Recent Advances of Magnetic Gold Hybrids and Nanocomposites, and Their Potential Biological Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Synthesis
2.1. Coprecipitation Methods
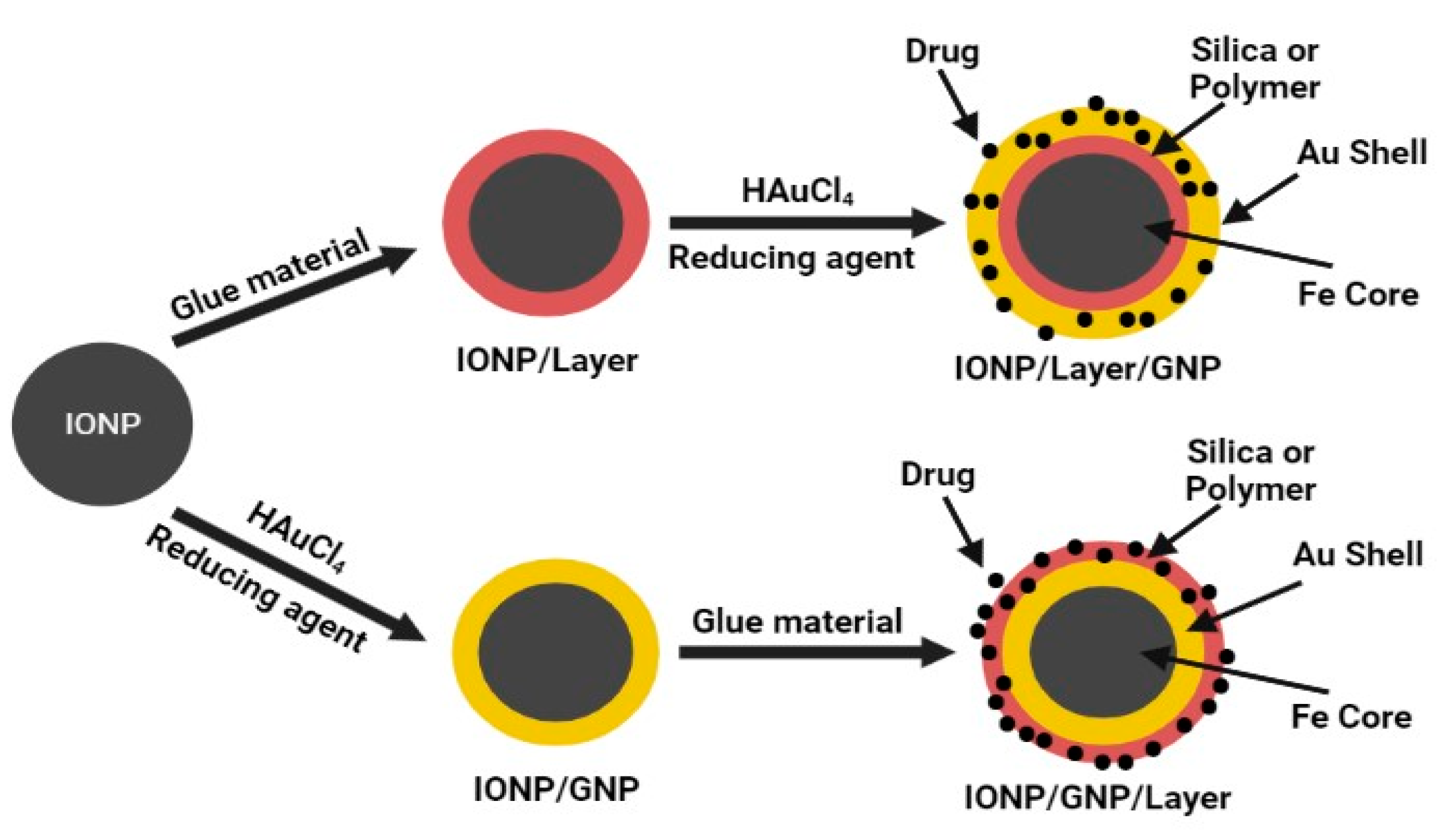
2.1.1. Coprecipitation Methods for mGNP with Intermediate Layer
2.1.2. Coprecipitation Methods for mGNP without Intermediate Layer
| mGNP and Method | Size | Stability | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEGylated mGNP1-DOX2 (Coprecipitation method) | TEM3 shows size of 10 nm and 24 nm for MNP4 and mGNP, respectively, with thickness of gold shell about 11–15 nm. DLS5 indicated diameter of MNP and mGNP as 12 ± 3 nm and 29 ± 4 nm, respectively, being consistent with results of TEM. | In Vitro stability depicted mGNP as highly stabile at 4 °C with homogeneity and dispersity. Photothermal response of mGNP was photostable during temperature elevation via irradiation for 30 min. | [23] |
| Au-Fe Janus mGNP (Thermal decomposition method) | Sizes of two different MNP were observed via TEM as ~16 nm and ~20 nm. Effect of gold nanostar growth on MNP was observed for Janus mGNP as 16.25 nm and 20.41 nm, respectively. | Janus mGNP were functionalized with 4-MBA6 and thiol terminated PEG7 to enhance colloidal stability in water, PBS and cell media. Also, high gold to iron ratio was significant for MR8 and CT9 imaging. | [57] |
| Fe/Au immobilized on PE10 (Microemulsion method) | Diameter of mGNP were ~10 nm with magnetic core of 8 nm and gold shell of 2 nm. | Colloidal stability was increased by immobilization of mGNP on PE foils. | [58] |
| Fe/Au mGNP (Brust Schiffrin method) | mGNP with 5 to 100 nm size and high monodispersity were obtained. | During thermally activated protocols, for purpose of formulation development, size of MNP and GNP11 were raised from 4.4 to 4.5 nm and 2 to 6.4 nm, respectively, indicating coalescence and growth of GNP. | [59] |
2.2. Thermal Decomposition Techniques
2.2.1. Thermal Decomposition Techniques for mGNP with Intermediate Layer
2.2.2. Thermal Decomposition Techniques for mGNP without Intermediate Layer
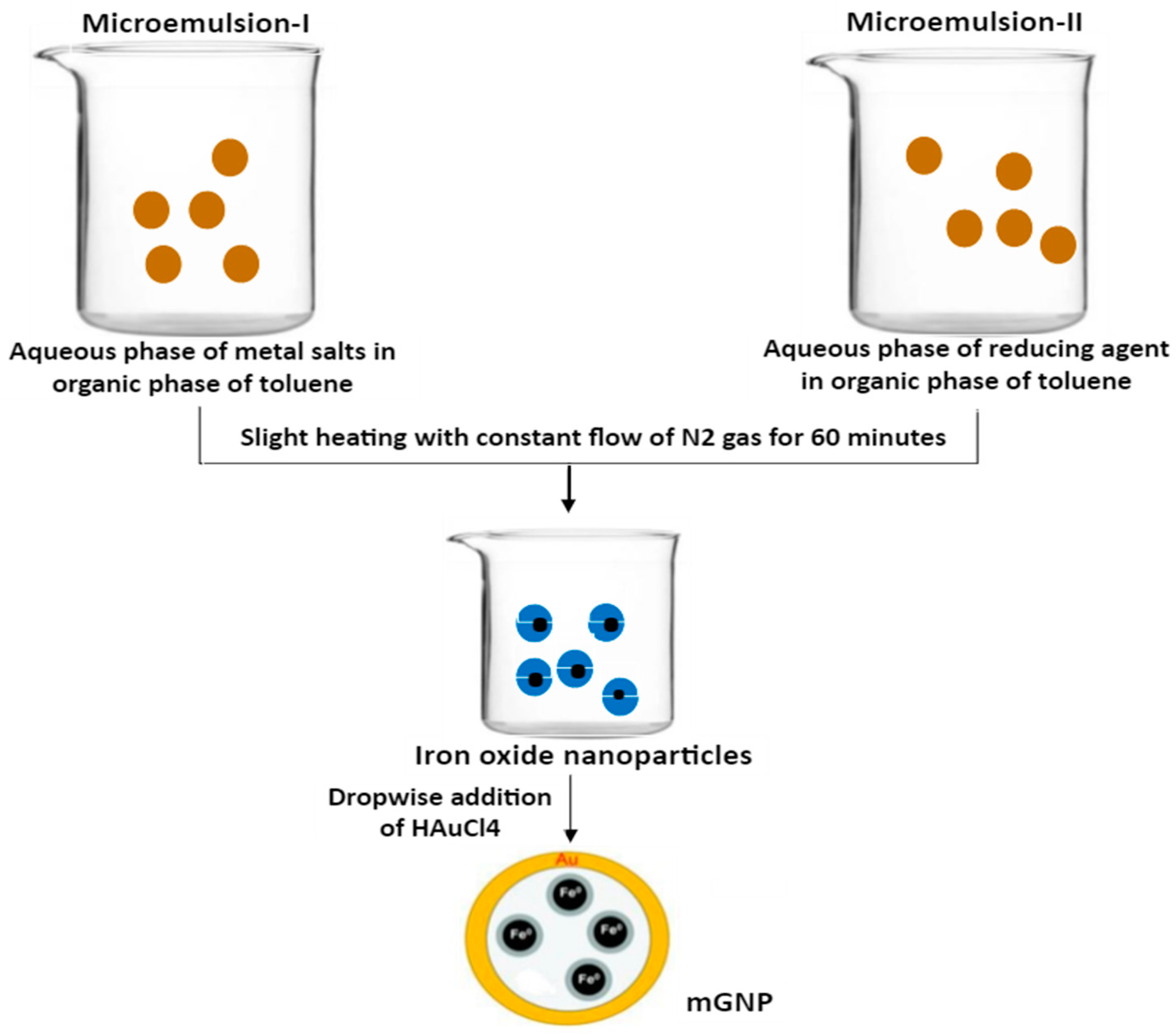
2.3. Microemulsion and Reverse Micelle Method
2.4. Brust–Schiffrin Method
3. Biological Applications of mGNP
3.1. mGNP as Drug and Gene Delivery Carriers
3.2. mGNP as Imaging Agents
3.3. Advantages of Au Coating over Magnetic NPs for MRI
3.4. mGNP as Biosensors
3.5. mGNP in Neuro-Regeneration and Neuro-Degenerative Disorders
3.6. mGNP in Arthritis
3.7. Gold-Magnetic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Therapeutic Effects
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwizera, E.A.; Chaffin, E.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X. Synthesis and properties of magnetic-optical core–shell nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17137–17153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohajer, F.; Ziarani, G.M.; Badiei, A. New advances on Au–magnetic organic hybrid core–shells in MRI, CT imaging, and drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 6517–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkistani, M.A.M.; Komalla, V.; Kayser, V. Recent Advances in the Use of Iron–Gold Hybrid Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlenkrich, J.; Zámbó, D.; Schlosser, A.; Rusch, P.; Bigall, N.C. Revealing the Effect of Nanoscopic Design on the Charge Carrier Separation Processes in Semiconductor-Metal Nanoparticle Gel Networks. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2101712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, A.; Schlenkrich, J.; Zámbó, D.; Rosebrock, M.; Graf, R.T.; Escobar Cano, G.; Bigall, N.C. Interparticle Interaction Matters: Charge Carrier Dynamics in Hybrid Semiconductor–Metal Cryoaerogels. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 2200055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, R.; Friedrich, B.; Mühlberger, M.; Cebulla, N.; Schreiber, E.; Tietze, R.; Cicha, I.; Alexiou, C.; Dutz, S.; Boccaccini, A.R. Synthesis and characterization of citrate-stabilized gold-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, I.S.; Rodrigues, A.R.O.; Rodrigues, C.P.; Almeida, B.G.; Pires, A.; Pereira, A.; Araújo, J.; Castanheira, E.; Coutinho, P.J. Development of novel magnetoliposomes containing nickel ferrite nanoparticles covered with gold for applications in thermotherapy. Materials 2020, 13, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Yue, X.; Gao, N.; Tang, J.; Lv, X.; Hou, J. Microwave method synthesis of magnetic ionic liquid/gold nanoparticles as ultrasensitive SERS substrates for trace clopidol detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 3063–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantechi, E.; Castillo, P.M.; Conca, E.; Cugia, F.; Sangregorio, C.; Casula, M.F. Assessing the hyperthermic properties of magnetic heterostructures: The case of gold–iron oxide composites. Interface Focus 2016, 6, 20160058–20160067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhdarzadeh, M.; Atyabi, F.; Saei, A.A.; Varnamkhasti, B.S.; Omidi, Y.; Fateh, M.; Ghavami, M.; Shanehsazzadeh, S.; Dinarvand, R. Theranostic MUC-1 aptamer targeted gold coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging and photothermal therapy of colon cancer. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 143, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Lau-Truong, S.; Mammeri, F.; Ammar, S. Star-shaped Fe3-xO4-Au core-shell nanoparticles: From synthesis to SERS application. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwizera, E.A.; Chaffin, E.; Shen, X.; Chen, J.; Zou, Q.; Wu, Z.; Gai, Z.; Bhana, S.; O’Connor, R.; Wang, L. Size-and shape-controlled synthesis and properties of magnetic–plasmonic core–shell nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. 2016, 120, 10530–10546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reguera, J.; de Aberasturi, D.J.; Winckelmans, N.; Langer, J.; Bals, S.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Synthesis of Janus plasmonic–magnetic, star–sphere nanoparticles, and their application in SERS detection. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 191, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Pang, X.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, W.; Lin, Z. Precisely size-tunable magnetic/plasmonic core/shell nanoparticles with controlled optical properties. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 12259–12264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.M.; Tavallaie, R.; Sandiford, L.; Tilley, R.D.; Gooding, J.J. Gold coated magnetic nanoparticles: From preparation to surface modification for analytical and biomedical applications. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 7528–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, W.; Zhou, X.; Nie, W.; Chen, L.; Qiu, K.; Zhang, Y.; He, C. Au/polypyrrole@ Fe3O4 nanocomposites for MR/CT dual-modal imaging guided-photothermal therapy: An in vitro study. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4354–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Ji, H.; Yu, P.; Niu, J.; Farooq, M.; Akram, M.W.; Udego, I.; Li, H.; Niu, X. Surface modification of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, S.B.; Kim, D.-H.; Guo, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Gogineni, V.R.; Larson, A.C. Biofunctionalized hybrid magnetic gold nanoparticles as catalysts for photothermal ablation of colorectal liver metastases. Radiology 2017, 285, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Fatehbasharzad, P.; Colombo, M.; Fiandra, L.; Prosperi, D. Multifunctional magnetic gold nanomaterials for cancer. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihov, S.V.; Ivanenkov, Y.A.; Krechetov, S.P.; Veselov, M.S.; Sviridenkova, N.V.; Savchenko, A.G.; Klyachko, N.L.; Golovin, Y.I.; Chufarova, N.V.; Beloglazkina, E.K. Recent advances in the synthesis of Fe3O4@ AU core/shell nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 394, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Crozals, G.; Bonnet, R.; Farre, C.; Chaix, C. Nanoparticles with multiple properties for biomedical applications: A strategic guide. Nano Today 2016, 11, 435–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamipour, S.; Sadjadi, M.; Farhadyar, N. Fabrication and spectroscopic studies of folic acid-conjugated Fe3O4@ Au core–shell for targeted drug delivery application. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 148, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbialy, N.S.; Fathy, M.M.; Reem, A.-W.; Darwesh, R.; Abdel-Dayem, U.A.; Aldhahri, M.; Noorwali, A.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A. Multifunctional magnetic-gold nanoparticles for efficient combined targeted drug delivery and interstitial photothermal therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Grasso, M.F.; Cui, X.; Silva, R.N.; Zhang, P. Sensitive and label-free SERS detection of single-stranded DNA assisted by silver nanoparticles and gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2020, 3, 2626–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panday, R.; Abdalla, A.M.; Miao, Y.; Li, X.; Neupane, M.; Ouyang, C.; Yang, G. Polyethylenimine-coated gold-magnetic nanoparticles for ADAM10 siRNA delivery in prostate cancer cells. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2020, 35, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.M.F.A.; Lai, W.-F.; Mikrani, R.; Jabeen, M.; Naveed, M.; Abbas, M.; Farooq, M.A.; Ahsan, A.; Kassim, S.A.; Khan, G.J.; et al. Synthetic NRG-1 functionalized DNA nanospindels towards HER2/neu targets for in vitro anti-cancer activity assessment against breast cancer MCF-7 cells. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 182, 113133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, M.M.F.A.; Sohail, M.; Mirjat, A.A.; Naveed, M.; Majeed, F.; Raza, F.; Farooq, M.A.; Mikrani, R.; Khan, S.; Abbas, M.; et al. PLL-alginate and the HPMC-EC hybrid coating over the 3D DNA nanocubes as compact nanoparticles for oral administration. Appl. Nanosci. 2019, 9, 2105–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Baig, M.M.F.A.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.-S.; Wu, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.-C.; Zhu, H.-L. A DNA-based nanocarrier for efficient cancer therapy. J. Pharm. Anal. 2021, 11, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Same, S.; Aghanejad, A.; Nakhjavani, S.A.; Barar, J.; Omidi, Y. Radiolabeled theranostics: Magnetic and gold nanoparticles. BioImpacts: BI 2016, 6, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherukula, K.; Manickavasagam Lekshmi, K.; Uthaman, S.; Cho, K.; Cho, C.-S.; Park, I.-K. Multifunctional inorganic nanoparticles: Recent progress in thermal therapy and imaging. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbialy, N.S.; Fathy, M.M.; Khalil, W.M. Doxorubicin loaded magnetic gold nanoparticles for in vivo targeted drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 490, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinen, A.B.; Guan, C.M.; Ferrer, J.R.; Barnaby, S.N.; Merkel, T.J.; Mirkin, C.A. Nanoparticle probes for the detection of cancer biomarkers, cells, and tissues by fluorescence. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10530–10574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiani, A.; Esquevin, A.; Lepareur, N.; Bourguet, P.; Le Jeune, F.; Gauvrit, J.-Y. Main applications of hybrid PET-MRI contrast agents: A review. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2016, 11, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khani, T.; Alamzadeh, Z.; Sarikhani, A.; Mousavi, M.; Mirrahimi, M.; Tabei, M.; Irajirad, R.; Abed, Z.; Beik, J. Fe3O4@ Au core–shell hybrid nanocomposite for MRI-guided magnetic targeted photo-chemotherapy. Lasers Med. Sci. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, N.K.; Ghoubaira, J.A.; Bassil, E.P.; Tantawi, H.N.; Eid, A.H. Metal-based nanoparticles: Promising tools for the management of cardiovascular diseases. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2021, 36, 102433–102445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.-M.; Park, K.-H.; Mun, C.H.; Park, Y.-B.; Yoo, K.-H. Drug-loaded gold/iron/gold plasmonic nanoparticles for magnetic targeted chemo-photothermal treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomaterials 2015, 61, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Xu, Z.; Gu, L.; Xu, H.; Han, F.; Chen, B.; Pan, X. Preparation and antibacterial properties of gold nanoparticles: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, S.; Serrano Garcia, R.; Gun’ko, Y.K. Multimodal magnetic-plasmonic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.D.; Gwenin, V.V.; Gwenin, C.D. Magnetic functionalized nanoparticles for biomedical, drug delivery and imaging applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mousavi, M.; Fini, E. Silanization mechanism of silica nanoparticles in bitumen using 3-aminopropyl triethoxysilane (APTES) and 3-glycidyloxypropyl trimethoxysilane (GPTMS). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 3231–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.T.; Sai, D.C.; Luu, Q.M.; Tran, H.T.; Quach, T.D.; Kim, D.H.; Nguyen, N.H. Synthesis of bifunctional Fe3O4@ SiO2-Ag magnetic–plasmonic nanoparticles by an ultrasound assisted chemical method. J. Electron. Mater. 2017, 46, 3646–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannu, R.; Karthikeyan, V.; Velu, N.; Arumugam, C.; Roy, V.A.; Gopalan, A.-I.; Saianand, G.; Sonar, P.; Lee, K.-P.; Kim, W.-J. Polyethylene glycol coated magnetic nanoparticles: Hybrid nanofluid formulation, properties and drug delivery prospects. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Qian, W.; Yang, S.; Sun, J.; Gong, T. A facile and green synthetic route for preparation of heterostructure Fe3O4@ Au nanocomposites. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomaterials, Nanomaterials and Composite Materials 2016 (CBNCM 2016), Chengdu, China, 4–6 November 2016; pp. 2001–2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hecold, M.; Buczkowska, R.; Mucha, A.; Grzesiak, J.; Rac-Rumijowska, O.; Teterycz, H.; Marycz, K. The effect of PEI and PVP-stabilized gold nanoparticles on equine platelets activation: Potential application in equine regenerative medicine. J. Nanomater. 2017, 1, 8706921. [Google Scholar]
- Elbarbary, A.M.; Bekhit, M.; El Fadl, F.I.A.; Sokary, R. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetically Retrievable Fe3O4/Polyvinylpyrrolidone/Polystyrene Nanocomposite Catalyst for Efficient Catalytic Oxidation Degradation of Dyes Pollutants. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2021, 32, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Note, C.; Kosmella, S.; Koetz, J. Poly (ethyleneimine) as reducing and stabilizing agent for the formation of gold nanoparticles in w/o microemulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 290, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Tejada, M.d.M.; Viota, J.L.; Rudzka, K.; Delgado, A.V. Preparation of multi-functionalized Fe3O4/Au nanoparticles for medical purposes B Biointerfaces. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 128, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, O.S.; Zekri, A.; Imam, H.; Khaled, H.; Abdel-Kader, M. Synthesis of the newly developed core-shell Au/Fe3O4 magnato-plasmonic nanocomposite in cancer cells. Life Sci. J. 2014, 11, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Pati, S.S.; Singh, L.H.; Guimarães, E.; Mantilla, J.; Coaquira, J.; Oliveira, A.; Sharma, V.K.; Garg, V.K. Magnetic chitosan-functionalized Fe3O4@ Au nanoparticles: Synthesis and characterization. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 684, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Meng, X.; Liu, T.; Fu, C.; Hao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Ren, J. Multifunctional Fe3O4@ P (St/MAA)@ chitosan@ Au core/shell nanoparticles for dual imaging and photothermal therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4966–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-L.; Yeh, Y.-W.; Chen, J.-M.; Hong, Y.-J.; Huang, T.-L.; Deng, Z.-Y.; Wu, C.-H.; Liao, S.-H.; Wang, L.-M. Influence of magnetoplasmonic γ-Fe2O3/Au core/shell nanoparticles on low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Qi, F.; Zhou, H.; Jia, S.; Gao, Y.; Koh, K.; Yin, Y. Fe3O4@ Au nanoparticles as a means of signal enhancement in surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy for thrombin detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 212, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, J.L.; Fleming, D.A.; Stone, M.B.; Schiffer, P.; Williams, M.E. Synthesis of Fe oxide core/Au shell nanoparticles by iterative hydroxylamine seeding. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Kim, J.P.; Bahng, J.H.; Kotov, N.A.; Lee, J. Self-Assembly Mechanism of Spiky Magnetoplasmonic Supraparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, Y.; Song, S.; Yang, X.; Xing, J.; Chen, J. Magnetic gold nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and its application in the delivery of FITC into KG-1 cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 7716–7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, J.; de Aberasturi, D.J.; Henriksen-Lacey, M.; Langer, J.; Espinosa, A.; Szczupak, B.; Wilhelm, C.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Janus plasmonic–magnetic gold–iron oxide nanoparticles as contrast agents for multimodal imaging. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 9467–9480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kvitek, O.; Reznickova, A.; Zelenakova, A.; Zelenak, V.; Orendac, M.; Svorcik, V. Immobilization of Fe@ Au superparamagnetic nanoparticles on polyethylene. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 110, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-Y.; Schadt, M.J.; Wang, L.; Lim, I.-I.S.; Njoki, P.N.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, M.-Y.; Luo, J.; Zhong, C.-J. Fabrication of magnetic core@ shell Fe oxide@ Au nanoparticles for interfacial bioactivity and bio-separation. Langmuir 2007, 23, 9050–9056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, J.; Choi, H.W.; Lee, J.; Park, H.; Kang, Y.; Kim, I.-S.; Lee, B.-H. Poly-paclitaxel/cyclodextrin-SPION nano-assembly for magnetically guided drug delivery system. J. Control. Release 2016, 231, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.e.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wang, C.; Xie, J.; Sun, S. Synthesis and stabilization of monodisperse Fe nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 10676–10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantechi, E.; Roca, A.G.; Sepúlveda, B.; Torruella, P.; Estrade, S.; Peiro, F.; Coy, E.; Jurga, S.; Bastús, N.G.; Nogués, J. Seeded growth synthesis of Au–Fe3O4 heterostructured nanocrystals: Rational design and mechanistic insights. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 4022–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kostevšek, N.; Žužek Rožman, K.; Arshad, M.S.; Spreitzer, M.; Kobe, S.; Šturm, S.O. Multimodal hybrid FePt/SiO2/Au nanoparticles for nanomedical applications: Combining photothermal stimulation and manipulation with an external magnetic field. J. Phys. Chem 2015, 119, 16374–16382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wei, T.; Yu, J.; Hou, Y.; Cai, K.; Liang, X.-J. Multifunctional metal rattle-type nanocarriers for MRI-guided photothermal cancer therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3386–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.K.; Song, Y.; Kim, J.; Park, E.Y.; Lee, J. Preparation of concave magnetoplasmonic core-shell supraparticles of gold-coated iron oxide via ion-reducible layer-by-layer method for surface enhanced Raman scattering. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 499, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhana, S.; Lin, G.; Wang, L.; Starring, H.; Mishra, S.R.; Liu, G.; Huang, X. Near-infrared-absorbing gold nanopopcorns with iron oxide cluster core for magnetically amplified photothermal and photodynamic cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 11637–11647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Hachtel, J.A.; Chisholm, M.F.; Pantelides, S.T.; Laromaine, A.; Roig, A. Magnetic gold nanotriangles by microwave-assisted polyol synthesis. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 14039–14046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-P.; Liao, P.-Y.; Su, C.-H.; Yeh, C.-S. Formation of oligonucleotide-gated silica shell-coated Fe3O4-Au core–shell nanotrisoctahedra for magnetically targeted and near-infrared light-responsive theranostic platform. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10062–10075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, A.; Singh, N.K.; Soni, M.; Soni, A. Deposition of thin films by chemical solution-assisted techniques. In Chemical Solution Synthesis for Materials Design and Thin Film Device Applications, 1st ed.; Soumen Das, S.D., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 79–117. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Fu, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Fu, C.; Wang, S.; Guo, W.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z. Microenvironment-driven bioelimination of magnetoplasmonic nanoassemblies and their multimodal imaging-guided tumor photothermal therapy. Acs Nano 2016, 10, 7094–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutonnet, M.; Kizling, J.; Stenius, P.; Maire, G. The preparation of monodisperse colloidal metal particles from microemulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1982, 5, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassireslami, E.; Ajdarzade, M. Gold coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as effective nanoparticles to eradicate breast cancer cells via photothermal therapy. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 8, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ielo, I.; Rando, G.; Giacobello, F.; Sfameni, S.; Castellano, A.; Galletta, M.; Drommi, D.; Rosace, G.; Plutino, M.R. Synthesis, chemical–physical characterization, and biomedical applications of functional gold nanoparticles: A review. Molecules 2021, 26, 5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brust, M.; Walker, M.; Bethell, D.; Schiffrin, D.J.; Whyman, R. Synthesis of thiol-derivatised gold nanoparticles in a two-phase liquid–liquid system. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1994, 1, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Casillas, G.; Khanal, S.; Bahena, D.; Velazquez-Salazar, J.J.; Mejia, S.; Ponce, A.; Dravid, V.P.; Whetten, R.L.; Mariscal, M.M. Structure and composition of Au/Co magneto-plasmonic nanoparticles. MRS Commun. 2013, 3, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri-Ledari, R.; Zhang, W.; Radmanesh, M.; Mirmohammadi, S.S.; Maleki, A.; Cathcart, N.; Kitaev, V. Multi-stimuli nanocomposite therapeutic: Docetaxel targeted delivery and synergies in treatment of human breast cancer tumor. Small 2020, 16, 2002733–2002753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, V.; Sood, A.; Kumari, S.; Kumaran, S.S.; Jain, T.K. Hydrophobically modified sodium alginate conjugated plasmonic magnetic nanocomposites for drug delivery & magnetic resonance imaging. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101470–101481. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.-Q.; Xu, M.; Dhawan, U.; Liu, W.-C.; Wu, K.-T.; Liu, X.-R.; Lin, C.; Zhao, G.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chung, R.-J. Iron–gold alloy nanoparticles serve as a cornerstone in hyperthermia-mediated controlled drug release for cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5499–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmadi, A.; Shirazi, H.; Pourbagher, N.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Omidfar, K. An electrochemical immunosensor for digoxin using core–shell gold coated magnetic nanoparticles as labels. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Bancroft, E.A.; Chen, J.; Srinivasan, R.; Wang, Y. Magnetic Fields and Magnetically Stimulated Gold-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Differentially Modulate L-Type Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel Activity in Midbrain Neurons. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.-X. Promoting neuroregeneration by applying dynamic magnetic fields to a novel nanomedicine: Superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO)-gold nanoparticles bounded with nerve growth factor (NGF). Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, M.; Guo, Y.; Tu, K.; Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Tong, X.; Wu, W.; Qi, L.; Shi, D. Targeted chimera delivery to ovarian cancer cells by heterogeneous gold magnetic nanoparticle. Nanotechnology 2016, 28, 025101–025115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torresan, V.; Forrer, D.; Guadagnini, A.; Badocco, D.; Pastore, P.; Casarin, M.; Selloni, A.; Coral, D.; Ceolin, M.; Fernandez van Raap, M.B. 4D multimodal nanomedicines made of Nonequilibrium Au–Fe alloy nanoparticles. Acs Nano 2020, 14, 12840–12853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheradmand, E.; Poursalehi, R.; Delavari, H. Optical and magnetic properties of iron-enriched Fe/FexOy@ Au magnetoplasmonic nanostructures. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debouttière, P.-J.; Roux, S.; Vocanson, F.; Billotey, C.; Beuf, O.; Favre-Réguillon, A.; Lin, Y.; Pellet-Rostaing, S.; Lamartine, R.; Perriat, P.; et al. Design of Gold Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 2330–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, P.; Chen, M.; Hui, W.; Vermorken, A.; Luo, Z.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Cui, Y. Gold magnetic nanoparticle conjugate-based lateral flow assay for the detection of IgM class antibodies related to TORCH infections. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhadizadeh, M.H.; Talemi, R.P. Synergistic effect of magnetite and gold nanoparticles onto the response of a label-free impedimetric hepatitis B virus DNA biosensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alunni, A.; Bally-Cuif, L. A comparative view of regenerative neurogenesis in vertebrates. Development 2016, 143, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, N.-K.; Kim, H.F.; Shim, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.W.; Kwak, C.; Sim, S.-E.; Choi, J.-H.; Ahn, S.; Yoo, J. A transducible nuclear/nucleolar protein, mLLP, regulates neuronal morphogenesis and synaptic transmission. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morelli, S.; Piscioneri, A.; Messina, A.; Salerno, S.; Al-Fageeh, M.B.; Drioli, E.; Bartolo, L.D. Neuronal growth and differentiation on biodegradable membranes. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2015, 9, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faroni, A.; Mobasseri, S.A.; Kingham, P.J.; Reid, A.J. Peripheral nerve regeneration: Experimental strategies and future perspectives. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 82, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Yan, T.-H.; Li, J.; Xiao, Z.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.-C.; Pellois, J.-P. Superparamagnetic iron oxide–gold nanoparticles conjugated with porous coordination cages: Towards controlled drug release for non-invasive neuroregeneration. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2021, 35, 102392–102405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkernelle, J.; Keilhoff, G. Growth factor choice is critical for successful functionalization of nanoparticles. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, M.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.-X. Engineered nanomedicine for neuroregeneration: Light emitting diode-mediated superparamagnetic iron oxide-gold core-shell nanoparticles functionalized by nerve growth factor. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 21, 102052–102086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yuan, M.; Madison, C.; Eitan, S.; Wang, Y. Blood-brain Barrier Crossing using Magnetic Stimulated Nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2022, 345, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, U.; Sohail, M.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Khan, S.; Hussain, Z.; Kousar, M.; Mohsin, S.; Abbasi, M.; Shah, S.A. Chitosan based thermosensitive injectable hydrogels for controlled delivery of loxoprofen: Development, characterization and in-vivo evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Imran, M.; Butt, T.T.; Shah, S.W.A.; Sohail, M.; Malik, A.; Das, S.; Thu, H.E.; Adam, A.; Hussain, Z. Curcumin based nanomedicines as efficient nanoplatform for treatment of cancer: New developments in reversing cancer drug resistance, rapid internalization, and improved anticancer efficacy. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 80, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Khan, S.; Imran, M.; Sohail, M.; Shah, S.W.A.; de Matas, M. PEGylation: A promising strategy to overcome challenges to cancer-targeted nanomedicines: A review of challenges to clinical transition and promising resolution. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, M.F.H.; Machado, A.R.T.; Antunes, L.M.; Souza, T.E.; Freitas, V.A.; Oliveira, L.C.; Rodrigues, J.L.; Pereira, M.C.; Barbosa, F. Gold-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles attenuate collagen-induced arthritis after magnetic targeting. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 194, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Jie, M.-M.; Yang, M.; Tang, L.; Chen, S.-Y.; Sun, X.-M.; Tang, B.; Yang, S.-M. Magnetic Gold Nanoparticle-Labeled Heparanase Monoclonal Antibody and its Subsequent Application for Tumor Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Magnetic Gold Nanoparticles | Biological Applications | References |
|---|---|---|
| Au/Fe3O4/PVA1 | Multi-stimuli mGNP2 for synergistic and targeted DXL3 delivery for MCF-7 human breast cancer cells | [77] |
| PBMA-NH24 grafted thiolated sodium alginate | Paclitaxel loaded hydrophobically modified theranostic mGNP for PLC/PRF/5 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells | [78] |
| mGNP-DOX5 | Theranostic mGNP showing efficacy against Ehrlich carcinoma tumor model in mice | [23] |
| Fe–Au alloy mGNP | Serves as targeted drug carrier for delivery of MTX6 to hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HepG2) with hyperthermia controlled MTX release | [79] |
| HA7-PEI8-Au/Fe3O4 | Effectively suppress growth of prostate cancer (PC3) cells in vitro by magnectially targeted delivery of ADAM10 siRNA loaded HA-PEI-Au/Fe3O4 | [25] |
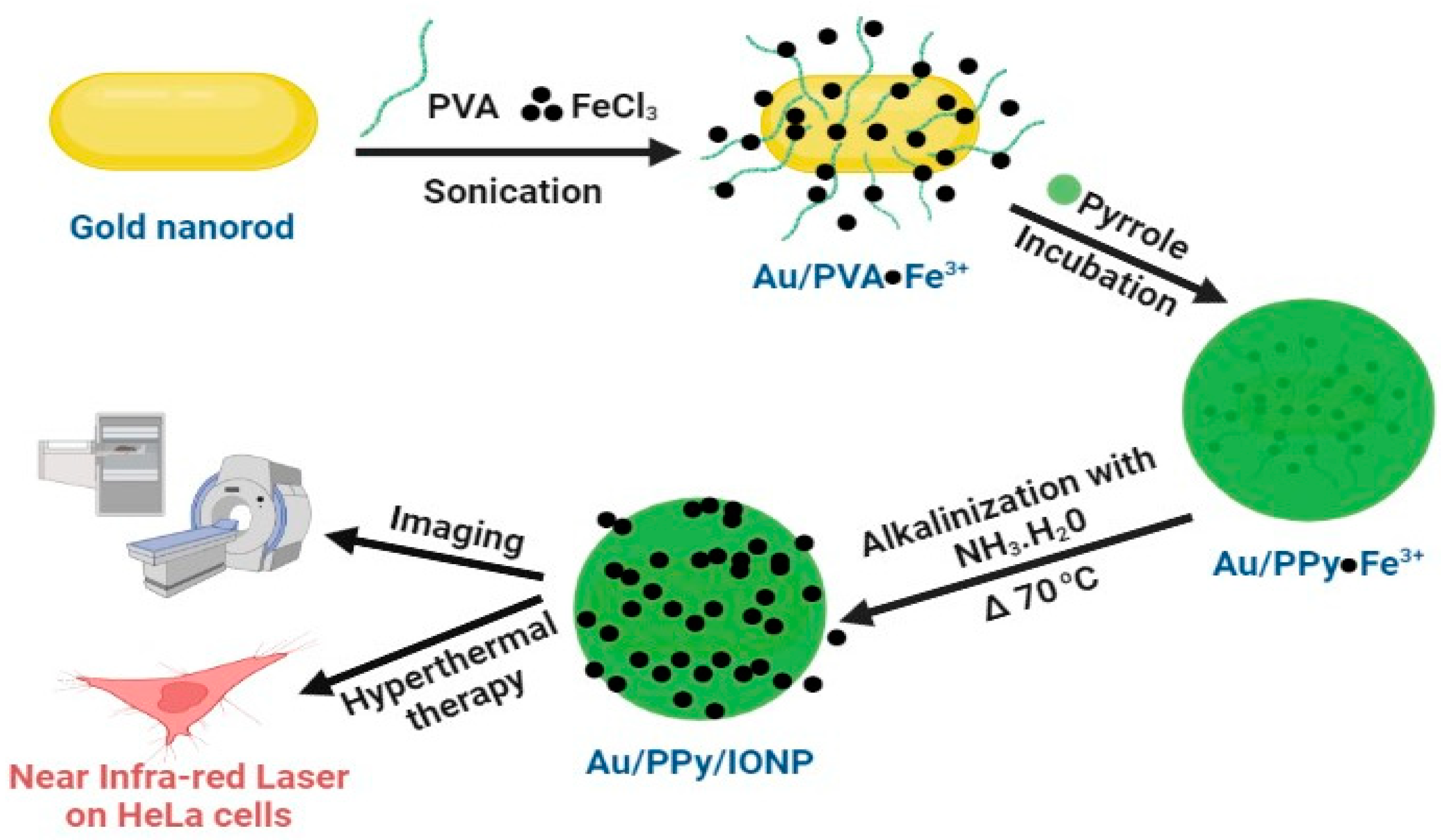
| Au/PPy9@Fe3O4 | Multi-purpose mGNP for magnetically guided photothermal therapy and contrast agent for MR10 and CT11 imaging | [16] |
| Au-Fe Janus mGNP | Contrast agents for multimodal imaging by MR, CT, and photoacoustic imaging to visualize cellular uptake | [57] |
| Antigen labeled Fe3O4-Au | Used as immunosensors to detect digoxin in range from 0.5 to 5 ng mL−1 in biological samples | [80] |
| SMS12-Au-SPION13 | Targeted strategy for Parkinson’s disease where SMS promoted intracellular uptake of Au-SPION to delay blockage of L-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channel in midbrain neurons | [81] |
| NGF14 functionalized SPION-Au | Magnetically driven cellular uptake of mGNP was enhanced onto adrenal phaeochromocytoma (PC-12) cells due to NGF functionalization in addition to NGF induced neurite length elongation | [82] |
| PLGA15/Au/Fe/Au-RGD16 | MTX loaded PLGA/Au/Fe/Au-RGD hybrid nanoparticles are magnetically guided chemo-photothermal carriers used as anti-inflammatory agents for RA17 and enable in vivo T2-MRI | [36] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elmi, G.R.; Saleem, K.; Baig, M.M.F.A.; Aamir, M.N.; Wang, M.; Gao, X.; Abbas, M.; Rehman, M.U. Recent Advances of Magnetic Gold Hybrids and Nanocomposites, and Their Potential Biological Applications. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8040038
Elmi GR, Saleem K, Baig MMFA, Aamir MN, Wang M, Gao X, Abbas M, Rehman MU. Recent Advances of Magnetic Gold Hybrids and Nanocomposites, and Their Potential Biological Applications. Magnetochemistry. 2022; 8(4):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8040038
Chicago/Turabian StyleElmi, Gul Rehman, Kalsoom Saleem, Mirza Muhammad Faran Ashraf Baig, Muhammad Naeem Aamir, Minglian Wang, Xiuli Gao, Muhammad Abbas, and Masood Ur Rehman. 2022. "Recent Advances of Magnetic Gold Hybrids and Nanocomposites, and Their Potential Biological Applications" Magnetochemistry 8, no. 4: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8040038
APA StyleElmi, G. R., Saleem, K., Baig, M. M. F. A., Aamir, M. N., Wang, M., Gao, X., Abbas, M., & Rehman, M. U. (2022). Recent Advances of Magnetic Gold Hybrids and Nanocomposites, and Their Potential Biological Applications. Magnetochemistry, 8(4), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8040038








