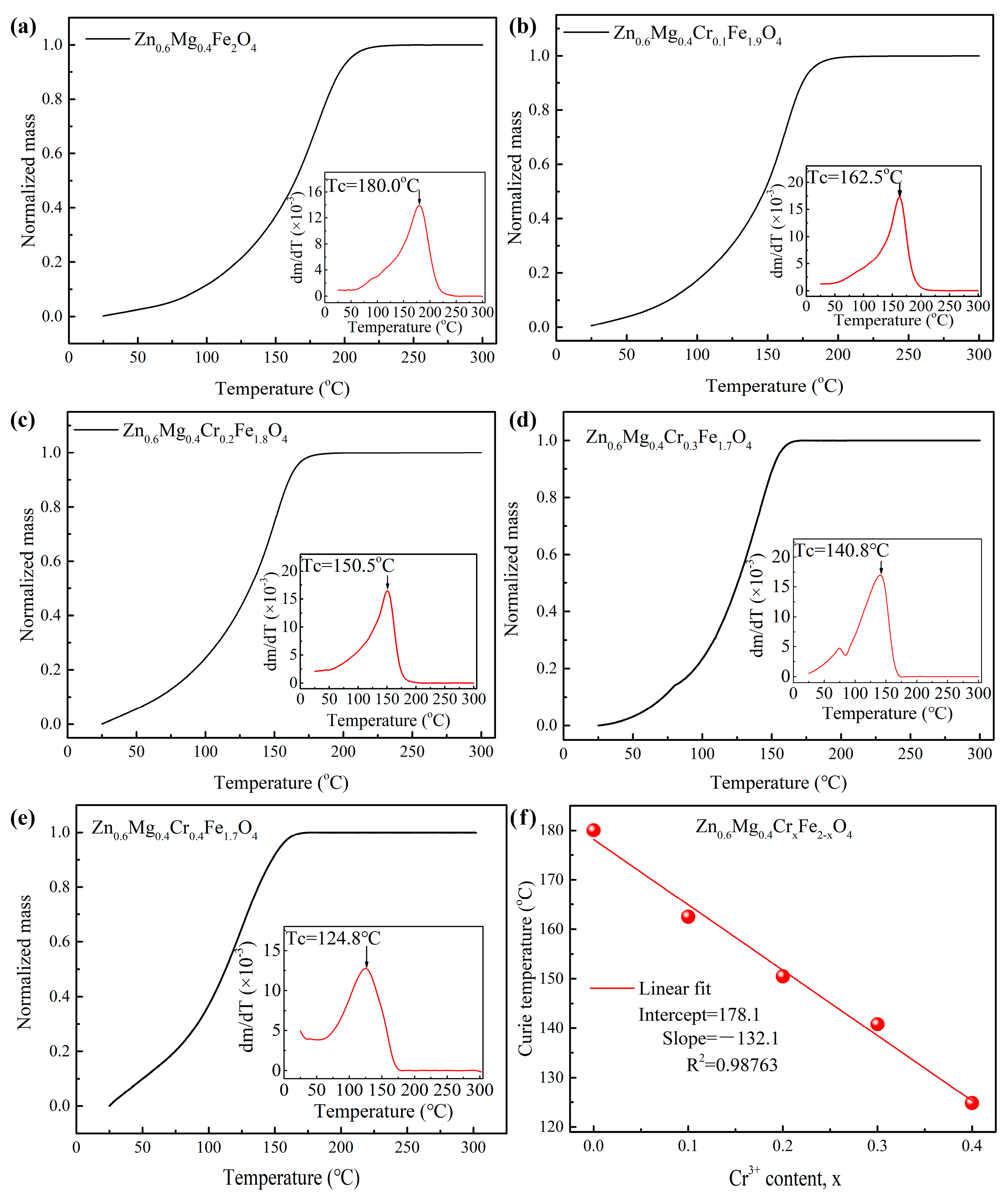
3.3. Curie Temperature
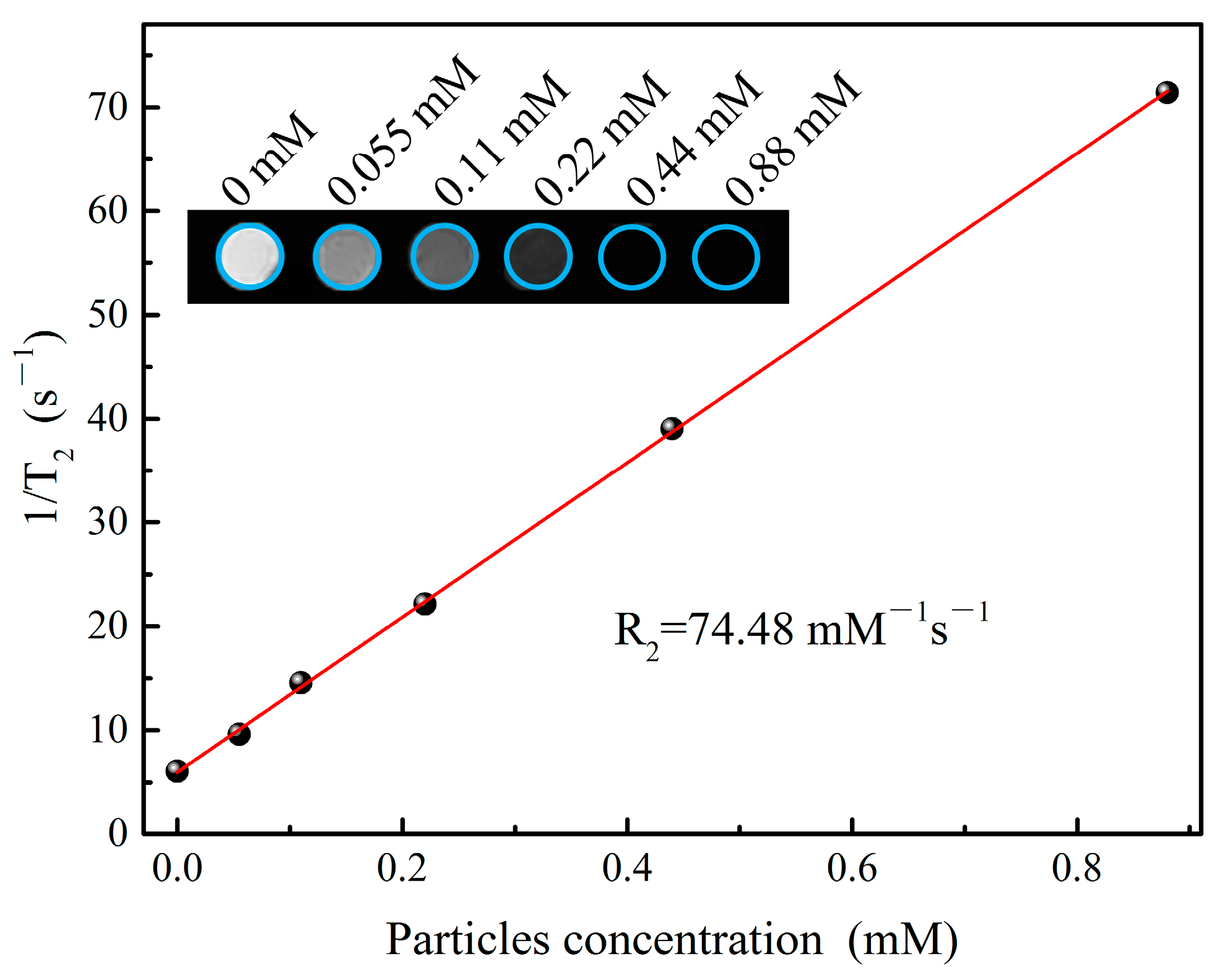
3.4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Experiments
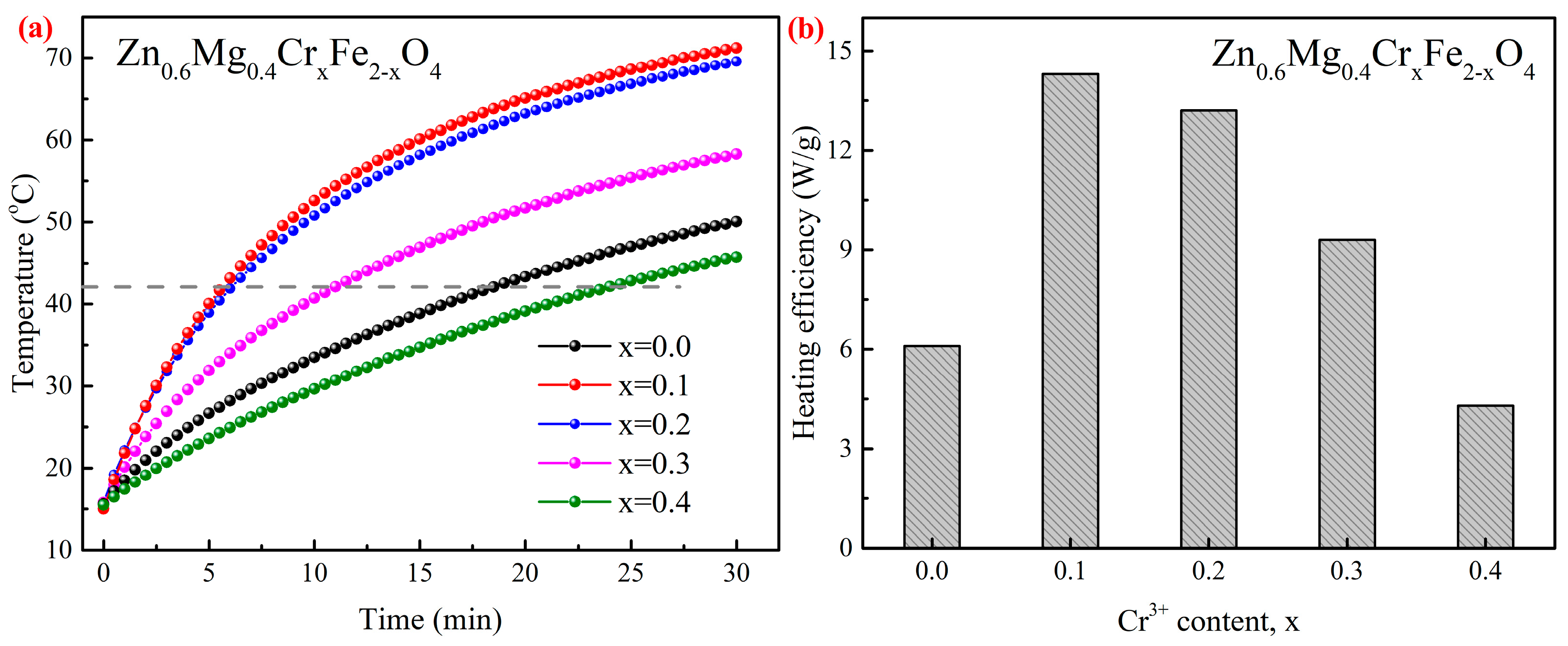
3.5. Magnetic Heating Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Somvanshi, S.B.; Khedkar, M.V.; Kharat, P.B.; Jadhav, K.M. Influential Diamagnetic Magnesium (Mg2+) Ion Substitution in Nano-Spinel Zinc Ferrite (ZnFe2O4): Thermal, Structural, Spectral, Optical and Physisorption Analysis. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 8640–8650. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, S.N.; Pawar, A.M.; Tilekar, S.K.; Ladgaonkar, B.P. Investigation of Magnesium Substituted Nano Particle Zinc Ferrites for Relative Humidity Sensors. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2016, 244, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hashim, M.; Alimuddin; Kumar, S.; Shirsath, S.E.; Kotnala, R.K.; Shah, J.; Kumar, R. Influence of Cr3+ Ion on the Structural, AC Conductivity and Magnetic Properties of Nanocrystalline Ni-Mg Ferrite. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Thakur, P.; Kumar, M.; Barman, P.B.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, V. Enhancement in A-B Super-Exchange Interaction with Mn Substitution in Mg-Zn Ferrites as a Heating Source in Hyperthermia Applications. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 13661–13669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, H.; Shokrollahi, H.; Sharifi, I.; Gheisari, K.H. Magnetic and Structural Studies of the Mn-Doped Mg-Zn Ferrite Nanoparticles Synthesized by the Glycine Nitrate Process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 3741–3747. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, M.; Bigham, A.; Hassanzadeh Tabrizi, S.A.; Abbastabar Ahangar, H. Copper-Substituted Spinel Zn-Mg Ferrite Nanoparticles as Potential Heating Agents for Hyperthermia. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 101, 3649–3661. [Google Scholar]
- Gangaswamy, D.R.S.; Bharadwaj, S.; Chaitanya Varma, M.; Choudary, G.; Rao, K.H. Unusual Increase in Permeability in Cobalt Substituted Ni-Zn-Mg Ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 468, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, R.B.; Narayankar, C.U.; Patil, R.P.; Patil, R.H.; Patil, S.B. Investigation of Structural and Magnetic Properties of Novel Zn-Substituted Ni-Mg Ferrites. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 515. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.A.; Khan, M.N.I.; Chowdhury, F.U.Z.; Hossain, M.M.; Rahaman, M.Z.; Hoque, S.M.; Matin, M.A.; Uddin, M.M. Study of Physical Properties Towards Optimizing Sintering Temperature of Y-substituted Mg-Zn Ferrites. Results Phy. 2019, 14, 102517. [Google Scholar]
- Jasrotia, R.; Suman; Verma, A.; Verma, R.; Godara, S.K.; Ahmed, J.; Mehtab, A.; Ahmad, T.; Puri, P.; Kalia, S. Photocatalytic Degradation of Malachite Green Pollutant Using Novel Dysprosium Modified Zn-Mg Photocatalysts for Wastewater Remediation. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 29111–29120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somvanshi, S.B.; Jadhav, S.A.; Khedkar, M.V.; Kharat, P.B.; More, S.D.; Jadhav, K.M. Structural, Thermal, Spectral, Optical and Surface Analysis of Rare Earth Metal Ion (Gd3+) Doped Mixed Zn-Mg Nano-Spinel Ferrites. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 13170–13179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.F.; Al-Wafi, R.; Abdo, M.A. Zn-Mg-La Nanoferrites for Storage and High Frequency Devices with Augmenting the Photocatalytic Performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 826, 154125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasrotia, R.; Kumari, N.; Verma, R.; Suman; Godara, S.K.; Ahmed, J.; Alshehri, S.M.; Pandit, B.; Thakur, S.; Himanshi; et al. Effect of Rare Earth (Nd3+) Metal Doping on Structural, Morphological, Optical and Magnetic Traits of Zn-Mg Nano-Ferrites. J. Rare Earths, 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.F.; Wageh, S.; Al-Wafi, R.; Abdo, M.A. Enhanced Magnetic, Dielectric Properties and Photocatalytic Activity of Doped Mg-Zn Ferrite Nanoparticles by Virtue of Sm3+ Role. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 856, 157437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasrotia, R.; Suman; Verma, A.; Verma, R.; Ahmed, J.; Godara, S.K.; Kumar, G.; Mehtab, A.; Ahmad, T.; Kalia, S. Photocatalytic Dye Degradation Efficiency and Reusability of Cu-Substituted Zn-Mg Spinel Nanoferrites for Wastewater Remediation. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 48, 102865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.F.; Abdo, M.A.; El-Dek, S.I. Improvement of Physico-Mechanical Properties of Mg–Zn Nanoferrites via Cr3+ Doping. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 422, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralkar, S.J.; Kadam, R.H.; More, S.S.; Shirsath, S.E.; Mane, M.L.; Patil, S.; Mane, D.R. Substitutional Effect of Cr3+ Ions on the Properties of Mg–Zn Ferrite Nanoparticles. Phys. B: Condensed Matter 2012, 407, 4338–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, X.; Li, H.; Dong, D.; Zuo, X.; Wu, C. Magnetic Nanoparticles with Low Curie Temperature and High Heating Efficiency for Self-regulating Temperature Hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 489, 165382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Ding, S.; Yang, R.; Wu, C.; Zhang, W. Research Progress on Magnetic Nanoparticles for Magnetic Induction Hyperthermia of Malignant Tumor. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 5909–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, A.; Liu, S.; Jin, C.; Chen, L.; Lv, Y. Hydrothermal Mg1−xZnxFe2O4 spinel ferrites: Phase formation and mechanism of saturation magnetization. Mater. Lett. 2013, 105, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yang, R.; Wu, C.; Zhang, W. Effect of Chromium Ion Substitution of ZnCo Ferrites on Magnetic Induction Heating. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 830, 154724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zuo, X.; Niu, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Guan, S.; Silva, S.R.P. Novel Nanoparticles with Cr3+ Substituted Ferrite for Self-Regulating Temperature Hyperthermia. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 13929–13937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, G.V.; Murali, N.; Raju, M.K.; Krishan, B.; Parajuli, D.; Choppara, P.; Narayana, P.L. Influence of Cr3+ Substituted NiZnCo Nano-ferrites: Structural, Magnetic and DC electrical resistivity properties. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 128, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Parveen, A.; Azam, A. Structural, Electrical, and Optomagnetic Tweaking of Zn Doped CoFe2−xZnxO4−δ Nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 414, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Wang, G.; Zhuo, L.; Ge, J.; Cui, L. Facile Route to α-FeOOH and α-Fe2O3 Nanorods and Magnetic Property of α-Fe2O3 Nanorods. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 5196–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, T.P.; Fay, M.; Zhu, Y.; Brown, P.D. Process Map for the Hydrothermal Synthesis of α-Fe2O3 Nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 18689–18698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biomedicine. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mmelesi, O.K.; Masunga, N.; Kuvarega, A.; Nkambule, T.T.; Mamba, B.B.; Kefeni, K.K. Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles and Nanocomposites: Photocatalytic, Antimicrobial Activity and Toxicity in Water Treatment. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2021, 123, 105523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, H.; Godara, S.K.; Srivastava, A.K. Synthesis and Investigation of Structural, Morphological, and Magnetic Properties of the Manganese Doped Cobalt-Zinc Spinel Ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 896, 162966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himakar, P.; Murali, N.; Parajuli, D.; Veeraiah, V.; Samatha, K.; Mammo, T.W.; Batoo, K.M.; Hadi, M.; Raslan, E.H.; Adil, S.F. Magnetic and DC Electrical Properties of Cu Doped Co–Zn Nanoferrites. J. Electron. Mater. 2021, 50, 3249–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yang, R.; Wu, C.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W. The Heating Efficiency of Magnetic Nanoparticles under an Alternating Magnetic Field. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haïk Dunn, I.; Jacobo, S.E.; Bercoff, P.G. Structural and Magnetic Influence of Yttrium-For-Iron Substitution in Cobalt Ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 691, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephson, L.; Lewis, J.; Jacobs, P.; Hahn, P.F.; Stark, D.D. The Effects of Iron Oxides on Proton Relaxivity. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1988, 6, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Yang, L.; Gao, J.; Chen, X. Structure-Relaxivity Relationships of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1804567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Ma, L.; Li, A.; Xin, J.; Wei, R.; Lin, H.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; Gao, J. The Roles of Morphology on the Relaxation Rates of Magnetic Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 4605–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavhan, G.B.; Babyn, P.S.; Thomas, B.; Shroff, M.M.; Haacke, E.M. Principles, Techniques, and Applications of T2*-Based MR Imaging and Its Special Applications. RadioGraphics 2009, 29, 1433–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.L.; Zheng, S.; Hong, R.Y.; Deng, S.Z.; Guo, L.B.; Hu, R.-H.; Gao, B.; Huang, M.; Cheng, L.; Liu, G.-R.; et al. Folic Acid-Conjugated Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia and MRI in Vitro and in Vivo. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 307, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, S.X.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, H.L.; Lei, H.; Lan, M.B.; Cheng, Z.X.; Wang, X.L.; Dou, S.X.; Max Lu, G.Q. Ultrasmall Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles as Positive Contrast Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Yu, X.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Wu, C.; Zhang, W.; Guo, W. Effect of Mg Doping on Magnetic Induction Heating of Zn-Co Ferrite Nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 851, 156907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatooti, S.; Mozaffari, M.; Reiter, G.; Zahn, D.; Dutz, S. An Investigation on the Heat Dissipation in Zn-Substituted Magnetite Nanoparticles, Coated with Citric Acid and Pluronic F127 for Hyperthermia Application. Phys. B 2022, 625, 413468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kawashita, M.; Araki, N.; Mitsumori, M.; Hiraoka, M.; Doi, M. Magnetite Nanoparticles with High Heating Efficiencies for Application in the Hyperthermia of Cancer. Mater. Sci. Engin. C 2010, 30, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranoo, S.; Lahiri, B.B.; Damodaran, S.P.; Philip, J. Tuning Magnetic Heating Efficiency of Colloidal Dispersions of Iron Oxide Nano-Clusters by Varying the Surfactant Concentration during Solvothermal Synthesis. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, X.; Yang, R.; Wu, C.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W. Effect of Cr3+ Doping on Magnetic Properties of Zn-Mg Ferrite Nanoparticles. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9070181
Yu X, Yang R, Wu C, Liu B, Zhang W. Effect of Cr3+ Doping on Magnetic Properties of Zn-Mg Ferrite Nanoparticles. Magnetochemistry. 2023; 9(7):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9070181
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xiaogang, Renpeng Yang, Chengwei Wu, Bo Liu, and Wei Zhang. 2023. "Effect of Cr3+ Doping on Magnetic Properties of Zn-Mg Ferrite Nanoparticles" Magnetochemistry 9, no. 7: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9070181
APA StyleYu, X., Yang, R., Wu, C., Liu, B., & Zhang, W. (2023). Effect of Cr3+ Doping on Magnetic Properties of Zn-Mg Ferrite Nanoparticles. Magnetochemistry, 9(7), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9070181






