Brain Redox Imaging Using In Vivo Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Imaging and Nitroxide Imaging Probes
Abstract
1. Introduction
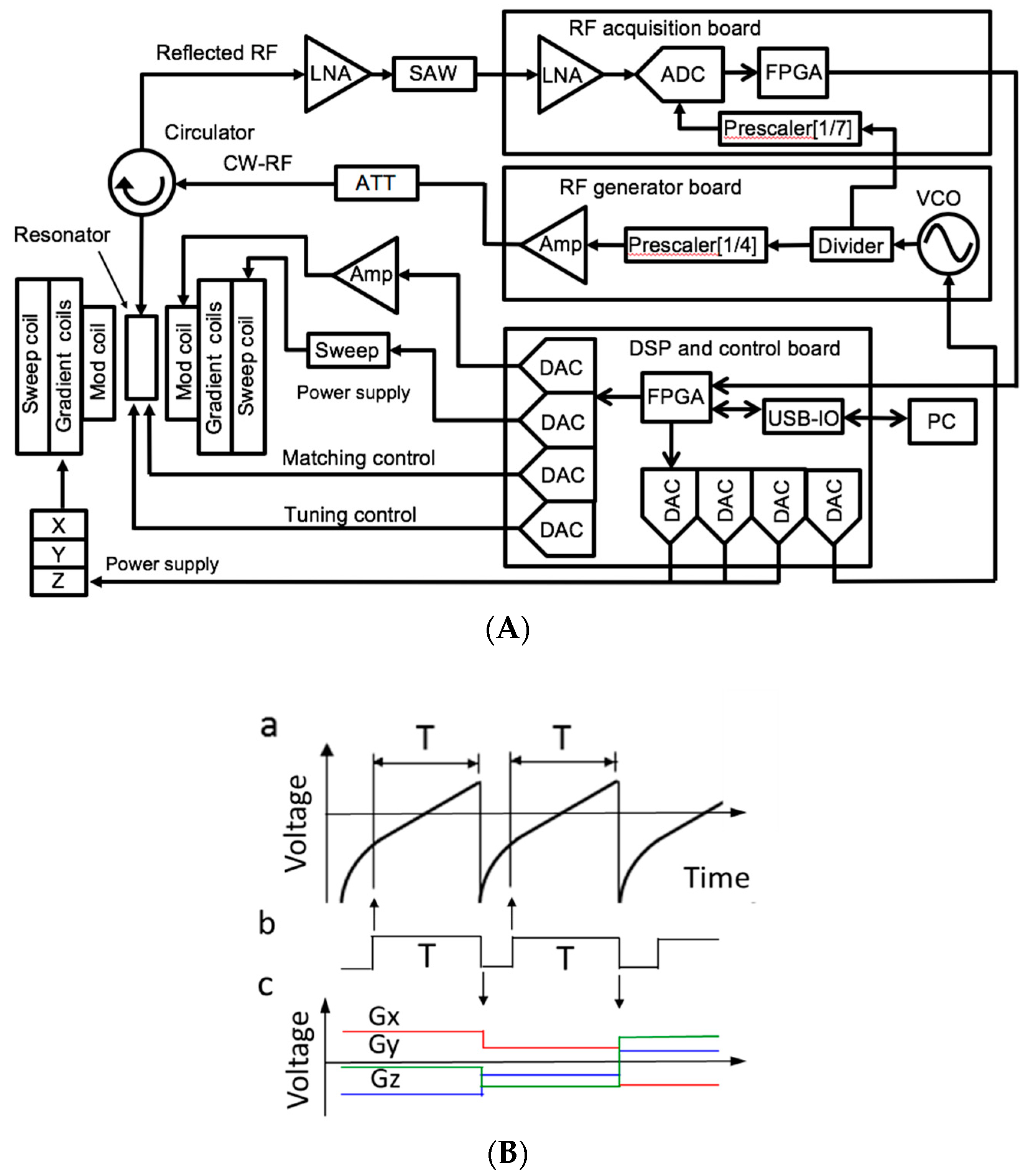
2. In Vivo EPR Imaging Instrument for Small Animals
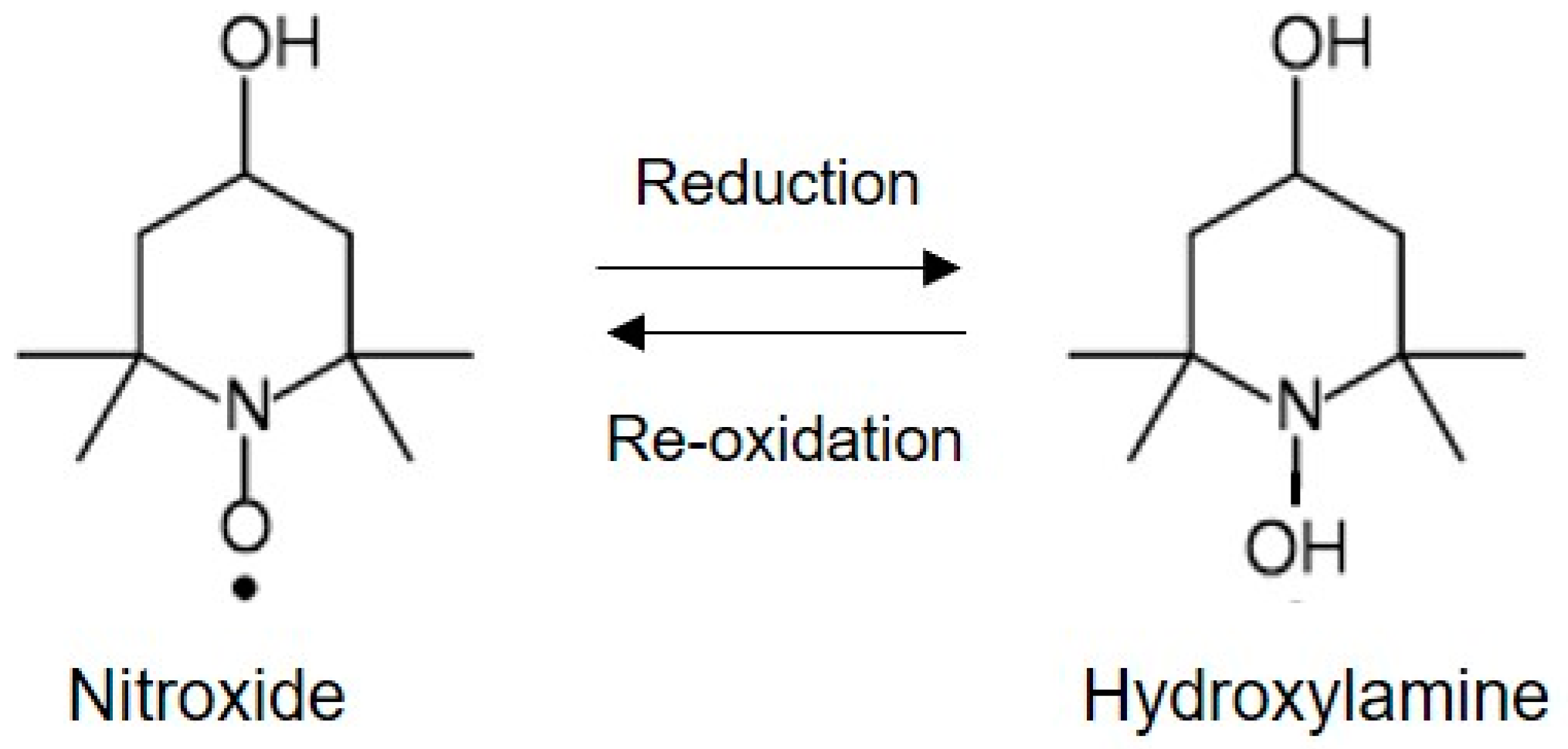
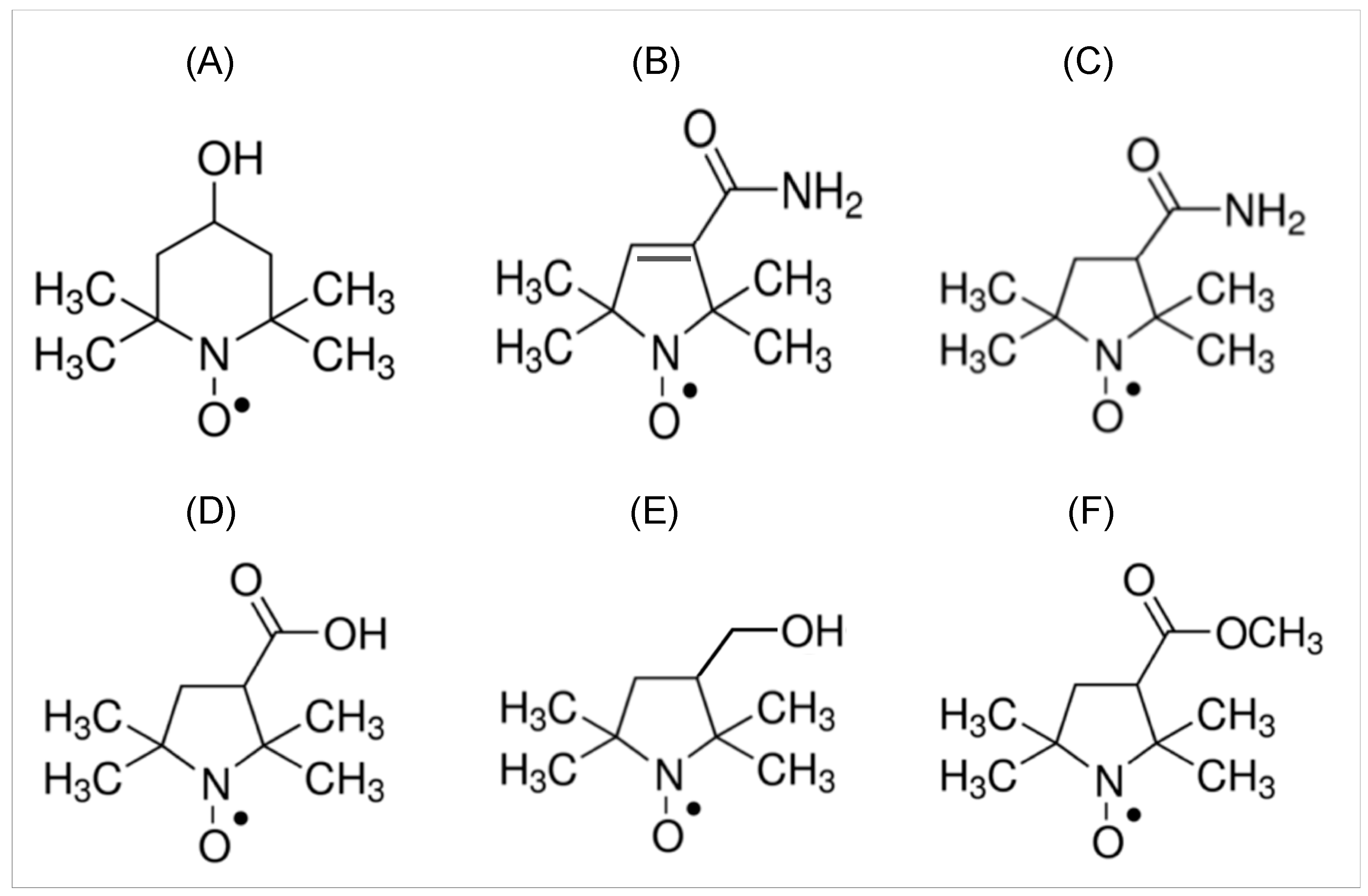
3. Nitroxide Imaging Probes for EPR Imaging Study
4. Coregistration EPR/NMR Imaging
5. Brain Redox Imaging by CW-EPR Imager
5.1. Three-Dimensional EPR Imaging of the Mouse Head
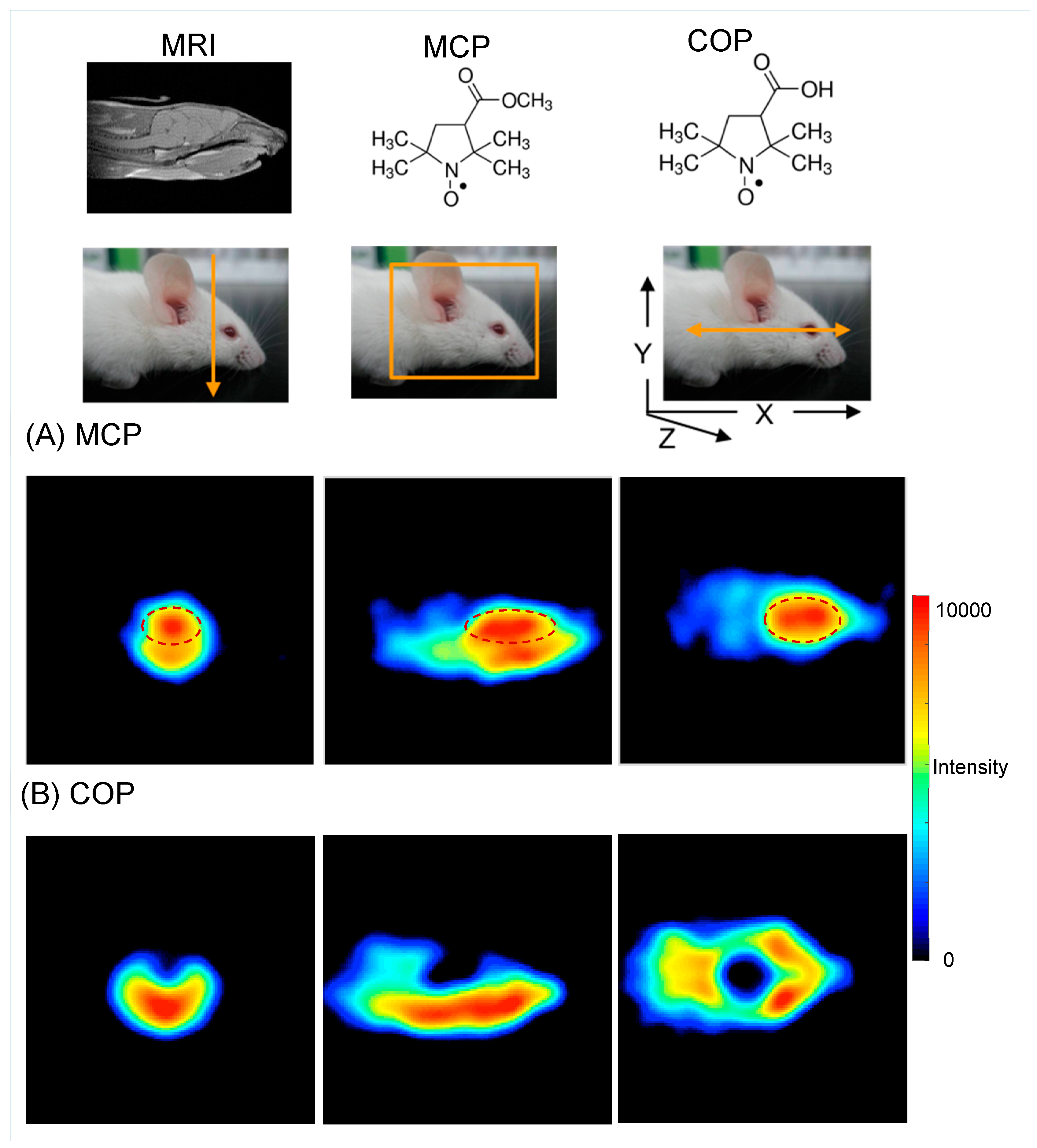
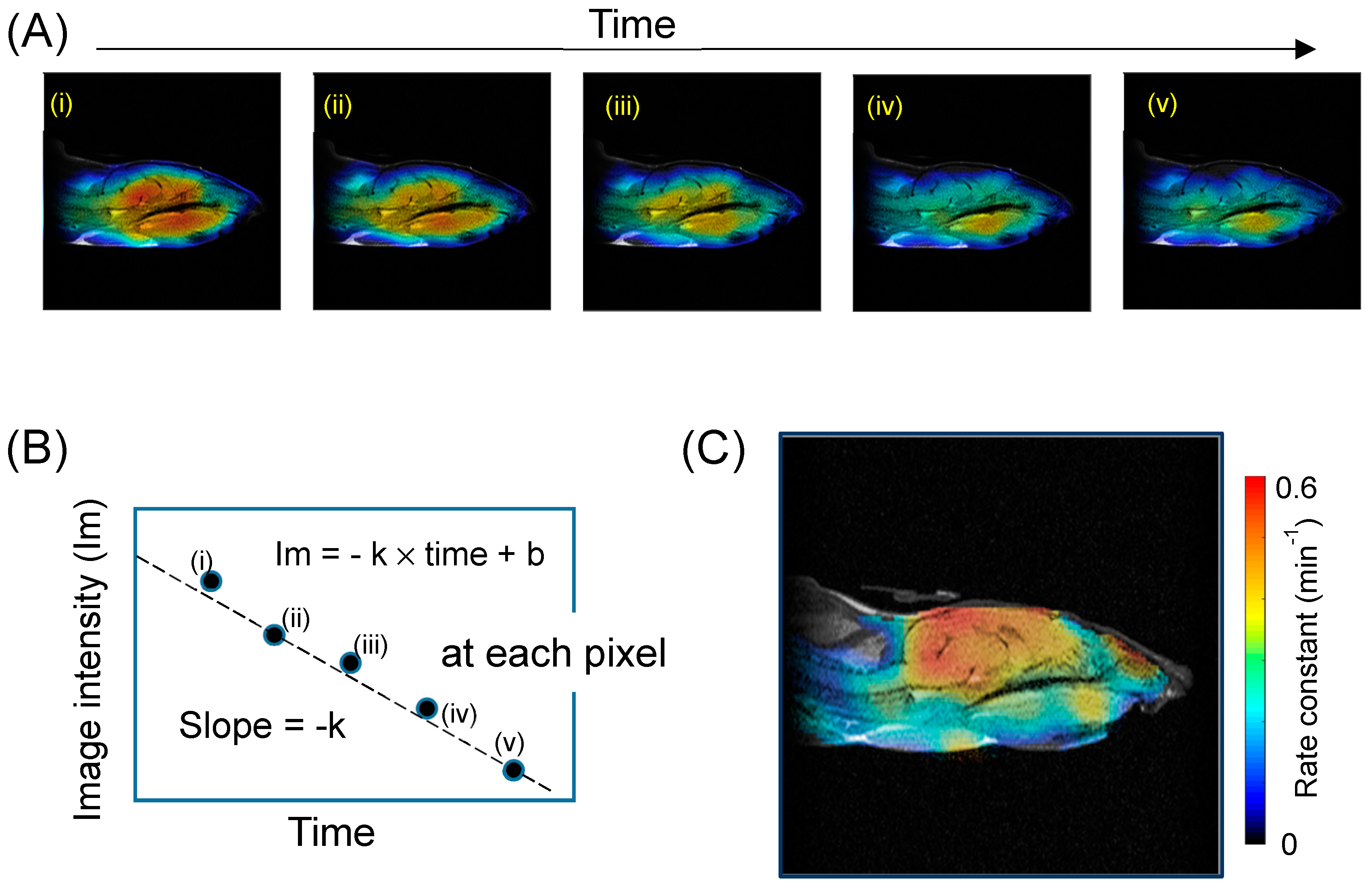
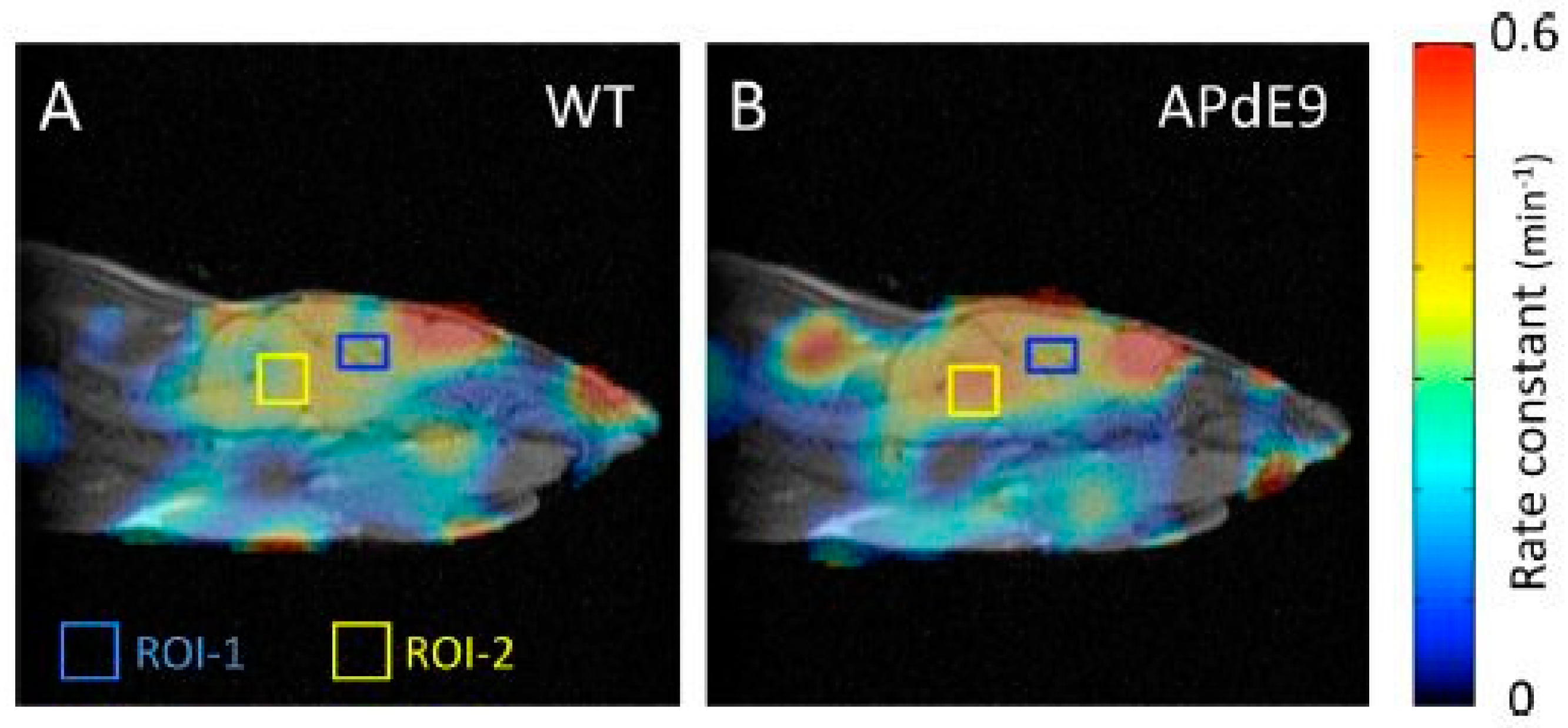
5.2. Redox Mapping
5.3. Glutathione (GSH) Mapping
6. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CMP | 3-carbamoyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethylpyrrolidin-1-oxyl |
| COP | 3-carboxy-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-1-pyrrolidin-1-oxyl |
| CTPO | 3-carbamoyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-3-pyrrolin-1-oxyl |
| MCP | 3-methoxycarbonyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethylpyrrrolidine-1-oxyl |
| Tempol | 4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl |
| HMP | 3-hydroxymethyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethylpyrrolidine-1-oxyl |
| ADC | analog-to-digital converter |
| AFC | automatic frequency control |
| Amp | amplifier |
| BPF | band pass filter |
| DAC | digital analog convertor |
| DDC | digital down-converter (DDC) |
| DSP | digital signal processor |
| FPGA | field programmable gate array |
| LNA | a low noise amplifier (LNA) |
| RF | radio frequency |
| VCO | voltage controlled oscillator |
References
- Dikalov, S. Cross talk between mitochondria and NADPH oxidases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamanaka, R.B.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species regulate cellular signaling and dictate biological outcomes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson disease. Nature reviews. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tramutola, A.; Lanzillotta, C.; Perluigi, M.; Butterfield, D.A. Oxidative stress, protein modification and Alzheimer disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2017, 133, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janzen, E.G. Spin trapping. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poyer, J.L.; Floyd, R.A.; McCay, P.B.; Janzen, E.G.; Davis, E.R. Spin-trapping of the trichloromethyl radical produced during enzymic NADPH oxidation in the presence of carbon tetrachloride or bromotrichloromethane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1978, 539, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berliner, L.J.; Fujii, H. Magnetic resonance imaging of biological specimens by lectron paramagnetic resonance of nitroxide spin labels. Science 1985, 227, 517–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berliner, L.J.; Fujii, H.; Wan, X.M.; Lukiewicz, S.J. Feasibility study of imaging a living murine tumor by electron paramagnetic resonance. Magn. Reson. Med. 1987, 4, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpern, H.J.; Peric, M.; Yu, C.; Barth, E.D.; Chandramouli, G.V.; Makinen, M.W.; Rosen, G.M. In vivo spin-label murine pharmacodynamics using low-frequency electron paramagnetic resonance imaging. Biophys. J. 1996, 71, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, S.; Kumashiro, H.; Tsuchihashi, N.; Ogata, T.; Ono, M.; Kamada, H.; Yoshida, E. In vivo analysis of nitroxide radicals injected into small animals by L-band ESR technique. Phys. Med. Biol. 1989, 34, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsumi, H.; Muto, E.; Masuda, S.; Hamada, A. In vivo ESR measurement of free radicals in whole mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 172, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweier, J.L.; Kuppusamy, P. Electron paramagnetic resonance measurements of free radicals in the intact beating heart: A technique for detection and characterization of free radicals in whole biological tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 5703–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasch, R.C. Work in progress: Methods of contrast enhancement for NMR imaging and potential applications. A subject review. Radiology 1983, 147, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.M.; Matsumoto, S.; Bernardo, M.; Sowers, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Krishna, M.C.; Mitchell, J.B. Magnetic resonance imaging of organic contrast agents in mice: Capturing the whole-body redox landscape. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soule, B.P.; Hyodo, F.; Matsumoto, K.; Simone, N.L.; Cook, J.A.; Krishna, M.C.; Mitchell, J.B. The chemistry and biology of nitroxide compounds. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 1632–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swartz, H.M.; Sentjurc, M.; Morse, P.D., 2nd. Cellular metabolism of water-soluble nitroxides: Effect on rate of reduction of cell/nitroxide ratio, oxygen concentrations and permeability of nitroxides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 888, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyodo, F.; Matsumoto, S.; Devasahayam, N.; Dharmaraj, C.; Subramanian, S.; Mitchell, J.B.; Krishna, M.C. Pulsed EPR imaging of nitroxides in mice. J. Magn. Reson. 2009, 197, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emoto, M.C.; Matsuoka, Y.; Yamada, K.I.; Sato-Akaba, H.; Fujii, H.G. Non-invasive imaging of the levels and effects of glutathione on the redox status of mouse brain using electron paramagnetic resonance imaging. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 485, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emoto, M.C.; Sato-Akaba, H.; Matsuoka, Y.; Yamada, K.I.; Fujii, H.G. Non-invasive mapping of glutathione levels in mouse brains by in vivo electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) imaging: Applied to a kindling mouse model. Neurosci Lett 2018, 690, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demsar, F.; Walczak, T.; Morse, P.D.I.; Bacic, G.; Zolnai, Z.; Swartz, H.M. Detection of diffusion and distribution of oxygen by fast-scan EPR imaging. J. Magn. Reson. 1988, 76, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alecci, M.; Colacicchi, S.; Indovina, P.L.; Momo, F.; Pavone, P.; Sotgiu, A. Three-dimensional in vivo ESR imaging in rats. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1990, 8, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H.; Ogata, T.; Tsuchihashi, N.; Hiramatsu, M.; Mori, N. A spatiotemporal study on the distribution of intraperitoneally injected nitroxide radical in the rat head using an in vivo ESR imaging system. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1996, 14, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samouilov, A.; Caia, G.L.; Kesselring, E.; Petryakov, S.; Wasowicz, T.; Zweier, J.L. Development of a hybrid EPR/NMR coimaging system. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 58, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato-Akaba, H.; Abe, H.; Fujii, H.; Hirata, H. Slice-selective images of free radicals in mice with modulated field gradient electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 59, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Sato-Akaba, H.; Kawanishi, K.; Hirata, H. Mapping of redox status in a brain-disease mouse model by three-dimensional EPR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato-Akaba, H.; Emoto, M.C.; Hirata, H.; Fujii, H.G. Design and testing of a 750 MHz CW-EPR digital console for small animal imaging. J. Magn. Reson. 2017, 284, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Zweier, J.L. Cardiac applications of EPR imaging. NMR Biomed. 2004, 17, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, H.; Lin, Y.; Itoh, O.; Ueda, Y.; Nakajima, A.; Ogata, T.; Sato, T.; Ohya-Nishiguchi, H.; Kamada, H. EPR imaging for in vivo analysis of the half-life of a nitroxide radical in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex of rats after epileptic seizures. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Utsumi, H. Synthesis and imaging of blood-brain-barrier permeable nitroxyl-probes for free radical reactions in brain of living mice. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1997, 42, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, H.; Itoh, O.; Aoyama, M.; Obara, H.; Ohya, H.; Kamada, H. In vivo temporal EPR imaging of the brain of rats by using two types of blood-brain barrier-permeable nitroxide radicals. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2002, 20, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, A.; Ito, R.; Fujii, H.; Hirata, H. Simultaneous molecular imaging based on electron paramagnetic resonance of 14N- and 15N-labelled nitroxyl radicals. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 3245–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Villamena, F.A.; Song, Y.; Sun, J.; Rockenbauer, A.; Zweier, J.L. Synthesis of 14N- and 15N-labeled trityl-nitroxide biradicals with strong spin-spin interaction and improved sensitivity to redox status and oxygen. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 7796–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, Y.; Wang, X.; Amasaka, M.; Itto, K.; Xu, S.; Arimoto, H.; Fujii, H.; Hirata, H. Simultaneous imaging of an enantiomer pair by electron paramagnetic resonance using isotopic nitrogen labeling. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, W.; Miyake, Y.; Hirata, H. Artifact suppression in electron paramagnetic resonance imaging of (14)N- and (15)N-labeled nitroxyl radicals with asymmetric absorption spectra. J. Magn. Reson. 2014, 247, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Deng, Y.; Li, H.; Kuppusamy, P.; Zweier, J.L. EPR/NMR co-imaging for anatomic registration of free-radical images. Magn. Reson. Med. 2002, 47, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawada, Y.; Hirata, H.; Fujii, H. Use of multi-coil parallel-gap resonators for co-registration EPR/NMR imaging. J. Magn. Reson. 2007, 184, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Aoki, M.; Haishi, T.; Itoh, K.; Sakata, M. Development of an ESR/MR dual-imaging system as a tool to detect bioradicals. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2006, 5, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, M.C.; Russo, A.; Mitchell, J.B.; Goldstein, S.; Dafni, H.; Samuni, A. Do nitroxide antioxidants act as scavengers of O2-. or as SOD mimics? J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 26026–26031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuni, A.; Mitchell, J.B.; DeGraff, W.; Krishna, C.M.; Samuni, U.; Russo, A. Nitroxide SOD-mimics: Modes of action. Free Radic. Res. Commun. 1991, 12–13 Pt 1, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, S.M.; Tochner, Z.; Krishna, C.M.; Glass, J.; Wilson, L.; Samuni, A.; Sprague, M.; Venzon, D.; Glatstein, E.; Mitchell, J.B.; et al. Tempol, a stable free radical, is a novel murine radiation protector. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 1750–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, J.B.; Russo, A.; Kuppusamy, P.; Krishna, M.C. Radiation, radicals, and images. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 899, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, C.S. Effects of tempol and redox-cycling nitroxides in models of oxidative stress. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 126, 119–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Kawanishi, K.; Sato-Akaba, H.; Emoto, M.; Hirata, H. Detection of blood-brain barrier disruption in a mouse model of transient cerebral ischemia by EPR imaging. In Proceedings of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 19th Annual Meeting, Montreal, QC, Canada, 9–13 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bacic, G.; Pavicevic, A.; Peyrot, F. In vivo evaluation of different alterations of redox status by studying pharmacokinetics of nitroxides using magnetic resonance techniques. Redox Biol. 2016, 8, 226–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epel, B.; Sundramoorthy, S.V.; Krzykawska-Serda, M.; Maggio, M.C.; Tseytlin, M.; Eaton, G.R.; Eaton, S.S.; Rosen, G.M.; Kao, J.P.Y.; Halpern, H.J. Imaging thiol redox status in murine tumors in vivo with rapid-scan electron paramagnetic resonance. J. Magn. Reson. 2017, 276, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khramtsov, V.V. In Vivo Molecular Electron Paramagnetic Resonance-Based Spectroscopy and Imaging of Tumor Microenvironment and Redox Using Functional Paramagnetic Probes. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Li, H.; Ilangovan, G.; Cardounel, A.J.; Zweier, J.L.; Yamada, K.; Krishna, M.C.; Mitchell, J.B. Noninvasive imaging of tumor redox status and its modification by tissue glutathione levels. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Emoto, M.C.; Yamato, M.; Sato-Akaba, H.; Yamada, K.; Matsuoka, Y.; Fujii, H.G. Brain imaging in methamphetamine-treated mice using a nitroxide contrast agent for EPR imaging of the redox status and a gadolinium contrast agent for MRI observation of blood-brain barrier function. Free Radic. Res. 2015, 49, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.G.; Sato-Akaba, H.; Emoto, M.C.; Itoh, K.; Ishihara, Y.; Hirata, H. Noninvasive mapping of the redox status in septic mouse by in vivo electron paramagnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 31, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, A.; Emoto, M.C.; Suzuki, S.; Iwahara, N.; Hisahara, S.; Kawamata, J.; Suzuki, H.; Yamauchi, A.; Sato-Akaba, H.; Fujii, H.G.; et al. Evaluation of oxidative stress in the brain of a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease by in vivo electron paramagnetic resonance imaging. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 85, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischley, L.K.; Lau, R.C.; Shankland, E.G.; Wilbur, T.K.; Padowski, J.M. Phase IIb Study of Intranasal Glutathione in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2017, 7, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharan, S.; Mandal, P.K. The emerging role of glutathione in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 40, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.I.; Kuppusamy, P.; English, S.; Yoo, J.; Irie, A.; Subramanian, S.; Mitchell, J.B.; Krishna, C.M. Feasibility and assessment of non-invasive in vivo redox status using electron paramagnetic resonance imaging. Acta Radiol. 2002, 43, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soikkeli, M.; Horkka, K.; Moilanen, J.O.; Timonen, M. Synthesis, Stability and Relaxivity of TEEPO-Met: An Organic Radical as a Potential Tumour Targeting Contrast Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Molecules 2018, 23, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujii, H.G.; Emoto, M.C.; Sato-Akaba, H. Brain Redox Imaging Using In Vivo Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Imaging and Nitroxide Imaging Probes. Magnetochemistry 2019, 5, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5010011
Fujii HG, Emoto MC, Sato-Akaba H. Brain Redox Imaging Using In Vivo Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Imaging and Nitroxide Imaging Probes. Magnetochemistry. 2019; 5(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujii, Hirotada G., Miho C. Emoto, and Hideo Sato-Akaba. 2019. "Brain Redox Imaging Using In Vivo Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Imaging and Nitroxide Imaging Probes" Magnetochemistry 5, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5010011
APA StyleFujii, H. G., Emoto, M. C., & Sato-Akaba, H. (2019). Brain Redox Imaging Using In Vivo Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Imaging and Nitroxide Imaging Probes. Magnetochemistry, 5(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5010011



