Abstract
Physical property inversion techniques are the methods to reveal the internal structures of Earth’s lithosphere. In this study, we introduce an Occam-type inversion algorithm into a spherical coordinate system, and invert the magnetization based on the three-component magnetic anomalies. The synthetic model tests show that the inversion effects of the vertical components are relatively stable, while the anti-noise ability is strong. We apply the algorithm to a set of vertical component anomalies derived from the satellite magnetic field model and obtain Dabie orogen 3D magnetization distribution. Multiple magnetic sources are identified within the orogen and adjacent areas, and the related tectonic evolution processes are analyzed. The significant magnetization characteristics of the orogen can be associated with mantle upwelling caused by the Early Cretaceous lithospheric delamination, along with the partial melting of the mafic–ultramafic lower crust that had not participated in the delamination. The magnetic sources near the Mozitan–Xiaotian fault, and those located in the western Dabie area, are also restricted by Mesozoic and Jurassic–Cretaceous deep melt activities, respectively. The study provides evidence for the suture line position of the plate subduction in the deep lithosphere. Furthermore, the results display certain indications of mineralization activities in the middle–lower Yangtze Valley metallogenic belt.
1. Introduction
The Dabie orogen is located in the middle section of the Qinling-Dabie-Sulu orogen in China, which was formed by the subduction of the northern margin of the South China Craton (SCC) during the Triassic period and the continental collision with the North China Craton (NCC) [1,2]. It is the world’s largest high-pressure (HP) and ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) metamorphic belt, and is well-known worldwide because of the discovery of coesite and diamond in its eclogite rocks [3,4,5]. During the past 30 years, many important scientific issues have been studied, such as the formed conditions of UHP minerals and the exhumated mechanism of deep rocks, including a large number of petrological, chronological, and geochemical studies. An in-depth understanding of the original rock properties, metamorphic evolution history, and deep fluid activities in the region has been gained [6,7,8,9,10]. In terms of geophysics, deep seismic investigations [11,12,13,14,15], electromagnetic exploration [16], and experimental gravity studies [17] have been carried out to reveal the crustal structures and upper mantle tectonic environment of the Dabie orogen. As for magnetic exploration studies, they mainly focus on the geological interpretation of magnetic anomalies at present [18,19]. In-depth research regarding the lithospheric 3D magnetic structure is still lacking.
Paleomagnetism is directly related to the lithospheric magnetic field [20,21,22,23]. The lithospheric magnetic field arises from the magnetization of rocks in the crust and upper mantle. Because the rocks change in magnetism with tectonic evolution, they have a footprint of structural evolution [24]. Understanding the magnetic structure of the orogenic lithosphere has important theoretical significance for investigating the deep dynamics of the convergent boundaries of plates, as well as the deep processes of magmatic activities and the metallogenic backgrounds of important mineral accumulation areas.
Having the advantage of global coverage independent of the ruggedness and remoteness of the terrain, the magnetic potential field development derived from the satellite (such as SWARM) allows for an unprecedented opportunity to use the magnetic vector field to image the magnetic structures of geological interest. The regional lithospheric magnetic anomaly derived from the global Earth magnetic models that often show good correspondence with geological structures has been increasingly used in geological analyses [25,26,27,28]. However, due to the errors caused by eliminating the main magnetic fields, the magnetic anomalies often do not correspond to the geological structure units in some areas [29]. Arkani-Hamed and Strangway point out that the global scalar magnetic responses and the sources are not directly relative [30]. In high or low latitudes, the anomalies generated by magnetic sources may have different shapes, and even the values will be reversed. Therefore, to better understand lithospheric magnetism, many researchers have applied various inversion methods to convert magnetic data into susceptibility or magnetization [31,32,33,34]. It has been found that the Occam-type inversion method is less dependent on the initial model, and is widely used in gravity and electromagnetic research.
For applications of inversion in regional or even global magnetic data, Earth’s curvature cannot be ignored, and we operate by necessity in a spherical coordinate system. In previously used magnetization inversion methods (including vector magnetization), the remanent magnetization effect was often considered [31,35,36,37]. Compared to the oceanic crust, induced magnetization has been found to play a significant role in continental crust magnetic anomalies [38,39]. Currently, not much is known about remanent magnetization structures that may exist on the continents. The induced magnetization and remanent magnetization cannot be decoupled effectively [40,41]. Therefore, in practical applications, the remanent magnetization in continental crusts is generally ignored [24,42,43]. In the inversion processes outlined below, it is assumed that the lithospheric magnetic fields in the study area are mainly dominated by induced magnetization to simplify the model and data parameter spaces.
The vertical component field data sets used in this study come from the satellite magnetic field model EMM2017. The model was compiled from satellite, ocean, aeromagnetic, and geomagnetic survey data. Its crustal field model originated from the geomagnetic anomaly grid data EMAG2-v3 with a resolution of two arc minutes. In the model, spherical harmonic functions are up to 790, and the resolvable spatial wavelength is as fine as 51 km. The method used for calculating the magnetic data of the lithosphere included stripping the core magnetic field (orders ) from the total magnetic field.
The remainder of this paper is as follows: a brief introduction of this inversion method and a synthetic model, and experiments with inversion of three-component magnetic anomaly data sets, are presented in Section 2. Section 3 details the tectonic setting of the Dabie orogen and the characteristics of the lithospheric vertical component magnetic field. The validity of the magnetic sources’ depth is analyzed in Section 4. We discuss the interior 3D magnetization structures of the orogen in Section 5. Section 6 clarifies the tectonic evolution processes related to the origin of central magnetic bodies. Finally, in Section 7, we present the conclusions of this study. The main objectives of this study are to recover the magnetic sources in the orogenic lithosphere and analyze the relationship between the magnetic bodies and tectonic activities.
2. Methodology and Synthetic Model Analysis
2.1. Inversion Method
Since the observational data sets are much smaller than the unknown variables, the inverse problem is usually ill-posed. In this study, the Occam-type inversion algorithm was used to solve the ill-posed problem [44]. The general form of constructing the objective function and minimizing it was as follows:
where the Lagrange multiplier was used as the regularization parameter of the preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithm [45] in order to balance the data misfit function and the model objective function .
We introduced a weighting function; the re-weighted data misfit function and model objective function are defined as
where is a linear function that maps the model parameter vector to magnetic field data , which is expressed as the forward kernel function matrix, represents the corresponding modification of the observational data column vector, is the modification of to the initial reference model , indicates the data space weighting matrix, is the weighting parameter of the minimum model constraint, and is used to represent the radial, latitude, and longitude directions in the spherical coordinate system, respectively. denotes the relative weight of the smoothest model objective function along three different directions on the sphere, and refers to the radial weighting function.
In this study, the radial weighting function introduced by Wang et al. [46] was utilized to overcome the sharp attenuation of the magnetic kernel function. The radial weighting function was as follows:
where km is the average radius of Earth, is the average height of the observation point, refers to the radial distance from the center of the model cell to the center of Earth, and is the radial weighting factor.
Then, by using the finite difference instead of the partial differential to discretize the objective function of the model, the discretization form of the objective function was obtained as follows:
where represents the weighted matrix after discretization, is the weighting coefficient of each item in the model objective function, denotes the differential operator along each direction of , and refers to the discrete matrix of the radial weighting function. This study also introduced the PCG algorithm to improve computational efficiency.
2.2. Model Design
To verify the effects of the inversion method, a set of models were established, as shown in Table 1 and Figure 1. , , and were used to represent the three-component magnetic anomalies in the north–east–down directions of the spherical local coordinates. The forward calculation height was set to 4 km. The grid size was , and the cell size was km. Two cases were considered for the inversion of the magnetic data sets. The first was without noise, and the second included adding a 5% noise signal to the superimposed three-component magnetic anomalies. The noise level and inversion results are shown in Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4, respectively.

Table 1.
Geometric and magnetic parameters of the synthetic model.
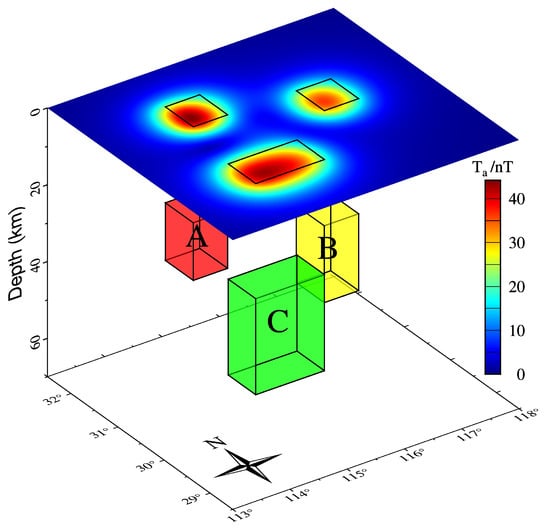
Figure 1.
Synthetic model and total magnetic anomaly amplitude, in which the top rectangular box represents the actual model.

Figure 2.
Synthetic model’s three-component magnetic anomalies , , and : (a–c) cases without noise; (d–f) cases with 5% noise signal.
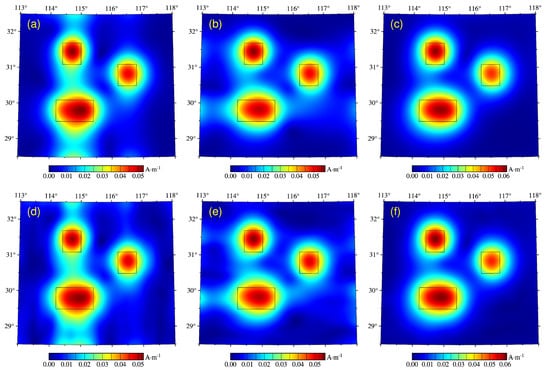
Figure 3.
Horizontal slices of inversion results for three-component magnetic anomalies (depth = 37.5 km): (a–c) inversion results of , , and without noise; (d–f) inversion results of , , and with 5% noise signal.
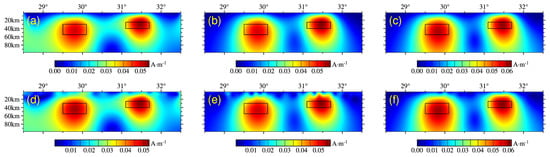
Figure 4.
Vertical slices of inversion results for three-component magnetic anomalies (longitude = 114.7°): (a–c) inversion results of , , and without noise; (d–f) inversion results of , , and with 5% noise signal.
2.3. Analysis of the Inversion Results
It was determined that the inverted magnetization based on three-component magnetic anomalies fit the model well, as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4. The inversion results of the and components produced small amounts of false anomalies at the boundaries of the corresponding directions, and the components were relatively stable.
The noise signal was found to significantly impact the shallow parts of the and components and have little impact on the components. In terms of numerical values, the inversion results deviated several times from the set model parameters. This is because the Occam-type inversion algorithm obtained a smooth model and could not obtain a clear-cut boundary of the model. Moreover, considering computational efficiency, the cell division of the model’s underground space was not small enough. Together, these factors caused many values to be matched outside of the model boundaries in the iterative processes, resulting in significant gaps between the inversion results and those of the model. In contrast, the inversion values of the components were closer to the original model parameters than those of the other two components.
Generally, the components were relatively stable and had higher anti-noise abilities. Therefore, the vertical component anomaly was used to invert the actual data in this study.
In the model test, we obtained good inversion results ( takes 3). Additionally, we then applied the same parameter value to the magnetic data inversion.
3. Lithospheric Magnetic Field
3.1. Tectonic Setting
The western part of the Dabie orogen is connected to the Qinling orogen. The eastern end of the Dabie orogen is cut off by the left-handed strike-slip of the Tanlu fault, which separates from the Sulu orogen of the Shandong Peninsula for nearly 500 km [47,48]. The formation of UHP rocks indicates that the crustal rocks were subducted to depths of more than 100 km and then rapidly exhumed [5,49,50]. The orogen is composed of a series of metamorphic units bounded by faults. Tectonically, the NE–SW striking fault zone F6 divides the orogen into eastern Dabie and western Dabie. Four metamorphic units are further divided in eastern Dabie: northern Huaiyang (NHY) tectonic belt, northern Dabie complex (NDC) unit, UHP metamorphic belt, and HP metamorphic belt. The NHY and HP belts are two relatively low-grade metamorphic rock units [51]. The lithology of the NHY mainly comprises Neoproterozoic igneous rocks and Neoproterozoic pre-Triassic sedimentary rocks. The Foziling Group is the main component of the NHY, with the development of low-metamorphic sandstone, graphite schist, amphibolite, and greisen. Their original rocks are shallow marine carbonate and calcareous mudstone, and contain a volcanic rock interlayer. The majority of them have undergone greenschist facies metamorphism, and have partially experienced amphibolite facies metamorphism [52,53]. Traditionally, the HP unit is referred to as the Susong Formation, composed of gneiss, schist, metamorphic phosphorite, and marble, with the metamorphic grade decreasing significantly from north to south [15]. The metamorphic rocks in this unit are mainly metasedimentary rocks, which can be subdivided into three metamorphic zones. The northern zone is composed of thick magnetite quartzite, garnet greisen schist, and mica schist interlayers. The middle zone contains garnet mica-quartzose schist, amphibolite, marble, quartzite, and thin phosphate rock. The southern zone is composed of chlorite schist, mica schist, and greisen schist. The NDC is mainly composed of orthogneiss with a small amount of amphibole, marble, mafic ore, and felsic granite [54]. It is characterized by strong metamorphism, deformation, and extensive migmatization. The main rock types of the UHP metamorphic belt include eclogite, gneiss, schist, and quartz–jadeite marble. All tectonic units contain numerous Cretaceous magmatic rocks and post-collisional mafic–ultramafic intrusions [55,56].
3.2. Characteristics of the Lithospheric Vertical Component Magnetic Anomaly Field
The intensities of the vertical component magnetic anomalies observed at aeromagnetic altitudes in the study area ranged from −220 nT to 284 nT. The interior of the orogen exhibits strong magnetic anomalies, which can be divided into three magnetic anomaly zones with different features from north to south. The NHY of the eastern Dabie showed a band-shaped negative highly magnetic anomaly in the NWW trend. The central part of the orogen displayed a beaded positive magnetic anomaly, and its spatial distribution was consistent with the overall extension direction of the mountain uplift. The southern part was bounded by Dawu–Hongan–Xishui–Taihu, with a stable positive magnetic anomaly. As indicated by F5 in Figure 5, apparent characteristics of a magnetic anomaly gradient zone were observed, which reflected the differences in the magnetic sources on both sides. The eastern part of the orogen was controlled by the Tanlu fault zone and was characterized by alternating positive and negative magnetic anomalies extending along the NNE strike. The magnetic anomalies in the surrounding blocks were found to be relatively weak. For example, the NCC was characterized mainly by a string of positive magnetic anomalies in the near EW direction. Meanwhile, the SCC was characterized mainly by wide and gentle alternating positive and negative magnetic anomalies. Several apparent positive magnetic anomalies were located mainly to the south of F6 and to the northeast of the Congyang and Jiangnan fault zones.
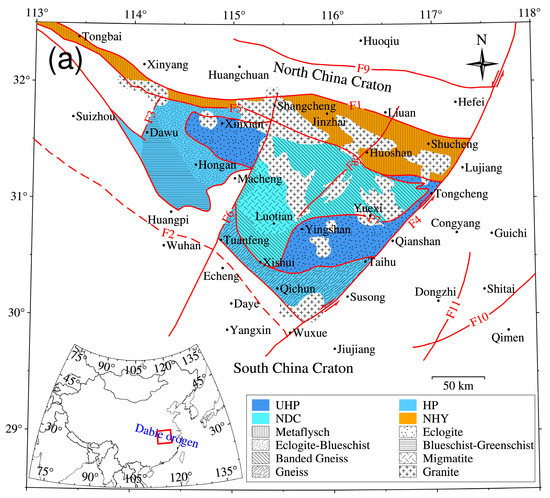
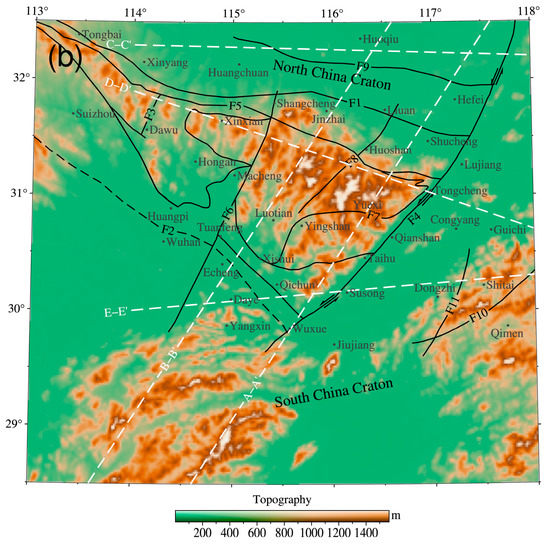
Figure 5.
(a) Simplified geological map of the Dabie orogen (modified from [57]); (b) topographic map of the Dabie orogen. F1. Xinyang–Shucheng fault zone; F2. Xiangfan–Guangji fault zone; F3. Dawu fault; F4 Tancheng–Lujiang fault zone; F5. Tongbai–Shangcheng–Mozitan–Xiaotian fault zone; F6. Shangcheng–Macheng–Tuancheng fault zone; F7. Wuhe–Shuihou fault zone; F8. Huoshan–Luotian fault zone; F9. Feizhong fault zone; F10. Jiangnan fault zone; F11. Gegong fault. Note: in the figure, the white dashed lines show the positions of the studied profiles.
The magnetic anomalies with different strikes and intensities in the Dabie orogen and its adjacent areas reflected diverse structural characteristics. In the present study, to understand the deeper magnetic structures of Earth’s lithosphere, the vertical component anomalies were calculated at a height of 30 km (Figure 6). When compared to the aeromagnetic altitude results, it was observed that the interior of the orogen still showed strong magnetic anomalies. However, the gentle magnetic anomalies in most shallow parts of the surrounding blocks disappeared, while the aforementioned positive magnetic anomalies still existed. In general, the deep parts of the crystalline basement in the orogen and the basement of the areas corresponding to the surrounding blocks’ magnetic anomalies were composed of ferromagnetic materials.
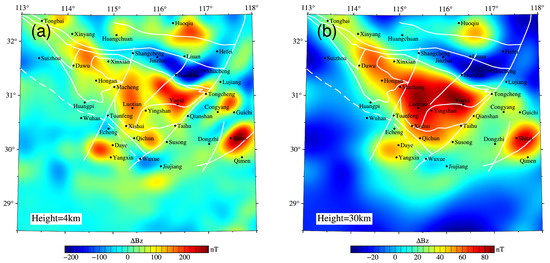
Figure 6.
Distribution of the lithospheric vertical component magnetic anomalies in the Dabie orogen: (a) calculation results at the height of 4 km; (b) calculation results at the height of 30 km.
4. Discussion Regarding the Validity of the Magnetic Sources’ Depth
In the depths of the lithosphere, the magnetism of rocks is controlled by ferromagnetic minerals [58]. More than 190 mafic–ultramafic intrusions in the Dabie orogen [59,60] are characterized by high iron contents and abundant magnetite [61], and usually exhibit strong magnetism. Their exposure also implies that there are pathways or remaining structures enhancing material migration in the interior of the lithosphere. Moreover, the magnetic rock masses need to be of a specific minimum size to generate the magnetic anomaly responses. The large area of Cretaceous granite exposed inside the orogen indicates that there must be a corresponding magma supply system underground. After the magma erupts, the supply system can be filled by mafic–ultramafic magma. Although granite (except for I-type granite) is usually weakly magnetic, the mafic–ultramafic rocks are speculated to be several times the thickness of the granite bodies [60], which are thought to be a potentially important source of large-scale, highly magnetic anomalies.
Temperature has a significant influence on the magnetism of minerals. The ferromagnetism will be the transition into paramagnetism while the temperature levels of ferromagnetic minerals reach or exceed the Curie point [62]. Traditionally, the Curie point isothermal surface is located near or above the crust–mantle boundary. However, the existence of some ferromagnetic minerals with a high Curie point indicates that the Curie point may be located in the upper mantle. For example, some Fe-Ni-Co-Cu alloys may be formed during serpentinization, when the Curie point can be as high as 1100 °C [63]. During the plate’s subduction, serpentinite releases water that carries fluid active elements into the mantle wedge, causing a further decrease in the surrounding temperature [64]. Recent studies have also shown that near the subduction zone, the uppermost layer of the mantle may be magnetic [65,66,67,68]. In summary, when the temperature of the upper mantle does not exceed the Curie point of ferromagnetic minerals, the upper mantle can potentially produce magnetic anomalies.
5. 3D magnetization Inversion Results and Discussion
The horizontal and vertical slices of the lithospheric magnetization of the Dabie orogen are shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8, respectively. The position of the profile lines is shown in Figure 5, with the five profiles crossing all of the magnetic bodies. The deep seismic refraction profile provides the crustal layered structure model of the orogen [11]. The magnetic bodies were determined to be mainly distributed in the eastern Dabie. Among these, the features of the field source near the MXF (Mozitan–Xiaotian fault) were the most obvious. Three sets of magnetic bodies (Figure 7a–c) were distinguishable from the middle and upper crust bounded by this fault and F8, which were continuous in the horizontal direction from the deeper layers to close to the Moho. The displayed tendencies to extend into the upper mantle are shown in Figure 7d,e and Figure 8a. The magnetic source of the HP metamorphic belt in the eastern Dabie was an independent anomaly (Figure 8a). The two sets of magnetic sources along the profile (Figure 8a) were consistent with the results obtained by Yang and Li [17] based on a continuous wavelet transform method in the horizontal extension. The field source in the Luotian area was determined to be dome-like with both wings drooping and central uplift, which was continuous in the depth direction, from the upper crust to the upper mantle (Figure 8b). The magnetic body in the western Dabie was mainly distributed in the middle and lower crust, with relatively weak magnetization (Figure 8d). Three magnetic sources were found in the NCC of the study area (Figure 8c). Their corresponding geological or tectonic units included the Huangchuan Basin, Fuyang fault, and Hefei Basin. The magnetic source of the Hefei Basin was the largest. As detailed in Figure 7, four obvious target sources were observed in the SCC, from west to east and north to south. These corresponded with the southeastern Hubei ore cluster, Jiurui ore cluster, Lucong ore cluster, and Jiangnan fault zone, respectively, which are traditionally referred to as the middle–lower Yangtze Valley metallogenic belt. The seismic reflections in the Lucong ore cluster showed that the depth of the Moho surface was reduced from 35 km in the Tanlu fault zone to 30 km [69]. Therefore, the magnetic body in this area occurred within the middle and lower parts of the crust.
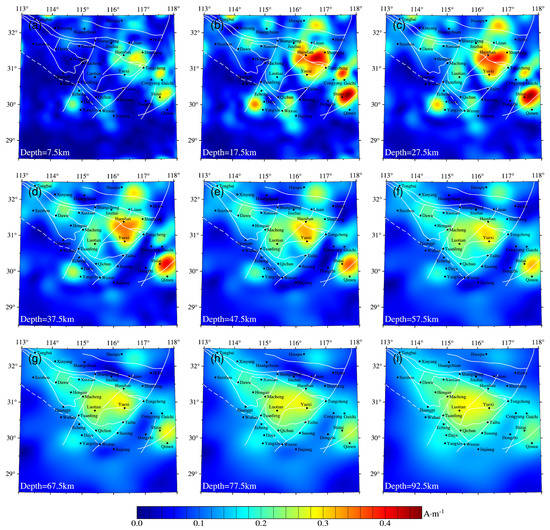
Figure 7.
Horizontal slices of 3D magnetization inversion at different depths: (a–h) divided horizontal slice results for depth starting from 7.5 km and increasing by 10 km, respectively; (i) slicing result at a depth of 92.5 km. Note: the white lines are a series of faults.
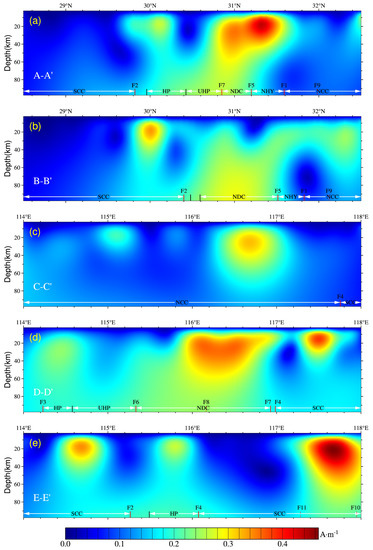
Figure 8.
Vertical slices of 3D magnetization inversion along the profile lines: (a–e) correspond to the profile lines in the topographic map, respectively. SCC—South China Craton; NCC—North China Craton; NHY—northern Huaiyang tectonic belt; NDC—northern Dabie complex unit; HP—high-pressure metamorphic belt; UHP—ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt; F1–F11 represent fault zones.
The different features of the magnetic field sources indicate the various formation conditions. Large-scale magmatic activities [70,71] and regional doming occurred [49,72,73] in the Dabie orogen during the Early Cretaceous, forming the Luotian dome and Yuexi dome of the NDC [74,75]. The dome tectonics were later denuded, and the middle and lower crustal rock masses were exposed. The magnetic source in the Luotian area was consistent with the dome’s center (Figure 8b), and its distributions corresponded to the formation pattern of the dome. The basic granulite was exposed in the Huilan Mountain neighborhood in the Luotian area, indicating that the rocks experienced granulite facies metamorphism in the Early Cretaceous [76]. The emplacement ages of the mafic–ultramafic intrusions exposed in the NDC located far from the tectonic boundary coincided with large-scale post-collisional magmatism [6]. Additionally, the positions of the magnetic bodies in Luotian and Yuexi corresponded well with the core of the thermal dome extension during that period [77]. During the Early Cretaceous period (approximately 130 Ma), large-scale mafic lower crustal delamination and de-rooting events occurred in the orogen [78]. Therefore, we believed that the magnetic sources nearby the Luotian and Yuexi domes were related to the subsequent upwelling of the mantle and the intrusions of partially molten mafic–ultramafic magmatic rocks in the middle and lower crust that had not participated in the Early Cretaceous delamination processes.
From the middle and lower crust to the upper mantle below the MXF, the magnetic sources were no longer controlled by two sets of nearly orthogonal faults, and were mixed with the field source in the Yuexi dome (Figure 7d,e). The mafic–ultramafic intrusions exposed along the MXF included both alpine-type peridotite and pyroxene-gabbro intrusions produced by crust–mantle interactions. These are products of syn-collision intrusion processes [59]. In summary, the magnetic source under the MXF exhibited the complexity of multiple stages of generation. In addition to the same factors as forming the magnetic source of the Yuexi dome, they were also restricted by the deep melt of the Mesozoic.
A large area of Early Cretaceous granite rocks was exposed in the eastern Dabie HP metamorphic belt, illustrating that the magnetic source in this area was related to the residue of the granite intruding along with the weak tectonic belts or shear zones. The location was relatively shallow, and the ferromagnetic minerals were considered to have originated from the lower crust.
Multiple stages of granitic intrusions formed the Lingshan plutons of the western Dabie during the Jurassic–Cretaceous period [79,80]. The surface area of the plutons was more than 800 km2, which means that there is a huge residual structure of magma beneath it. The magnetic source beneath the plutons occurred within a wide range in the horizontal direction, which might be related to the magmatic activities during this period. Moreover, it extended to the depths of the mantle, suggesting that the mixing of mantle-derived materials may have occurred.
As extensional movements and magmatism strongly modified the collision patterns in the later stages of the orogen, the early suture line lacked clear petrological and tectonic evidence. Its location has been controversial [72,81,82]. Without considering the Curie point constraints of the ferromagnetic minerals, the magnetic bodies from the deeper lithosphere would be restricted by the tectonic lines, as detailed in Figure 7e–i. They were confined to the interior of the orogen bounded by the tectonic units, showing the more robust and quite different magnetization characteristics from those of the surrounding blocks, and F5 (Figure 8a,b) was the northern boundary. Deep seismic wide-angle reflection/refraction studies have revealed that the Moho is cut off at 41 km below the MXF [83], which may indicate the locations of the magnetic source intrusions. Zircon Hf-O isotopes represent that the subducted continental crust of the ancient protoliths generally lost 18O, suggesting that the subducted intrusions originated from the SCC [84,85]. Based on these pieces of evidence, the faults of F5 were supposed to be the suture line between the SCC and NCC in the crust–mantle boundary or upper mantle. This hypothesis was confirmed by the magnetic anomalies of the vertical component calculated at the height of 30 km, as shown in Figure 6.
The fault tectonic activities in the Hefei Basin mainly occurred from the Early Cretaceous to the Paleogene. During this period, the faults passing through the central part of the basin were activated, with the reverse faults transitioning into normal faults [86]. It is considered that the magnetic body with high magnetization located in the central part of the basin may be related to the extension activities of the area during this period.
As previously mentioned, the magnetic sources in the SCC were mainly distributed along the middle–lower Yangtze Valley metallogenic belt, and those in the deep lithosphere were closely related to magmatic activities. Although the tectonic settings of the formations of the magmatic belts in the region are still controversial, it is known that large-scale magmatic activities mainly occurred during the Early Cretaceous. From the perspective of depth, the magnetic source under the southeastern Hubei ore cluster and the Jiangnan fault might have the participation of mantle-derived materials. Xu et al. [87] suggested that the mantle-derived characteristics of the magmatic rocks in the middle–lower Yangtze Valley metallogenic belt were the results of underplating, and the basaltic magma enriched in the mantle intruded into the bottom of the lower crust, which melted and then separated and crystallized. We believe that this type of process correlates with our inversion results.
6. Tectonic Processes Related to the Formations of the Magnetic Sources
The Dabie orogen has experienced multiple stages of subduction and exhumation. The formation of the magnetic sources is inseparable from the related tectonic activities. Based on the analysis results outlined above, the tectonic evolution processes of the recovered magnetic sources in the orogen are as follows:
During the Middle Triassic (approximately 245 Ma), the SCC subducted under the NCC collided with the mantle and sutured below F5. The slab breakoff (approximately 225 Ma) [88] promoted UHP metamorphic rocks’ rapid uplift and return under buoyancy. Simultaneously, disturbances to the upper mantle caused by the breaking off of the subducted slabs induced syn-collision magmatism. As a result, large amounts of mafic–ultramafic magma with mixed crust and mantle sources intruded into the shallow crust along with the weaker parts of the structures. They were then exposed to the surface along F5 due to the subsequent uplifting and denudation.
During the Jurassic (approximately 180 Ma), the plates continued to converge and squeeze, and the UHP rock masses were further exhumed. Sporadic, distributed, small-scale magmatic intrusions accompanied this. Only the remaining structures in the depths of the Lingshan pluton in the western Dabie might have contributed to the highly magnetic anomalies of the aeromagnetic altitude during this period. The magnetic sources were mainly derived from the molten mafic–ultramafic magma of the lower crust, which intrusions of mantle-derived materials may have accompanied.
During the Early Cretaceous period (approximately 145–130 Ma), the crust was shortened laterally due to the continuous convergence and collision of the northern and southern plates. Meanwhile, the lower crust continued to thicken and increase in density, leading to gravitational collapse and delamination of the high-density mafic lower crust under the anatexis. At approximately 130 Ma, the mode of the orogen changed from compression and contraction to extension. Subsequent de-rooting, and delamination of the lower crust, caused mantle upwelling. With the participation of fluids from the upper and middle crust, the lower crust of the SCC, which was deeply subducted in the Triassic, melted, partially due to the heat from the mantle. Additionally, extensive magmatic intrusions and migmatization were followed by extension and detachment of the external tectonic units bounded by F5 and F7 to the north and south, accompanied by strong denudation. Within the NDC, the tectonic activities manifested as rapid differential uplifts. The Luotian and Yuexi dome structures were formed, which promoted the development of sedimentary basins along the boundaries of the orogen. At the same time, Early Cretaceous magmatic activities occurred throughout the entire Dabie orogen, the Huangchuan–Hefei Basin, and the middle–lower Yangtze Valley metallogenic belt.
7. Conclusions
We have introduced the Occam-type inversion algorithm into a spherical coordinate system, and illustrated it using synthetic examples and application to the EMM2017 model data of the Dabie orogen. The lithospheric 3D magnetization distribution of the Dabie orogen was obtained. The main conclusions are as follows:
- (1)
- The inversion of vertical magnetic component anomalies has the best effect and anti-noise ability.
- (2)
- The Tongbai–Shangcheng–Mozitan–Xiaotian fault zone was supposed to be the location where SCC and NCC collided and sutured at the crust–mantle boundary or the upper mantle.
- (3)
- The magnetic sources inside the orogen were multi-staged and multi-sourced. Their formation was determined to be mainly related to the mantle upwelling caused by the Early Cretaceous lithospheric delamination, as well as the partial melting of the mafic–ultramafic lower crust that had not participated in the delamination. The Mesozoic and Jurassic–Cretaceous deep melt activities also restricted the magnetic sources near the MXF and those in the western Dabie, respectively.
- (4)
- We found intimate relations between the magnetic sources of the SCC and the mineralization activities in this area.
Author Contributions
L.Z.: conceptualization, investigation, data processing, geological interpretation, and writing—original draft; S.C.: investigation, data processing, and review and editing; G.L.: review and editing; Z.Z.: review and editing; X.C.: geological interpretation and review and editing; Y.M.: investigation, drawing pictures, and proofreading the manuscript; L.W.: geological interpretation and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41974148 and 41704138). the Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Department of China (No. 2017JJ3069); the Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Share Gas Resource Exploitation (No. E21722); the Project of Doctoral Foundation of Hunan University of Science and Technology (No. E51651); and the Science and Technology Innovation Leading Project of High-Tech Industry of Hunan Province, China (No. 2020GK2067).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ames, L.; Tilton, G.R.; Zhou Gaozhi, Z.G. Timing of collision of the sino-korean and yangtse cratons; U-pb zircon dating of coesite-bearing eclogites. Geology 1993, 21, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, B.R.; Ratschbacher, L.; Liou, J.G. Subduction, collision and exhumation in the ultrahigh-pressure qinling-dabie orogen. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2004, 226, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, A.I.; Xu, S.T.; Sengör, A.M.C. Coesite from the dabie shan eclogites, central china. Eur. J. Mineral. 1989, 1, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Liou, J.G.; Mao, H.K. Coesite-bearing eclogite from the dabie mountains in central china. Geology 1989, 17, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutong, X.; Wen, S.; Yican, L.; Laili, J.; Shouyuan, J.; Okay, A.I.; Sengor, A.M.C. Diamond from the dabie shan metamorphic rocks and its implication for tectonic setting. Science 1992, 256, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, B.R.; Ratschbacher, L.; Webb, L.; Ireland, T.; Walker, D.; Shuwen, D. U/pb zircon ages constrain the architecture of the ultrahigh-pressure qinling-dabie orogen, china. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1998, 161, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Fu, B.; Gong, B.; Li, L. Stable isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks from the dabie-sulu orogen in china: Implications for geodynamics and fluid regime. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2003, 62, 105–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, D.L.; Ayers, J.C.; Gao Shan, G.S.; Miller, C.F.; Zhang Hongfei, Z.H. Geochemical, age, and isotopic constraints on the location of the sino-korean/yangtze suture and evolution of the northern dabie complex, east central china. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2004, 116, 698–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.F. A perspective view on ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism and continental collision in the dabie-sulu orogenic belt. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 3081–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, Y. Tectonic evolution of a composite collision orogen: An overview on the qinling–tongbai–hong’an–dabie–sulu orogenic belt in central china. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 1402–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zeng, R.; Mooney, W.D.; Hacker, B.R. A crustal model of the ultrahigh-pressure dabie shan orogenic belt, china, derived from deep seismic refraction profiling. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 10857–10869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.C.; Klemperer, S.L.; Teng, W.B.; Liu, L.X.; Chetwin, E. Crustal structure and exhumation of the dabie shan ultrahigh-pressure orogen, eastern china, from seismic reflection profiling. Geology 2003, 31, 435–438. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Gao, R.; Cong, B.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Li, Q.; Huang, D. Crustal structure of the southern dabie ultrahigh-pressure orogen and yangtze foreland from deep seismic reflection profiling. Terr. Nova 2004, 16, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y. Crustal structure across the dabie–sulu orogenic belt revealed by seismic velocity profiles. J. Geophys. Eng. 2007, 4, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y. Crustal structure beneath the dabie orogenic belt from ambient noise tomography. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 313–314, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.X.; Zhang, S.; Griffin, W.L.; Yang, Y.J.; Yang, B.; Luo, Y.H.; Zhu, L.P.; Afonso, J.C.; Lei, B.H. How did the dabie orogen collapse? Insights from 3-d magnetotelluric imaging of profile data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 5169–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y. Crustal structure of the dabie orogenic belt (eastern china) inferred from gravity and magnetic data. Tectonophysics 2018, 723, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Geng, J.; Chen, B.; Yang, F.; Wu, J.; Yu, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. 3d geophysical characterization of the sulu-dabie orogen and its environs. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2012, 192–193, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Haobo, P.; Xiao, W. Analysis of relationship of lithosphere geomagnetic field and tectonic in eastern-dabie area (in chinese with english abstract). J. Geod. Geodyn. 2019, 39, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Duermeijer, C.E.; Nyst, M.; Meijer, P.T.; Langereis, C.G.; Spakman, W. Neogene evolution of the aegean arc: Paleomagnetic and geodetic evidence for a rapid and young rotation phase. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2000, 176, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hinsbergen, D.J.J.; Dekkers, M.J.; Bozkurt, E.; Koopman, M. Exhumation with a twist: Paleomagnetic constraints on the evolution of the menderes metamorphic core complex, western turkey. Tectonics 2010, 29, TC3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymakcı, N.; Langereis, C.; Özkaptan, M.; Özacar, A.A.; Gülyüz, E.; Uzel, B.; Sözbilir, H. Paleomagnetic evidence for upper plate response to a step fault, sw anatolia. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 498, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazos, I.; Sboras, S.; Chousianitis, K.; Kondopoulou, D.; Pikridas, C.; Bitharis, S.; Pavlides, S. Temporal evolution of crustal rotation in the aegean region based on primary geodetically-derived results and palaeomagnetism. Acta Geod. Geophys. 2022, 57, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Kang, G.; Li, G.; Bai, C. Crustal magnetic anomaly in the ordos region and its tectonic implications. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 109, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Kang, G.; Bai, C.; Li, G. Distribution of the crustal magnetic anomaly and geological structure in xinjiang, china. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 77, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, N.; Anand, S.P.; Rajaram, M.; Rao, P.R. A relook into the crustal architecture of laxmi ridge, northeastern arabian sea from geopotential data. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 124, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, J. Variations in moho and curie depths and heat flow in eastern and southeastern asia. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2016, 37, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idárraga-García, J.; Vargas, C.A. Depth to the bottom of magnetic layer in south america and its relationship to curie isotherm, moho depth and seismicity behavior. Geod. Geodyn. 2018, 9, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.F.; An, Z.C.; Huang, B.C.; Golovkov, V.P.; Rotanova, N.M.; Kharitonov, A.L. Distribution of apparent magnetization for asia. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2000, 43, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkani Hamed, J.; Strangway, D.W. Lateral variations of apparent magnetic susceptibility of lithosphere deduced from magsat data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1985, 90, 2655–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelièvre, P.G.; Oldenburg, D.W. A 3d total magnetization inversion applicable when significant, complicated remanence is present. Geophysics 2009, 74, L21–L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Chen, C.; Liang, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Lane, R. 3-d inversion of regional magnetic data in spherical coordinates and its preliminary application in australia. Aseg Ext. Abstr. 2013, 2013, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, H.; Geng, M.; Zuo, B. 3d magnetization vector inversion of magnetic data: Improving and comparing methods. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2017, 174, 4421–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, X.; Zuo, B.; Zhang, H.; Geng, M.; Ou, Y.; Yang, T.; Vatankhah, S. Susceptibility and remanent magnetization inversion of magnetic data with a priori information of the köenigsberger ratio. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 221, 1090–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Di, Q.Y.; Xu, K.; Wang, R. Magnetization vector inversion equations and forword and inversed 2-d model study (in chinese with english abstract). Chin. J. Geophys. 2004, 47, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shearer, S.E.; Haney, M.M.; Dannemiller, N. Comprehensive approaches to 3d inversion of magnetic data affected by remanent magnetization. Geophysics 2010, 75, L1–L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, X.; Xi, Y.; Liu, T.; Xu, S. 2d sequential inversion of total magnitude and total magnetic anomaly data affected by remanent magnetization. Geophysics 2015, 80, K1–K12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Counil, J.; Cohen, Y.; Achache, J. The global continent-ocean magnetization contrast. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1991, 103, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maus, S.; Haak, V.; Potsdam, G. Is the long wavelength crustal magnetic field dominated by induced or by remanent magnetisation? J. Indian Geophys. Union 2002, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lesur, V.; Gubbins, D. Using geomagnetic secular variation to separate remanent and induced sources of the crustal magnetic field. Geophys. J. Int. 2000, 142, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulot, G.; Olsen, N.; Thébault, E.; Hemant, K. Crustal concealing of small-scale core-field secular variation. Geophys. J. Int. 2009, 177, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemant, K.; Maus, S. Why no anomaly is visible over most of the continent–ocean boundary in the global crustal magnetic field. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2005, 149, 321–333. [Google Scholar]
- Hemant, K.; Mitchell, A. Magnetic field modelling and interpretation of the Himalayan-tibetan plateau and adjoining north indian plains. Tectonophysics 2009, 478, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, S.C.; Parker, R.L.; Constable, C.G. Occam’s inversion; A practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data. Geophysics 1987, 52, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkington, M. 3-d magnetic imaging using conjugate gradients. Geophysics 1997, 62, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, C. 3d joint inversion of magnetic amplitude and gravity gradiometry data in spherical coordinates. In Proceedings of the SEG New Orleans Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 August 2015; SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, pp. 1553–1557. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, A.; Nie, S.Y. An indentation model for the north and south china collision and the development of the tan-lu and honam fault system. Tectonics 1993, 12, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiao, Y.; Liou, D.; Chen, Y.; Ge, N.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, S.; Cong, B.; Zhang, R.; Hart, S.R.; et al. Collision of the north china and yangtse blocks and formation of coesite-bearing eclogites: Timing and processes. Chem. Geol. 1993, 109, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, B.R.; Ratschbacher, L.; Webb, L.; Dong Shuwen, D.S. What brought them up? Exhumation of the dabie shan ultrahigh-pressure rocks. Geology 1995, 23, 743–746. [Google Scholar]
- Chopin, C. Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism: Tracing continental crust into the mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 212, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Yang, Y.; Deng, L.P. New u-pb geochronological constraints on formation and evolution of the susong complex zone in the dabie orogen. Acta Geol. Sin. 2017, 91, 1915–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.C.; Cong, B.L. Tectonic framework of the ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic zone from the dabie mountains. Sci. Geol. Sin. 1998, 14, 481–492. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Zhou, J.B.; Wu, Y.B.; Xie, Z. Low-grade metamorphic rocks in the dabie-sulu orogenic belt: A passive-margin accretionary wedge deformed during continent subduction. Int. Geol. Rev. 2005, 47, 851–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, S.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Hu, S. Geochemical and sr-nd-pb isotopic compositions of cretaceous granitoids: Constraints on tectonic framework and crustal structure of the dabieshan ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt, china. Chem. Geol. 2002, 186, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.F.; Zheng, Y.F. Remelting of subducted continental lithosphere: Petrogenesis of mesozoic magmatic rocks in the dabie-sulu orogenic belt. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2009, 52, 1295–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Wu, K.; Yang, K. Emplacement and deformation of shigujian syntectonic granite in central part of the dabie orogen: Implications for tectonic regime transformation. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, G.; Zhu, Z.; Cao, S. An improved 3d magnetization inversion based on smoothness constraints in spherical coordinates. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, B.R.; Shive, P.N. Magnetic mineralogy of the lower continental crust. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Deng, S. Emplacement age for the mafic-ultramafic plutons in the northern dabie mts. (Hubei): Zircon u-pb, sm-nd and40ar/39ar dating. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2002, 45, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.R.; Zhang, H.F.; Gao, S. Rock-constitution of various structural layers of the present crust in the dabie orogenic belt, central china (in chinese with english abstract). Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2004, 23, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, S.; Yang, H.; Ding, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, W. Distribution of igneous rocks in china revealed by aeromagnetic data. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 129, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubangoh, R.U.; Pacca, I.G.; Nyobe, J.B.; Hell, J.; Ateba, B. Petromagnetic characteristics of cameroon line volcanic rocks. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2005, 142, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggerty, S.E.; Toft, P.B. Native iron in the continental lower crust: Petrological and geophysical implications. Science 1985, 229, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Yuan, H.L.; Nan, L.; Zhang, L. The behavior of fluid mobile elements during serpentinization and dehydration of serpentinites in subduction zones. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2020, 36, 141–153. [Google Scholar]
- Blakely, R.J.; Brocher, T.M.; Wells, R.E. Subduction-zone magnetic anomalies and implications for hydrated forearc mantle. Geology 2005, 33, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purucker, M.E.; Clark, D.A. Mapping and Interpretation of the Lithospheric Magnetic Field; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 311–337. [Google Scholar]
- Ferré, E.C.; Friedman, S.A.; Martín-Hernández, F.; Feinberg, J.M.; Till, J.L.; Ionov, D.A.; Conder, J.A. Eight good reasons why the uppermost mantle could be magnetic. Tectonophysics 2014, 624–625, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré, E.C.; Martín-Hernández, F.; Purucker, M.; Clark, D.A. Thematic issue: Crustal and mantle sources of magnetic anomalies. Tectonophysics 2014, 624–625, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.T.; Shi, D.N.; Tang, J.T.; Wu, M.A.; Chang, Y.F. Probing on deep structure of middle and lower reaches of the yangtze metallogenic belt and typical ore concentration area: A review of annual progress of sinoprobe-03 (in chinese with english abstract). Acta Geosci. Sin. 2011, 32, 257–268. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.Q.; Yang, K.G.; Ming, H.L.; Lin, G.C. The timing of tectonic transition from compression to extension in dabieshan: Evidence from mesozoic granites. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2004, 47, 453–462. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wyman, D.A.; Xu, J.; Jian, P.; Zhao, Z.; Li, C.; Xu, W.; Ma, J.; He, B. Early cretaceous adakitic granites in the northern dabie complex, central china: Implications for partial melting and delamination of thickened lower crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 2609–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, B.R.; Ratschbacher, L.; Webb, L.; Mcwilliams, M.O.; Ireland, T.; Calvert, A.; Dong, S.; Wenk, H.; Chateigner, D. Exhumation of ultrahigh-pressure continental crust in east central china: Late triassic-early jurassic tectonic unroofing. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 13339–13364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, M.; Lin, W.; Schärer, U.; Shu, L.; Sun, Y.; Arnaud, N. Continental subduction and exhumation of uhp rocks. Structural and geochronological insights from the dabieshan (east china). Lithos 2003, 70, 213–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.C.; Yang, W.R. Uplift evolution during mesozoic-cenozoic of the dabie orogenic belt: Evidence from the tectono-chronology (in chinese with english abstract). Earth Sci.-J. China Univ. Geosci. 1998, 23, 461–467. [Google Scholar]
- You, Z.D.; Suo, S.T.; Zhong, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z.M.; Wei, B. The extensional tectonics and retrometamorphic processes subsequent to the high-pressure and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic events in Dabieshan, China. Cont. Dyn. 1998, 3, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.G.; Li, Q.L.; Hou, Z.H.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y. Cooling history and exhumation mechanism of the ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks in the dabie mountains, central China (in chinese with english abstract). Acta Petrol. Sin. 2005, 21, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.H.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Ma, C.Q.; Reiners, P.W. Geochronological constraints on the post-collisional (150-75 ma) thermal extension in the dabieshan orogen, central china. Gondwana Res. 2001, 4, 829–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.G.; He, Y.S.; Wang, S.J. Process and mechanism of mountain-root removal of the dabie orogen--constraints from geochronology and geochemistry of post-collisional igneous rocks. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 4411–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Su, H.; Ma, C. Formation-age, tectonic setting and ascertainment of a-type granite on the lingshan pluton in dabie orogenic belt (in chinese with english abstract). J. Xinyang Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2009, 22, 222–226. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Jiao, R.; Wang, X.; Xu, C. Late-orogenic granitoids (174~161 ma) in the dabie orogenic belt (in chinese with english abstract). Geol. Miner. Resour. South China 2010, 26, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.G.; Chen, Y.Z.; Jagouty, E. Geochemical and geochonological constraints on the tectonic outline of the dabie mountains, central china: A continent-microcontinent-continent collision model. Cont. Dyn. 1998, 3, 14–31. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, S.; Jahn, B.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Chen, G.; Wu, W. Geochemistry and geochronology of eclogites from the northern dabie mountains, central china. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2005, 25, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Xu, P.F.; Liu, J.S.; Yin, Z.X.; Qin, J.Y.; Zhang, X.K.; Zhang, C.K.; Zhao, J.R. The crustal velocity structure of the continental deep subduction belt: Study on the eastern dabie orogen by wide-angle reflection/refraction (in chinese with english abstract). Chin. J. Geophys. 2003, 46, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Wu, Y.B.; Zhao, Z.F.; Zhang, S.B.; Xu, P.; Wu, F.Y. Metamorphic effect on zircon lu-hf and u-pb isotope systems in ultrahigh-pressure eclogite-facies metagranite and metabasite. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 240, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, J.; Gong, B.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X. Zircon u-pb dating of water-rock interaction during neoproterozoic rift magmatism in south china. Chem. Geol. 2007, 246, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.H.; Zhong, J.H.; Liu, Z.Q. Activity characteristics and controlling factors of the faults in the hefei basin (in chinese with english abstract). Geotecton. Etm Etallogenia 2007, 31, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.F.; Shinjo, R.; Defant, M.J.; Qiang, W.; Rapp, R.P. Origin of mesozoic adakitic intrusive rocks in the ningzhen area of east china: Partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust? Geology 2002, 30, 1111–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huw Davies, J.; von Blanckenburg, F. Slab breakoff: A model of lithosphere detachment and its test in the magmatism and deformation of collisional orogens. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1995, 129, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).