Assessment of the Breeding Potential of a Set of Genotypes Selected from a Natural Population of Akebia trifoliata (Three–Leaf Akebia)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Culture Conditions
2.2. Phenotypic Evaluation
2.3. Analysis of Nutritional Components
2.3.1. TF Content
2.3.2. TFAA Content
2.4. Evaluation of SSR Markers
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Diversity of Phenotypic Traits
3.2. Diversity of Nutritional Components
3.3. Relationships among Morphological and Nutritional Traits
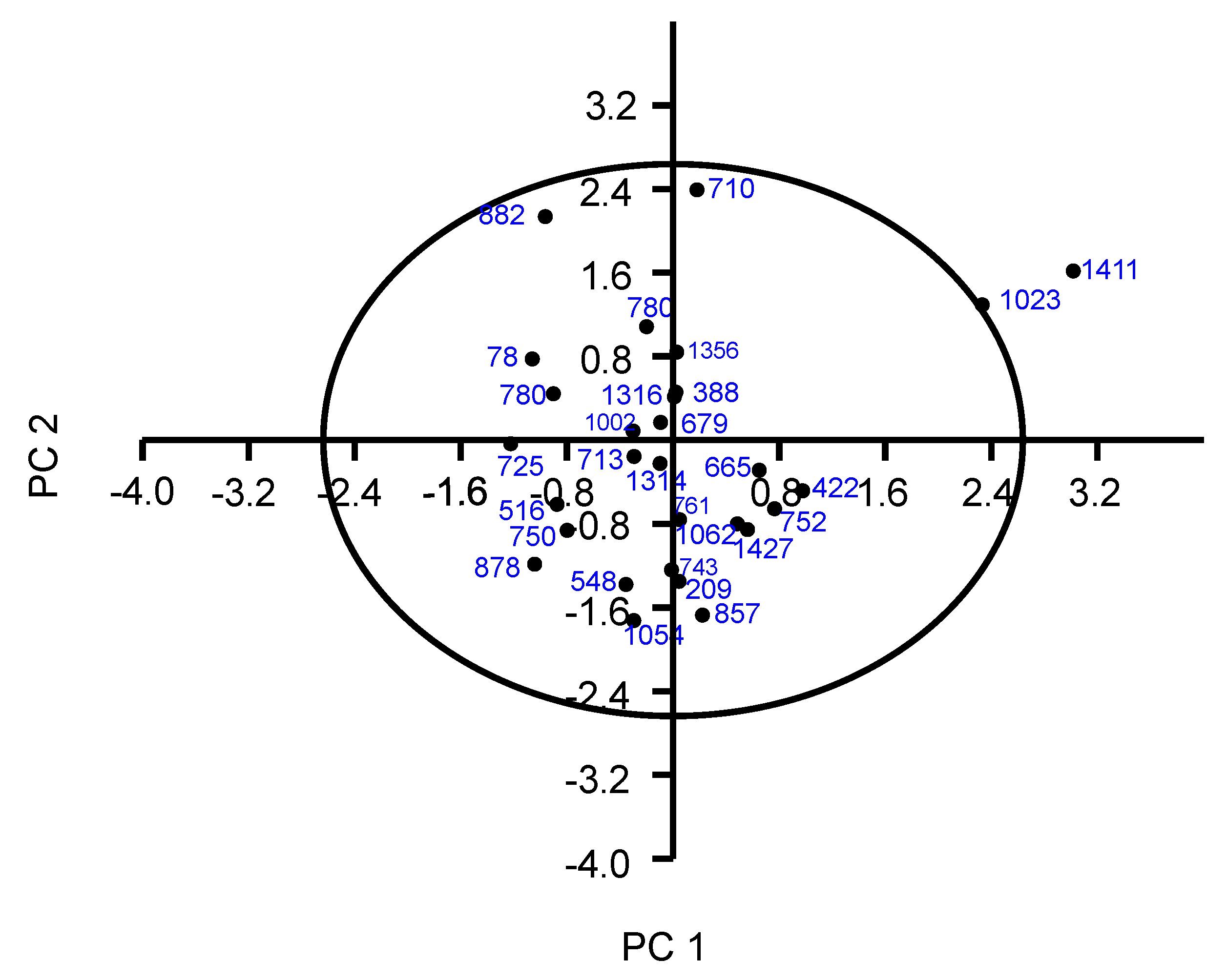
3.4. Principal Component Analysis
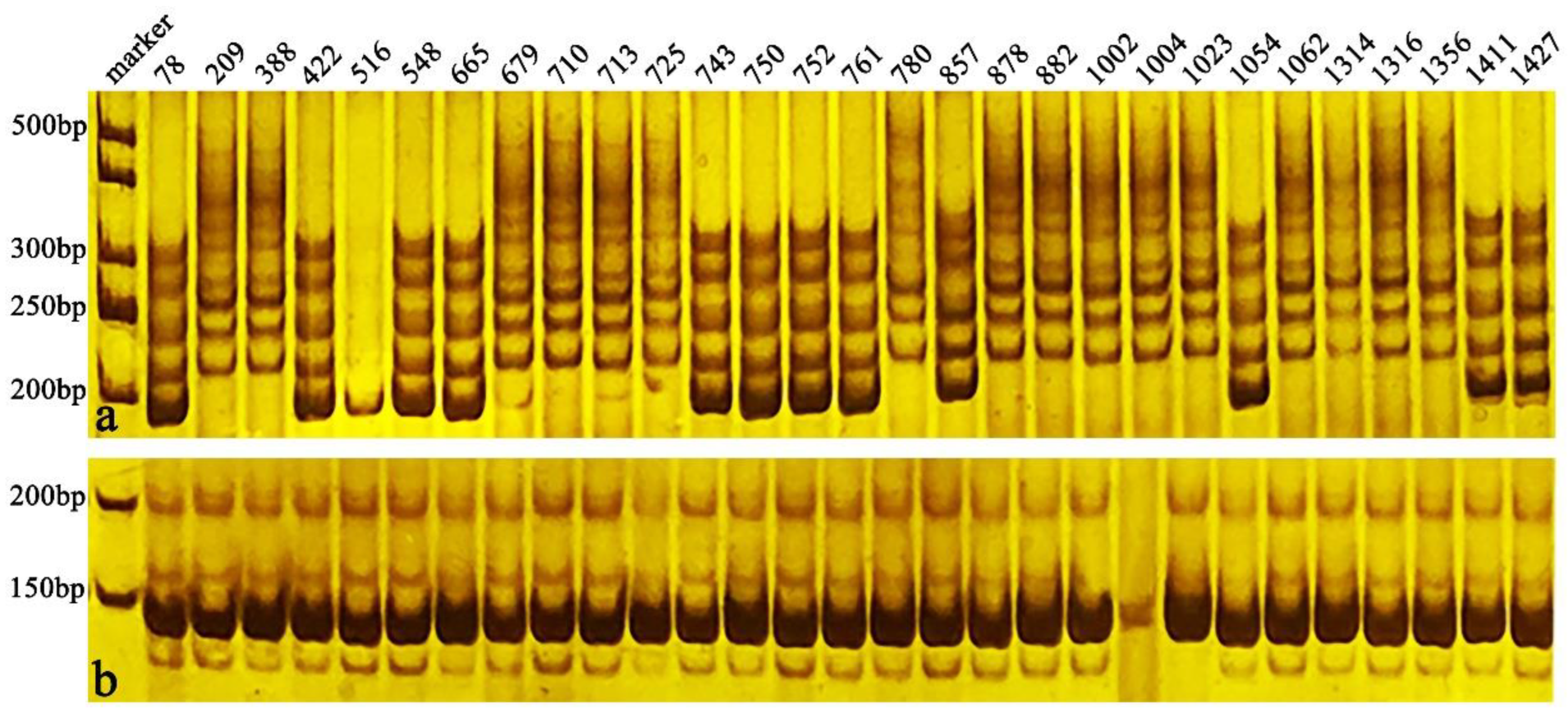
3.5. SSR Analysis
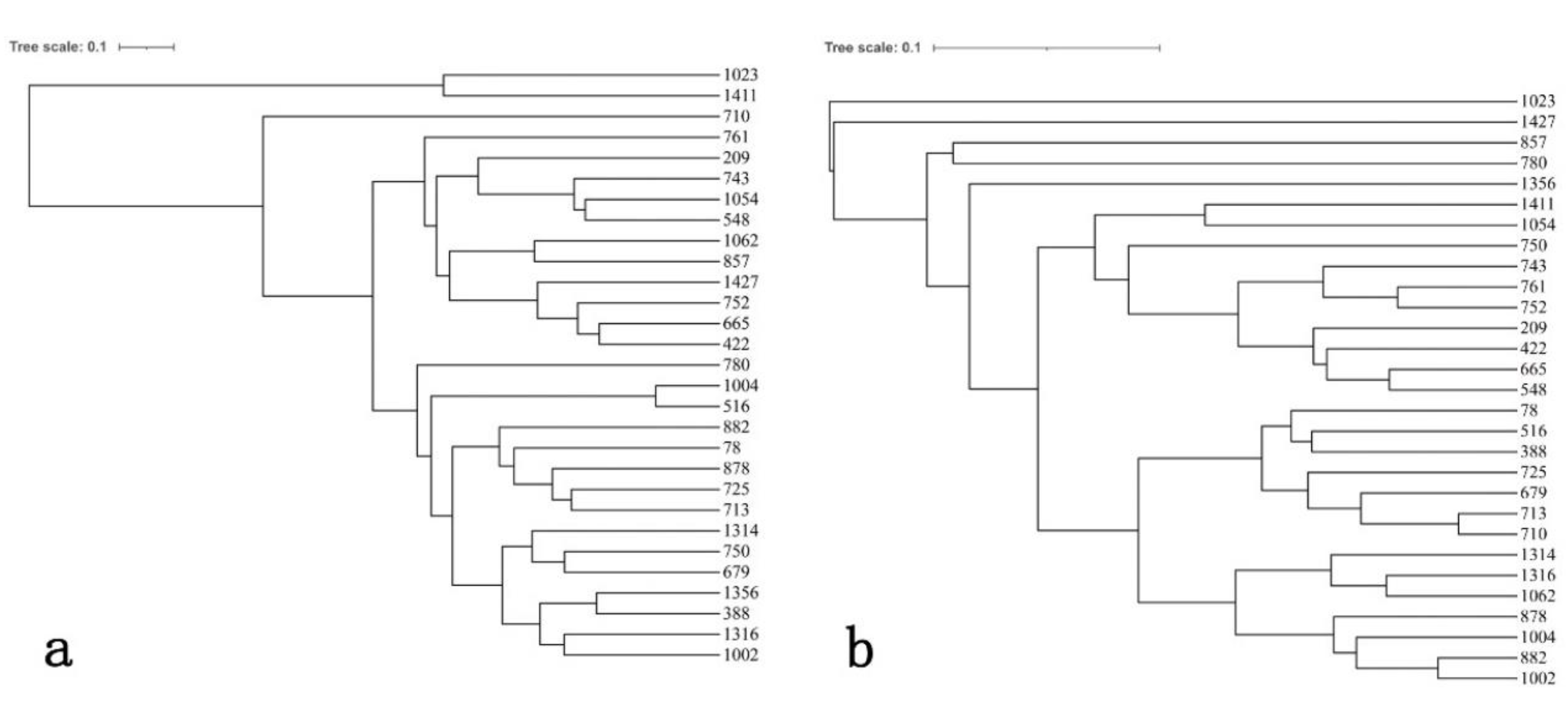
3.6. Cluster Analysis Based on Phenotypic Traits and SSR Data
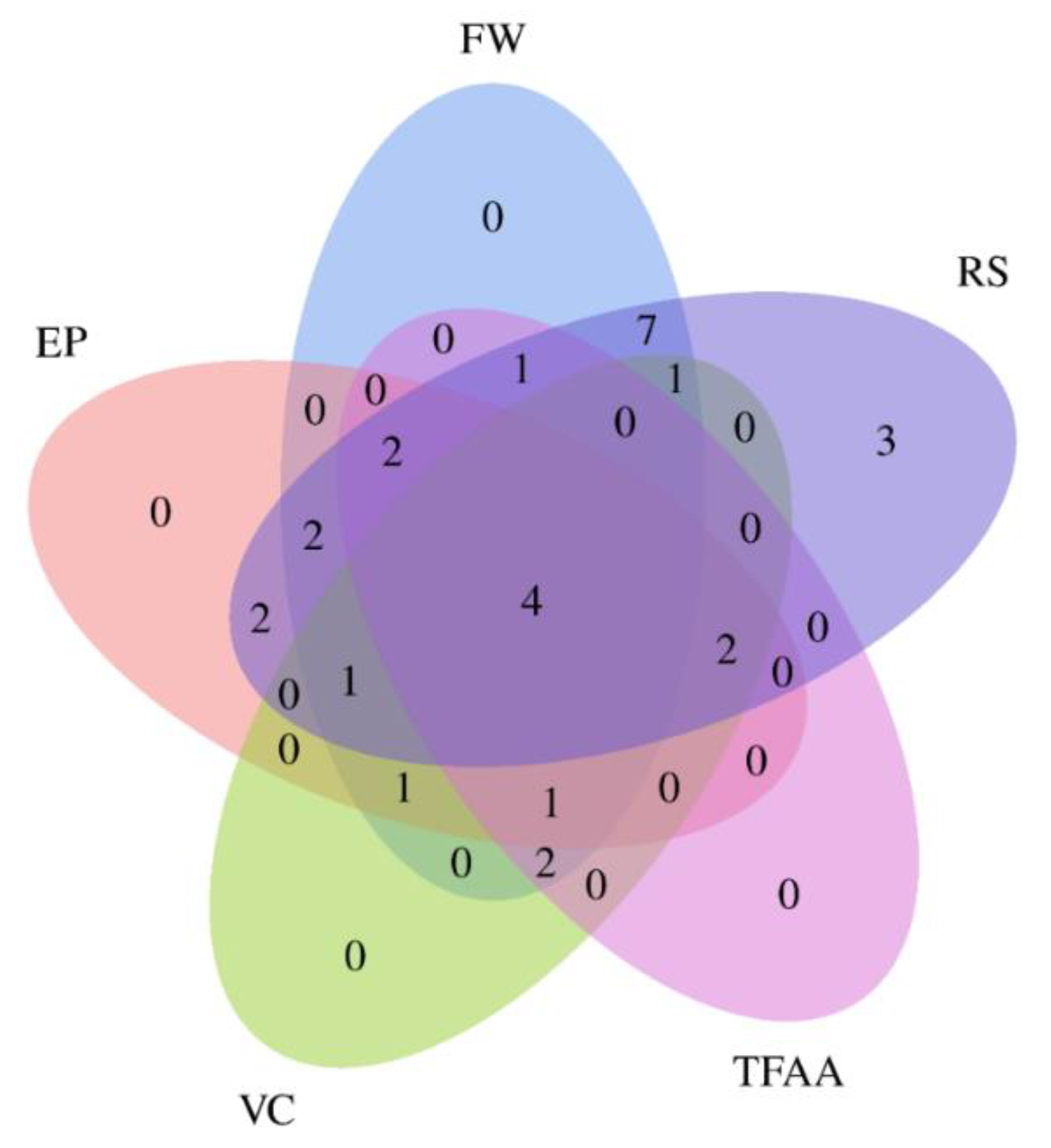
3.7. Identification of Promising Genotypes
4. Discussion
4.1. Importance of Genetic Diversity in A. trifoliata Breeding
4.2. Genetic Improvement of A. trifoliata
4.3. Progressive Improvement of A. trifoliata as a New Commercial Fruit through Successive Selection
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kong, X.X. Delectis Florae Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae Agendae Academiae Sinicae Edita. Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae. Tomus 29; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, R.; Kawasaki, T. Pericarp saponins of Akebia quinata Decne. II. Arjunolic and norarjunolic acids, and their glycosides. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1976, 24, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, R.; Kawasaki, T. Pericarp saponins of Akebia quinata Decne. I. Glycosides of hederagenin and oleanolic acid. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1976, 24, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, J.G.; Li, J.R. Study on the biological characteristics and nutritional components of the fruit of Akebia trifoliata. Guihaia 1991, 11, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hua, X.; Shi, S.; Hu, J.; Peng, H.; Qiang, Z.; Sun, W. Physicochemical and functional properties of the protein isolate and major fractions prepared from Akebia trifoliata var. Australia seed. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Z.; Chen, X. Application of vertical greening as a new model of expanding urban green spaces. J. Landsc. Res. 2013, 3, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. The Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Pepublic of China; China Medicine Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. The Japanese Herbal Pharmacopoeia; Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare: Tokyo, Japan, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Food and Drug Administration. The Korean Herbal Pharmacopoeia; Korea Food and Drug Administration: Seoul, Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.K. Fatty acids analysis in decaisnea insignis and Akebia trifoliata seed oil by GC-MS. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2007, 5, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.Q.; Zhu, X.M.; Xiong, H.; Bai, C.Q. Optimized refining and fatty acid composition of Akebia trifoliata var. australis seed oil. Food Sci. 2013, 34, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B. Cultivation and application of Akebia trifoliata. China Flowers Hortic. 2016, 4, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Yao, X.; Zhong, C.; Chen, X.; Huang, H. Akebia: A potential new fruit crop in China. HortScience 2010, 45, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ren, H.; Xu, Q.L.; Zhong, Y.Z.; Wu, P.; Wei, X.Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, X. Antibacterial oleanane-type triterpenoids from pericarps of Akebia trifoliata. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.H.; Bu, F.W.; Wang, Z.Y. Fruit development and character performance of the offspring of Akebia trifoliata. Hunan Agric. Sci. 2006, 1, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, D.S.; Mu, Z.P.; Cao, Y. Development and utilization of Akebia trifoliata resources. Hunan For. Sci. Technol. 1993, 20, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Xiong, D.S.; Zhu, J.T. Study on respiratory physiology and fresh-keeping conditions of Akebia trifoliata. J. Fruit Sci. 2003, 20, 512–514. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, S.; Yao, X.; Zhong, C.; Zhao, T.; Huang, H. Genetic analysis of fruit traits and selection of superior clonal lines in Akebia trifoliata (Lardizabalaceae). Euphytica 2018, 214, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Yao, X.; Zhong, C.; Zhao, T.; Huang, H. Effectiveness of recurrent selection in Akebia trifoliata (Lardizabalaceae) breeding. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 246, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liang, J.; Tan, Q.; Ou, L.; Song, S. Insights into triterpene synthesis and unsaturated fatty-acid accumulation provided by chromosomal-level genome analysis of Akebia trifoliata subsp. australis. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, B.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z. Genome survey sequencing and genetic diversity of cultivated Akebia trifoliata assessed via phenotypes and SSR markers. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.; Huang, S. First report of nigrospora sphaerica causing fruit dried-shrink disease in Akebia trifoliata from China. Plant Dis. 2021, 32, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Ke, J.; Tan, L.T.; Medison, R.G.; Sun, Z. First report of leaf spot on Akebia trifoliata caused by phytophthora nicotianae in China. Plant Dis. 2020, 105, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Deng, L.; Feng, D.; Zhong, C.; Li, L. First report of anthracnose caused by colletotrichum gloeosporioides on Akebia trifoliata in China. Plant Dis. 2020, 105, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.J.; Zhong, S.F.; Yang, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, W.; Yang, H.; Guan, J.; Fu, P.; Tan, F.Q.; Ren, T.H.; et al. Identification and characterization of NBS resistance genes in Akebia trifoliate. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nambi, V.E.; Thangavel, K.; Rajeswari, K.A.; Manickavasagan, A.; Geetha, V. Texture and rheological changes of Indian mango cultivars during ripening. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 117, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Zhao, S.C.; Ma, J.X.; Dong, L.; Qiu, L.J. Molecular footprints of domestication and improvement in soybean revealed by whole genome re-sequencing. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanagh, C.R.; Chao, S.; Wang, S.; Huang, B.E.; Stephen, S.; Kiani, S.; Forrest, K.; Saintenac, C.; Brownguedira, G.L.; Akhunova, A. Genome-wide comparative diversity uncovers multiple targets of selection for improvement in hexaploid wheat landraces and cultivars. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8057–8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gepts, P. The contribution of genetic and genomic approaches to plant domestication studies. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 18, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, J. Development of SSR markers via de novo transcriptome assembly in Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz. Genome 2019, 62, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, W.; Fu, P.; Zhong, S.F.; Guan, J.; Luo, P.G. Developmental Stages of Akebia trifoliata fruit based on volume. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2021, 39, 822–830. [Google Scholar]
- Farahani, M.; Salehi-Arjmand, H.; Khadivi, A.; Akramian, M. Phenotypic diversity among Morus alba var. nigra genotypes as revealed by multivariate analysis. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 248, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal, N.M.; Bustamante, C.A.; Civello, P.M.; Martínez, G. Effect of ethylene and 1-MCP treatments on strawberry fruit ripening. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, R. Food Analysis: Analytical and Quality Control Methods for the Food Manufacturer and Buyer; Leonard Hill Books: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Oyeleke, O.A. Outlines of Food Analysis; Department of Biochemistry, University of Ilorin: Ilorin, Nigeria, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Liu, T.; Luo, P.G. Resistance performance of wheat stripe rust resistance gene Yr41 and its effect on yield parameters in F2 populations under field conditions. Crop Prot. 2020, 134, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, T.G.; Chen, W.Q.; Zhong, S.F.; Zhang, H.Y. Wheat WCBP1 encodes a putative copper-binding protein involved in stripe rust resistance and inhibition of leaf senescence. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xiang, Z.P.; Chen, W.Q.; Huang, Q.L.; Liu, T.G.; Li, Q.; Zhong, S.F.; Zhang, M.; Guo, J.W.; Lei, L. Reevaluation of two quantitative trait loci for type II resistance to fusarium head Blight in wheat germplasm PI 672538. Phytopathology 2017, 107, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norusis, M.J. Spss 11.0 guide to data analysis. Compr. Psychiatry 2000, 49, 397–400. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Y.; Harper, D. Past: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Electronica 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GENALEX 6: Genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2010, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, F.; Boyle, T.; Yeh, F.C.; Boyle, T.J.B. Population genetic analysis of co-dominant and dominant markers and quantitative traits. Belg. J. Bot. 1996, 129, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Sichuan Agriculture University. A. trifoliata Genome Assembly Sequence and RNA-seq Data, NCBI. 2021. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/671772 (accessed on 11 June 2021).
- Costa, J.L.; Jesus, O.; Oliveira, G.A.F.; Oliveira, E. Effect of selection on genetic variability in yellow passion fruit. Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2012, 12, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubaya, A.; Salah, M.B.; Marzougui, N.; Ferchichi, A. Pomological characterization of the mulberry tree (Morus spp.) in the south of Tunisia. J. Arid. Land Stud. 2009, 19, 157–159. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, H.; Akagi, T.; Tao, R. Quantitative characterization of fruit shape and its differentiation pattern in diverse persimmon (Diospyros kaki) cultivars. Sci. Hort 2018, 228, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badenes, M.L.; Byrne, D.H. Fruit Breeding; Springer: Now York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Khadivi-Khub, A.; Anjam, K. Morphological characterization of Prunus scoparia using multivariate analysis. Plant Syst. Evol. 2014, 300, 1361–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witcombe, J.R.; Joshi, A.; Joshi, K.D.; Sthapit, B.R. Farmer participatory crop improvement-varietal selection and breeding methods and their impact on biodiversity. Exp. Agric. 1996, 32, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purugganan, M.D.; Fuller, D.Q. The nature of selection during plant domestication. Nature 2009, 457, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.G.; Hu, X.Y.; Ren, Z.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Shu, K.; Yang, Z.J. Allelic analysis of stripe rust resistance genes on wheat chromosome 2BS. Genome 2008, 51, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.G.; Luo, H.Y.; Chang, Z.J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, M.; Ren, Z.L. Characterization and chromosomal location of Pm40 in common wheat: A new gene for resistance to powdery mildew derived from elytrigia intermedium. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Frégeau-Reid, J. Breeding line selection based on multiple traits. Cropence 2008, 48, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, C.; Baloch, F.S.; Ozkan, H. Genetic analysis of some physical properties of bread wheat grain (Triticum aestivum L. em Thell). Turk. J. Agric. 2009, 33, 525–535. [Google Scholar]
- Matteo, A.D.; Russo, R.; Graziani, G.; Ritieni, A.; Vaio, C.D. Characterization of autochthonous sweet cherry cultivars (Prunus avium L.) of southern Italy for fruit quality, bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2782–2794. [Google Scholar]
- Mccouch, S. Diversifying selection in plant breeding. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, F.D.; Brandon, S.G.; Bruce, D.S. The molecular genetics of crop domestication. Cell 2006, 127, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.B. Understanding crop genetic diversity under modern plant breeding. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimalasiri, P.; Wills, R.B.H. Simultaneous analysis of ascorbic acid and dehydroascorbic acid in fruit and vegetables by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1983, 256, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smanalieva, J.; Iskakova, J.; Oskonbaeva, Z.; Wichern, F.; Darr, D. Determination of physicochemical parameters, phenolic content, and antioxidant capacity of wild cherry plum (Prunus divaricata ledeb) from the walnut-fruit forests of kyrgyzstan. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 2293–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhore, N.S.; Surwade, S.A.; Swami, S.B.; Hakor, N.J. Studies on physico-chemical properties of pineapple fruit and development of pineapple peeler. Agric. Eng. Today 2017, 3, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hajare, S.N.; Saxena, S.; Kumar, S.; Wadhawan, S.; Mishra, B.B.; Parte, M.N.; Gautam, S.; Sharma, A. Quality profile of litchi (Litchi chinensis) cultivars from India and effect of radiation processing. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2010, 9, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galili, G.; Amir, R.; Fernie, A.R. The regulation of essential amino acid synthesis and accumulation in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
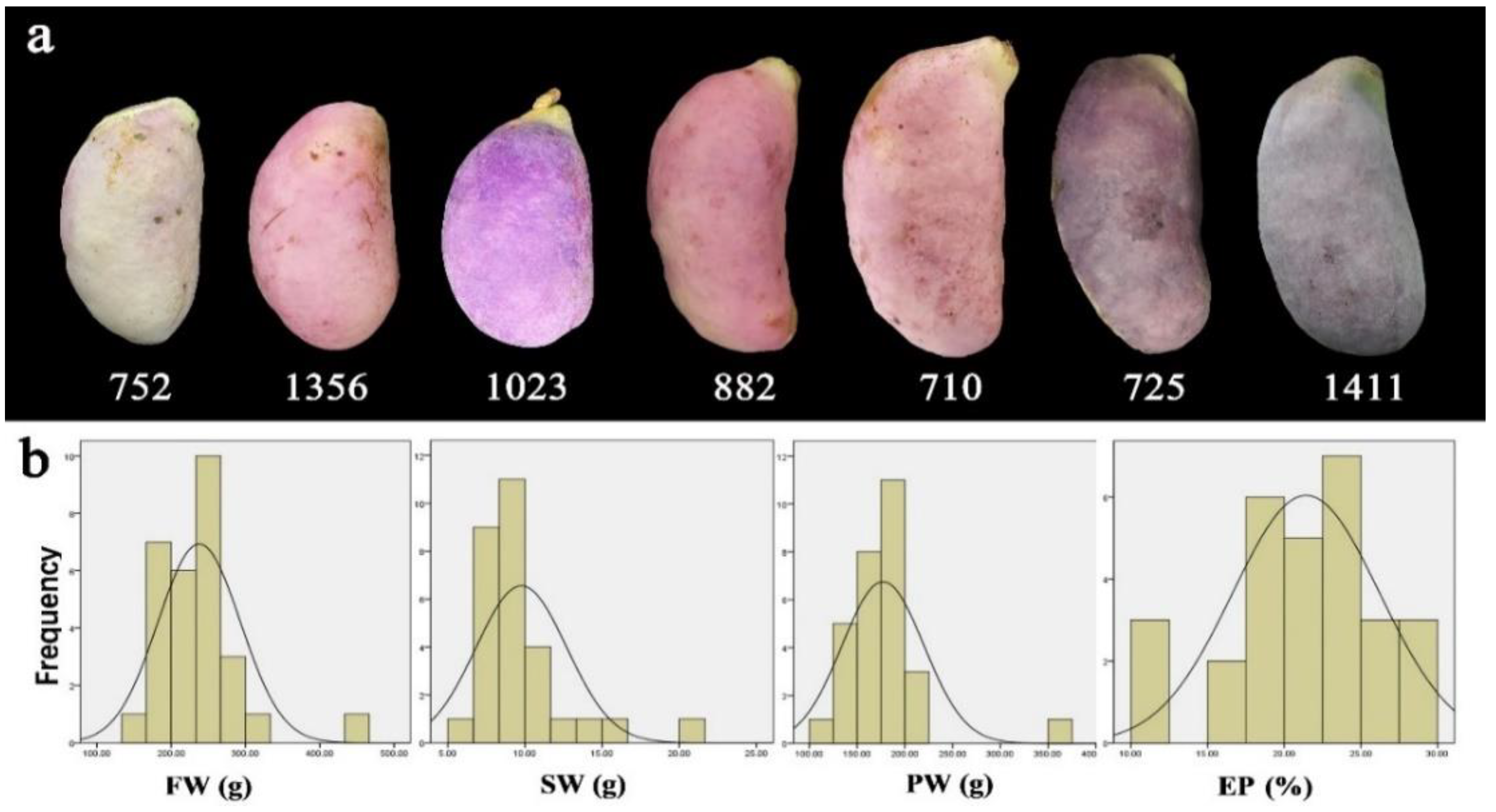
| No. | Trait | Abbreviation | Type a | Unit | Min | Max | Mean | SD | CV (%) | I |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fruit color | FC | M | Code | 1 | 9 | 3.76 | 1.74 | 46.3 | 1.82 |
| 2 | Fruit shape | FS | M | Code | 1 | 7 | 2.06 | 4.79 | 43.0 | 1.78 |
| 3 | Growth period | GP | M | Day | 150 | 180 | 167.1 | 6.84 | 4.10 | 2.72 |
| 4 | Fruit weight | FW | M | g | 135.2 | 446.9 | 237.7 | 54.7 | 23.0 | 2.54 |
| 5 | Peel weight | PW | M | g | 100.5 | 354.4 | 177.1 | 42.1 | 23.8 | 2.43 |
| 6 | Seed weight | SW | M | g | 6.15 | 20.2 | 9.8 | 2.89 | 29.6 | 2.65 |
| 7 | Pericarp thickness | PT | M | cm | 0.69 | 1.31 | 1.09 | 0.13 | 12.4 | 2.81 |
| 8 | Longitudinal diameter | LD | M | cm | 10.1 | 16.3 | 12.9 | 1.21 | 9.39 | 2.68 |
| 9 | Transverse diameter | TD | M | cm | 5.35 | 7.57 | 6.15 | 0.52 | 8.43 | 2.68 |
| 10 | Proportion of seeds | PoS | M | % | 3.27 | 7.19 | 4.23 | 0.83 | 19.7 | 2.71 |
| 11 | Seed/pulp | S/p | M | % | 12.7 | 73.5 | 23.5 | 12.3 | 52.5 | 2.05 |
| 12 | Edible proportion | EP | M | % | 10.7 | 29.5 | 21.4 | 4.71 | 21.9 | 2.73 |
| 13 | Vitamin C | VC | N | mg/100 g | 6.72 | 54.4 | 18.0 | 10.9 | 60.3 | 2.13 |
| 14 | Reducing sugar | RS | N | g/100 g | 8.71 | 18.22 | 12.9 | 2.79 | 21.5 | 2.82 |
| 15 | Protein | Pro | N | g/100 g | 0.32 | 0.67 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 14.6 | 2.64 |
| 16 | Total flavonoids | TF | N | mg/g | 1.01 | 29.1 | 3.55 | 5.38 | 151.6 | 0.79 |
| 17 | Titratable acid | TA | N | g/100 g | 0.039 | 0.082 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 16.7 | 2.93 |
| 18 | Total free amino acids | TFAAs | N | ng/mg | 312.4 | 1443.1 | 706.4 | 287.4 | 40.7 | 2.57 |
| 19 | Total hydrolyzed amino acids | THAAs | N | ng/mg | 1663.3 | 3940.0 | 3174.8 | 534.3 | 16.8 | 2.50 |
| Trait | FW | PW | PT | LD | TD | SW | Pos | S/p | EP | V C | RS | Pro | TF | TA | THAA | TFAA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FW | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| PW | 0.961 ** | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| PT | 0.241 | 0.362 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| LD | 0.921 ** | 0.823 ** | 0.170 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| TD | 0.759 ** | 0.634 ** | −0.109 | 0.824 ** | 1 | |||||||||||
| SW | 0.688 ** | 0.617 ** | −0.174 | 0.721 ** | 0.755 ** | 1 | ||||||||||
| Pos | −0.147 | −0.18 | −0.431 | −0.028 | 0.131 | 0.534 * | 1 | |||||||||
| S/p | −0.219 | −0.053 | −0.024 | −0.325 | −0.21 | 0.046 | 0.291 | 1 | ||||||||
| EP | 0.193 | −0.066 | −0.284 | 0.351 | 0.353 | 0.13 | −0.083 | −0.786 ** | 1 | |||||||
| VC | 0.482 * | 0.332 | −0.092 | 0.642 ** | 0.539 * | 0.446 * | 0.089 | −0.296 | 0.542 * | 1 | ||||||
| RS | −0.018 | −0.163 | −0.268 | 0.218 | 0.394 | 0.112 | 0.053 | −0.440 | 0.523 * | 0.315 | 1 | |||||
| Pro | 0.428 | 0.481 * | −0.019 | 0.278 | 0.255 | 0.241 | −0.096 | 0.214 | −0.167 | 0.195 | −0.063 | 1 | ||||
| TF | 0.315 | 0.151 | −0.448 | 0.466 * | 0.612 ** | 0.532 * | 0.320 | 0.011 | 0.331 | 0.628 ** | 0.147 | 0.151 | 1 | |||
| TA | −0.182 | −0.145 | 0.096 | −0.284 | −0.323 | −0.228 | −0.133 | 0.069 | −0.032 | −0.093 | −0.150 | −0.175 | −0.315 | 1 | ||
| TFAA | −0.191 | −0.049 | 0.098 | −0.378 | −0.251 | −0.198 | −0.091 | 0.563 ** | −0.566 ** | −0.543 * | −0.323 | 0.270 | −0.259 | 0.015 | 1 | |
| THAA | 0.246 | 0.219 | 0.004 | 0.252 | 0.316 | 0.100 | −0.143 | 0.141 | 0.042 | 0.171 | 0.078 | 0.522 * | 0.212 | −0.067 | 0.314 | 1 |
| Trait | Component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | |
| Fruit weight (FW) | 0.868 ** | 0.398 | −0.225 | −0.007 | 0.051 |
| Peel weight (PW) | 0.726 ** | 0.423 | −0.234 | −0.041 | 0.012 |
| Pericarp thickness (PT) | −0.13 | 0.326 | −0.606 ** | 0.399 | 0.006 |
| Longitudinal diameter (LD) | 0.941 ** | 0.155 | −0.238 | 0.06 | −0.02 |
| Transverse diameter (TD) | 0.917 ** | 0.035 | 0.091 | −0.081 | −0.023 |
| Seed/pulp (SP) | −0.375 | 0.570 | 0.600 ** | −0.082 | 0.040 |
| Seed weight (SD) | 0.796 ** | 0.14 | 0.011 | −0.431 | 0.04 |
| Edible proportion (EP) | 0.457 | −0.67 ** | −0.148 | 0.234 | 0.154 |
| Vitamin C (VC) | −0.492 | 0.626 ** | −0.03 | 0.264 | 0.11 |
| Reducing sugar (RS) | 0.352 | −0.595 ** | 0.087 | 0.443 | −0.177 |
| Protein (Pro) | 0.277 | 0.423 | 0.618 ** | 0.291 | 0.03 |
| Total flavonoids (TF) | 0.512 | −0.27 | 0.517 | −0.587 ** | −0.071 |
| Titratable acid (TA) | −0.15 | −0.109 | −0.068 | −0.128 | 0.955 ** |
| Total free amino acids (TFAAs) | −0.446 | 0.64 ** | 0.334 | 0.02 | 0.036 |
| Total hydrolyzed amino acids (THAAs) | 0.306 | 0.31 | 0.583 ** | 0.50 | 0.22 |
| Total eigenvalues | 5.037 | 2.683 | 1.674 | 1.218 | 1.041 |
| % of Variance | 35.9 | 19.2 | 11.9 | 8.698 | 7.433 |
| Cumulative % | 35.9 | 55.1 | 67.1 | 75.8 | 83.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, J.; Fu, P.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhong, S.; Chen, W.; Yang, H.; Chen, C.; Yang, H.; Luo, P. Assessment of the Breeding Potential of a Set of Genotypes Selected from a Natural Population of Akebia trifoliata (Three–Leaf Akebia). Horticulturae 2022, 8, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020116
Guan J, Fu P, Wang X, Yu X, Zhong S, Chen W, Yang H, Chen C, Yang H, Luo P. Assessment of the Breeding Potential of a Set of Genotypes Selected from a Natural Population of Akebia trifoliata (Three–Leaf Akebia). Horticulturae. 2022; 8(2):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020116
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Ju, Peng Fu, Xianshu Wang, Xiaojiao Yu, Shengfu Zhong, Wei Chen, Hao Yang, Chen Chen, Huai Yang, and Peigao Luo. 2022. "Assessment of the Breeding Potential of a Set of Genotypes Selected from a Natural Population of Akebia trifoliata (Three–Leaf Akebia)" Horticulturae 8, no. 2: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020116
APA StyleGuan, J., Fu, P., Wang, X., Yu, X., Zhong, S., Chen, W., Yang, H., Chen, C., Yang, H., & Luo, P. (2022). Assessment of the Breeding Potential of a Set of Genotypes Selected from a Natural Population of Akebia trifoliata (Three–Leaf Akebia). Horticulturae, 8(2), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020116






