Magnetic Nanomaterials and Nanostructures in Sample Preparation Prior to Liquid Chromatography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
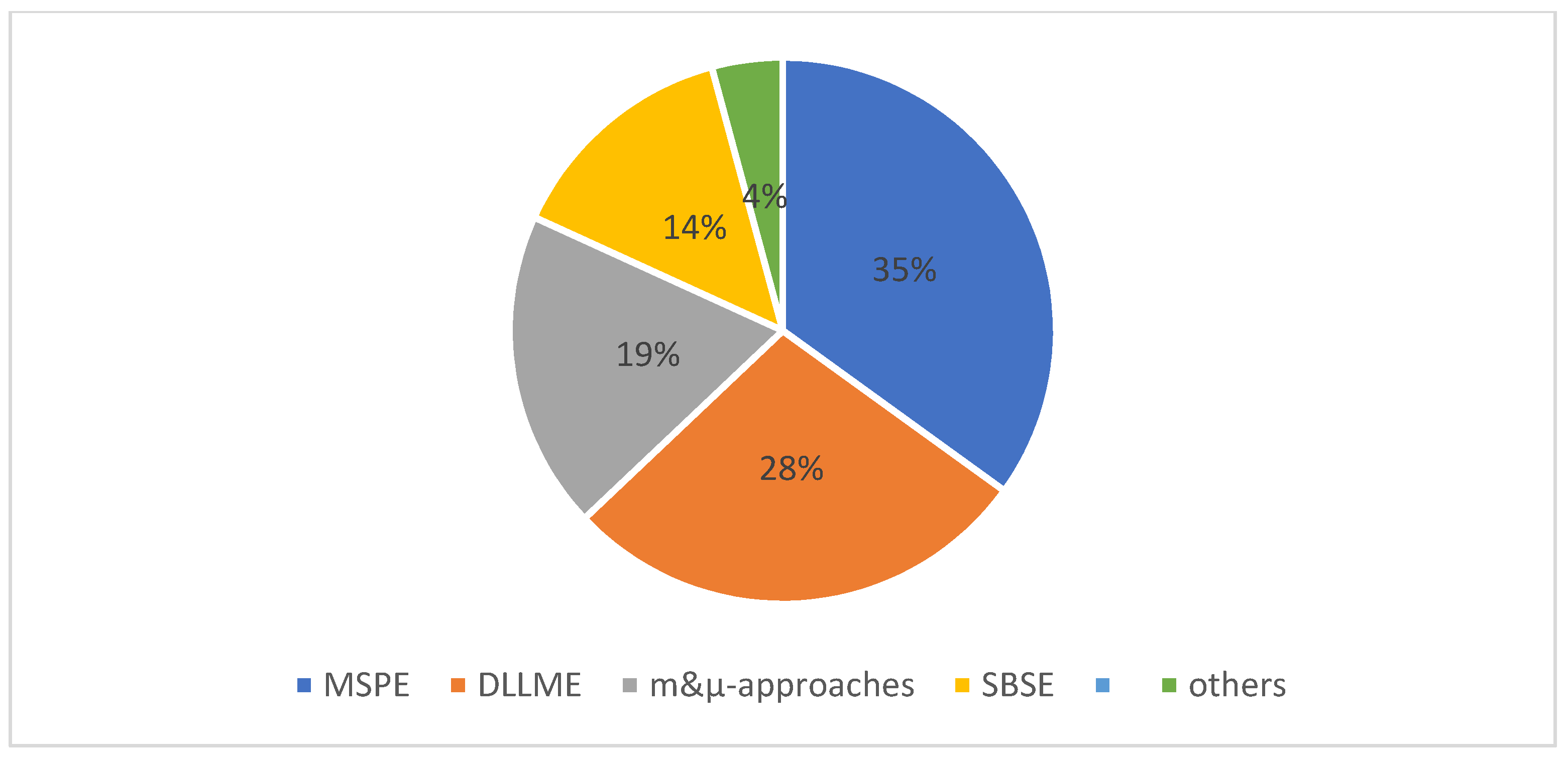
2. Magnetic Sample Preparation Methods
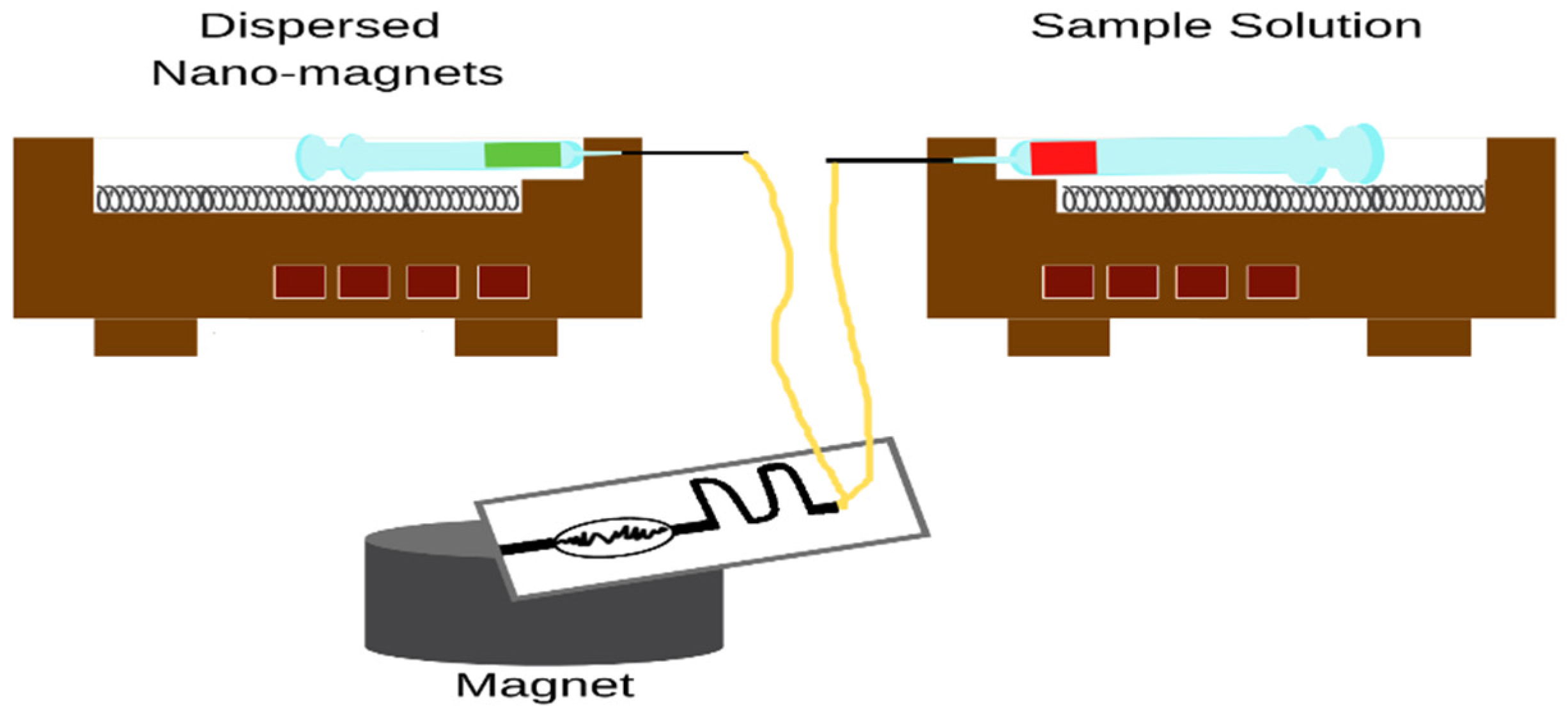
2.1. Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction (MSPE)
2.1.1. On-Line MSPE
2.1.2. Solid Phase Microextraction (SPME)
2.1.3. Dispersive Magnetic Solid Phase Microextraction on Microfluidic Devices
2.1.4. Dispersive Micro-Solid Phase Extraction (D-μ-SPE)
2.2. MIL-DLLME
2.3. Single Drop Microextraction (SDME)
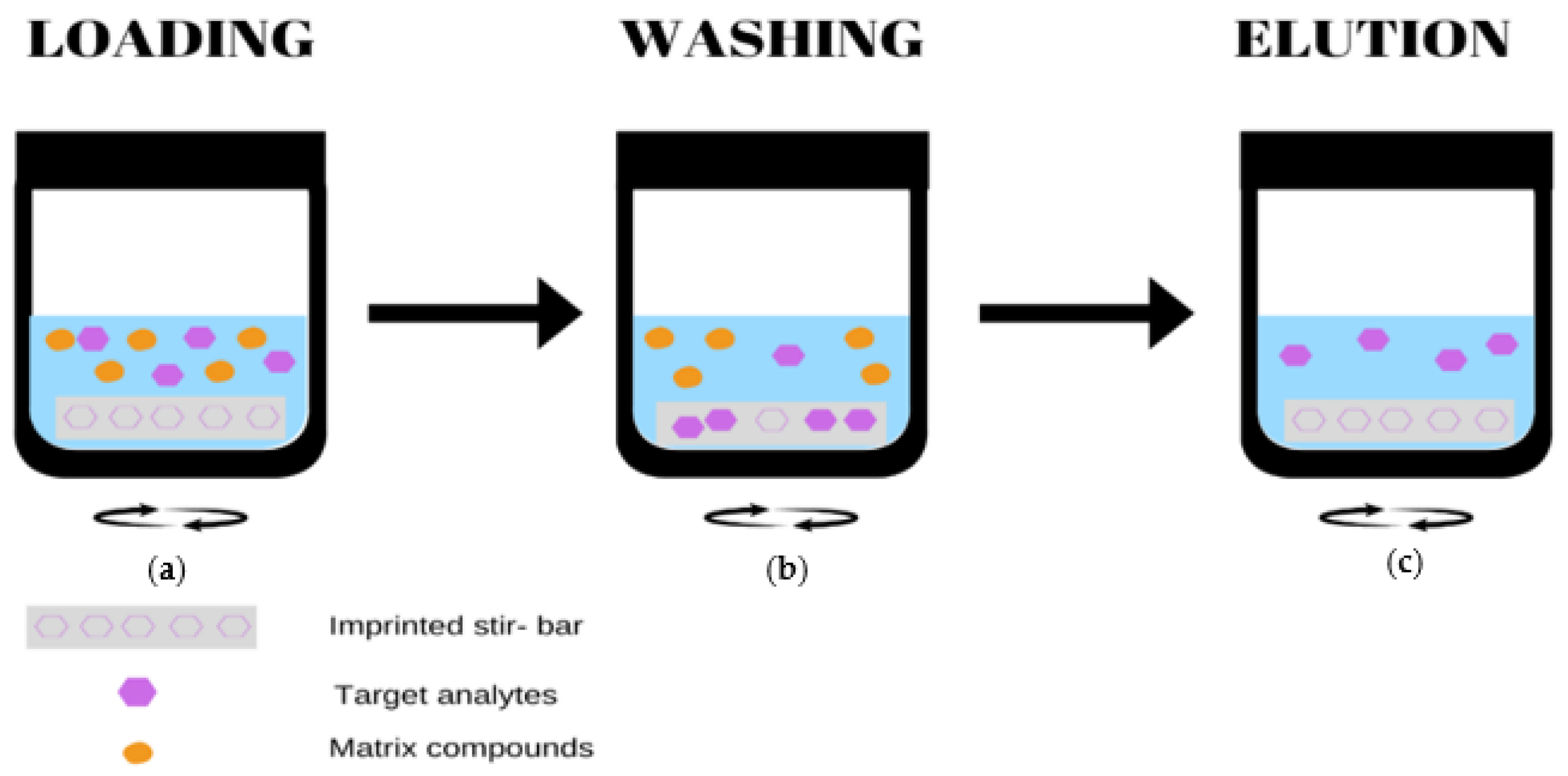
2.4. Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction (SBSE)
3. Epilogue
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.S.; Zhu, G.T.; Luo, Y.B.; Yuan, B.F.; Feng, Y.Q. Synthesis and applications of functionalized magnetic materials in sample preparation. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 45, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanidou, V.F. Trends in microextraction techniques for sample preparation. Separations 2018, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G. Magnetic separation techniques in sample preparation for biological analysis: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 101, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manousi, N.; Rosenberg, E.; Deliyanni, E.; Zachariadis, G.A.; Samanidou, V. Magnetic solid-phase extraction of organic compounds based on graphene oxide nanocomposites. Molecules 2020, 25, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagarová, I. Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction as a Promising Technique for Fast Separation of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Ionic Species: A Review of Recent Advances. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2020, 2020, 8847565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, M.; Yamini, Y.; Faraji, M. Evolution of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2342–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M. Magnetic ionic liquids in analytical sample preparation: A literature review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Rocío-Bautista, P.; Pino, V.; Afonso, A.M. Ionic liquids in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 51, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissoudi, M.; Samanidou, V. Recent advances in applications of ionic liquids in miniaturized microextraction techniques. Molecules 2018, 23, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, T.; Yao, S. Magnetic ionic liquid aqueous two-phase system coupled with high performance liquid chromatography: A rapid approach for determination of chloramphenicol in water environment. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1481, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Peng, B.; Zhou, W.; Gao, H. Ionic liquid-linked dual magnetic microextraction: A novel and facile procedure for the determination of pyrethroids in honey samples. Talanta 2013, 107, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, H.; Lv, F.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gan, N. A headspace sorptive extraction method with magnetic mesoporous titanium dioxide@covalent organic frameworks composite coating for selective determination of trace polychlorinated biphenyls in soils. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1572, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.; Vidal, L.; Canals, A. Hydrophilic magnetic ionic liquid for magnetic headspace single-drop microextraction of chlorobenzenes prior to thermal desorption-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4679–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wierucka, M.; Biziuk, M. Application of magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic solid-phase extraction in preparing biological, environmental and food samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 59, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; He, H. Surface molecularly imprinted polymers fabricated by differential UV–vis spectra and reverse prediction method for the enrichment and determination of sterigmatocystin. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.N.; Matos, B.N.; Gratieri, T.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gelfuso, G.M. Development and validation of a simple chromatographic method for simultaneous determination of clindamycin phosphate and rifampicin in skin permeation studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 159, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, B.G.; Sartori, A.V.; de MORAES, M.H.P.; Cardoso, M.H.W.M.; Jacob, S.D.C. Validation and application of an analytical method for the determination of mycotoxins in crackers by UPLC-MS/MS. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 39, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. An insight into toxicity and human-health-related adverse consequences of cosmeceuticals—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pažoureková, S.; Hojerová, J.; Klimová, Z.; Lucová, M. Dermal absorption and hydrolysis of methylparaben in different vehicles through intact and damaged skin: Using a pig-ear model in vitro. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, T.; Yang, H.; Shi, C.; Yu, J.; Yu, H.; Chen, P.; Di, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, S. An in vitro assessment for human skin exposure to parabens using magnetic solid phase extraction coupled with HPLC. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Huang, Y.; Luo, Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, X. Preparation of highly fluorinated and boron-rich adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones in water and milk samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1601, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, H.; Xu, H. A novel aptamer-based online magnetic solid phase extraction method for simultaneous determination of urinary 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine and monohydroxylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Talanta 2019, 201, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoro Leal, P.; Vereda Alonso, E.; López Guerrero, M.M.; Cordero, M.T.S.; Cano Pavón, J.M.; García de Torres, A. Speciation analysis of inorganic arsenic by magnetic solid phase extraction on-line with inductively coupled mass spectrometry determination. Talanta 2018, 184, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawliszyn, J. Theory of Solid-Phase Microextraction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 9780124160170. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo-Parodi, N.; Kaziur, W.; Stojanović, N.; Jochmann, M.A.; Schmidt, T.C. Solventless microextraction techniques for water analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerín, C.; Salafranca, J.; Aznar, M.; Batlle, R. Critical review on recent developments in solventless techniques for extraction of analytes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 809–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastkari, N.; Ahmadkhaniha, R.; Yunesian, M. Single-walled carbon nanotubes as an effective adsorbent in solid-phase microextraction of low level methyl tert-butyl ether, ethyl tert-butyl ether and methyl tert-amyl ether from human urine. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, H.; Razmi, H.; Jouyban, A. Preparation and characterization of ceramic/carbon coated Fe 3O 4 magnetic nanoparticle nanocomposite as a solid-phase microextraction adsorbent. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1245, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidi, S.; Ranjbar, M.H.; Baharfar, M.; Shanehsaz, M.; Tajik, M. A promising design of microfluidic electromembrane extraction coupled with sensitive colorimetric detection for colorless compounds based on quantum dots fluorescence. Talanta 2019, 194, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alidoust, M.; Yamini, Y.; Baharfar, M.; Seidi, S.; Rasouli, F. Microfluidic-enabled versatile hyphenation of electromembrane extraction and thin film solid phase microextraction. Talanta 2021, 224, 121864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmandi, M.; Yamini, Y.; Baharfar, M.; Karami, M. Dispersive magnetic solid phase microextraction on microfluidic systems for extraction and determination of parabens. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1188, 339183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Magnetic layered double hydroxide/zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanocomposite as a novel adsorbent for enrichment of four endocrine disrupting compounds in milk samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, B.; Balke, B.; Felser, C.; Mudring, A.V. Dysprosium room-temperature ionic liquids with strong luminescence and response to magnetic fields. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 7635–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, X.; Jin, R.; Zhang, H.; Song, D. Magnetic ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of triazine herbicides in vegetable oils by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1373, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merib, J.; Spudeit, D.A.; Corazza, G.; Carasek, E.; Anderson, J.L. Magnetic ionic liquids as versatile extraction phases for the rapid determination of estrogens in human urine by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4689–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, E.; Soylak, M. Ionic liquid-linked dual magnetic microextraction of lead(II) from environmental samples prior to its micro-sampling flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Talanta 2013, 116, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokosa, J.M. Selecting an extraction solvent for a greener liquid phase microextraction (LPME) mode-based analytical method. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przyjazny, A. Extraction|Liquid-Phase Microextraction, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780081019832. [Google Scholar]
- Jeannot, M.A.; Przyjazny, A.; Kokosa, J.M. Single drop microextraction-Development, applications and future trends. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2326–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafra, G.; Vieira, A.A.; Merib, J.; Anderson, J.L.; Carasek, E. Single drop microextraction in a 96-well plate format: A step toward automated and high-throughput analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1063, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di, S.; Ning, T.; Yu, J.; Chen, P.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Zhu, S. Recent advances and applications of magnetic nanomaterials in environmental sample analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 126, 115864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Álvarez, M.; Turiel, E.; Martín-Esteban, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer monolith containing magnetic nanoparticles for the stir-bar sorptive extraction of triazines from environmental soil samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1469, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antoniou, G.; Samanidou, V. Magnetic Nanomaterials and Nanostructures in Sample Preparation Prior to Liquid Chromatography. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8030029
Antoniou G, Samanidou V. Magnetic Nanomaterials and Nanostructures in Sample Preparation Prior to Liquid Chromatography. Magnetochemistry. 2022; 8(3):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8030029
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntoniou, Georgios, and Victoria Samanidou. 2022. "Magnetic Nanomaterials and Nanostructures in Sample Preparation Prior to Liquid Chromatography" Magnetochemistry 8, no. 3: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8030029
APA StyleAntoniou, G., & Samanidou, V. (2022). Magnetic Nanomaterials and Nanostructures in Sample Preparation Prior to Liquid Chromatography. Magnetochemistry, 8(3), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8030029






