Abstract
In this study, a new technology was tested for its efficacy in the conservation of tomato fruits. An initial experiment was conducted to determine the effects of eugenol on the main quality parameters of Raf tomato fruits; then, a main experiment was performed to test the effectiveness of the new technology. In both experiments, fruits of the tomato cultivar Raf at the mature green stage were used. The preliminary experiment demonstrated the effectiveness of eugenol in maintaining fruit quality during the postharvest life of the fruit. In the main experiment, the fruits were packed using a sachet filled with a mixture consisting of 10:1:1 clinoptilolite clay, ground clove buds, and activated charcoal. This mixture was evaluated against a commercial ethylene scavenger composed mainly of KMnO4-impregnated sepiolite. Three lots of fruits were used: One batch was considered as the control, where the fruits were not packed but kept in an open box at room temperature. The fruits in the other two batches were packed in 2 L PET containers with lids at a rate of three fruits per container, and a sachet of ground cloves and a commercial scavenger was added inside each container in each batch. The containers were kept at room temperature, and the following main quality parameters were analyzed: ethylene production rate, firmness, color, content of soluble solids, and pigments. The results showed that ground clove buds led to a reduction in ethylene production which was associated with a delay in maturation and could be a good alternative for use in the active fruit packaging of horticultural products.
1. Introduction
Technologies used to extend the postharvest lives of fruits and vegetables include ethylene removal by means of ventilation, the use of ethylene scavengers, or the use of ethylene binding inhibitors such as 1-methylcyclopropene (1MCP). Ethylene scavengers are based on the oxidation of ethylene via potassium permanganate. This compound is impregnated on clay, and different commercial presentations are available [1,2,3]. Ethylene absorbents based on active charcoal are also available on the market (Sekisui Jushi Co., Osaka, Japan; Mitsubishi Chemical Company, Tokio, Japan). The use of these ethylene absorbents as additives in plastic films for packaging has also been reported [4,5]. However, one of the most innovative technologies in relation to ethylene is the use of 1-MCP, a compound that interacts with ethylene receptors and thereby prevents ethylene-dependent responses [6,7]. Other technologies widely used include controlled atmosphere storage and active packaging, which is based on incorporating active substances into the packaging. These substances interact with plant products in different ways, such as eliminating volatile compounds or adding compounds that offer fungicide activities [8]. Among the compounds with fungicidal activities, essential oils (EOs) have been widely used due to their potential benefits in protecting fruit and vegetables from microbial spoilage. The most commonly used essential oils (EOs) include thymol, eugenol, eucalyptol, menthol, and carvacrol, which are incorporated into the packaging via direct incorporation, including incorporation into plastic polymers or the use of a coating to cover the polymer [9]. Direct incorporation provides a simple way to test active packaging and consists of inserting oil-impregnated sterile gauze inside the packaging to avoid contact with fruits [10]. The packaging is then immediately closed tightly to minimize vaporization. This method has been widely used in several studies, generally in combination with Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) and EOs to maintain the quality of the fruits and vegetables. However, most studies aimed at reducing the losses caused by fungal and microbial spoilage.
By contrast, Ban et al. (2020) [11] did not use direct incorporation but instead employed microencapsulated ginger essential oil as the carrier to release the oil into the package’s headspace. Essential oils are commonly used in food and the postharvest industry due to their capacity to kill microorganism. The antimicrobial and antifungal activities of eugenol, thymol, eucalyptol, and other EOs have been shown in vivo both during postharvest of fruits and in other plant-derived products such as fruit juices [12,13].
The antimicrobial and antifungal activities of eugenol, thymol, eucalyptol, and other EOs have been demonstrated in vivo both in postharvest fruits and in other plant products such as fruit juices. Overall, thymol is especially effective against Botrytis because the percentage of damaged grapes inoculated with this fungus was reduced. Carvacrol was also found to be very effective in reducing spoilage in fresh-cut kiwifruit but was not effective when applied to melon [14]. However, in tomato fruits, thymol was effective in reducing the incidence of Alternaria and Botrytis. Although the use of essential oils has been focused on reducing the losses and spoilage caused by microbiological agents, studies show that EOs also have an effect on the quality of the fruit. Serrano et al. [15] indicated that EOs could be a useful tool to increase the shelf-lives of fruits and vegetables. Guillen et al. [16] also found that MAP conditions and the addition of a mixture of three EOs (eugenol, thymol, and carvacrol) were able to delay the ripening process of Black Amber plum by delaying changes in color and losses of firmness. In general, the combined use of MAP and EOs improves the overall quality of fruits by maintaining their organoleptic and functional properties and delaying the ripening process. The application of EOs interferes with the ripening of fruits [15]. The reasons why EOs can delay ripening are not known, but it seems that essential oils interfere with ethylene [17]. In general, some compounds that bind to the ethylene receptor induce a response, but others prevent such a response. These compounds are known as ethylene antagonists [18]. However, except for silver thiosulfate and cyclopropenes, all ethylene antagonists require continuous exposure [17]. The ethylene-binding domain appears to be accessible by relatively large molecules that contain ten or more carbons [19]. Sisler et al. [17] further noted that many natural compounds of plant origin compete with ethylene receptors and provided an extensive list including limonene, carveol, estragole, eugenol, and others. Serrano et al. [15] suggested that future trends in the use of EOs should be focused on the use of active packaging able to release active compounds in the head space. Therefore, new methods to apply EOs are necessary as their direct incorporation in sterile gauze is useful only for scientific purposes. In this context, Pongjaruwat [20] used sachets containing silica gel as carriers for EOs, and Montero-Prado et al. [9] presented a new method consisting of a label with EOs attached to the plastic packaging.
The tomato cultivar Raf, which is grown traditionally in the province of Almería, is characterized by high organoleptic quality and a very short shelf life [21]. The high price of Raf tomatoes on the market is mainly because the fruit offers good sensory combinations, including a mixture of sweetness, firmness, and acidity, which enables the fruit to produce an excellent aroma and exquisite flavors. However, all these characteristics are quickly lost over time because the Raf tomato possesses strong climacteric characteristics and rapidly becomes soft with intense red coloring [22]. Such a short shelf-life is a handicap for Raf Tomato, as this kind of tomato is eaten raw and appreciated by consumers in the breaker and turning stages [23,24]. The Raf tomato fruit loses much of its quality in the pink ripening stage and then completely loses its commercial value in the red stage.
This present study details the effectiveness of a new essential oil-based technology in which eugenol is supplied by ground clove buds. In addition, two trials were performed to evaluate the effects of eugenol on the postharvest quality attributes of Raf tomato fruits. In the preliminary experiment, eugenol was applied via direct incorporation. Then, in the main experiment, eugenol was replaced by ground clove buds, thereby producing the new essential oil-based technology, which was subsequently compared with an ethylene scavenger containing potassium permanganate.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preliminary Test
An initial experiment was conducted to determine the effects of eugenol on the main fruit quality parameters of Raf tomato. Fresh market tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum L. cv Raf) were hand-picked in a greenhouse of the Higher Engineering School (University of Almería) at the green mature stage according to the USDA standard tomato color classification chart [25]. At the laboratory, the tomatoes were selected to obtain three homogenous lots. Each lot was composed of 60 fruits packed in 2 L containers featuring snap-on lids of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), with three fruits per container and 20 containers per lot. Two lots were treated with eugenol obtained from Sigma-Aldrich, Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA) at concentrations of 40 and 60 µL, applied to sterile gauze, and placed inside the plastic containers avoiding contact with the fruits, just before the containers were tightly closed. The third lot was considered as the control and was not supplemented with a dose of eugenol. All containers were maintained at room temperature (20 °C). Some physicochemical parameters (ethylene production rate, color, firmness, and soluble solids content (SSC)) were analyzed at harvest and every three days during the 9-day storage time. Ethylene production rate, however, was assessed daily. Color changes were quantified with L*, a*, and b* parameters (CIELAB color space system) using a Minolta colorimeter CR200 (Minolta Camera, Osaka, Japan). L* represents the lightness and define the position on the black–white axis, while a* and b* parameters represent the chroma and define the position on the red–green axis and yellow–blue axis respectively. The color records of individual L*, a*, and b* parameters were taken as the means of two determinations for each tomato along the equatorial axis. Firmness was measured using a texture analyzer (TA-XT2 PLUS, Stable MicroSystems, Godalming, UK), and the fruits were subjected to compression tests using a 120 mm Ø flat steel plate mounted on the machine. For each fruit, a force that achieved 10% deformation of the fruit diameter was applied. The flat plate speed before, during, and after the test was 2 mm·s-1, and the maximum peak force (g) was also recorded. The content of soluble solids in the tomato juice was determined using the refractometer Index (°Brix). The tomatoes in each container were crushed and homogenized, and then an aliquot of 1 mL was measured with an ATAGO N1 digital refractometer. The ethylene production rate was determined every day. The fruits were analyzed for each treatment in 4 replicates of 3 fruits each. The fruits were enclosed in sealed 3.5 liter containers for 1 h at 20 °C. After this incubation period, gas samples were taken, and ethylene content was determined three times using a gas chromatograph (Varian 3900 GC) fitted with a flame ionization detector (FID). The ethylene production rate was expressed as nanoliters per gram per hour (nL·g−1·h−1).
2.2. Main Experiment
In this study, we assessed a new method for incorporating eugenol as the active compound in packaging. A sachet of cheese tissue similar in size to a tea bag was filled with 2 g of a mixture consisting of 10:1:1 of clinoptilolite clay (0.1–0.05 mm Ø), ground clove buds, and activated charcoal (hereafter referred as ‘Ground clove’). Clove buds were purchase in a local supermarket from commercial clove Ducros (MacCormick & Company, Baltimore, MD, USA).
This mixture was evaluated against Keepfresh® (Blue Teck Systems, Madrid, Spain) a commercial ethylene scavenger mainly composed of KMnO4-impregnated sepiolite (hereafter referred as ‘Commercial scavenger’). Raf tomatoes from the experimental field of the Higher Engineering School (University of Almería) were harvested at the green mature stage according to USDA standards [25]. In the laboratory, the selected fruits were divided into three batches of 90 fruits each. One batch was considered as the control. The fruits were not packed and were maintained in the open box at room temperature. The fruits of the other two batches were packed in containers with the same characteristics as those used in the preliminary experiment and at the same rate of three fruits per container. A sachet of the Ground clove or Commercial scavenger was added inside each container of each batch. After being closed, the containers were all kept at room temperature, and some fruit quality parameters (color, firmness, SSC, and ethylene production rate) were evaluated every two days during the 10-day storage time, following the same methodology described in the preliminary experiment. Pigment content (total chlorophyll, β-carotene, and lycopene) was assessed following the methodology proposed by Nagata and Yamashita [26] whereby the pigments were evaluated spectrophotometrically. One gram of pericarp of the fruit was homogenized with acetone–hexane (4:6 v/v), the mixture was shaken, and two phases were separated. An aliquot from upper solution was analyzed spectrophotometrically at 663, 645, 505, and 453 nm. Total chlorophyll, β-carotene, and lycopene contents were calculated according the equations of Nagata y Yamashita [26].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The data obtained were initially checked using a Kolmogorov–Smirnov test to assess data normality. Then, an analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was performed, with the time of storage and treatments as the sources of variation. When the F-test from the ANOVA was significant, mean comparisons were performed using an LSD post hoc test. All the statistical analyses were completed using a Statgraphic Centurion XVI (STATGRAPHICS. Statpoint Technologies, Inc., Warrenton, VA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Preliminary Test
The effects of eugenol on ethylene production are shown in Figure 1. The fruits show a clear pattern. Much less ethylene was released from the treated fruits than from the control fruits, which resulted in a sharp decline, reaching the lowest level at first and second day of storage. Conversely, ethylene production in the control fruits showed a slow and steady increase up to 4 days of storage, when the maximum peak was recorded, and then ethylene production decreased continuously and steadily. A climacteric peak was registered for the control fruits, while for the fruits treated with eugenol, a maximum ethylene production peak was not observed. For ethylene production, there was no dose effect, as no differences were found between the ethylene production of fruits treated with 60 or 40 microliters of eugenol. Differences were found only between the fruits treated after 1 day of storage, as the fruits treated with 60 microliters of eugenol produced less ethylene than the fruits treated with 40 microliters of eugenol.
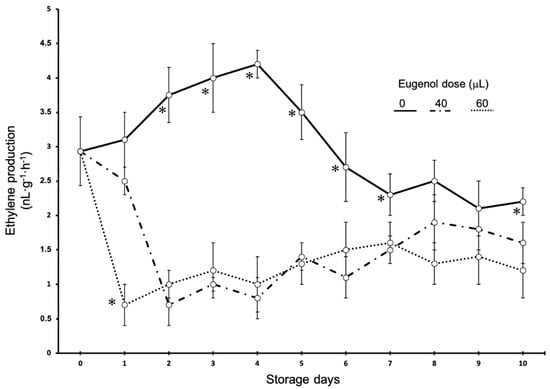
Figure 1.
Time course of ethylene production in Raf tomato fruits treated with different eugenol doses. Vertical bars show the standard error (SE) (n = 12). ✻ indicates significant differences within each eugenol dose according to the LSD test at p < 0.05. The lack of a symbol indicates no differences.
Effect of Eugenol on Some Fruit Quality Characteristics
Table 1 shows the main fruit quality characteristics. The content of soluble solids was 6.3 at harvest and did not vary significantly during the storage time. Although the application of eugenol resulted in an increase in SSC, this was not statistically significant and was only reflected in an increase of 0.7 degrees Brix at best. Rapid softening is one of the most noticeable features of the Raf tomato that occurs during ripening; a loss of firmness can occur very quickly if the fruit is not kept under cold storage. The evolution of firmness during storage depended on the eugenol treatments. At harvest, the fruits presented high firmness. However, under postharvest storage at 20 °C, there was a sharp loss of firmness during the first 3 days and later, while firmness was retained longer in the treated fruits. The effect of eugenol was remarkable. Notably, the softening rate was decreased, which meant that the fruits remained firmer than the control fruits after 9 days of storage.

Table 1.
Effect of eugenol doses on SSC (expressed as the Brix degree) and firmness (expressed in g) in Raf tomato fruits.
In terms of color (Table 2), the Raf tomato is commonly characterized by a green color at the optimum stage of harvest, but during storage, the control tomatoes showed greater variations in color, with significant decreases in the L* and a* parameters and slight decreases in b*. Conversely, in the treated fruits, the values of parameter a* increased more slowly and were related to the dose of eugenol applied. The result after eugenol application was that the fruits remained green for a longer time, while the control fruits turned red much earlier. In other words, at the end of the experiment, the control fruits featured a very intense red color (red mature, according to the USDA tomato-ripening chart), in contrast to the treated fruits, whose colors were not as intense (pink or light red, according to the USDA tomato-ripening chart).

Table 2.
Effect of eugenol doses on the color CieLab parameters (L*, a*, b*) in Raf tomato fruits.
3.2. Main Experiment
Figure 2 shows the effects of the Control, Commercial scavenger, and Ground clove fruits on color and rate of ethylene production. The results indicate that both the Commercial scavenger and Ground clove delayed the ripening of the fruits, which was reflected by a delay in the appearance of red coloring, as well as a delay in the appearance of the ethylene production peak. The maximum amount of ethylene produced was significantly lower in the Commercial scavenger fruits, while ethylene production was similar between the control and Ground clove fruits. Among the control fruits, the evolution of color was rapid, reaching positive values for parameter a* on the fourth day of storage. However, among the rest of the fruits, parameter a* reached positive values only after eight days of storage. The slow color change among the treated fruits can be visualized in the tangent of the line of fit from parameter a*, which presents values of 3.657 (R2 = 0.9318) and 3.92 (R = 0.9726) for fruits preserved with the ethylene scavenger and ground cloves, respectively, while the slope of the line of fit for the control fruits was greater (67,371 (R = 0.9966)).
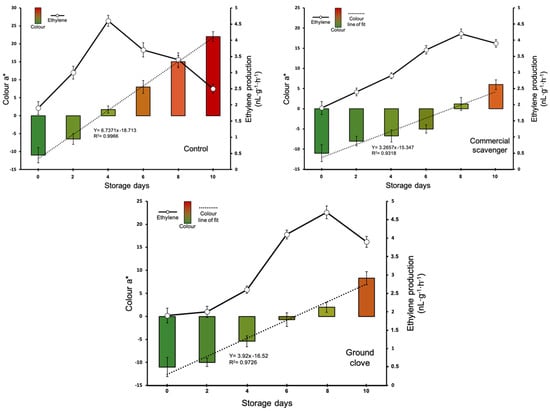
Figure 2.
Evolution of the ethylene production rate and color (parameter a*) for Raf tomatoes packaged and not packaged (control) with the commercial scavenger or ground clove. Vertical bars show the standard error (SE) (n = 15).
Effect on Fruit Quality Characteristics
The data in Table 3 show the content of soluble solids and firmness of the fruit during postharvest time. No differences were found between the various treatments, but significant differences in firmness were observed. All the fruits, regardless of their storage method, presented a loss of firmness during the postharvest period, which was more pronounced among the control fruits, while for the fruits stored with the commercial scavenger and ground cloves, the loss of firmness was slower and more gradual. No differences were found between the treated fruits on any of the storage days—only between the control and treated fruits. These differences began to appear at 2 days after harvest.

Table 3.
Evolution of CSS (expressed as the Brix degree) and firmness (expressed as g) in Raf tomatoes packaged and not packaged (control) with the commercial scavenger or ground clove.
Figure 3 shows the evolution of the total chlorophyll, carotenes, and lycopene in the fruits studied. As expected, during the postharvest period, the chlorophyll content decreased, while the content of carotene and lycopene increased. However, a clear effect of the treatments was observed. Starting from the fourth day of storage, significant differences in the content of all pigments could be observed between the control and treated fruits. The loss of chlorophyll was more pronounced in the control fruits, as was the increase in carotenes and lycopene. There were almost no differences between the commercial scavenger and ground cloves. Differences between the two treatment types were observed for chlorophyll content only on days 4 and 6 of storage and for lycopene only on day 6 of storage.
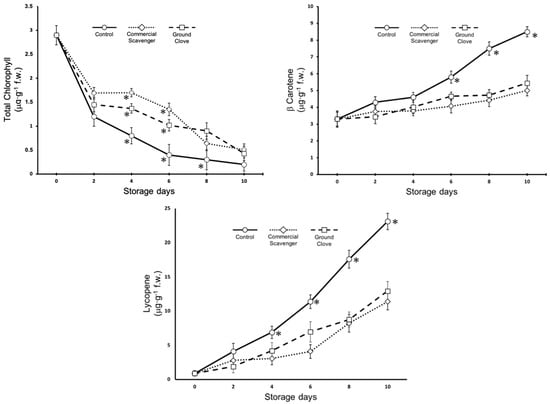
Figure 3.
Evolution of total chlorophyll, β-carotene and lycopene in Raf tomatoes packaged and not packaged (control) with the Commercial scavenger or Ground clove. Vertical bars show the standard error (SE) (n = 15). ✻ indicates significant differences within treatments according to the LSD test at p < 0.05. The lack of a symbol indicates no differences.
Figure 4 shows the tomato fruits at harvest and after 9 days of storage for both the preliminary and main experiment.
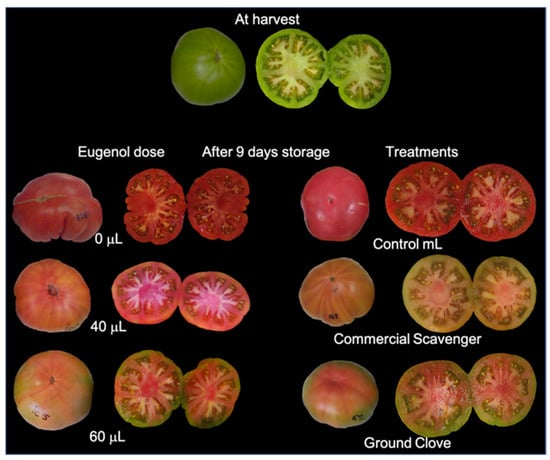
Figure 4.
Tomato fruit at harvest and after 9 days of storage for preliminary experiment (left) and main experiment (Right).
4. Discussion
The Raf tomato is characterized by an extremely short shelf-life and is, therefore, a very perishable product. Raf tomato is considered to be a gourmet product intended for fresh consumption. In its red ripe state, Raf tomato loses its commercial value. Only in the mature green, breaker, and turning stages is Raf tomato appreciated by consumers as a tasty, crunchy fruit with high-quality aroma, flavor, and juiciness [27]. Due to these consumer preferences, the loss of quality is very noticeable when the Raf tomato ripens, at which point the fruits soften, assume an intense red color, and become less juicy with a weaker aroma and flavor. These changes can be delayed through the application of eugenol (Table 1 and Table 2) and are associated with lower ethylene production and a notable delay in the production of peak ethylene (Figure 1). The effects on ethylene production of applying essential oils to fruits is well established, and it was previously found that the application of rosemary and eucalyptus essential oil reduced ethylene production in tomato [28]. In table grapes [15], treatments with different essential oils, including eugenol, were associated with reduced ethylene production. Regardless of the essential oil applied, lower ethylene production was observed. Our study observed similar results when the fruits were treated with eugenol (Figure 1). Color changes during the ripening of tomato fruits are closely related to their climacteric characteristics and, therefore, to the presence of ethylene. Lower ethylene production resulted in a delay in the appearance of the typical red color of ripe tomato. Color changes are related to the transition from chloroplast to chromoplast. This process, in turn, leads to carotenoid synthesis and chlorophyll breakdown [29], which is related to ethylene production. Indeed, most of the genes involved in chromoplast differentiation are ethylene-induced [30,31] i.e., in ripening tomato fruits, homologues of the rice STAY-GREEN gene, identified for participates in chlorophyll turnover during senescence.
However, very few studies in the literature explored the application of eugenol to tomato fruits, and even fewer analyzed the Raf cultivar. Overall, the effects on ripening are based on interference with ethylene caused by eugenol’s competition with ethylene for the ethylene receptor. However, continuous exposure is required [6,17,18]. In both our experiments (the preliminary and main experiment), the application of eugenol was continuous (gauze impregnated with eugenol and ground cloves were kept inside the containers throughout the experiment).
The proposed methodology provides a simple, straightforward, and natural way of supplying eugenol to increase the shelf-lives of fruits. However, it can be argued that the dose of eugenol cannot be controlled and depends on the type, agronomic practices, or origin of the clove buds.
The primary component in clove essential oil is eugenol, usually in concentrations ranging from 70% to 95%. However, note that this wide range is due to variability in the method of extraction [32,33]. Nevertheless, given that the dose of eugenol required to achieve acceptable results is very low (in the order of 60 microliters (Table 1)), the concentration range of eugenol in clove essential oil should not be considered a limiting factor. Moreover, in clove oil, there are also other major compounds, such as b-caryophyllene (4–21%) and eugenyl acetate (0.5–21%), as well as many other minority compounds, which all contribute to the properties of the clove oil. Indeed, there are numerous studies in which clove oil—instead of eugenol alone—was applied in the postharvest period, but, as mentioned above, these studies focused on antifungal and antimicrobial properties, rather than the possibility of increasing the shelf-lives of the fruits [34,35]. It should be kept in mind that as the content of essential oil in clove buds can differ depending on different factors, such as geographical origin, crop method as well as the freshness of the cloves, it would be convenient to study whether this variability could affect negatively the effectiveness of technology proposed, although we think that if it affects, it will be slightly because as we have seen in the preliminary experiment the amount of eugenol that has an effect on maintaining the quality of tomato fruits is low.
The presence of ground clove buds was clearly detected by smell when opening the containers. However, only a slight smell of cloves was perceived, which quickly disappeared once the fruits were removed from the container. In our study, no clove flavor was detected in the tomatoes, possibly because eugenol produced much less residual flavor than other essential oils such as thymol. Similarly, Valero et al. [10], who combined menthol and eugenol as active packaging for grapes, found that the residual flavor of eugenol was much less than that of menthol, which was clearly detectable. Baldwin et al. [36] also carried out a quantitative analysis of the volatiles in the fruits of two tomato cultivars during ripening and found that eugenol was the only volatile compound that decreased significantly during ripening. These factors alongside the fact that the Raf tomato is considered to have a very enjoyable flavor may explain why the taste of cloves was not detected.
The use of potassium permanganate as a sequestrant is a widely used technique [1], but there is concern among consumers about its toxicity and the environmental damage that its widespread use may cause. As noted by Álvarez-Hernández et al. [3], permanganate-based ethylene scavengers are an environmentally friendly tool that can be used in the packaging of horticultural products; such scavengers require proper handling and relevant safety measures but are otherwise very simple and straightforward. Nevertheless, consumer concerns persist. We believe that the use of ground cloves can help overcome consumer concerns about toxicity and environmental problems. Clove buds are not only a natural product, but are also commonly used by consumers themselves as spices in their own cooking.
5. Conclusions
In the main experiment, we have compared two technologies based on two different features. While the presence of permanganate was found to oxidize ethylene and properly act as a scavenger, the effects of ground clove were mainly due to its eugenol content binding to the ethylene-binding domain, thereby acting as an ethylene antagonist. Despite these two different modes of action, the results were similar, and we believe that the use of ground clove buds represents a good alternative for use in the active fruit packaging of horticultural products.
Author Contributions
Conceptualized, conceived, and designed the experiments: L.F.D. and J.L.V.; managed crop: L.F.D. and M.V.A.; performed the experiments and formal analysis: L.F.D., C.A. and M.G.; writing—original draft preparation: L.F.D., M.G. and J.L.V.; writing—review and editing: J.L.V.; supervision, grant management, and funding acquisition, M.G. and J.L.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partly financed by Iberocons S.A. and funds from the research groups of which the authors are members.
Acknowledgments
L.F.D. would like to thank Iberocons S.A. for the facilities provided for his stay in Spain. The authors thank Carmen Fernandez-Mañas for her assistance in laboratory tasks.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wei, H.; Seidi, F.; Zhang, T.; Jin, Y.; Xiao, H. Ethylene scavengers for the preservation of fruits and vegetables: A review. Food Chem. 2021, 337, 127750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Romero, D.; Bailén, G.; Serrano, M.; Guillén, F.; Valverde, J.M.; Zapata, P.; Castillo, S.; Valero, D. Tools to maintain postharvest fruit and vegetable quality through the inhibition of ethylene action: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Hernández, M.H.; Martínez-Hernández, G.B.; Avalos-Belmontes, F.; Castillo-Campohermoso, M.A.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C.; Artés-Hernández, F. Potassium Permanganate-Based Ethylene Scavengers for Fresh Horticultural Produce as an Active Packaging. Food Eng. Rev. 2019, 11, 159–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeiren, L.; Devlieghere, F.; VanBeen, M.; De Kruijf, N.; Debevere, J. Development in the Active Packaging of Foods. J. Food Technol. Afr. 2000, 5, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrwa, J.; Barska, A. Innovations in the food packaging market: Active packaging. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisler, E.C. The discovery and development of compounds counteracting ethylene at the receptor level. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, D.J. Suppression of Ethylene Responses Through Application of 1-Methylcyclopropene: A Powerful Tool for Elucidating Ripening and Senescence Mechanisms in Climacteric and Nonclimacteric Fruits and Vegetables. HortScience 2008, 43, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antunes, M.D.C.; Cavaco, A.M. The use of essential oils for postharvest decay control. A review. Flavour Fragr. J. 2010, 25, 351–366. [Google Scholar]
- Montero-Prado, P.; Rodriguez-Lafuente, A.; Nerin, C. Active label-based packaging to extend the shelf-life of ‘Calanda’ peach fruit: Changes in fruit quality and enzymatic activity. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2011, 60, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, D.; Valverde, J.M.; Martínez-Romero, D.; Guillén, F.; Castillo, S.; Serrano, M. The combination of modified atmosphere packaging with eugenol or thymol to maintain quality, safety and functional properties of table grapes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2006, 41, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhou, B.; Liu, H. Ginger essential oil-based microencapsulation as an efficient delivery system for the improvement of Jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) fruit quality. Food Chem. 2020, 306, 125628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M.; Henika, P.R.; Levin, C.E.; Mandrell, R.E. Antibacterial activities of plant essential oils and their components against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica in apple juice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6042–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arasu, M.V.; Viayaraghavan, P.; Ilavenil, S.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Choi, K.C. Essential oil of four medicinal plants and protective properties in plum fruits against the spoilage bacteria and fungi. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 133, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roller, S.; Seedhar, P. Carvacrol and cinnamic acid inhibit microbial growth in fresh-cut melon and kiwifruit at 4 °C and 8 °C. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 35, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.; Martínez-Romero, D.; Guillén, F.; Valverde, J.M.; Zapata, P.; Castillo, S.; Valero, D. The addition of essential oils to MAP as a tool to maintain the overall quality of fruits. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, F.; Valero, D.; Zapata, P.J.; Castillo, S.; Martínez-Romero, D.; Serrano, M. A novel active packaging based on MAP and addition of essential oils maintains plum quality and enhances antioxidant properties. Acta Hortic. 2013, 1012, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisler, E.C.; Grichko, V.P.; Serek, M. Interaction of ethylene and other compounds with the ethylene receptor: Agonists and antagonists. In Ethylene Action in Plants; Khan, N.A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sisler, E.C.; Serek, M. Compounds Interacting with the Ethylene Receptor in Plants. Plant Biol. 2003, 5, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grichko, V.P.; Sisler, E.C.; Serek, M. Anti-ethylene properties of monoterpenes and some other naturally occurring compounds in plants. SAAS Bull. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2003, 16, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Pongjaruwat, W. Effect of Modified Atmosphere on Storage Life of Purple Passionfruit and Red Tamarillo. Ph.D. Thesis, Massey University, Auckland, New Zealand, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán, M.; Sánchez, A.; Díaz, J.R.; Valenzuela, J.L. Postharvest quality of three tomato cultivars. Acta Hortic. 2009, 821, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, M.; Sánchez, A.; Salas, M.C.; Del Moral, F.; Valenzuela, J.L. Relationship between pectin-methyl esterase activity and softening in “Raf” tomato fruit. Acta Hortic. 2012, 934, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, F.; Castillo, S.; Zapata, P.J.; Martínez-Romero, D.; Valero, D.; Serrano, M. Efficacy of 1-MCP treatment in tomato fruit: 2. Effect of cultivar and ripening stage at harvest. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2006, 42, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, F.; Castillo, S.; Zapata, P.J.; Martínez-Romero, D.; Serrano, M.; Valero, D. Efficacy of 1-MCP treatment in tomato fruit: 1. Duration and concentration of 1-MCP treatment to gain an effective delay of postharvest ripening. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2007, 43, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. United States Standard for Grades of Fresh Tomatoes; United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Marketing Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; Volume 13.
- Nagata, N.; Yamashita, I. Simple method for simultaneous determination of chlorophyll and carotenoids in tomato. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1992, 61, 686–687. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, M.J.; López, J.G.; Luján, J.F.C.; Ortíz, F.L.; Pereznieto, H.B.; Toresano, F.; Camacho, F. Effect of genetic and phenotypic factors on the composition of commercial marmande type tomatoes studied through HRMAS NMR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2014, 142, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xylia, P.; Ioannou, I.; Chrysargyris, A.; Stavrinides, M.C.; Tzortzakis, N. Quality Attributes and Storage of Tomato Fruits as Affected by an Eco-Friendly, Essential Oil-Based Product. Plants 2021, 10, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egea, I.; Barsán, C.; Bian, W.; Purgatto, E.; Latché, A.; Chervin, C.; Bouzayen, M.; Pech, J.C. Chromoplast Differentiation: Current Status and Perspectives. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlova, R.; Rosin, M.F.; Busscher-Lange, J.; Parapunova, V.; Do, P.T.; Fernie, A.R.; Fraser, P.D.; Baxter, C.; Angement, G.C.; de Maag, R.A. Transcriptome and Metabolite Profiling Show That APETALA2a Is a Major Regulator of Tomato Fruit Ripening. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 923–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sadali, N.M.; Sowden, R.G.; Ling, Q.; Jarvis, R.P. Differentiation of chromoplasts and other plastids in plants. Plant Cell Rep. 2019, 38, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Razafimamonjison, G.; Jahiel, M.; Duclos, T.; Ramanoelina, P.; Fawbush, F.; Danthu, P. Bud, leaf and stem essential oil composition of Syzygium aromaticum from Madagascar, Indonesia and Zanzibar. Int. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 224–233. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.A.; Shahinuzzaman, M.; Rana, M.S.; Yaakob, Z. Study of chemical composition and medicinal properties of volatile oil from clove buds (Eugenia caryophyllus). Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 8, 895–899. [Google Scholar]
- Peralta-Ruiz, Y.; Tovar, C.D.G.; Sinning-Mangonez, A.; Coronell, E.A.; Marino, M.F.; Chaves-Lopez, C. Reduction of Postharvest Quality Loss and Microbiological Decay of Tomato ‘Chonto’ (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Using Chitosan-E Essential Oil-Based Edible Coatings under Low-Temperature Storage. Polymers 2020, 12, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Cai, N.; Chen, J.; Wan, C. Clove Essential Oil as an Alternative Approach to Control Postharvest Blue Mold Caused by Penicillium italicum in Citrus Fruit. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baldwin, E.A.; Nisperos-Carriedo, M.O.; Moshonas, M.G. Quantitative Analysis of Flavor and Other Volatiles and for Certain Constituents of Two Tomato Cultivars during Ripening. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1991, 116, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).