Protein Hydrolysate Combined with Hydroponics Divergently Modifies Growth and Shuffles Pigments and Free Amino Acids of Carrot and Dill Microgreens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Growth Conditions, Plant Material, and Experimental Design
2.2. Biostimulant Application
2.3. Harvest, Biometric Parameters, and Colorimetric Indices Determination
2.4. Mineral Content Determination
2.5. Total Phenols Determination
2.6. Pigment and Total Ascorbic Acid Determination
2.7. Anthocyanins, Soluble Carbohydrates, Soluble Proteins, and Amino Acids
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
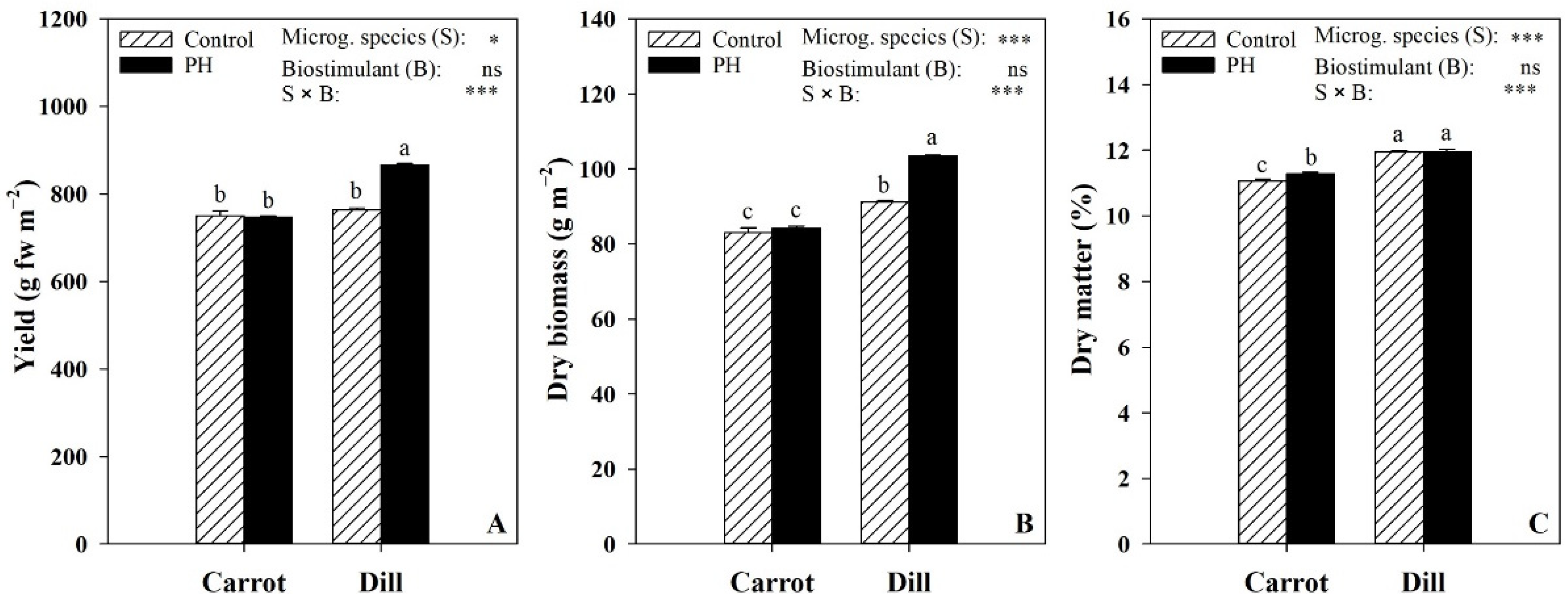
3.1. Yield and Color Parameters
3.2. Microgreen Pigments and Total Ascorbic Acid
3.3. Microgreen Anthocyanins and Total Phenols
3.4. Nitrate and Mineral Contents
3.5. Starch and Reduced Sugar Contents
3.6. Soluble Protein and Amino Acid Contents
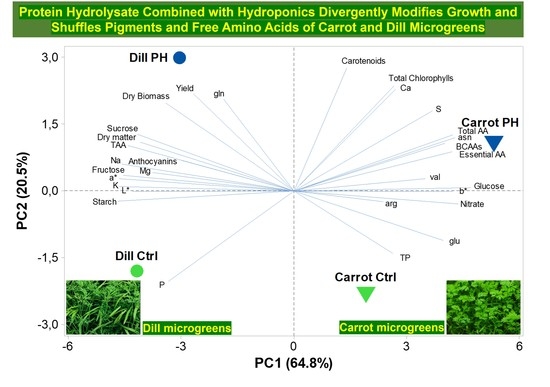
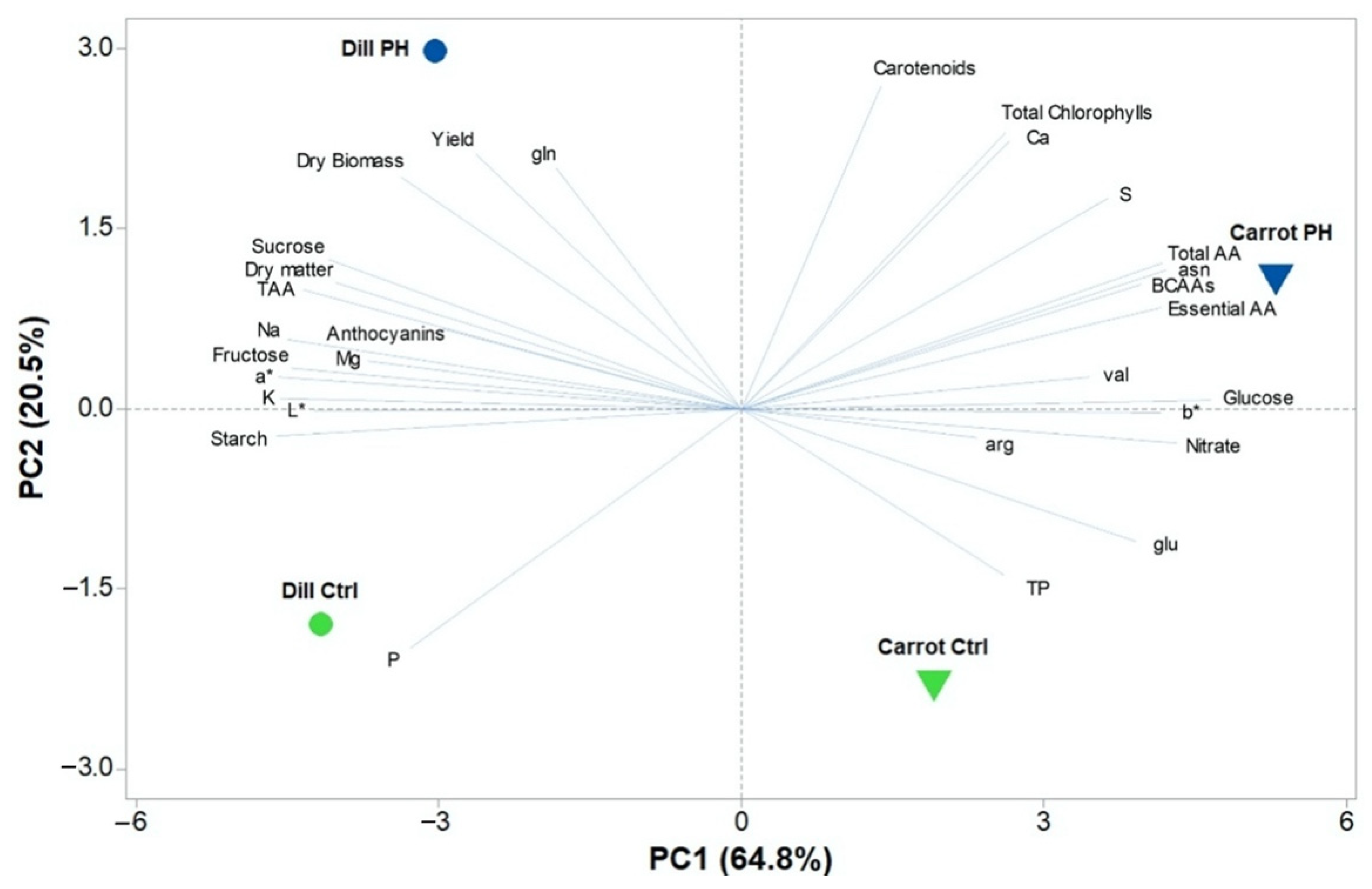
3.7. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kyriacou, M.C.; Rouphael, Y.; Di Gioia, F.; Kyratzis, A.; Serio, F.; Renna, M.; De Pascale, S.; Santamaria, P. Micro-scale vegetable production and the rise of microgreens. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 57, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracciolo, F.; El-Nakhel, C.; Raimondo, M.; Kyriacou, M.C.; Cembalo, L.; de Pascale, S.; Rouphael, Y. Sensory attributes and consumer acceptability of 12 microgreens species. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriacou, M.C.; El-Nakhel, C.; Pannico, A.; Graziani, G.; Zarrelli, A.; Soteriou, G.A.; Kyratzis, A.; Antoniou, C.; Pizzolongo, F.; Romano, R. Ontogenetic Variation in the Mineral, Phytochemical and Yield Attributes of Brassicaceous Microgreens. Foods 2021, 10, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriacou, M.C.; El-Nakhel, C.; Soteriou, G.A.; Graziani, G.; Kyratzis, A.; Antoniou, C.; Ritieni, A.; De Pascale, S.; Rouphael, Y. Preharvest Nutrient Deprivation Reconfigures Nitrate, Mineral, and Phytochemical Content of Microgreens. Foods 2021, 10, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enssle, N. Microgreens: Market Analysis, Growing Methods and Models. 2020. Available online: https://csusm-dspace.calstate.edu/handle/10211.3/217154 (accessed on 4 August 2020).
- Kyriacou, M.C.; El-Nakhel, C.; Pannico, A.; Graziani, G.; Soteriou, G.A.; Giordano, M.; Palladino, M.; Ritieni, A.; De Pascale, S.; Rouphael, Y. Phenolic constitution, phytochemical and macronutrient content in three species of microgreens as modulated by natural fiber and synthetic substrates. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Gioia, F.; De Bellis, P.; Mininni, C.; Santamaria, P.; Serio, F. Physicochemical, agronomical and microbiological evaluation of alternative growing media for the production of rapini (Brassica rapa L.) microgreens. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgari, R.; Negri, M.; Santoro, P.; Ferrante, A. Quality Evaluation of Indoor-Grown Microgreens Cultivated on Three Different Substrates. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriello, M.; Formisano, L.; Pannico, A.; El-Nakhel, C.; Fascella, G.; Duri, L.G.; Cristofano, F.; Gentile, B.R.; Giordano, M.; Rouphael, Y. Nutrient Solution Deprivation as a Tool to Improve Hydroponics Sustainability: Yield, Physiological, and Qualitative Response of Lettuce. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofano, F.; El-Nakhel, C.; Pannico, A.; Giordano, M.; Colla, G.; Rouphael, Y. Foliar and Root Applications of Vegetal-Derived Protein Hydrolysates Differentially Enhance the Yield and Qualitative Attributes of Two Lettuce Cultivars Grown in Floating System. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galieni, A.; Falcinelli, B.; Stagnari, F.; Datti, A.; Benincasa, P. Sprouts and microgreens: Trends, opportunities, and horizons for novel research. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Biostimulants in Agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colla, G.; Hoagland, L.; Ruzzi, M.; Cardarelli, M.; Bonini, P.; Canaguier, R.; Rouphael, Y. Biostimulant action of protein hydrolysates: Unraveling their effects on plant physiology and microbiome. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceccarelli, A.V.; Miras-Moreno, B.; Buffagni, V.; Senizza, B.; Pii, Y.; Cardarelli, M.; Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G.; Lucini, L. Foliar application of different vegetal-derived protein hydrolysates distinctively modulates tomato root development and metabolism. Plants 2021, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Kniel, K.E. Survival and Transfer of Murine Norovirus within a Hydroponic System during Kale and Mustard Microgreen Harvesting. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bulgari, R.; Baldi, A.; Ferrante, A.; Lenzi, A. Yield and quality of basil, Swiss chard, and rocket microgreens grown in a hydroponic system. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2017, 45, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccinelli, M.; Malorgio, F.; Rosellini, I.; Pezzarossa, B. Production of selenium-biofortified microgreens from selenium-enriched seeds of basil. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5601–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formisano, L.; Ciriello, M.; El-Nakhel, C.; De Pascale, S.; Rouphael, Y. Dataset on the Effects of Anti-Insect Nets of Different Porosity on Mineral and Organic Acids Profile of Cucurbita pepo L. Fruits and Leaves. Data 2021, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellburn, A.R. The Spectral Determination of Chlorophylls a and b, as well as Total Carotenoids, Using Various Solvents with Spectrophotometers of Different Resolution. J. Plant Physiol. 1994, 144, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampfenkel, K.; Van Montagu, M.; Inzé, D. Extraction and determination of ascorbate and dehydroascorbate from plant tissue. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 225, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Corrado, G.; Colla, G.; De Pascale, S.; Dell’Aversana, E.; D’Amelia, L.I.; Fusco, G.M.; Carillo, P. Biostimulation as a Means for Optimizing Fruit Phytochemical Content and Functional Quality of Tomato Landraces of the San Marzano Area. Foods 2021, 10, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carillo, P.; Kyriacou, M.C.; El-Nakhel, C.; Pannico, A.; dell’Aversana, E.; D’Amelia, L.; Colla, G.; Caruso, G.; De Pascale, S.; Rouphael, Y. Sensory and functional quality characterization of protected designation of origin ‘Piennolo del Vesuvio’ cherry tomato landraces from Campania-Italy. Food Chem. 2019, 292, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodrow, P.; Ciarmiello, L.F.; Annunziata, M.G.; Pacifico, S.; Iannuzzi, F.; Mirto, A.; D’Amelia, L.; Dell’Aversana, E.; Piccolella, S.; Fuggi, A.; et al. Durum wheat seedling responses to simultaneous high light and salinity involve a fine reconfiguration of amino acids and carbohydrate metabolism. Physiol. Plant. 2017, 159, 290–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciarmiello, L.F.; Piccirillo, P.; Carillo, P.; De Luca, A.; Woodrow, P. Determination of the genetic relatedness of fig (Ficus carica L.) accessions using RAPD fingerprint and their agro-morphological characterization. South Afr. J. Bot. 2015, 97, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoora, M.D.; Babu, D.R.; Srividya, N. Nutrient composition, oxalate content and nutritional ranking of ten culinary microgreens. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriacou, M.C.; El-Nakhel, C.; Graziani, G.; Pannico, A.; Soteriou, G.A.; Giordano, M.; Ritieni, A.; De Pascale, S.; Rouphael, Y. Functional quality in novel food sources: Genotypic variation in the nutritive and phytochemical composition of thirteen microgreens species. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.J.; Llort, K.F.; Pill, W.G. Factors affecting the growth of microgreen table beet. Int. J. Veg. Sci. 2010, 16, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, E.R.; Luo, Y.; Buchanan, R.L. Microgreen nutrition, food safety, and shelf life: A review. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 870–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, C.J.; Pill, W.G. Cultural practices to speed the growth of microgreen arugula (roquette; Eruca vesicaria subsp. sativa). J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nakhel, C.; Pannico, A.; Graziani, G.; Giordano, M.; Kyriacou, M.C.; Ritieni, A.; De Pascale, S.; Rouphael, Y. Mineral and Antioxidant Attributes of Petroselinum crispum at Different Stages of Ontogeny: Microgreens vs. Baby Greens. Agronomy 2021, 11, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, G.; Rouphael, Y. Biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucini, L.; Miras-Moreno, B.; Rouphael, Y.; Cardarelli, M.; Colla, G. Combining Molecular Weight Fractionation and Metabolomics to Elucidate the Bioactivity of Vegetal Protein Hydrolysates in Tomato Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Hernández, J.M.; Benítez-García, I.; Mazorra-Manzano, M.A.; Ramírez-Suárez, J.C.; Sánchez, E. Strategies for production, characterization and application of protein-based biostimulants in agriculture: A review. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 80, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, G.; Nardi, S.; Cardarelli, M.; Ertani, A.; Lucini, L.; Canaguier, R.; Rouphael, Y. Protein hydrolysates as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, D.M.; Beaulieu, J.C.; Shewfelt, R. Color, flavor, texture, and nutritional quality of fresh-cut fruits and vegetables: Desirable levels, instrumental and sensory measurement, and the effects of processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 50, 369–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Cunha, N.M.; Georgousopoulou, E.N.; Dadigamuwage, L.; Kellett, J.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Thomas, J.; McKune, A.J.; Mellor, D.D.; Naumovski, N. Effect of long-term nutraceutical and dietary supplement use on cognition in the elderly: A 10-year systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 280–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, H.E.; Azlan, A.; Tang, S.T.; Lim, S.M. Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: Colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1361779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padayatty, S.J.; Katz, A.; Wang, Y.; Eck, P.; Kwon, O.; Lee, J.-H.; Chen, S.; Corpe, C.; Dutta, A.; Dutta, S.K. Vitamin C as an antioxidant: Evaluation of its role in disease prevention. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2003, 22, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, H.W.; Leenhardt, F.; Coudray, C.; Remesy, C. Minerals and phytic acid interactions: Is it a real problem for human nutrition? Int. J. food Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Lester, G.E.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Assessment of Vitamin and Carotenoid Concentrations of Emerging Food Products: Edible Microgreens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7644–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USDA (United State Departement of Agriculture). Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/ (accessed on 30 July 2021).
- Regulation (EC) No. 1924/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 December 2016 on nutritional and health claims made on foods. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 49, 9–25.
- Hord, N.G.; Tang, Y.; Bryan, N.S. Food sources of nitrates and nitrites: The physiologic context for potential health benefits. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, G.; Kim, H.J.; Kyriacou, M.C.; Rouphael, Y. Nitrate in fruits and vegetables. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 237, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Codling, E.E.; Luo, Y.; Nou, X.; Lester, G.E.; Wang, Q. Microgreens of Brassicaceae: Mineral composition and content of 30 varieties. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 49, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyriacou, M.C.; El-Nakhel, C.; Pannico, A.; Graziani, G.; Soteriou, G.A.; Giordano, M.; Zarrelli, A.; Ritieni, A.; De Pascale, S.; Rouphael, Y. Genotype-Specific Modulatory Effects of Select Spectral Bandwidths on the Nutritive and Phytochemical Composition of Microgreens. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colla, G.; Rouphael, Y.; Canaguier, R.; Svecova, E.; Cardarelli, M. Biostimulant action of a plant-derived protein hydrolysate produced through enzymatic hydrolysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G.; Giordano, M.; El-Nakhel, C.; Kyriacou, M.C.; De Pascale, S. Foliar applications of a legume-derived protein hydrolysate elicit dose-dependent increases of growth, leaf mineral composition, yield and fruit quality in two greenhouse tomato cultivars. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 226, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howitt, S.M.; Udvardi, M.K. Structure, function and regulation of ammonium transporters in plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2000, 1465, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theobald, H.E. Dietary Calcium and Health; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- De la Fuente, B.; López-García, G.; Máñez, V.; Alegría, A.; Barberá, R.; Cilla, A. Evaluation of the bioaccessibility of antioxidant bioactive compounds and minerals of four genotypes of Brassicaceae microgreens. Foods 2019, 8, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gharibzahedi, S.M.T.; Jafari, S.M. The importance of minerals in human nutrition: Bioavailability, food fortification, processing effects and nanoencapsulation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 62, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tränkner, M.; Tavakol, E.; Jákli, B. Functioning of potassium and magnesium in photosynthesis, photosynthate translocation and photoprotection. Physiol. Plant. 2018, 163, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renna, M.; Castellino, M.; Leoni, B.; Paradiso, V.M.; Santamaria, P. Microgreens production with low potassium content for patients with impaired kidney function. Nutrients 2018, 10, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, M.; Scholl, U.I.; Yue, P.; Björklund, P.; Zhao, B.; Nelson-Williams, C.; Ji, W.; Cho, Y.; Patel, A.; Men, C.J.; et al. K+ channel mutations in adrenal aldosterone-producing adenomas and hereditary hypertension. Science 2011, 331, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavaiuolo, M.; Cocetta, G.; Bulgari, R.; Spinardi, A.; Ferrante, A. Identification of innovative potential quality markers in rocket and melon fresh-cut produce. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradiso, V.M.; Castellino, M.; Renna, M.; Gattullo, C.E.; Calasso, M.; Terzano, R.; Allegretta, I.; Leoni, B.; Caponio, F.; Santamaria, P. Nutritional characterization and shelf-life of packaged microgreens. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5629–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Z.; Lester, G.E.; Park, E.; Saftner, R.A.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Evaluation and correlation of sensory attributes and chemical compositions of emerging fresh produce: Microgreens. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2015, 110, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatments | L* | a* | b* | Chroma | Hue Angle | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microgreen species | ||||||
| Carrot | 33.90 ± 0.18 | −10.75 ± 0.32 | 33.98 ± 1.72 | 35.64 ± 1.73 | 107.6 ± 0.40 | |
| Dill | 37.88 ± 0.60 | −8.39 ± 0.06 | 27.44 ± 0.52 | 28.70 ± 0.52 | 106.9 ± 0.26 | |
| Biostimulant | ||||||
| Control | 36.37 ± 1.18 | −9.29 ± 0.37 | 29.38 ± 0.41 | 30.82 ± 0.50 | 107.4 ± 0.48 | |
| PH | 35.41 ± 0.70 | −9.84 ± 0.70 | 32.04 ± 2.58 | 33.52 ± 2.67 | 107.1 ± 0.19 | |
| Microgreen species | Biostimulant | |||||
| Carrot | Control | 33.79 ± 0.13 c | −10.08 ± 0.23 b | 30.18 ± 0.44 b | 31.82 ± 0.49 b | 108.5 ± 0.16 a |
| PH | 34.01 ± 0.36 c | −11.41 ± 0.15 c | 37.78 ± 0.45 a | 39.47 ± 0.43 a | 106.8 ± 0.26 c | |
| Dill | Control | 38.94 ± 0.55 a | −8.49 ± 0.03 a | 28.57 ± 0.08 c | 29.82 ± 0.09 c | 106.4 ± 0.21 c |
| PH | 36.82 ± 0.59 b | −8.28 ± 0.05 a | 26.30 ± 0.27 d | 27.58 ± 0.27 d | 107.5 ± 0.09 b | |
| Source of variance | (p-value) | |||||
| Microgreen species | *** | *** | ** | ** | ns | |
| Biostimulant | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Microgreen species × Biostimulant | * | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| Treatments | Total Chlorophylls | Carotenoids | Chlorophyll a/b Ratio | Chlorophylls/Carotenoids Ratio | Anthocyanins | Total Ascorbic Acid | Total Phenols | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg g−1 fw) | (mg g−1 fw) | (mg 100 g−1 fw) | (mg AA 100 g−1 fw) | (mg gallic a. eq. 100 g−1 dw) | ||||
| Microgreen species | ||||||||
| Carrot | 1.146 ± 0.101 | 0.316 ± 0.011 | 1.94 ± 0.044 | 3.60 ± 0.20 | 10.35 ± 3.26 | 70.35 ± 3.81 | 4.11 ± 0.13 | |
| Dill | 1.032 ± 0.083 | 0.316 ± 0.013 | 1.99 ± 0.059 | 3.24 ± 0.14 | 26.92 ± 2.31 | 137.8 ± 5.24 | 3.69 ± 0.19 | |
| Biostimulant | ||||||||
| Control | 0.893 ± 0.036 | 0.291 ± 0.008 | 2.08 ± 0.022 | 3.06 ± 0.06 | 17.40 ± 6.41 | 102.3 ± 11.28 | 3.99 ± 0.08 | |
| PH | 1.285 ± 0.042 | 0.340 ± 0.001 | 1.85 ± 0.010 | 3.78 ± 0.13 | 19.87 ± 1.27 | 105.9 ± 19.21 | 3.81 ± 0.25 | |
| Microgreen species | Biostimulant | |||||||
| Carrot | Control | 0.927 ± 0.041 | 0.292 ± 0.007 | 2.03 ± 0.015 | 3.18 ± 0.06 | 3.13 ± 0.65 d | 77.68 ± 4.31 c | 3.87 ± 0.14 b |
| PH | 1.365 ± 0.040 | 0.340 ± 0.002 | 1.84 ± 0.014 | 4.02 ± 0.12 | 17.58 ± 0.71 c | 63.01 ± 0.57 d | 4.35 ± 0.07 a | |
| Dill | Control | 0.859 ± 0.059 | 0.291 ± 0.017 | 2.12 ± 0.017 | 2.95 ± 0.04 | 31.67 ± 1.29 a | 126.9 ± 3.48 b | 4.10 ± 0.01 ab |
| PH | 1.205 ± 0.030 | 0.340 ± 0.001 | 1.86 ± 0.014 | 3.54 ± 0.10 | 22.16 ± 1.53 b | 148.8 ± 2.34 a | 3.27 ± 0.11 c | |
| Source of variance | (p-value) | |||||||
| Microgreen species | ns | ns | ns | ns | ** | *** | ns | |
| Biostimulant | *** | *** | *** | *** | ns | ns | ns | |
| Microgreen species × Biostimulant | ns | ns | ns | ns | *** | *** | *** | |
| Treatments | Nitrate (mg kg−1 fw) | P (mg g−1 dw) | K (mg g−1 dw) | Ca (mg g−1 dw) | Mg (mg g−1 dw) | S (mg g−1 dw) | Na (mg g−1 dw) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microgreen species | ||||||||
| Carrot | 602.7 ± 7.21 | 2.51 ± 0.10 | 10.18 ± 0.32 | 7.77 ± 0.16 | 2.58 ± 0.14 | 2.91 ± 0.25 | 0.50 ± 0.02 | |
| Dill | 252.4 ± 28.12 | 2.70 ± 0.08 | 14.87 ± 0.36 | 7.33 ± 0.33 | 3.80 ± 0.21 | 2.28 ± 0.19 | 1.10 ± 0.03 | |
| Biostimulant | ||||||||
| Control | 402.3 ± 94.99 | 2.80 ± 0.05 | 13.10 ± 1.11 | 7.03 ± 0.19 | 3.21 ± 0.43 | 2.12 ± 0.12 | 0.82 ± 0.13 | |
| PH | 452.7 ± 61.97 | 2.41 ± 0.06 | 11.96 ± 1.03 | 8.06 ± 0.10 | 3.17 ± 0.18 | 3.07 ± 0.18 | 0.78 ± 0.14 | |
| Microgreen species | Biostimulant | |||||||
| Carrot | Control | 614.4 ± 10.85 a | 2.72 ± 0.02 | 10.66 ± 0.45 | 7.41 ± 0.02 b | 2.31 ± 0.03 c | 2.37 ± 0.08 | 0.53 ± 0.02 |
| PH | 591.0 ± 2.35 a | 2.29 ± 0.02 | 9.71 ± 0.29 | 8.12 ± 0.08 a | 2.85 ± 0.14 bc | 3.45 ± 0.10 | 0.46 ± 0.01 | |
| Dill | Control | 190.3 ± 4.58 c | 2.87 ± 0.07 | 15.53 ± 0.25 | 6.65 ± 0.16 c | 4.11 ± 0.30 a | 1.88 ± 0.11 | 1.11 ± 0.04 |
| PH | 314.5 ± 8.69 b | 2.53 ± 0.04 | 14.22 ± 0.39 | 8.01 ± 0.21 a | 3.48 ± 0.19 ab | 2.69 ± 0.11 | 1.09 ± 0.04 | |
| Source of variance | (p-value) | |||||||
| Microgreen species | *** | ns | *** | ns | *** | ns | *** | |
| Biostimulant | ns | *** | ns | *** | ns | ** | ns | |
| Microgreen species × Biostimulant | *** | ns | ns | * | * | ns | ns | |
| Treatments | Starch (mg g−1 dw) | Glucose (mg g−1 dw) | Fructose (mg g−1 dw) | Sucrose (mg g−1 dw) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microgreen species | |||||
| Carrot | 31.97 ± 2.05 | 118.8 ± 1.76 | 21.96 ± 0.28 | 1.88 ± 0.08 | |
| Dill | 54.16 ± 2.63 | 100.4 ± 1.35 | 36.79 ± 0.83 | 3.58 ± 0.13 | |
| Biostimulant | |||||
| Control | 47.23 ± 5.23 | 106.6 ± 3.87 | 30.42 ± 3.60 | 2.58 ± 0.39 | |
| PH | 38.90 ± 5.10 | 112.6 ± 4.48 | 28.33 ± 3.06 | 2.89 ± 0.39 | |
| Microgreen species | Biostimulant | ||||
| Carrot | Control | 36.28 ± 0.95 | 115.2 ± 0.45 | 22.40 ± 0.34 | 1.75 ± 0.12 |
| PH | 27.66 ± 1.27 | 122.4 ± 1.46 | 21.52 ± 0.28 | 2.02 ± 0.02 | |
| Dill | Control | 58.18 ± 4.02 | 98.04 ± 1.14 | 38.44 ± 0.55 | 3.41 ± 0.22 |
| PH | 50.15 ± 1.50 | 102.8 ± 1.44 | 35.13 ± 0.63 | 3.76 ± 0.10 | |
| Source of variance | (p-value) | ||||
| Microgreen species | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| Biostimulant | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Microgreen species × Biostimulant | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Compounds | Microgreen Species | Biostimulant | Microgreen Species × Biostimulant | ANOVA | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carrot | Dill | t-Test | Control | PH | t-Test | Carrot | Dill | ||||
| Control | PH | Control | PH | ||||||||
| Soluble proteins | 43.05 ± 2.35 | 43.24 ± 1.42 | ns | 39.11 ± 0.89 | 47.18 ± 0.51 | *** | 38.01 ± 1.48 | 48.10 ± 0.24 | 40.21 ± 0.71 | 46.26 ± 0.65 | ns |
| Ala | 4.28 ± 0.16 | 3.50 ± 0.33 | ns | 3.81 ± 0.30 | 3.96 ± 0.32 | ns | 4.27 ± 0.10 | 4.28 ± 0.34 | 3.35 ± 0.47 | 3.65 ± 0.55 | ns |
| Arg | 1.80 ± 0.12 | 1.67 ± 0.07 | ns | 1.70 ± 0.07 | 1.77 ± 0.13 | ns | 1.59 ± 0.08 b | 2.01 ± 0.14 a | 1.82 ± 0.05 ab | 1.53 ± 0.06 b | ** |
| Asn | 38.63 ± 3.97 | 23.74 ± 2.32 | ** | 24.25 ± 2.59 | 38.11 ± 4.17 | * | 29.84 ± 1.18 b | 47.41 ± 0.29 a | 18.66 ± 0.91 c | 28.81 ± 0.60 b | *** |
| Asp | 5.84 ± 0.48 | 3.66 ± 0.37 | ** | 5.52 ± 0.64 | 3.97 ± 0.44 | ns | 6.78 ± 0.44 | 4.89 ± 0.27 | 4.27 ± 0.50 | 3.05 ± 0.23 | ns |
| GABA | 14.34 ± 0.38 | 15.24 ± 0.47 | ns | 14.40 ± 0.43 | 15.19 ± 0.44 | ns | 13.83 ± 0.61 | 14.86 ± 0.28 | 14.96 ± 0.46 | 15.52 ± 0.89 | ns |
| Gln | 27.95 ± 0.55 | 31.10 ± 2.23 | ns | 27.83 ± 0.60 | 31.22 ± 2.18 | ns | 28.86 ± 0.36 b | 27.04 ± 0.74 b | 26.80 ± 0.78 b | 35.40 ± 2.39 a | * |
| Glu | 4.56 ± 0.33 | 1.26 ± 0.12 | *** | 3.18 ± 0.91 | 2.64 ± 0.60 | ns | 5.16 ± 0.40 a | 3.96 ± 0.16 b | 1.20 ± 0.19 c | 1.32 ± 0.19 c | * |
| Gly | 1.99 ± 0.11 | 1.27 ± 0.11 | *** | 1.66 ± 0.16 | 1.60 ± 0.23 | ns | 1.88 ± 0.20 | 2.09 ± 0.11 | 1.43 ± 0.17 | 1.11 ± 0.07 | ns |
| His | 1.49 ± 0.06 | 0.87 ± 0.03 | *** | 1.17 ± 0.13 | 1.20 ± 0.17 | ns | 1.44 ± 0.03 | 1.54 ± 0.13 | 0.89 ± 0.05 | 0.85 ± 0.04 | ns |
| Ile | 2.18 ± 0.19 | 1.78 ± 0.15 | ns | 1.62 ± 0.09 | 2.34 ± 0.13 | *** | 1.81 ± 0.07 | 2.55 ± 0.20 | 1.43 ± 0.03 | 2.12 ± 0.03 | ns |
| Leu | 1.66 ± 0.07 | 1.30 ± 0.10 | * | 1.33 ± 0.08 | 1.63 ± 0.12 | ns | 1.50 ± 0.02 | 1.82 ± 0.03 | 1.15 ± 0.00 | 1.44 ± 0.18 | ns |
| Lys | 0.529 ± 0.037 | 0.597 ± 0.045 | ns | 0.499 ± 0.021 | 0.627 ± 0.043 | * | 0.453 ± 0.003 | 0.605 ± 0.035 | 0.544 ± 0.012 | 0.649 ± 0.086 | ns |
| MEA | 2.62 ± 0.13 | 2.47 ± 0.26 | ns | 2.55 ± 0.23 | 2.54 ± 0.19 | ns | 2.69 ± 0.19 | 2.55 ± 0.21 | 2.40 ± 0.45 | 2.53 ± 0.36 | ns |
| Met | 0.254 ± 0.010 | 0.241 ± 0.016 | ns | 0.262 ± 0.007 | 0.233 ± 0.016 | ns | 0.261 ± 0.015 | 0.248 ± 0.016 | 0.262 ± 0.003 | 0.219 ± 0.030 | ns |
| Orn | 1.10 ± 0.05 | 0.85 ± 0.15 | ns | 1.12 ± 0.11 | 0.83 ± 0.11 | ns | 1.13 ± 0.06 | 1.06 ± 0.08 | 1.10 ± 0.23 | 0.60 ± 0.05 | ns |
| Phe | 0.89 ± 0.08 | 0.52 ± 0.04 | ** | 0.60 ± 0.06 | 0.81 ± 0.11 | ns | 0.72 ± 0.05 b | 1.06 ± 0.02 a | 0.47 ± 0.01 c | 0.57 ± 0.06 c | * |
| Pro | 3.33 ± 0.27 | 3.79 ± 0.33 | ns | 3.06 ± 0.16 | 4.05 ± 0.28 | * | 2.88 ± 0.11 | 3.79 ± 0.39 | 3.25 ± 0.29 | 4.32 ± 0.41 | ns |
| Ser | 4.54 ± 0.32 | 3.43 ± 0.38 | * | 4.05 ± 0.52 | 3.93 ± 0.31 | ns | 5.10 ± 0.30 | 3.99 ± 0.33 | 3.00 ± 0.39 | 3.86 ± 0.61 | ns |
| Thr | 0.836 ± 0.08 | 0.647 ± 0.08 | ns | 0.590 ± 0.05 | 0.893 ± 0.06 | ** | 0.699 ± 0.02 | 0.974 ± 0.11 | 0.481 ± 0.02 | 0.813 ± 0.01 | ns |
| Trp | 0.557 ± 0.04 | 0.571 ± 0.04 | ns | 0.528 ± 0.02 | 0.599 ± 0.04 | ns | 0.499 ± 0.03 | 0.614 ± 0.06 | 0.557 ± 0.02 | 0.584 ± 0.08 | ns |
| Tyr | 2.04 ± 0.11 | 1.81 ± 0.21 | ns | 1.76 ± 0.15 | 2.09 ± 0.17 | ns | 1.96 ± 0.17 | 2.11 ± 0.17 | 1.55 ± 0.21 | 2.07 ± 0.34 | ns |
| Val | 3.72 ± 0.34 | 2.99 ± 0.15 | ns | 3.10 ± 0.08 | 3.61 ± 0.40 | ns | 2.96 ± 0.08 bc | 4.48 ± 0.03 a | 3.23 ± 0.08 b | 2.75 ± 0.23 c | *** |
| Essential AA | 13.92 ± 0.91 | 11.18 ± 0.21 | * | 11.39 ± 0.31 | 13.71 ± 1.00 | * | 11.94 ± 0.36 b | 15.90 ± 0.33 a | 10.84 ± 0.22 c | 11.52 ± 0.23 bc | ** |
| BCAAs | 7.56 ± 0.59 | 6.06 ± 0.13 | * | 6.04 ± 0.13 | 7.58 ± 0.58 | * | 6.27 ± 0.16 b | 8.85 ± 0.23 a | 5.82 ± 0.11 b | 6.31 ± 0.11 b | *** |
| Total AA | 125.1 ± 4.14 | 103.3 ± 4.82 | ** | 104.6 ± 5.50 | 123.9 ± 4.54 | * | 116.3 ± 2.70 | 133.9 ± 0.72 | 92.82 ± 2.44 | 113.8 ± 0.77 | ns |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Nakhel, C.; Ciriello, M.; Formisano, L.; Pannico, A.; Giordano, M.; Gentile, B.R.; Fusco, G.M.; Kyriacou, M.C.; Carillo, P.; Rouphael, Y. Protein Hydrolysate Combined with Hydroponics Divergently Modifies Growth and Shuffles Pigments and Free Amino Acids of Carrot and Dill Microgreens. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7090279
El-Nakhel C, Ciriello M, Formisano L, Pannico A, Giordano M, Gentile BR, Fusco GM, Kyriacou MC, Carillo P, Rouphael Y. Protein Hydrolysate Combined with Hydroponics Divergently Modifies Growth and Shuffles Pigments and Free Amino Acids of Carrot and Dill Microgreens. Horticulturae. 2021; 7(9):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7090279
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Nakhel, Christophe, Michele Ciriello, Luigi Formisano, Antonio Pannico, Maria Giordano, Beniamino Riccardo Gentile, Giovanna Marta Fusco, Marios C. Kyriacou, Petronia Carillo, and Youssef Rouphael. 2021. "Protein Hydrolysate Combined with Hydroponics Divergently Modifies Growth and Shuffles Pigments and Free Amino Acids of Carrot and Dill Microgreens" Horticulturae 7, no. 9: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7090279
APA StyleEl-Nakhel, C., Ciriello, M., Formisano, L., Pannico, A., Giordano, M., Gentile, B. R., Fusco, G. M., Kyriacou, M. C., Carillo, P., & Rouphael, Y. (2021). Protein Hydrolysate Combined with Hydroponics Divergently Modifies Growth and Shuffles Pigments and Free Amino Acids of Carrot and Dill Microgreens. Horticulturae, 7(9), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7090279