A Na+/H+ Antiporter Gene from Rosa multiflora (RmNHX2) Functions in Salt Tolerance via Modulating ROS Levels and Ion Homeostasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
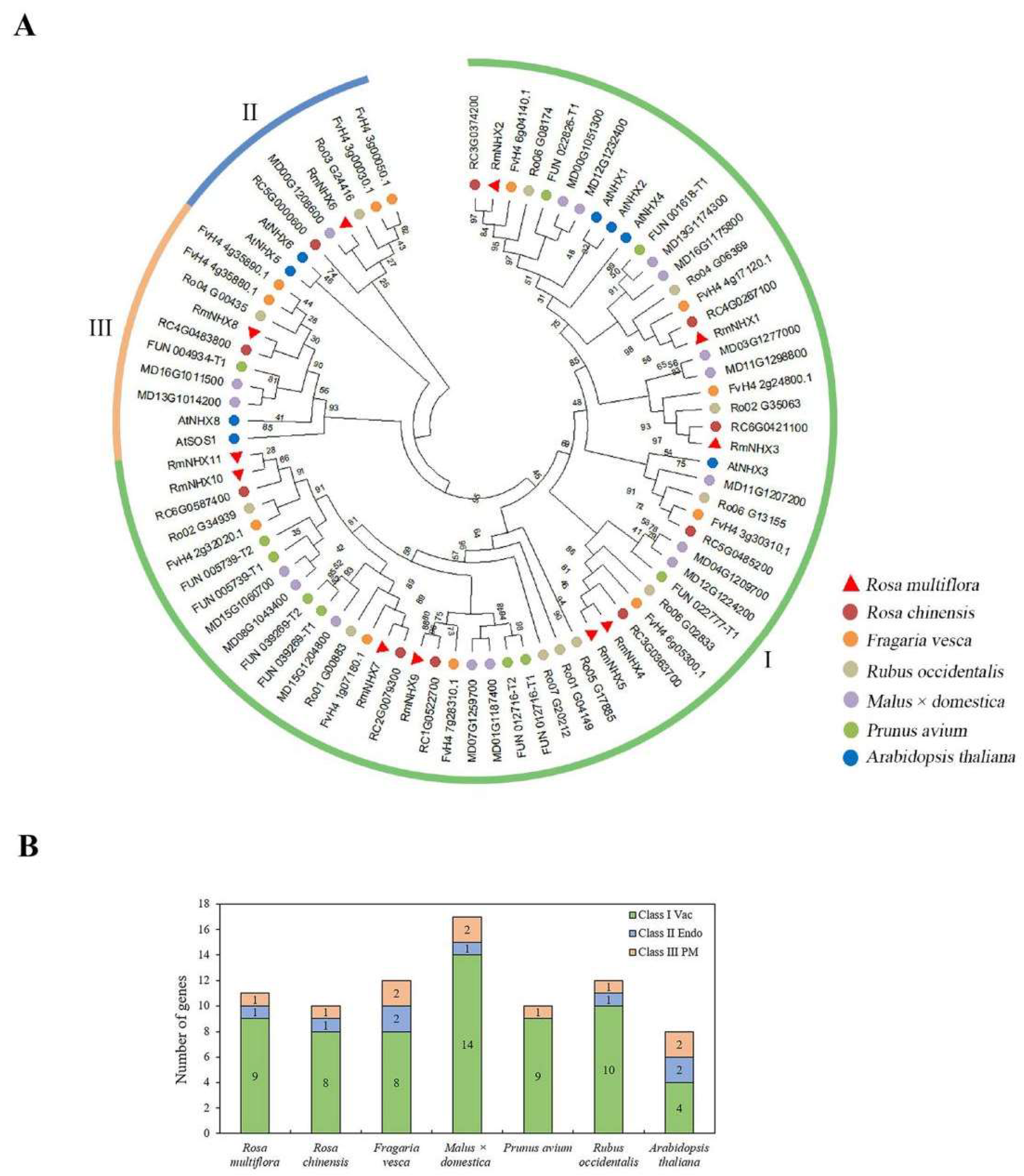
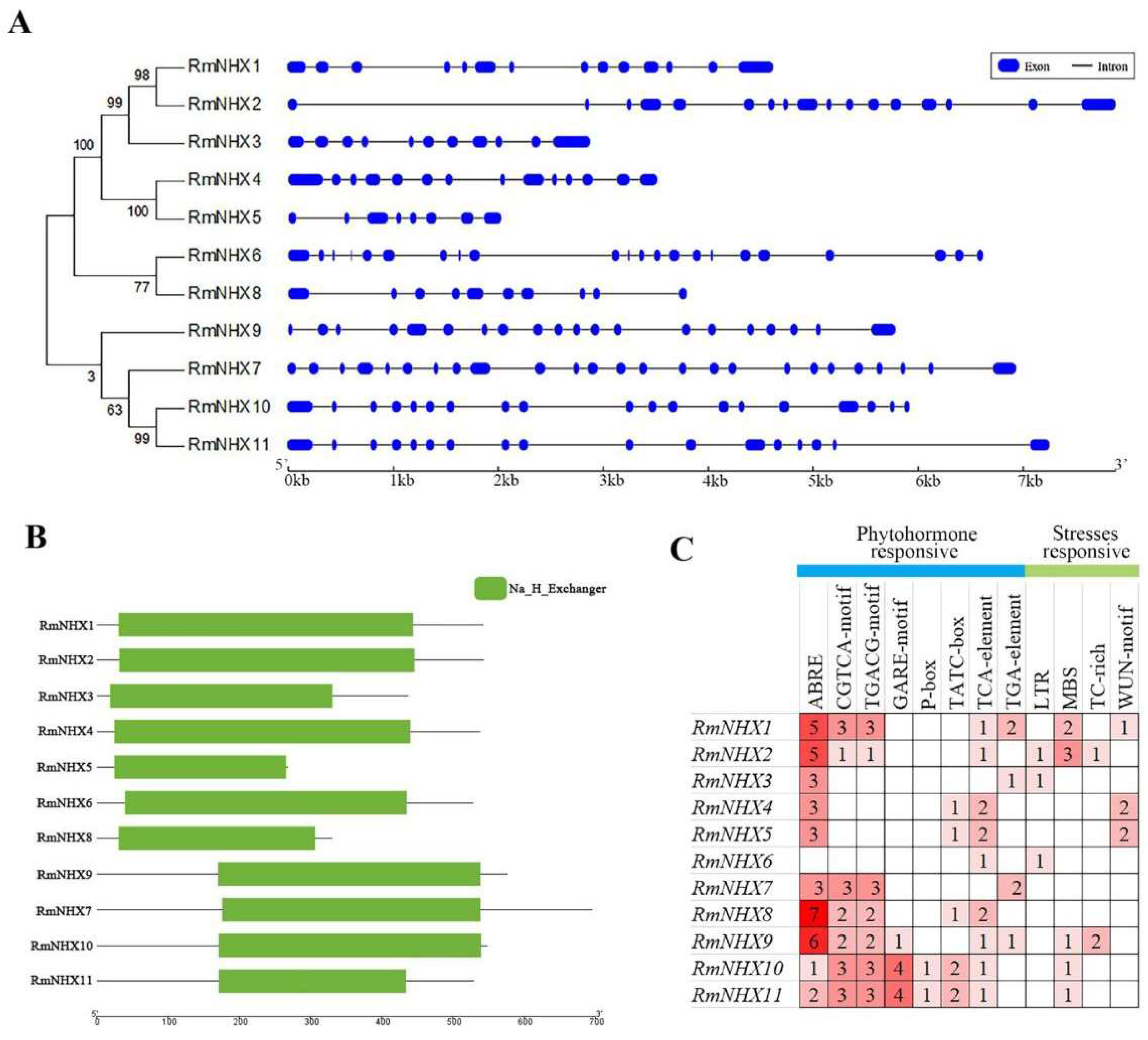
2.1. Identification of RmNHXs in Rosa multiflora
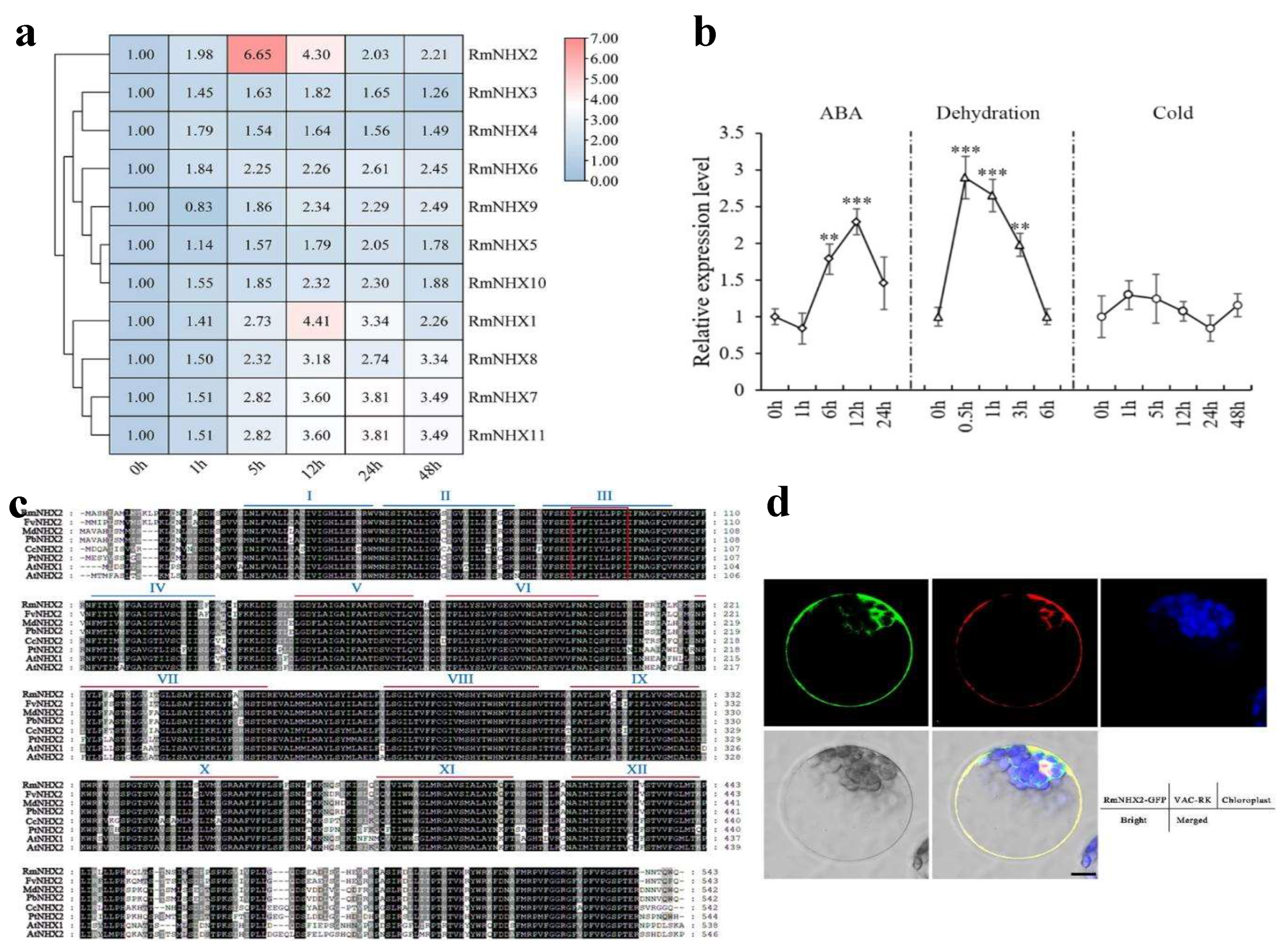
2.2. Expression Pattern and Subcellular Localization of RmNHXs
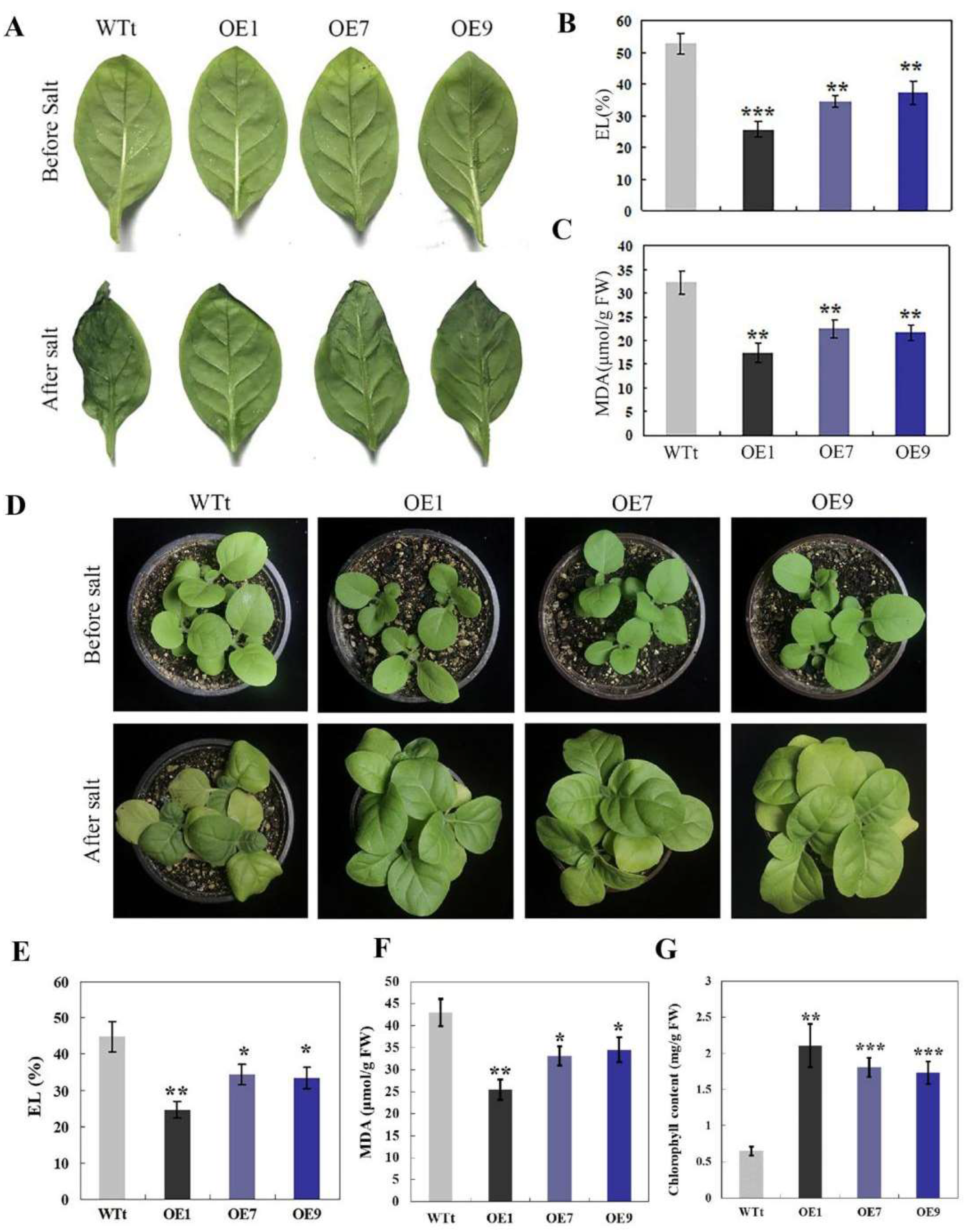
2.3. RmNHX2 Overexpression in Tobacco Led to Enhanced Salt Tolerance
2.4. Silencing of RmNHX2 in R. multiflora Conferred Sensitivity to Salt Stress
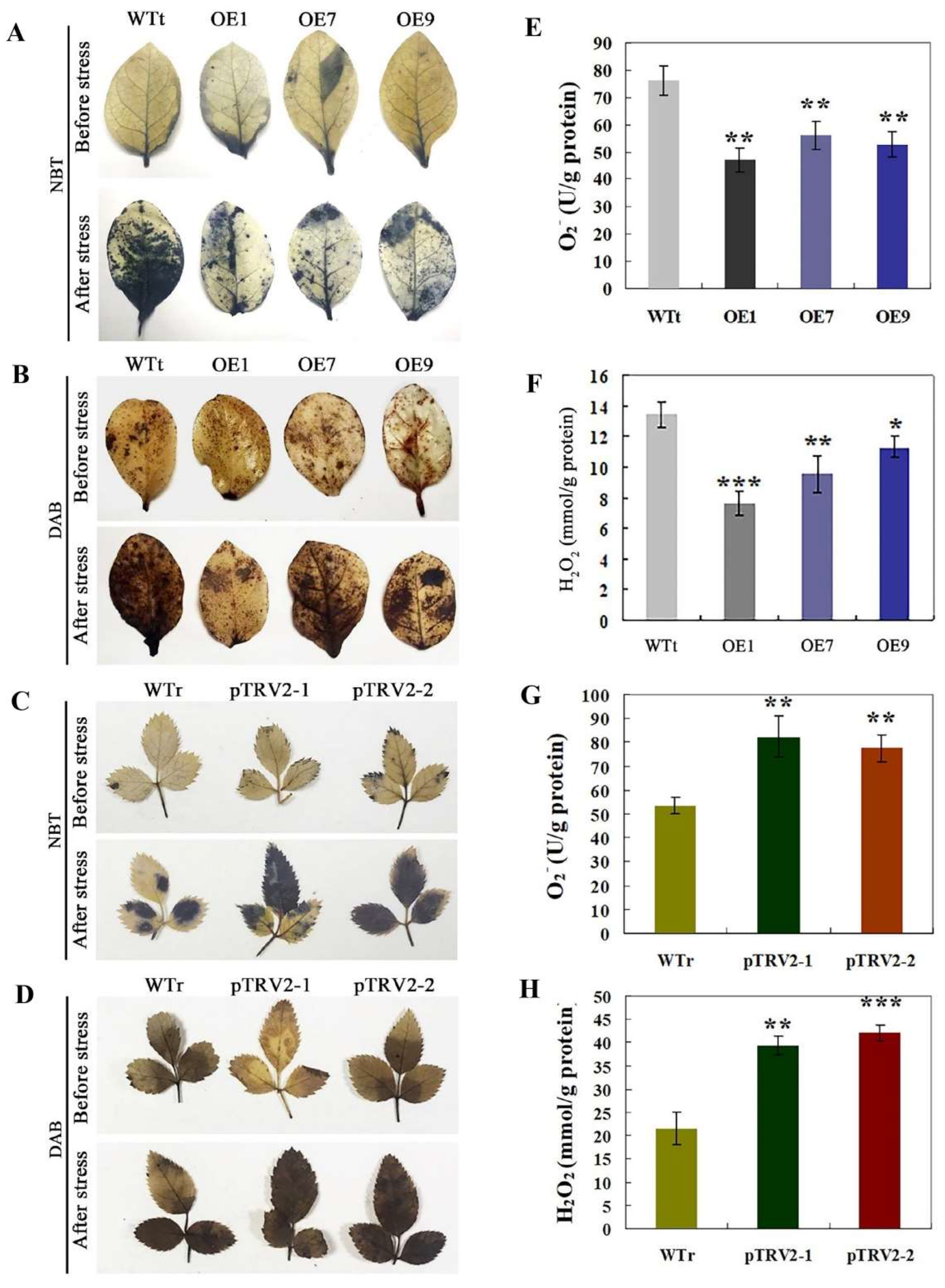
2.5. Analysis of H2O2 and O2− in Transgenic Tobacco and R. multiflora Silenced Plants under Salt Stress
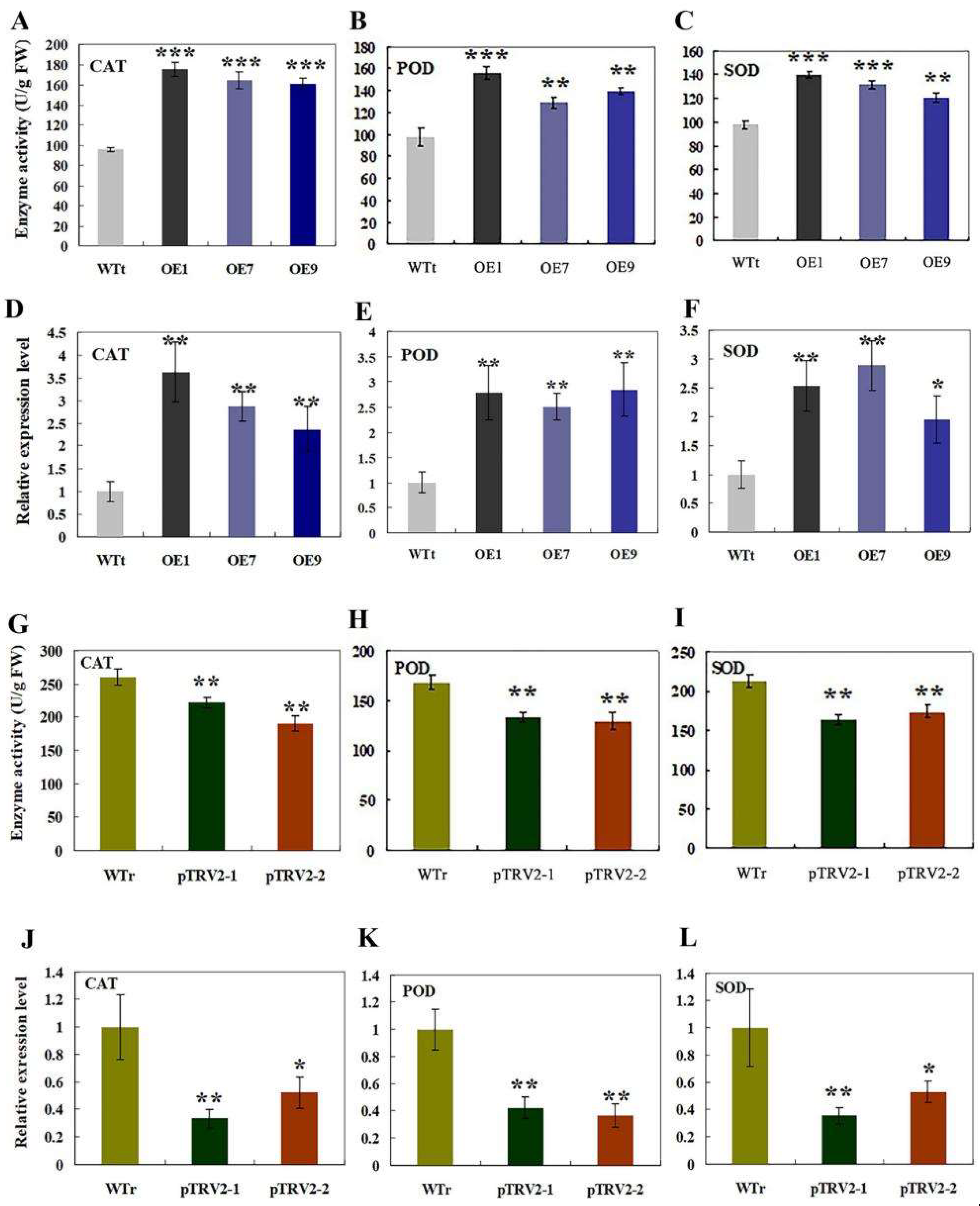
2.6. Analysis of Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and Expression Levels of the Encoding Genes in Transgenic Tobacco and R. multiflora Silenced Plants under Salt Stress
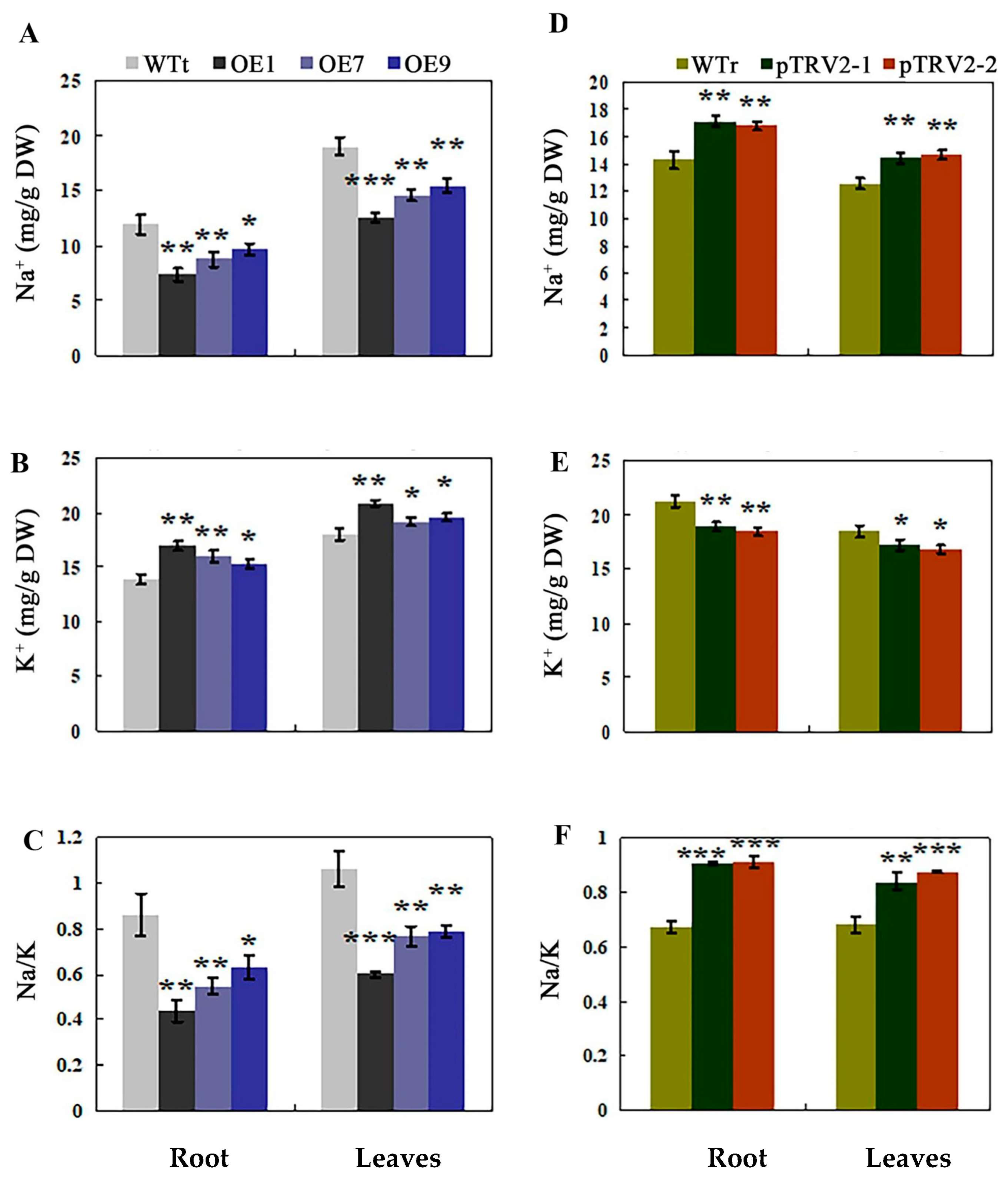
2.7. Opposite Accumulation of Na+ and K+ in Transgenic Tobacco and Rosa multiflora Silenced Plants under Salt Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of the NHX Family Genes in Rosa multiflora
4.2. Gene Structure, Conserved Motif and Promoter Analyses
4.3. Plant Material and Stress Treatment
4.4. RNA Extracting Process and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Study (qRT-PCR)
4.5. Isolation of RmNHX2 and Sequence Analysis
4.6. Subcellular Localizing Process of RmNHX2
4.7. Generation of RmNHX2-Overexpressing Tobacco Lines
4.8. Generation of RmNHX2 Silenced Plants by Virus-Induced Gene Silencing (VIGS)
4.9. Salt Stress Tolerance Assay
4.10. Physiological Analyses
4.11. In Situ Histochemical Staining of ROS
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahajan, S.; Tuteja, N. Cold, salinity and drought stresses: An overview. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 444, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002, 53, 247–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronzucker, H.J.; Britto, D.T. Sodium transport in plants: A critical review. New Phytol. 2011, 189, 54–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Mogami, J.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. ABA-dependent and ABA-independent signaling in response to osmotic stress in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 21, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud, E.; Aken, O.V.; Ho, L.H.M.; Whelan, J. The transcription factor ABI4 is a regulator of mitochondrial retrograde expression of Alternative oxidase. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Cheng, Z.H.; Zhao, K.; Yao, W.J.; Sun, X.M.; Jiang, T.B.; Zhou, B. Functional characterization of poplar NAC13 gene in salt tolerance. Plant Sci. 2019, 281, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phukan, U.J.; Jeena, G.S.; Tripathi, V.; Shukla, R.K. MaRAP2-4, a waterlogging-responsive ERF from Mentha, regulates bidirectional sugar transporter AtSWEET10 to modulate stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 16, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.L.; Ge, H.M.; Wang, X.K.; Tang, R.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.G.; Lan, W.; Luan, S.; Yang, L. Overexpression of pyrabactin resistance-like abscisic acid receptors enhances drought, osmotic, and cold tolerance in transgenic poplars. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Wang, M.C.; Xu, F.; Quan, T.Y.; Peng, K.Q.; Xiao, L.T.; Xia, G. Wheat oxophytodienoate reductase gene TaOPR1 confers salinity tolerance via enhancement of abscisic acid signaling and reactive oxygen species scavenging. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelake, R.M.; Kadam, U.S.; Kumar, R.; Pramanik, D.; Singh, A.K.; Kim, J.Y. Engineering drought and salinity tolerance traits in crops through CRISPR-mediated genome editing: Targets, tools, challenges, and perspectives. Plant Commun. 2022, 6, 208–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjara, M.; Zhu, L.F.; Shen, G.X.; Payt, P.; Zhang, H. Expression of an Arabidopsis sodium/proton antiporter gene (AtNHX1) in peanut to improve salt tolerance. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2012, 6, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.J.; Ma, Q.; Wu, G.Q.; Pei, W.; Jing, H.; Wang, S.M. ZxNHX controls Na+ and K+ homeostasis at the whole-plant level in Zygophyllum xanthoxylum through feedback regulation of the expression of genes involved in their transport. Ann. Bot. 2015, 115, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deinlein, U.; Stephan, A.B.; Horie, T.; Luo, W.; Schroeder, J.I. Plant salt-tolerance mechanisms. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassil, E.; Blumwald, E. The ins and outs of intracellular ion homeostasis: NHX type cation/H+ transporters. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassil, E.; Tajima, H.; Liang, Y.; Ohto, M.; Ushijima, K.; Nakano, R.; Esumi, T.; Coku, A.; Belmonte, M.; Blumwald, E. The Arabidopsis Na+/H+ antiporters NHX1 and NHX2 control vacuolar pH and K+ homeostasis to regulate growth, flower development, and reproduction. Plant Cell. 2011, 23, 3482–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Du, J.; Feng, H.; Blumwald, E.; Yu, L.; Xu, G. Two NHX-type transporters from Helianthus tuberosus improve the tolerance of rice to salinity and nutrient deficiency stress. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 6, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.Z.; Wang, C.M.; Xing, C.H.; Yang, T.Y.; Yan, J.X.; Gao, J.Z.; Li, D.; Wang, R.; Blumwald, E.; Zhang, S.; et al. Overexpression of PbrNHX2 gene, a Na+/H+ antiporter gene isolated from Pyrus betulaefolia, confers enhanced tolerance to salt stress via modulating ROS levels. Plant Sci. 2019, 285, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Hu, Y.Z.; Zeng, Y.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.C. Molecular characterization and functional analysis of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene (HcNHX1) from Halostachys caspica. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 1889–1899. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Zhang, H.; Blumwald, E.; Xia, T. A novel plant vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene evolved by DNA shuffling confers improved salt tolerance in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22999–23006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouiaa, S.; Khoudi, H.; Leidi, E.O.; Pardo, J.M.; Masmoudi, K. Expression of wheat Na+/H+ antiporter TNHXS1 and H+-pyrophosphatase TVP1 genes in tobacco from a bicistronic transcriptional unit improves salt tolerance. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 79, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Patel, M.K.; Mishra, A.; Jha, B. In planta transformed cumin (Cuminum cyminum L.) plants, overexpressing the SbNHX1 gene showed enhanced salt endurance. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wei, Z.W.; Liang, D.; Zhou, S.S.; Li, Y.H.; Liu, C.H.; Ma, F.W. Enhanced salt resistance in apple plants overexpressing a Malus vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene is associated with differences in stomatal behavior and photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 70, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Feng, F.J.; Dong, L.; Cheng, L.L.; Ma, F.W.; Shi, S.G. Overexpression of a Malus vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene (MdNHX1) in apple rootstock M.26 and its influence on salt tolerance. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2010, 102, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.J.; Wei, T.L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.S.; Liu, J.H. Overexpression of PtrbHLH, a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor from Poncirus trifoliata, confers enhanced cold tolerance in pummelo (Citrus grandis) by modulation of H2O2 level via regulating a CAT gene. Tree Physiol. 2020, 39, 2045–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.J.; Liu, J.H. The transcription factor CsbHLH18 of sweet orange functions in modulation of cold tolerance and homeostasis of reactive oxygen species by regulating the antioxidant gene. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 2677–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.; Suzuki, N.; Ciftci-Yilmaz, S.; Mittler, R. Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitzschke, A.; Djamei, A.; Bitton, F.; Hirt, H. A major role of the MEKK1-MKK1/2-MPK4 pathway in ROS signalling. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Yan, G. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt: Tress responses. New Phytol. 2017, 217, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Meng, J.J.; Xing, J.Y.; Yang, S.; Wan, S.B. The K+/H+ antiporter AhNHX1 improved tobacco tolerance to NaCl stress by enhancing K+ retention. J. Plant Biol. 2017, 60, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuteja, N. Mechanisms of high salinity tolerance in plants. Method Enzymol. 2007, 428, 419–438. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, L.M.; Schumaker, K.S.; Zhu, J.K. Cell signaling during cold, drought, and salt stress. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.; Frank, M.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools, a toolkit for biologists integrating various biological data handling tools with a userfriendly interface. Mol Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔct method. Methods 2002, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Ma, X.; Zhang, G.; Song, S.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, L.; Miao, Y.; Song, C.-P. A receptor-like kinase mediates ammonium homeostasis and is important for the polar growth of root hairs in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2014, 26, 1497–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaskheli, A.J.; Ahmed, W.; Ma, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhou, X.; Gao, J. RhERF113 functions in ethylene-induced petal senescence by modulating cytokinin content in rose. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 2442–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Pei, H.X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Yang, R.; Meng, Y.; You, J.; Gao, J.; Ma, N. TRV–GFP: A modifed Tobacco rattle virus vector for effcient and visualizable analysis of gene function. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, C.; Du, C.X.; Shao, G.Y.; Cui, Y.Y. RcMYBPA2 of Rosa chinensis functions in proanthocyanidin biosynthesis and enhances abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2019, 137, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Inoue, H.; Moriguchi, T. Salt stress-mediated changes in free polyamine titers and expression of genes responsible for polyamine biosynthesis of apple in vitro shoots. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2008, 62, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, G.Q.; Kang, H.H.; Zhou, S.M.; Wang, W. TaPUB1, a putative E3 ligase gene from wheat, enhances salt stress tolerance in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 1673–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Li, Z.Y.; Chen, W.; Xing, W.; Yang, J.; Cui, Y.Y. Overexpression of RmICE1, a bHLH transcription factor from Rosa multiflora, enhances cold tolerance via modulating ROS levels and activating the expression of stress-responsive genes. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 178, 104160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, H.; Shen, Y.; Chen, L.; Cui, Y.; Luo, P. A Na+/H+ Antiporter Gene from Rosa multiflora (RmNHX2) Functions in Salt Tolerance via Modulating ROS Levels and Ion Homeostasis. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9030290
Luo H, Shen Y, Chen L, Cui Y, Luo P. A Na+/H+ Antiporter Gene from Rosa multiflora (RmNHX2) Functions in Salt Tolerance via Modulating ROS Levels and Ion Homeostasis. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(3):290. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9030290
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Haiyan, Yuxiao Shen, Linmei Chen, Yongyi Cui, and Ping Luo. 2023. "A Na+/H+ Antiporter Gene from Rosa multiflora (RmNHX2) Functions in Salt Tolerance via Modulating ROS Levels and Ion Homeostasis" Horticulturae 9, no. 3: 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9030290
APA StyleLuo, H., Shen, Y., Chen, L., Cui, Y., & Luo, P. (2023). A Na+/H+ Antiporter Gene from Rosa multiflora (RmNHX2) Functions in Salt Tolerance via Modulating ROS Levels and Ion Homeostasis. Horticulturae, 9(3), 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9030290





