Abstract
Halophytes have evolved to tolerate high salinity environments. The halophyte glasswort (Salicornia and Sarcocornia species) grows by the sea or in salty soils and can be consumed with pleasure. In this study, the cultivation of glasswort was studied by testing the effects of different electrical conductivity (EC) levels (10, 15, 20, 25, 30 and 35 mS cm−1) of a nutrient solution. Salicornia perennis Mill. was grown on floating systems in unheated greenhouse conditions. To adjust the different EC levels, sodium chloride was added to the Hoagland nutrient solution (EC: 2 mS cm−1). Plant growth and yield parameters, shoot color, evapotranspiration, and shoot nutrient content were determined. Among the tested EC levels, the highest plant height (33.56 cm), shoot (172.75 g) and root fresh weights (41.74 g), stem diameter (7.85 mm), and fresh biomass (2864.06 g m−2) were obtained from an EC level of 25 mS cm−1. There were no significant differences in shoot color excluding b* and chroma values. It was concluded that glasswort could be grown in hydroponic systems as a new crop and that an EC value of 25 mS cm−1 is the most appropriate for the cultivation of Salicornia perennis Mill. on floating systems.
1. Introduction
The world population is projected to reach 9.7 billion in 2050 [1] and this consequently will result in a food increase need of at least 70% [2]. Increasing population and food demands have exerted great pressure on agricultural production and the availability of resources. In addition, the impact of climate change on agriculture is evident and well known [3].
In recent years, salinity is one of the most common and critical problems threatening global food security and environmental sustainability [4]. Saline areas have been increasing by 10% annually due to various reasons [5,6]. It is predicted that 50% of all arable land will be affected by salinity by 2050 [7].
Salinization causes the loss of soil fertility and desertification and negatively affects vegetation and beneficial microorganisms [8]. Salt stress impairs plant growth due to water stress, excessive intake of elements such as sodium (Na+) and chlorine (Cl−) and imbalance in nutrient intake. Likewise, typically with salinity, oxidative stress occurs due to the generation of reactive oxygen species [9,10]. Different methods, such as the use of amendments, appropriate irrigation, drainage and land-use strategies, cultivation of tolerant genotypes, conservation agriculture, phytoremediation, and bioremediation, are techniques that have been used to reclaim the soils and mitigate the effects of salinity [4].
Studies on the use of salt-resistant plants against salinity have gained more prominence in recent years. Halophytes are considered to be one of the best plants since they have the potential of salt-responsive genes and promoters [11]. Research on halophytes can contribute to (i) garnering more information concerning the mechanisms of survival and maintaining productivity in salt water, which subsequently could be practical in developing tolerant varieties of traditional crops, (ii) evaluating the long-term feasibility of agriculture in high salinity, and (iii) becoming a direct source of potential new crops [12]. Halophytes are commercial alternatives to traditional agricultural products and can be used as fodder, energy, oilseed, and protein crops. It is predicted that halophytes may be an important component of the agricultural system in the 21st century [13].
Halophytes have evolved to tolerate high salinity environments; they are plants that survive by growing within a salt concentration of 200 mM NaCl or higher and constitute approximately 1% of the world’s flora. The salinity tolerance of halophytes is based on the uptake and distribution of Na+, K+ and Cl− and the synthesis of osmoprotectants or organic compatible solutes [14]. Glasswort (Salicornia and Sarcocornia species), which is one of the most important halophyte genera in the world today, is considered to be one of the most salt-resistant plants growing in salty regions [15]. It can tolerate 1000 mM or more of NaCl [16].
Salicornia’s name is derived from the Latin word for “salt” and the genus Salicornia is represented by approximately 25 to 30 species worldwide [17]. Sarcocornia is a halophytic, edible, succulent plant belonging to the Amaranthaceae family. To date, it is comprised of 28 species in saline environments worldwide; its morphological and taxonomic properties are similar to Salicornia, which is well known and has a commercial value [18]. The succulent shoots of species belonging to both genera have gained commercial importance under various names. Sarcocornia species, unlike Salicornia, are perennials, meaning they can be harvested throughout the year. Therefore, Sarcocornia species are considered promising gourmet vegetables to explore in the context of climate change, soil and water salinization, and eco-sustainability [19]. The origin of Sarcocornia perennis Mill. is Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts in West and South Europe and North Africa [20].
The species Salicornia and Sarcocornia have the potential of usage for multiple purposes (such as food, pharmaceuticals, bioethanol production, biofilter, and phytoremediation). The oriental pharmacopoeia has reported some medicinal uses for the treatment of oxidative stress (such as asthma and diabetes); as a source of vitamin A, minerals, and fatty acids; and as a vegetable. Some studies have also demonstrated its benefits as an edible species in terms of nutritional properties [21]. It is reported that the Salicornia plant contains high levels of ascorbic and dehydroascorbic acids (<100 mg 100 g−1) and carotenoids (5 mg 100 g−1) [15,22]. Salicornia species are promising as functional foods considering their high nutritional value in terms of mineral compounds, including Mg, Na, Ca, Fe, and K, and many bioactive compounds such as phytosterols, polysaccharides, and phenolic compounds, especially flavonoids and phenols [23]. A study conducted with Sarcocornia perennis Mill. showed that total antioxidant capacities were found to be significant with high antimicrobial activity potential [24].
Although the various benefits of Salicornia and Sarcocornia species are known, scientific research on these plants is still very limited. Studies were conducted focusing on multiple factors, such as those affecting growing conditions, yield, nutritional values, day length [25], varying salt levels [26,27,28,29] and irrigation with sea water [30,31,32,33,34] or salty water [35,36,37] as well as the effects of the harvest period and storage conditions [38,39] on the nutritional profile [40,41,42] and plant anatomical characteristics [43]. The mapping of suitable areas for cultivation [44], methods of monitoring the salinity adaptation feature [45], and the soil improvement effect were also studied and comprehensive reviews were prepared [15,20,21,32,46,47,48].
These species can be grown in insulated wetlands and irrigated with sewage water with high salinity or effluents from aquaculture to increase sustainability [49]. Additionally, the cultivation period can be controlled. It is reported that the yield (harvested biomass) is higher in hydroponic systems, but there is a need for optimization in the nutrient solution [50]. In this study, we studied Salicornia perennis Mill., which is one of the halophytes living in salty areas [51] and aimed to grow this species on floating systems and to test different salinity levels of nutrient solution on plant growth and yield parameters, shoot color, evapotranspiration, and shoot nutrient content.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Site, Plant Material and Growing Conditions
This research was carried out in an unheated polycarbonate greenhouse (528 m2) located at the Batı Raman Campus of Batman University (37°47′22″ N, 41°03′55″ E, altitude 550 m) during the spring season of 2022.
The plant material was collected from the Antalya province (Türkiye) (36°50′32″ N, 31°08′44″ E, altitude 0 m). The EC and pH values of the site were 18.4 mS cm−1 and 7.88, respectively. The species was identified by Prof. Dr. Ahmet Emre Yaprak (Ankara University) as Salicornia perennis Mill. (formerly Sarcocornia perennis Mill.). The average height of cuttings used in this study was 7 cm with 0.9 g average weight.
A total of 6 floating systems were used in the experiment. Each system was composed of ponds (113 cm × 300 cm × 25 cm) covered with polyethylene foil. Styrofoam with a thickness of 20 mm was placed on the solution to float the plants. Based on the daily measurements via an oxygen meter, oxygen was provided to the plant roots with an air motor. In the study, the average amount of dissolved oxygen applied to the solution was 6.4 mg L−1.
The plants were placed at a distance of 15 cm between the rows and 20 cm on the row with a plant density of 17.7 plants per m2. The experiment was conducted once and each replication had 20 plants with 60 plants having 3.39 m2 in each treatment. On 21 February 2022, the cuttings were placed in plastic pots with a diameter of 5 cm and with holes at the bottom and side surfaces. Plants were harvested once 15 weeks later on 6 June 2022.
Tunnels were constructed with the same width of ponds and 110 cm height since the wind had thrown the polycarbonates off the roof before the planting. (Figure 1). Temperatures within the tunnels varied between 7.6 and 21.8 °C with an average of 15.2 °C. The temperature of the nutrient solution was an average of 16.6 °C.

Figure 1.
Plants on the first day (a) and harvesting date (b).
2.2. Nutrient Solution and Treatments
The water and nutrient requirements of the plants were covered with a complete nutrient solution prepared according to the results of the water analysis (Table 1). A nutrient solution of Hoagland and Arnon [52] was used: (mg L−1) N 210, P 31, K 234, Ca 160, Mg 34, S 64, Fe 2.5, Mn 0.5, Zn 0.05, Cu 0.02, B 0.5 and Mo 0.01 with an electrical conductivity of (EC) 2 mS cm−1 and a pH of 8.34.

Table 1.
Water analysis.
Six EC levels of nutrient solution were tested. Salinity levels were adjusted by adding sodium chloride into the Hoagland nutrient solution as 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, and 35 mS cm−1 (Figure 2). The nutrient solution was not replaced and/or not completed during the growing period. The differences in EC levels during the study were EC: 10 + 0.6 mS cm−1, EC: 15 + 0.63 mS cm−1, EC: 20 + 0.67 mS cm−1, EC: 25 + 1.01 mS cm−1, EC: 30 + 0.89 mS cm−1, and EC: 35 + 0.97 mS cm−1.
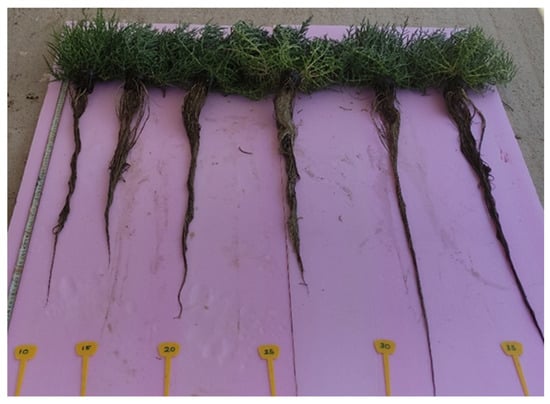

Figure 2.
Glasswort plants at different EC levels (10, 15, 20, 25, 30, and 35 mS cm−1).
2.3. Measurements and Calculations
At harvest, ten plants from each replicate of treatments were randomly selected for plant growth measurements. Plant height from the Styrofoam surface to the top of the plants was measured with a ruler and the results were expressed in cm. For the root length, plants were cut 1 cm above the root collar and measured with a ruler until the root tip, and the results were recorded in cm. Shoots and roots were weighed for fresh weight (g) and then dried in a thermos-ventilated oven at 65 °C and weighed for the dry weight (g). Stem diameter was indicated in millimeters (mm) by measuring with a digital caliper. The shoot-to-root ratio was calculated by dividing the fresh shoot weight by the fresh root weight. Fresh biomass was determined as g m−2 by weighing the fresh weights of all plants in the experiment, and the results were calculated over m2. Shoot color values were measured with a colorimeter (NR10QC Precision Colorimeter, China) and a mean L*, a*, b*, chroma and hue angle values were determined. The lightness (L*) value determines the brightness, the a* value determines the green color, the b* value determines the yellow color, the chroma (C*) value determines the saturation of the color and the hue (h°) value determines the angle of the color. The chroma [C* = (a*2 + b*2) ½] and hue angle [h° = arctan (b*/a*)] were also calculated.
In the study, evapotranspiration (ET) was calculated by subtracting the amount of solution on the last day from the amount on the first day (847.5 L) and the results were expressed as L plant−1. Water use efficiency (WUE) was calculated as the ratio of fresh biomass to water consumption [53].
For mineral analysis, shoots of each treatment were dried in a Memmert UN160 oven for 24 h at 70 °C. The dried samples were ground with a Spice & Herb Grinder/IC-10B brand/model herb grinder and passed to sieves. The concentrations of Mg, Zn, Mn, Fe, and P were determined from nitric acid digestions (Berghof Speedwave MWS-2 Microwave Pressure Digestion) and ICP-OES (Plasma optical emission spectrometry) analyses. K, Ca, and Na analyses were performed with a Flame photometer (Perkin Elmer ICP-OES Optima 2100 DV. and Jenway PFP7). Chloride analysis was determined according to the Mohr salt determination method [54].
2.4. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
The experimental design was randomized parcels with three replicates. To determine any statistically significant differences, data were subjected to analysis of variance by using an SPSS 17.0 package program. Duncan’s Multiple Range Test at a 5% significance level (p < 0.05) was used to determine the differences between the means.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Plant Growth
It was demonstrated that Salicornia perennis Mill., a common species along the western and southern coastline of Türkiye [55], could be grown successfully in hydroponics. However, the effects of different EC levels of nutrient solution on measured plant growth parameters were observed to be significant (Figure 3). Plant height varied between 26.93 and 33.56 cm. It was the highest at EC levels of 20 and 25 mS cm−1 with an average of 33.3 cm followed by 35 and 30 mS cm−1. Plant height was lower at 19.5, 19.8, 1.6, 10 and 5.1% at 10, 15, 20, 30 and 35 mS cm−1, respectively compared with 25 mS cm−1 having the highest value (Figure 3A).
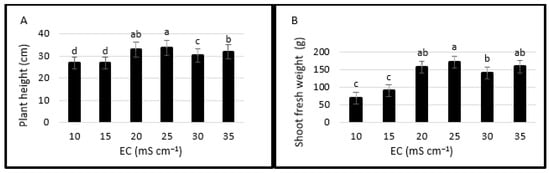
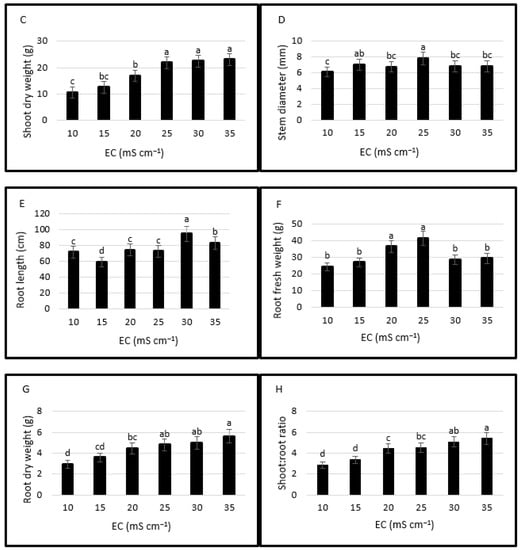
Figure 3.
Effects of salinity levels on plant growth parameters (plant height (A), shoot fresh weight (B), shoot dry weight (C), stem diameter (D), root length (E), root fresh weight (F), root dry weight (G), shoot: root ratio (H). Error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean. Different letters mean statistically significant difference at p < 0.05.
Shoot fresh weights were the lowest at EC levels of 10 and 15 mS cm−1. Shoot fresh weight at 25 mS cm−1 was higher at 145.4, 90.1, 9.9, 22.3 and 8.5% than at 10, 15, 20, 30 and 35 mS cm−1, respectively (Figure 3B). Shoot dry weight was higher at 25, 30 and 35 mS cm−1 compared to the lower EC levels (Figure 3C). Stem diameter changed between 6.1 mm (the lowest in 10 mS cm−1) and 7.85 mm (the highest in 25 mS cm−1) (Figure 3D).
Root length was the highest (94.9 cm) at the EC level of 30 mS cm−1 and it was 1.32, 1.60, 1.27, 1.31 and 1.14 times higher than at 10, 15, 20, 25 and 35 mS cm−1 (Figure 3E). Root fresh weight was the highest at 25 mS cm−1 while the highest root dry weight was at 35 mS cm−1 (Figure 3F,G). Root morphological features of halophytes are affected by salinity [56,57] and increasing salinity may increase the root dry weight and length and modify root anatomy due to the adaption mechanism of species; however, the response may change with the genotypes and nutrition application [58].
Shoot: root ratio gradually increased with increasing salinity [31] and the highest ratio (5.41) was at 35 mS cm−1. Shoot: root ratio at 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 mS cm−1 was lower at 46.95, 37.34, 17.93, 15.53, and 5.73%, respectively (Figure 3H).
In the natural habitats of Salicornia species, soil salinity of the samples obtained from the sites was predominated by Salicornia europaea ranging from 18.9 to 142.8 mS cm−1 at Rittman, Ohio [59], which indicates the presence of Na and Cl in the Salicornia zone [60], 63.1 and 38.5 mS cm−1 in the industry area and natural saline site in Poland, respectively [46], and 70 ± 6 mS cm−1 in unprotected and open grazing area in Adana, Türkiye [61]. In the pot experiments, testing different seawater and/or salinity treatments (25, 50, 75, and 100% seawater), it was determined that the response of plants showed differences in growing stages, in particular, at germination and with ecotypes [29,31,46,50].
In this experiment, plant height, shoot fresh and dry weights, root fresh weight, and stem diameter were the highest at 25 mS cm−1. In all measured parameters in terms of plant growth, there were lower values at the lower EC levels (10 and 15 mS cm−1) (Figure 3A–H). Araus et al. [29] compared three salinity levels, namely fresh water (0.3 mS cm−1), brackish water (25 mS cm−1), and seawater (40 mS cm−1) and the highest seed weight, shoot biomass, plant height, and branch number of two S. europaea ecotypes were obtained from the brackish water having an EC level of 25 mS cm−1. These results reveal that plant growth performance is higher at moderate salinity levels around 25 mS cm−1; however, the plant response yields variations in different species, ecotypes [62,63], growing conditions [25,64], plant density [65], harvest regime [25], and nutrition [58].
3.2. Fresh Biomass
The effects of different EC levels of nutrient solution on measured fresh biomass were observed to be significant. The highest fresh biomass was 2864.06 g m−2 at the EC level of 25 mS cm−1 and followed by 2703.56 and 2457.15 g m−2 at 35 and 20 mS cm−1, respectively. The yield was 100.5 and 80% higher at 25 mS cm−1 compared to 10 and 15 mS cm−1, respectively (Figure 4). It was 16.6, 26.3 and 5.9% higher at 25 mS cm−1 than at 20, 30 and 35 mS cm−1, respectively.
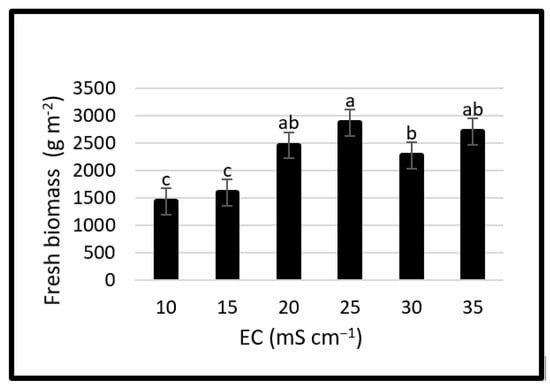
Figure 4.
Effects of salinity levels on fresh biomass. Error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean. Different letters mean statistically significant difference at p < 0.05.
For leafy vegetables, yield potential greatly depends on biomass accumulation. The fresh biomass production of some halophytic species grown in hydroponics is affected by growing conditions, plant density, and salinity levels of the nutrient solution [66]. Biomass is significantly and positively correlated with the EC level of the growing medium [67]. Ventura et al. [25] reported that the total yield of two annual Salicornia and two perennial Sarcocornia ecotypes decreased with the increase of seawater rate above 50% and the cumulative yields of Salicornia types were between 13.4 and 16.04 kg m−2 after 6 harvests until flowering while Sarcocornia types skipping the reproductive stage produced more (20.04 and 28.43 kg m−2) in a year. Seedling establishment of S. dolichostachya among the 5 salinity regimes (0, 100, 200, 400 and 700 mM NaCl) was optimum in 100 mM based on the biomass increase, morphology, and taste [50]. Plant growth of S. rubra was optimum at 200 mM NaCl among the salinity levels of 0, 200, 400, 600, 800, and 1000 mM NaCl [68]. Plant growth of S. bigelovii reduced in 6 to 10 vs. 200 mM NaCl [69]. Shoot fresh weight of S. europaea had no phytotoxicity or deficiency at 100 and 300 mM NaCl while plant growth was restricted at 0, 500 and 700 mM NaCl [70], whereas S. europaea tolerated salinity levels up to 500 mM NaCl; however, plant growth performance was better in moderate salinities [71].
Boni [72] tested 2 (0 and 30 g L−1) and 4 (0, 10, 20 and 30 g L−1) salt concentrations in 2 experiments, respectively, and concluded that the fresh yield was above 7 kg m−2 in less than 5 weeks up to salinity levels of 20 g L−1. Not only yield values but also plant growth parameters impact the yield of Salicornia species. In an experiment conducted with high-yielding Salicornia genotypes at Marine Environment Research Center (United Arab Emirates), fresh shoots harvested twice yielded up to 23.7 t ha−1 when the aquaculture effluents were used [63]. S. brachiata above-ground biomass varied in sampling sites and the highest biomass was observed in March ranging from 0.73 to 4.89 t ha−1 [73]. Comparing our yield results with previous studies, the requisite salinity level at the root zone is similar to previous studies. However, in terms of fresh biomass, there are either similar or higher/lower ones closely related to growing conditions, length of production, harvested plant size, number of harvests, and whether they are from field or hydroponics.
3.3. Evapotranspiration
Evaporation is a combination of transpiration and evaporation. However, it is not easy to distinguish since both processes go together [74]. In floating systems, the amount of water loss through evaporation could be negligible because the ponds were covered with Styrofoam panels [75]. In this study, evapotranspiration altered between 6.89 and 10.9 L plant−1. The lowest and the highest ET were at 10 (6.89 L plant−1) and 25 (10.9 L plant−1) mS cm−1, respectively. Evapotranspiration was lower at 36.79, 26.42, 22.75, 20.73 and 14.95% at 10, 15, 20, 30 and 35 mS cm−1, respectively, compared with 25 mS cm−1 having the highest value (Table 2). The highest ET is related to higher yield and plant growth values at 25 mS cm−1. WUE was lower in the lower EC levels (10 and 15 mS cm−1) having also lower fresh biomass. Higher WUE is related to better plant growth and higher fresh biomass [69,76].

Table 2.
Evapotranspiration (L plant−1) and WUE (kg m−3).
3.4. Color
In this study, there were no significant differences in terms of L*, a*, and h° values among treatments whereas b* and C* values were found to be statistically significant (Table 3). In shoots of Salicornia perennis Mill., the b* value, which indicates a blue–yellow spectrum from −60 (blue) to +60 (yellow), was the highest (15.51) in the lowest EC treatment (10 mS cm−1). This shows that the yellow color tone was more intense in the shoots of those plants. Similarly, the C* value, which expresses the intensity or color saturation of the shoots, was the highest (15.67) at 10 mS cm−1, indicating that these shoots were brighter. L*, a*, and h° values of shoots of Salicornia perennis Mill. varied between 30.56 and 32.94, −2.42 and −1.79, and 96.95 and 105.77, respectively. These results are consistent with a report that the L*, C* and h° values of Salicornia perennis Mill. shoots were 31, 20.6 and 117.1 in May and 30, 17.3 and 123.2 in July at harvest [39]. Changes in color are associated with changes in chlorophyll content and carotenoids with increasing salinity [45,77].

Table 3.
Shoot color analysis.
3.5. Shoot Mineral Content
The effects of different EC levels of nutrient solution on shoot mineral content of S. perennis Mill. were found to be significant (Table 4a,b). Na concentration of the glassworts was in the range of 10.34–17.53%. Although the Na values were in the same statistical group over 15 mS cm−1, they were 4.85, 3.29 and 10.23% lower at 35 mS cm−1 than at 30, 25, and 20 mS cm−1, respectively (Table 4a). The percentage of Na in dry weight increased as EC levels increased. The obtained values were found to be compatible with previous studies [39,78,79]. Cl content was also high in increasing EC levels. The accumulation of NaCl in the shoots is ta characteristic of Salicornia as a halophyte adjusting osmotic potential and the Na content of shoots is associated with the concentration in the root zone [35,70].

Table 4.
(a) Na, K, Cl contents and salt concentrations of Salicornia perennis Mill. at different EC levels. (b) Shoot mineral contents of Salicornia perennis Mill. at different EC levels.
The K value was between 4.87 and 3.97% at the EC value of 35 and 10 mS cm−1, respectively. K content decreased as the EC value increased in particular at the EC level of 20 mS cm−1. (Table 4a). As sodium uptake increased, potassium consumption decreased [80]. The Na+/K+ ratio was 2.12, 2.48, 3.67, 4.10, 4.06 and 4.42 at 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 and 35 mS cm−1, respectively. A low Na+/K+ ratio is nutritionally critical because diets with high Na+/K+ ratios have been associated with the incidence of hypertension. In our study, the Na+/K+ ratio of the glassworts was in the range of 2.12–4.42. Altay et al. [79] reported the Na+/K+ ratio of the glassworts in the range of 5.64–10.15 which could be related to the origin of species collected from nature. The salt concentration values fluctuated between 55.58 and 23.40% in the EC value of 35 and 10 mS cm−1, respectively; salt concentration values increased as the EC value increased (Table 4a).
Cl concentration was lower at 57.9, 52.62, 29.47, 6.31 and 4.21% at 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 mS cm−1, respectively, compared with 35 mS cm−1 having the highest value (Table 4a). As the EC level increased, the Cl content increased [31,35]. The salt concentration values fluctuated between 55.58 and 23.40% at the EC value of 35 and 10 mS cm−1, respectively. Salt concentration values increased as the EC value increased (Table 4a).
Mg, P, Fe, Mn, and Zn were the highest at 10 mS cm−1, which was the lowest tested EC treatment. P and Mg contents displayed a similar response and decreased with the increasing salt concentrations. Ca content was the lowest at 10 mS cm−1 and the highest at 20 mS cm−1. Although there were slight changes in statistical groups, Fe, Mn, and Zn also indicated a decreasing trend with the increase of EC levels (Table 4b).
As the NaCl concentration increased, plants’ magnesium uptake decreased. Magnesium is commonly found in significant amounts in all green vegetables due to its relationship with chlorophyll [81]. The Mg concentration value was lower at 10.32, 16.46, 31.15, 27.38, and 38.99% at 15, 20, 25, 30, and 35 mS cm−1, respectively, compared with 10 mS cm−1 (5833 mg kg−1) having the highest value (Table 4b). As reported by Altay et al. [79], the Mg concentration of glasswort species was in the range of 680–15,700 mg kg−1.
In our study, P concentration was lower at 8.5, 20.76, 26.94, 20.81, and 32.10% at 15, 20, 25, 30, and 35 mS cm−1, respectively, compared with 10 mS cm−1 (1941 mg kg−1) having the highest value (Table 4b). Antunes et al. [39] reported the P content of Sarcocornia perennis as 2200.1 mg kg−1. As the salt increased, the P content was found to be lower, which is in harmony with salinity studies conducted with different vegetables [82].
Ca concentration was in the range of 1683.18 −2037.54 mg kg−1. Shoot Ca content was 21.05, 10.20, 1.80 11.59, and 9.01% higher at 10,15, 25, 30, and 35 mS cm−1, respectively compared with 20 mS cm−1 (Table 4b). Due to the difference in salinity levels of the salt marshes that the plants were collected from, these were observed to be lower than Lopes et al. [81] and Antunes et al. [39].
The highest Fe content was 68.1 mg kg−1 at an EC level of 10 mS cm−1 and followed by 15 mS cm−1 at 61.04 mg kg−1 (Table 4b). In our study, the Fe content of Salicornia perennis Mill. was detected to be lower than Salicornia europea reported by Al-Jaloud et al. [78] while it was higher than Salicornia ramosissima published by Lopes et al. [81]. The highest Mn content was 73.04 mg kg−1 in the EC level of 25 mS cm−1 (Table 4b). Although the Mn values were in the same statistical group, they were 0.85% higher in 25 mS cm−1 than in 10 mS cm−1. The Mn element content of Salicornia perennis Mill. was found to be higher than Salicornia europea [78]. In our study, the Zn concentration varied between 23.94 mg kg−1 (the lowest in 30 mS cm−1) and 41.09 mg kg−1 (the highest in 10 mS cm−1) and these observations were in harmony with previous studies. Antunes et al. [39] reported the Zn content of Sarcocornia perennis and Salicornia ramosissima as 21.2 mg kg−1 and 33.9 mg kg−1 respectively. Al-Jaloud et al. [78] reported the mean Zn concentration of Salicornia europea as 24.48 mg kg−1.
In the study, the differences in EC levels of the nutrient solution changed between +0.6 and +1 mS cm−1; however, shoot mineral contents were in harmony with previous studies although nutrient elements decreased with increasing EC levels excluding Na and Cl.
4. Conclusions
This study, conducted with Salicornia perennis Mill., has demonstrated that glasswort plants as a new crop in floating systems have a potential for commercial production considering the yield performance without any nutrient deficiency. The yield was higher at moderate EC level of nutrient solution, and it was concluded that the EC level of nutrient solution could be adjusted to 25 mS cm−1 with NaCl for hydroponic production. However, more research is needed on how plant density, harvest numbers, and growing conditions affect the yield.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.O. and Y.T.; methodology, E.O. and Y.T.; software, E.O. and Y.T.; investigation, E.O. and Y.T.; resources, E.O. and Y.T.; writing—original draft preparation, E.O. and Y.T.; writing—review and editing, E.O. and Y.T.; visualization, E.O. and Y.T.; supervision, E.O. and Y.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- UN—United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Prospects. Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/423). 2019. Available online: https://population.un.org/wpp/publications/files/wpp2019_highlights.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- Marondedze, C.; Liu, X.; Huang, S.; Wong, C.; Zhou, X.; Pan, X.; An, H.; Xu, N.; Tian, X.; Wong, A. Towards a tailored indoor horticulture: A functional genomics guided phenotypic approach. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.K. Impact of climate change on agriculture production and its sustainable solutions. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 2, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Sarkar, B.; Jat, H.S.; Sharma, P.C.; Bolan, N.S. Soil salinity under climate change: Challenges for sustainable agriculture and food security. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, A.; Riaz, S.; Ashraf, M.; Foolad, M.R. Gene Expression profiling of plants under salt stress. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2011, 30, 435–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butcher, K.; Wick, A.F.; DeSutter, T.; Chatterjee, A.; Harmon, J. Soil Salinity: A Threat to Global Food Security. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 2189–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Bano, A.; Khan, N. Climate change and salinity effects on crops and chemical communication between plants and plant growth-promoting microorganisms under stress. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 618092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isayenkov, S.V.; Maathuis, F.J.M. Plant salinity stress: Many unanswered questions remain. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global predictions of primary soil salinization under changing climate in the 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Tanna, B. Halophytes: Potential resources for salt stress tolerance genes and promoters. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Nahar, K.; Alam, M.; Bhowmik, P.C.; Hossain, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Prasad, M.N.V.; Ozturk, M.; Fujita, M. Potential use of halophytes to remediate saline soils. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 589341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, S.S.; Ramachandran, S. Chapter 15—Potential uses of halophytes for biofuel production: Opportunities and challenges. In Sustainable Biofuel; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 425–448. [Google Scholar]
- Flowers, T.J.; Colmer, T.D. Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 945–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Pérez, S.; Piernik, A.; Chanona-Pérez, J.J.; Grigore, M.N.; Perea-Flores, M.J. An overview of the emerging trends of the Salicornia L. genus as a sustainable crop. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 191, 104606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Jiang, P.; Chen, X.; Fan, P.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Multiple compartmentalization of sodium conferred salt tolerance in Salicornia europaea. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 51, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadereit, G.; Ball, P.; Beer, S.; Mucina, L.; Sokoloff, D.; Teege, P.; Yaprak, A.E.; Freitag, H. A taxonomic nightmare comes true: Phylogeny and biogeography of glassworts (Salicornia L., Chenopodiaceae). Taxon 2007, 56, 1143–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, S.; Ball, P.; Mucina, L.; Kadereit, G. Phylogeny, biogeography and ecological diversification of Sarcocornia (Salicornioideae, Amaranthaceae). Ann. Bot. 2015, 115, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custódio, L.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Pereira, C.G.; Castañeda-Loaiza, V.; Fernandes, E.; Standing, D.; Sagi, M. A review on Sarcocornia species: Ethnopharmacology, nutritional properties, phytochemistry, biological activities and propagation. Foods 2021, 10, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loconsole, D.; Cristiano, G.; De Lucia, B. Glassworts: From wild salt marsh species to sustainable edible crops. Agriculture 2019, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S. Salicornia: Evaluating the halophytic extremophile as a food and a pharmaceutical candidate. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guil, J.L.; Rodríguez-Garcí, I.; Torija, E. Nutritional and toxic factors in selected wild edible plants. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1997, 51, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ramos, F.; Leiva-Portilla, D.; Rodríguez-Núñez, K.; Pacheco, P.; Briones-Labarca, V. Mathematical modeling and quality parameters of Salicornia fruticosa dried by convective drying. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tünek, M. Investigation of Antioxidant Parameters and Antimicrobial Properties of Glasswort (Sarcocornia perennis L.). Master’s Thesis, Department of Chemistry, Science Science Institute, Adnan Menderes University, Aydın, Türkiye, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ventura, Y.; Wuddineh, W.A.; Shpigel, M.; Samocha, T.M.; Klim, B.C.; Cohen, S.; Sagi, M. Effects of day length on flowering and yield production of Salicornia and Sarcocornia species. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 130, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodendo-Gomez, S.; Wharmby, C.; Castillo, J.M.; Mateos-Naranjo, E.; Luque, C.J.; de Cires, A.; Luque, T.; Davy, A.J.; Figueroa, M.E. Growth and photosynthetic responses to salinity in anextreme halophyte, Sarcocornia fruticose. Physiol. Plant. 2006, 128, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, A.B. The Investigation of Glasswort (Salicornia europea) Cultuvation Possibilities under Different Saline Conditions. Master’s Thesis, Department of Horticulture, Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences, Namık Kemal University, Tekirdağ, Türkiye, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, A.R.; Castaneda-Loaiza, V.; Salazar, M.; Nunes, C.; Quintas, C.; Gama, F.; Barreira, L. Influence of cultivation salinity in the nutritional composition, antioxidant capacity and microbial quality of Salicornia ramosissima commercially produced in soilless systems. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araus Ortega, J.L.; Rezzouk, F.Z.; Thushar, S.; Shahid, M.; Elouafi, I.A.; Bort Pie, J.; Serret Molins, M.D. Effect of irrigation salinity and ecotype on the growth, physiological indicators and seed yield and quality of Salicornia europaea. Plant Sci. 2021, 304, 110819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal, M.S. Salicornia Production in Kuwait. World Appl. Sci. J. 2009, 6, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Ventura, Y.; Wuddineh, W.A.; Myrzabayeva, M.; Alikulov, Z.; Khozin-Goldberg, I.; Shpigel, M.; Sagi, M. Effect of seawater concentration on the productivity and nutritional value of annual Salicornia and perennial Sarcocornia halophytes as leafy vegetable crops. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 128, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, Y.; Sagi, M. Halophyte crop cultivation: The case for Salicornia and Sarcocornia. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 92, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Torres, R.; Troyo-Diéguez, E.; Nieto-Garibay, A.; Lucero-Vega, G.; Magallón-Barajas, F.J.; García-Galindo, E.; Fimbres-Acedo, Y.; Murillo-Amador, B. Environmental and management considerations for adopting the halophyte Salicornia bigelovii Torr. as a sustainable seawater-irrigated crop. Sustainability 2020, 12, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianciotto, O.; Aras Martin, F.; Arce, M.E.; Selzer, L.; Ortega Garcia, J.; Paoulo, G.; Cardenas, L.A.G.; Robledo, A.; Rueda Puento, E.O. Farming with drip sea water irrigation for Salicornia production in Tierra del Fuego, Argentina. Biotecnia 2021, 23, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, S.R.; Benes, S.E.; Grattan, S.R.; Benes, S.E.; Peters, D.W.; Diaz, F. Feasibility of irrigating pickleweed (Salicornia bigelovii Torr) with hyper-saline drainage water. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, S-149–S-156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Jaradat, A.A.; Rao, N.K. Use of marginal water for Salicornia bigelovii Torr. Planting in the United Arab Emirates. In Developments in Soil Salinity Assessment and Reclamation: Innovative Thinking and Use of Marginal Soil and Water Resources in Irrigated Agriculture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, S.; Shah, M.T. Successful cultivation of Salicornia brachiata—A sea asparagus utilizing ro reject water: A sustainable solution. Int. J. Waste Resour. 2018, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Cai, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, C. Nutritional characterization and changes in quality of Salicornia bigelovii Torr. during storage. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.D.; Gago, C.; Guerreiro, A.; Sousa, A.R.; Julião, M.; Miguel, M.G.; Panagopoulos, T. Nutritional characterization and storage ability of Salicornia ramosissima and Sarcocornia perennis for fresh vegetable salads. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, M.H.; Park, H.-J.; Cho, J.Y. Salicornia herbacea: Botanical, chemical and pharmacological review of halophyte marsh plant. J. Med. Plants Res. 2009, 3, 548–555. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.Y.; Cho, J.Y.; Ma, Y.K.; Park, K.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Ham, K.S.; Lee, H.J.; Park, K.H.; Moon, J.H. Dicaffeoylquinic acid derivatives and flavonoid glucosides from glasswort (Salicornia herbacea L.) and their antioxidative activity. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, L.R.; Maltez, H.F.; de Gois, J.S.; Borges, D.L.G.; Borges, G.S.C.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Fett, R. Mineral composition and bioaccessibility in Sarcocornia ambigua using ICP-MS. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 47, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcin, T.A.; Akcin, A.; Yalcın, E. Anatomical changes induced by salinity stress in Salicornia freitagii (Amaranthaceae). Braz. J. Bot. 2017, 40, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yamani, W.; Kennedy, S.; Sgouridis, S.; Yousef, L.F. A land suitability study for the sustainable cultivation of the halophyte Salicornia bigelovii: The case of Abu Dhabi, UAE. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2013, 27, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Pérez, S.; Piernik, A.; Ludwiczak, A.; Duszyn, M.; Szmidt-Jaworska, A.; Chanona-Pérez, J.J. Image and fractal analysis as a tool for evaluating salinity growth response between two Salicornia europaea populations. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, A.; Panuccio, M.R.; Piernik, A. Ecology, distribution and ecophysiology of Salicornia europaea L. In Sabkha Ecosystems: Volume IV: Cash Crop Halophyte and Biodiversity Conservation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ventura, Y.; Eshel, A.; Pasternak, D.; Sagi, M. The development of halophyte-based agriculture: Past and present. Ann. Bot. 2015, 115, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, M.; Altay, V.; Orçen, N.; Yaprak, A.E.; Tuğ, G.N.; Güvensen, A. A little-known and a little-consumed natural resource: Salicornia. In Global Perspectives on Underutilized Crops; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 83–108. [Google Scholar]
- Buhmann, A.; Papenbrock, J. Biofiltering of aquaculture effluents by halophytic plant plants: Basic principles, current issues and future perspectives. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 92, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Buhmann, A.K.; Flowers, T.J.; Seal, C.E.; Papenbrock, J. Salicornia as a crop plant in temperate regions: Selection of genetically characterized ecotypes and optimization of their cultivation conditions. AoB Plants 2014, 6, plu071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroca, M.J.; Guiné, R.P.; Amado, A.M.; Ressurreição, S.; da Silva, A.M.; Marques, M.P.M.; de Carvalho, L.A.E. The drying process of Sarcocornia perennis: Impact on nutritional and physico-chemical properties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 4443–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoagland, D.R.; Arnon, D.I. The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. In Circular; California Agricultural Experiment Station: Davis, CA, USA, 1950; Volume 347, p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, G.; Xu, X.; Huang, Q. Effects of water stress on processing tomatoes yield, quality and water use efficiency with plastic mulched drip irrigation in sandy soil of the Hetao Irrigation District. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacar, B. Bitki ve Toprağın Kimyasal Analizleri III; Ankara Üniversitesi Ziraat Fakültesi Eğitim, Araştırma ve Geliştirme Vakfı Yayınları: Ankara, Türkiye, 1995; No: 3; p. 705. [Google Scholar]
- Yaprak, A.E. Sarcocornia obclavata (Amaranthaceae) a new species from Türkiye. Phytotaxa 2012, 49, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Orenga, S.; Llinares, J.V.; Al Hassan, M.; Fita, A.; Collado, F.; Lisón, P. Physiological and morphological characterisation of Limonium species in their natural habitats, insights into their abiotic stress responses. Plant Soil 2020, 449, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Ge, S.; Peng, B.; Zhang, K.; Hu, M.; Mai, W.; Tian, C. Root morphology and rhizosphere characteristics are related to salt tolerance of Suaeda salsa and Beta vulgaris L. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 677767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moatabarniya, S.; Rad, A.C.; Sima, N.A.K.; Askari, H.; Zeinalabedini, M.; Hesarkhani, Z.; Ghaffari, M.R. Morphological and anatomical changes of Salicornia roots are associated with different salinity and nutrients conditions in contrasting genotypes. Rhizosphere 2022, 24, 100629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, I.A.; Benner, D.K.; McGraw, D.C. The distribution and growth of Salicornia europaea on an inland salt pan. Ecology 1979, 60, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehl, T.E.; Ungar, I.A. Growth and ion accumulation in Salicornia europaea under saline field conditions. Oecologia 1982, 54, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, C.; Farhan, M.; Khairo, A.; Ozer, G.; Cetin, M.; Ortas, I.; Islam, K. Evaluating Salicornia as a potential forage crop to remediate high groundwater-table saline soil under continental climates. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2017, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agawu, E.T. Comparison between Salicornia and Sarcocornia Ecotypes to Optimize Yield for Vegetable Production Applying Highly Saline Irrigation. Master’s Thesis, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, the Jacob Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research, The Albert Katz International School for Desert Studies, Beersheba, Israel, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ICBA—International Center for Biosaline Agriculture. ICBA Achieves Progress in Breaking Salicornia Yield Ceiling. 2018. Available online: https://www.biosaline.org/news/2018-05-10-6466 (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- Zapata-Sifuentes, G.; Preciado-Rangel, P.; Guillén-Enríquez, R.R.; Bernal, F.S.; Holguin-Peña, R.J.; Borbón-Morales, C.; Rueda-Puente, E.O. Lipid and Yield Evaluation in Salicornia bigelovii by the Influence of Chitosan-IBA, in Conditions of the Sonora Desert. Agronomy 2021, 11, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, J.B.; Gohil, R.H.; Patolia, J.S.; Shah, M.T.; Parmar, D.R. A study on Salicornia (S. brachiata Roxb.) in salinity ingressed soils of India. Int. J. Agric. Res. 2006, 1, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, T.; Bertacchi, A.; Pistelli, L.; Pardossi, A.; Pecchia, S.; Toffanin, A.; Sanmartin, C. Biological and agronomic traits of the main halophytes widespread in the Mediterranean region as potential new vegetable crops. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, A.P.; Chaudhary, D.R.; Jha, B. Biomass production, nutrient cycling, and carbon fixation by Salicornia brachiata Roxb.: A promising halophyte for coastal saline soil rehabilitation. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2016, 18, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Gul, B.; Weber, D.J. Effect of salinity on the growth and ion content of Salicornia rubra. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2001, 32, 2965–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Zheng, Y. Potential of Producing Salicornia bigelovii hydroponically as a vegetable at moderate NaCl salinity. HortScience 2014, 49, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.W.; An, J.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Son, D.; Sohn, Y.G.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.J. The growth and accumulation of osmotic solutes of the halophyte common glasswort (Salicornia europaea) under salinity conditions. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 2013, 51, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Algharib, A.M.; Orçen, N.; Nazarian, G.R. Effect of salt stress on plant growth and physiological parameters of common glasswort (Salicornia europaea). Int. J. Biosci. 2016, 8, 218–227. [Google Scholar]
- Boni, A. Uno Studio Sulla Coltura Idroponica e la Conservazione Post-Raccolta Della Salicornia europaea. Scienze Agrarie, Alimentari E Agro-Ambientali. Master’s Thesis, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, D.R.; Rathore, A.P.; Jha, B. Aboveground, belowground biomass and nutrients pool in Salicornia brachiata at coastal area of India: Interactive effects of soil characteristics. Ecol. Res. 2018, 33, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 300, p. D05109. [Google Scholar]
- Miceli, A.; Moncada, A.; Sabatino, L.; Vetrano, F. Effect of gibberellic acid on growth, yield, and quality of leaf lettuce and rocket grown in a floating system. Agronomy 2019, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, B.; Assareh, M.H.; Rasuoli, B.; Arzani, H.; Jafari, A.A. Effect of salinity on growth, ion content and water status of glasswort (Salicornia herbacea L.). Casp. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 8, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Itle, R.A.; Kabelka, E.A. Correlation between L* a* b* color space values and carotenoid content in pumpkins and squash (Cucurbita spp.). HortScience 2009, 44, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jaloud, A.A.; Al-Saiady, M.Y.; Assaeed, A.M.; Chaudhary, S.A. Some halophyte plants of Saudi Arabia, their composition and relation to soil properties. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2001, 5, 531–534. [Google Scholar]
- Altay, A.; Celep, G.S.; Yaprak, A.E.; Baskose, I.; Bozoglu, F. Glassworts as possible anticancer agents against human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells with their nutritive, antioxidant and phytochemical profiles. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1600290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushakova, S.A.; Kovaleva, N.P.; Gribovskaya, I.V.; Dolgushev, V.A.; Tikhomirova, N.A. Effect of NaCl concentration on productivity and mineral composition of Salicornia europaea as a potential crop for utilization NaCl in LSS. Adv. Space Res. 2005, 36, 1349–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.; Roque, M.J.; Cavaleiro, C.; Ramos, F. Nutrient value of Salicornia ramosissima—A green extraction process for mineral analysis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 104, 104135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyas, U. The Effects of Different Salt and Leonardit Applications on Seedling Growth of Common Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Master’s Thesis, Department of Field Crops, Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences, Bingöl University, Bingöl, Türkiye, 2020. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).