Green Synthesis of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: Principles of Green Chemistry and Raw Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
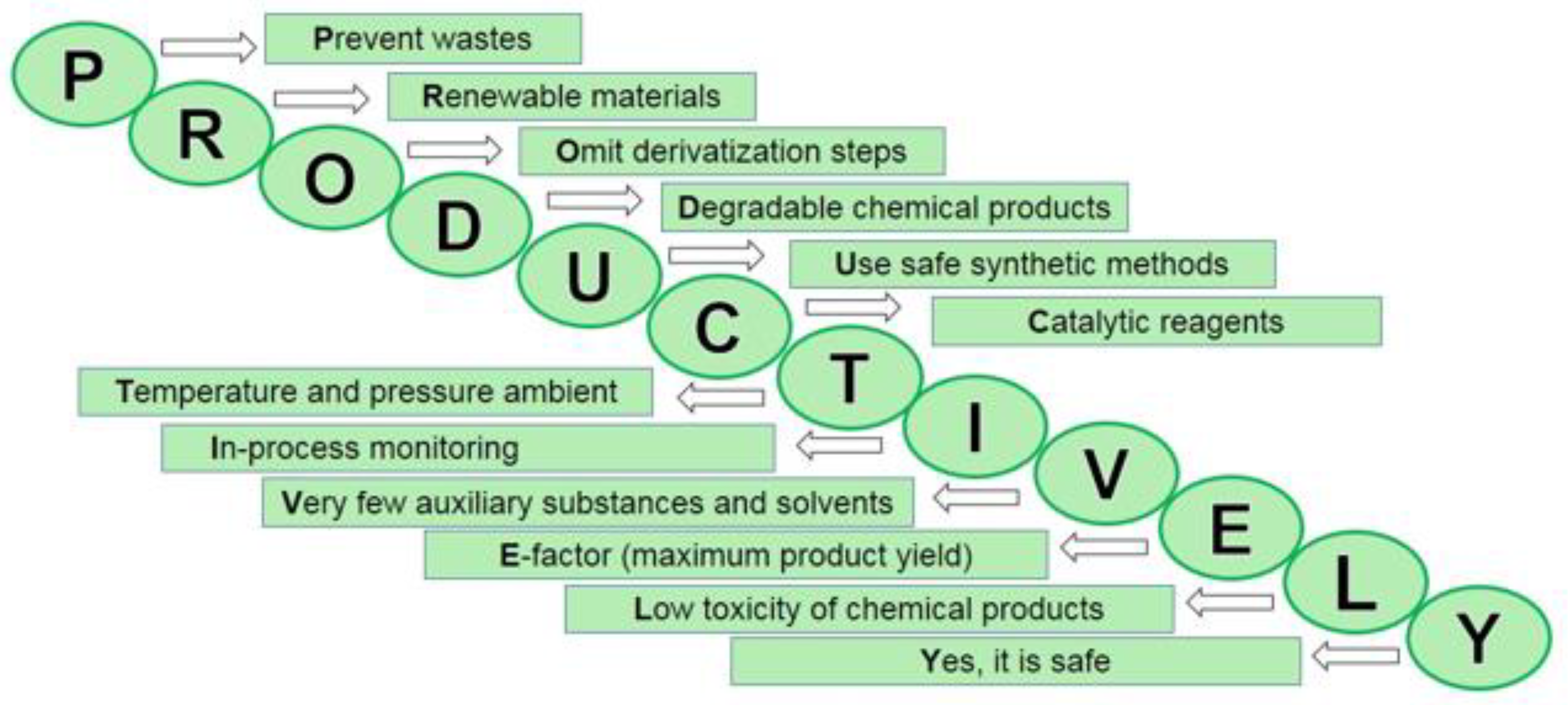
2. The Principles of “Green” Chemistry
- prevention of waste (chemical synthesis design that prevents waste rather than its disposal or utilization);
- maximum increase of components—“atom economy” (design of synthesis to maximize raw materials ratio in the final product with the least or no amount of waste);
- development of less dangerous chemical syntheses (generating and using substances with minimal or zero toxicity);
- design of safe chemicals and products (chemicals that are effective yet non-toxic);
- use of safe solvents and reaction conditions (minimize or exclude the use of solvents or other auxiliary chemicals, and if necessary—use the safest of them);
- increase energy efficiency (identify and minimize the consequences caused by using energy in chemical synthesis. Initiate chemical reactions at room temperature and pressure, if possible);
- use of renewable raw materials (sources of renewable raw materials are agricultural products or waste);
- avoidance of chemical derivatives (minimize or eliminate the use of blocking or protective groups or any temporary modifications, if possible);
- use of non-stoichiometric catalysts (minimization of waste by implementation of catalytic reactions, use of effective catalysts in small quantities that can promote the reaction repeatedly);
- design of degradable chemicals and products (non-persistent, which decompose into safe substances);
- real-time analysis of pollution (elimination or minimization of by-products through interfering with the process during synthesis);
- minimizing the possibility of accidents (such as releases, explosions and fires) through designing safer chemicals and their physical forms (solid, liquid or gaseous).
2.1. Prevention (Reducing) of Waste/by-Products
2.2. Maximum Inclusion of Reagents (Source Materials) in the Final Product
2.3. Prevention or Minimization of Harmful Products
2.4. Development of Safer Chemicals
2.5. Energy Requirements for the Chemical Synthesis
2.6. Selection of Proper Solvent
2.7. Selection of Proper Source Materials
2.8. The Use of Catalysts
2.9. Biodegradation of Obtained Products
2.10. Strengthening Analytical Methods for Controlling Harmful Compounds
2.11. Development of Production Units
3. Raw Materials for “Green” Chemistry
3.1. Transition to Renewable Raw Materials
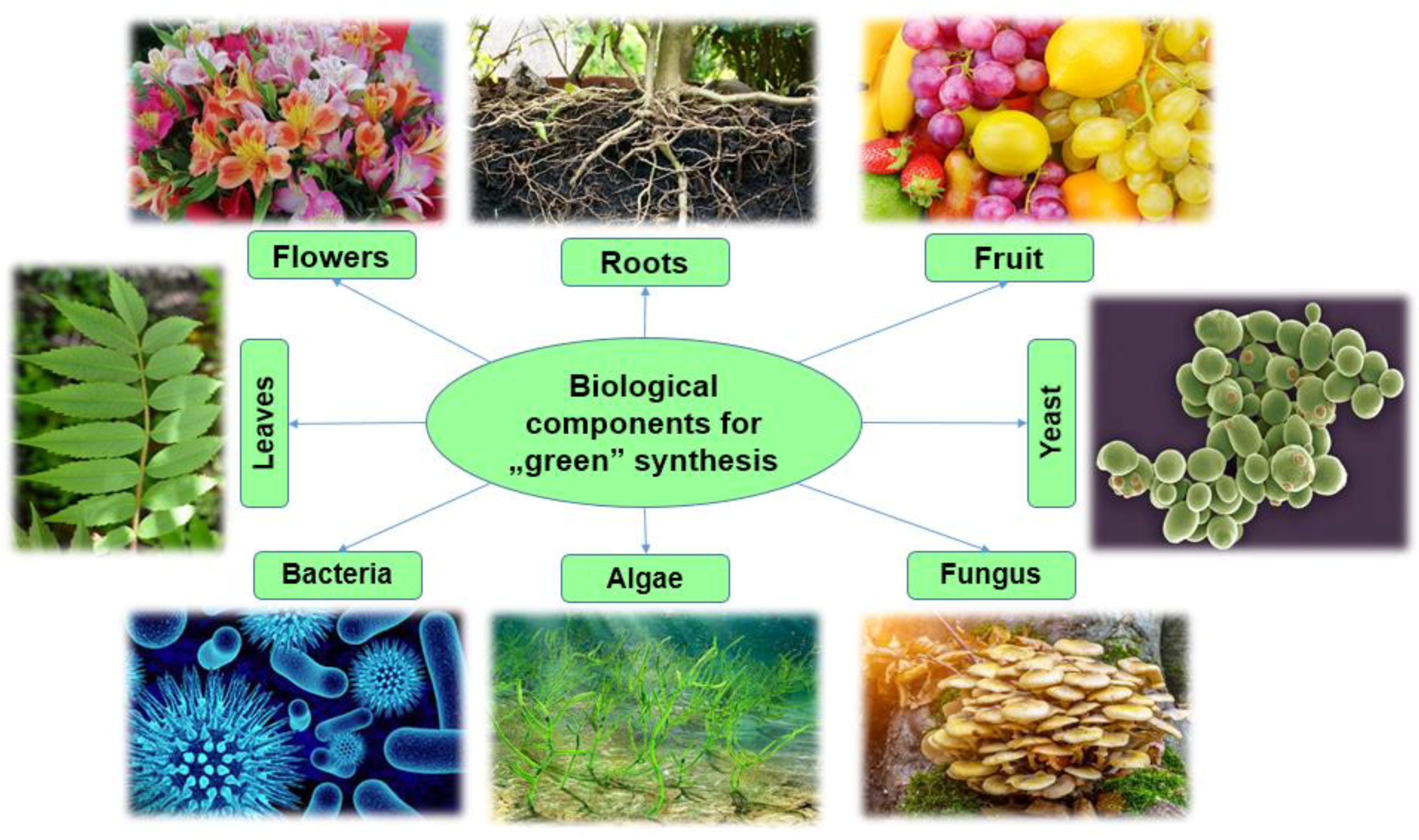
3.2. Biological Components for “Green” Synthesis
3.2.1. Bacteria
3.2.2. Fungi
3.2.3. Yeast
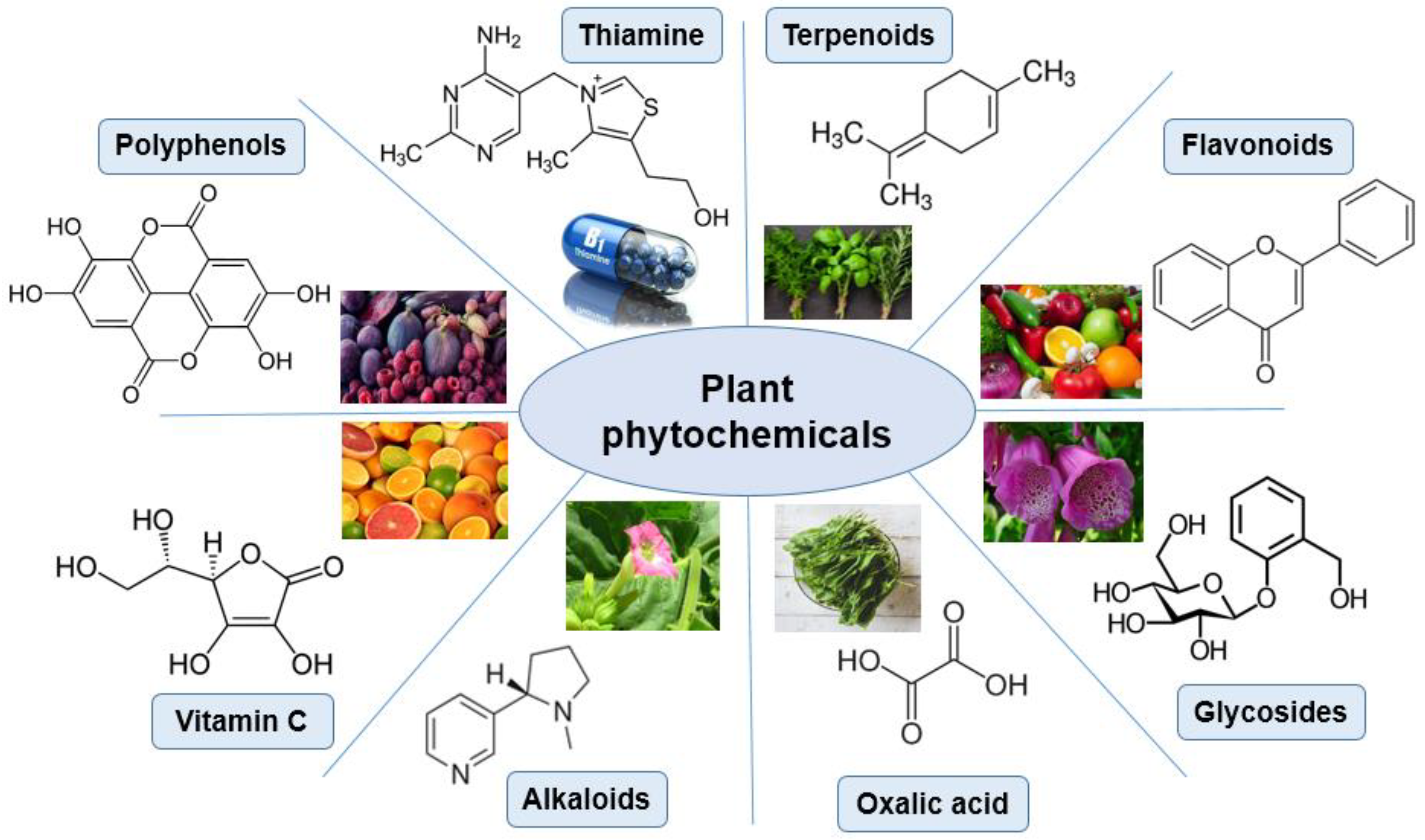
3.2.4. Plants
3.3. Solvent-Based ”Green” Synthesis”
4. “Green” Synthesis and the Use of Magnetic Nanoparticles
4.1. Effect of Magnetic Nanoparticles on Environmental Restoration
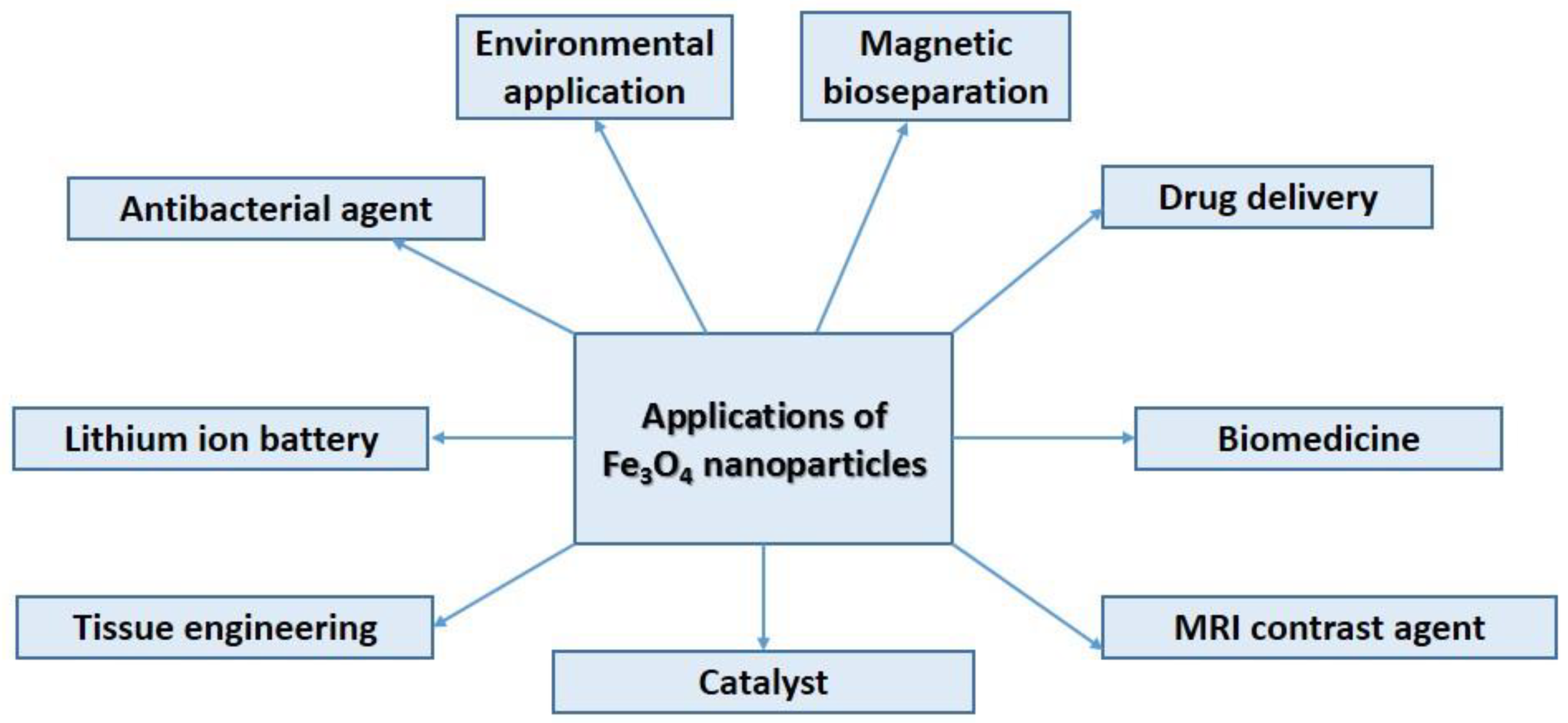
4.2. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide (Magnetite) Nanoparticles and Their Application
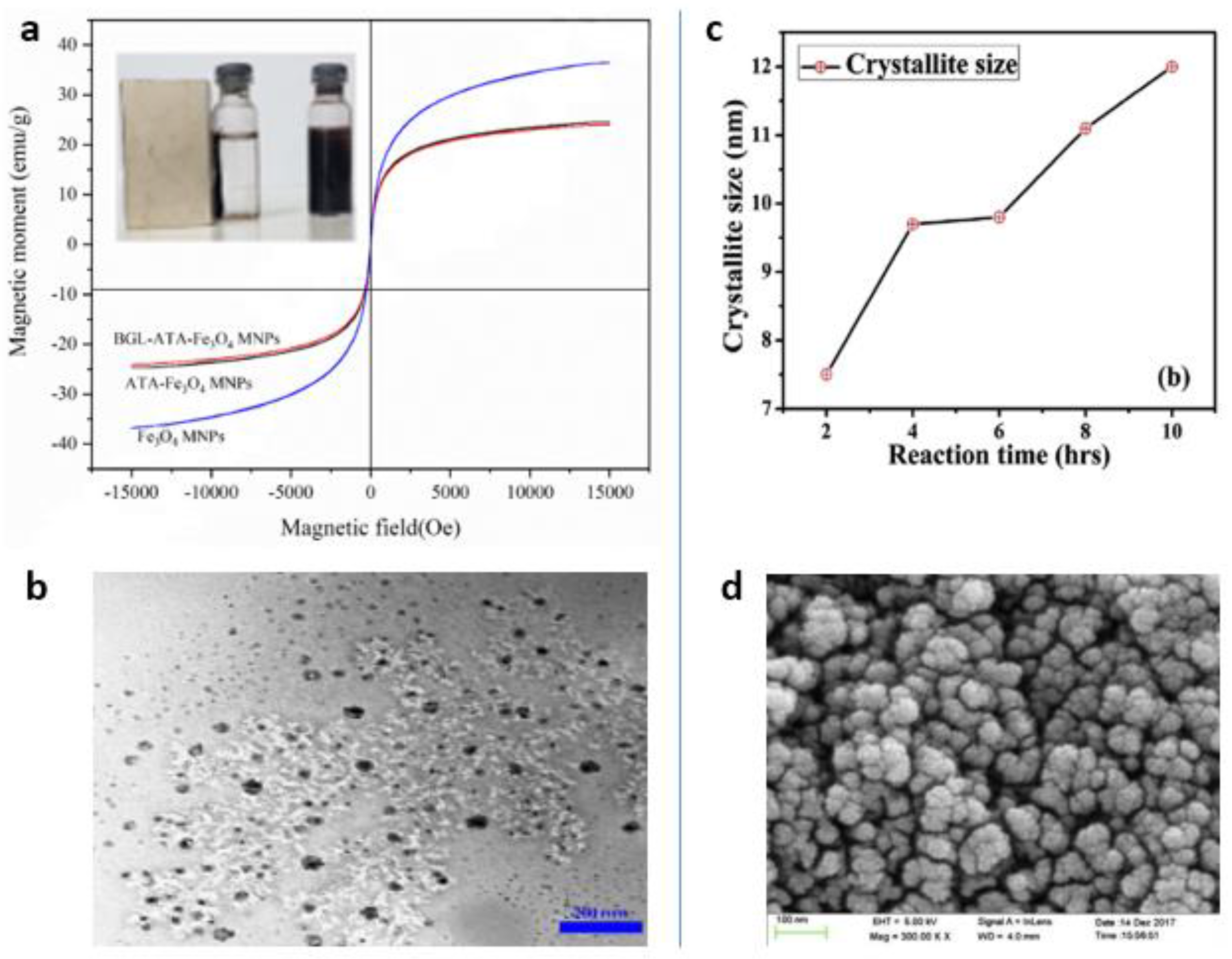
4.3. ”Green” Synthesis of Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
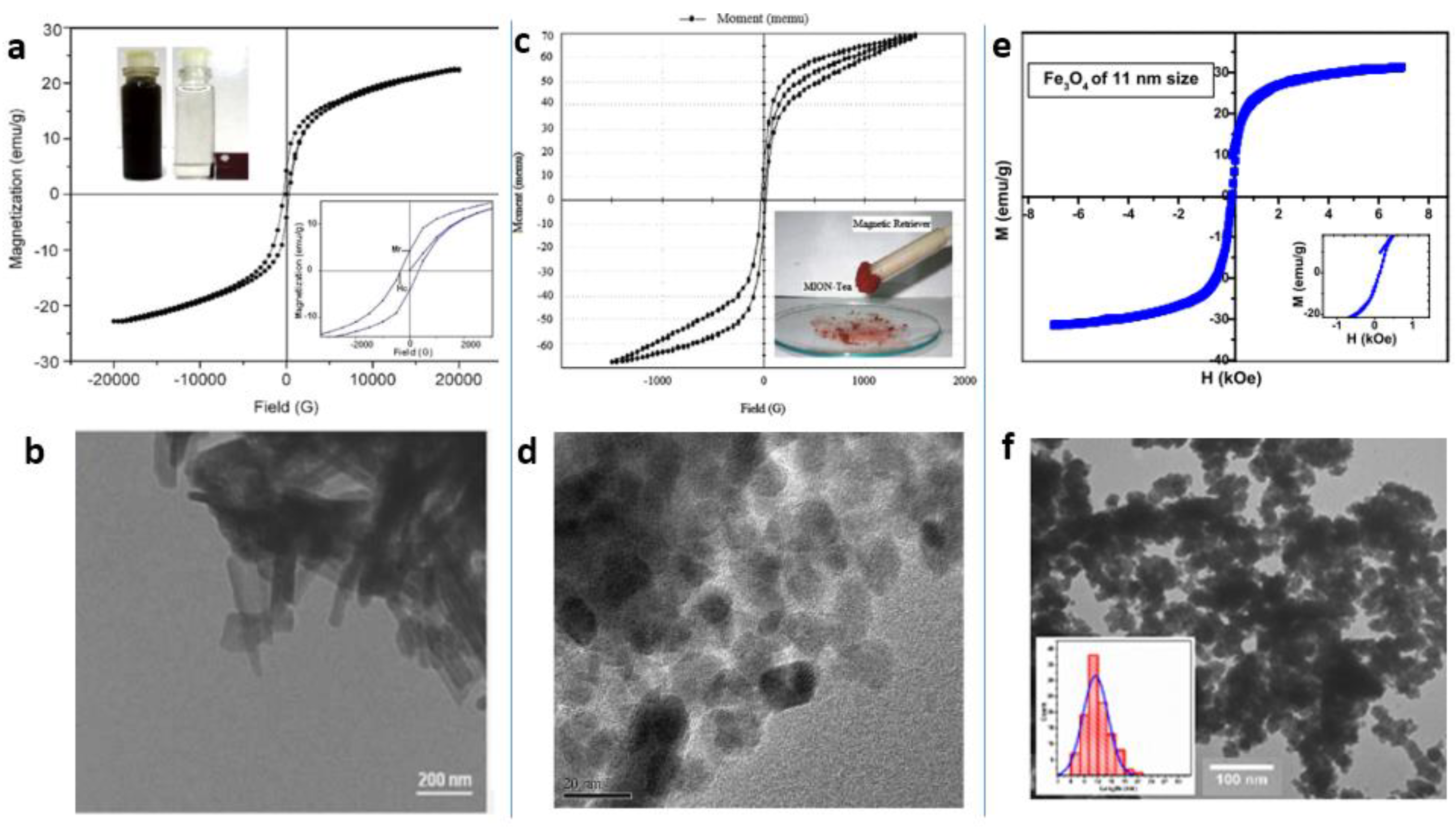
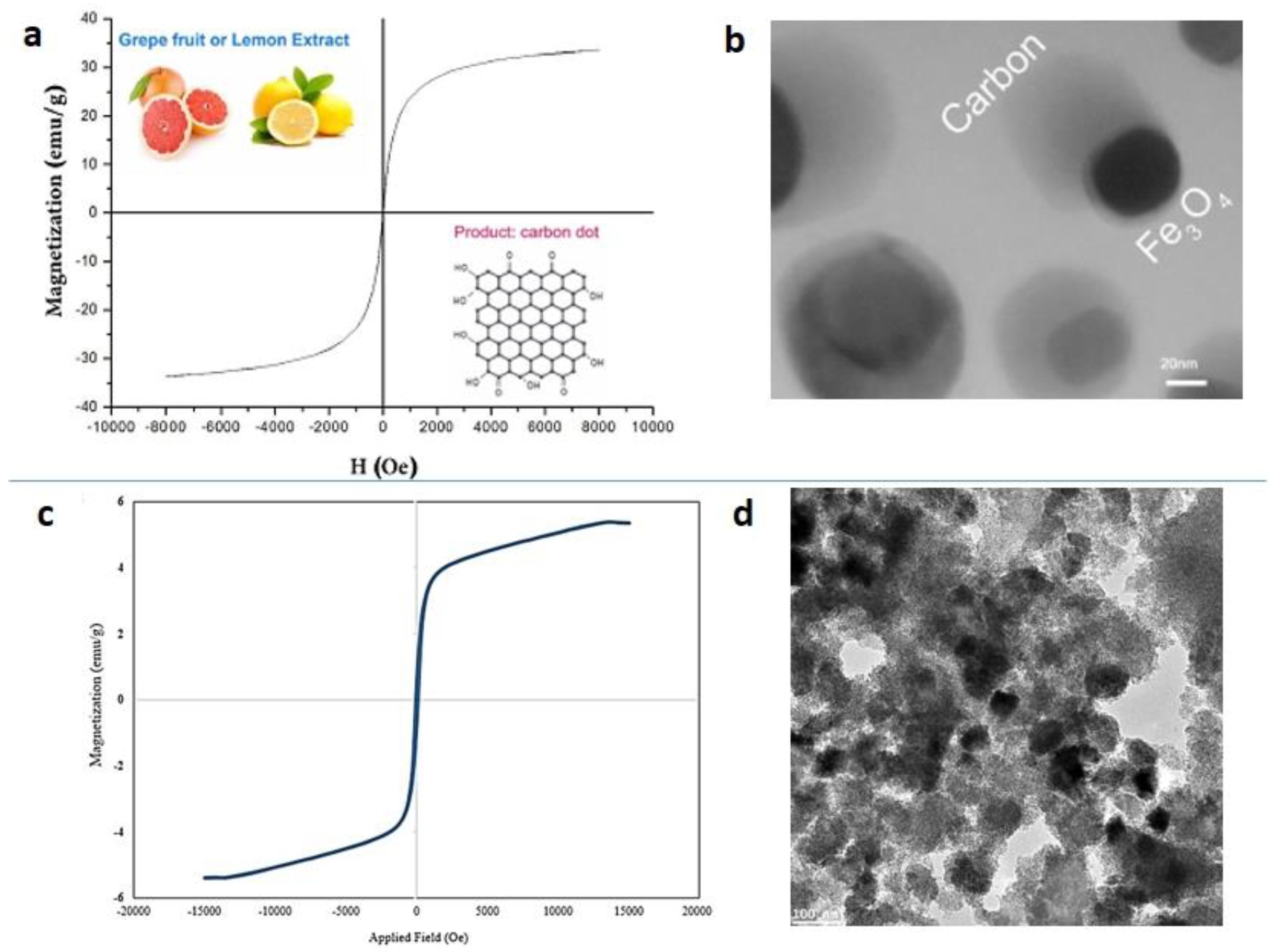
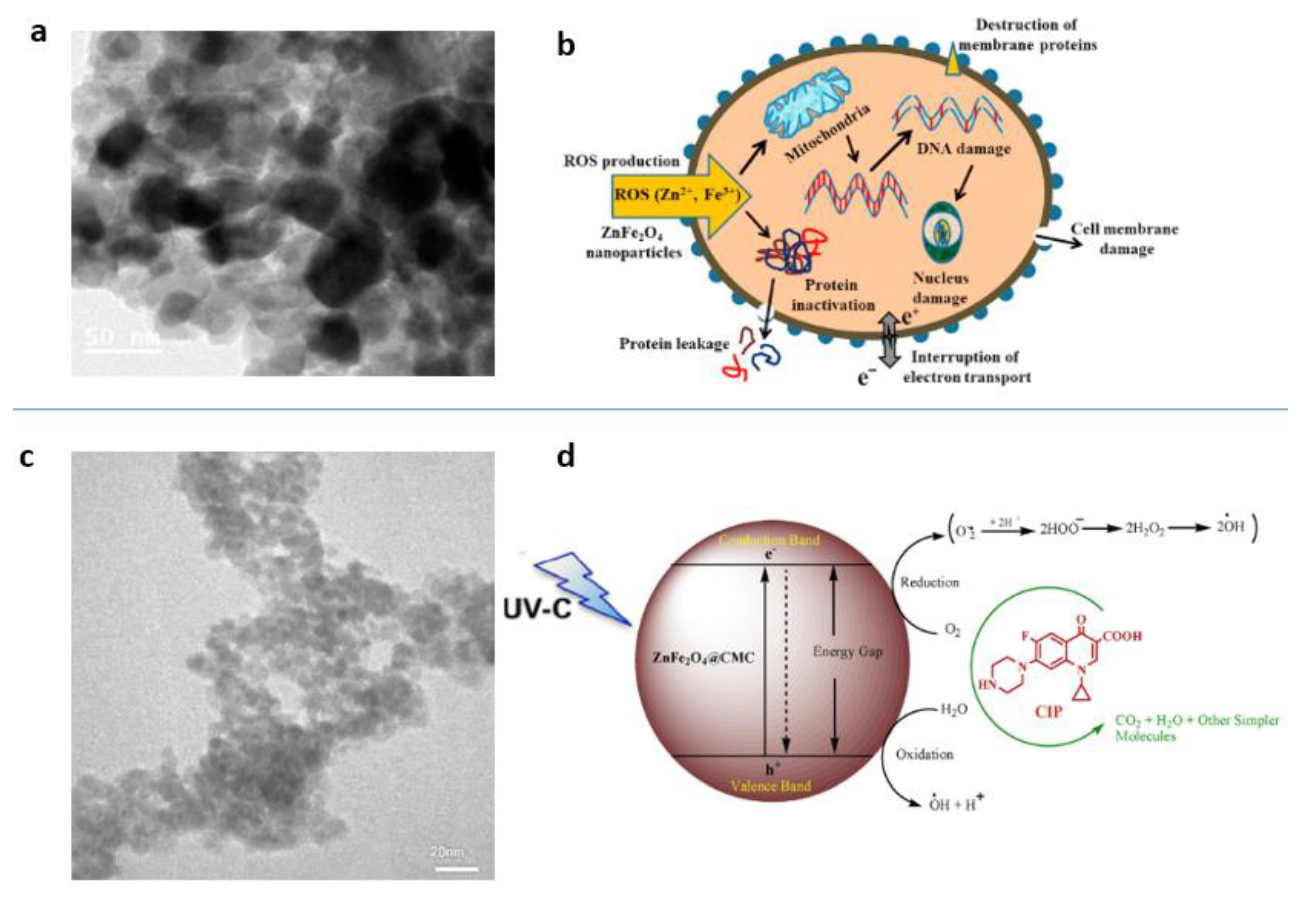
4.4. “Green” Synthesis of Spinel Magnetic Nanoparticles
5. “Green” Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles
5.1. Silver Nanoparticles

5.2. Gold Nanoparticles
5.3. Platinum Nanoparticles
5.4. Palladium Nanoparticles
6. Future Perspectives
- (1)
- to create various chemical associations, organizations and institutes, whose missions will be studying of cleaner reactions, products and processes;
- (2)
- to promote “green” chemistry among universities and research laboratories in order to develop economically sustainable technologies for clean production;
- (3)
- to introduce methods of “green” synthesis of chemicals in industrial enterprises;
- (4)
- to train future scientists in universities, who in the future will solve regional and global environmental problems (nowadays, most industrial developments are related mainly to economic efficiency, rather than environmental friendliness of processes);
- (5)
- to ensure environmental protection at the legislative level;
- (6)
- to use innovative alternative methods of minimal production of undesired chemicals in order to preserve human health and reduce harmful effects on the environment, namely: use alternative (renewable) sources of raw materials; use less hazardous reagents; use alternative solvents (ionic liquids, water, etc.) during the synthesis of organic matter; use “green” catalysts that affect energy consumption and reduce the production of unwanted by-products and waste; minimize energy consumption at every stage of the industrial process.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, M.; Chatterjee, S. Chapter 11—Green synthesis of metal/metal oxide nanoparticles toward biomedical applications: Boon or bane. In Micro and Nano Technologies; Shukla, A.K., Iravani, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 265–301. ISBN 978-0-08-102579-6. [Google Scholar]
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bourne, R.A.; Poliakoff, M. Green chemistry: What is the way forward? Mendeleev Commun. 2011, 21, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doble, M.; Kruthiventi, A.K. Green Chemistry and Engineering; Academic, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; ISBN 9780123725325. [Google Scholar]
- Vrček, I.V.; Žuntar, I.; Petlevski, R.; Pavičić, I.; Dutour Sikirić, M.; Ćurlin, M.; Goessler, W. Comparison of in vitro toxicity of silver ions and silver nanoparticles on human hepatoma cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Wang, J.; Yu, S.; Wang, P.; Sun, C. Tunable electronic properties of free-standing Fe-doped GaN nanowires as high-capacity anode of lithium-ion batteries. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Wang, A.; Xie, K.; Zhu, J.; Chen, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Su, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, C.; et al. Electrochemical detection of silver ions by using sulfur quantum dots modified gold electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passeri, D.; Angeloni, L.; Rossi, M. Magnetic Force Microscopy and Magnetic Nanoparticles: Perspectives and Challenges; Springer: Hillerød, Denmark, 2021; pp. 285–300. [Google Scholar]
- Sifford, J.; Walsh, K.J.; Tong, S.; Bao, G.; Agarwal, G. Indirect magnetic force microscopy. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 2348–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, B.; Bertoni, G.; Fragouli, D.; Falqui, A.; Salerno, M.; Diaspro, A.; Cingolani, R.; Athanassiou, A. Magnetic Force Microscopy and Energy Loss Imaging of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, S.; Braun, K.F.; Eberbeck, D.; Gustafsson, S.; Olsson, E.; Schumacher, H.W.; Siegner, U. Quantitative measurement of the magnetic moment of individual magnetic nanoparticles by magnetic force microscopy. Small 2012, 8, 2675–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordova, G.; Attwood, S.; Gaikwad, R.; Gu, F.; Leonenko, Z. Magnetic force microscopy characterization of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs). Nano Biomed. Eng. 2014, 6, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krivcov, A.; Schneider, J.; Junkers, T.; Möbius, H. Magnetic Force Microscopy of in a Polymer Matrix Embedded Single Magnetic Nanoparticles. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Mater. Sci. 2019, 216, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Qiu, R.; Song, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, D. Mechanical manipulation of magnetic nanoparticles by magnetic force microscopy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 443, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeloni, L.; Passeri, D.; Reggente, M.; Rossi, M.; Mantovani, D.; Lazzaro, L.; Nepi, F.; De Angelis, F.; Barteri, M. Experimental issues in magnetic force microscopy of nanoparticles. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1667, 020010. [Google Scholar]
- Ahluwalia, V.K.; Kidwai, M. New Trends in GREEN CHEMISTRY; Kluwer Academic Publishers with Anamaya Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2004; ISBN 978-94-015-7102-9. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, J.C.; Cannon, A.S.; Dye, K.M. Green chemistry. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2004, 24, 775–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Arends, I.W.C.E.; Hanefeld, U. Green Chemistry and Catalysis; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; ISBN 9783527307159. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Si, C.; Ni, Y. Green mussel-inspired lignin magnetic nanoparticles with high adsorptive capacity and environmental friendliness for chromium(III) removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Dutta, T.; Kim, K.H.; Rawat, M.; Samddar, P.; Kumar, P. “Green” synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: Applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, K.N.; Mhatre, S.S.; Parikh, R.Y. Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind Kumar, J.; Joshua Amarnath, D.; Anuradha Jabasingh, S.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Vijai Anand, K.; Narendrakumar, G.; Karthick Raja Namasivayam, S.; Krithiga, T.; Sunny, S.; Purna Pushkala, S.; et al. One pot Green Synthesis of Nano magnesium oxide-carbon composite: Preparation, characterization and application towards anthracene adsorption. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.I.M. Green synthesis and characterizations of copper nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 240, 122283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Yadav, K.; Jagadevan, S. A comprehensive review on green synthesis of nature-inspired metal nanoparticles: Mechanism, application and toxicity. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraof, M.; Hasanin, M.S.; Farag, M.M.; Ahmed, H.Y. Green synthesis of bacterial cellulose/bioactive glass nanocomposites: Effect of glass nanoparticles on cellulose yield, biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abisharani, J.M.; Devikala, S.; Kumar, R.D.; Arthanareeswari, M.; Kamaraj, P. Green synthesis of TiO2 Nanoparticles using Cucurbita pepo seeds extract. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 14, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintelu, S.A.; Folorunso, A.S.; Folorunso, F.A.; Oyebamiji, A.K. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for biomedical application and environmental remediation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironyuk, I.F.; Soltys, L.M.; Tatarchuk, T.R.; Savka, K.O. Methods of Titanium Dioxide Synthesis (Review). Phys. Chem. Solid State 2020, 21, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironyuk, I.F.; Soltys, L.M.; Tatarchuk, T.R.; Tsinurchyn, V.I. Ways to Improve the Efficiency of TiO2-based Photocatalysts (Review). Phys. Chem. Solid State 2020, 21, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ruqeishi, M.S.; Mohiuddin, T.; Al-Saadi, L.K. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanorods from deciduous Omani mango tree leaves for heavy oil viscosity treatment. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 4084–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasu, M.V.; Arokiyaraj, S.; Viayaraghavan, P.; Kumar, T.S.J.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Kaviyarasu, K. One step green synthesis of larvicidal, and azo dye degrading antibacterial nanoparticles by response surface methodology. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 190, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandeira, M.; Giovanela, M.; Roesch-Ely, M.; Devine, D.M.; da Silva Crespo, J. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: A review of the synthesis methodology and mechanism of formation. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 15, 100223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezealisiji, K.M.; Siwe-Noundou, X.; Maduelosi, B.; Nwachukwu, N.; Krause, R.W.M. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Solanum torvum (L) leaf extract and evaluation of the toxicological profile of the ZnO nanoparticles–hydrogel composite in Wistar albino rats. Int. Nano Lett. 2019, 9, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumaran, M.; Dhinagaran, G.; Venkatachalam, K.; Sagadevan, S.; Gunasekaran, S.; Podder, J.; Mohammad, F.; Shahid, M.M.; Oh, W.C. Green synthesis of cuprous oxide nanoparticles for environmental remediation and enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. Optik 2020, 214, 164849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumesh, K.R.; Kanthavel, K. Green Synthesis of Aluminium Oxide Nanoparticles and its Applications in Mechanical and Thermal Stability of Hybrid Natural Composites. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 2189–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Ilakiya, R.; Kalaiyan, G.; Thambidurai, S.; Kannan, P.; Prabu, K.M.; Suresh, N.; Jothilakshmi, R.; Karthick Kumar, S.; Kandasamy, M. Green Synthesis of Copper Oxide Nanostructures using Cynodon dactylon and Cyperus rotundus Grass Extracts for Antibacterial Applications. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 12525–12537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.S.; Fouda, A. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Prospective Biotechnological Applications: An Overview. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 344–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Gautam, P.K.; Verma, A.; Singh, V.; Shivapriya, P.M.; Shivalkar, S.; Sahoo, A.K.; Samanta, S.K. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles as effective alternatives to treat antibiotics resistant bacterial infections: A review. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 25, e00427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Batjikh, I.; Hurh, J.; Han, Y.; Huo, Y.; Ali, H.; Li, J.F.; Rupa, E.J.; Ahn, J.C.; Mathiyalagan, R.; et al. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from root extract of Scutellaria baicalensis and its photocatalytic degradation activity using methylene blue. Optik 2019, 184, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayappa, M.D.; Ramaiah, C.K.; Kumar, M.A.P.; Suresh, D.; Prabhu, A.; Devasya, R.P.; Sheikh, S. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from the leaf, stem and in vitro grown callus of Mussaenda frondosa L.: Characterization and their applications. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 3057–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, A.M.; Sivasankarapillai, V.S.; Rahdar, A.; Joseph, J.; Sadeghfar, F.; Anuf A., R.; Rajesh, K.; Kyzas, G.Z. Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles with antibacterial and antifungal activity. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1211, 128107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabaani, M.; Rahaiee, S.; Zare, M.; Jafari, S.M. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using loquat seed extract; Biological functions and photocatalytic degradation properties. LWT 2020, 134, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.F.V.; Fagundes, A.P.; Macuvele, D.L.P.; de Carvalho, E.F.U.; Durazzo, M.; Padoin, N.; Soares, C.; Riella, H.G. Green synthesis of zirconia nanoparticles based on Euclea natalensis plant extract: Optimization of reaction conditions and evaluation of adsorptive properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 583, 123915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elemike, E.E.; Onwudiwe, D.C.; Fayemi, O.E.; Botha, T.L. Green synthesis and electrochemistry of Ag, Au, and Ag–Au bimetallic nanoparticles using golden rod (Solidago canadensis) leaf extract. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghojavand, S.; Madani, M.; Karimi, J. Green Synthesis, Characterization and Antifungal Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Using Stems and Flowers of Felty Germander. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 2987–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, M.; Hoseinpour, V.; Ghaemi, N.; Shakeri, A. Procedure optimization for green synthesis of manganese dioxide nanoparticles by Yucca gloriosa leaf extract. Int. Nano Lett. 2019, 9, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrababu, P.; Cheriyan, S.; Raghavan, R. Aloe vera leaf extract-assisted facile green synthesis of amorphous Fe2O3 for catalytic thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Długosz, O.; Chwastowski, J.; Banach, M. Hawthorn berries extract for the green synthesis of copper and silver nanoparticles. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, T.; Ghosh, N.N.; Das, M.; Adhikary, R.; Mandal, V.; Chattopadhyay, A.P. Green synthesis of antibacterial and antifungal silver nanoparticles using Citrus limetta peel extract: Experimental and theoretical studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ali, H.; Hurh, J.; Han, Y.; Batjikh, I.; Rupa, E.J.; Anandapadmanaban, G.; Park, J.K.; Yang, D.-C. The assessment of photocatalytic activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles from the roots of Codonopsis lanceolata synthesized by one-pot green synthesis method. Optik 2019, 184, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, P.A.; Nava, O.; Soto-Robles, C.A.; Chinchillas-Chinchillas, M.J.; Garrafa-Galvez, H.E.; Baez-Lopez, Y.A.; Valdez-Núñez, K.P.; Vilchis-Nestor, A.R.; Castro-Beltrán, A. Improved photocatalytic efficiency of SnO2 nanoparticles through green synthesis. Optik 2020, 206, 164299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, A.; Mishra, V.; Chundawat, T.S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from green algae (Botryococcus braunii) and its catalytic behavior for the synthesis of benzimidazoles. Chem. Data Collect. 2019, 20, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellapandian, C.; Ramkumar, B.; Puja, P.; Shanmuganathan, R.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Kumar, P. Gold nanoparticles using red seaweed Gracilaria verrucosa: Green synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility studies. Process Biochem. 2019, 80, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, R.S.; Sundaramanickam, A.; Srinath, R.; Ramesh, T.; Saranya, K.; Meena, M.; Surya, P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by bloom forming marine microalgae Trichodesmium erythraeum and its applications in antioxidant, drug-resistant bacteria, and cytotoxicity activity. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2019, 23, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Kanchi, S.; Bisetty, K. Biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles: A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 3576–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, D.; Das, N.; Das, N.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Sarmah, P.; Ghosh, K.; Chandel, M.; Rout, J.; Pandey, P.; Ghosh, N.N.; et al. Alga-mediated facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Photophysical, catalytic and antibacterial activity. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarance, P.; Luvankar, B.; Sales, J.; Khusro, A.; Agastian, P.; Tack, J.-C.; Al Khulaifi, M.M.; AL-Shwaiman, H.A.; Elgorban, A.M.; Syed, A.; et al. Green synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using endophytic fungi Fusarium solani and its in-vitro anticancer and biomedical applications. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanty, S.; Bakshi, M.; Ghosh, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Das, P.; Das, S.; Chaudhuri, P. Green Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mediated by Filamentous Fungi Isolated from Sundarban Mangrove Ecosystem, India. Bionanoscience 2019, 9, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhipa, H. Chapter 5—Mycosynthesis of nanoparticles for smart agricultural practice: A green and eco-friendly approach. In Micro and Nano Technologies; Shukla, A.K., Iravani, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 87–109. ISBN 978-0-08-102579-6. [Google Scholar]
- Owaid, M.N. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Pleurotus (oyster mushroom) and their bioactivity: Review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2019, 12, 100256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, G.; Das, P.; Saha, A.K. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Mushroom Extract of Pleurotus giganteus: Characterization, Antimicrobial, and α-Amylase Inhibitory Activity. Bionanoscience 2019, 9, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosiak, M.; Giersz, J.; Jankowski, K. Analytical monitoring of selenium nanoparticles green synthesis using photochemical vapor generation coupled with MIP-OES and UV–Vis spectrophotometry. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçay, F.A.; Avcı, A. Effects of process conditions and yeast extract on the synthesis of selenium nanoparticles by a novel indigenous isolate Bacillus sp. EKT1 and characterization of nanoparticles. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 2233–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraj, A.; Kumar, V.; Sunder, R.; Parthasarathy, K.; Kasivelu, G. Commercial Yeast Extracts Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Chloride Nanoparticles and their Anti-mycobacterial Activity. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 31, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, M.; He, F.; Li, Z.; Zhu, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Z.; Gao, F.; Zeng, M. Biosynthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Using Yeast Extract as Reducing and Capping Agents. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Shahid, M.; Noman, M.; Bilal Khan Niazi, M.; Zubair, M.; Almatroudi, A.; Khurshid, M.; Tariq, F.; Mumtaz, R.; Li, B. Bioprospecting a native silver-resistant Bacillus safensis strain for green synthesis and subsequent antibacterial and anticancer activities of silver nanoparticles. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 24, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar-Encarnación, E.; Escárcega-González, C.E.; Vasto-Anzaldo, X.G.; Cantú-Cárdenas, M.E.; Morones-Ramírez, J.R. Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized through Green Methods Using Escherichia coli Top 10 (Ec-Ts) Growth Culture Medium Exhibit Antimicrobial Properties against Nongrowing Bacterial Strains. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 4637325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.P.; Kang, M.; Niyonizigiye, I.; Singh, A.; Kim, J.-O.; Seo, Y.B.; Kim, G.-D. Extracellular synthesis of gold nanoparticles using the marine bacterium Paracoccus haeundaensis BC74171T and evaluation of their antioxidant activity and antiproliferative effect on normal and cancer cell lines. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 183, 110455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hossain, A.; Qiu, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Sun, G.; Li, B. Green-Synthesization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from Garlic and Its Antifungal Activity against Wheat Fusarium Head Blight Pathogen Fusarium graminearum. Nanomater. 2020, 10, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, S.; Leghari, S.A.K.; Ryma, N.U.A.; Farooqi, S.A. Green Synthesis of Metal-Based Nanoparticles and Their Applications; Scrivener, Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2018; ISBN 9781119418900. [Google Scholar]
- Tatarchuk, T.; Liaskovska, M.; Kotsyubynsky, V.; Bououdina, M. Green synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles using Cydonia oblonga extract: Structural and mössbauer studies. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 672, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaskovska, M.; Tatarchuk, T.; Bououdina, M.; Mironyuk, I. Green Synthesis of Magnetic Spinel Nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials (NANO2018), Kyiv, Ukraine, 27–30 August 2019; Volume 222. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Aziz, H.M.; Farag, R.S.; Abdel-Gawad, S.A. Carbamazepine Removal from Aqueous Solution by Green Synthesis Zero-Valent Iron/Cu Nanoparticles with Ficus Benjamina Leaves’ Extract. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2019, 13, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, J.A.A.; Salah Eddine, L.; Abderrhmane, B.; Alonso-González, M.; Guerrero, A.; Romero, A. Green synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles by pheonix dactylifera leaf extract and evaluation of their antioxidant activity. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 17, 100280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu Demirezen, D.; Yıldız, Y.Ş.; Yılmaz, Ş.; Demirezen Yılmaz, D. Green synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles using Ficus carica (common fig) dried fruit extract. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 127, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, M. Green synthesis of 3D tripyramid TiO2 architectures with assistance of aloe extracts for highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of antibiotic ciprofloxacin. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 260, 118149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrasbi, S.; Kouhbanani, M.A.J.; Beheshtkhoo, N.; Ghasemi, Y.; Amani, A.M.; Taghizadeh, S. Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles Using Plantago major Leaf Extract and Their Application as a Catalyst for the Decolorization of Azo Dye. Bionanoscience 2019, 9, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifipour, R.; Nozari, M.; Pishkar, L. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles using Tragopogon Collinus Leaf Extract and Study of Their Antibacterial Effects. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 2926–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijani, H.Q.; Pourseyedi, S.; Torkzadeh Mahani, M.; Khatami, M. Green synthesis of zinc sulfide (ZnS) nanoparticles using Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni and evaluation of its cytotoxic properties. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1175, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouafia, A.; Laouini, S.E. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles by aqueous leaves extract of Mentha Pulegium L.: Effect of ferric chloride concentration on the type of product. Mater. Lett. 2020, 265, 127364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, H.-Y.; Lam, S.-M.; Sin, J.-C. Green synthesis of magnetic Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles via Hibiscus rosa-sinensis leaf extracts for boosted photocatalytic, antibacterial and antifungal activities. Mater. Lett. 2019, 242, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemilugba, O.T.; Sakho, E.H.M.; Parani, S.; Mavumengwana, V.; Oluwafemi, O.S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Combretum erythrophyllum leaves and its antibacterial activities. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2019, 31, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, R.S.; Sandeman, S.; Ray, S.; Savina, I.N.; Ashtami, J.; Mohanan, P.V. Green synthesis of Pluronic stabilized reduced graphene oxide: Chemical and biological characterization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 179, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, I.; Mondal, M.; Sakthivel, N. Chapter 3—Green synthesis of phytogenic nanoparticles. In Micro and Nano Technologies; Shukla, A.K., Iravani, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 37–73. ISBN 978-0-08-102579-6. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Atarod, M.; Sajjadi, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Issaabadi, Z. Chapter 6—Plant-Mediated Green Synthesis of Nanostructures: Mechanisms, Characterization, and Applications. In An Introduction to Green Nanotechnology; Sajadi, M.S., Atarod, M., Nasrollahzadeh, M., Isaabadi, Z., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 28, pp. 199–322. ISBN 1573-4285. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.; Raja, N.I.; Iqbal, M.; Aslam, S. Applications of Plant Flavonoids in the Green Synthesis of Colloidal Silver Nanoparticles and Impacts on Human Health. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A Sci. 2019, 43, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, H.; Kumari, P.; Bontempi, E.; Yadav, S. Medicinal plants: Treasure trove for green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 24, 101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, G.; Rai, P.; Pandey, A. Chapter 1—Green synthesis of nanoparticles: A greener approach for a cleaner future. In Micro and Nano Technologies; Shukla, A.K., Iravani, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–26. ISBN 978-0-08-102579-6. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, N.U.; Jalil, K.; Shahid, M.; Muhammad, N.; Rauf, A. Pistacia integerrima gall extract mediated green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their biological activities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 2310–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.U.; Jalil, K.; Shahid, M.; Rauf, A.; Muhammad, N.; Khan, A.; Shah, M.R.; Khan, M.A. Green synthesis and biological activities of gold nanoparticles functionalized with Salix alba. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 2914–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathy, S.; Patra, A.; Ahirwar, B.; Hussain, M.D. Process optimization for green synthesis of gold nanoparticles mediated by extract of Hygrophila spinosa T. Anders and their biological applications. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2020, 121, 113830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangamani, N.; Bhuvaneshwari, N. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Simarouba glauca leaf extract and their biological activity of micro-organism. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 732, 136587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijaya Kumar, P.; Mary Jelastin Kala, S.; Prakash, K.S. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Croton Caudatus Geisel leaf extract and their biological studies. Mater. Lett. 2019, 236, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.A.; Eisa, N.E.; Virk, P.; Hendi, A.A.; Ortashi, K.M.O.O.; Mahgoub, A.S.A.; Elobeid, M.A.; Eissa, F.Z. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization, cytotoxicity, and anti-bacterial activities. Mater. Lett. 2019, 256, 126608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadil, K.R.; Pandey, N.; Mussatto, S.I.; Jha, H. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using acacia lignin, their cytotoxicity, catalytic, metal ion sensing capability and antibacterial activity. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behravan, M.; Hossein Panahi, A.; Naghizadeh, A.; Ziaee, M.; Mahdavi, R.; Mirzapour, A. Facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Berberis vulgaris leaf and root aqueous extract and its antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, M.; Anand, R.; Datt, R.; Gupta, V.; Arya, S. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Extract of Rosa brunonii Lindl and Their Morphological, Biological and Photocatalytic Characterizations. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2019, 29, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Ghosal, K.; Jana, N.K.; Mukherjee, A.; Basak, P. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using belladonna mother tincture and its efficacy as a potential antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agent. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 228, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavamukulya, Y.; Maina, E.N.; Meroka, A.M.; Madivoli, E.S.; El-Shemy, H.A.; Wamunyokoli, F.; Magoma, G. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Highly Stable Silver Nanoparticles from Ethanolic Extracts of Fruits of Annona muricata. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.F.; Tasharrofi, N.; Saber, M.M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Teucrium polium leaf extract and assessment of their antitumor effects against MNK45 human gastric cancer cell line. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1208, 127889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayapriya, M.; Dhanasekaran, D.; Arulmozhi, M.; Nandhakumar, E.; Senthilkumar, N.; Sureshkumar, K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Piper longum catkin extract irradiated by sunlight: Antibacterial and catalytic activity. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2019, 45, 3617–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmila, G.; Thirumarimurugan, M.; Muthukumaran, C. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Tecoma castanifolia leaf extract: Characterization and evaluation of its antioxidant, bactericidal and anticancer activities. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Singh, J.; Rawat, M. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Punica Granatum leaf extract and its application towards photocatalytic degradation of Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 dye. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R.; Hasan, M.M.; Eldesoky, G.E.; Khaleque, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Naushad, M. Facile mercury detection and removal from aqueous media involving ligand impregnated conjugate nanomaterials. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 290, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naushad, M.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Awual, M.R.; Alam, M.M.; Eldesoky, G.E. Adsorption kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic studies for the adsorption of Pb2+ and Hg2+ metal ions from aqueous medium using Ti(IV) iodovanadate cation exchanger. Ionics 2015, 21, 2237–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Naushad, M. Adsorptive removal of noxious cadmium ions from aqueous medium using activated carbon/zirconium oxide composite: Isotherm and kinetic modelling. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 310, 113025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusaravanan, S.; Sivarajasekar, N.; Vivek, J.S.; Paramasivan, T.; Naushad, M.; Prakashmaran, J.; Gayathri, V.; Al-Duaij, O.K. Phytoremediation of heavy metals: Mechanisms, methods and enhancements. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 1339–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karfa, P.; Madhuri, R. Green tiny magnets: An economic and eco-friendly remedy for environmental damage. In Green Metal Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Applications; Wiley-Scrivener: Beverly, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 245–292. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, L.M.; Parize, A.L.; Rubim, J.C. Green Synthesis and Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles. Handb. Green Chem. 2012, 8, 61–88. [Google Scholar]
- Tatarchuk, T.; Myslin, M.; Lapchuk, I.; Shyichuk, A.; Murthy, A.P.; Gargula, R.; Kurzydło, P.; Bogacz, B.F.; Pędziwiatr, A.T. Magnesium-zinc ferrites as magnetic adsorbents for Cr(VI) and Ni(II) ions removal: Cation distribution and antistructure modeling. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarchuk, T.; Myslin, M.; Lapchuk, I.; Olkhovyy, O.; Danyliuk, N.; Mandzyuk, V. Synthesis, structure and morphology of magnesium ferrite nanoparticles, synthesized via “green” method. Phys. Chem. Solid State 2021, 22, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Dief, A.M.; Abdel-Fatah, S.M. Development and functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles as powerful and green catalysts for organic synthesis. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, Y.P.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Ahmad Khairudin, N.B.B.; Mohamad, S.E.B.; Naiki, T.; Lee, K.X. Green biosynthesis of superparamagnetic magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles and biomedical applications in targeted anticancer drug delivery system: A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 13, 2287–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, L.L.; Galstyan, A.; Holler, E.; Ljubimova, J.Y. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for imaging, targeting and treatment of primary and metastatic tumors of the brain. J. Control. Release 2020, 320, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolade, O.P.; Williams, A.B.; Benson, N.U. Green synthesis of iron-based nanomaterials for environmental remediation: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 13, 100279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, A. Green Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles and Its Application in Preparation of Fe3O4/Cellulose Magnetic Nanocomposite: A Suitable Proposal for Drug Delivery Systems. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 3552–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, I.; Nazar, N.; Ata, S.; Sultan, M.; Ali, A.; Abbas, A.; Jilani, K.; Kamal, S.; Sarim, F.M.; Khan, M.I.; et al. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using pomegranate seeds extract and photocatalytic activity evaluation for the degradation of textile dye. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 6115–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpagavinayagam, P.; Vedhi, C. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Avicennia marina flower extract. Vacuum 2019, 160, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakami, M.; Renuka, R.; Thilagavathi, T. Green synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles via Cinnamomum verum bark extract for biological application. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104420. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, P.; Anweshan, A.; Purkait, M.K. Green synthesis and environmental application of iron-based nanomaterials and nanocomposite: A review. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Islam, M.; Tabassum, S.; Fernandes, N.F.; Carcache de Blanco, E.J.; Zia, M. Green synthesis of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles using Rhus punjabensis extract and their biomedical prospect in pathogenic diseases and cancer. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1185, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yu, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Bian, D.; Wang, Y. Green Synthesis of Magnetic Adsorbent Using Groundwater Treatment Sludge for Tetracycline Adsorption. Engineering 2019, 5, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesús Ruíz-Baltazar, Á.; Reyes-López, S.Y.; de Lourdes Mondragón-Sánchez, M.; Robles-Cortés, A.I.; Pérez, R. Eco-friendly synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Evaluation of their catalytic activity in methylene blue degradation by kinetic adsorption models. Results Phys. 2019, 12, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Guo, M.; Weng, X.; Zhang, W.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. Modified green synthesis of Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles for pH responsive drug release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakzad, K.; Alinezhad, H.; Nasrollahzadeh, M. Green synthesis of Ni@Fe3O4 and CuO nanoparticles using Euphorbia maculata extract as photocatalysts for the degradation of organic pollutants under UV-irradiation. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 17173–17182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Lin, Y.; Sarkar, B.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles using red peanut skin extract: Synthesis mechanism, characterization and effect of conditions on chromium removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 558, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, R.; Gharanfoli, M.; Gholamin, M.; Darroudi, M.; Chamani, J.; Sadri, K. Green synthesis of 99mTc-labeled-Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Quince seeds extract and evaluation of their cytotoxicity and biodistribution in rats. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1196, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Tu, G.; Tsang, P.E.; Xiao, S.; Fang, Z. Green synthesis of iron-based nanoparticles from extracts of Nephrolepis auriculata and applications for Cr(VI) removal. Mater. Lett. 2019, 234, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, S.; Kumar, B.N.; Prathima, B.; SubbaRao, Y.; Jyothi, N.V.V. A novel green synthesis of Fe3O4 magnetic nanorods using Punica Granatum rind extract and its application for removal of Pb(II) from aqueous environment. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niraimathee, V.A.; Subha, V.; Ernest Ravindran, R.S.; Renganathan, S. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles from Mimosa pudica root extract. Int. J. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 15, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunge, S.; Singh, S.; Sinha, A. Magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles from tea waste for arsenic removal. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 356, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, A.; Saeed, A.; Shoaib, M.; Iqbal, S.; Bashir, M.I.; Waqas, M.; Hussain, M.N.; Abbas, N. Eco-friendly synthesis of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles with tunable size: Dielectric, magnetic, thermal and optical studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 198, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagasubbulakshmi, S.; Kadirvelu, K. Green synthesis of Iron oxide nanoparticles using Lagenaria siceraria and evaluation of its Antimicrobial activity. Def. Life Sci. J. 2017, 2, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhi, D.K.; Panigrahi, T.K.; Parida, K.; Singh, S.K.; Mishra, P.M. Green Synthesis of Fe3O4/RGO Nanocomposite with Enhanced Photocatalytic Performance for Cr(VI) Reduction, Phenol Degradation, and Antibacterial Activity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 10551–10562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, N.; Garg, V.K. Green Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Loaded Sawdust Carbon for Cadmium (II) Removal from Water: Regeneration and Mechanism; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 208, ISBN 9198120581. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadian-Fard-Fini, S.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Ghanbari, D. Hydrothermal green synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4-carbon dots by lemon and grape fruit extracts and as a photoluminescence sensor for detecting of E. coli bacteria. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 203, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnadozie, E.C.; Ajibade, P.A. Green synthesis and characterization of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using Chromolaena odorata root extract for smart nanocomposite. Mater. Lett. 2020, 263, 127145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, M.; Alijani, H.Q.; Fakheri, B.; Mobasseri, M.M.; Heydarpour, M.; Farahani, Z.K.; Khan, A.U. Super-paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): Greener synthesis using Stevia plant and evaluation of its antioxidant properties. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Khodaiyan, F.; Hadi Razavi, S. Green construction of recyclable amino-tannic acid modified magnetic nanoparticles: Application for β-glucosidase immobilization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karade, V.C.; Dongale, T.D.; Sahoo, S.C.; Kollu, P.; Chougale, A.D.; Patil, P.S.; Patil, P.B. Effect of reaction time on structural and magnetic properties of green-synthesized magnetic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 120, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, I.; Zunita Pratiwi, E.; Prio Wicaksono, W. Synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles using Parkia speciosa Hassk pod extract and photocatalytic activity for Bromophenol blue degradation. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 46, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarchuk, T.; Naushad, M.; Tomaszewska, J.; Kosobucki, P.; Myslin, M.; Vasylyeva, H.; Ścigalski, P. Adsorption of Sr(II) ions and salicylic acid onto magnetic magnesium-zinc ferrites: Isotherms and kinetic studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 26681–26693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarchuk, T.; Al-Najar, B.; Bououdina, M.; Ahmed, M.A.A. Catalytic and Photocatalytic Properties of Oxide Spinels. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Martínez, L., Kharissova, O., Kharisov, B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1701–1750. ISBN 978-3-319-68254-9. [Google Scholar]
- Tatarchuk, T.; Shyichuk, A.; Trawczyńska, I.; Yaremiy, I.; Pędziwiatr, A.T.; Kurzydło, P.; Bogacz, B.F.; Gargula, R. Spinel cobalt(II) ferrite-chromites as catalysts for H2O2 decomposition: Synthesis, morphology, cation distribution and antistructure model of active centers formation. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 27517–27530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarchuk, T.; Shyichuk, A.; Sojka, Z.; Gryboś, J.; Naushad, M.; Kotsyubynsky, V.; Kowalska, M.; Kwiatkowska-Marks, S.; Danyliuk, N. Green synthesis, structure, cations distribution and bonding characteristics of superparamagnetic cobalt-zinc ferrites nanoparticles for Pb(II) adsorption and magnetic hyperthermia applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 328, 115375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diodati, S.; Pandolfo, L.; Caneschi, A.; Gialanella, S.; Gross, S. Green and low temperature synthesis of nanocrystalline transition metal ferrites by simple wet chemistry routes. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 1027–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelli, A.; Dolcet, P.; Diodati, S.; Gardonio, S.; Innocenti, C.; Badocco, D.; Gialanella, S.; Pastore, P.; Pandolfo, L.; Caneschi, A.; et al. Pursuing the stabilisation of crystalline nanostructured magnetic manganites through a green low temperature hydrothermal synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 3359–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joulaei, M.; Hedayati, K.; Ghanbari, D. Investigation of magnetic, mechanical and flame retardant properties of polymeric nanocomposites: Green synthesis of MgFe2O4 by lime and orange extracts. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 176, 107345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, M.; Taufiq, A.; Hidayat, A. Green synthesis of CrFe2O4 nanoparticles using Cucumis sativus as a natural surfactant. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 3221–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhukara Naik, M.; Bhojya Naik, H.S.; Nagaraju, G.; Vinuth, M.; Raja Naika, H.; Vinu, K. Green synthesis of zinc ferrite nanoparticles in Limonia acidissima juice: Characterization and their application as photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. Microchem. J. 2019, 146, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhukara Naik, M.; Bhojya Naik, H.S.; Nagaraju, G.; Vinuth, M.; Vinu, K.; Viswanath, R. Green synthesis of zinc doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Structural, optical, photocatalytic and antibacterial studies. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2019, 19, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, P.; Sharma, A.; Kaur, B.; Goyal, N.; Gautam, S. Green synthesized (Ocimum sanctum and Allium sativum) Ag-doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for antibacterial application. Vacuum 2019, 161, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradnia, F.; Taghavi Fardood, S.; Ramazani, A.; Gupta, V.K. Green synthesis of recyclable MgFeCrO4 spinel nanoparticles for rapid photodegradation of direct black 122 dye. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2020, 392, 112433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini Nasab, N.; Safari, J. Synthesis of a wide range of biologically important spiropyrans and spiroacenaphthylenes, using NiFe2O4@SiO2@Melamine magnetic nanoparticles as an efficient, green and reusable nanocatalyst. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1193, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udhaya, P.A.; Meena, M. Albumen Assisted Green Synthesis of NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles and Their Physico-Chemical Properties. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 9, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hunaiti, A.; Al-Said, N.; Halawani, L.; Haija, M.A.; Baqaien, R.; Taher, D. Synthesis of magnetic CuFe2O4 nanoparticles as green catalyst for toluene oxidation under solvent-free conditions. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 4945–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routray, K.L.; Saha, S.; Behera, D. Green synthesis approach for nano sized CoFe2O4 through aloe vera mediated sol-gel auto combustion method for high frequency devices. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 224, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakootian, M.; Nasiri, A.; Asadipour, A.; Kargar, E. Facile and green synthesis of ZnFe2O4@CMC as a new magnetic nanophotocatalyst for ciprofloxacin degradation from aqueous media. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 129, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardood, S.T.; Moradnia, F.; Mostafaei, M.; Afshari, Z.; Faramarzi, V.; Ganjkhanlu, S. Biosynthesis of MgFe 2 O 4 magnetic nanoparticles and their application in photodegradation of malachite green dye and kinetic study. Nanochem Res. 2019, 4, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Gayathri Manju, B.; Raji, P. Green Synthesis of Nickel–Copper Mixed Ferrite Nanoparticles: Structural, Optical, Magnetic, Electrochemical and Antibacterial Studies. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 7710–7720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrak, K.; Ramazani, A.; Taghavi Fardood, S. Eco-friendly synthesis of Mg0.5Ni0.5AlxFe2-xO4 magnetic nanoparticles and study of their photocatalytic activity for degradation of direct blue 129 dye. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 382, 111942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Martín, C.; Souza, B.E.; Van der Auweraer, M.; Hofkens, J.; Tan, J.-C. Highly luminescent silver-based MOFs: Scalable eco-friendly synthesis paving the way for photonics sensors and electroluminescent devices. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 21, 100817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, K.; Cao, D.; Eldin Fouad, D.; Hussain Shah, A.; Qadeer Dayo, A.; Zhu, K.; Nazim Lakhan, M.; Mehdi, G.; Dong, S. Green synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic application of silver nanoparticles synthesized by various plant extracts. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 8248–8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, G.A.; Esparza, R.; López-Miranda, J.L.; Hernández-Martínez, A.R.; España-Sánchez, B.L.; Elizalde-Peña, E.A.; Estevez, M. Green synthesis of Ag nanoflowers using Kalanchoe Daigremontiana extract for enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 180, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashmi, B.N.; Harlapur, S.F.; Avinash, B.; Ravikumar, C.R.; Nagaswarupa, H.P.; Anil Kumar, M.R.; Gurushantha, K.; Santosh, M.S. Facile green synthesis of silver oxide nanoparticles and their electrochemical, photocatalytic and biological studies. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 111, 107580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, V.; Vasanthi, S.; Shalini, S.; Shah, S.A.A.; Tripathy, M.; Paliwal, N. Green synthesis, characterization, antibacterial, antioxidant and photocatalytic activity of Parkia speciosa leaves extract mediated silver nanoparticles. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Kumar, S.; Sengupta, S. Green synthesis of nano silver on TiO2 catalyst for application in oxidation of thiophene. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 199, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, M.A.; Bello, I.T.; Shittu, H.A.; Awodele, M.K.; Adedokun, O.; Sanusi, Y.K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) for optical and photocatalytic applications: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 805, 12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalaf, M.I.; Hussein, R.H.; Hamza, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Nigella sativa extract alleviates diabetic neuropathy through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2410–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfuraydi, A.A.; Devanesan, S.; Al-Ansari, M.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Ranjitsingh, A.J. Eco-friendly green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from the sesame oil cake and its potential anticancer and antimicrobial activities. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 192, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, M.; Poorani, G.; Boomi, P.; Varunkumar, K.; Anand, K.; Chuturgoon, A.A.; Saravanan, M.; Gurumallesh Prabu, H. Green synthesis of anisotropic silver nanoparticles from the aqueous leaf extract of Dodonaea viscosa with their antibacterial and anticancer activities. Process Biochem. 2019, 80, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femi-Adepoju, A.G.; Dada, A.O.; Otun, K.O.; Adepoju, A.O.; Fatoba, O.P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using terrestrial fern (Gleichenia Pectinata (Willd.) C. Presl.): Characterization and antimicrobial studies. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girón-Vázquez, N.G.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, C.M.; Soto-Robles, C.A.; Nava, O.; Lugo-Medina, E.; Castrejón-Sánchez, V.H.; Vilchis-Nestor, A.R.; Luque, P.A. Study of the effect of Persea americana seed in the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial properties. Results Phys. 2019, 13, 102142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Morales, L.; Espinoza-Gómez, H.; Flores-López, L.Z.; Sotelo-Barrera, E.L.; Núñez-Rivera, A.; Cadena-Nava, R.D.; Alonso-Núñez, G.; Espinoza, K.A. Study of the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using a natural extract of dark or white Salvia hispanica L. seeds and their antibacterial application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 489, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, K.M.; Quezada-Cervantes, C.T.; Hernández-Iturriaga, M.; Luna-Bárcenas, G.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R.; Mendoza, S. Fruit peels waste for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial activity against foodborne pathogens. LWT 2019, 103, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Salih, E. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles Using Biopolymers and Plant Extracts. In Green Metal Nanoparticles; Kanchiб, S., Ahmed, S., Eds.; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 293–319. [Google Scholar]
- Adyani, S.H.; Soleimani, E. Green synthesis of Ag/Fe3O4/RGO nanocomposites by Punica Granatum peel extract: Catalytic activity for reduction of organic pollutants. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 2711–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.H.; Mustafa, D.E. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles mediated by traditionally used medicinal plants in Sudan. Int. Nano Lett. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Noman, M.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Hussain, S.; Manzoor, N.; Wang, X.; Li, B. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles transformed synthetic textile dye into less toxic intermediate molecules through LC-MS analysis and treated the actual wastewater. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banasiuk, R.; Krychowiak, M.; Swigon, D.; Tomaszewicz, W.; Michalak, A.; Chylewska, A.; Ziabka, M.; Lapinski, M.; Koscielska, B.; Narajczyk, M.; et al. Carnivorous plants used for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindhu, M.R.; Umadevi, M.; Esmail, G.A.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Arasu, M.V. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Moringa oleifera flower and assessment of antimicrobial and sensing properties. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 205, 111836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Topuz, F.; Yildiz, Z.I.; Uyar, T. One-step green synthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles embedded in electrospun cyclodextrin nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreyra Maillard, A.P.V.; Gonçalves, S.; Santos, N.C.; López de Mishima, B.A.; Dalmasso, P.R.; Hollmann, A. Studies on interaction of green silver nanoparticles with whole bacteria by surface characterization techniques. Biochim. Biophys. Act Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göl, F.; Aygün, A.; Seyrankaya, A.; Gür, T.; Yenikaya, C.; Şen, F. Green synthesis and characterization of Camellia sinensis mediated silver nanoparticles for antibacterial ceramic applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 250, 123037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, S.; Shojaosadati, S.A. Rapid and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Diospyros lotus extract: Evaluation of their biological and catalytic activities. Polyhedron 2019, 171, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aygün, A.; Özdemir, S.; Gülcan, M.; Cellat, K.; Şen, F. Synthesis and characterization of Reishi mushroom-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles for the biochemical applications. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Aragão, A.P.; de Oliveira, T.M.; Quelemes, P.V.; Perfeito, M.L.G.; Araújo, M.C.; Santiago, J. de A.S.; Cardoso, V.S.; Quaresma, P.; de Souza de Almeida Leite, J.R.; da Silva, D.A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the seaweed Gracilaria birdiae and their antibacterial activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 4182–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, M.; Sharifi, I.; Nobre, M.A.L.; Zafarnia, N.; Aflatoonian, M.R. Waste-grass-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of their anticancer, antifungal and antibacterial activity. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2018, 11, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, J.; Begum, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Kumar, S. A novel green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their catalytic action in reduction of Methylene Blue dye. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2017, 27, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, A.; Tavakkoli Yaraki, M.; Lajevardi, A.; Rezaei, Z.; Ghorbanpour, M.; Tanzifi, M. Ultrasonic-assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Mentha aquatica leaf extract for enhanced antibacterial properties and catalytic activity. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2020, 35, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeniyi, M.A.; Okumah, V.C.; Adebayo-Tayo, B.C.; Odeniyi, O.A. Green synthesis and cream formulations of silver nanoparticles of Nauclea latifolia (African peach) fruit extracts and evaluation of antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 15, 100197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Qin, L.; Huang, D.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Li, B.; He, J.; Yi, H.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, M.; et al. Chitosan functionalized activated coke for Au nanoparticles anchoring: Green synthesis and catalytic activities in hydrogenation of nitrophenols and azo dyes. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 255, 117740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadiyan, Z.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Teow, S.-Y.; Peh, S.-C.; Mohamad, S.E.; Mohd Taib, S.H. Green fabrication of biologically active magnetic core-shell Fe3O4/Au nanoparticles and their potential anticancer effect. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, P.; Surendran, L.; Sudhagar, B.; Ranjith Santhosh Kumar, D.S. Facile green synthesis of gold nanoparticles from marine algae Gelidiella acerosa and evaluation of its biological Potential. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Yin, J.; Zhao, X.; Fu, Y.; Jin, X.; Liu, X.; Jiao, T. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Sargassum carpophyllum extract and its application in visual detection of melamine. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 603, 125293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, Z.; Bódai, V.; Szakacs, G.; Erdélyi, B.; Fogarassy, Z.; Sáfrán, G.; Varga, T.; Kónya, Z.; Tóth-Szeles, E.; Szucs, R.; et al. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles by thermophilic filamentous fungi. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandakrishnan, M.; Palanisamy, S.; Vinosha, M.; Kalanjiaraja, B.; Mohandoss, S.; Manikandan, R.; Tabarsa, M.; You, S.G.; Prabhu, N.M. Facile green route synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Caulerpa racemosa for biomedical applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 101345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabestarian, H.; Homayouni-Tabrizi, M.; Soltani, M.; Namvar, F.; Azizi, S.; Mohamad, R.; Shabestarian, H. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using sumac aqueous extract and their antioxidant activity. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Radadi, N.S. Green synthesis of platinum nanoparticles using Saudi’s Dates extract and their usage on the cancer cell treatment. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 330–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.V.; Jelastin Kala, S.M.; Prakash, K.S. Green synthesis derived Pt-nanoparticles using Xanthium strumarium leaf extract and their biological studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrucka, R.; Romaniuk-Drapała, A.; Kaczmarek, M. Evaluation of biological synthesized platinum nanoparticles using Ononidis radix extract on the cell lung carcinoma A549. Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrucka, R. Biofabrication of platinum nanoparticles using Fumariae herba extract and their catalytic properties. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puja, P.; Kumar, P. A perspective on biogenic synthesis of platinum nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 211, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, A.; Ali, A.; Ali, S.; Mahmood, A.; Kusuma, H.S.; Nazir, A.; Yaseen, M.; Khan, M.I.; Ghaffar, A.; Abbas, M.; et al. Biogenic and eco-benign synthesis of platinum nanoparticles (Pt NPs) using plants aqueous extracts and biological derivatives: Environmental, biological and catalytic applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 9093–9107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, M.; Islami, M.R.; Tikdari, A.M. Green synthesis of Pd nanoparticles supported on modified Nonpareil almond shell using almond hull extract: A beneficial nanocatalyst for convenient reduction of organic dyes. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 18111–18122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioria, E.; Signorini, C.; Wisniewski, F.; Gutierrez, L. Green synthesis of time-stable palladium nanoparticles using microfluidic devices. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami-Vartooni, A.; Rostami, L.; Bagherzadeh, M. Green synthesis of Fe3O4/bentonite-supported Ag and Pd nanoparticles and investigation of their catalytic activities for the reduction of azo dyes. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 21377–21387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksono, W.P.; Kadja, G.T.M.; Amalia, D.; Uyun, L.; Rini, W.P.; Hidayat, A.; Fahmi, R.L.; Nasriyanti, D.; Leun, S.G.V.; Ariyanta, H.A.; et al. A green synthesis of gold–palladium core–shell nanoparticles using orange peel extract through two-step reduction method and its formaldehyde colorimetric sensing performance. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2020, 24, 100535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathula, C.; Subalakshmi, K.; Kumar, K.A.; Yadav, H.; Ramesh, S.; Shinde, S.; Shrestha, N.K.; Mallikarjuna, K.; Kim, H. Ultrasonically driven green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles by Coleus amboinicus for catalytic reduction and Suzuki-Miyaura reaction. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 192, 111026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, M.; Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Ghadiri, A.M.; Fatahi, Y.; Dinarvand, R.; Webster, T.J. High-gravity-assisted green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: The flowering of nanomedicine. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2020, 30, 102297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioria, E.; Wisniewski, F.; Gutierrez, L. Microreactors for the continuous and green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: Enhancement of the catalytic properties. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olajire, A.A.; Mohammed, A.A. Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using Ananas comosus leaf extract for solid-phase photocatalytic degradation of low density polyethylene film. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J.; Cui, T.; Chen, S.; Ma, G.; Guo, X.; Wang, L. Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using lentinan for catalytic activity and biological applications. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 38265–38270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Topuz, F.; Uyar, T. Facile and green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles loaded into cyclodextrin nanofibers and their catalytic application in nitroarene hydrogenation. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 3146–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrutham, S.; Maragoni, V.; Guttena, V. One-step green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using neem gum (Azadirachta Indica): Characterization, reduction of Rhodamine 6 G dye and free radical scavenging activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 4505–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

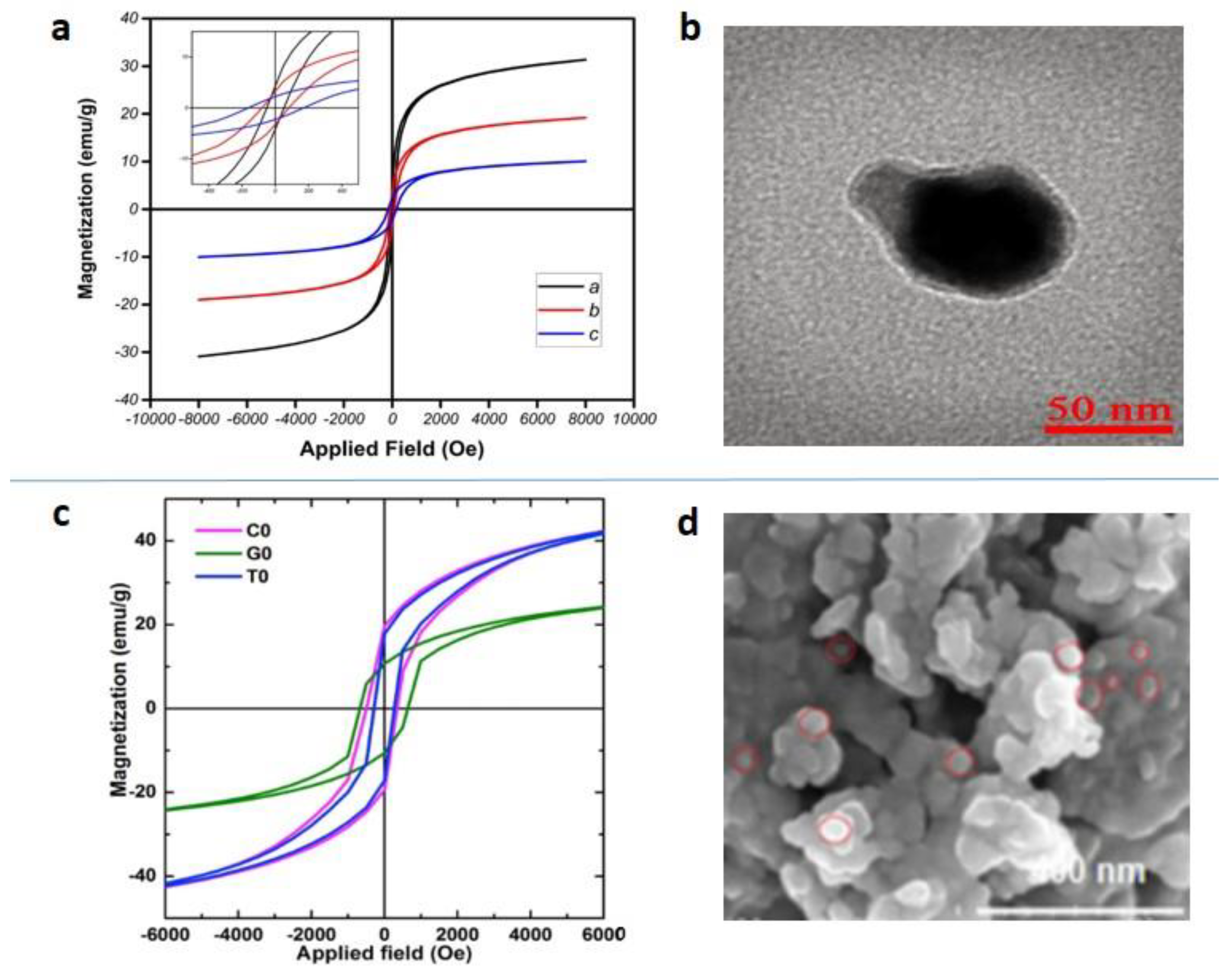
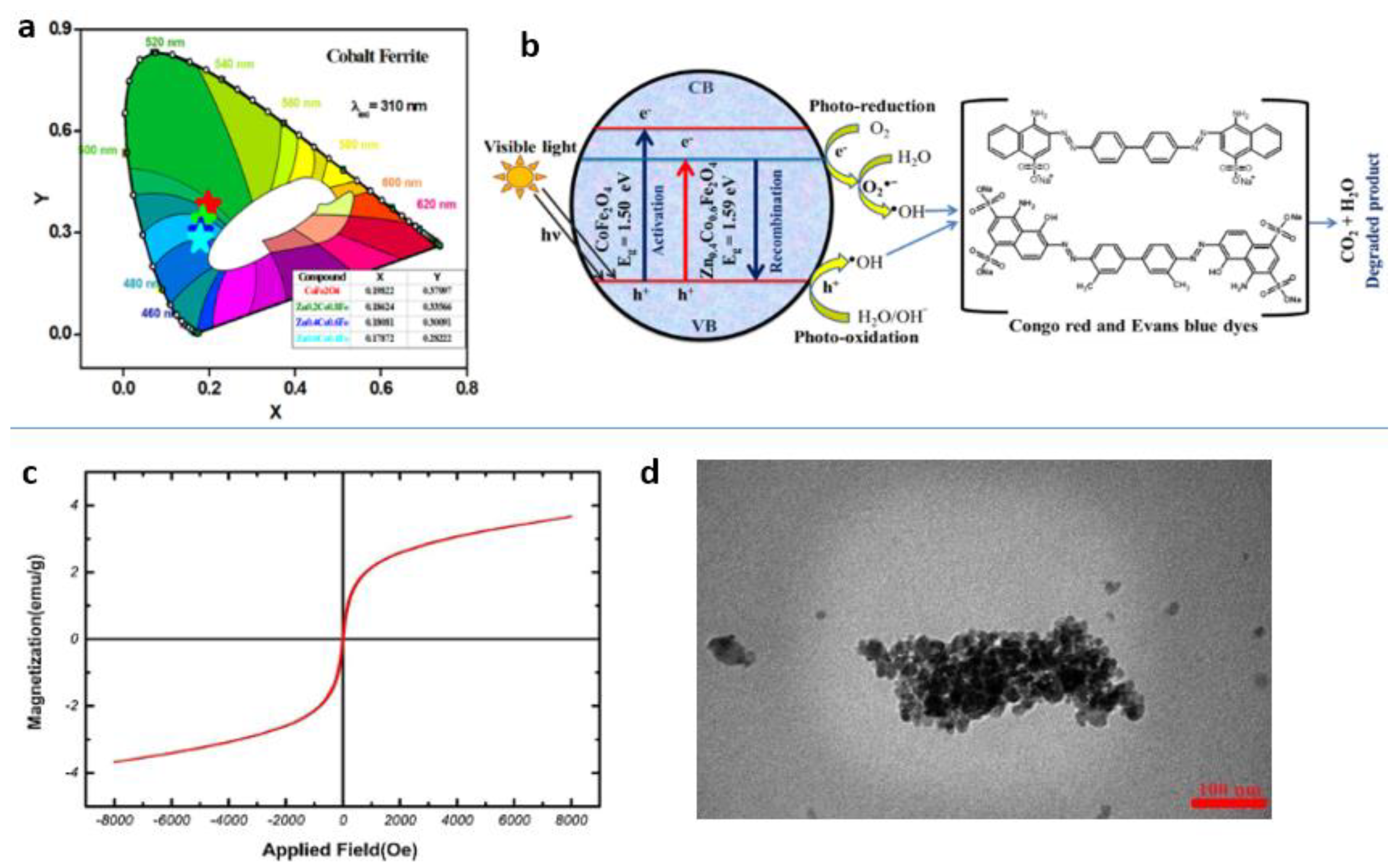
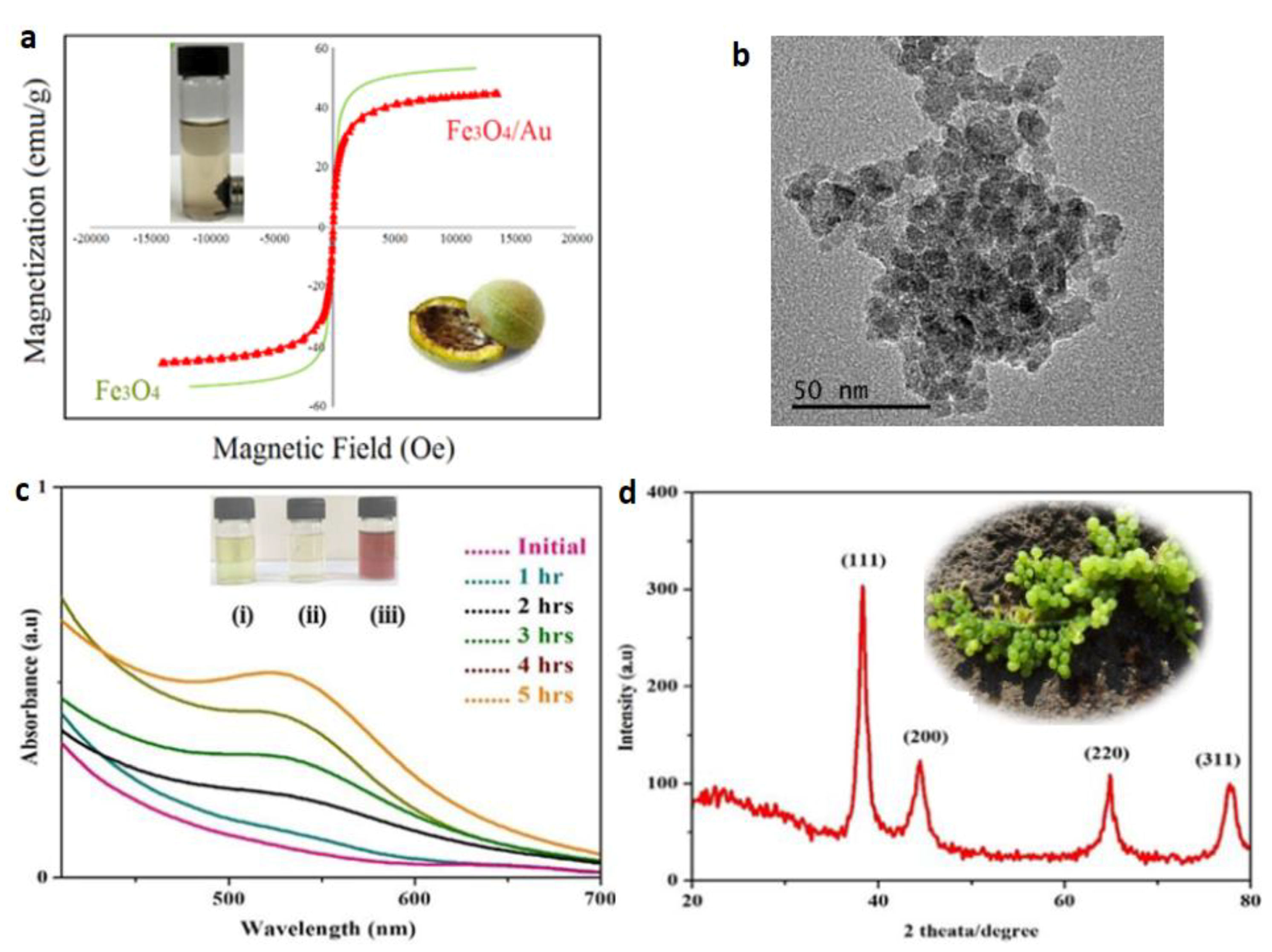
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soltys, L.; Olkhovyy, O.; Tatarchuk, T.; Naushad, M. Green Synthesis of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: Principles of Green Chemistry and Raw Materials. Magnetochemistry 2021, 7, 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7110145
Soltys L, Olkhovyy O, Tatarchuk T, Naushad M. Green Synthesis of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: Principles of Green Chemistry and Raw Materials. Magnetochemistry. 2021; 7(11):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7110145
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoltys, Liubov, Ostap Olkhovyy, Tetiana Tatarchuk, and Mu. Naushad. 2021. "Green Synthesis of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: Principles of Green Chemistry and Raw Materials" Magnetochemistry 7, no. 11: 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7110145
APA StyleSoltys, L., Olkhovyy, O., Tatarchuk, T., & Naushad, M. (2021). Green Synthesis of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: Principles of Green Chemistry and Raw Materials. Magnetochemistry, 7(11), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7110145






