Impact of Various Salinity Levels and Fusarium oxysporum as Stress Factors on the Morpho-Physiological and Yield Attributes of Onion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Impact of Salinity on FOC Performance in Laboratory
2.2. Analysis of Physio-Chemical Behavior of Soil
2.3. Preparation of Saline Soil
2.4. Physiological Assays
2.5. Antioxidant Enzymes Assays
2.6. Growth Assays
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
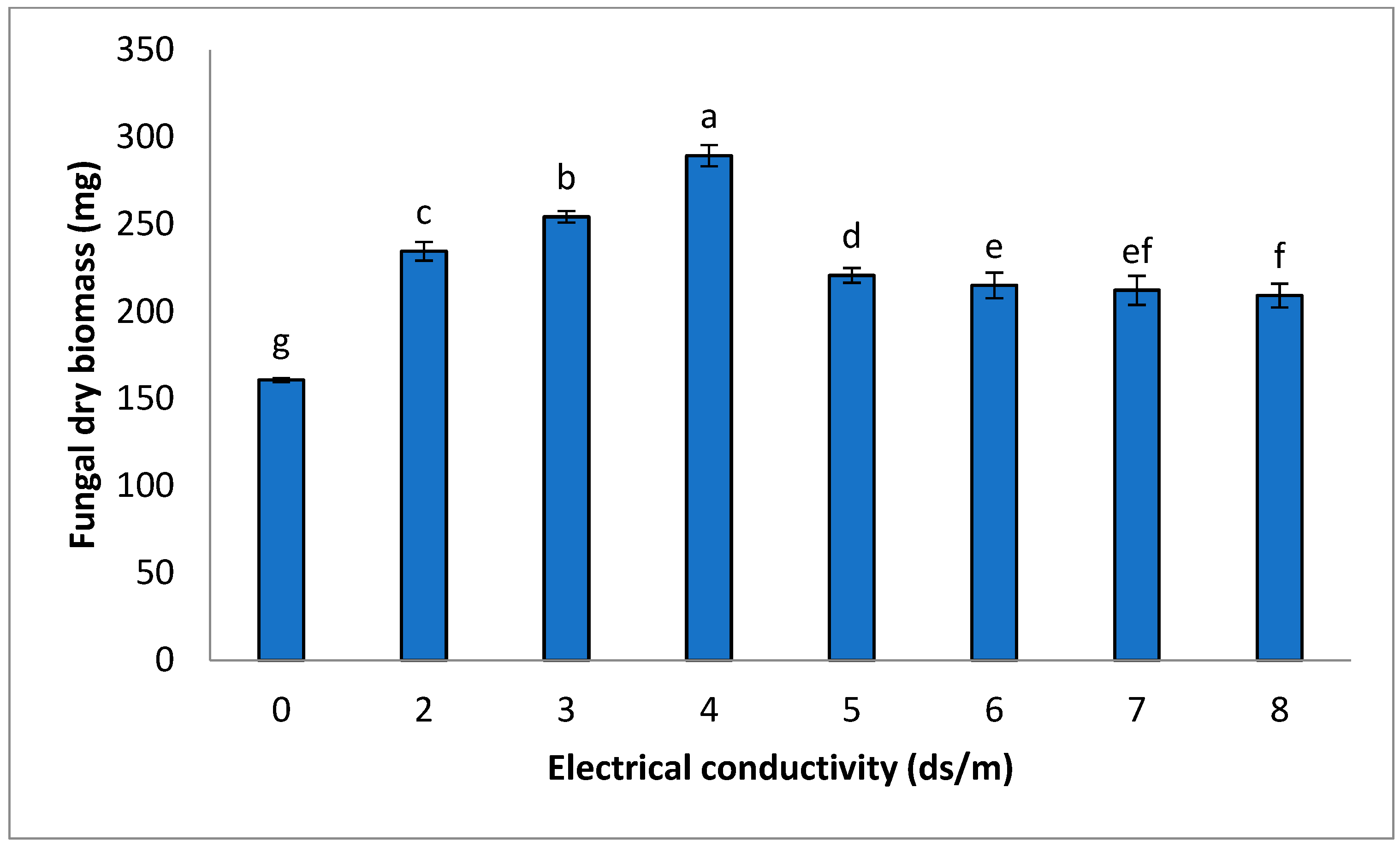
3.1. Impact of Saline Solution on Fungal (FOC) Growth in Controlled Conditions
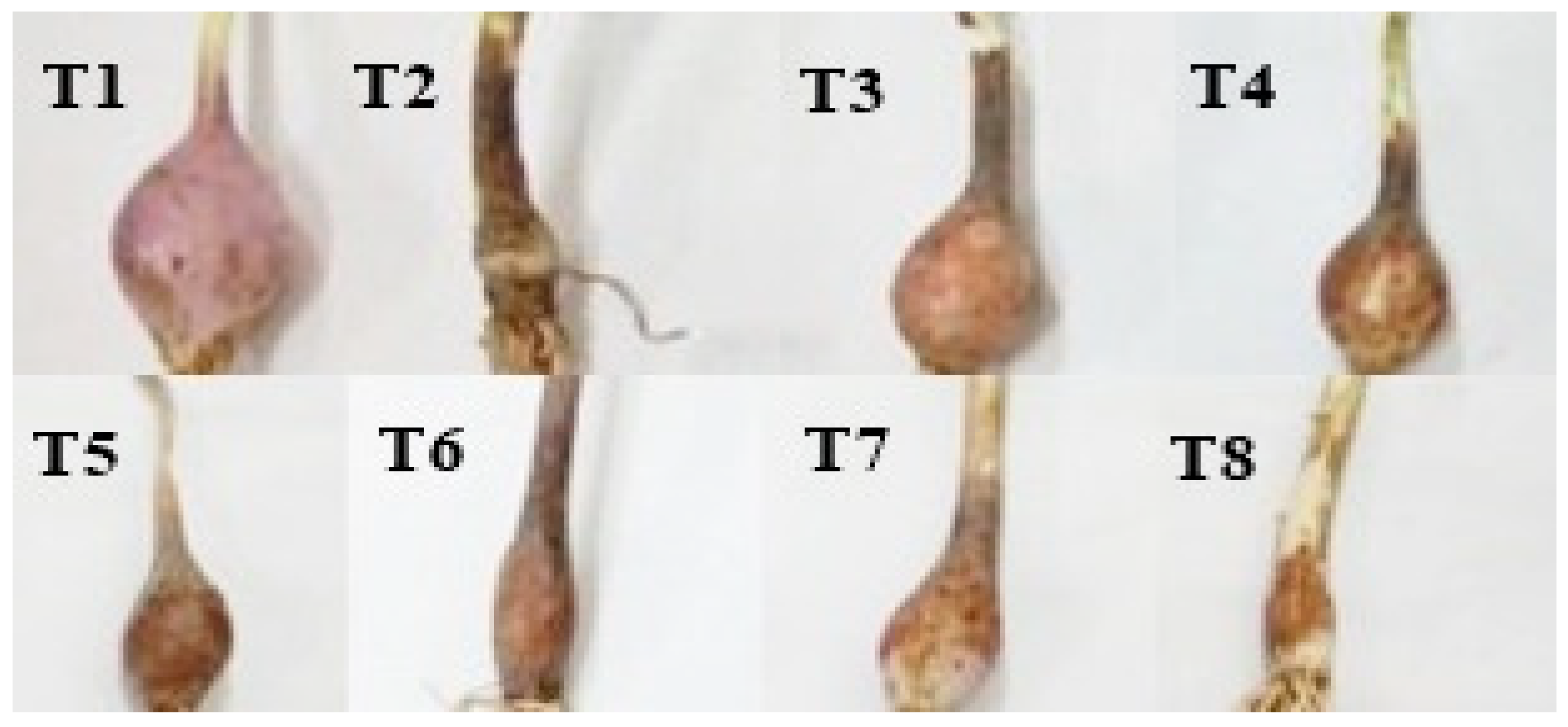
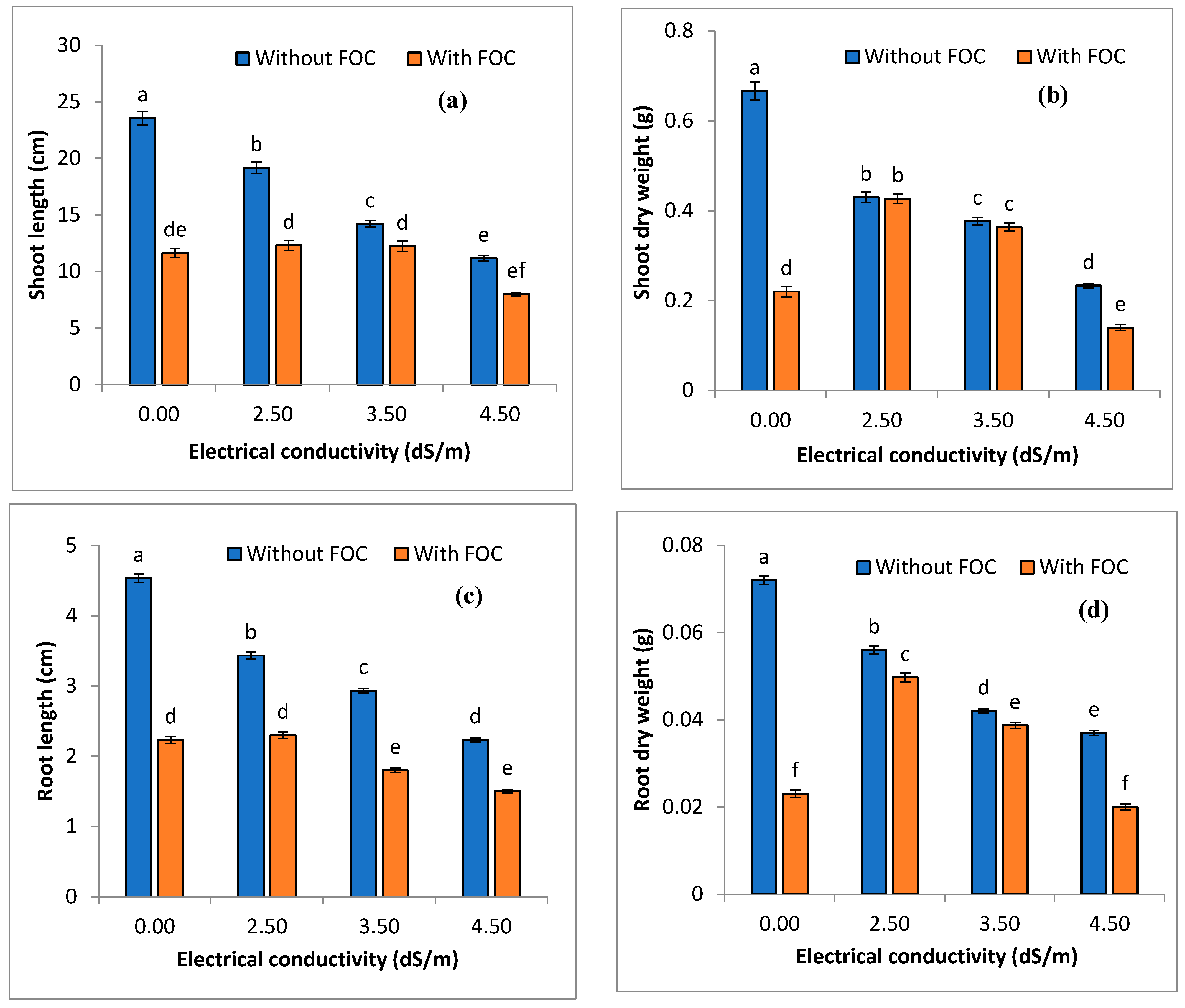
3.2. Impact of FOC on Growth Attributes of Onions under Stressed Condition
3.3. Impact of Stress Conditions on Physiological Attributes of Onions
3.4. Impact of Stress Conditions on Biochemical Attributes of Onions
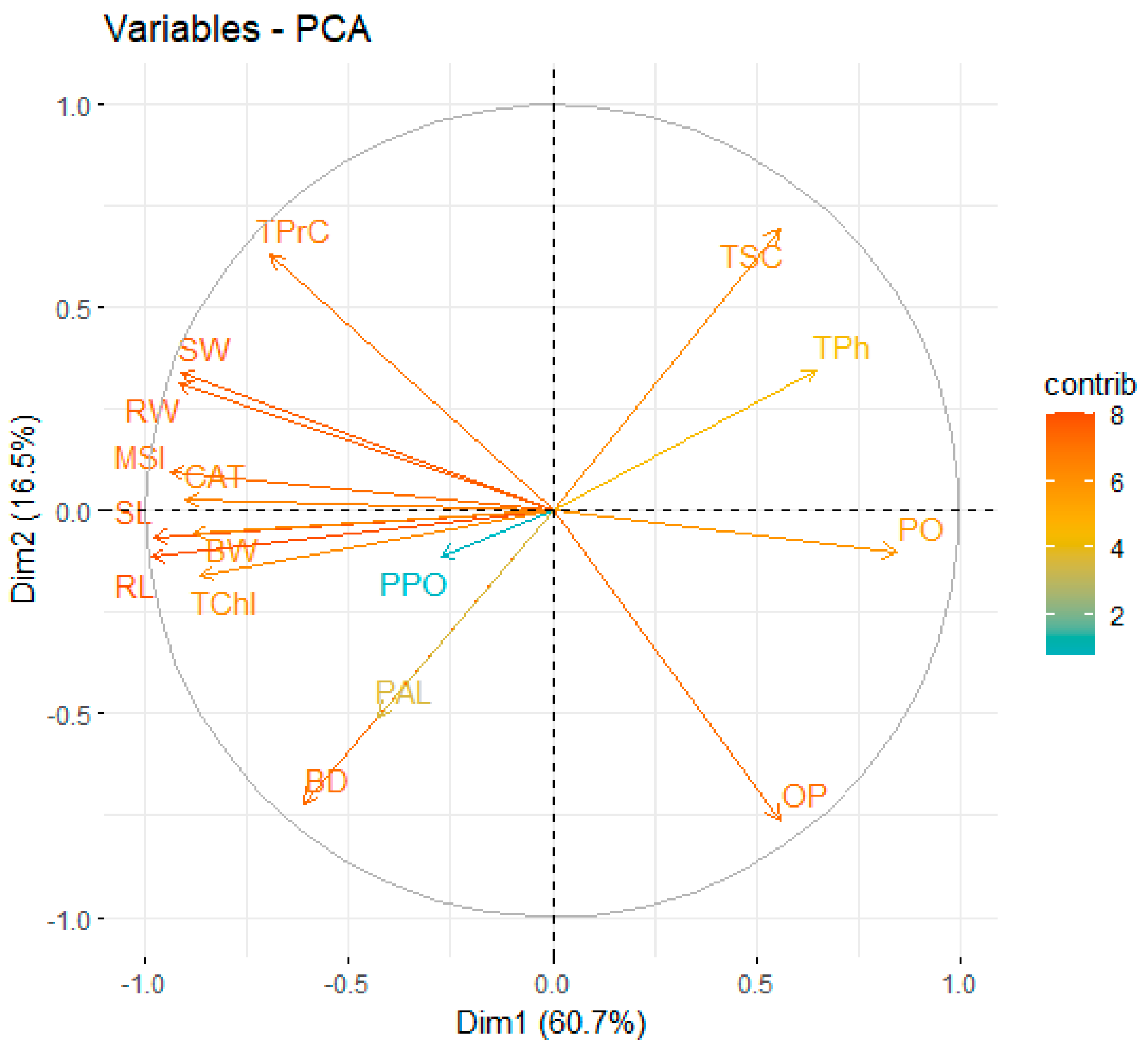
3.5. Correlation and Principal Component Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kibria, M.G.; Hoque, M.A. A Review on Plant Responses to Soil Salinity and Amelioration Strategies. Open J. Soil Sci. 2019, 9, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.; Sarwar, G.; Shah, S.H.; Muhammad, S. Soil Salinity Research in 21st Century in Pakistan: Its Impact on Availability of Plant Nutrients, Growth and Yield of Crops. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2021, 52, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboob, W.; Khan, A.; Shirazi, M.U. Induction of Salt Tolerance in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Seedlings through Exogenous Application of Proline. Pak. J. Bot. 2016, 48, 861–867. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, R.M.A.; Serralheiro, R.P. Soil Salinity: Effect on Vegetable Crop Growth. Management Practices to Prevent and Mitigate Soil Salinization. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourasia, K.N.; More, S.J.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, D.; Singh, B.; Bhardwaj, V.; Kumar, A.; Das, S.K.; Singh, R.K.; Zinta, G.; et al. Salinity responses and tolerance mechanisms in underground vegetable crops: An integrative review. Planta 2021, 255, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Davranov, K.; Wirth, S.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F. Impact of soil salinity on the plant-growth–promoting and biological control abilities of root associated bacteria. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Crop Water Information; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2021. Available online: https://www.fao.org/land-water/databases-and-software/crop-information/en/ (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Economic Survey of Pakistan (ESP), Government of Pakistan, Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Livestock; Federal Bureau of Statistics: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2021.
- Le, D.; Audenaert, K.; Haesaert, G. Fusarium basal rot: Profile of an increasingly important disease in Allium spp. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2021, 46, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.M.; Sahi, S.T.; Habib, A.; Ashraf, W.; Zeshan, M.A.; Raheel, M.; Shakeel, Q. Management of Fusarium Basal Rot of Onion caused by Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cepae through Desert Plants Extracts. Sarhad J. Agric. 2021, 37, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamyuktha, J.; Sheela, J.; Rajinimala, N.; Jeberlinprabina, B.; Ravindran, C. Survey on Onion Basal Rot Disease Incidence and Evaluation of Aggregatum Onion (Allium cepa L. Var. Aggregatum Don.) Genotypes Against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Cepae. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2020, 9, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, C.S.; Mandal, S.; Sharma, S.; Nourbakhsh, S.S.; Goldman, I.; Guzman, I. Recent Advances in Onion Genetic Improvement. Agronomy 2021, 11, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Irulappan, V.; Bagavathiannan, M.V.; Senthil-Kumar, M. Impact of Combined Abiotic and Biotic Stresses on Plant Growth and Avenues for Crop Improvement by Exploiting Physio-morphological Traits. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Cheng, Z.; Ahmad, H.; Hayat, S. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as defenses against a broad range of plant fungal infections and case study on ROS employed by crops against Verticillium dahliae wilts. J. Plant Interact. 2018, 13, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, A.; Meraj, S.; Nafisa; Khan, K.A.; Javaid, M.A. Influence of salinity and Fusarium oxysporum as the stress factors on morpho-physiological and yield attributes in onion. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2018, 24, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, E.O. Soil pH and Lime Requirement. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Page, A.L., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America J.: Madison, AL, USA, 1982; pp. 199–223. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; Agric. Handbook No 60; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; Volume 78, p. 154.
- Pang, H.-C.; Li, Y.-Y.; Yang, J.-S.; Liang, Y.-S. Effect of brackish water irrigation and straw mulching on soil salinity and crop yields under monsoonal climatic conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1971–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coşkuntuna, A.; Özer, N. Biological control of onion basal rot disease using Trichoderma harzianum and induction of antifungal compounds in onion set following seed treatment. Crop Prot. 2008, 27, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capell, B.; Dorffling, K. Genotype-specific differences in chilling tolerance of maize in relation to chilling-induced changes in water status and abscisic acid accumulation. Physiol. Plant. 1993, 88, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenthaler, K.; Welburn, A.R. Determination of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1983, 11, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N. A photometric adaptation of the Somogyi method for the determination of glucose. J. Biol. Chem. 1944, 153, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saneoka, H.; Moghaieb, R.E.A.; Premachandra, G.S.; Fujita, K. Nitrogen nutrition and water stress effects on cell membrane stability and leaf water relations in Agrostis palustris Huds. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2004, 52, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanek, H.; Kuzniak-Gebarowska, E.; Herka, K. Elicitation of Defence Responses in Bean Leaves by Botrytis cinerea Polygalacturonase. Acta Physiol. Plant. 1991, 13, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Gauillard, F.; Richardforget, F.; Nicolas, J. New Spectrophotometric Assay for Polyphenol Oxidase Activity. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 215, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarathna, K.C.; Shetty, S.A.; Shetty, H.S. Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase Activity in Pearl Millet Seedlings and its Relation to Downy Mildew Disease Resistance. J. Exp. Bot. 1993, 265, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, C.P.; Singh, M.B. Phenolics. In Plant Enzymology and Histo Enzymology; Kalyani Publishers: New Delhi, India, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson, D.P.; Pascholati, S.E.; Hagerman, A.E.; Butler, L.G.; Nicholson, R.L. Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase and Hydroxycinnamate: Mesocotyls Inoculated with Helminthosporium maydis or Helminthosporium carbonum. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1984, 25, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maehly, A.C.; Chance, B. The Assay of Catalases and Peroxidases. Methods Biochem. Anal. 1954, 1, 357–424. [Google Scholar]
- Boumaaza, B.; Benada, M.H.; Boudalia, S.; Benzohra, I.E.; Gacemi, A.; Khaladi, O.; Benkhelifa, M. Effect of salinity levels on antifungal activity of essential oil from Thymus against Fusarium oxysporum. Rev. Fac. Agron. (LUZ) 2022, 39, e223941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A.; Koriem, A.; Younis, S.; Elian, M. Effect of some salts on the mycelial growth and spore germination of fungi caused fruit rot of sweet pepper post-harvest diseases pathogens. J. Prod. Dev. 2021, 26, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumaaza, B.; Benkhelifa, M.; Belkhoudja, M. Effects of two salts compounds on mycelial growth, sporulation, and spore germination of six isolates of Botrytis cinerea in the Western North of Algeria. Int. J. Microbiol. 2015, 2015, 572626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Plemenitaš, A.; Oren, A. Strategies of adaptation of microorganisms of the three domains of life to high salt concentrations. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A. Insights into the sequence parameters for halophilic adaptation. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmajdoub, B.; Marschner, P. Responses of Soil Microbial Activity and Biomass to Salinity After Repeated Additions of Plant Residues. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Nakahara, K.; Tanaka, S.; Shigyo, M.; Ito, S.I. Genetic and pathogenic variability of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cepae Isolated from onion and Welsh onion in JP. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gull, A.; Lone, A.; Wani, N.I. Biotic and Abiotic Stresses in Plants. Abiotic Biot. Stress Plants 2019, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gad, N.; Hassan, N.M.; Sayed, S.A.A.E. Influence of Cobalt on Tolerating Climatic Change (Salinity) in Onion Plant with Reference to Physiological and Chemical Approach. Plant Arch. 2020, 20, 1496–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Palma, J.M.; Sandalio, L.M.; Corpas, F.J.; Romero-Puertas, M.C.; McCarthy, I.; del Río, L.A. Plant proteases, protein degradation, and oxidative stress: Role of peroxisomes. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 40, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansha, M.Z.; Habib, A.; Ashraf, W.; Shakeel, Q.; Raheel, M.; Zaman, Q.; Aatif, H.M.; Tahir, M. Impact of Resistance Inducers on Biochemical Attributes of Onion Leaves against Purple Blotch (Alternaria porri). Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 9773–9784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Yang, K.; Erhunmwunsee, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Pan, S.; Yang, D.; Lu, G.; Ma, D.; Tian, J. Inhibitory effect of cinnamaldehyde on Fusarium solani and its application in postharvest preservation of sweet potato. Food Chem. 2023, 408, 135213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, X.; Gao, F.; Liu, Y.; Lang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, D. Effect of ultrasound combined with exogenous GABA treatment on polyphenolic metabolites and antioxidant activity of mung bean during germination. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2023, 94, 106311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| EC (dS m−1) | Sodium Chloride | Sodium Sulphate | Calcium Chloride | Magnesium Sulphate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.024 | 0.042 | 0.020 | 0.011 |
| 3 | 0.032 | 0.067 | 0.045 | 0.024 |
| 4 | 0.036 | 0.090 | 0.072 | 0.039 |
| 5 | 0.038 | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.057 |
| 6 | 0.039 | 0.146 | 0.154 | 0.083 |
| 7 | 0.119 | 0.221 | 0.119 | 0.064 |
| 8 | 0.134 | 0.249 | 0.136 | 0.074 |
| Treatment | Osmotic Potential (Mpa) | Total Chlorophyll Content (mg/g) | Membrane Stability Index (%) | Total Sugar Content (mg/g) | Total Phenolics (mg/g) | Total Protein Content (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | −1.01 b | 0.97 a | 88.66 a | 1.38 g | 2.80 f | 1.83 a |
| T2 | −0.82 d | 0.82 c | 73.33 b | 0.91 h | 3.90 e | 0.82 f |
| T3 | −0.93 c | 0.91 b | 58.33 c | 1.47 f | 6.50 a | 1.37 c |
| T4 | −0.76 e | 0.81 c | 51.00 e | 2.14 e | 5.75 b | 0.86 e |
| T5 | −0.53 f | 0.80 cd | 38.00 g | 2.47 d | 5.39 c | 0.61 h |
| T6 | −1.08 a | 0.77 de | 55.00 d | 5.04 a | 6.63 a | 1.62 b |
| T7 | −0.76 e | 0.75 ef | 46.33 f | 4.80 b | 5.37 c | 0.96 d |
| T8 | −0.74 e | 0.74 f | 47.33 f | 3.28 c | 4.81 d | 0.67 g |
| Variables | BD | BW | CAT | MSI | OP | PAL | PO | PPO |
| BW | 0.57 ** | |||||||
| Cat | 0.41 ** | 0.82 ** | ||||||
| MSI | 0.51 ** | 0.79 ** | 0.79 ** | |||||
| OP | 0.14 | −0.39 | −0.45 ** | −0.64 ** | ||||
| PAL | 0.52 ** | 0.41 ** | 0.54 ** | 0.12 | 0.23 | |||
| PO | −0.33 | −0.62 ** | −0.83 ** | −0.69 ** | 0.48 ** | −0.58 ** | ||
| PPO | 0.13 | −0.15 | 0.23 | 0.26 | −0.10 | 0.21 | −0.56 ** | |
| RL | 0.70 ** | 0.84 ** | 0.84 ** | 0.92 ** | −0.48 ** | 0.45 ** | −0.79 ** | 0.29 |
| RW | 0.32 | 0.72 ** | 0.78 ** | 0.91 ** | −0.73 ** | 0.15 | −0.80 ** | 0.32 |
| SL | 0.62 ** | 0.83 ** | 0.83 ** | 0.92 ** | −0.46 ** | 0.39 | −0.84 ** | 0.36 |
| SW | 0.30 | 0.79 ** | 0.79 ** | 0.85 ** | −0.70 ** | 0.24 | −0.84 ** | 0.24 |
| TChl | 0.76 ** | 0.81 ** | 0.63 ** | 0.76 ** | −0.43 ** | 0.43 ** | −0.58 ** | 0.03 |
| TPh | −0.54 ** | −0.73 ** | −0.65 ** | −0.69 ** | 0.01 | −0.21 | 0.40 ** | −0.06 |
| TPrC | 0.04 | 0.63 ** | 0.59 ** | 0.65 ** | −0.89 ** | 0.07 | −0.60 ** | −0.07 |
| TSC | −0.93 ** | −0.42 ** | −0.35 | −0.54 ** | −0.07 | −0.38 | 0.27 | −0.28 |
| RL | RW | SL | SW | TChl | TPh | TPrC | ||
| RW | 0.87 ** | |||||||
| SL | 0.96 ** | 0.90 ** | ||||||
| SW | 0.85 ** | 0.95 ** | 0.89 ** | |||||
| TChl | 0.89 ** | 0.69 ** | 0.80 ** | 0.70 ** | ||||
| TPh | −0.63 ** | −0.50 ** | −0.70 ** | −0.49 ** | −0.42 ** | |||
| TPrC | 0.62 ** | 0.77 ** | 0.58 ** | 0.82 ** | 0.64 ** | −0.09 | ||
| TSC | −0.66 ** | −0.31 | −0.57 ** | −0.21 | −0.68 ** | 0.49 ** | 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mansha, M.Z.; Aatif, H.M.; Ikram, K.; Hanif, C.M.S.; Sattar, A.; Iqbal, R.; Zaman, Q.u.; Al-Qahtani, S.M.; Al-Harbi, N.A.; Omar, W.A.; et al. Impact of Various Salinity Levels and Fusarium oxysporum as Stress Factors on the Morpho-Physiological and Yield Attributes of Onion. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070786
Mansha MZ, Aatif HM, Ikram K, Hanif CMS, Sattar A, Iqbal R, Zaman Qu, Al-Qahtani SM, Al-Harbi NA, Omar WA, et al. Impact of Various Salinity Levels and Fusarium oxysporum as Stress Factors on the Morpho-Physiological and Yield Attributes of Onion. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(7):786. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070786
Chicago/Turabian StyleMansha, Muhammad Zeeshan, Hafiz Muhammad Aatif, Kamran Ikram, Ch. Muhammad Shahid Hanif, Abdul Sattar, Rubab Iqbal, Qamar uz Zaman, Salem Mesfir Al-Qahtani, Nadi Awad Al-Harbi, Wael A. Omar, and et al. 2023. "Impact of Various Salinity Levels and Fusarium oxysporum as Stress Factors on the Morpho-Physiological and Yield Attributes of Onion" Horticulturae 9, no. 7: 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070786
APA StyleMansha, M. Z., Aatif, H. M., Ikram, K., Hanif, C. M. S., Sattar, A., Iqbal, R., Zaman, Q. u., Al-Qahtani, S. M., Al-Harbi, N. A., Omar, W. A., & Ibrahim, M. F. M. (2023). Impact of Various Salinity Levels and Fusarium oxysporum as Stress Factors on the Morpho-Physiological and Yield Attributes of Onion. Horticulturae, 9(7), 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070786








