Structure and Magnetic Properties of Fe-B-La-Al Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ingots
3.2. Tapes
4. Conclusions
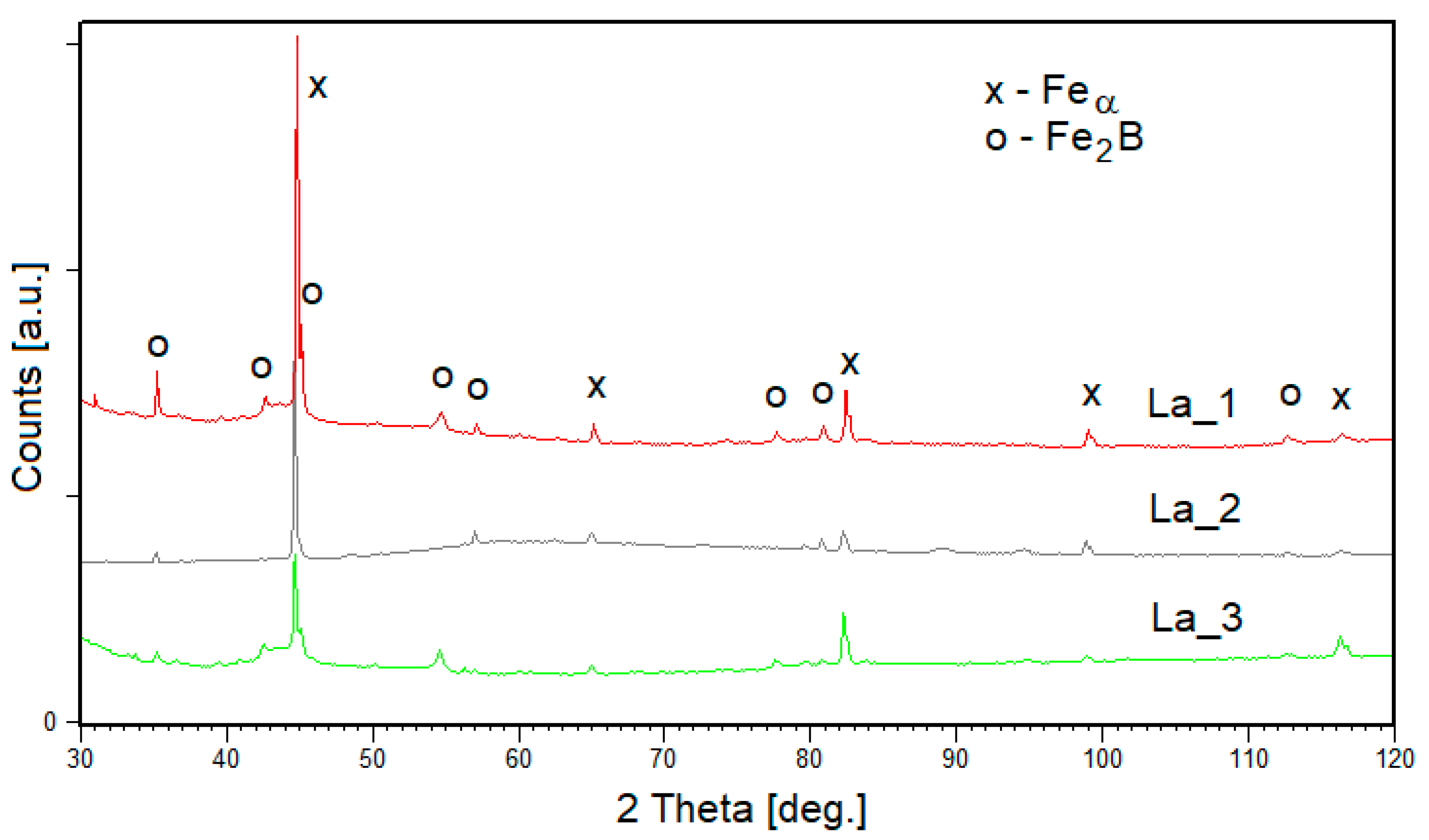
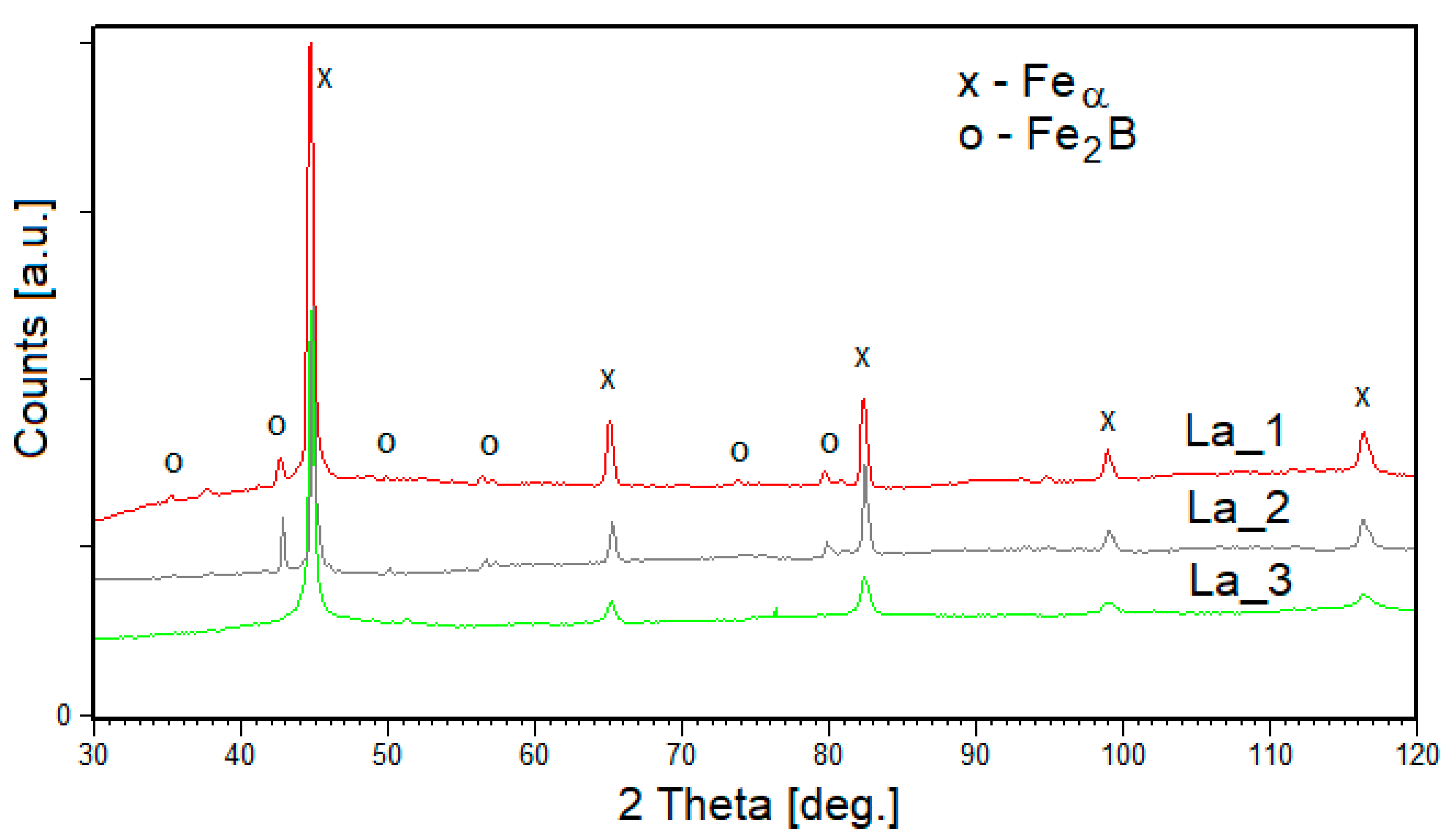
- The X-ray diffraction analysis of the ingots and tapes of the Fe-B-La-Al alloys showed that the solid and Fe2B phases are present. In the structure of the samples, La_1 and La_3 ingots occur about 70% wt.% of Feα phase and about 30% of Fe2B phase. The structure of La_2 ingot contains mainly Feα phase (98 wt.%). The La_1 and La_2 samples in tape form consist of about 70–80 wt.% of Feα phase and about 20–30 wt.% of Fe2B phase. The La_3 sample contains mainly Feα phase.
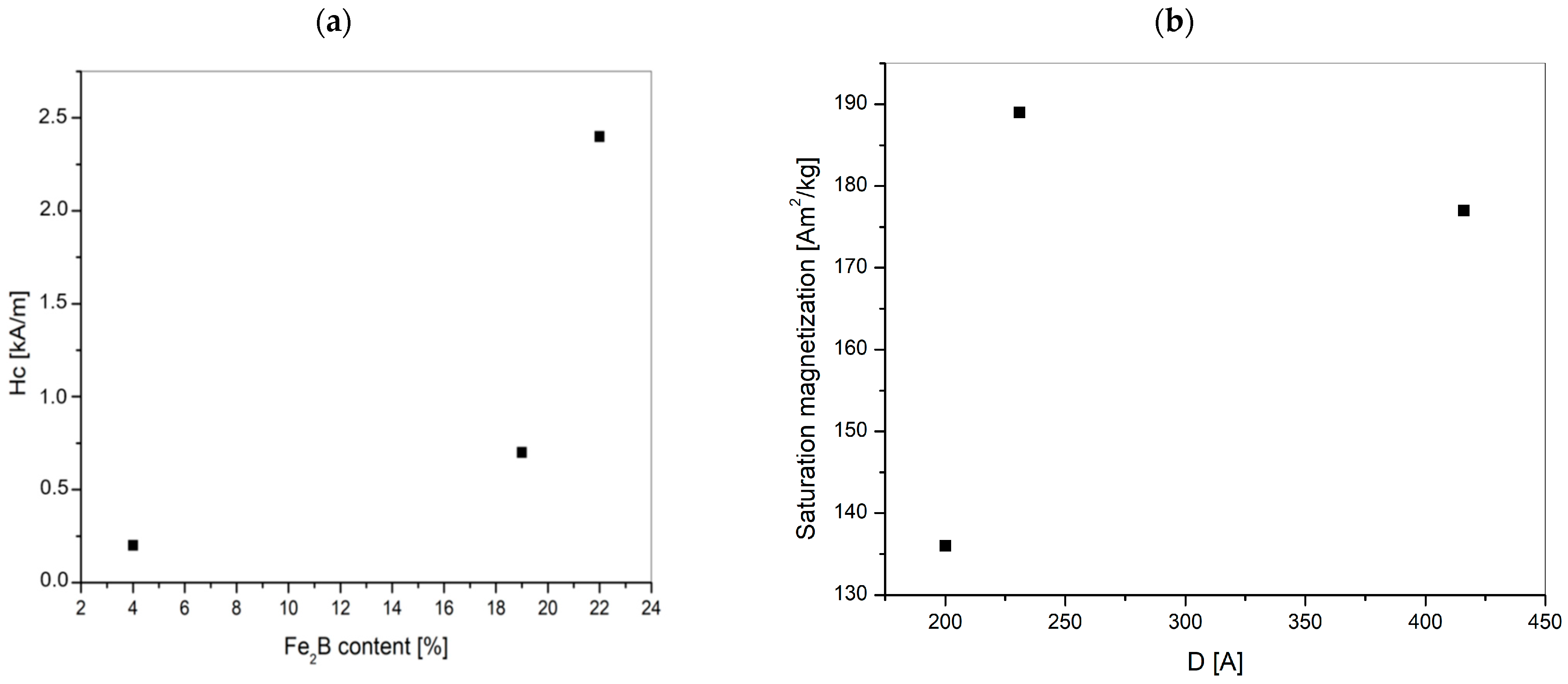
- The structure of both La_1 and La_2 tapes consists of about 80% of solid solution based on the Feα phase and about 20% of Fe2B phase. The structure of the La_3 sample containing mainly Feα phase (96 wt.%). It can be seen that the quantitative proportion of the phases depends on the degree of crystallinity of the products. The largest crystallites are formed for the La_2 sample and reach the size of 400 and 500 Å for the solid solution Feα type and Fe2B, respectively.
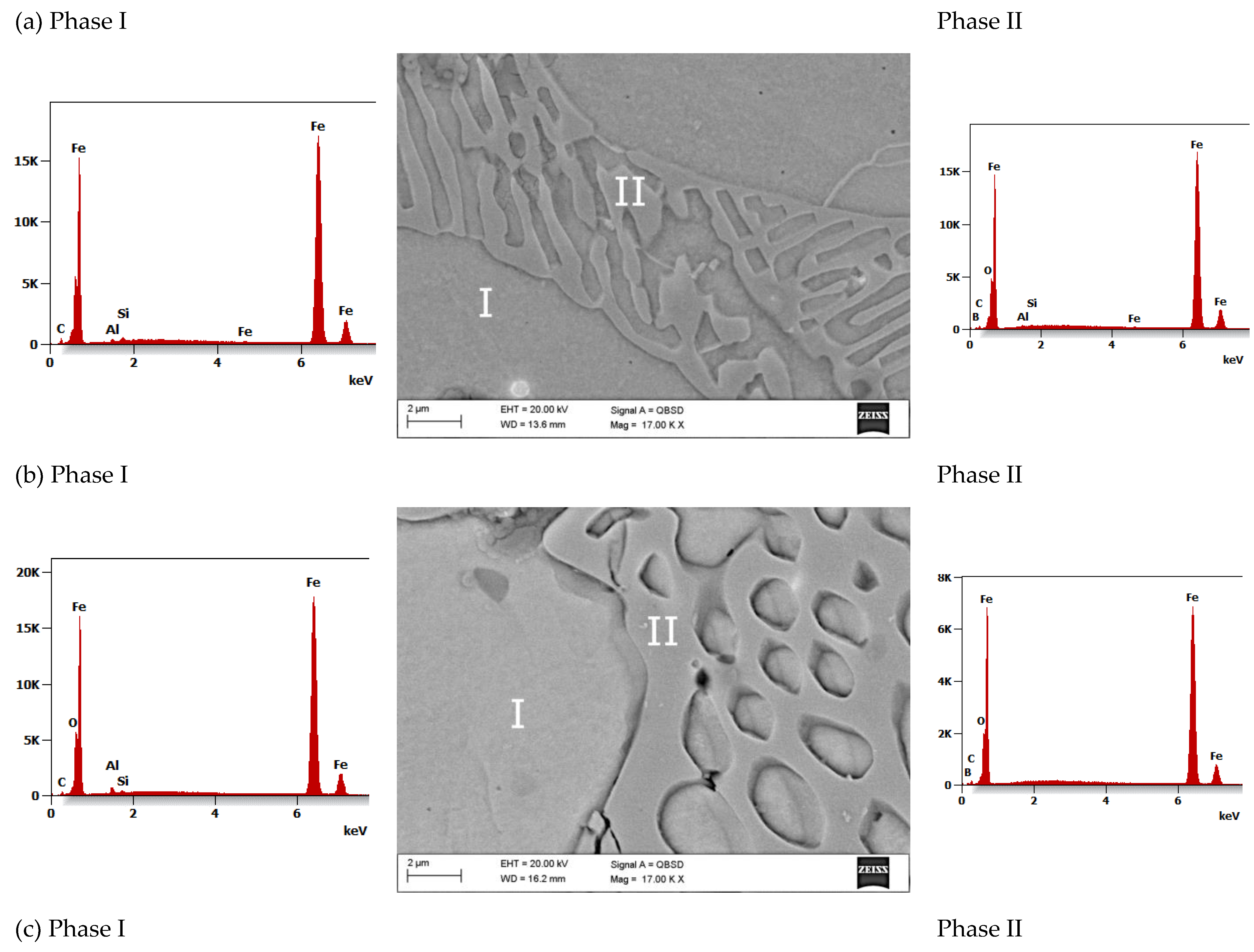
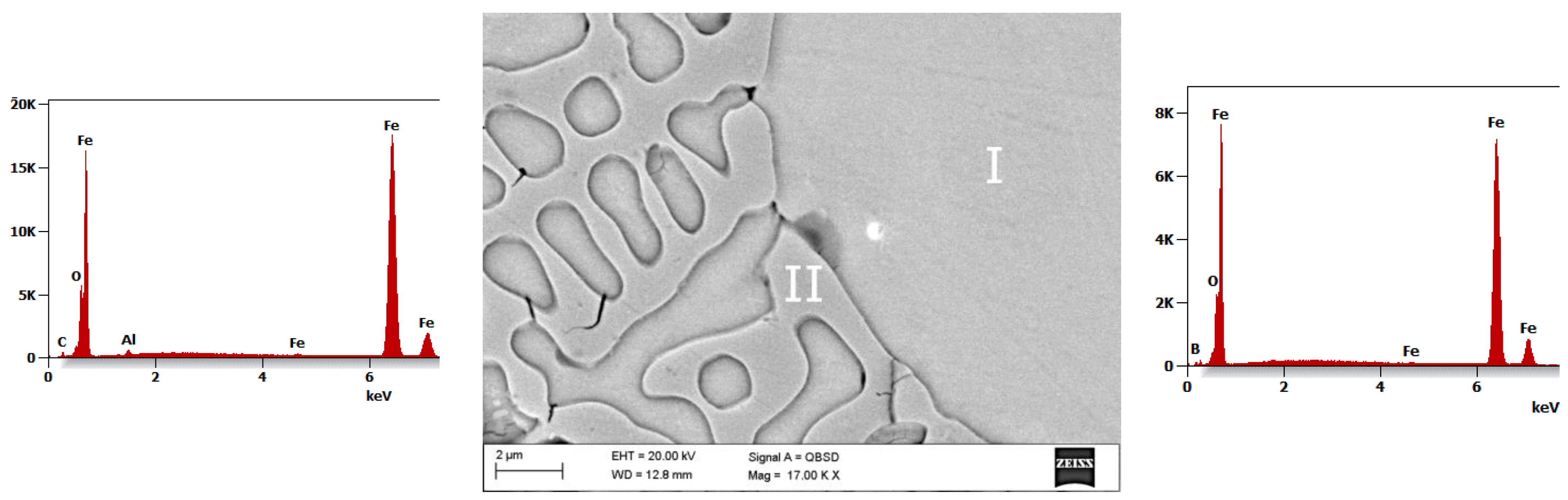
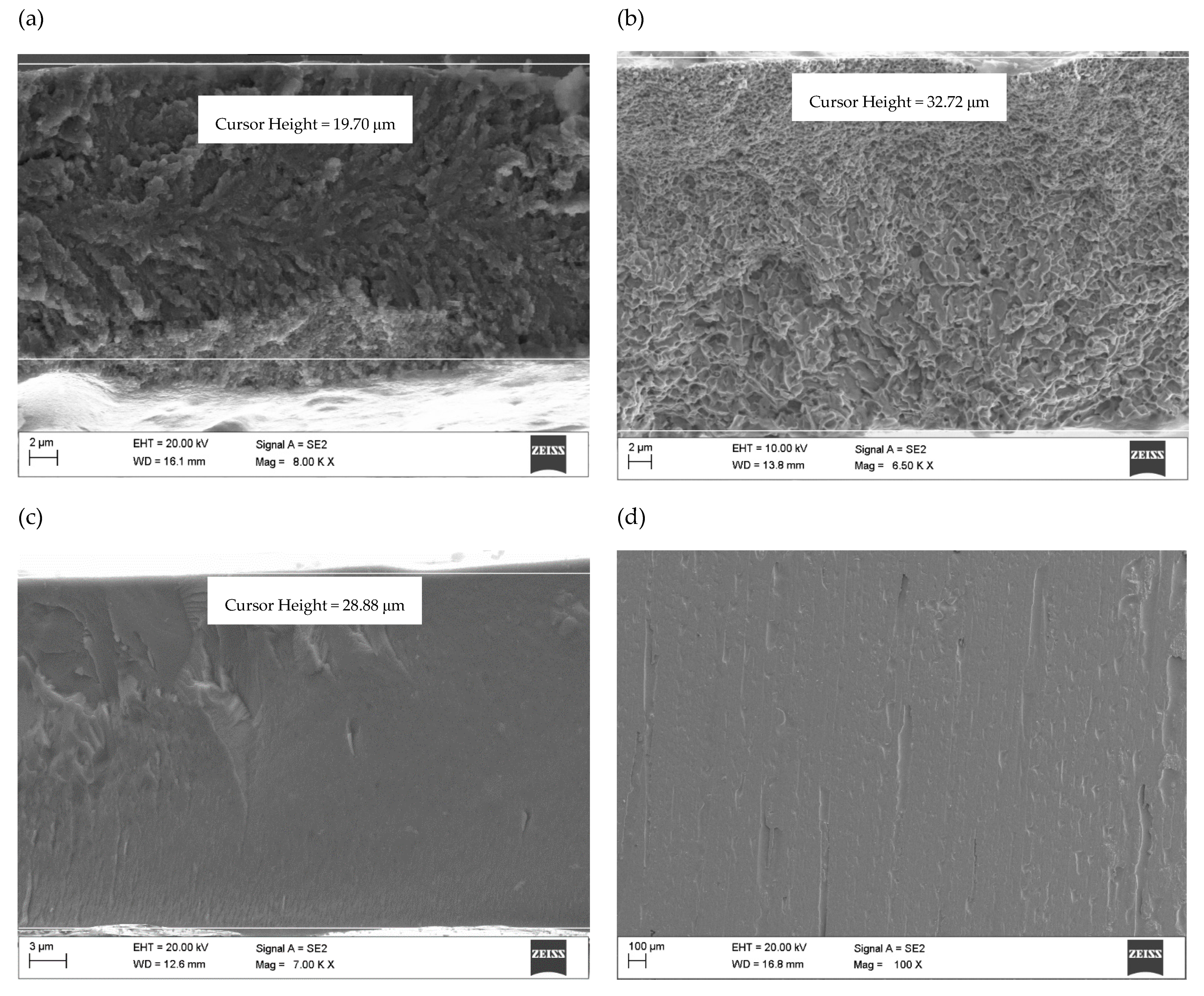
- The SEM fracture morphology of the alloys annealed has a vein, chevron pattern, and smooth character.
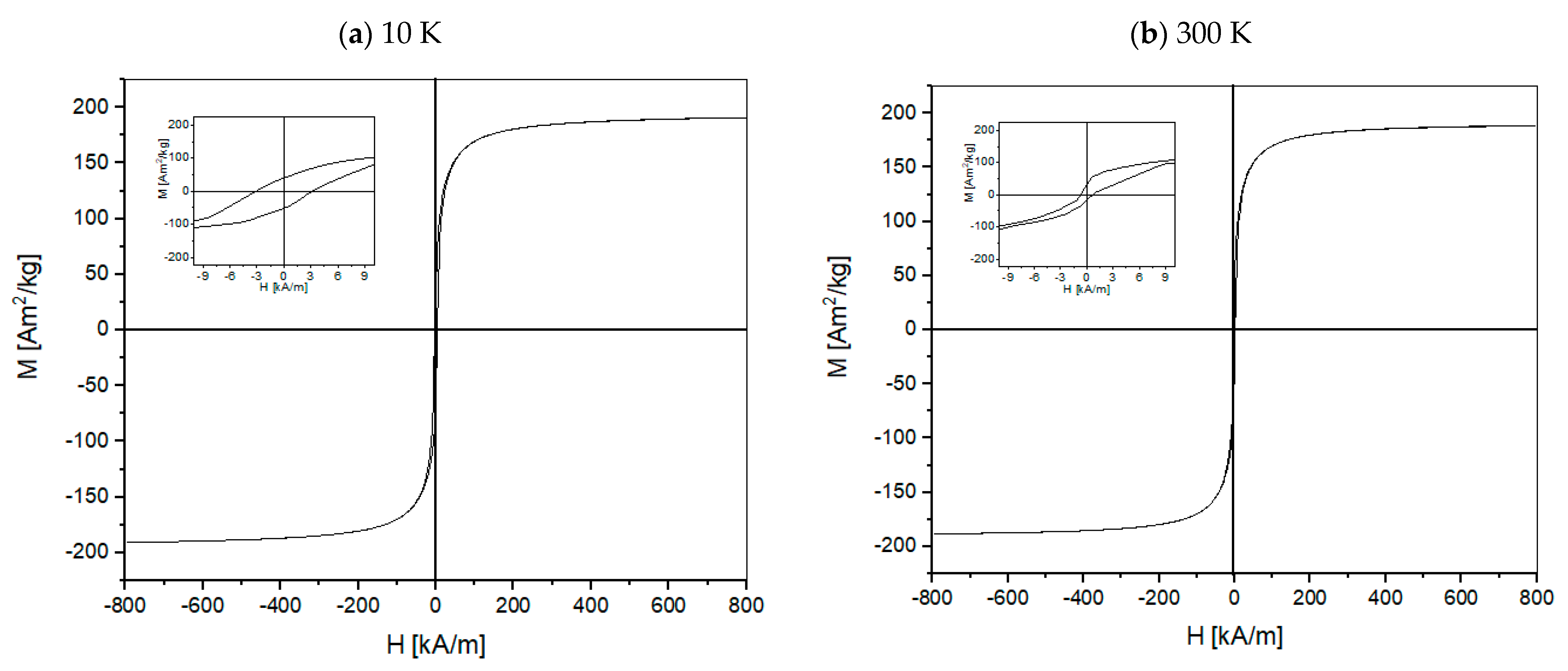
- The lowest coercive force Hc occurs at the temperature of 300 K (~27 °C), this value for La_1 is 2.4 kA/m, for La_2: 0.7 kA/m and for La_3 - 0.2 kA/m. The highest value of saturation magnetization is for La_2 tapes. The magnetic properties of alloys are dependent on the type of crystal structure.
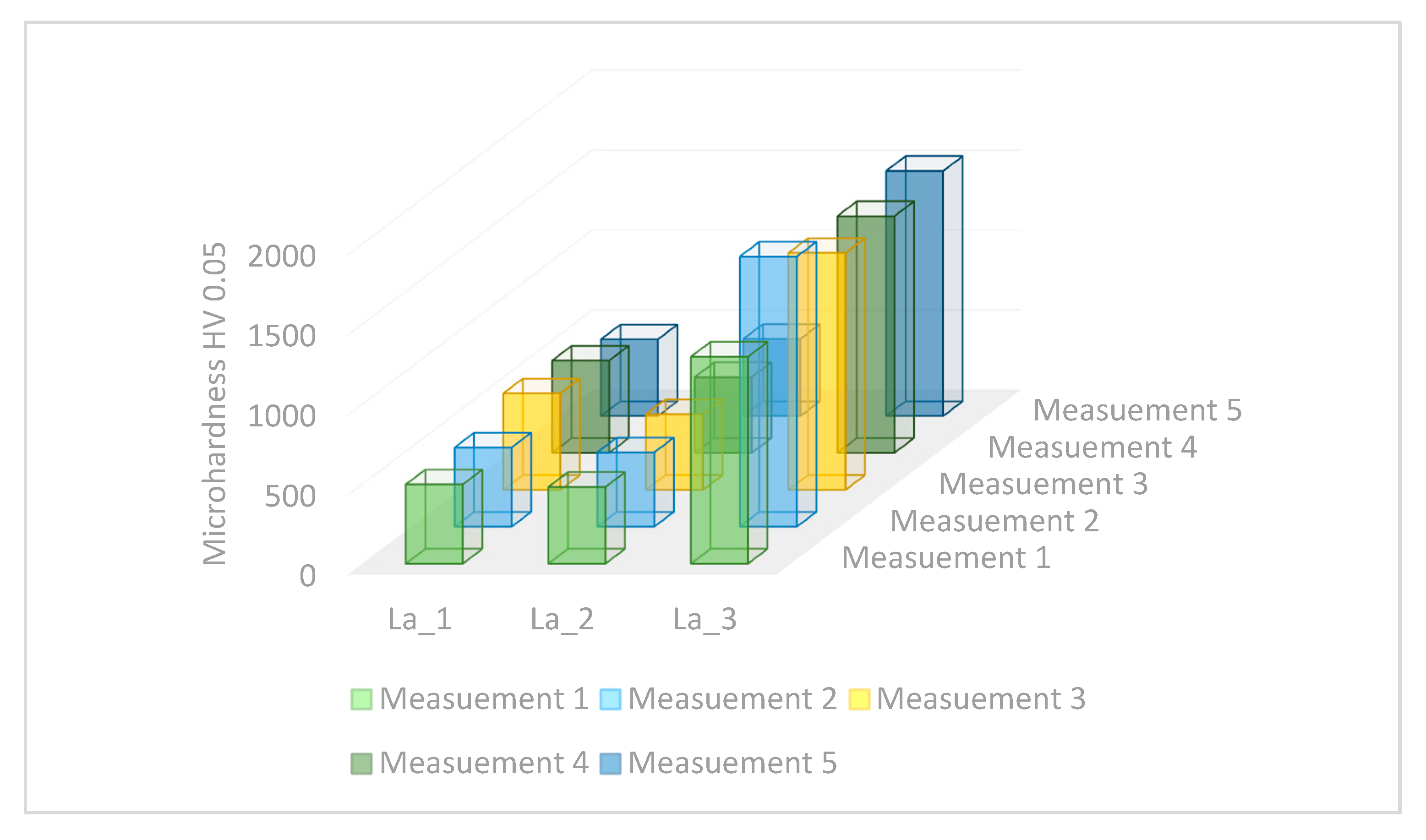
- The average microhardness value of the La_3, La_2, and La_1 alloy tapes is 1494 HV, 530 HV, and 474 HV, respectively. The average values of microhardness of the Fe-B-La-Al alloy ingots are significantly lower than tapes. The microhardness value of phase I (solid solution based on the Feα) varies between 201 and 276 HV. Phase II (eutectic mixture of Feα and Fe2B phase) exhibits the highest hardness (365 HV) in the La_1 ingot.
- The highest value of microhardness (1494 HV) was identified for the sample with the highest concentration of lanthanum (1 at.%) and aluminum (1 at.%). The average microhardness of the La_1 alloy tapes is medium (530 HV) and the average microhardness value of the La_2 alloy tapes is the lowest (474 HV).
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gielen, D.; Boshell, F.; Saygin, D.; Bazilian, M.D.; Wagner, N.; Gorini, R. The role of renewable energy in the global energy transformation. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 24, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drygała, A. Influence of TiO2 film thickness on photovoltaic properties of dye-sensitized solar cells. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 642, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulima, R. Ecological Magnetic Refrigerators. Pr. Inst. Elektrotech. 2013, 261, 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.; Kawanami, T.; Hirano, S.; Ikegawa, M.; Fumoto, K. Improvement of room temperature magnetic refrigerator using air as heat transfer fluid. In Proceedings of the 2008 Second International Conference on Thermal Issues in Emerging Technologies, Cairo, Egypt, 17–20 December 2008; pp. 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypulec, W.; Konopka-Ciupał, G. Effective use of the energy and clean environment—Main directions of development in the refrigeration, ventilation and air conditioning industry. Polityka Energy 2008, 11, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Liu, M.; Egolf, P.W.; Kitanovski, A. A review of magnetic refrigerator and heat pump prototypes built before the year 2010. Int. J. Refrig. 2010, 33, 1029–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. Curie temperature modeling of magnetocaloric lanthanum manganites using Gaussian process regression. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 512, 166998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. Relative cooling power modeling of lanthanum manganites using Gaussian process regression. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 20646–20653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Song, M.; Huang, L.; Ding, D.; Xia, L. Large magnetic entropy change and adiabatic temperature rise of Fe85B12La3 amorphous alloy. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2020, 583, 412014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschneidner, K.A., Jr.; Pecharsky, V.K.; Tsokol, A.O. Recent developments in magnetocaloric materials. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2005, 68, 1479–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesz, S.; Szewczyk, R.; Szewieczek, D.; Bieńkowski, A. The structure and magnetoelastic properties of the Fe-based amorphous alloy with Hf addition. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 157–158, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrobak, A.; Kaleta, A.; Kwapulinski, P.; Kubisztal, M.; Haneczok, G. Magnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Iron-Based Amorphous Alloys and Nanocrystalline Composites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 1512–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesz, S. Effect of cooling rates on the structure, density and micro-indentation behavior of the Fe, Co-based bulk metallic glass. Mater. Charact. 2017, 124, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesz, S. A Study of Structure and Magnetic Properties of Low Purity Fe-Co-Based Metallic Glasses. Materials 2017, 10, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikos, A. Influence of Cooling Rate on Glass Forming Ability of Alloys from Fe-Zr-Si-Cu System; Warsaw University of Technology: Warszawa, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Calka, A.; Radlinski, A.P. Formation of amorphous Fe-B alloys by mechanical alloying. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1991, 58, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Hirao, K.; Soga, N. Second-order Doppler shift in Mössbauer spectra of Fe-B and Fe-P amorphous alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, 3299–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzniak, R.; Dmowski, W. Low-temperature magnetic susceptibility of Fe-B amorphous alloys (abstract). J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 63, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.D.; Budnick, J.I.; Ford, J.C.; Hines, W.A.; Sanchez, F.H.; Hasegawa, R. Crystallization of Fe-B amorphous alloys: A NMR and X-ray study. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 61, 3231–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Soga, N.; Hirao, K.; Kimura, K. Mössbauer spectroscopic study on bonding characteristics of iron in Fe–B and Fe–P amorphous alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1986, 60, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feszczenko-Czopiwski, I. Stale naborowywane (cementowane borem). Prz. Tech. 1926, 64, 525–540. [Google Scholar]
- Luborsky, F.E.; Liebermann, H.H. Crystallization kinetics of Fe-B amorphous alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1978, 33, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, Y.; Oguma, S.; Yamauchi, K. New Fe-based soft magnetic alloys composed of ultrafine grain structure. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, 6044–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Shinohara, Y.; Gook, J.S. Thermal and Magnetic Properties of Bulk Fe-Based Glassy Alloys Prepared by Copper Mold Casting. Mater. Trans. JIM 1995, 36, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Kim, H.-Y.; Shen, B.; Nishiyama, N.; Inoue, A. Crystallization and Magnetic Properties of Fe40Co40Cu0.5Al2Zr9Si4B4.5 and Fe62Co9.5Gd3.5Si10B15 Amorphous Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2003, 44, 1562–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Willard, M.A.; Laughlin, D.E.; McHenry, M.E.; Thoma, D.; Sickafus, K.; Cross, J.O.; Harris, V.G. Structure and magnetic properties of (Fe0.5Co0.5)88Zr7B4Cu1 nanocrystalline alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 6773–6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, S.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, L.; He, J.; Song, Y.; Deng, C.; Zhao, J. Effect of minor lanthanum on the microstructures, tensile and electrical properties of Al-Fe alloys. Mater. Des. 2020, 195, 108991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, X.; Kar-Narayan, S.; Mathur, N.D. Caloric materials near ferroic phase transitions. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasek, J.; Stokłosa, Z. Investigation of material properties by means of magnetic methods. Eng. Trans. 2006, 54, 51–69. [Google Scholar]
- Chrobak, A.; Nosenko, V.; Haneczok, G.; Boichyshyn, L.; Karolus, M.; Kotur, B. Influence of rare earth elements on crystallization of Fe82Nb2B14RE2 (RE=Y, Gd, Tb and Dy) amorphous alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozieł, T.; Kędzierski, Z. Vitrification of Alloys with Liquid Miscibility Gap; AGH Press: Kraków, Poland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Babilas, R.; Spilka, M.; Młynarek, K.; Łoński, W.; Łukowiec, D.; Radoń, A.; Kądziołka-Gaweł, M.; Gębara, P. Glass-Forming Ability and Corrosion Resistance of Al88Y8−xFe4+x (x = 0, 1, 2 at.%) Alloys. Materials 2021, 14, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.A. The Rietvel Method; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- McCusker, L.B.; Von Dreele, R.B.; Cox, D.E.; Louër, D.; Scardi, P. Rietveld refinement guidelines. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1999, 32, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolus, M. Applications of Rietveld refinement in Fe–B–Nb alloy structure studies. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 175, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.K.; Hall, W.H. X-ray line broadening from filed aluminium and wolfram. Acta Metall. 1953, 1, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dośpiał, M.; Olszewski, J.; Nabiałek, M.; Pietrusiewicz, P.; Kaczmarzyk, T. The microstructure and magnetic properties of Nd8.5Tb1.5Fe83Zr1B6 ribbons obtained at various cooling rates. Nukleonika 2015, 60, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C.D.J.; Shin, K.-H.; Zhou, P.Y. Applications of Assymetric Hysteresis Loops in Amorphous Alloys. J. Korean Magn. Soc. 1995, 5, 579–582. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, A.J.; Rodgers, J.W. The crystal structure of the heusler alloys. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1934, 144, 340–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, A.; Vazquez, M.; Kulik, T.; Prados, C. Analysis of the dependence of spin-spin correlations on the thermal treatment of nanocrystalline materials. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 51, 3581–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazquez, J.S.; Franco, V.; Conde, C.F.; Conde, A.; Ferenc, J.; Kulik, T.; Kiss, L.F. Correlation between microstructure and temperature dependence of magnetic properties in Fe60Co18(Nb,Zr)6B15Cu1 alloy series. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 093928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G.; Varga, L.K. Exchange softening in nanocrystalline alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2000, 215, 506–512. [Google Scholar]
- Flohrer, S.; Herzer, G. Random and uniform anisotropy in soft magnetic nanocrystalline alloys (invited). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G. Grain structure and magnetism of nanocrystalline ferromagnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1989, 25, 3327–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G. Magnetization process in nanocrystalline ferromagnets. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1991, 133, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G. Nanocrystalline soft magnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1996, 157, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Elements, at.% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy Indications | Fe | B | La | Al | Other |
| La_1 | 87 | 12 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.4 |
| La_2 | 87 | 12 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
| La_3 | 85 | 12 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Phase | Feα | Fe2B |
|---|---|---|
| Sample | ||
| La_1 | 72 | 28 |
| La_2 | 98 | 2 |
| La_3 | 71 | 29 |
| Sample | Feα | Fe2B | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical (ICDD PDF4+ Card: 04-016-6734) | Refined (RR) a/c [Å] | Crystallite Size D [Å] | Lattice Strain η [%] | Theoretical (ICDD PDF4+ Card: 04-003-2125) | Refined (RR) a/c [Å] | Crystallite Size D [Å] | Lattice Strain η [%] | |
| La_1 | a = 2.8690 | 2.8688(5) | >1000 | 0.11 | a = 5.0990 | 5.1146(6) | >1000 | 0.08 |
| c = 4.2400 | 4.2509(6) | |||||||
| La_2 | Space Group: Im-3m | 2.8694(6) | >1000 | 0.02 | Space Group: I4/mcm | 5.1018(2) | >1000 | 0.01 |
| 4.2488(3) | ||||||||
| La_3 | Crystallographic System: Cubic | 2.8690(8) | 303 | 0.11 | Crystallographic System: Tetragonal | 5.1041(4) | ~1000 | 0.03 |
| 4.2491(1) | ||||||||
| Sample | La_1 | La_2 | La_3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microhardness of phase I [HV] | 276 ± 96 | 256 ± 72 | 201 ± 19 |
| Microhardness of phase II [HV] | 365 ± 40 | 357 ± 41 | 339 ± 23 |
| Phase Sample | Feα | Fe2B |
|---|---|---|
| La_1 | 78 | 22 |
| La_2 | 81 | 19 |
| La_3 | 96 | 4 |
| Sample | Feα | Fe2B | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical (ICDD PDF4+ Card: 04-016-6734) | Refined (RR) a/c [Å] | Crystallite Size D [Å] | Lattice Strain η [%] | Theoretical (ICDD PDF4+ Card: 04-003-2125) | Refined (RR) a/c [Å] | Crystallite Size D [Å] | Lattice Strain η [%] | |
| La_1 | a = 2.8690 | 2.8671(4) | 231 | 1.13 | a = 5.0990 | 5.1136(3) | 160 | 0.20 |
| c = 4.2400 | 4.2428(5) | |||||||
| La_2 | Space Group: Im-3m | 2.8709(1) | 416 | 0.06 | Space Group: I4/mcm | 5.1085(2) | 538 | 0.05 |
| 4.2478(3) | ||||||||
| La_3 | Crystallographic System: Cubic | 2.8703(4) | 200 | 0.16 | Crystallographic System: Tetragonal | 5.1388(2) | 160 | 0.20 |
| 4.1991(4) | ||||||||
| Sample | Measurement Temperature [K] | Saturation Magnetization Ms [Am2/kg] | Corecive Force Hc [kA/m] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 178 | 4.3 | |
| 40 | 178 | 5.5 | |
| La_1 | 100 | 181 | 3.6 |
| 200 | 180 | 4.4 | |
| 300 | 177 | 2.4 | |
| 10 | 191 | 3.1 | |
| 40 | 191 | 1.9 | |
| La_2 | 100 | 193 | 2.8 |
| 200 | 191 | 1.8 | |
| 300 | 189 | 0.7 | |
| 10 | 142 | 1.0 | |
| La_3 | 40 | 143 | 0.6 |
| 300 | 136 | 0.2 |
| Sample | La_1 | La_2 | La_3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average measurement [HV] | 530 ± 56 | 474 ± 7 | 1494 ± 141 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lesz, S.; Kwapuliński, P.; Karolus, M.; Gołombek, K.; Hrapkowicz, B.; Zarychta, A.; Babilas, R.; Popis, J.; Janiak, P. Structure and Magnetic Properties of Fe-B-La-Al Alloy. Magnetochemistry 2021, 7, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7090129
Lesz S, Kwapuliński P, Karolus M, Gołombek K, Hrapkowicz B, Zarychta A, Babilas R, Popis J, Janiak P. Structure and Magnetic Properties of Fe-B-La-Al Alloy. Magnetochemistry. 2021; 7(9):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7090129
Chicago/Turabian StyleLesz, Sabina, Piotr Kwapuliński, Małgorzata Karolus, Klaudiusz Gołombek, Bartłomiej Hrapkowicz, Adam Zarychta, Rafał Babilas, Julia Popis, and Patrycja Janiak. 2021. "Structure and Magnetic Properties of Fe-B-La-Al Alloy" Magnetochemistry 7, no. 9: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7090129
APA StyleLesz, S., Kwapuliński, P., Karolus, M., Gołombek, K., Hrapkowicz, B., Zarychta, A., Babilas, R., Popis, J., & Janiak, P. (2021). Structure and Magnetic Properties of Fe-B-La-Al Alloy. Magnetochemistry, 7(9), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7090129








