Solvent-Induced Hysteresis Loop in Anionic Spin Crossover (SCO) Isomorph Complexes
Abstract
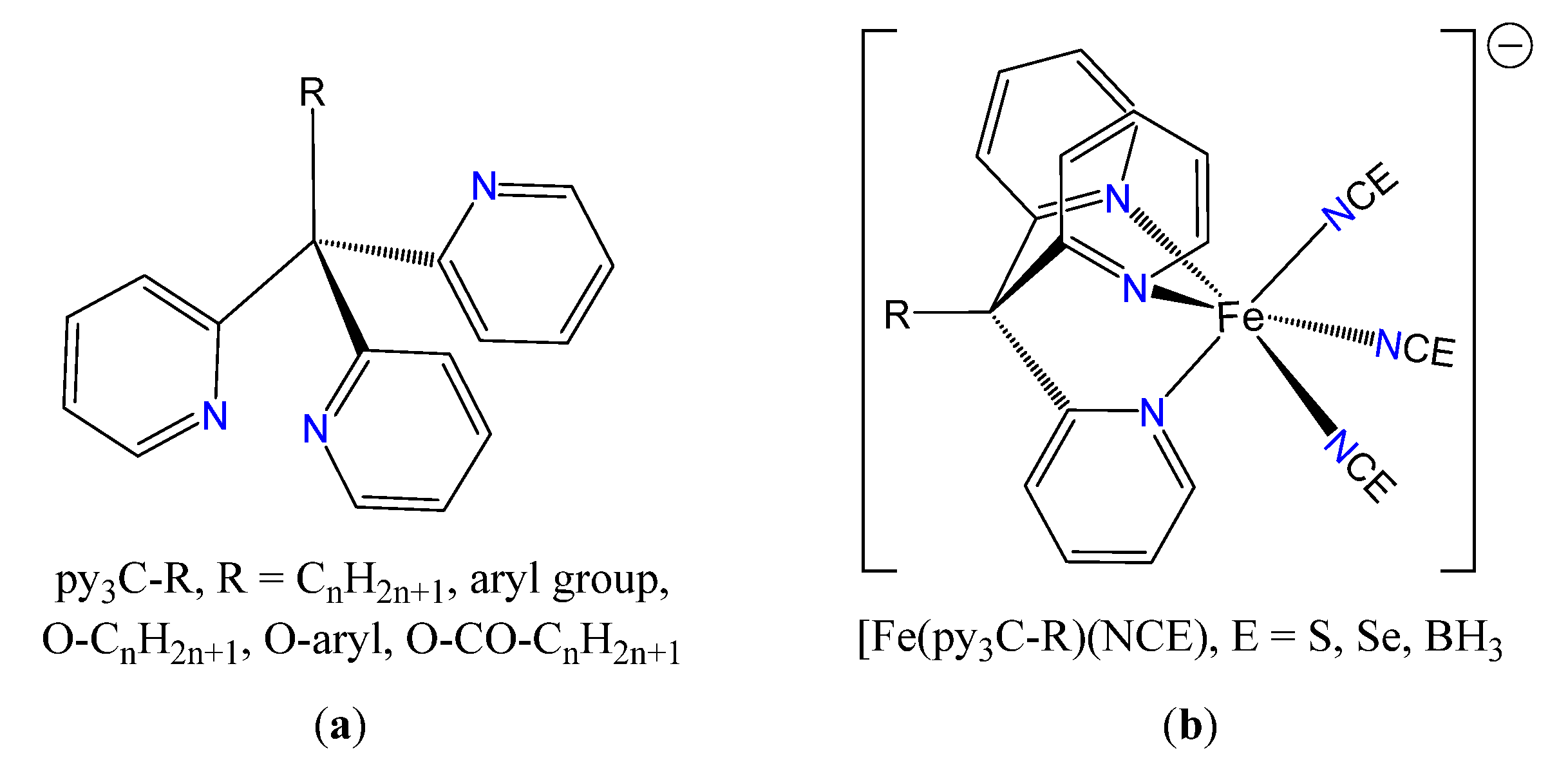
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Syntheses
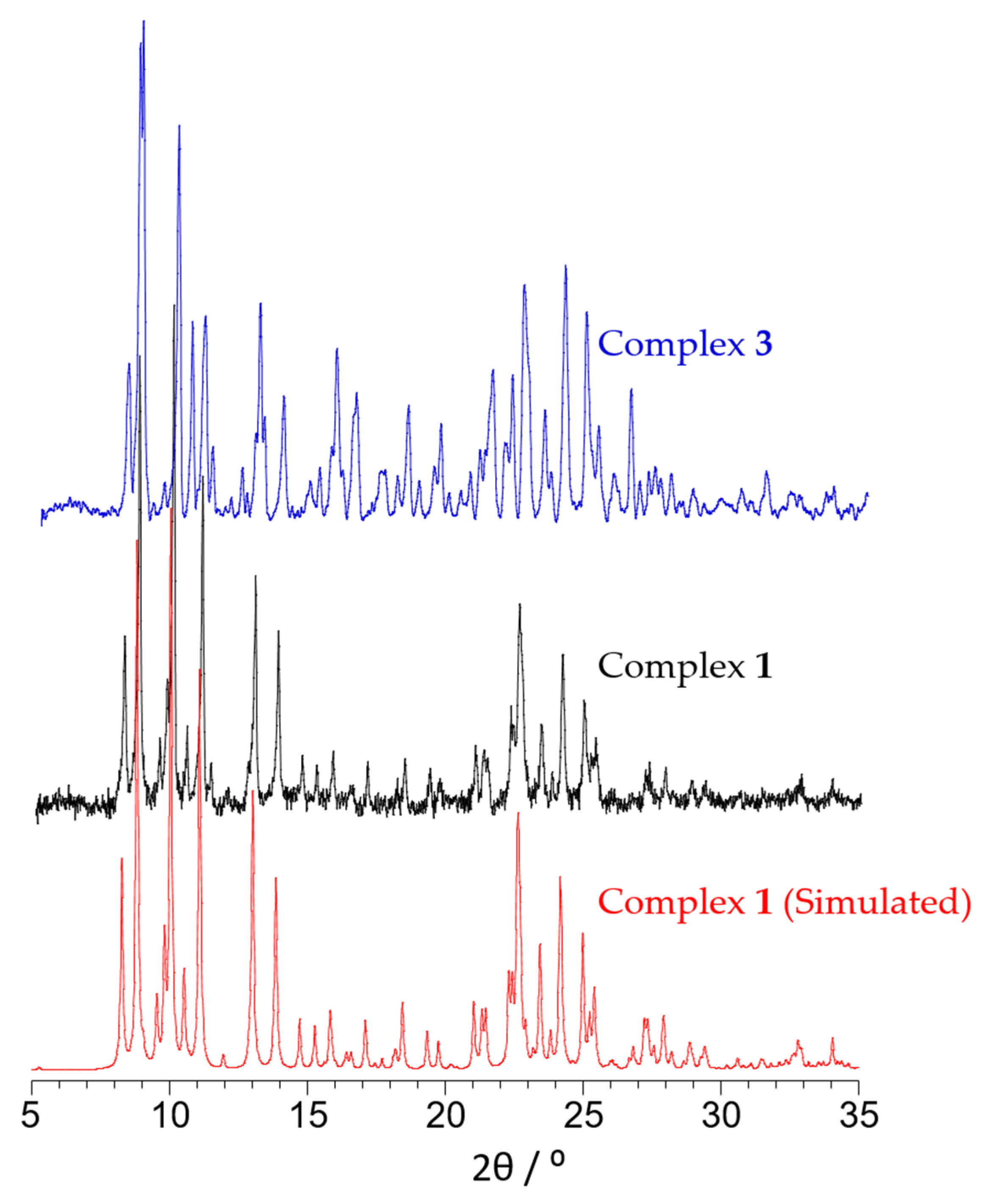
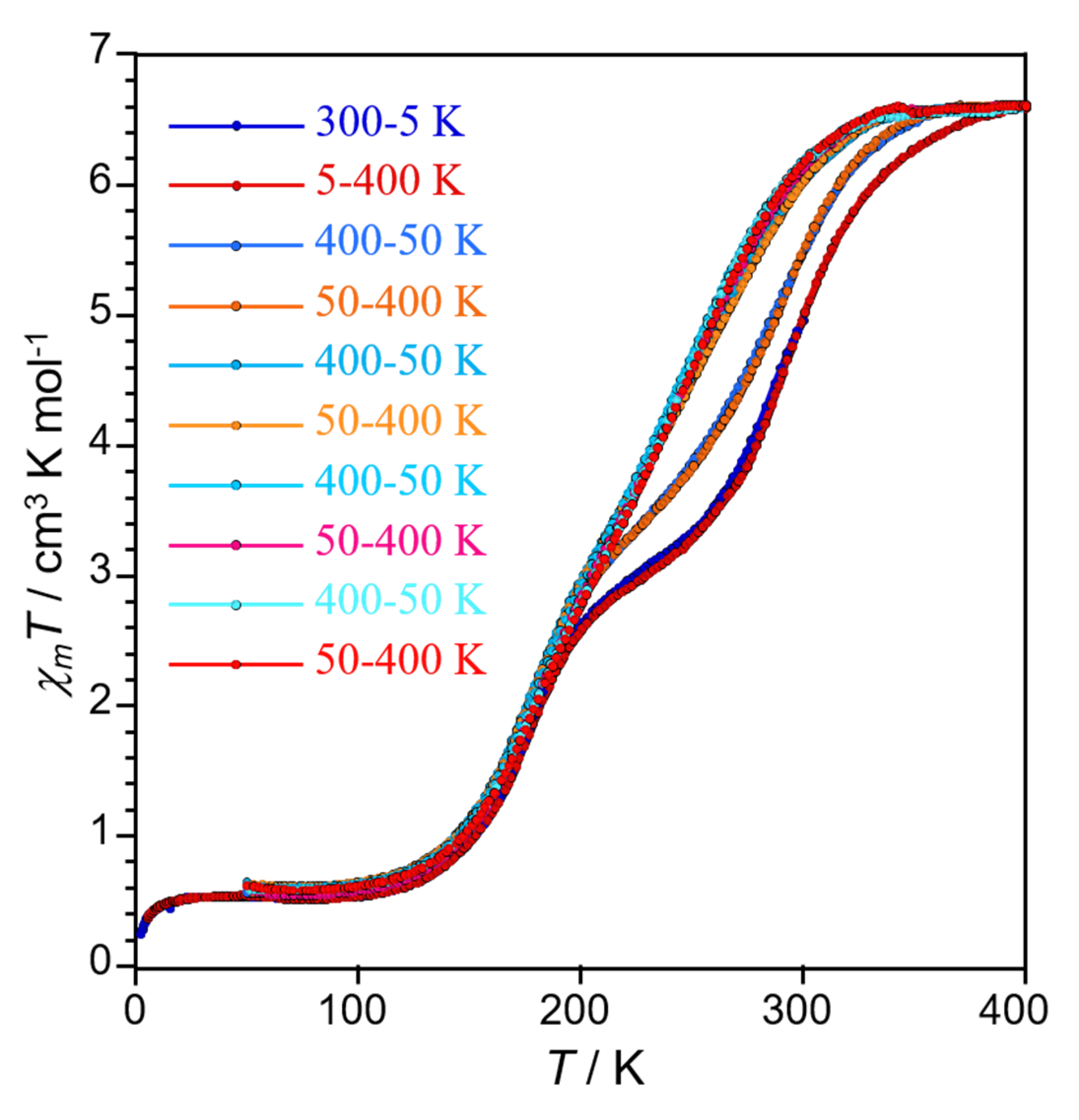
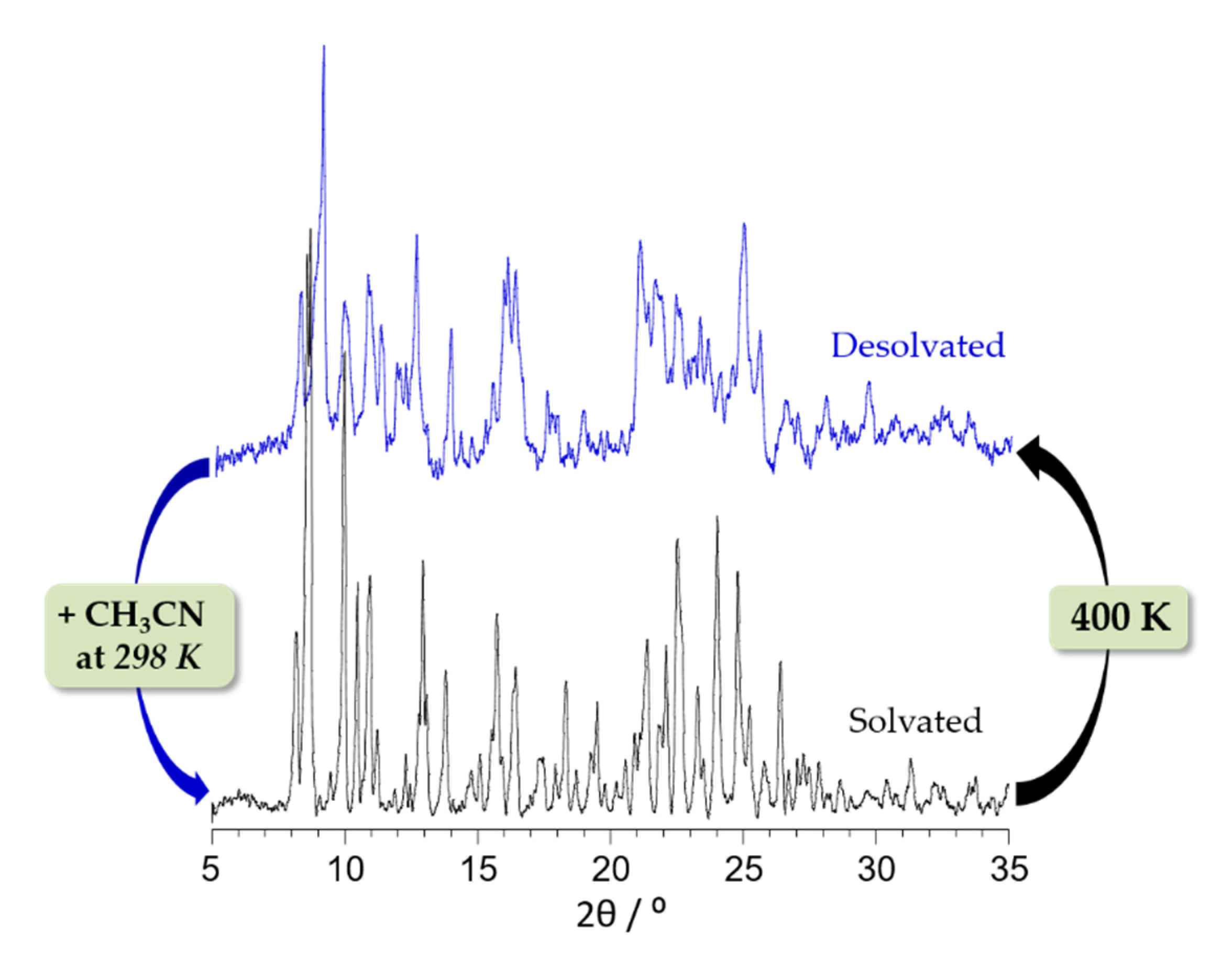
2.2. Structural Characterization and Magnetic Properties
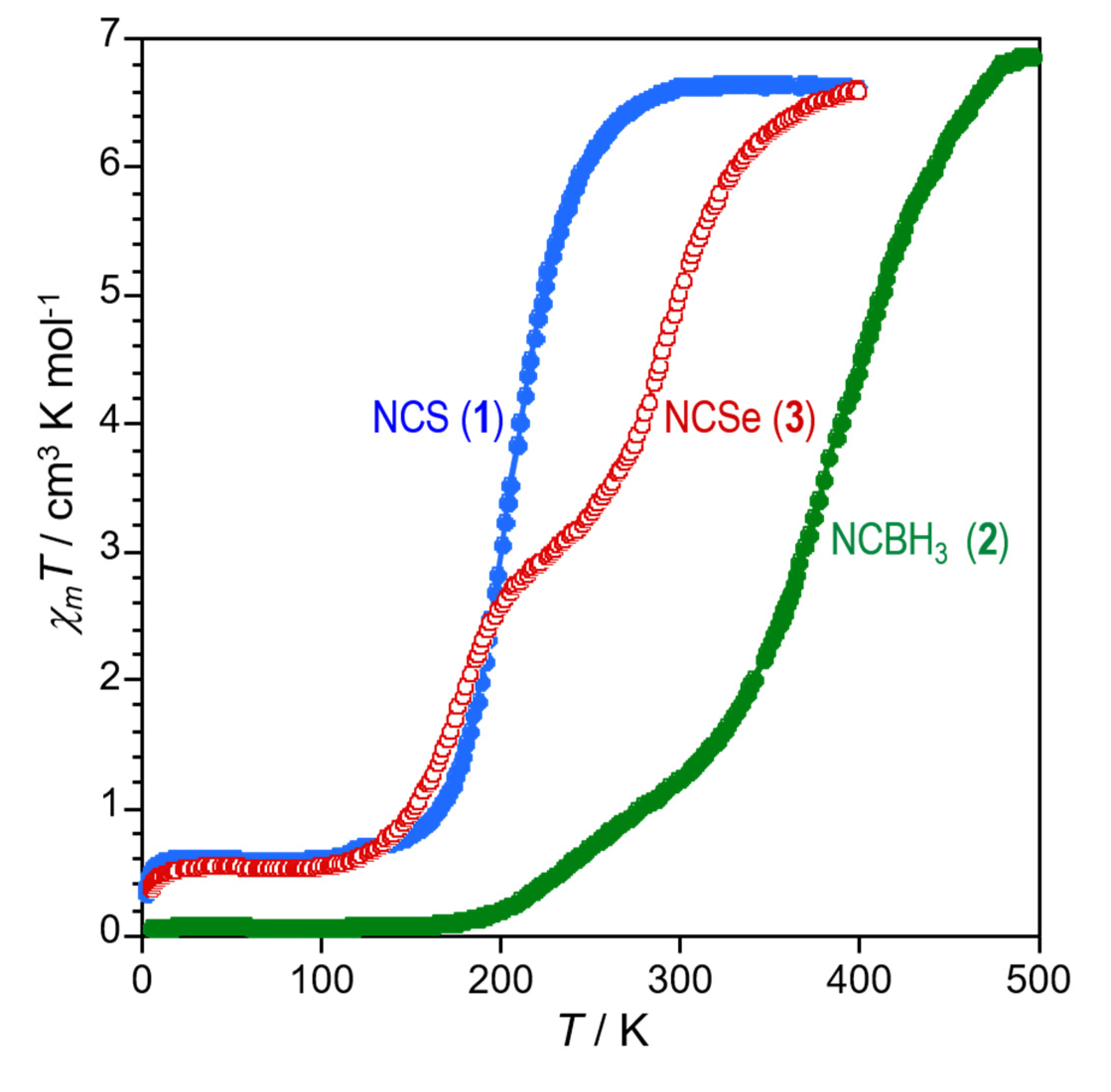
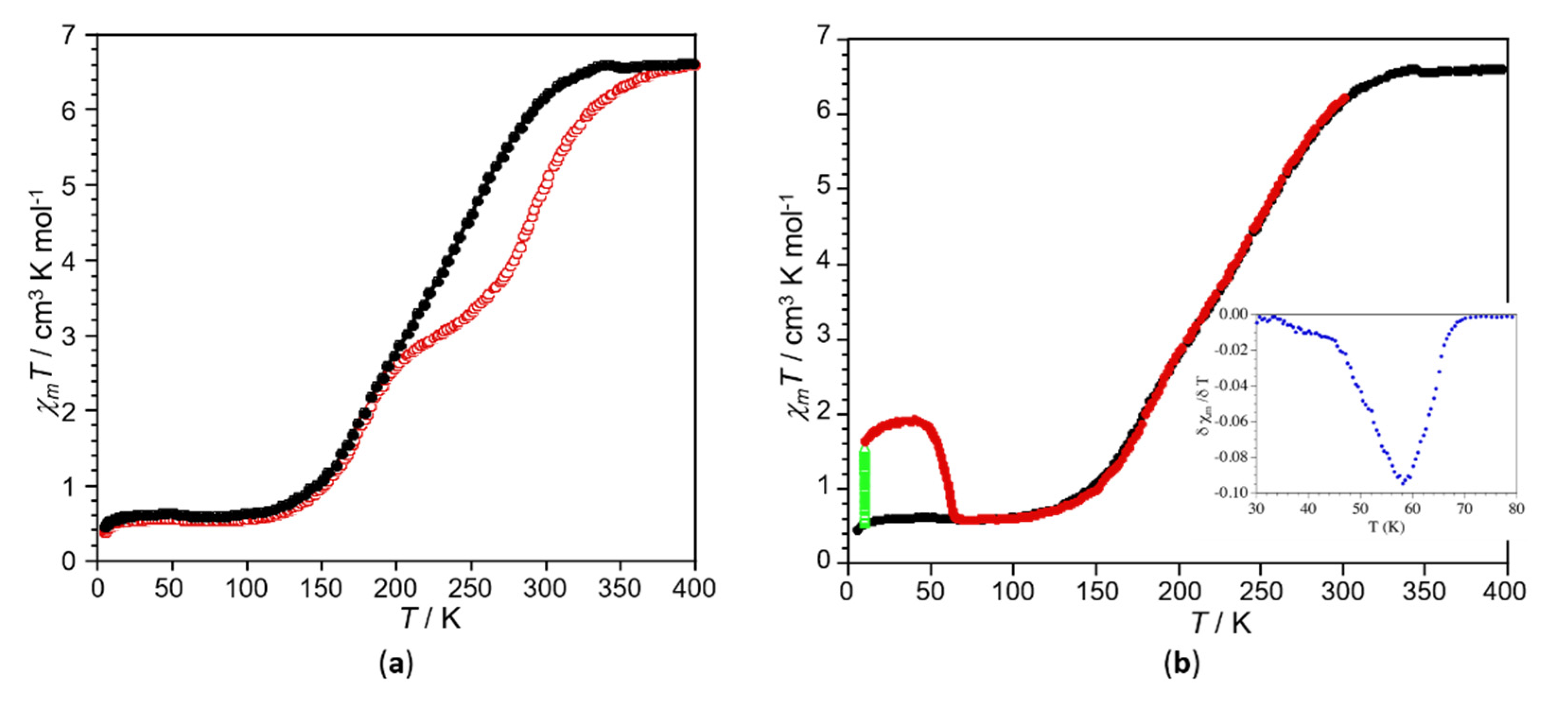
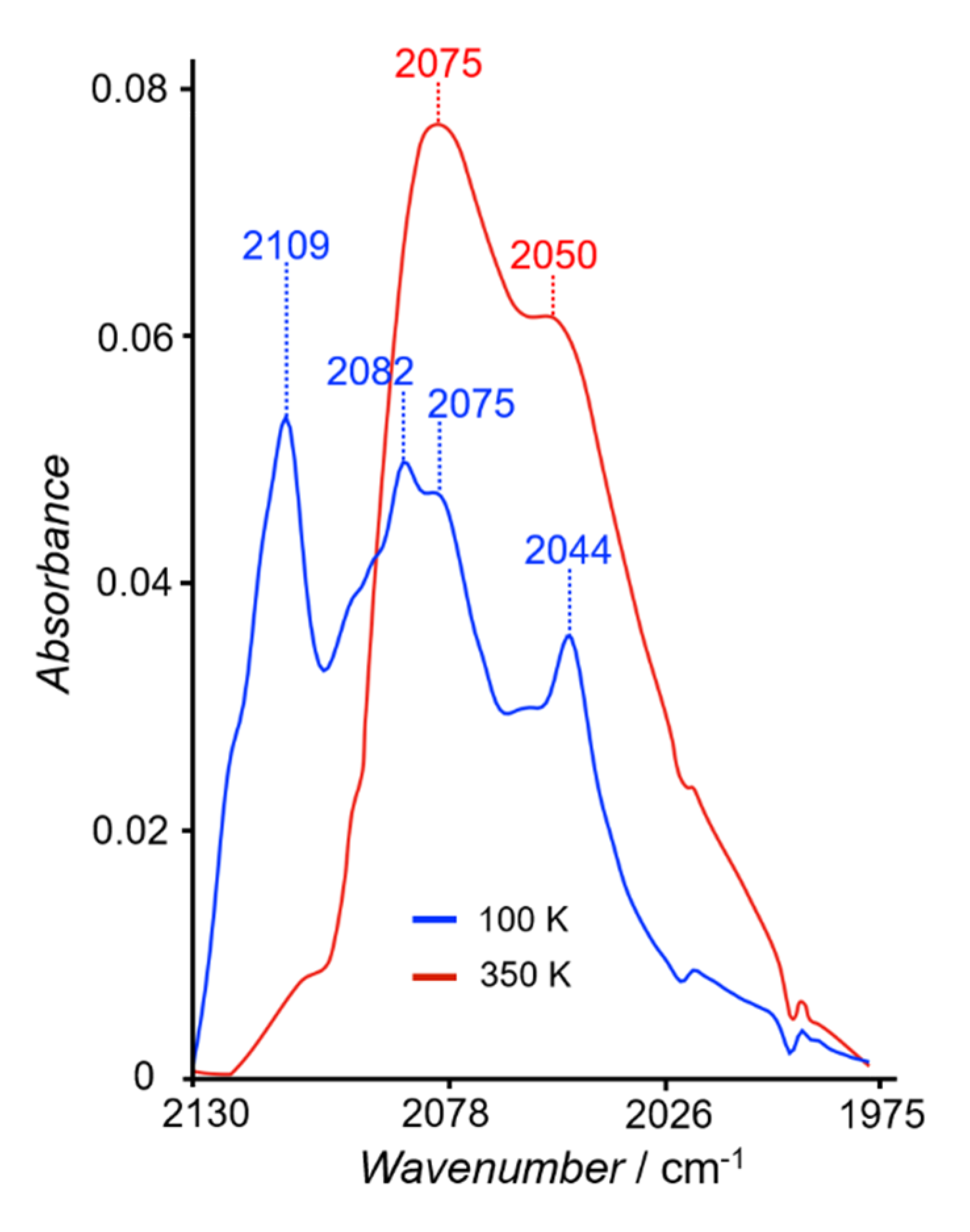
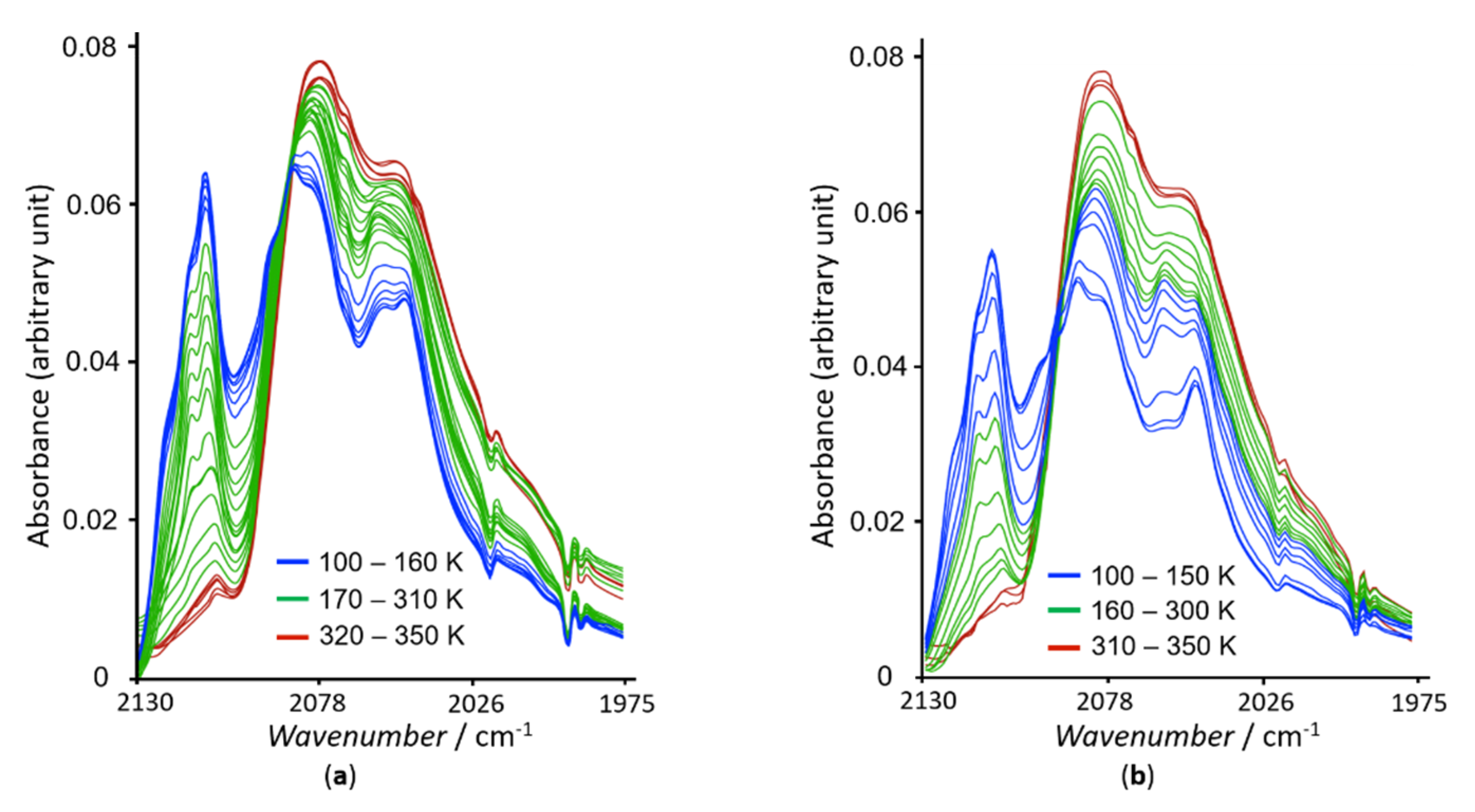
2.3. Variable Temperature Magnetic Properties and Infrared Spectroscopy
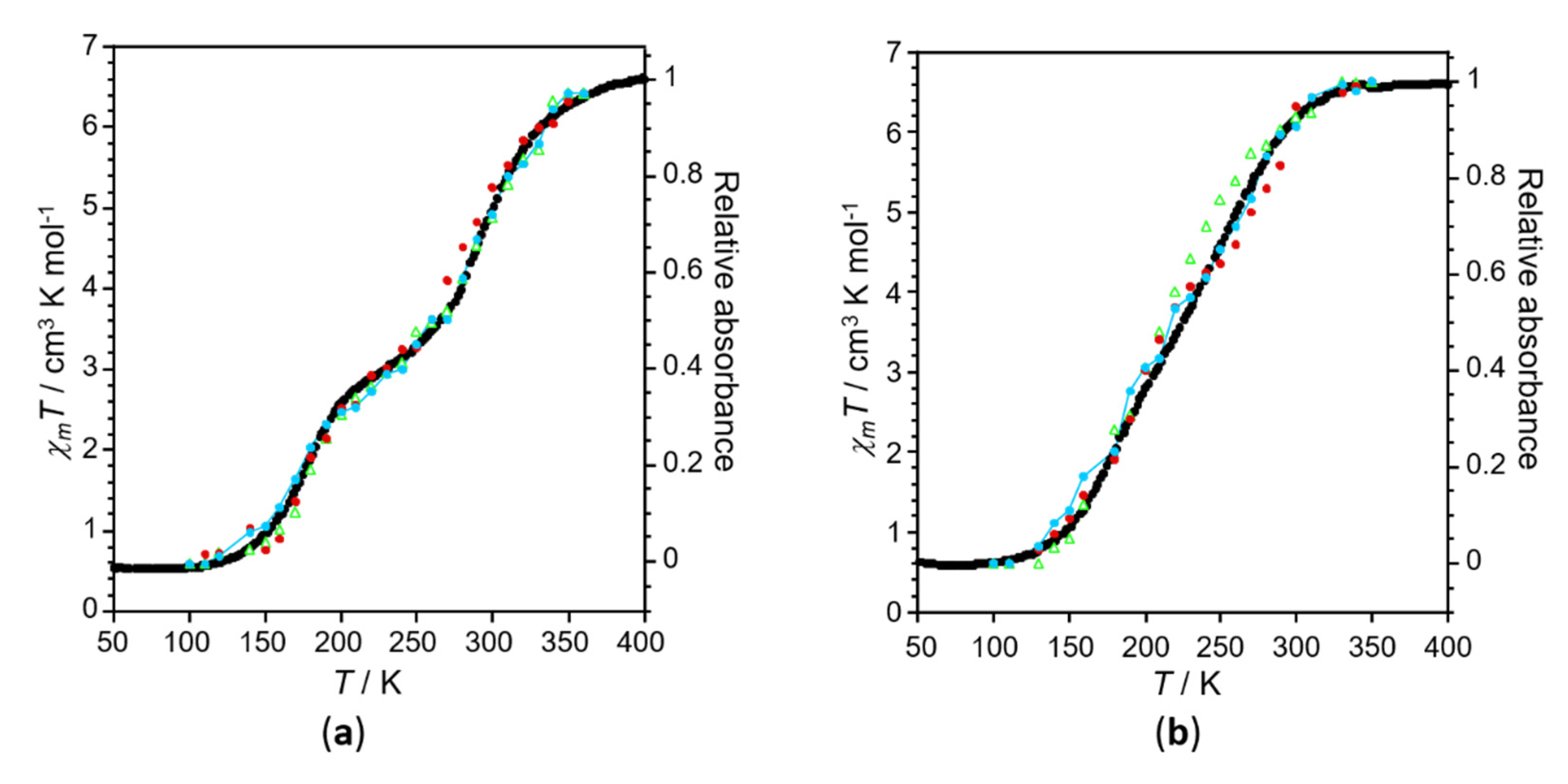
2.4. Magneto-Spectroscopic Relationships
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Starting Materials
3.2. Synthesis of [Fe(py3C-OEt)2][Fe(py3C-OEt)(NCSe)3]2·2CH3CN (3)
3.3. Characterization of the Materials
3.4. Magnetic Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cobo, S.; Molnár, G.; Real, J.-A.; Bousseksou, A. Multilayer Sequential Assembly of Thin Films That Display Room-Temperature Spin Crossover with Hysteresis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5786–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, O.; Martinez, C.J. Spin-transition polymers: From molecular materials toward memory devices. Science 1998, 279, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Ruben, M. Sublimable Spin-Crossover Complexes: From Spin-State Switching to Molecular Devices. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 7502–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, K.S.; Kepert, C.J. Cooperativity in Spin Crossover Systems: Memory, Magnetism and Microporosity. In Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds I; Gütlich, P., Goodwin, H.A., Eds.; Topics in Current Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 233, pp. 195–228. [Google Scholar]
- Létard, J.-F.; Guionneau, P.; Goux-Capes, L. Towards Spin Crossover Applications. In Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds III; Gütlich, P., Goodwin, H.A., Eds.; Topics in Current Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 235, pp. 221–249. [Google Scholar]
- Bousseksou, A.; Molnar, G.; Salmon, L.; Nicolazzi, W. Molecular spin crossover phenomenon: Recent achievements and prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3313–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueckes, T.; Kim, K.; Joselevich, E.; Tseng, G.Y.; Cheung, C.-L.; Lieber, C.M. Carbon Nanotube-Based Nonvolatile Random Access Memory for Molecular Computing. Science 2000, 289, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galet, A.; Gaspar, A.B.; Carmen Muñoz, M.; Bukin, G.V.; Levchenko, G.; Real, J.-A. Tunable Bistability in a Three-Dimensional Spin-Crossover Sensory- and Memory-Functional Material. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 2949–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartual-Murgui, C.; Akou, A.; Thibault, C.; Molnar, G.; Vieu, C.; Salmon, L.; Bousseksou, A. Spin-crossover metal–organic frameworks: Promising materials for designing gas sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapresta-Fernandez, A.; Titos-Padilla, S.; Herrera, J.M.; Salinas-Castillo, A.; Colacio, E.; Capitan-Vallvey, L.F. Photographing the synergy between magnetic and colour properties in spin crossover material [Fe(NH2trz)3](BF4)2: A temperature sensor perspective. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linares, J.; Codjovi, E.; Garcia, Y. Pressure and temperature spin crossover sensors with optical detection. Sensors 2012, 12, 4479–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuéllar, M.P.; Lapresta-Fernández, A.; Herrera, J.M.; Salinas-Castillo, A.; del Carmen Pegalajar, M.; Titos-Padilla, S.; Colacio, E.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F. Thermochromic sensor design based on Fe(II) spin crossover/polymers hybrid materials and artificial neural networks as a tool in modelling. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 208, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Jimenez, S.; Feltham, H.L.C.; Brooker, S. Non-Porous Iron(II)-Based Sensor: Crystallographic Insights into a Cycle of Colorful Guest-Induced Topotactic Transformations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15067–15071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaicha, B.; Van Do, K.; Yangui, A.; Pittala, N.; Lusson, A.; Sy, M.; Bouchez, G.; Fourati, H.; Gómez-García, C.J.; Triki, S.; et al. Interplay between Spin-Crossover and Luminescence in a Multifunctional Single Crystal Iron(II) complex: Towards a New Generation of Molecular Sensors. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 6791–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halcrow, M.A. (Ed.) Spin-Crossover Materials, Properties and Applications; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, H.; Hrudka, J.J.; Igimbayeva, D.; Lawson Daku, L.M.; Shatruk, M. A Simple Approach for Predicting the Spin State of Homoleptic Fe(II) Tris-diimine Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6437–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittala, N.; Thétiot, F.; Charles, C.; Triki, S.; Boukheddaden, K.; Chastanet, G.; Marchivie, M. An unprecedented trinuclear FeII triazole-based complex exhibiting a concerted and complete sharp spin transition above room temperature. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 8356–8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatruk, M.; Phan, H.; Chrisostomo, B.A.; Suleimenova, A. Symmetry-breaking structural phase transitions in spin crossover complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 289–290, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajj, F.; Sebki, G.; Patinec, V.; Marchivie, M.; Triki, S.; Handel, H.; Yefsah, S. Macrocycle-based spin-crossover materials. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 10416–10423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setifi, F.; Milin, E.; Charles, C.; Thétiot, F.; Triki, S.; Gómez-García, C.G. Spin Crossover Iron(II) Coordination Polymer Chains: Syntheses, Structures, and Magnetic Characterizations of [Fe(aqin)2(μ-M(CN)4)] (M = Ni(II), Pt(II), aqin = Quinolin-8-amine). Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Ooidemizu, M.; Ikuta, Y.; Osa, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Iijima, S.; Kojima, M.; Dahan, F.; Tuchagues, J.-P. Interlayer Interaction of Two-Dimensional Layered Spin Crossover Complexes [FeIIH3LMe][FeIILMe]X (X− = ClO4−, BF4−, PF6−, AsF6−, and SbF6−; H3LMe = Tris[2-(((2-methylimidazol-4-yl)methylidene)amino)ethyl]amine). Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 8406–8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, V.; Sáenz de Pipaón, C.; Maldonado-Illescas, P.; Waerenborgh, J.C.; Martin, E.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Galán-Mascarós, J.-R. Easy Excited-State Trapping and Record High TTIESST in a Spin-Crossover Polyanionic Fe(II) Trimer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11924–11927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirosawa, N.; Oso, Y.; Ishida, T. Spin crossover and light-induced excited spin-state trapping observed for an iron (II) complex chelated with tripodal tetrakis(2-pyridyl) methane. Chem. Lett. 2012, 41, 716–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Ishida, T. Spin-crossover thermal hysteresis and light-induced effect on iron (II) complexes with tripodal tris (2-pyridyl) methanol. Polyhedron 2015, 85, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Ishida, T. Heating-rate dependence of spin-crossover hysteresis observed in an iron (II) complex having tris (2-pyridyl) methanol. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 7784–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Kaneto, T.; Yamasaki, M. An iron(II) complex tripodally chelated with 1,1,1-tris(pyridine-2-yl)ethane showing room-temperature spin-crosssover behaviour. Acta Cryst. Sect. C 2016, 72, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiro, A.; Some, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ishida, T. Iron(II) and 1,1,1-Tris(2-pyridyl)nonadecane Complex Showing an Order–Disorder-Type Structural Transition and Spin-Crossover Synchronized over Both Conformers. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 7672–7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuza, E.; Benmansour, S.; Cosquer, N.; Conan, F.; Pillet, S.; Gómez-García, C.J.; Triki, S. Spin Cross-Over (SCO) Anionic Fe(II) Complexes Based on the Tripodal Ligand Tris(2-pyridyl)ethoxymethane. Magnetochemistry 2020, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuza, E.; Mekuimemba, C.D.; Cosquer, N.; Conan, F.; Pillet, S.; Chastanet, C.; Triki, S. Spin Crossover and High-Spin State in Fe(II) Anionic Polymorphs Based on Tripodal Ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 6536–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.L.; Faller, J.W. Preparation and Reactions of the C3v Ligand Tris(2-pyridyl)methane and Its Derivatives. Inorg. Chem. 1982, 21, 3119–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, R.T.; Stack, T.D.P. Synthesis and Characterization of a Family of Systematically Varied Tris(2-pyridyl)methoxymethane Ligands: Copper(I) and Copper(II) Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 6615–6629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmansour, S.; Gómez-Claramunt, P.; Gómez-García, C.G. Effects of water removal on the structure and spin-crossover in an anilato-based compound. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 123904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmaczewski, R.; Bamiduro, F.; Shahid, N.; Cespedes, O.; Halcrow, M.A. Structural Transformations and Spin-Crossover in [FeL2]2+ Salts (L=4-{tert-Butylsulfanyl}-2,6-di{pyrazol-1-yl}pyridine): The Influence of Bulky Ligand Substituents. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 2082–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.J.; Roy, S.; Yadav, J.; Zeller, M.; Konar, S. Solvent-Induced Reversible Spin-Crossover in a 3D Hofmann-Type Coordination Polymer and Unusual Enhancement of the Lattice Cooperativity at the Desolvated State. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 13024–13028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phonsri, W.; Davies, C.G.; Jameson, G.N.L.; Moubaraki, B.; Murray, K.S. Spin Crossover, Polymorphism and Porosity to Liquid Solvent in Heteroleptic Iron(III) {Quinolylsalicylaldimine/Thiosemicarbazone-Salicylaldimine} Complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennartson, A.; Southon, P.; Sciortino, N.F.; Kepert, C.J.; Frandsen, C.; Mørup, S.; Piligkos, S.; McKenzie, C. Reversible Guest Binding in a Non-Porous FeII Coordination Polymer Host Toggles Spin Crossover. J. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 16066–16072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, T.D.; Tuna, F.; Malkin, T.L.; Kilner, C.A.; Halcrow, M.A. An iron(ii) complex exhibiting five anhydrous phases, two of which interconvert by spin-crossover with wide hysteresis. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-León, M.; Coronado, E.; Giménez-López, M.C.; Romero, F.M. Structural, Thermal, and 52Magnetic Study of Solvation Processes in Spin-Crossover [Fe(bpp)2][Cr(L)(ox)2]2·nH2O Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 11266–11276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayami, S.; Gu, Z.-Z.; Yoshiki, H.; Fujishima, A.; Sato, O. Iron(III) Spin-Crossover Compounds with a Wide Apparent Thermal Hysteresis around Room Temperature. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 11644–11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, Y.; Van Koningsbruggen, P.J.; Codjovi, E.; Lapouyade, R.; Kahn, O.; Rabardel, L. Non-classical FeII spin-crossover behaviour leading to an unprecedented extremely large apparent thermal hysteresis of 270 K: Application for displays. J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 857–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorai, M.; Seki, S. Phonon coupled cooperative low-spin 1A1 ↔ high-spin 5T2 transition in [Fe(phen)2(NCS)2] and [Fe(phen)2(NCSe)2] crystals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1974, 35, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, G.; Reiher, M.; Le Guennic, B.; Leibold, M.; Schindler, S.; Heinemann, F.W.; Schneider, S. Investigation of the low-spin to high-spin transition in a novel [Fe(pmea)(NCS)2] complex by IR and Raman spectroscopy and DFT calculations. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2006, 37, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Jung, Y.M.; Sarker, S.; Lee, J.-J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, K.; Oh, J.J.; Joo, S.-W. Temperature-dependent infrared spectrum of (Bu4N)2[Ru(dcbpyH)2(NCS)2] on nanocrystalline TiO2 surfaces. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 2010, 94, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, V.; Fernandes, J.-R. An Infrared Spectroscopic Study of the Low-Spin-High-spin transition in in FexMn1−x(Phen)2(NCS)2: A Composition-Induced Change in the Order of the Spin-State Transition. Chem. Phys. Let. 1990, 167, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, G.; Thomas, J.M.; Varma, V.; Kulkani, G.U.; Rao, C.N.R. An investigation of the first-order spin-state transition in the Fe(phen)2(NCS)2 EXAFS and infrared spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1996, 251, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, E.; de Waal, D.; Heyns, A.M. The spin-transition complexes [Fe(Htrz)3](ClO4)2 and [Fe(NH2trz)3](ClO4)2 I. FT-IR spectra of a low pressure and a low temperature phase transition. Mater. Res. Bull. 2000, 35, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, P.; Pillet, S.; Bendeif, E.-E.; Carteret, C.; Bouazaoui, M.; El Hamzaoui, H.; Capoen, B.; Salmon, L.; Hébert, S.; Ghanbaja, J.; et al. Room temperature bistability with wide thermal hysteresis in a spin crossover silica nanocomposite. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 1933–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, G.A.; Berry, J.F. Diamagnetic corrections and Pascal’s constants. J. Chem. Educ. 2008, 85, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
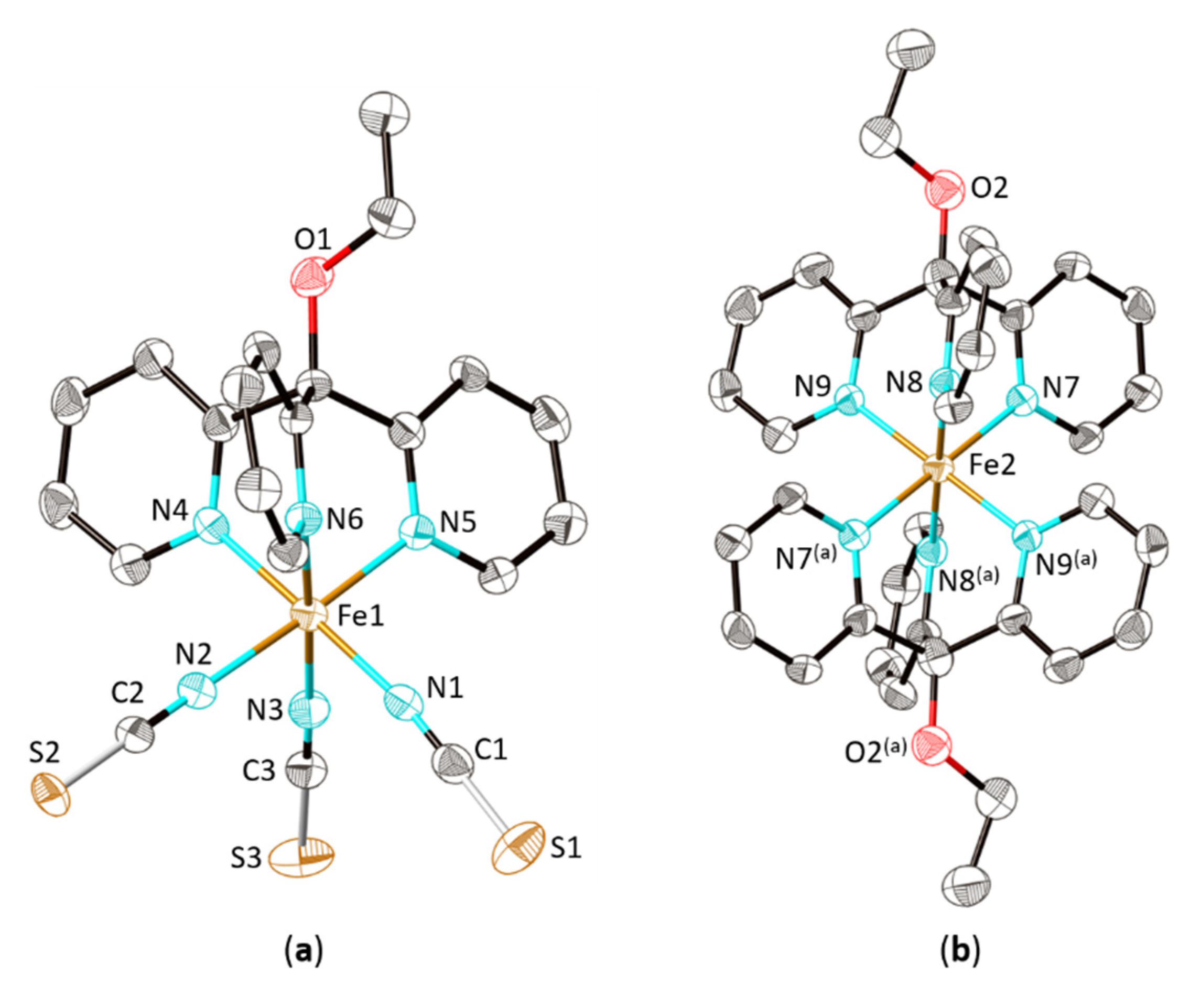

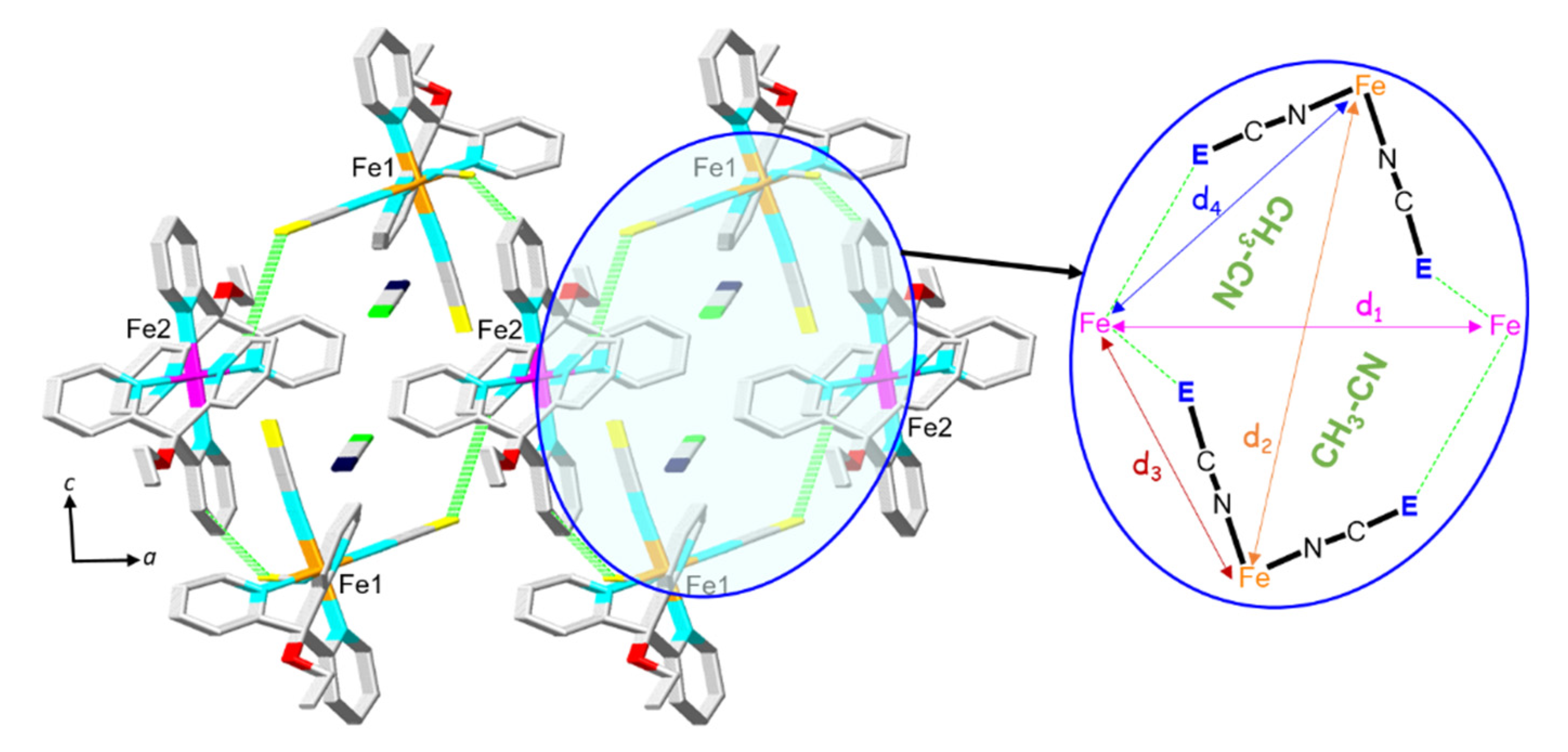
| 2 (E = BH3) | 1 (E = S) | 3 (E = Se) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| dN….E (relative increase) | 2.72 Å | 2.80 Å (+2.9 %) | 2.94 Å (+8.1 %) |
| T/Spin State | 200 K/LS | 100 K/LS | ― |
| d1 (relative increase) | 12.757 | 14.774 Å (+15.8%) | ― |
| d2 (relative increase) | 11.683 Å | 12.653 Å (+8.3%) | ― |
| d3 (relative increase) | 8.146 Å | 10.481 Å (+28.6%) | ― |
| d4 (relative decrease) | 9.125 Å | 8.907 Å (−2.4%) | ― |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cuza, E.; Benmansour, S.; Cosquer, N.; Conan, F.; Gómez-García, C.J.; Triki, S. Solvent-Induced Hysteresis Loop in Anionic Spin Crossover (SCO) Isomorph Complexes. Magnetochemistry 2021, 7, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7060075
Cuza E, Benmansour S, Cosquer N, Conan F, Gómez-García CJ, Triki S. Solvent-Induced Hysteresis Loop in Anionic Spin Crossover (SCO) Isomorph Complexes. Magnetochemistry. 2021; 7(6):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7060075
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuza, Emmelyne, Samia Benmansour, Nathalie Cosquer, Françoise Conan, Carlos J. Gómez-García, and Smail Triki. 2021. "Solvent-Induced Hysteresis Loop in Anionic Spin Crossover (SCO) Isomorph Complexes" Magnetochemistry 7, no. 6: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7060075
APA StyleCuza, E., Benmansour, S., Cosquer, N., Conan, F., Gómez-García, C. J., & Triki, S. (2021). Solvent-Induced Hysteresis Loop in Anionic Spin Crossover (SCO) Isomorph Complexes. Magnetochemistry, 7(6), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7060075








