Effect of Different Temperature Regimes on the Germination of Pseudolysimachion pusanensis (Y. N. Lee) Y. N. Lee Seeds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Collection and Seed Processing
2.2. Seed Morphology
2.3. Estimation of 1000-Seed Weight
2.4. Estimation of Initial Seed Moisture Content (MC)
2.5. Estimation of Total Protein Content
2.6. Total Crude Fat Extraction Using the Soxhlet Method
2.7. Germination Test and Index
2.8. Temperature Regimes
2.8.1. Experiment 1: Seven Constant Temperature Regimes
2.8.2. Experiment 2: Fifty-Nine Different Temperature Regimes
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Seed Morphology
3.2. Seed Characteristics
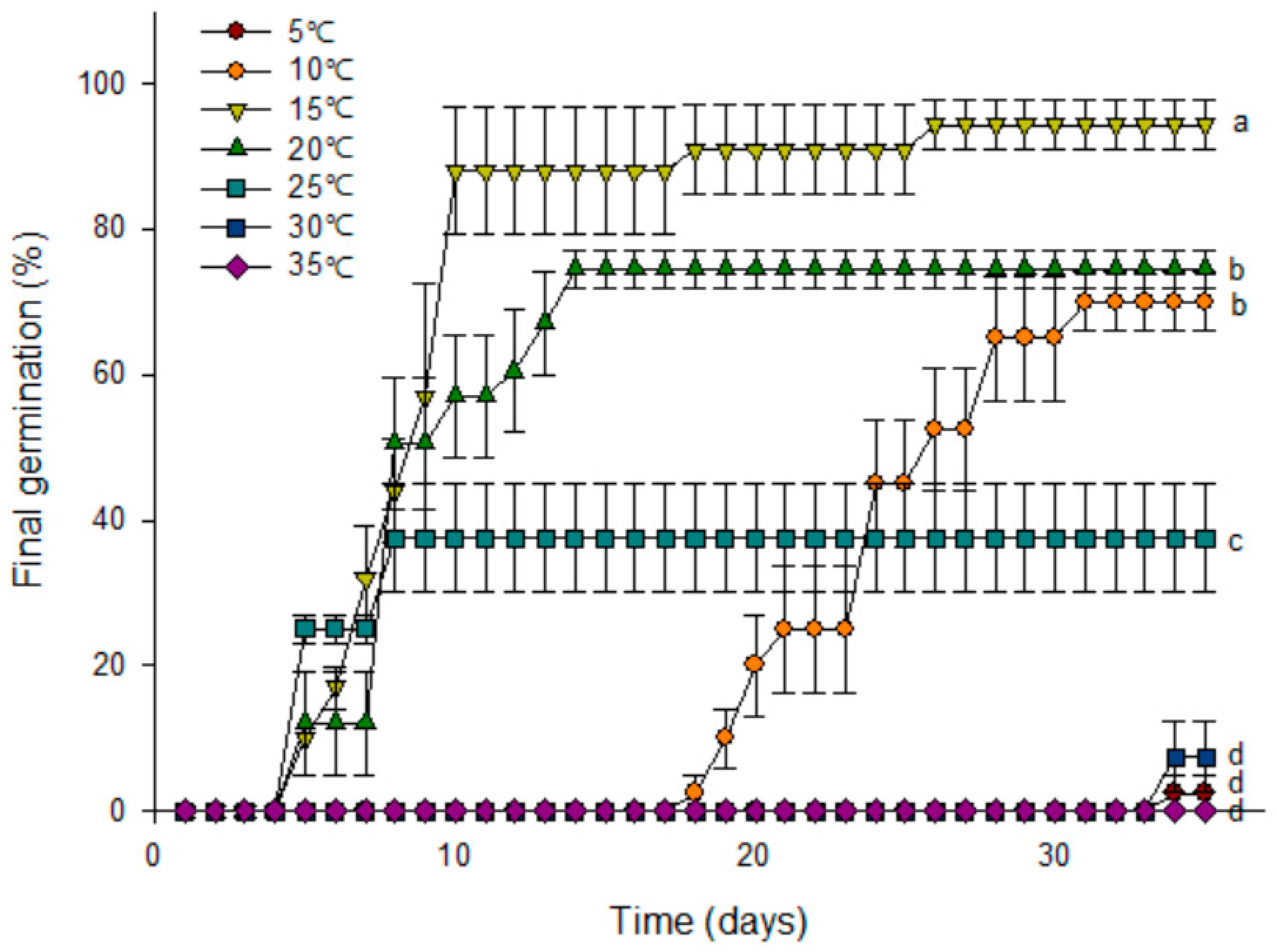
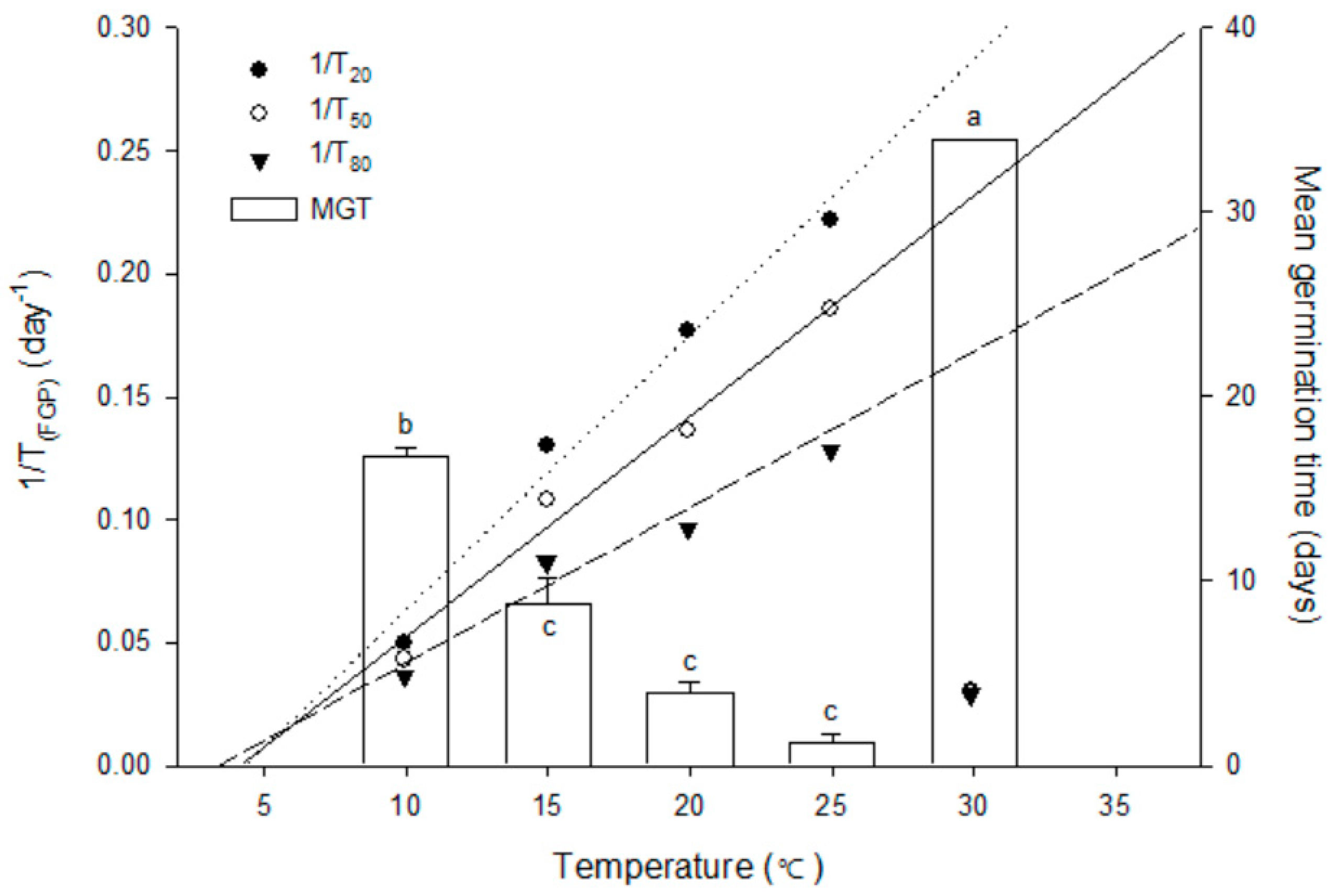
3.3. Constant Temperature Regimes
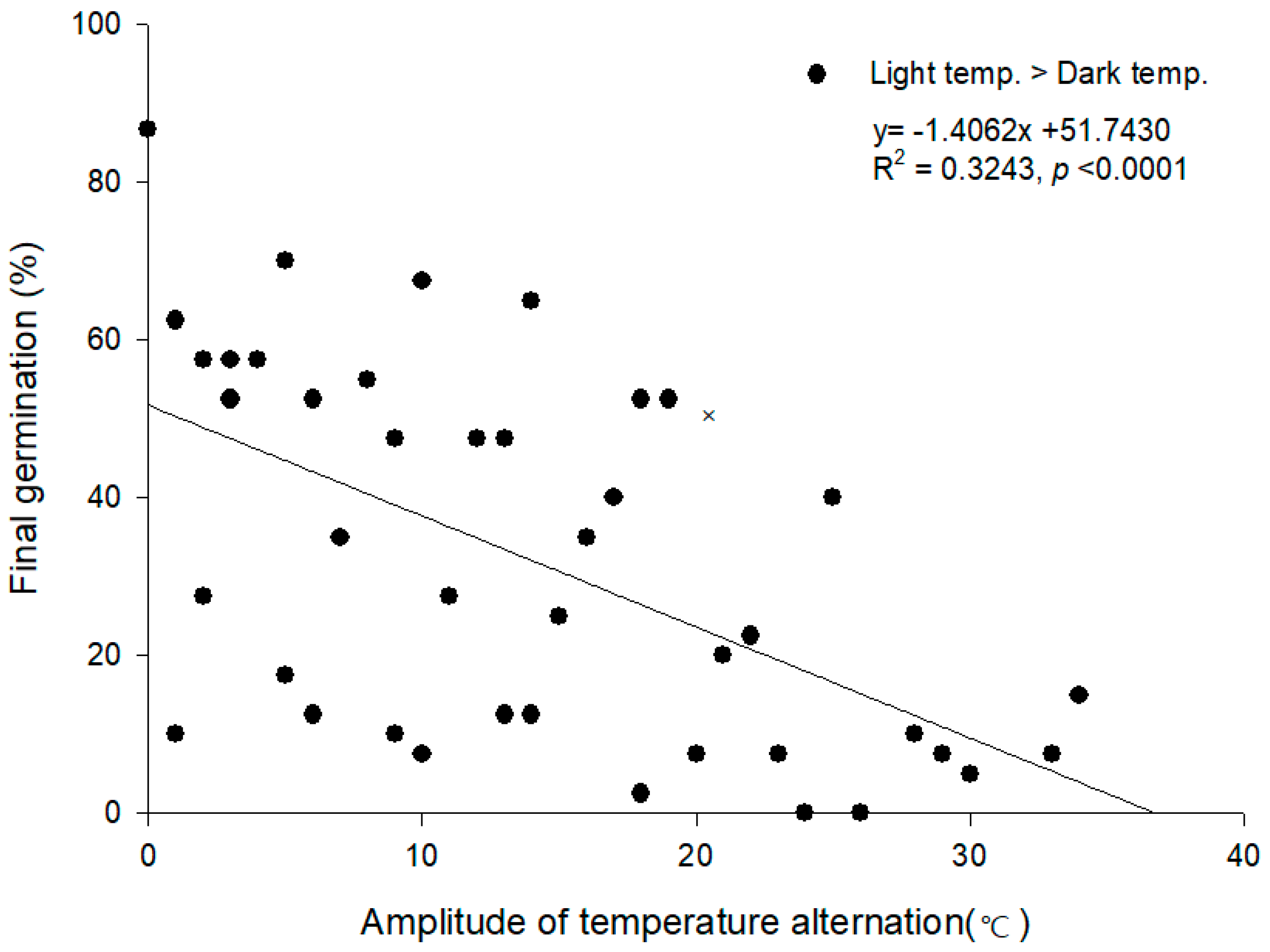
3.4. Alternating Temperature Regimes
4. Discussion
4.1. Seed Morphology and Characteristics
4.2. Temperature Regimes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albach, D.C.; Martínez-Ortega, M.M.; Chase, M.W. Veronica: Parallel morphological evolution and phylogeography in the Mediterranean. Plant Syst. Evol. 2004, 246, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albach, D.C.; Martínez-Ortega, M.M.; Delgado, L.; Weiss-Schneeweiss, H.; Özgökce, F.; Fischer, M.A. Chromosome numbers in Veroniceae (Plantaginaceae): Review and several new counts 1. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2008, 95, 543–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnock-Jones, P.; Albach, D.; Briggs, B.G. Botanical names in southern hemisphere Veronica (Plantaginaceae): Sect. Detzneria, sect. Hebe, and sect. Labiatoides. Taxon 2007, 56, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albach, D.C.; Meudt, H.M.; Oxelman, B. Piecing together the “new” Plantaginaceae. Am. J. Bot. 2005, 92, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosachev, P.; Mayland-Quellhorst, E.; Albach, D.C. Hybridization among species of Veronica subg. Pseudolysimachium in the Altai detected by SRAP markers. Nord. J. Bot. 2019, 37, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hawke, R.G. Comparative studies of Veronica and Veronicastrum. Plant Eval. Notes 2010, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.N. New taxa of Korean flora. Bull. Korea Plant Res. 2004, 4, 2–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.N. New plant names on flora of Korea, revised new ed. Bull. Korea Plant Res. 2005, 5, 40–64. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Forest Service. Korea Biodiversity Information System 2010. Available online: http://www.nature.go.kr/ (accessed on 28 October 2021).
- Song, S.J.; Shin, U.S.; Oh, H.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y. Seed germination responses and interspecific variations to different incubation temperatures in eight Veronica species native to Korea. Korean J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, H.J.; Shin, U.S.; Song, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Suh, G.U. Growth and flowering characteristics of 20 Veronica species. Flower Res. J. 2019, 27, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H. Growth and flowering responses of Korean native Veronica rotunda and Veronica longifolia to cold treatment and light conditions. Master’s Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, H.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Suh, G.U. Vegetative propagation of Veronica dahurica and Veronica pusanensis by stem cuttings with auxins. Rhizosphere 2021, 17, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, C.S.; Baek, S.G.; Yang, S.Y.; Park, C.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.H.; Park, Y.S. Species-specific seed vigor test of aging chive for restoration and regional adaptation under climate change. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2013, 18, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, F.R.; Probert, R.J. Advances in seed conservation of wild plant species: A review of recent research. Conserv. Physiol. 2013, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, C.; Laliberté, B.; Guarino, L. Trends in ex situ conservation of plant genetic resources: A review of global crop and regional conservation strategies. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2010, 57, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, D.J.; Dixon, K.W. Restoration seed banks—A matter of scale. Science 2011, 332, 424–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskin, C.C.; Baskin, J.M. Seeds: Ecology, Biogeography, and Evolution of Dormancy and Germination; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Donohue, K.; Rubio de Casas, R.; Burghardt, L.; Kovach, K.; Willis, C.G. Germination, postgermination adaptation, and species ecological ranges. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2010, 41, 293–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagmann, K.; Hautekèete, N.C.; Piquot, Y.; Meunier, C.; Schmitt, S.E.; Van Dijk, H. Seed dormancy distribution: Explanatory ecological factors. Ann. Bot. 2012, 110, 1205–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerin, J.; Thorpe, M.; Duval, D.; Jusaitis, M.; Ainsley, P. Germination of Veronica parnkalliana seeds in response to seasonal and fire cues. In Proceedings of the 5th Global Botanic Gardens Congress, Dunedin, New Zealand, 20–25 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, T.; Xian, M.; Khan, M.N.; Hu, L.; Xu, Z. Estimation of base temperature for germination of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) using different models. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2018, 20, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlla, D.; Benech-Arnold, R.L. A framework for the interpretation of temperature effects on dormancy and germination in seed populations showing dormancy. Seed Sci. Res. 2015, 25, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranal, M.A.; Santana, D.G.D. How and why to measure the germination process? Braz. J. Bot. 2006, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- International Seed Testing Association. International Rules for Seed Testing. Rules 1985. Seed Sci. Technol. 1985, 13, 299–513. [Google Scholar]
- International Seed Testing Association (ISTA). International Rules for Seed Testing 2015; The International Seed Testing Association: Bassersdorf, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC). Official Methods of Analysis AOAC International Methods 920.39; Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC): Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, R.H.; Roberts, E.H. The quantification of ageing and survival in orthodox seeds. Seed Sci. Technol. 1981, 9, 373–409. [Google Scholar]
- Coolbear, P.; Francis, A.; Grierson, D. The effect of low temperature pre-sowing treatment on the germination performance and membrane integrity of artificially aged tomato seeds. J. Exp. Bot. 1984, 35, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed Information Database: Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Available online: http://data.kew.org/sid/ (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Schopmeyer, C.S. Seeds of woody plants in the United States. In Agriculture Handbook; No. 450; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Penfield, S.; MacGregor, D.R. Effects of environmental variation during seed production on seed dormancy and germination. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, T.H.; Raper, C.D. Seed germinability as affected by the environmental temperature of the mother plant. Tob. Sci. 1975, 19, 98–100. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; MacGregor, D.R.; Dave, A.; Florance, H.; Moore, K.; Paszkiewicz, K.; Smirnoff, N.; Graham, I.A.; Penfield, S. Maternal temperature history activates Flowering Locus T in fruits to control progeny dormancy according to time of year. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18787–18792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.; Footitt, S.; Tang, A.; Finch-Savage, W.E. Predicted global warming scenarios impact on the mother plant to alter seed dormancy and germination behaviour in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bewley, J.D.; Black, M. Biochemistry of Seeds in Relation to Germination; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Vertucci, C.W.; Roos, E.E. Theoretical basis of protocols for seed storage. Plant Physiol. 1990, 94, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walters, C.; Engels, J. The effects of storing seeds under extremely dry conditions. Seed Sci. Res. 1998, 8, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rajjou, L.; Duval, M.; Gallardo, K.; Catusse, J.; Bally, J.; Job, C.; Job, D. Seed germination and vigor. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol 2012, 63, 507–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaban, M. Biochemical aspects of protein changes in seed physiology and germination. Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biomed. Res. 2013, 8, 885–898. [Google Scholar]
- Priestley, D.A. Seed Aging: Implications for Seed Storage and Persistence in the Soil; Comstock Associates: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Ponquett, R.T.; Smith, M.T.; Ross, G. Lipid autoxidation and seed ageing: Putative relationships between seed longevity and lipid stability. Seed Sci. Res. 1992, 2, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauss, M.J.; Venable, D.L. Seed germination in desert annuals: An empirical test of adaptive bet hedging. Am. Nat. 2000, 155, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venable, D.L. Bet hedging in a guild of desert annuals. Ecology 2007, 88, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.H.; Nam, K.W. Characteristics of seed germination in Heteropappus arenarius Kitam. native to Korea as influenced by temperature. Korean J. Plant Res. 2009, 22, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.H.; Jang, K.H.; Hur, S.D. Variation of seed and germination characteristics of natural populations of Abies koreana Wilson, a Korean endemic species. J. Korean Soc. For. Sci. 2010, 99, 849–854. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, S.C.; Gutterman, Y.; Evenari, M. The influence of the origin of the mother plant on yield and germination of their caryopses in Aegilops ovata. Planta 1972, 105, 155164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halloran, G.M.; Collins, W.J. Physiological predetermination of the order of hardseededness breakdown in subterranean clover (Trifolium subterraneum L.). Ann. Bot. 1974, 38, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsohn, R.; Globerson, D. Daucus carota (carrot) seed quality: I. Effects of seed size on germination, emergence and plant growth under subtropical conditions. II. The importance of the primary umbel in carrot-seed production. In Seed Production; Hebblethwaite, P.D., Ed.; Butterworths: London, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 637–646. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, M.-H.; Lim, J.-H.; Park, C.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Na, C.-S. Effect of Different Temperature Regimes on the Germination of Pseudolysimachion pusanensis (Y. N. Lee) Y. N. Lee Seeds. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7120577
Lee M-H, Lim J-H, Park C-H, Kim J-H, Na C-S. Effect of Different Temperature Regimes on the Germination of Pseudolysimachion pusanensis (Y. N. Lee) Y. N. Lee Seeds. Horticulturae. 2021; 7(12):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7120577
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Mi-Hyun, Jin-Hyun Lim, Cho-Hee Park, Jun-Hyeok Kim, and Chae-Sun Na. 2021. "Effect of Different Temperature Regimes on the Germination of Pseudolysimachion pusanensis (Y. N. Lee) Y. N. Lee Seeds" Horticulturae 7, no. 12: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7120577
APA StyleLee, M.-H., Lim, J.-H., Park, C.-H., Kim, J.-H., & Na, C.-S. (2021). Effect of Different Temperature Regimes on the Germination of Pseudolysimachion pusanensis (Y. N. Lee) Y. N. Lee Seeds. Horticulturae, 7(12), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7120577





