The Effects of Different Fertilization Practices in Combination with the Use of PGPR on the Sugar and Amino Acid Content of Asparagus officinalis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design and Cultivation Practices
2.3. Soil Analyses
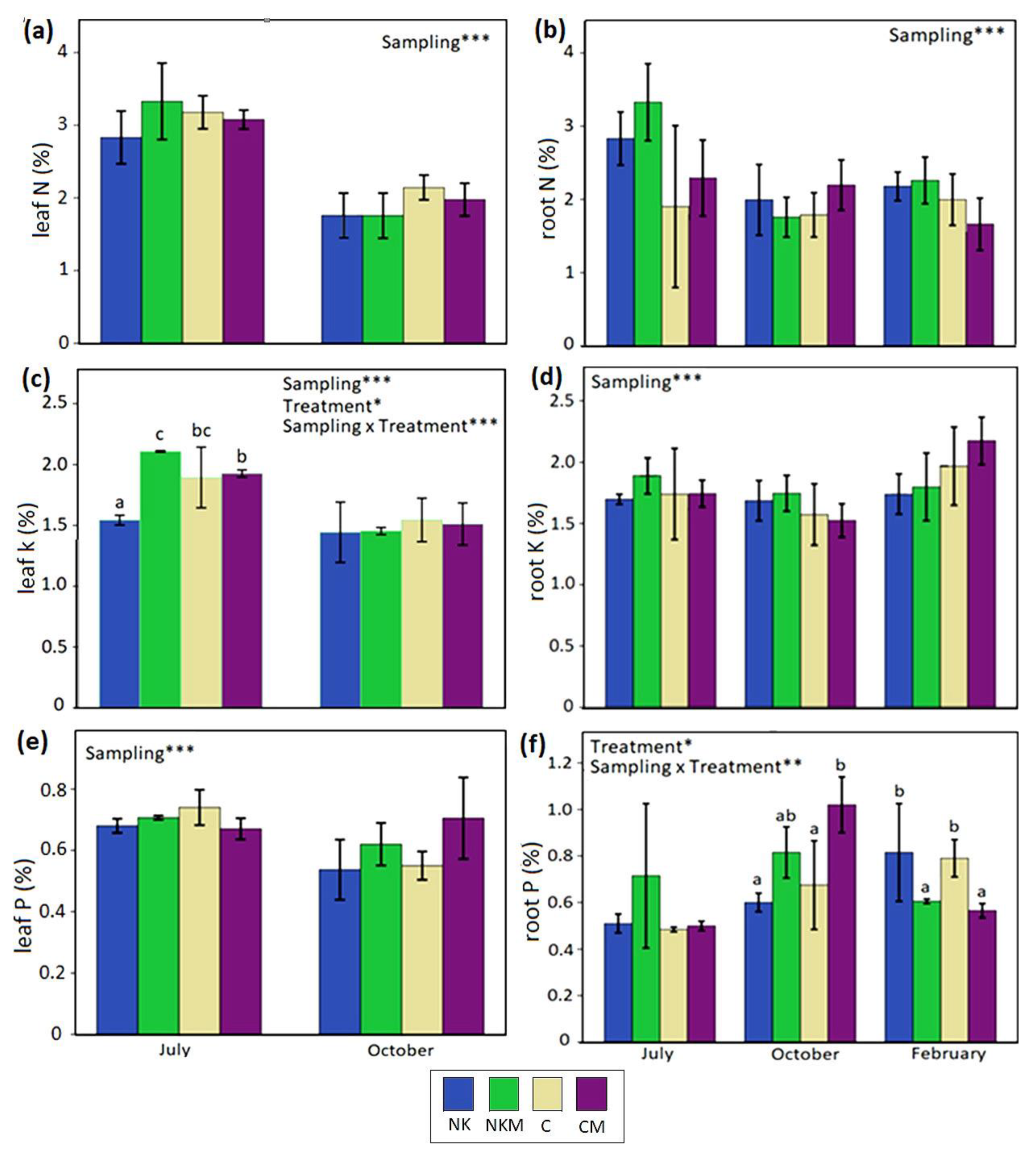
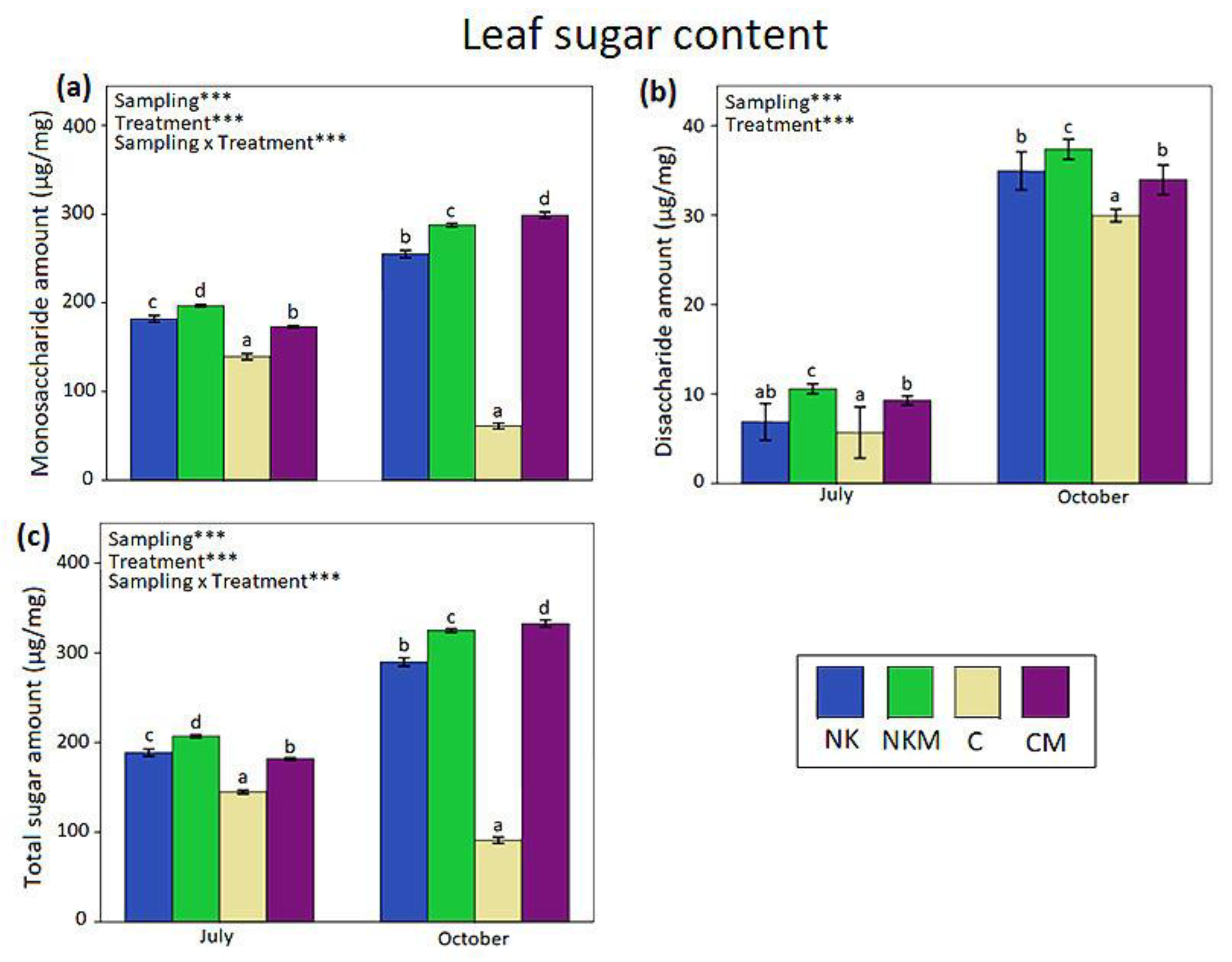
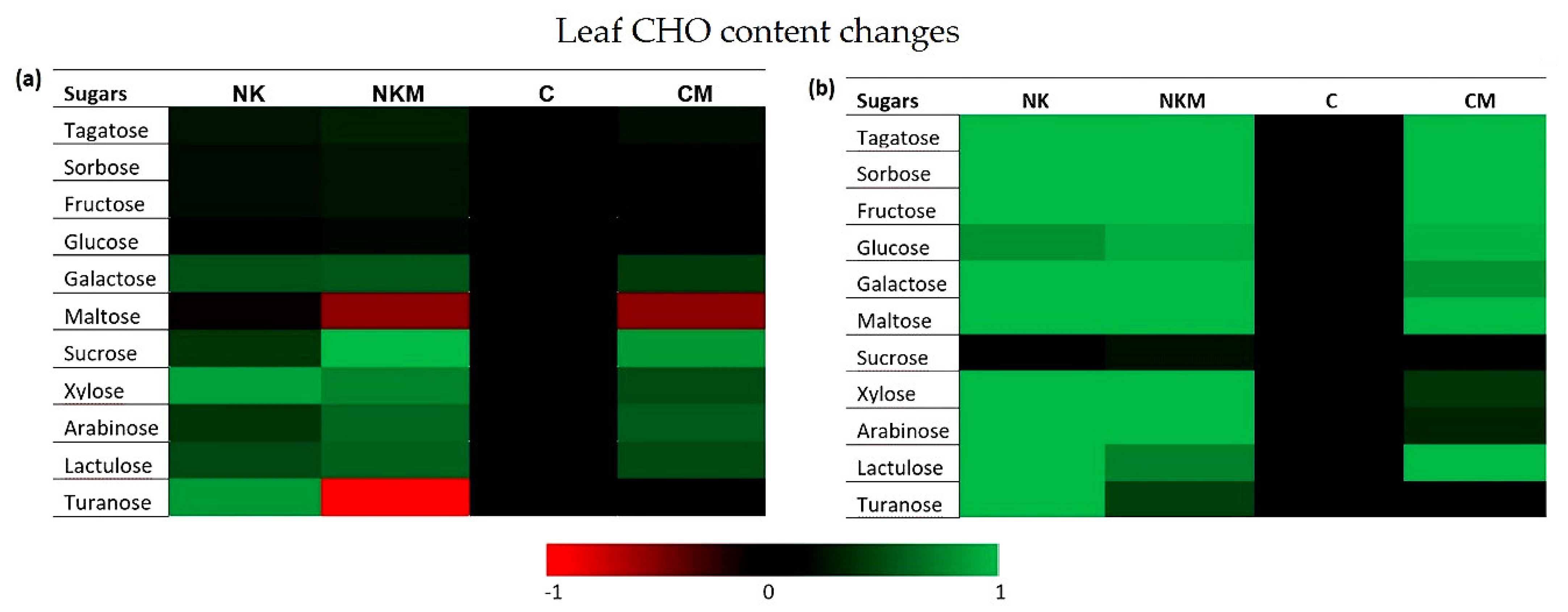
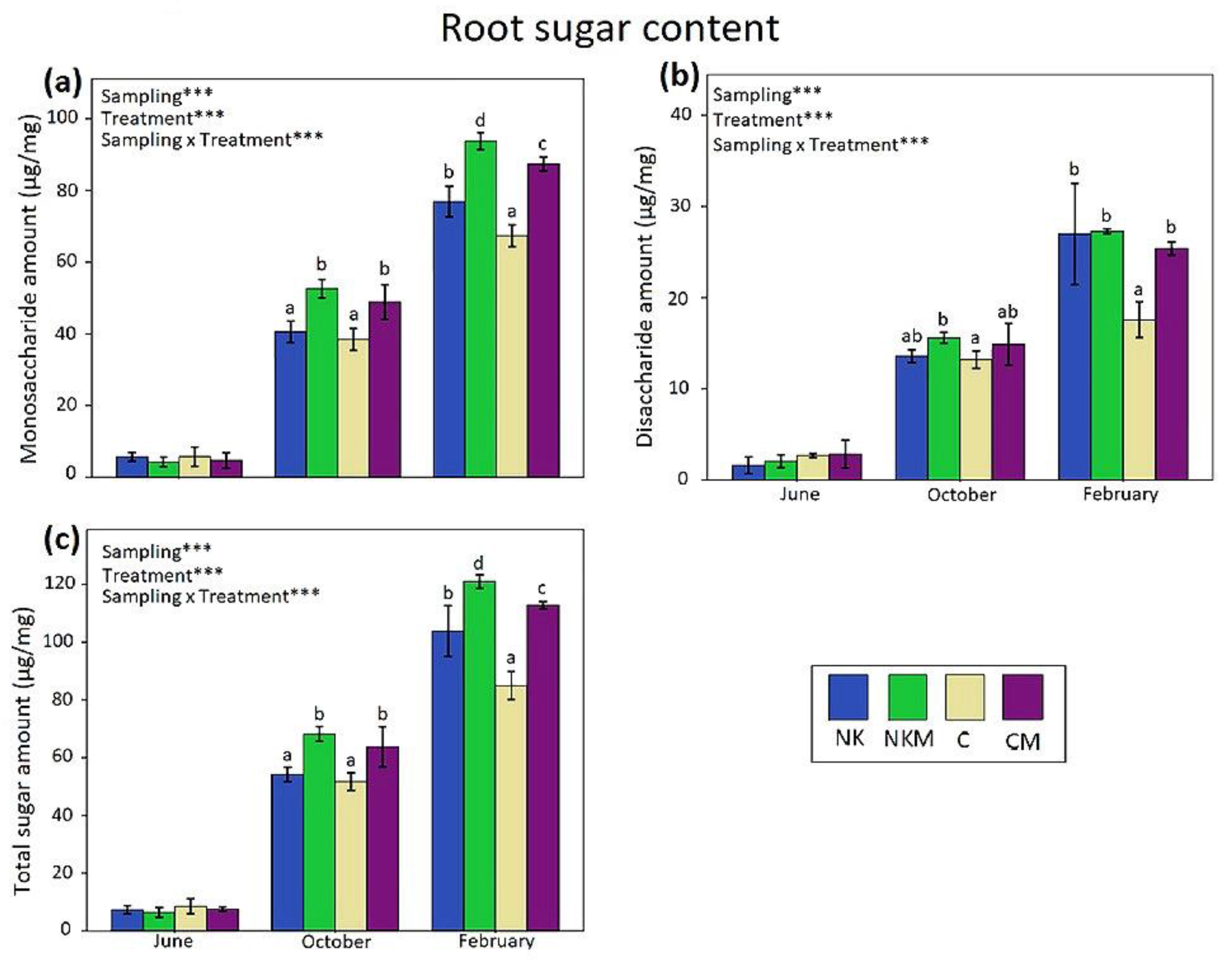
2.4. Plant Tissue Analyses
2.5. GC-MS Metabolite Profile Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
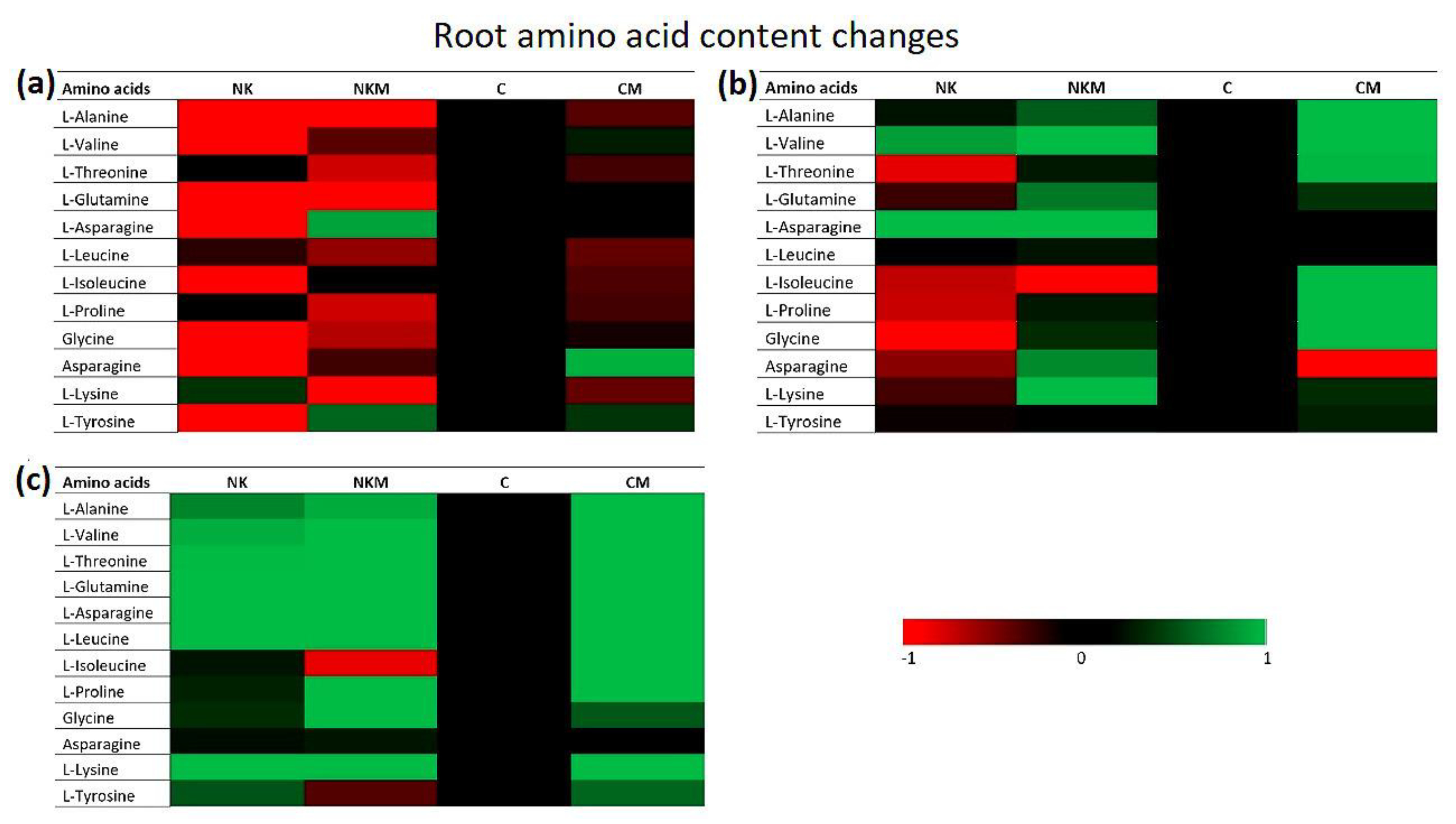
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pegiou, E.; Mumm, R.; Acharya, P.; de Vos, R.C.H.; Hall, R.D. Green and white Asparagus (Asparagus officinalis): A source of developmental, chemical and urinary intrigue. Metabolites 2020, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.R.; Sinton, S.M.; Butler, R.C.; Drost, D.T.; Paschold, P.J.; van Kruistum, G.; Poll, J.T.K.; Garcin, C.; Pertierra, R.; Vidal, I.; et al. Carbohydrates and yield physiology of asparagus—A global overview. Acta Hortic. 2008, 776, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifford, R.M.; Evans, L.T. Photosynthesis, carbon partitioning, and yield. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1981, 32, 485–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drost, D.T. Asparagus. In The Physiology of Vegetable Crops; CAB International: Wantage, UK, 1997; pp. 621–649. [Google Scholar]
- Fagard, M.; Launay, A.; Clement, G.; Courtial, J.; Dellagi, A.; Farjad, M.; Krapp, A.; Soulie, M.C.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. Nitrogen metabolism meets phytopathology. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 5643–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galili, G.; Avin-Wittenberg, T.; Angelovici, R.; Fernie, A.R. The role of photosynthesis and amino acid metabolism in the energy status during seed development. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratelli, R.; Pilot, G. Regulation of amino acid metabolic enzymes and transporters in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 5535–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baqir, H.A.; Zeboon, N.H.; Al-behadili, A.A.J. The role and importance of aminoacids within plants: A review. Plant Arch. 2019, 19, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Vijay, N.; Kumar, A.; Bhoite, A. Influence of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer on biochemical contents of Asparagus racemosus (Willd.) root tubers. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 3, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hossain, K.L.; Rahman, M.; Banu, M.A.; Khan, T.R.; Ali, M.S. Nitrogen fertilizer effects on the agronomic aspects of Asparagus racemosus. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2006, 5, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, D.C. Nitrogen-potassium interactions in asparagus. In IX International Asparagus Symposium; Acta Horticulturae: Washinghton, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 421–426. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, M.; Srinivasan, R.; Chaudhary, M.; Choudhary, M.; Jat, L.K. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) for sustainable agriculture: Perspectives and challenges. In PGPR Amelioration in Sustainable Agriculture; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 129–157. [Google Scholar]
- Swarnalakshmi, K.; Yadav, V.; Tyagi, D.; Dhar, D.W.; Kannepalli, A.; Kumar, S. Significance of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria in grain legumes: Growth, promotion and crop production. Plants 2020, 9, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.P.; Yadav, J.; Tiwari, K.N. Enhancement of nodulation and yield of chickpea by co-inoculation of indigenous Mesorhizobium spp. and plant growth–promoting rhizobacteria in eastern Uttar Pradesh. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2012, 43, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishraa, P.K.; Bishta, S.C.; Jeevanandana, K.; Kumara, S.; Bisht, J.K.; Bhatt, J.C. Synergistic effect of inoculating plant growth-promoting Pseudomonas spp. and Rhizobium leguminosarum-FB1 on growth and nutrient uptake of rajmash (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Agron. Soil Sci. 2014, 60, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, R.; Pal, K.K.; Bhatt, D.M.; Chauhan, S.M. Growth promotion and yield enhancement of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) by application of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Microbiol. Res. 2004, 159, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.K.; Bisht, S.C.; Ruwari, P.; Joshi, G.K.; Singh, G.; Bisht, J.K.; Bhatt, J.C. Bioassociative effect of cold tolerant Pseudomonas spp. and Rhizobium leguminosarum-PR1 on iron acquisition, nutrient uptake and growth of lentil (Lens culinaris L.). Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2011, 47, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Frankenberger, W.T., Jr. Plant growth-regulating substances in the rhizosphere: Microbial production and functions. Adv. Agron. 1997, 62, 45–151. [Google Scholar]
- Teale, W.D.; Paponov, I.A.; Palme, K. Auxin in action: Signalling, transport and the control of plant growth and development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Radnezhad, H.; Abari, M.F.; Sadeghi, M.; Kashi, G. Effect of biofertilizers and plant growth promoting bacteria on the growth characteristics of the herb Asparagus officinalis. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2016, 14, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddycoat, S.M.; Greenberg, B.M.; Wolyn, D.J. The effect of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on asparagus seedlings and germinating seeds subjected to water stress under greenhouse conditions. Can. J. Microbiol. 2009, 55, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesemoye, A.O.; Torbert, H.A.; Kloepper, J.W. Enhanced plant nutrient use efficiency with PGPR and AMF in an integrated nutrient management system. Can. J. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymak, H.C. Potential of PGPR in agricultural innovations. In Plant Growth and Health Promoting Bacteria. Microbiology Monographs; Maheshwari, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Drost, D. High phosphorus applications at planting improve asparagus root growth and yield. In XI International Asparagus Symposium; Acta Horticulturae: Washinghton, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Mehboob, I.; Naveed, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Ashraf, M. Potential of rhizobia for sustainable production of non-legumes. In Crop Production for Agricultural Improvement; Ashraf, M., Öztürk, M., Ahmad, M., Aksoy, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bradstreet, R.B. Kjeldahl method for organic nitrogen. Anal. Chem. 1954, 26, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E. Chemical Analysis of Ecological Materials; Blackwell Scientific Publishing: Oxford, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; Mavromatis, A. Banana cultivars, cultivation practices, and physicochemical properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, A.; Landing, W.; Bizimis, M.; Morton, P. Determination of Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in seawater using high resolution magnetic sector inductively coupled mass spectrometry (HR-ICP-MS). Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 665, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainalidou, A.; Tanou, G.; Belghazi, M.; Samiotaki, M.; Diamantidis, G.; Molassiotis, A.; Karamanoli, K. Integrated analysis of metabolites and proteins reveal aspects of the tissue-specific function of synthetic cytokinin in kiwifruit development and ripening. J. Proteom. 2016, 143, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Escobar, R.; Moreno, R.; Garcıa-Creus, M. Seasonal changes of mineral nutrients in olive leaves during the alternate-bearing cycle. Sci. Hortic. 1999, 82, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Rojas, R.; Amaro-Lopez, M.A.; Zurera-Cosano, G. Mineral elements distribution in fresh asparagus. J. Food Compos. Anal. 1992, 5, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, H.; Kailuweit, D. Is asparagus cultivation dangerous to the environment? Nitrogen balance of asparagus. CAB Abstr. 1999, 35, 433–436. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, T.T.; Pin, U.L.; Ghazali, A.H.A. Influence of external nitrogen on nitrogenase enzyme activity and auxin production in Herbaspirillum seropedicae (Z78). Trop. Life Sci. Res. 2015, 26, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Bashan, Y.; de Bashan, L. How the plant growth-promoting bacterium Azospirillum promotes plant growth: A critical assessment. Adv. Agron. 2010, 108, 77–136. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, A.; Travaglia, C.; Bottini, R.; Piccoli, P. Participation of abscisic acid and gibberellins produced by endophytic Azospirillum in the alleviation of drought effects in maize. Botany 2009, 87, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, T.; Feng, P.; Yao, D.; Gao, F.; Hong, X. Effect of K fertilization during fruit development on tomato quality, K uptake, water and K use efficiency under deficit irrigation regime. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 250, 106831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinert, C.H.; Sonntag, F.; Egert, B.; Pawelzik, E.; Kulling, S.E.; Smit, I. The effect of K fertilization on the metabolite profile of tomato fruit (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 159, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, R. Sucrose transporters in plants: Update on function and structure. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2000, 465, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bick, J.A.; Neelam, A.; Smith, E.; Nelson, S.J.; Hall, J.L.; Williams, L.E. Expression analysis of a sucrose carrier in the germinating seedling of Ricinus communis. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 38, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, R.; Brandner, J.; Schulz, A.; Gahrtz, M.; Sauer, N. Phloem loading by the PmSuc2 sucrose carrier from Plantago major occurs into companion cells. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pressman, E.; Schaffer, A.A.; Compton, D.; Zamski, E. Seasonal changes in the carbohydrate content of two cultivars of asparagus. Sci. Hortic. 1993, 53, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.R.; Cloughley, C.G.; Jamieson, P.D.; Sinton, S.M. A model of asparagus growth physiology. Acta Hortic. 2002, 589, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorke, R.; Dlugai, S.; Krampe, S.; Boles, E. Characterisation of mammalian GLUT glucose transporters in a heterologous yeast expression system. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2003, 13, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Kanai, M.; Osakabe, Y.; Ohiraki, H.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Monosaccharide absorption activity of Arabidopsis roots depends on expression profiles of transporter genes under high salinity conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 43577–43586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidon, Z.Z.; Cebola, F. An overview on drought induced changes in plant growth, water relations and photosynthesis. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2012, 24, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamer, S.; Schädler, M.; Bonte, D. Dual benefit from a belowground symbiosis: Nitrogen fixing rhizobia promote growth and defense against a specialist herbivore in a cyanogenic plant. Plant Soil 2011, 341, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.C.; Singh, S.K.; Prakash, S. Bio-control and plant growth promotion potential of siderophore producing endophytic Streptomyces from Azadirachta indica A. Juss. J. Basic Microb. 2011, 51, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Scagel, C.F.; Cheng, L.; Fuchigami, L.H.; Rygiewicz, P.T. Soil temperature and plant growth stage influence nitrogen uptake and amino acid concentration of apple during early spring growth. Tree Physiol. 2001, 21, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe, L.A. Amino acids in the rhizosphere: From plants to microbes. Am. J. Bot. 2013, 100, 1692–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chea, L.; Pfeiffer, B.; Schneider, D.; Daniel, R.; Pawelzik, E.; Naumann, M. Morphological and metabolite responses of potatoes under various phosphorus levels and their amelioration by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
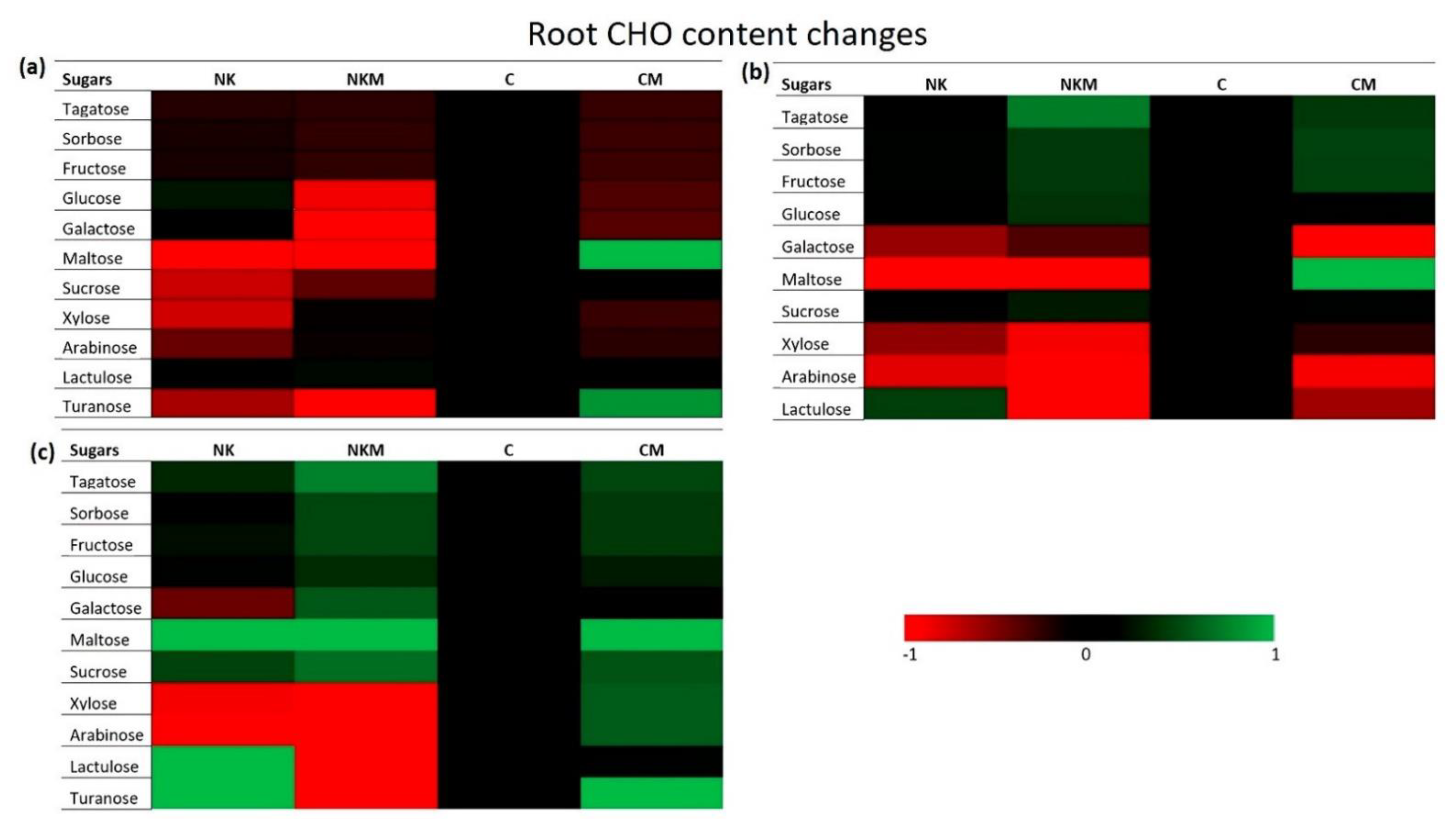
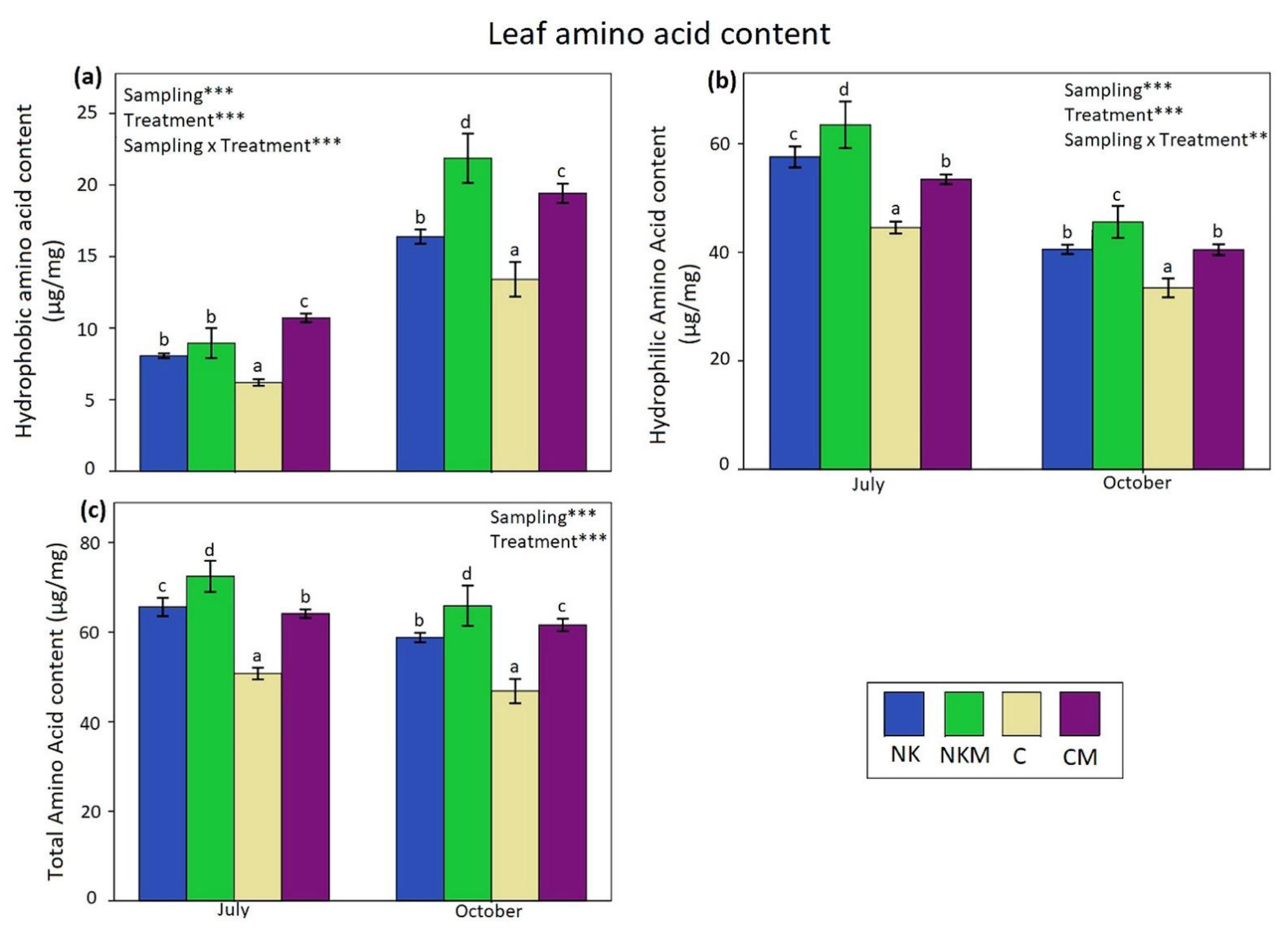
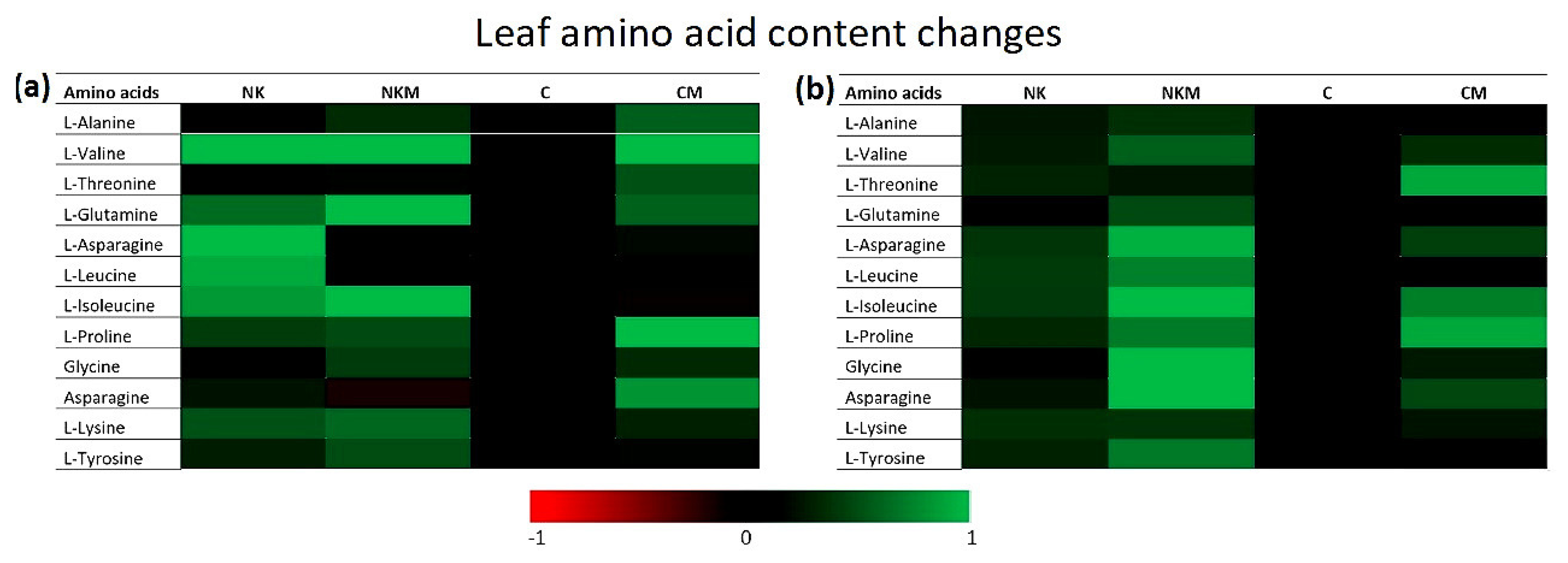
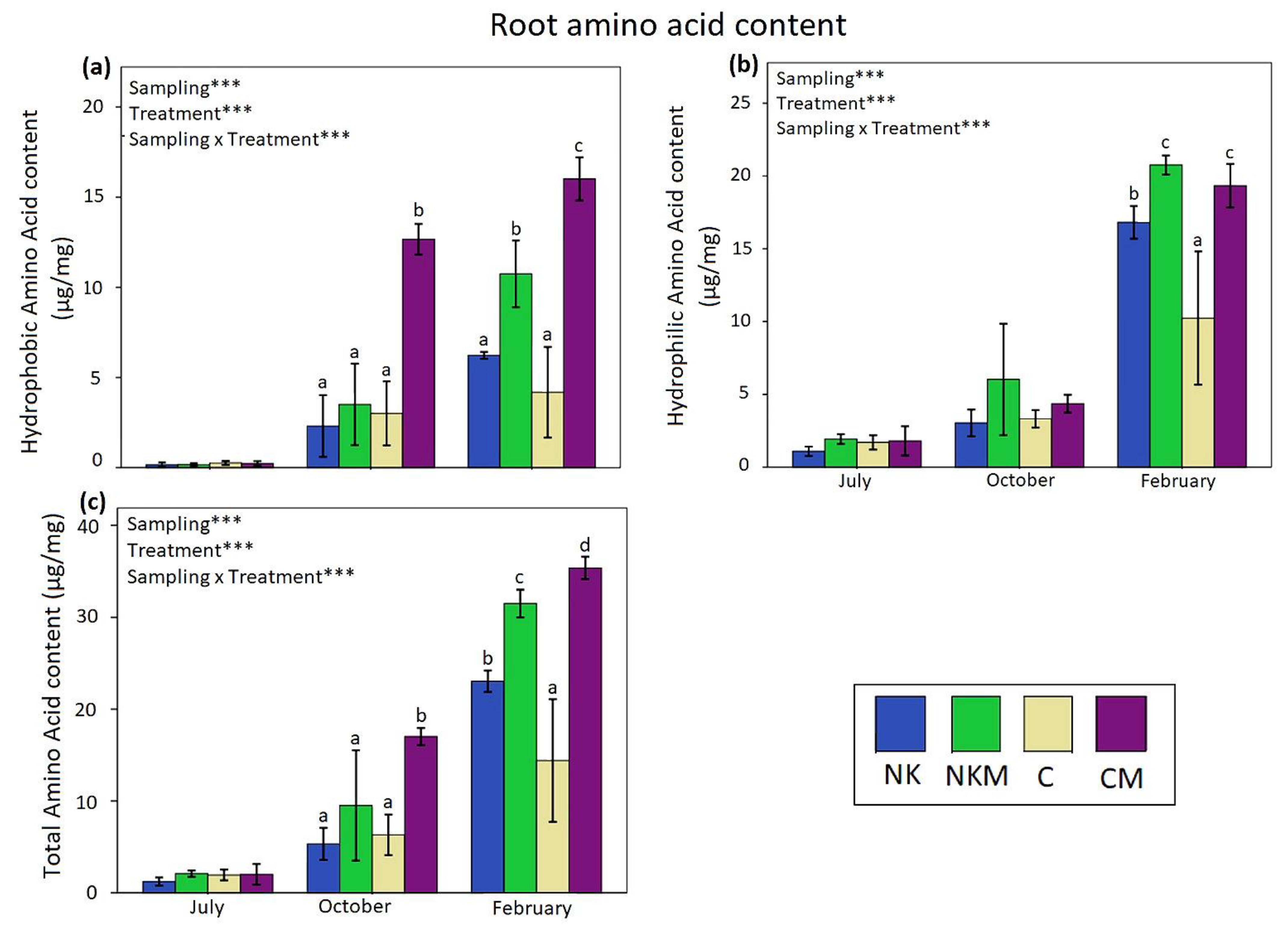
| Soil Variables | Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 6.18 |
| EC (mS/cm) | 1.74 |
| Organic matter (%) | 5.34 |
| NO3-N (mg kg−1 dw) | 27.37 |
| Phosphorus (mg kg−1 dw) | 18.75 |
| Potassium (mg kg−1 dw) | 158.75 |
| Magnesium (mg kg−1 dw) | 159.17 |
| Calcium (mg kg−1 dw) | 1938.83 |
| Iron (mg kg−1 dw) | 78.64 |
| Copper (mg kg−1 dw) | 1.49 |
| Boron (mg kg−1 dw) | 0.61 |
| Manganese (mg kg−1 dw) | 3.38 |
| Zinc (mg kg−1 dw) | 3.16 |
| Treatments | Applications |
|---|---|
| KNO3 fertilizer (NK) | 25 kg/acre of 13-0-46 (N-P-K) |
| KNO3 fertilizer with PGPR (NKM) | 25 kg/acre of 13-0-46 of (N-P-K) and 500 mL/acre Azoriz |
| NH4NO3 fertilizer (C) | 30 kg/acre of 34-0-0 (N-P-K) |
| NH4NO3 fertilizer with PGPR (CM) | 30 kg/acre of 34-0-0 (N-P-K) and 500 mL/acre Azoriz |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xekarfotakis, N.; Chatzistathis, T.; Mola, M.; Demirtzoglou, T.; Monokrousos, N. The Effects of Different Fertilization Practices in Combination with the Use of PGPR on the Sugar and Amino Acid Content of Asparagus officinalis. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7110507
Xekarfotakis N, Chatzistathis T, Mola M, Demirtzoglou T, Monokrousos N. The Effects of Different Fertilization Practices in Combination with the Use of PGPR on the Sugar and Amino Acid Content of Asparagus officinalis. Horticulturae. 2021; 7(11):507. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7110507
Chicago/Turabian StyleXekarfotakis, Nikolaos, Theocharis Chatzistathis, Magkdi Mola, Triantafyllia Demirtzoglou, and Nikolaos Monokrousos. 2021. "The Effects of Different Fertilization Practices in Combination with the Use of PGPR on the Sugar and Amino Acid Content of Asparagus officinalis" Horticulturae 7, no. 11: 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7110507
APA StyleXekarfotakis, N., Chatzistathis, T., Mola, M., Demirtzoglou, T., & Monokrousos, N. (2021). The Effects of Different Fertilization Practices in Combination with the Use of PGPR on the Sugar and Amino Acid Content of Asparagus officinalis. Horticulturae, 7(11), 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7110507








