Mechanism of Tolerance to Head-Splitting of Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata L.): A Review of Current Knowledge and Future Directions
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Introduction to and Evaluation of the Head-Splitting Properties of Cabbage
3. Study on Anatomic Properties of Head-Splitting Properties of Cabbage and Other Internal Factors
4. QTL Location of Head-Splitting Properties of Cabbage
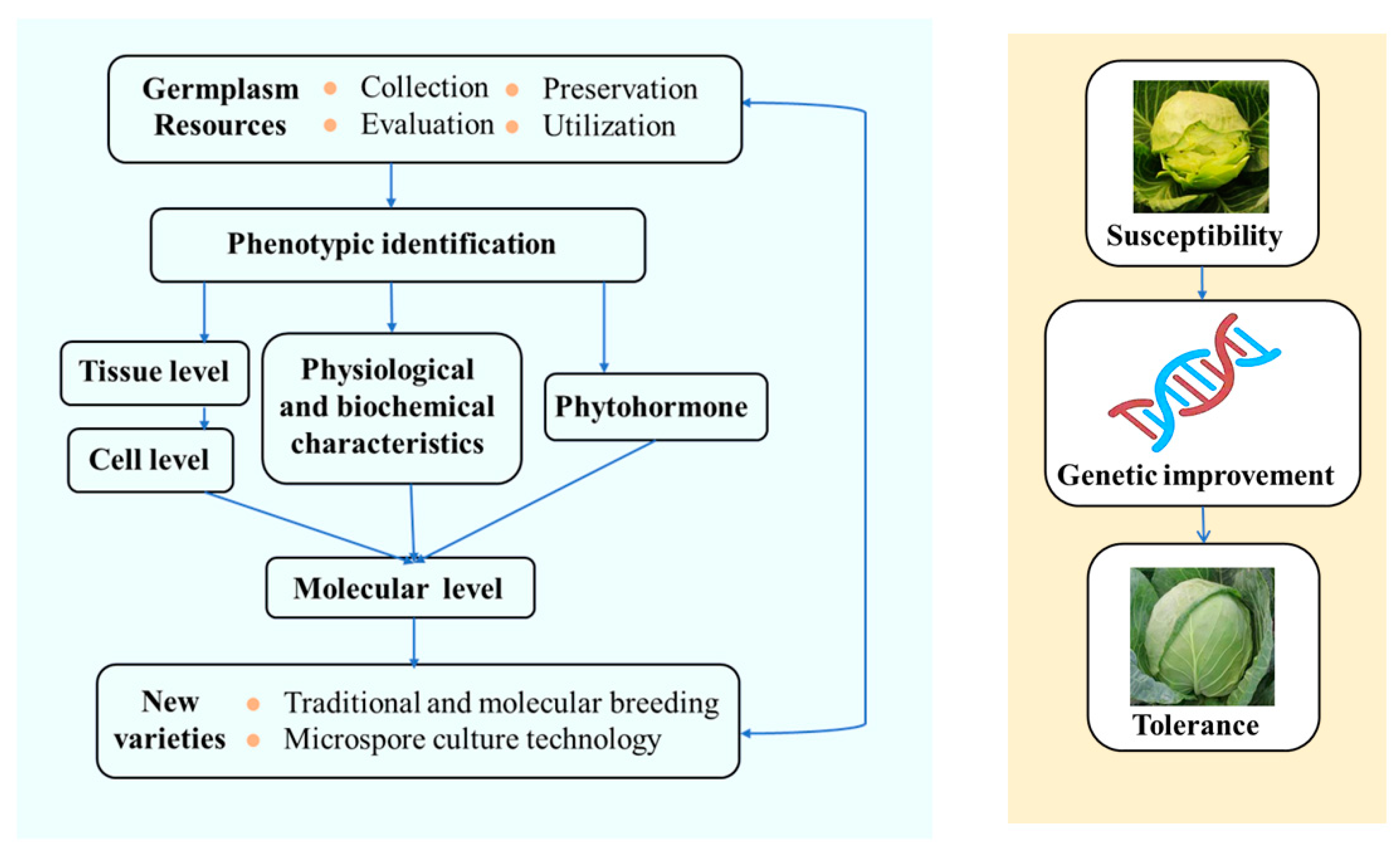
5. Conclusions and Prospect
5.1. The Role of Substances That Regulate Cell Water Potential, the Development, Ductility and Toughness of the Cell Walls
5.2. The Role of Calcium Ions, Expansin Gene and Plant Hormones
5.3. The Importance of Breeding Cabbage Varieties with Head-Splitting Tolerance

Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teshome, S.; Bobo, T. Adaptability Studies of Head Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) Varieties at Adola Rede Areas, Southern Oromia, Ethiopia. Int. J. Afr. Asian Stud. 2018, 51, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Wang, P.; Yang, L.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, M.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J. Carotenoid Biosynthetic Genes in Cabbage: Genome-Wide Identification, Evolution, and Expression Analysis. Genes 2021, 12, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, M.E.; Velasco, P. Glucosinolates in Cabbage foods: Bioavailbility in food and significance for human health. Phytochem. Rev. 2007, 7, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiczkowski, W.; Szawara-nowak, D.; Topolska, J. Red cabbage anthocyanins: Profile, isolation, identification, and antioxidant activity. Food Res. Int. 2012, 51, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Upadhyay, A.K.; Bahadur, A.; Singh, D.B.; Singh, K.; Rai, M. Antioxidant phytochemicals in cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata). Sci. Hortic. 2006, 108, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.Z.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S.J.; Yang, L.M.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Lv, H.H.; Fang, Z.Y.; Hou, X.L. Genome-wide identification and analysis of cytokinin dehydrogenase/oxidase (CKX) family genes in Brassica oleracea L. reveals their involvement in response to Plasmodiophora brassicae infections. Hortic. Plant J. 2022, 8, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, V.V.; Bharadiya, P.S.; Aghav, V.D. Effect of organic and inorganic sources of nitrogen on growth and yield of cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.). Asian J. Hortic. 2010, 5, 291–293. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.M.; Fang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhuang, M.; Lv, H.H.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.L.; Liu, Y.M.; Li, Z.S.; Han, F.Q. Research Progress on Cabbage Genetic Breeding During ‘The Thirteenth Five-year Plan’ in China. China Veg. 2021, 1, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2023. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/zh/#data/QCL (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- Li, Q.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Su, Y.; Zhang, T. Breeding of cabbage lines resistant to both head splitting and fusarium wilt via an isolated microspore culture system and marker-assisted selection. Euphytica 2020, 216, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liliana, A.S.; Melchor, J.; Rosalba, T.R.; David, E.M.; María, A.E.; Juan, L.V. Effectiveness of Chemical and Thermal Treatments on Control Rhizopus stolonifer Fruit Infection Comparing Tomato Cultivars with Different Sensitivities to Cracking. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2754. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura, K.; Shimizu, M.; Kawanabe, T.; Pu, Z.; Kodama, T.; Kaji, M.; Osabe, K.; Fujimoto, R.; Okazaki, K. Assessment of DNA markers for seed contamination testing and selection of disease resistance in cabbage. Euphytica 2017, 213, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.H.; Liu, H.; Xu, Z.M.; Cheng, Y.A.; Yang, A.P. Effects of irrigation, topdressing and cultivation density on the cracked sphericity of cabbage. In Proceedings of the 7th Symposium of Cruciferous Branch of Chinese Society of Horticulture and Proceedings of Chinese Society of Horticulture Conference, Beijing, China, 14 October 2009; pp. 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y. The New Standard Classification about the Leafy Head Cracking of Spring Cabbage. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2009, 37, 10951–10952. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, A.S.; Liu, Y.M.; Fang, Z.Y.; Yan, J.Y. Research Progress of Head splitting on Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata L.). Plant Genet. Resour. 2011, 2, 307–310. [Google Scholar]
- Peet, M.M. Fruit cracking in tomato. Horttechnology 1992, 2, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.J.; Wen, N.S. Preliminary Report on Application Technology of Organic Fertilizer for Cabbage Cultivation. China Cucurbits Veg. 2006, 3, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.P.; Dai, Z.L.; Pan, Y.F. Effect of Plug Seedling Age on the Marketing and Nursery Period of Cabbage. Agric. Sci. 2010, 6, 217–218. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Qin, W.B.; Dai, Z.L.; Pan, Y.F.; Yao, Y.M. Comparative trial of new varieties of overwintering kale in the Yangtze River basin. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 179–180. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.F.; Dai, Z.L.; Mao, Z.L.; Wu, G.P. Effect of seedling age on yield and harvesting season of kale. Jiangxi J. Agric. 2010, 22, 64–65. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, W.X.; Li, X.N.; Choi, S.R.; Nguyen, V.D.; Dhandapani, V.; Kim, Y.Y.; Ramchiary, N.; Kim, J.G.; Edwards, D.; Batley, J.; et al. Mapping QTLs of tolerance to head splitting in cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata L.). Mol. Breed 2015, 35, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.S. Inheritance of head splitting in cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.). Euphytica 1972, 21, 507–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.Y.; Kang, S.H.; Chen, B.G.; Su, Y.Y.; Yan, F.Q.; Li, S.F. Establishment of Grade Standard on Resistance to Head-bursting of Brassica oleracea L. Under Alpine Environment Conditions of Northwest Hebei. China Cucurbits Veg. 2021, 34, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.M.; Zhang, E.H.; Cheng, Y.A.; Yang, A.P.; Ma, Q.S. Preliminary Report on the Identification Method of Head-splitting Tolerance of Cabbage in Spring as Well as the Standard. In Proceedings of the 6th Symposium of Cruciferous Branch of Chinese Society of Horticulture and Proceedings of Chinese Society of Horticulture Conference, Wuhan, China, 28 November 2008; pp. 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.B.; Liu, Y.M.; Fang, Z.Y.; Yang, L.M.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Sun, P.T. Genetic Analysis of Head-splitting Resistance Traits in cabbage. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2012, 39, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.B.; Zeng, A.S.; Liu, Y.M.; Shen, H.L.; Xiao, X.G.; Li, Z.S.; Fang, Z.Y.; Yang, L.M.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, Y.Y. Evaluation Method of Screening of Germplasm with High Resistance to Head-splitting in Cabbage. Plant Genet. Resour. 2015, 16, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, W.X.; Kim, Y.Y.; Li, X.N.; Choi, S.R.; Wang, Y.B.; Sung, C.K.; Im, S.; Ramchiary, N.; Zhou, G.S.; Lim, Y.P. Anatomic Characteristics Associated with Head Splitting in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, A.S.; Liu, Y.M.; Fang, Z.Y.; Yang, L.M.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, J.F.; Sun, P. Studies on the Relationship between Splitting-tolerant Characteristics and Surface Micro-configuration and Cell Tissue Structure of Leaf in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata L.). Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2009, 24, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Cao, Q.H.; Zhou, Z.L.; Zhao, D.L.; Li, A.; Li, Y.Y.; Tang, J. Advances of Relaxation Factors of Plant Cell Walls—Expansin. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2013, 41, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.L.; Sun, C.Q.; Pan, Y.P.; Qin, W.B.; Yao, Y.M.; Pan, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.C. Effect of Nitrogen Application Rates on Head-splitting Resistance of Cabbage cultivar Ruigan 20. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 29, 450–452. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, A.S.; Liu, Y.M.; Fang, Z.Y.; Yang, L.M.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, J.F.; Sun, P.T. Relationship between endogenous hormone content and Head-splitting Character during Brassica oleraca L. var. capitata L. Vegetative Period. China Veg. 2009, 20, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.B. Construction of High-Density Genetic Linkage Map and Mapping of Splitting Resistant, Color and Shape of the Head in Cabbage; China Agricultural University: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.B.; Zhang, E.H.; Xu, Z.M.; Zhang, M.L.; Liu, X. Study on the Correlation between Qualitative Characters and Head-Splitting of Spring Cabbage. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 2016, 47, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Fang, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Yang, L.M.; Sun, P.T. Studies on Combining Ability and Heritability of splitting-resistance Characteristic in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.). China Veg. 2009, 2, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.B.; Liu, Y.M.; Shen, H.L.; Xiao, X.G.; Li, Z.S.; Fang, Z.Y.; Yang, L.M.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, Y.Y. Inheritance Analysis and Quantitative Trait Loci Detection of Head Splitting Tolerance in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata). HortScience 2015, 50, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.B.; Liu, Y.M.; Li, Z.S.; Fang, Z.Y.; Yang, L.M.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, Y.Y. QTL Analysis of Head Splitting Resistance in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata) Using SSR and InDel Makers Based on Whole-Genome Re-Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.B.; Li, Q.; Yi, D.X.; Liu, L.J.; Fu, C.Z.; Zhang, T.Z. Genetic Analysis of Traits Related to Head in White Cabbage. North. Hortic. 2019, 8, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.W.; Chen, J.X.; Tai, X.; Ren, Y.Y.; Bo, T.Y. QTL Mapping of cabbage Head-splitting Time of Cabbage based on QTL-seq Technique. In Proceedings of the 2018 Academic Annual Meeting of Chinese Society for Horticultural Science and Proceedings of the Conference of Chinese Society for Horticultural Science, Qingdao, China, 17 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.M.; Fang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhuang, M.; Lv, H.H.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.L.; Liu, Y.M.; Li, Z.S.; Han, F.Q. Recent Advances of Disease and Stress Resistant Breeding of Cabbage in China. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2020, 47, 1678–1688. [Google Scholar]
- Khadivi-Khub, A. Physiological and genetic factors influencing fruit cracking. Acta Physiol. Plant 2014, 37, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Lopez, A.; Jeon, S.; de Freitas, S.T.; Yu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Labavitch, J.M.; Tian, S.; Powell, A.L.T.; Mitcham, E. Disassembly of the fruit cell wall by the ripening-associated polygalacturonase and expansin influences tomato cracking. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Sai, G.; Alexandre, J. Bio-fertilizer application induces soil suppressiveness against Fusarium wilt disease by reshaping the soil microbiome. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 114, 238–247. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, R.; Liang, Y.C.; Wakelin, S.A. Supplementing chemical fertilizer with an organic component increases soil biological function and quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 96, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, X.J.; Li, C.Q.; Ren, X.S. Progress of the Mechanism and Control Measures for Head Splitting in Cabbage. J. Chang. Veg. 2008, 39, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Amari, T.; Abdelly, C. Biochemical responses of Digitaria commutata and Cenchrus ciliaris to water stress: Antioxidative reactions, proline and soluble sugars accumulation. Bioagro 2021, 33, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.W.; Lin, K.H.; Wu, C.W. Effects of Betaine and Chitin on Water Use Effi-ciency in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. capitata). HortScience 2020, 55, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.Q.; Gu, K.D.; Zhang, L.L.; Sun, C.H.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, C.K.; Wang, W.Y.; Du, M.C.; Hu, D.G. MdbHLH3 modulates apple soluble sugar content by activating phosphofructokinase gene expression. J. Integr. Plant. Biol. 2022, 64, 884–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ra, T.; Sonoda, Y. The role of macronutrients for cabbage-head formation. I. Contribution to cabbage-head formation of nitrogen, phosphorus or potassium supplied at different growth stages. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1979, 25, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, E.H.; Xu, Z.M.; Cheng, Y.A.; Li, H.W. Impact of Three Main Cultivated Factors on the Character of Spring Cabbage Dehiscent Leafy Head. J. Northwest AF Univ. 2009, 37, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.W.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, C.; Xu, R.X. Studies on Character of Cabbage Dehiscent Leafy Head. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 1994, 25, 344–346. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Tang, X.F.; Giovannoni, J.; Xiao, F.M.; Liu, Y.S. Functional characterization of a tomato COBRA-like gene functioning in fruit development and ripening. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, X.J. Studies on the Relationship Between Head-splitting and Leafy Structure, Calcium, Potassium, Waxiness Contents of Leaves in Cabbage; Southwest University: Chongqing, China, 2009; pp. 24–25. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Q.Y.; Wallrad, L.; Bader, O. Almutairi and Jörg Kudla Ca2+ signaling in plant responses to abiotic stresses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 287–300. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.Y.; Bai, J.H.; Duan, F.Q.; Xi, X.; Li, T.; Guo, J.P. Effect of CaCl2 Treatment on Cell Wall Degrading Enzymes Activities and Microstructure of Fruit Cracking of Ziziphus jujuba ‘Huping Zao’. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2019, 46, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove, D.J. Loosening of plant cell walls by expansins. Nature 2000, 407, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummell, D.A.; Howie, W.J.; Ma, C.; Dunsmuir, P. Postharvest fruit quality of transgenic tomatoes sup-pressed in expression of a ripening-related expansin. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2002, 25, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuypers, A.; Rosales, M.; de Ollas Valverde, C.; Gonzalez-Guzman, M.; Pi-tarch, Z.; Matus, J.; Candela, H.; Rambla, J.; Granell, A.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; et al. Identification of ABA-Mediated Genetic and Metabolic Responses to Soil Flooding in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L. Mill). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 613059. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M. Study on the Standard Classification About Leafy Head Cracking and Identi-Fication of Cracking Resistant Spring Cabbage; Northeast Agricultural University: Harbin, China, 2010; p. 40. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.W.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, R.; Chen, B.; Zhong, Z.J.; Jiang, F.L. SlGH9-15 regulates tomato fruit cracking with hormonal and abiotic stress responsiveness cis-elements. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
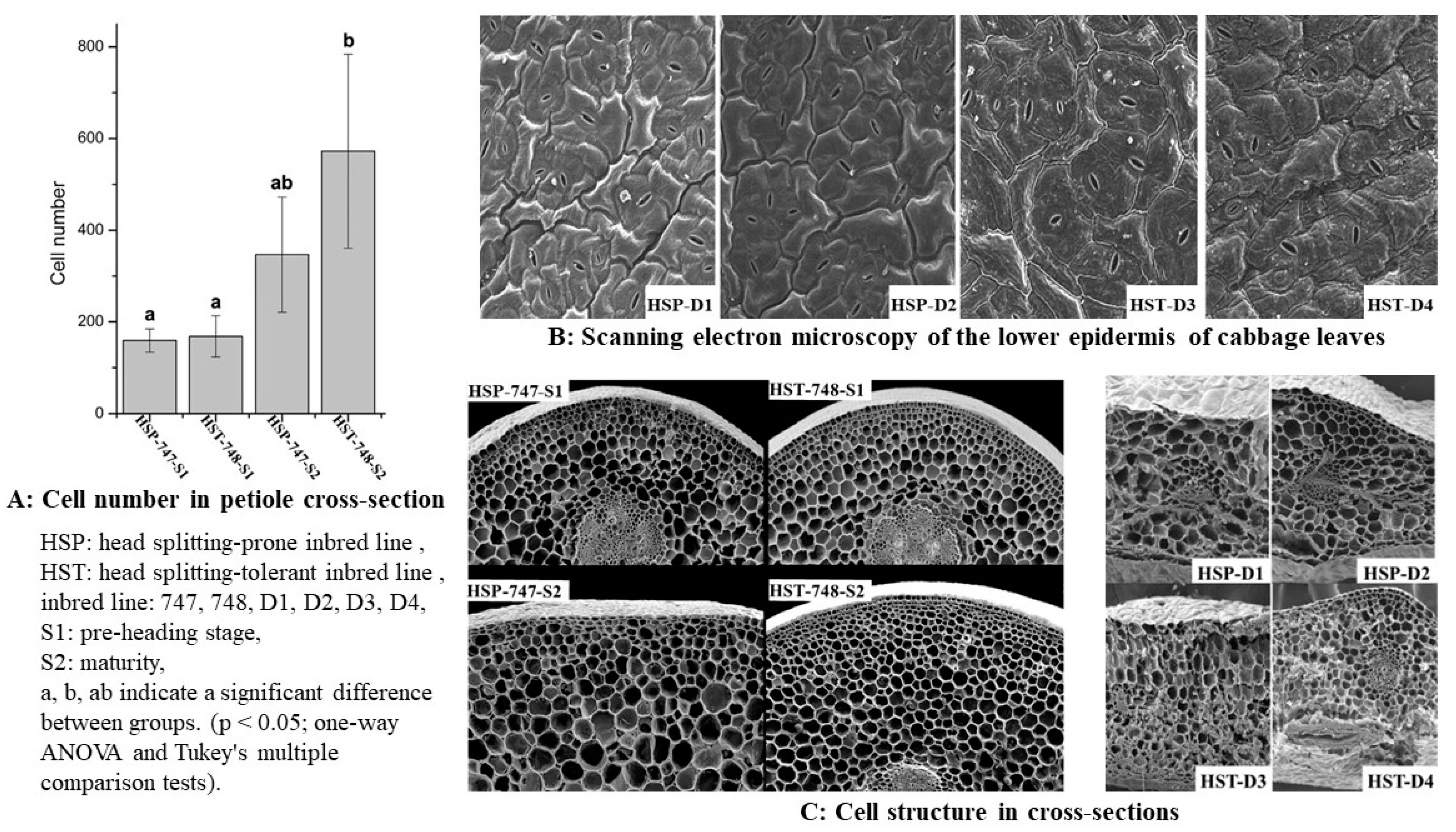
| Generations | Method | Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 cross combinations involving 6 backbone parents | Analyzing the combining ability and heritability of head-splitting tolerance | 1. Head-splitting tolerance was controlled by additive effect and non-additive effect, but mainly by additive effect. 2. GCA variance accounted for a large proportion of the total genetic variance; early generation selection should be emphasized. | Zhuang M. [34] |
| P1, P2, Two parental lines, their F1, F2, and two backcross progenies | Analyzing the combining ability and heritability of head-splitting tolerance | 1. It was concluded that there were at least three gene pairs for controlling head-splitting. 2. Gene action was mostly additive, but partial dominance for early splitting was detected. 3. Narrow sense heritability was estimated at 47%. | Chiang, M.S. [22] |
| P1, P2, F1, B1, B2, F2 | Mixed major gene plus polygene inheritance model | 1. The efficient selection should be in the early generation of F2 and B1 2. Head-splitting tolerance was controlled by two additive-dominant-epitasis major genes plus additive-dominant-epitasis polygenes 3. The additive effect for the two major genes was foremost, while there was some interaction effect between them 4. Head-splitting tolerance was dominated by major genes | Su Y.B. [25] |
| P1, P2, F1, F2, DH | Mixed major gene plus polygene inheritance model | 1. Head-splitting tolerance was controlled by three additive-epitasis major plus additive-epitasis polygenes 2. Head-splitting tolerance had higher heritability 3. Head-splitting tolerance was dominated by major genes, although the environmental factors had a great effect on it | Su Y.B. [36] |
| Pop | Year/ Method | Chr | QTL | Position (cM) | LOD | Marker Interval | R2 (%) | A | Primer/ Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DH | 2011 (MQM) | 4 | Hsr 4.2 | 100.0 | 3.01 | Scaffold12597a-Scaffold55516 | 9.1 | 9.19 | 2170 SSR markers, 1013 expressed sequence tag (EST)-SSR markers [35] |
| 7 | Hsr 7.1 | 7.3 | 4.03 | Scaffold195-BOE569 | 9.7 | –9.80 | |||
| 7 | Hsr 7.2 | 43.5 | 4.30 | Scaffold195-Scaffold46873 | 10.5 | –10.81 | |||
| 9 | Hsr 9.2 | 51.1 | 3.38 | Scaffold47852-Scaffold21727 | 9.1 | 10.84 | |||
| 2012 (MQM) | 4 | Hsr 4.1 | 51.8 | 3.05 | Scaffod61158-Scaffod38160 | 8.6 | 8.75 | ||
| 4 | Hsr 4.2 | 95.0 | 3.61 | Scaffold12597a-Scaffold55516 | 10.2 | 8.81 | |||
| 7 | Hsr 7.2 | 41.4 | 2.48 | Scafford728-Scaffold46873 | 7.1 | –7.62 | |||
| 9 | Hsr 9.3 | 126.4 | 3.06 | BOE344-B0E975 | 12.1 | –12.93 | |||
| 2011 (ICIM) | 4 | Hsr 4.2 | 95.0 | 2.55 | Scaffold12597a- Scaffold55516 | 5.6 | 6.87 | ||
| 6 | Hsr 6.1 | 68.0 | 2.73 | Scaffold37061-Scaffold1044 | 7.1 | 8.08 | |||
| 9 | Hsr 9.1 | 34.0 | 2.80 | Scaffold36132-Scaffold146827 | 9.2 | –9.08 | |||
| 9 | Hsr 9.2 | 58.0 | 2.54 | Scaffold21727-Scaffold13994 | 5.6 | 7.18 | |||
| 9 | Hsr 9.3 | 128.0 | 3.60 | BoE344-BoE975 | 10.1 | –9.38 | |||
| 2012 (ICIM) | 4 | Hsr4.2 | 95.0 | 5.41 | Scaffold12597a- Scaffold55516 | 11.1 | 9.15 | ||
| 6 | Hsr 6.1 | 66.0 | 2.67 | Scaffold37061-Scaffold1044 | 5.7 | 6.86 | |||
| 9 | Hsr 9.1 | 34.0 | 3.54 | Scaffold36132-Scaffold146827 | 10.6 | –9.14 | |||
| 9 | Hsr 9.2 | 58.0 | 2.79 | Scaffold21727-Scaffold13994 | 5.5 | 6.76 | |||
| 9 | Hsr 9.3 | 128.0 | 5.84 | BoE344-BoE975 | 13.9 | –10.40 | |||
| DH | 2011 (MQM) | 4 | Hsr 4.2 | 80 | 5.46 | SF12597a-SF11933 | 11.80 | 9.46 | 149 pairs of InDel primers, a set of 2170 SSR markers and 1013 expressed sequence tag (EST)-SSR markers [36] |
| 7 | Hsr 7.1 | 37.2 | 3.42 | SF46873-SF6178 | 7.70 | −6.78 | |||
| 7 | Hsr 7.2 | 68 | 3.74 | Indel112-Indel113 | 8.50 | −7.84 | |||
| 9 | Hsr 9.2 | 63.2 | 5.62 | SF13994-Indel146 | 13.60 | 10.94 | |||
| 2012 (MQM) | 4 | Hsr 4.1 | 23 | 3.86 | SF13319-Indel58 | 8.60 | 25.00 | ||
| 4 | Hsr4.2 | 81.4 | 5.61 | SF12597a-SF11933 | 12.80 | 10.78 | |||
| 7 | Hsr 9.2 | 63.2 | 5.48 | SF13994-Indel146 | 11.10 | −10.02 | |||
| 9 | Hsr 9.3 | 112.8 | 3.66 | BoE344-BoE975 | 7.44 | −6.92 | |||
| 2011 (ICIM) | 3 | Hsr 3.1 | 112 | 3.36 | Indel117-SF31711 | 5.50 | −6.78 | ||
| 3 | Hsr 3.2 | 143 | 7.31 | Indel42-SF10471 | 16.93 | 11.76 | |||
| 4 | Hsr 4.1 | 23 | 6.16 | SF13319-Indel58 | 12.56 | 10.18 | |||
| 4 | Hsr 4.2 | 80 | 6.96 | SF12597a-SF11933 | 12.86 | 10.37 | |||
| 9 | Hsr 9.2 | 63 | 5.74 | SF13994-Indel146 | 11.26 | 9.76 | |||
| 2012 (ICIM) | 3 | Hsr 3.2 | 143 | 7.86 | Indel42-SF10471 | 15.36 | 11.76 | ||
| 4 | Hsr 4.2 | 80 | 6.93 | SF12597a-SF11933 | 11.10 | 9.15 | |||
| 9 | Hsr 9.1 | 34 | 4.62 | SF36132-SF146827 | 9.20 | −9.08 | |||
| 9 | Hsr 9.2 | 63 | 5.93 | SF13994-Indel146 | 11.82 | 10.38 | |||
| 9 | Hsr 9.3 | 111 | 3.44 | BoE344-BoE975 | 8.67 | −8.20 | |||
| F2:3 | 2012 | 2 | SPL-2-1 | 47.51 | 6.16 | BRPGM0606-MR104 | 10.47 | 0.45 | SSR markers, 272 IP markers and BAC-derived simple sequence repeats (SSRs) [21] |
| 2014 | 2 | 37.71 | 6.05 | BRPGM0606-BRPGAW0693 | 14.95 | 0.37 | |||
| 2014 | 2 | SPL-2-2 | 30.41 | 4.56 | ACMF00872-BRPGAW606 | 2.18 | 0.29 | ||
| 2012 | 4 | SPL-4-1 | 49.21 | 5.46 | BRPGM0704-BRPG0433 | 7.84 | 0.58 | ||
| 2014 | 4 | 49.21 | 4.93 | ACNP0072-cnum246a | 8.93 | 0.30 | |||
| 2012 | 6 | SPL-6-1 | 32.71 | 4.71 | FTO036-BRPGN107 | 18.54 | 0.40 | ||
| 2012 | 6 | SPL-6-2 | 40.31 | 4.18 | FTO203-FTTO204 | 14.05 | 0.31 | ||
| 2014 | 6 | SPL-6-3 | 90.41 | 4.327 | BRPGM0639-ACMP00359 | 14.84 | 0.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, G.; Gu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Dong, Y.; Dong, H.; Song, X. Mechanism of Tolerance to Head-Splitting of Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata L.): A Review of Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9020251
Wang Y, Li Q, Zhang G, Gu L, Zhao Y, Zhou L, Dong Y, Dong H, Song X. Mechanism of Tolerance to Head-Splitting of Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata L.): A Review of Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(2):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9020251
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ying, Qiang Li, Guoli Zhang, Liqiang Gu, Yuqian Zhao, Lei Zhou, Yanqiu Dong, Haiquan Dong, and Xiaoming Song. 2023. "Mechanism of Tolerance to Head-Splitting of Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata L.): A Review of Current Knowledge and Future Directions" Horticulturae 9, no. 2: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9020251
APA StyleWang, Y., Li, Q., Zhang, G., Gu, L., Zhao, Y., Zhou, L., Dong, Y., Dong, H., & Song, X. (2023). Mechanism of Tolerance to Head-Splitting of Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata L.): A Review of Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Horticulturae, 9(2), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9020251







