Egyptian Opuntia ficus-indica (OFI) Residues: Recovery and Characterization of Fresh Mucilage from Cladodes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
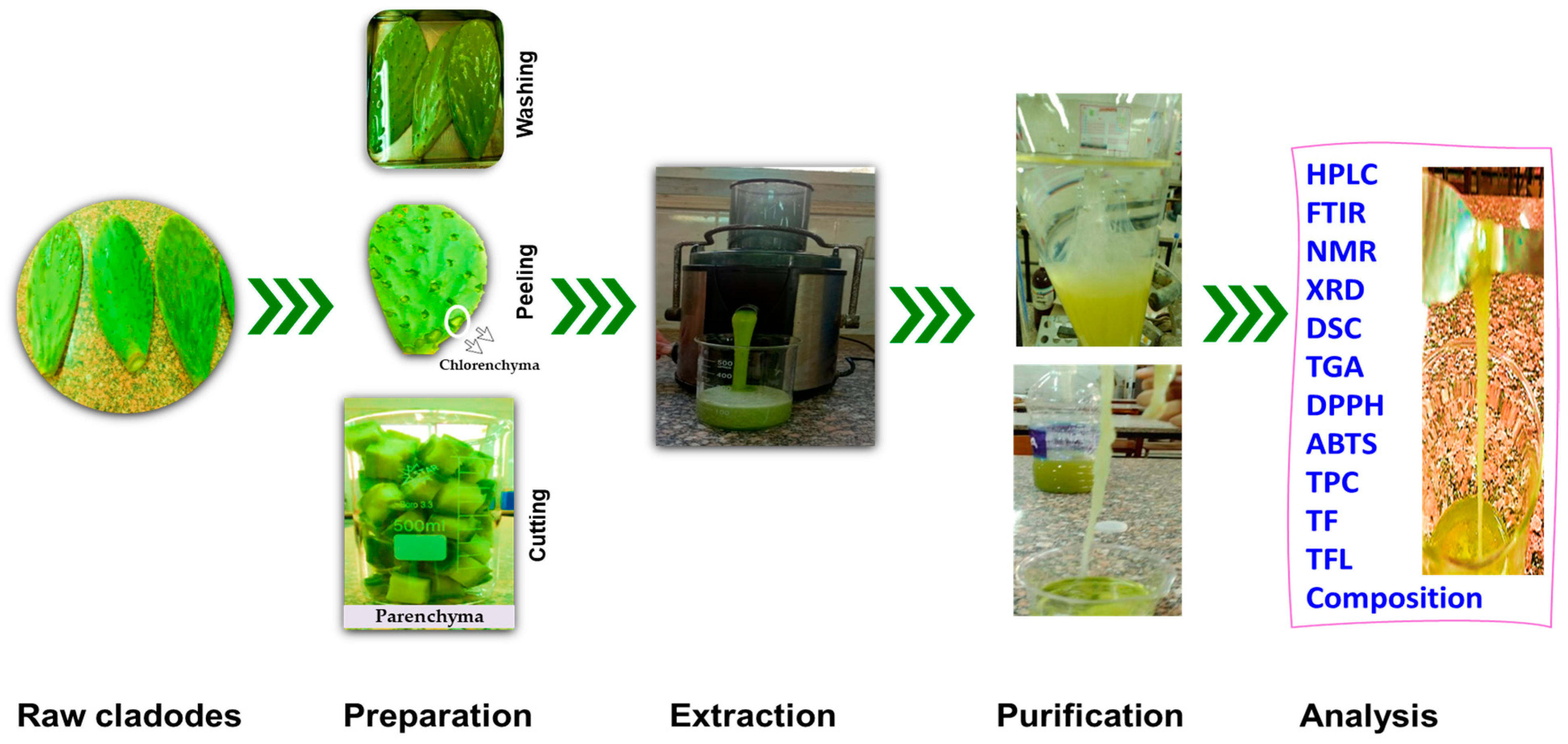
2.2. Raw Materials
2.3. Mucilage’s Extraction
2.4. Chemical Characterization
2.4.1. Chemical Composition
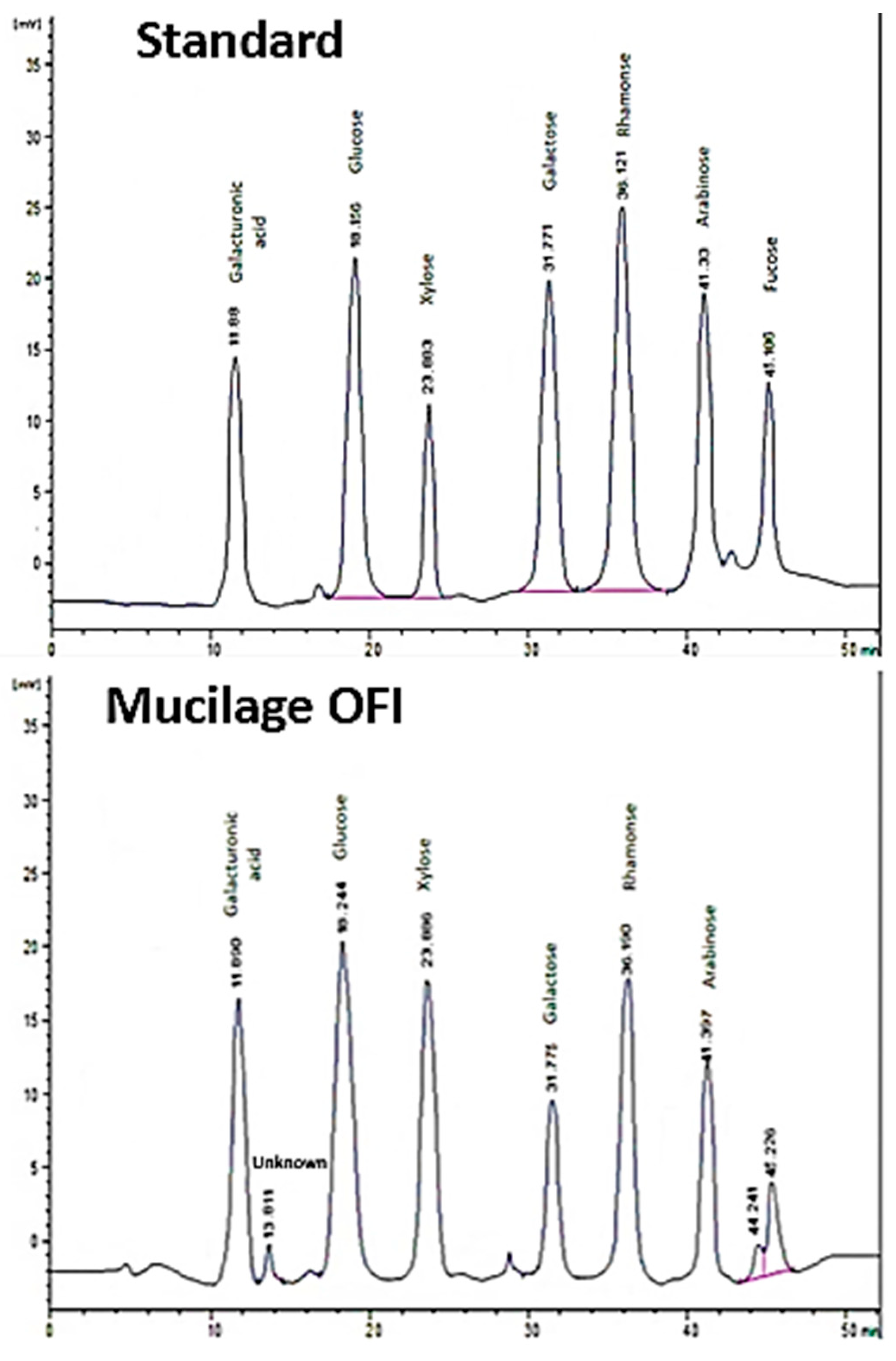
2.4.2. Sugar Composition
2.4.3. Antioxidant Polyphenols
2.5. Structural Properties
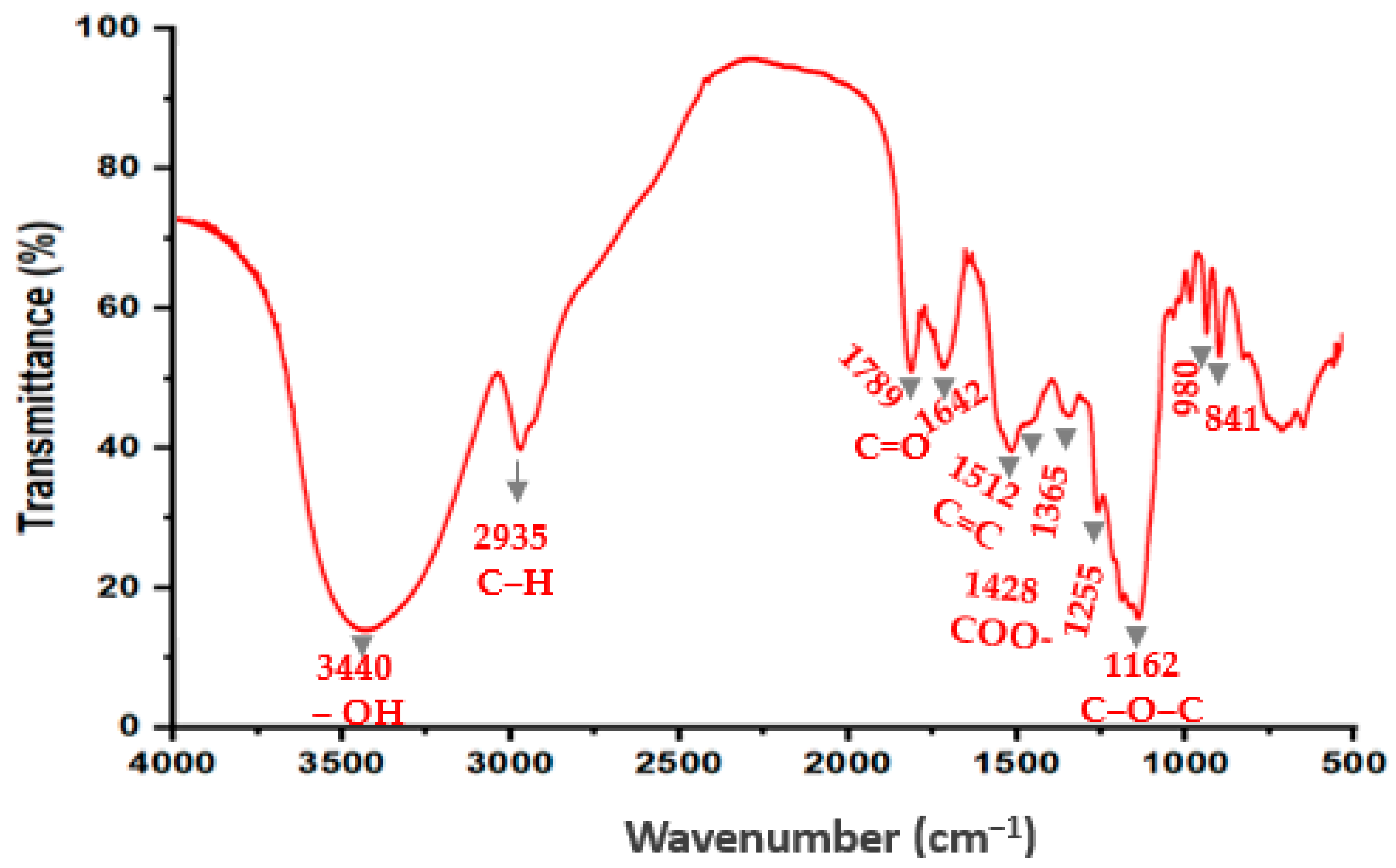
2.5.1. FTIR Analysis
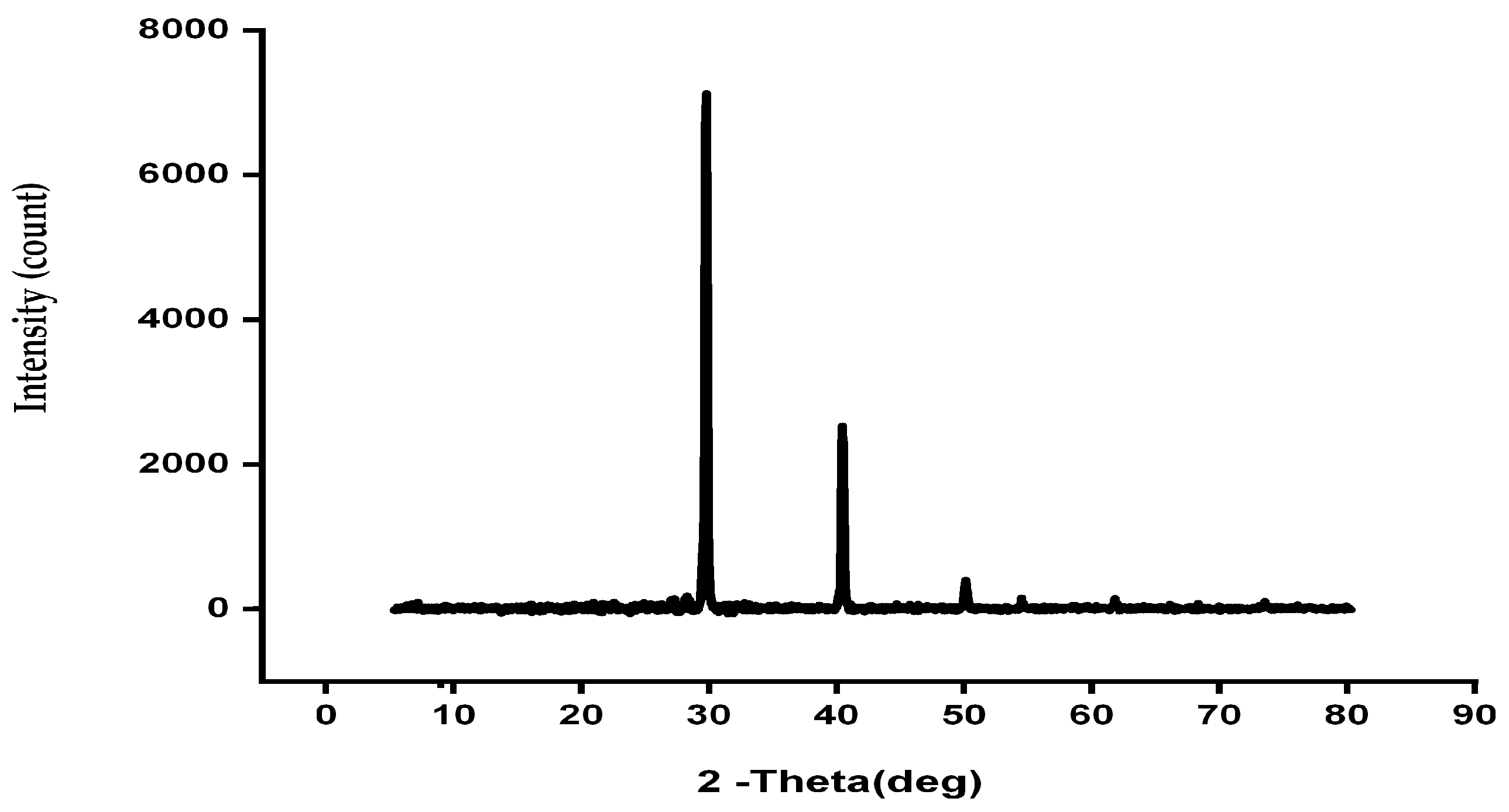
2.5.2. XRD Analysis
2.5.3. NMR Analysis
2.6. Thermal Properties
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Categorization
3.1.1. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Polyphenols
3.1.2. Sugar’s Composition
3.2. Structural Characterization
3.2.1. FTIR
3.2.2. XRD
3.2.3. NMR
3.3. Thermal Characterization
3.3.1. TGA
3.3.2. DSC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Carpena, M.; García-Oliveira, P.; Echave, J.; Pereira, A.G.; Lourenço-Lopes, C.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Agriculture waste valorisation as a source of antioxidant phenolic compounds within a circular and sustainable bioeconomy. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4853–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, T.J. Polymers for Food Applications: News. In Polymers for Food Applications; Gutiérrez, T., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, I.A.A.; Joshua Ashaolu, T.; Kamel, R.; Elkasabgy, N.A.; Afifi, S.M.; Farag, M.A. Mucilage as a functional food hydrocolloid: Ongoing and potential applications in prebiotics and nutraceuticals. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4738–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kučka, M.; Ražná, K.; Harenčár, L’.; Kolarovičová, T. Plant seed mucilage—Great potential for sticky matter. Nutraceuticals 2022, 2, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosif, M.M.; Najda, A.; Bains, A.; Kaushik, R.; Dhull, S.B.; Chawla, P.; Walasek-Janusz, M. A Comprehensive Review on Plant-Derived Mucilage: Characterization, Functional Properties, Applications, and Its Utilization for Nanocarrier Fabrication. Polymers 2021, 13, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukoulis, C.; Gaiani, C.; Hoffmann, L. Plant seed mucilage as emerging biopolymer in food industry applications. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 22, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, E.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Fathi, M.; Askari, G. Opuntia ficus-indica mucilage. In Emerging Natural Hydrocolloids; Razvi, S.M.A., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blando, F.; Albano, C.; Jiménez-Martínez, C.; Cardador Martínez, A. Opuntia ficus-indica [L.] Mill. and other Species: Source of Bioactives and their Molecular Mechanisms of Action to Promote Human Health. In Molecular Mechanisms of Functional Food; Campos-Vega, R., Oomah, B.D., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 193–237. Available online: https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Molecular+Mechanisms+of+Functional+Food-p-9781119804024 (accessed on 19 June 2023).
- Corrales-García, J.; Sáenz, C. Use of cladodes in food products. In Agro-Industrial Utilization of Cactus Pear; Sáenz, C., Ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; pp. 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Allegra, M.; Ianaro, A.; Tersigni, M.; Panza, E.; Tesoriere, L.; Livrea, M.A. Indicaxanthin from cactus pear fruit exerts anti-inflammatory effects in carrageenin-induced rat pleurisy. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzo, S.; Attanzio, A.; Calvi, P.; Mulè, F.; Tesoriere, L.; Allegra, M.; Amato, A. Indicaxanthin from Opuntia ficus-indica fruit ameliorates glucose dysmetabolism and counteracts insulin resistance in high-fat-diet-fed mice. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, E.Y.; Ezzat, M.I.; El Hefnawy, H.M.; Abdel-Sattar, E. An overview and update on the chemical composition and potential health benefits of Opuntia ficus-indica (L.) Miller. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.A.; Albuquerque, T.G.; Pereira, P.; Ramalho, R.; Vicente, F.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Costa, H.S. Opuntia ficus-indica (L.) Mill.: A Multi-Benefit Potential to Be Exploited. Molecules 2021, 26, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-González, F.; Pérez-González, J.; Muñoz-López, C.N.; Vargas-Solano, S.V.; Marín-Santibáñez, B.M. Influence of age on molecular characteristics and rheological behavior of nopal mucilage. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 6776–6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, C.M.; Arena, R.; Morghese, M.; Santulli, A.; Liguori, G.; Inglese, P. Seasonal characterization of nutritional and antioxidant properties of Opuntia ficus-indica [(L.) Mill.] mucilage. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, E.M.D.O.; Silva, N.H.D.; Lima Filho, J.L.D.; Brito, J.Z.D.; Silva, M.D.P.C.D. Study of carbohydrates present in the cladodes of Opuntia ficus-indica (fodder palm), according to age and season. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 30, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Padilla, M.; Rivera-Muñoz, E.M.; Gutiérrez-Cortez, E.; del López, A.R.; Rodríguez-García, M.E. Characterization of crystalline structures in Opuntia ficus-indica. J. Biol. Phys. 2015, 41, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Toit, A.; De Wit, M.; Hugo, A. Cultivar and harvest month influence the nutrient content of Opuntia spp. Cactus pear cladode mucilage extracts. Molecules 2018, 23, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Toit, A.; De Wit, M.; Fouché, H.J.; Venter, S.L.; Hugo, A. Relationship between weather conditions and the physicochemical characteristics of cladodes and mucilage from two cactus pear species. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, E.; Sáenz, C.; Aliaga, E.; Aceituno, C. Extraction and characterization of mucilage in Opuntia spp. J. Arid. Environ. 2007, 68, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrade Vieira, E.; De Magalhaes Cordeiro, A.M. Bioprospecting and potential of cactus mucilages: A bibliometric review. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrade Vieira, E.; Alves Alcantara, M.; Albuquerque dos Santos, N.; Duarte Gondim, A.; Iacomini, M.; Mellinger, C.; Tribuzy de Magalhaes Cordeiro, A.M. Mucilages of cacti from Brazilian biodiversity: Extraction, physicochemical and technological properties. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-García, M.; Gutiérrez-Cortez, E.; Bah, M.; Rojas-Molina, A.; Cornejo-Villegas, M.D.; Del Real, A.; Rojas-Molina, I. Comparative analysis of the chemical composition and physicochemical properties of the mucilage extracted from fresh and dehydrated Opuntia ficus-indica cladodes. Foods 2021, 10, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 20th ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- AACC American Association of Cereal Chemists. Approved Methods; American Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa, I.; Li, M.; Mamet, T.; Li, C. Maltodextrin or gum Arabic with whey proteins as wall-material blends increased the stability and physiochemical characteristics of mulberry microparticles. Food Biosci. 2019, 31, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, I.; Barakat, H.; El-Mansy, H.A.; Soliman, S.A. Optimizing bioactive substances extraction procedures from guava, olive and potato processing wastes and evaluating their antioxidant capacity. J. Food Chem. Nanotechnol. 2016, 2, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, I.; Nie, R.; Ge, Z.; Li, K.; Li, C. Understanding the shielding effects of whey protein on mulberry anthocyanins: Insights from multispectral and molecular modelling investigations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-González, S.; Martínez-Flores, H.E.; Chávez-Moreno, C.K.; Macías-Rodríguez, L.I.; Zavala-Mendoza, E.; Garnica-Romo, M.G.; Chacón-García, L. Extraction and Characterization of Mucilage from Wild Species of Opuntia. J. Food Process. Eng. 2014, 37, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarvie, D.; Parolis, H. Methylation analysis of the mucilage of Opuntia ficus-indica. Carbohydr. Res. 1981, 88, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blando, F.; Russo, R.; Negro, C.; De Bellis, L.; Frassinetti, S. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity against Staphylococcus aureus of Opuntia ficus indica (L.) Mill. cladode polyphenolic extracts. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheribi, R.; Puchot, L.; Verge, P.; Jaoued-Grayaa, N.; Mezni, M.; Habibi, Y.; Khwaldia, K. Development of plasticized edible films from Opuntia ficus-indica mucilage: A comparative study of various polyol plasticizers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 190, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.; Paula, C.D.D.; Lahbouki, S.; Meddich, A.; Outzourhit, A.; Rashad, M.; Souza, V.G. Opuntia spp.: An overview of the bioactive profile and food applications of this versatile crop adapted to arid lands. Foods 2023, 12, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.R.; Lee, H.J.; Park, Y.; Ra, K.S.; Shin, K.S.; Yu, K.W.; Suh, H.J. Mucilage removal from cactus cladodes (Opuntia humifusa Raf.) by enzymatic treatment to improve extraction efficiency and radical scavenging activity. LWT 2013, 51, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrè, A.M.; Zappia, C.; Capocasale, M. Physicochemical stability of blood orange juice during frozen storage. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20 (Suppl. S2), 1930–1943. [Google Scholar]
- Giuffrè, A.M.; Caracciolo, M.; Zappia, C.; Capocasale, M.; Poiana, M. Effect of heating on chemical parameters of extra virgin olive oil, pomace olive oil, soybean oil and palm oil. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2018, 30, 715. [Google Scholar]
- Procacci, S.; Bojórquez-Quintal, E.; Platamone, G.; Maccioni, O.; Vecchio, V.L.; Morreale, V.; Alisi, C.; Balducchi, R.; Bacchetta, L.J.N.R. Opuntia ficus-indica pruning waste recycling: Recovery and characterization of mucilage from cladodes. Nat. Resour. 2021, 12, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otálora, M.C.; Wilches-Torres, A.; Castaño, J.A.G. Extraction and physicochemical characterization of dried powder mucilage from Opuntia ficus-indica cladodes and Aloe vera leaves: A comparative study. Polymers 2021, 13, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petera, B.; Delattre, C.; Pierre, G.; Wadouachi, A.; Elboutachfaiti, R.; Engel, E.; Poughon, L.; Michaud, P.; Fenoradosoa, T.A. Characterization of arabinogalactan-rich mucilage from Cereus triangularis cladodes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuhiro, B.; Lillo, L.E.; Sáenz, C.; Urzúa, C.C.; Zárate, O. Chemical characterization of the mucilage from fruits of Opuntia ficus indica. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 63, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidouh, A.; Aouadi, S.; Heyraud, A. Extraction, fractionation and characterization of water-soluble polysaccharide fractions from myrtle (Myrtus communis L.) fruit. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.A.; de Freitas, R.A.; Sassaki, G.L.; Evangelista, P.H.L.; Sierakowski, M.R. Chemical structure and physical-chemical properties of mucilage from the leaves of Pereskia aculeata. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheribi, R.; Habibi, Y.; Khwaldia, K. Prickly pear peels as a valuable resource of added-value polysaccharide: Study of structural, functional and film forming properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Alvarenga Pinto Cotrim, M.; Mottin, A.C.; Ayres, E. Preparation and characterization of okra mucilage (Abelmoschus esculentus) edible films. Macromol. Symp. 2016, 367, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charuwat, P.; Boardman, G.; Bott, C.; Novak, J.T. Thermal degradation of long chain fatty acids. Water Environ. Res. 2018, 90, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Items | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | 92.17 ± 0.97 |
| Ashes (%) | 0.31 ± 0.04 |
| Proteins (%) | 0.82 ± 0.08 |
| Lipids (Ether extracts, %) | 0.07 ± 0.0 |
| Crude fibers (%) | 0.59 ± 0.08 |
| NFE (%) | 6.04 ± 0.06 |
| TPC (mg GAE/g) | 7.96 ± 0.9 |
| TF (mg QE/g) | 3.61 ± 0.85 |
| TFL (mg QE/g) | 1.47 ± 0.27 |
| AOA (DPPH•, µmol TE/g) | 26.15 ± 0.2 |
| AOA (ABTS+•, µmol TE/g) | 22.5 ± 1.73 |
| AOA (ORACFC, µmol TE/g) | 164.8 ± 7.86 |
| Monosaccharides | Content (mg/mL) |
|---|---|
| Galacturonic acid | 0.083 |
| Glucose | 0.055 |
| Xylose | 0.103 |
| Galactose | 0.040 |
| Rhamnose | 0.037 |
| Arabinose | 0.031 |
| Fucose | 0.023 |
| Total sugars by HPLC | 0.375 |
| Total sugars * by phenol-H2SO4 | 0.488 |
| Unknown | RT at 13.811 min with a peak area of 1.657%. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elshewy, A.; Blando, F.; Bahlol, H.; El-Desouky, A.; De Bellis, P.; Khalifa, I. Egyptian Opuntia ficus-indica (OFI) Residues: Recovery and Characterization of Fresh Mucilage from Cladodes. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070736
Elshewy A, Blando F, Bahlol H, El-Desouky A, De Bellis P, Khalifa I. Egyptian Opuntia ficus-indica (OFI) Residues: Recovery and Characterization of Fresh Mucilage from Cladodes. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(7):736. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070736
Chicago/Turabian StyleElshewy, Ahmed, Federica Blando, Hammam Bahlol, Ahmed El-Desouky, Palmira De Bellis, and Ibrahim Khalifa. 2023. "Egyptian Opuntia ficus-indica (OFI) Residues: Recovery and Characterization of Fresh Mucilage from Cladodes" Horticulturae 9, no. 7: 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070736
APA StyleElshewy, A., Blando, F., Bahlol, H., El-Desouky, A., De Bellis, P., & Khalifa, I. (2023). Egyptian Opuntia ficus-indica (OFI) Residues: Recovery and Characterization of Fresh Mucilage from Cladodes. Horticulturae, 9(7), 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070736










