Improving the Biocontrol Potential of Endophytic Bacteria Bacillus subtilis with Salicylic Acid against Phytophthora infestans-Caused Postharvest Potato Tuber Late Blight and Impact on Stored Tubers Quality
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Bacterial Strain, Pathogen, and Salicylic Acid Solution
2.3. Experiment Design
2.4. In Vivo and In Vitro Assay of Antagonistic Activity of B. subtilis 10–4 against Ph. infestans
2.5. Determination the Activity of Hydrolytic Enzymes: Amylases (AMY), Proteinases (PRO), Cellulases (CEL), and Inhibitors of Exogenous Hydrolases
2.6. Determination of Lipid Peroxidation (MDA) and Proline
2.7. Analysis of Starch, Total Dry Matter (TDM), Reducing Sugars (RS), and Ascorbic Acid (AsA)
2.8. Quantification of Glycoalkaloids (GA)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antagonistic Activity of Endophytic Strain of B. subtilis 10–4 against Ph. infestans
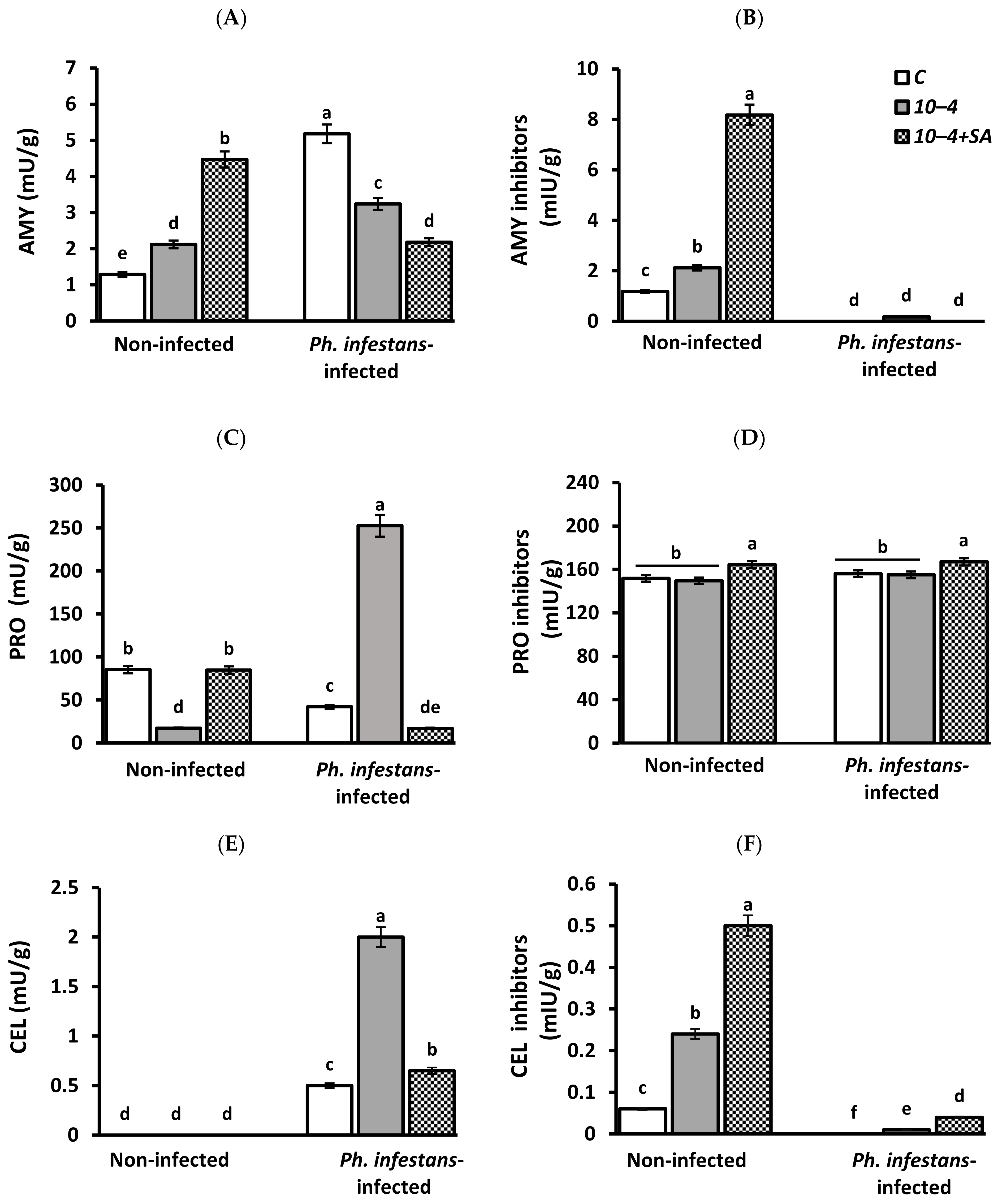
3.2. Activity of Hydrolytic Enzymes Protease (PRO), Amylase (AMY), Cellulase (CEL), and Inhibitors of Hydrolases
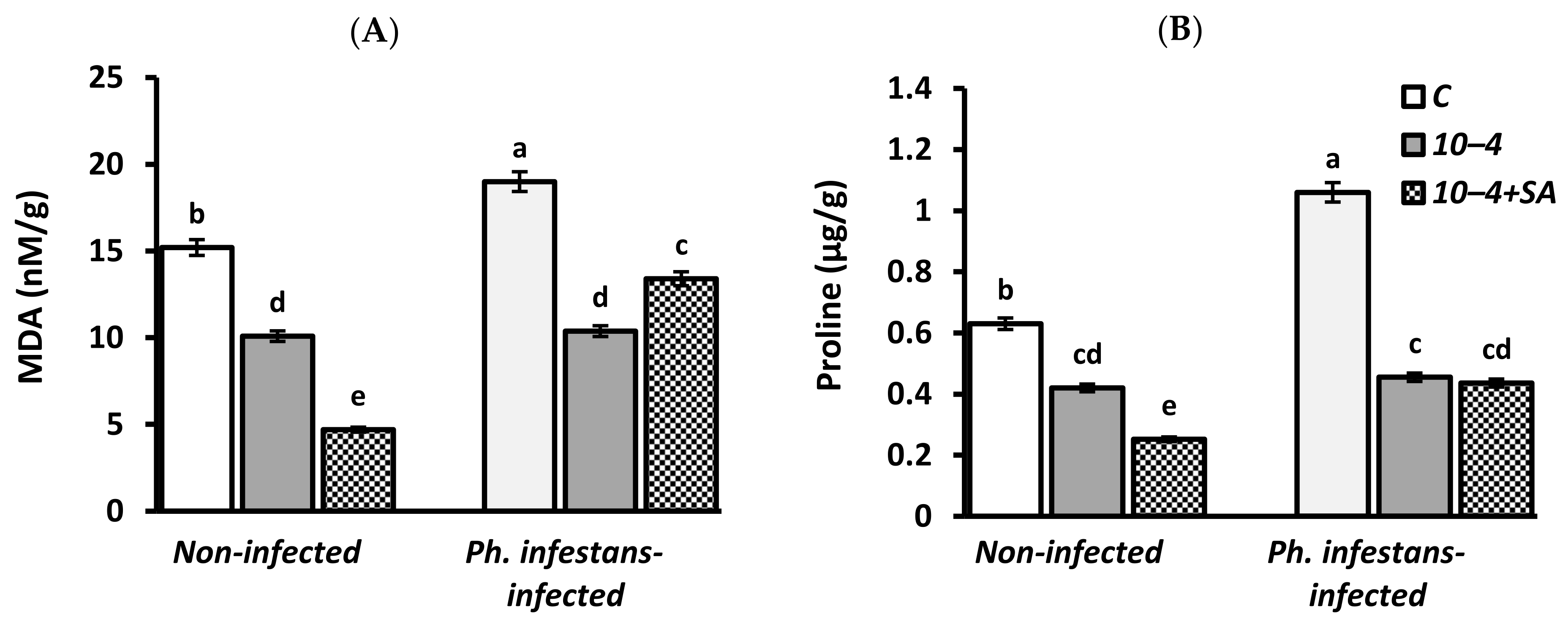
3.3. Malondialdehyde (MDA) and Proline Content
3.4. Starch, Total Dry Matter (TDM), Reducing Sugars (RS), and Ascorbic Acid (AsA) contents
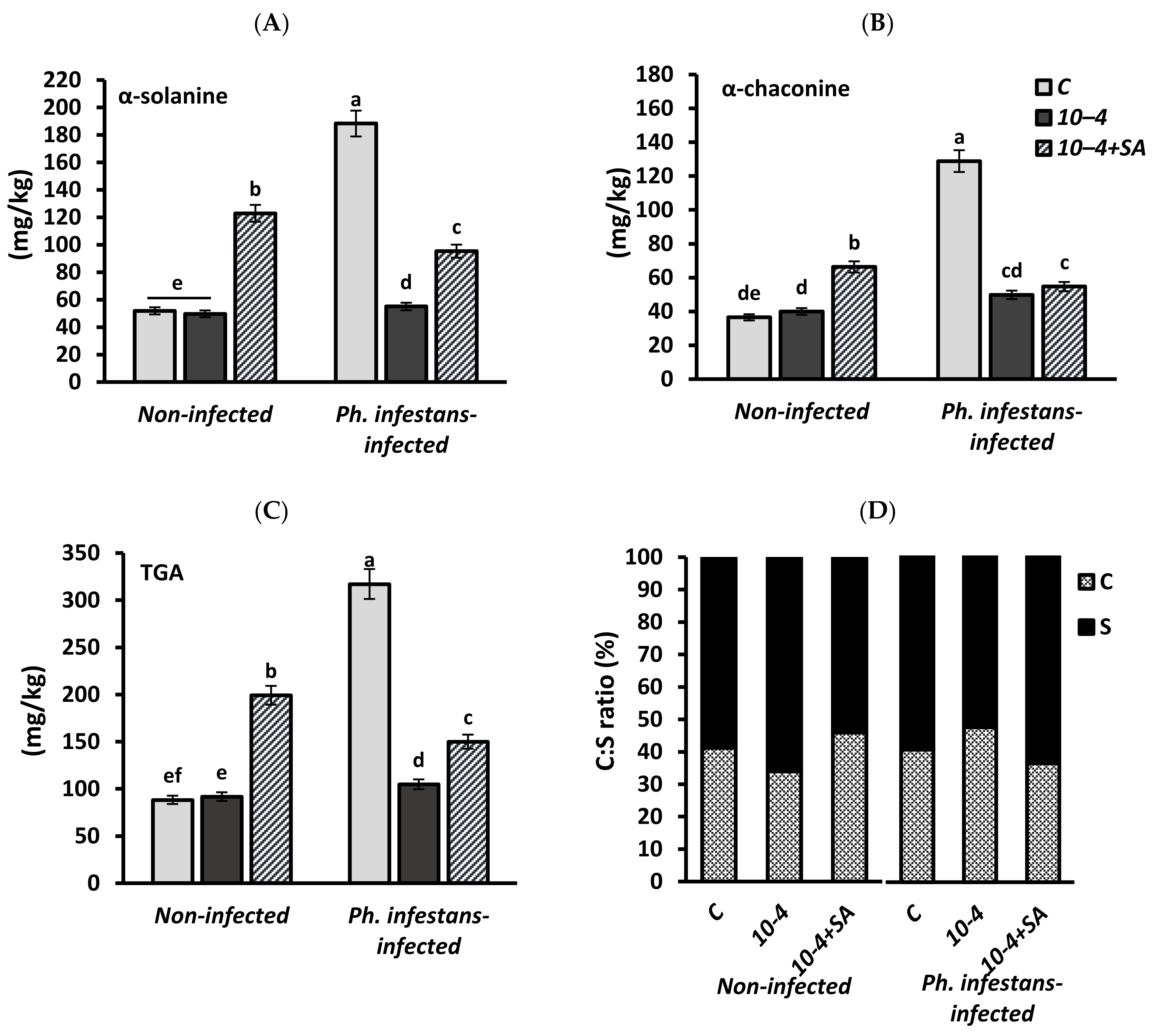
3.5. Glycoalkaloids (GA) α-Solanine and α-Chaconine Contents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT. FAOSTAT Database Collections. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2020. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/ (accessed on 27 October 2021).
- Storey, M. The Harvested Crop. In Potato Biology and Biotechnology: Advances and Perspectives; Vreugdenhil, D., Bradshaw, J., Gebhardt, C., Govers, F., Mackerron, D.K.L., Taylor, M., Ross, H.A., Eds.; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 441–470. [Google Scholar]
- Alamar, M.C.; Tosetti, R.; Landahl, S.; Bermejo, A.; Terry, L.A. Assuring potato tuber quality during storage: A future perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanter, M.; Elkin, C. Potato as a source of nutrition for physical performance. Am. J. Potato Res. 2019, 96, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAOSTAT. Food Losses and Waste. 2015. Available online: http://www.fao.org/food-loss-and-food-waste/en/ (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Fry, W. Phytophthora infestans: The plant (and R gene) destroyer. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2008, 9, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.; Kamoun, S.; Zody, M.; Jiang, R.; Handsaker, R.; Cano, L.M.; Grabherr, M.; Kodira, C.D.; Raffaele, S.; Torto-Alalibo, T.; et al. Genome sequence and analysis of the Irish potato famine pathogen Phytophthora infestans. Nature 2009, 461, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berhan, M. Review on epidemiology, sampling techniques, management strategies of late blight (Phytophthora infestans) of potato and its yield loss. Asian J. Adv. Res. 2021, 7, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Leesutthiphonchai, W.; Vu, A.L.; Ah-Fong, A.M.V.; Judelso, H.S. How does Phytophthora infestans evade control efforts? Modern insight into the late blight disease. Phytopathology 2018, 108, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haverkort, A.J.; Struik, P.C.; Visser, R.G.F.; Jacobsen, E. Applied biotechnology to combat late blight in potato caused by Phytophthora infestans. Potato Res. 2009, 52, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droby, S. Improving Quality and safety of fresh fruit and vegetables after harvest by the use of biocontrol agents and natural materials. Acta Hortic. 2006, 709, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastochkina, O.; Seifikalhor, M.; Aliniaeifard, S.; Baymiev, A.; Pusenkova, L.; Garipova, S.; Kulabuhova, D.; Maksimov, I. Bacillus spp.: Efficient biotic strategy to control postharvest diseases of fruits and vegetables. Plants 2019, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lastochkina, O.; Baymiev, A.; Shayahmetova, A.; Garshina, D.; Koryakov, I.; Shpirnaya, I.; Pusenkova, L.; Mardanshin, I.; Kasnak, C.; Palamutoglu, R. Effects of endophytic Bacillus subtilis and salicylic acid on postharvest diseases (Phytophthora infestans, Fusarium oxysporum) development in stored potato tubers. Plants 2020, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lastochkina, O.; Garshina, D.; Allagulova, C.; Fedorova, K.; Koryakov, I.; Vladimirova, A. Application of endophytic Bacillus subtilis and salicylic acid to improve wheat growth and tolerance under combined drought and Fusarium root rot stresses. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westers, L.; Westers, H.; Quax, W.J. Bacillus subtilis as cell factory for pharmaceutical proteins: A biotechnological approach to optimize the host organism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1694, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweers, J.C.; Barak, I.; Becher, D.; Driessen, A.J.; Hecker, M.; Kontinen, V.P.; Saller, M.J.; Vavrova, L.; van Dijl, J.M. Towards the development of Bacillus subtilis as a cell factory for membrane proteins and protein complexes. Microb. Cell Fact. 2008, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, Y.; Liu, C.; Fang, H.; Zhang, D. Bacillus subtilis: A universal cell factory for industry, agriculture, biomaterials and medicine. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, C.W.; Hinton, D.M. Bacterial endophytes: The endophytic niche, its occupants, and its utility. In Plant-Associated Bacteria; Gnanamanickam, S.S., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 155–194. [Google Scholar]
- Maksimov, I.V.; Pusenkova, L.I.; Abizgildina, R.R. Biopreparation with endophytic bacterium Bacillus subtilis 26D created postharvest protecting effect in potato tubers. Agric. Chem. 2011, 6, 43–48. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pusenkova, L.I.; Garipova, S.R.; Lastochkina, O.V.; Fedorova, K.A.; Mardanshin, I.S. Influence of endophytic bacteria Bacillus subtilis on harvest, quality of tubes and post-harvest diseases of potato. Agrochem. Her. J. 2021, 5, 73–79. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Obagwu, J.; Korsten, L. Integrated Control of citrus green and blue molds using Bacillus subtilis in combination with sodium bicarbonate or hot water. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2003, 28, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.B.; Chadar, H.; Wani, A.H.; Singh, S.; Upadhyay, N. Salicylic acid to decrease plant stress. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, R.; Wang, C.; Smith, D.; Gross, K.; Tian, M. MeSA and MeJA Increase steady-state transcript levels of alternative oxidase and resistance against chilling injury in sweet peppers (Capsicum annuum L.). Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, M.; Aghdam, M.S. Impact of salicylic acid on post-harvest physiology of horticultural crops. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, M.S.; Asghari, M.; Babalar, M.; Sarcheshmeh, M.A.A. Impact of salicylic acid on postharvest physiology of fruits and vegetables. In Eco-Friendly Technology for Postharvest Produce Quality; Academic Press: Bihar, India, 2016; pp. 243–268. [Google Scholar]
- Poveda, J. Use of plant-defense hormones against pathogen-diseases of postharvest fresh produce. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 111, 101521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossortcomission. Available online: http://reestr.gossortrf.ru/sorts/9908411/ (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Lastochkina, O.; Pusenkova, L.; Yuldashev, R.; Babaev, M.; Garipova, S.; Blagova, D.; Khairullin, R.; Aliniaeifard, S. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on some physiological and biochemical parameters of Triticum aestivum L. (wheat) under salinity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 121, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netrusov, A.I.; Egorova, M.A.; Zakharchuk, L.M. A Practical Course in Microbiology; Tsentr “Akademiya”: Moscow, Russia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Toral, L.; Rodríguez, M.; Béjar, V.; Sampedro, I. Antifungal activity of lipopeptides from Bacillus XT1 CECT 8661 against Botrytis cinerea. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsvetkov, V.O.; Shpirnaya, I.A.; Maksutova, V.O. A Method for the Quantitative Determination of Amylolytic Activity of Enzymes by Hydrolysis of a Substrate Immobilized in a Polyacrylamide Gel. Patent RU No. 2708087, 4 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tsvetkov, V.O.; Shpirnaya, I.A.; Maksutova, V.O. A Method for Quantitative Determination of the Proteolytic Activity of Enzymes by Hydrolysis of a Substrate Immobilized in a Polyacrylamide Gel. Patent RU No. 2701734, 1 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tsvetkov, V.O.; Shpirnaya, I.A.; Maksutova, V.O. Computer Software Registration Certificate. Patent RU No. 2018611900, 8 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Erlanger, B.F.; Kokowski, N.; Cohen, W. The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrutes of trypsin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1961, 95, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gofman, I.U.; Vaisblai, I.M. Determination of trypsin inhibitor in pea seeds. Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol. 1975, 5, 777–783. [Google Scholar]
- Health, R.L.; Packer, L. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1968, 125, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, l.S.; Waldern, R.P.; Teare, D. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil. 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthan, T.; Bergthaller, W.; Driedger, D.; Yeung, J.; Sporus, P. Starch from Alberta potatoes: Wet isolation and some physicochemical proprieties. Food Res. Int. 1999, 32, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmann, N.; Goian, M.; Ianculov, I.; Dumbravă, D.; Moldovan, C. Method to starch content determination from plants by specific weight. Sci. Pap. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 41, 814–818. [Google Scholar]
- GOST 24556-89. Methods for determination of vitamin C. In Products of Fruits and Vegetables Processing; Izdatelstvo Standartov: Moscow, Russia, 2003; Available online: http://docs.cntd.ru/document/gost-24556-89 (accessed on 18 January 2020).
- Knuthsen, P.; Jensen, U.; Schmidt, B.; Larsen, I.K. Glycoalkaloids in potatoes: Content of glycoalkaloids in potatoes for consumption. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2009, 22, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyousfi, N.; Lahlali, R.; Letrib, C.; Belabess, Z.; Ouaabou, R.; Ennahli, S.; Blenzar, A.; Barka, E.A. Improving the biocontrol potential of bacterial antagonists with salicylic acid against brown rot disease and impact on nectarine fruits quality. Agronomy 2021, 11, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.-M.; Zhu, S.; Kachroo, P.; Kachroo, A. Signal regulators of systemic acquired resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sorokan, A.; Burkhanova, G.; Alekseev, V.; Maksimov, I. The influence of co-treatment with Bacillus thuringiensis B-5351 and salicylic acid on the resistance of potato plants to Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary. Bull. Tomsk. State Univ. Biol. 2021, 53, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawoy, H.; Debois, D.; Franzil, L.; De Pauw, E.; Thonart, P.; Ongena, M. Lipopeptides as main ingredients for inhibition of fungal phytopathogens by Bacillus subtilis/amyloliquefaciens. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015, 8, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baindara, P.; Korpole, S. Lipopeptides: Status and strategies to control fungal infection. In Recent Trends in Antifungal Agents and Antifungal Therapy; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 97–121. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Ru, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y. Fengycin produced by Bacillus subtilis 9407 plays a major role in the biocontrol of apple ring rot disease. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 199, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janisiewicz, W.J.; Tworkoski, T.J.; Sharer, C. Characterizing the mechanism of biological control of postharvest diseases on fruit with a simple method to study competition for nutrients. Phytopathology 2000, 90, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.M.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.B.; Liu, S.X. A preliminary study on the biological control of postharvest diseases of Litchi fruit. J. Fruit Sci. 2001, 14, 185–186. [Google Scholar]
- Demoz, B.T.; Korsten, L. Bacillus subtilis attachment, colonization, and survival on avocado flowers and its mode of action on stem-end rot pathogens. Biol. Control 2006, 37, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastochkina, O.; Garshina, D.; Ibragimov, A. Enhanced performance of endophytic Bacillus subtilis in conjunction with salicylic acid meliorated simultaneous drought and Fusarium root rot stresses in Triticum aestivum L. Biol. Life Sci. Forum. 2021, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktuganov, G.E.; Galimzyanova, N.F.; Melent’ev, A.I.; Kuzmina, L.Y. Extracellular hydrolases of strain Bacillus sp. 739 and their involvement in the lysis of micromycete cell walls. Microbiology 2007, 76, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtseva, N.N.; Sof’in, A.V.; Revina, T.A.; Gvozdeva, E.L.; Ievleva, E.V.; Valueva, T.A. Secretion of proteolytic enzymes by three phytopathogenic microorganisms. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2013, 49, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, Z.; Takase, K.; Doui, N.; Momma, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Mizuno, H. Crystal structure of a catalytic-site mutant α-amylase from Bacillus subtilis complexed with maltopentaose. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 277, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machius, M.; Declerck, N.; Huber, R.; Wiegand, G. Activation of Bacillus licheniformis α-amylase through a disorder → order transition of the substrate-binding site mediated by a calcium–sodium–calcium metal triad. Structure 1998, 6, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dauter, Z.; Dauter, M.; Brzozowski, A.M.; Christensen, S.; Borchert, T.V.; Beier, L.; Wilson, K.S.; Davies, G.J. Can anomalous signal of sulfur become a tool for solving protein crystal structures? J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 38, 8385. [Google Scholar]
- Alikhajeh, J.; Khajeh, K.; Ranjbar, B.; Naderi-Manesh, H.; Lin, Y.H.; Liu, E.; Guan, H.H.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Chuankhayan, P.; Huang, Y.C.; et al. Structure of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens [alpha]-amylase at high resolution: Implications for thermal stability. Acta Cryst. 2010, 66, 121. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Song, L.; Shu, C.; Wang, P.; Deng, C.; Peng, Q.; Lereclus, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, D.; Zhang, J.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki strain HD73. Genome Announc. 2013, 1, e00080-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, S.L.; Daligault, H.E.; Davenport, K.W.; Jaissle, J.; Frey, K.G.; Ladner, J.T.; Broomall, S.M.; Bishop-Lilly, K.A.; Bruce, D.C.; Gibbons, H.S.; et al. Complete genome sequences for 59 Burkholderia isolates, both pathogenic and near neighbor. Genome Announc. 2013, 3, e00159-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldrian, P.; Voriskova, J.; Dobiasova, P.; Merhautova, V.; Lisa, L.; Valaskova, V. Production of extracellular enzymes and degradation of biopolymers by saprotrophic microfungi from the upper layers of forest soil. Plant Sci. 2011, 338, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gappa-Adachi, R.; Yano, K.; Takeuchi, S.; Morita, Y.; Uematsu, S. Phytophthora blight of southern star (Oxypetalum caeruleum) caused by Phytophthora palmivora in Japan. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2012, 78, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wu, G. Secretory pathway of cellulase: A mini-review. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, S.M.; van Dyk, J.S.; Pletschke, B.I. Bacillus subtilis SJ01 produces hemicellulose degrading multi-enzyme complexes. Bioresources 2012, 7, 1294–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Shevchenko, N.D.; Shpirnaya, I.A.; Salyakhova, A.F.; Tsvetkov, V.O.; Mardanshin, I.S.; Ibragimov, R.I. Activity of cellulase and pectinase inhibitors in potato tubers and leaves. Bull. Orenbg. State Univ. 2009, 6, 431–433. [Google Scholar]
- Stamogiannou, I.; Van Camp, J.; Smagghe, G.; Van de Walle, D.; Dewettinck, K.; Raes, K. Impact of phenolic compound as activators or inhibitors on the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ximenes, E.; Kim, Y.; Mosier, N.; Dien, B.; Ladisch, M. Inhibition of cellulases by phenols. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2010, 46, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Mosier, N.S.; Ladisch, M.R. Enzymatic digestion of liquid hot water pretreated hybrid poplar. Biotechnol. Prog. 2009, 25, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarullina, L.G.; Akhatovaa, A.R.; Kasimova, R.I. Hydrolytic enzymes and their proteinaceous inhibitors in regulation of plant–pathogen interactions. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 63, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusenkova, L.I.; Il’yasova, E.Y.; Lastochkina, O.V.; Maksimov, I.V.; Leonova, S.A. Changes in the species composition of the rhizosphere and phyllosphere of sugar beet under the impact of biological preparations based on endophytic bacteria and their metabolites. Eurasian Soil. Sci. 2016, 49, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, B.C.; Waxman, K.D.; Nenni, N.V.; Walker, L.P.; Bergstrom, G.C.; Gibson, D.M. Arsenal of plant cell wall degrading enzymes reflects host preference among plant pathogenic fungi. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2011, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paris, R.; Lamattina, L. Phytophthora infestans secretes extracellular proteases with necrosis inducing activity on potato. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 1999, 105, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarullina, L.G.; Sorokan, A.V.; Tsvetkov, V.O.; Burkhanova, G.F.; Kalatskaja, J.N. Influence of the genus Bacillus bacteria on the content of H2O2 and the activity of hydrolases and their inhibitors in potato plants during Phytophthora infestans Mont. de Bary infection. BIO Web Conf. 2020, 23, 02010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Meng, Y.; Shan, W. Two Phytophthora parasitica cysteine protease genes, PpCys44 and PpCys45, trigger cell death in various Nicotiana spp. and act as virulence factors. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 21, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Revina, T.A.; Parfenov, I.A.; Gvozdeva, E.L.; Gerasimova, N.G.; Valueva, T.A. Chymotrypsin and trypsin inhibitor isolated from potato tubers. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2011, 47, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Jha, A.B.; Dubey, R.S.; Pessarakli, M. Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolupaev, Y.E.; Yastreb, T.O. Physiological functions of nonenzymatic antioxidants of plants. Proc. KhNU 2015, 2, 6–25. [Google Scholar]
- Szabados, L.; Savouré, A. Proline: A multifunctional amino acid. Trend Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Potato glycoalkaloids and metabolites: Roles in the plant and in the diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8655–8681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluwaduge, D.I. Glycoalkaloids, bitter tasting toxicants in potatoes: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 3, 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, M.A.B.; Brunton, N. Food Glycoalkaloids: Distribution, Structure, Cytotoxicity, Extraction, and Biological Activity. In Alkaloids: Their Importance in Nature and Human Life; Kurek, J., Ed.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasnak, C.; Artik, N. Change in some glycoalkaloids of potato under different storage regimes. Potato Res. 2018, 61, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugała, M.; Zarzecka, K.; Dołęga, H.; Niewęgłowski, M.; Sikorska, A. The effect of biostimulants and herbicides on glycoalkaloid accumulation in potato. Plant Soil. Environ. 2016, 62, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, E.H.; Kuc, J. α-Solanine and α-chaconine as fungitoxic compounds in extracts of Irish potato tubers. Phytopathology 1968, 58, 776–781. [Google Scholar]
- Tingey, W.M. Glykoalkaloids as pest resistance factors. Potato J. 1984, 61, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Chandra, G. A brief review of potash management in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). J. Pharmac. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 1718–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, H.; Liu, Q.; He, S. The plasma membrane-localized sucrose transporter IbSWEET10 contributes to the resistance of sweet potato to Fusarium oxysporum. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Primarini, D.; Ohta, Y. Some enzyme properties of raw starch digesting amylases from Streptomyces sp. No. 4. Starch-Stärke 2000, 52, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Naumann, M.; Pawelzik, E. Cracking and fracture properties of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tubers and their relation to dry matter, starch, and mineral distribution. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 3149–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chebotar, V.K.; Kiprushkina, E.I. Application of microbial preparations in potato storage technologies. Dostiz. Nauk. Tekhniki APK 2015, 29, 33–35. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]

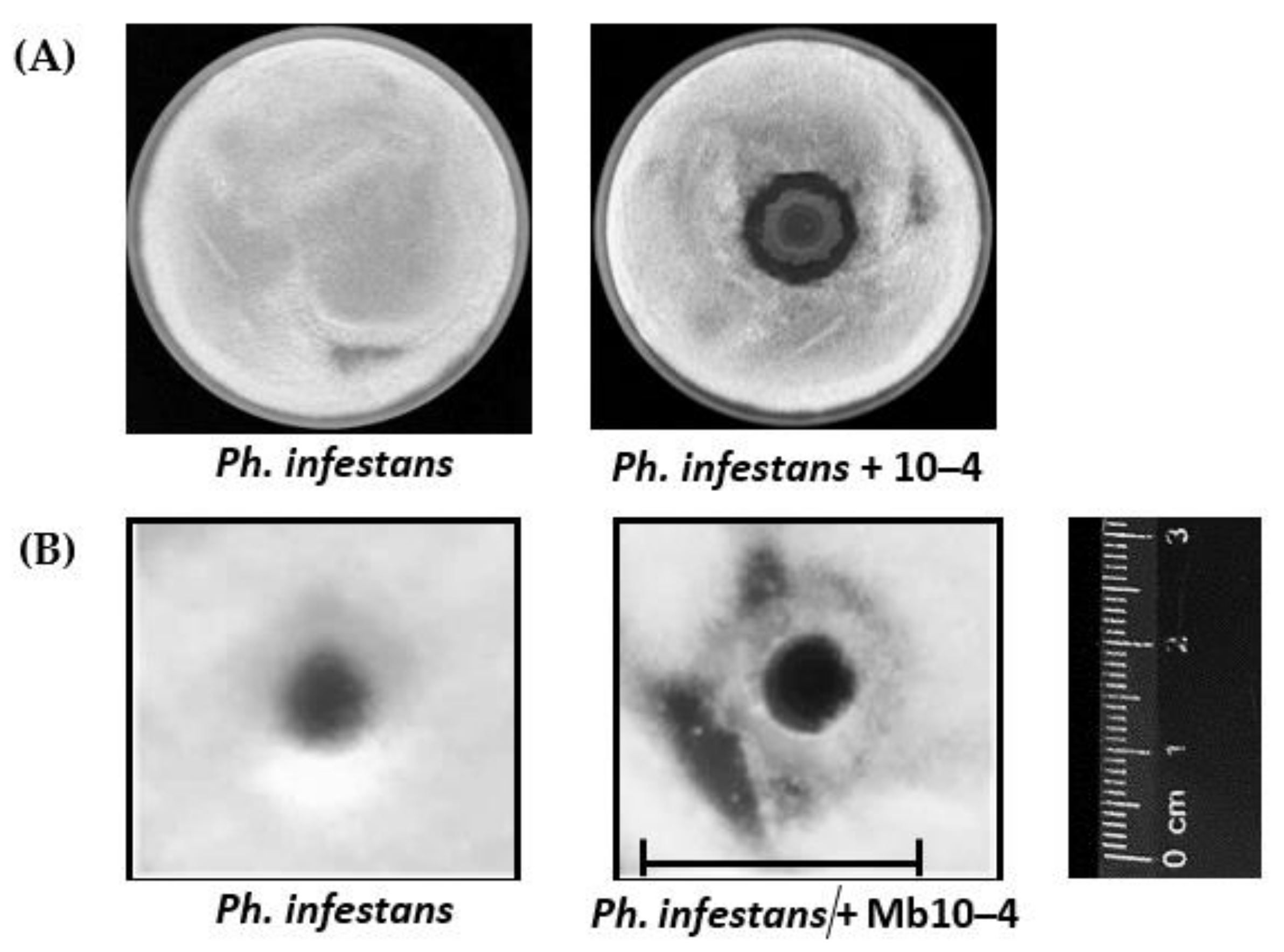

| 10–4 (CFU mL−1) | 0 | 103 | 104 | 105 | 106 | 107 | 108 |
| Pathogen growth inhibition zone (mm) * | 0 | 12.1 | 13.3 | 14.9 | 16.4 | 18.9 | 20.3 |
| 10–4 (CFU mL−1) + SA (0.05 mM) | 0 | 103 | 104 | 105 | 106 | 107 | 108 |
| Pathogen growth inhibition zone (mm) | 0 | 13.5 | 15.1 | 16.3 | 18.0 | 20.3 | 21.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lastochkina, O.; Pusenkova, L.; Garshina, D.; Kasnak, C.; Palamutoglu, R.; Shpirnaya, I.; Mardanshin, I.; Maksimov, I. Improving the Biocontrol Potential of Endophytic Bacteria Bacillus subtilis with Salicylic Acid against Phytophthora infestans-Caused Postharvest Potato Tuber Late Blight and Impact on Stored Tubers Quality. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020117
Lastochkina O, Pusenkova L, Garshina D, Kasnak C, Palamutoglu R, Shpirnaya I, Mardanshin I, Maksimov I. Improving the Biocontrol Potential of Endophytic Bacteria Bacillus subtilis with Salicylic Acid against Phytophthora infestans-Caused Postharvest Potato Tuber Late Blight and Impact on Stored Tubers Quality. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(2):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020117
Chicago/Turabian StyleLastochkina, Oksana, Liudmila Pusenkova, Darya Garshina, Cemal Kasnak, Recep Palamutoglu, Irina Shpirnaya, Il’dar Mardanshin, and Igor Maksimov. 2022. "Improving the Biocontrol Potential of Endophytic Bacteria Bacillus subtilis with Salicylic Acid against Phytophthora infestans-Caused Postharvest Potato Tuber Late Blight and Impact on Stored Tubers Quality" Horticulturae 8, no. 2: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020117
APA StyleLastochkina, O., Pusenkova, L., Garshina, D., Kasnak, C., Palamutoglu, R., Shpirnaya, I., Mardanshin, I., & Maksimov, I. (2022). Improving the Biocontrol Potential of Endophytic Bacteria Bacillus subtilis with Salicylic Acid against Phytophthora infestans-Caused Postharvest Potato Tuber Late Blight and Impact on Stored Tubers Quality. Horticulturae, 8(2), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020117








