Effects of Rootstock/Scion Combination and Two Irrigation Water Qualities on Cherry Tomato Yield and Postharvest Fruit Quality
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
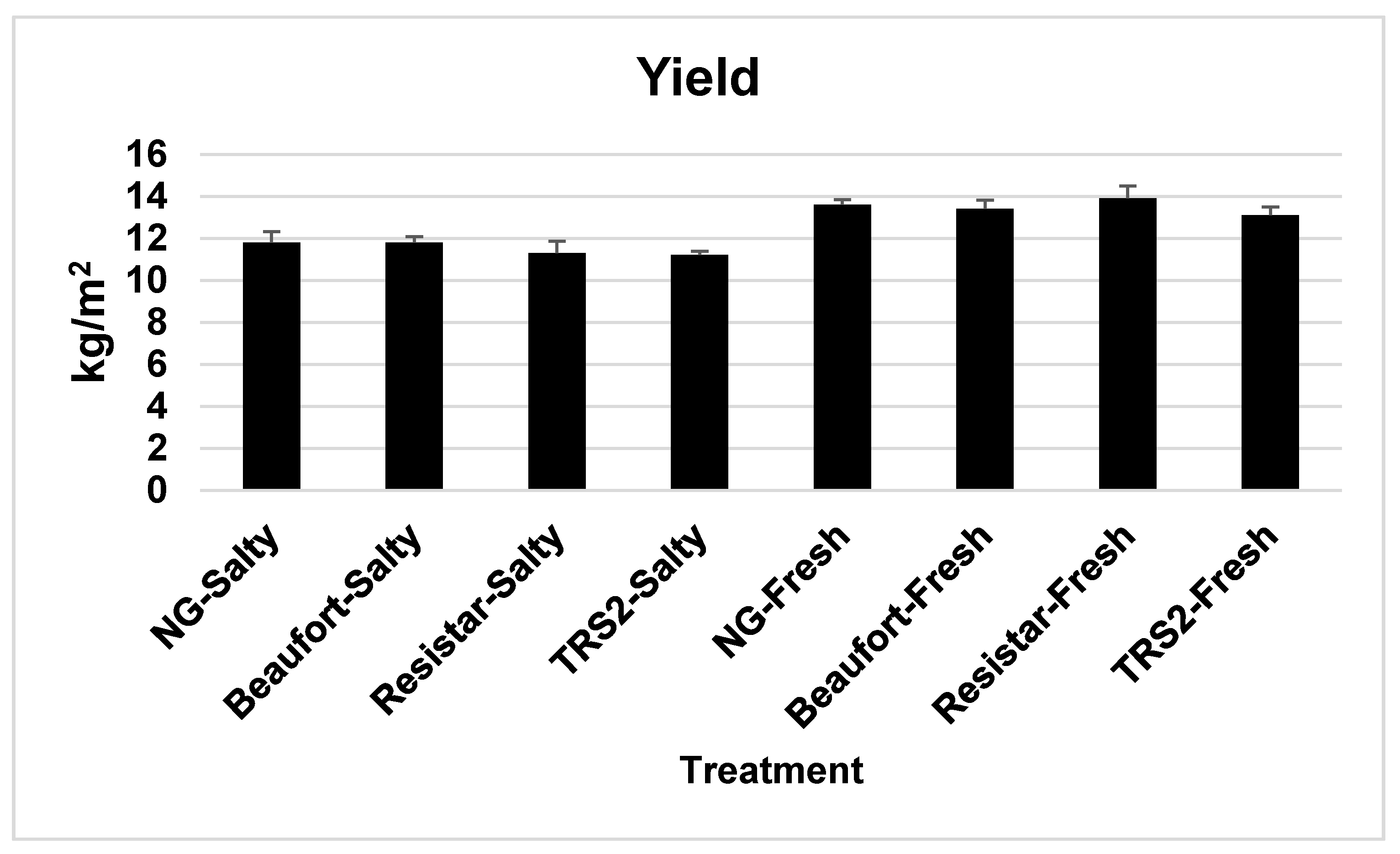
2.2. Yield/Fruit Weight
2.3. Postharvest Quality Parameters
2.4. Antioxidant Activity
2.5. Hedonics Test
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colla, G.; Rouphael, Y.; Leonardi, C.; Bie, Z. Role of grafting in vegetable crops grown under saline conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 127, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savvas, D.; Colla, G.; Rouphael, Y.; Schwarz, D. Amelioration of heavy metal and nutrient stress in fruit vegetables by grafting. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 127, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Grover, K.; Begna, S.; Angadi, S.; Shukla, M.; Steiner, R.; Auld, D. Physiological response of diverse origin spring safflower genotypes to salinity. J. Arid Land Stud. 2014, 24, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Fallik, E.; Ilic’, Z. Grafted vegetables—The influence of rootstock and scion on postharvest quality. Folia Hortic. 2014, 26, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, F.B.; Sanchez-Bel, P.; Estan, M.T.; Martinez-Rodriguez, M.M.; Moyano, E.; Morales, B.; Campos, J.F.; Garcia-Abellan, J.O.; Egea, M.I.; Fernandez-Garcia, N.; et al. The effectiveness of grafting to improve tomato fruit quality. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 125, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloni, B.; Cohen, R.; Karni, L.; Aktas, H.; Edelstein, M. Hormonal signaling in rootstock–scion interactions. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 127, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Kubota, A.C.; Tsao, S.J.; Bie, Z.; Echevarria, P.H.; Morra, L.; Oda, M. Current status of vegetable grafting: Diffusion, grafting techniques, automation. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 127, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, A.A.; Kondylis, A.; Passam, H.C. Fruit yield and quality of watermelon in relation to grafting. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2007, 5, 178–179. [Google Scholar]
- Bekhradi, F.; Kashi, A.; Delshad, M. Effect of three cucurbits rootstocks on vegetative and yield of ‘Charleston Gray’ watermelon. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2011, 5, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriacou, M.C.; Soteriou, G.A. Postharvest change in compositional, visual and textural quality of grafted watermelon cultivars. Acta Hortic. 2012, 934, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Schwarz, D.; Krumbein, A.; Colla, G. Impact of grafting on product quality of fruit vegetables. Sci. Hort. 2010, 127, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauromicale, G.; Longo, A.M.G.; Lo Monaco, A. The effect of organic supplementation of solarized soil on the quality of tomato fruit. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinkovic Vrcek, I.; Samobor, V.; Bojic, M.; Medic-Saric, M.; Vukobratovic, M.; Erhatic, R.; Horvat, D.; Matotan, Z. The effect of grafting on the antioxidant properties of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Span. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 9, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, F.; Signore, A.; Serio, F.; Santamaria, P. Grafting improves tomato salinity tolerance through sodium partitioning within the shoot. Hort. Sci. 2013, 48, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, A.; Hejazi, A.; al-Omran, A. Responses of grafted tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) to abiotic stresses in Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Savvas, D.; Savvas, A.; Ntatsi, G.; Ropokis, A.; Karapanos, I.; Krumbein, A.; Olympios, C. Effects of three commercial rootstocks on mineral nutrition, fruit yield, and quality of salinized tomato. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2011, 174, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Senge, M.; Dai, Y. Effects of salinity stress at different growth stages on tomato growth, yield, and water-use efficiency. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flexas, J.; Diaz-Espejo, A.; Galmés, J.; Kaldenhoff, R.; Medrano, H.; Ribas-Carbo, M. Rapid variations of mesophyll conductance in response to changes in CO2 concentration around leaves. Plant Cell Environ. 2007, 30, 1284–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsika-Sotiriou, M.; Traka-Mavrona, E. The cultivation of grafted melons in Greece, current status and prospects. Acta Hort. 2002, 579, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashide, T.; Nakano, A.; Yasuba, K. Yield and dry matter production of a Japanese tomato ‘Momotaro York’ are improved by grafting onto a Dutch rootstock ‘Maxifort’. J. Jpn. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2014, 83, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Bharti, N.; Saravaiya, S.N. Vegetable grafting: A surgical approach to combat biotic and abiotic stresses—A review. Agric. Rev. 2018, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, G.; Rouphael, Y.; Cardarelli, M.; Rea, E. Effect of salinity on yield, fruit quality, leaf gas exchange, and mineral composition of grafted watermelon plants. Hort. Sci. 2006, 41, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumbein, A.; Schwarz, D. Grafting: A possibility to enhance health-promoting and flavor compounds in tomato fruits of shaded plants? Sci. Hortic. 2013, 149, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchoff, D.H.; Gunter, C.C.; Louws, F.J. Comparative analysis of root system morphology on tomato rootstock. HortTechnology 2017, 27, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysin, O.; Louws, F.J. Decision tool for growers to evaluate economic impact of grafting technology adoption: An application to open-field conventional tomato production. HortTechnology 2015, 25, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatment/Water Quality | Rootstock | Fruit Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|
| Saline | Non-grafted | 17.1 |
| Saline | Beaufort | 18.7 |
| Saline | Resistar | 16.7 |
| Saline | TRS2 | 17.0 |
| Fresh | Non-grafted | 19.0 |
| Fresh | Beaufort | 19.2 |
| Fresh | Resistar | 19.5 |
| Fresh | TRS2 | 17.1 |
| LSD z | NS | |
| Mean weight with each water quality | ||
| Saline | 17.3 | |
| Fresh | 18.7 | |
| LSD | NS | |
| Mean weight with each rootstock | ||
| Non-grafted | 18.1 | |
| Beaufort | 19.0 | |
| Resistar | 18.0 | |
| TRS2 | 17.0 | |
| LSD | NS | |
| Table of Variance (F-value) | ||
| Water quality (W) | NS y | |
| Rootstock (R) | NS | |
| W × R | NS | |
| Water Quality | Rootstock | Weight Loss z (%) | Firmness (UF) y | TSS (%) x | TA (%) w | Decay (%) | Abscission (%) | Stem Freshness (1–3) v |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saline | NG u | 4.0 | 23.4 b t | 5.6 ab | 0.57 ab | 0.40 | 54.4 | 2.2 |
| Saline | Beaufort | 4.5 | 24.2 ab | 5.6 ab | 0.58 ab | 0.32 | 44.8 | 2.4 |
| Saline | Resistar | 3.2 | 28.4 a | 6.2 a | 0.62 a | 0.24 | 29.8 | 2.5 |
| Saline | TRS2 | 3.5 | 25.0 ab | 5.7 ab | 0.52 bc | 0.64 | 57.8 | 2.4 |
| Fresh | NG | 4.8 | 24.2 ab | 5.4 ab | 0.46 c | 1.08 | 66.8 | 2.2 |
| Fresh | Beaufort | 4.5 | 25.4 ab | 5.2 b | 0.48 c | 1.58 | 56.6 | 2.3 |
| Fresh | Resistar | 3.9 | 24.4 ab | 5.3 ab | 0.47 c | 0.28 | 56.6 | 2.3 |
| Fresh | TRS2 | 3.7 | 26.0 ab | 5.2 a | 0.48 c | 0.60 | 54.8 | 2.3 |
| LSD | NS | 1.5 | NS | 0.02 | NS | NS | NS | |
| Averages for each water quality | ||||||||
| Saline | 3.78 | 25.4 | 5.8 a | 0.6 a | 0.4 | 46.7 b | 2.4 a | |
| Fresh | 4.25 | 25.0 | 5.3 b | 0.5 b | 0.9 | 58.7 a | 2.3 b | |
| LSD | NS | NS | 0.2 | 0.01 | NS | 5.8 | 0.03 | |
| Averages for each rootstock | ||||||||
| NG | 4.40 | 23.8 b | 5.5 | 0.5 | 0.74 | 60.6 | 2.2 b | |
| Beaufort | 4.51 | 25.1 ab | 5.4 | 0.5 | 0.94 | 50.7 | 2.3 a | |
| Resistar | 3.55 | 26.4 a | 5.7 | 0.5 | 0.26 | 43.2 | 2.4 a | |
| TRS2 | 3.61 | 25.5 ab | 5.5 | 0.5 | 0.62 | 56.3 | 2.3 a | |
| LSD | NS | 1.0 | NS | NS | NS | NS | 0.05 | |
| Analysis of Variance (P-value) | ||||||||
| Water quality | NS s | NS | ** | **** | NS | * | * | |
| Rootstock | NS | * | NS | NS | NS | NS | ** | |
| W × R | NS | * | NS | * | NS | NS | NS | |
| Water Quality | Rootstock | Vitamin C (mg/100 g FW) | Lycopene (µg/g FW) | AOX (TEAC µM TE/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saline | NG z | 27.7 | 36.0 | 1.0 |
| Saline | Beaufort | 27.1 | 36.5 | 1.3 |
| Saline | Resistar | 29.5 | 42.7 | 1.3 |
| Saline | TRS2 | 24.6 | 38.1 | 1.2 |
| Fresh | NG | 22.4 | 37.4 | 1.0 |
| Fresh | Beaufort | 21.8 | 35.3 | 1.1 |
| Fresh | Resistar | 23.3 | 37.5 | 1.0 |
| Fresh | TRS2 | 24.4 | 36.5 | 1.1 |
| LSD | NS | NS | NS | |
| Average for each water quality | ||||
| Saline | 27.2 a y | 38.3 | 1.2 | |
| Fresh | 22.9 b | 36.7 | 1.0 | |
| LSD | 1.6 | NS | NS | |
| Average for each rootstock | ||||
| NG | 25.1 | 36.7 b | 1.0 | |
| Beaufort | 24.4 | 35.9 b | 1.2 | |
| Resistar | 26.4 | 40.1 a | 1.2 | |
| TRS2 | 24.4 | 37.3 b | 1.2 | |
| LSD | NS | 1.7 | NS | |
| Analysis of Variance (P-value) | ||||
| Water quality | * x | NS | NS | |
| Rootstock | NS | ** | NS | |
| W × R | NS | NS | NS | |
| Water Quality | Rootstock | Sweetness (1–5) z | Sourness (1–5) y | Off-Flavor (0–4) x | Texture (1–5) w | General Taste (1–5) v |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saline | NG u | 3.0 | 2.4 | 0.4 | 3.1 | 3.3 |
| Saline | Beaufort | 2.9 | 2.2 | 0.6 | 3.1 | 3.3 |
| Saline | Resistar | 3.2 | 2.4 | 0.6 | 3.3 | 3.4 |
| Saline | TRS2 | 3.0 | 2.3 | 0.7 | 3.4 | 3.3 |
| Fresh | NG | 2.6 | 2.1 | 0.6 | 3.2 | 3.0 |
| Fresh | Beaufort | 2.6 | 2.2 | 0.7 | 3.2 | 2.9 |
| Fresh | Resistar | 2.5 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 3.2 | 2.8 |
| Fresh | TRS2 | 2.7 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 3.2 | 2.9 |
| LSD | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| Averages for each water quality | ||||||
| Saline | 3.0 a | 2.3 a | 0.6 a | 3.2 | 3.3 a | |
| Fresh | 2.6 b | 2.0 b | 0.8 b | 3.2 | 2.9 b | |
| LSD | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | NS | 0.1 | |
| Averages for each rootstock | ||||||
| NG | 2.8 | 2.2 | 0.5 b | 3.3 | 3.1 | |
| Beaufort | 2.8 | 2.2 | 0.6 ab | 3.1 | 3.1 | |
| Resistar | 2.9 | 2.3 | 0.8 a | 3.3 | 3.1 | |
| TRS2 | 2.9 | 2.0 | 0.8a | 3.3 | 3.1 | |
| LSD | NS | NS | 0.2 | NS | NS | |
| Analysis of Variance (P-value) | ||||||
| Water quality | *** s | ** | * | NS | **** | |
| Rootstock | NS | NS | ** | NS | NS | |
| W × R | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu Glion, H.; Alkalai-Tuvia, S.; Zaaroor-Presman, M.; Chalupowicz, D.; Zanbar, M.; Amichai, M.; Cohen, S.; Shemer, T.; Sarig, S.; Fallik, E. Effects of Rootstock/Scion Combination and Two Irrigation Water Qualities on Cherry Tomato Yield and Postharvest Fruit Quality. Horticulturae 2019, 5, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae5020035
Abu Glion H, Alkalai-Tuvia S, Zaaroor-Presman M, Chalupowicz D, Zanbar M, Amichai M, Cohen S, Shemer T, Sarig S, Fallik E. Effects of Rootstock/Scion Combination and Two Irrigation Water Qualities on Cherry Tomato Yield and Postharvest Fruit Quality. Horticulturae. 2019; 5(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae5020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu Glion, Hiam, Sharon Alkalai-Tuvia, Merav Zaaroor-Presman, Daniel Chalupowicz, Mili Zanbar, Michal Amichai, Shabtai Cohen, Tsion Shemer, Shlomo Sarig, and Elazar Fallik. 2019. "Effects of Rootstock/Scion Combination and Two Irrigation Water Qualities on Cherry Tomato Yield and Postharvest Fruit Quality" Horticulturae 5, no. 2: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae5020035
APA StyleAbu Glion, H., Alkalai-Tuvia, S., Zaaroor-Presman, M., Chalupowicz, D., Zanbar, M., Amichai, M., Cohen, S., Shemer, T., Sarig, S., & Fallik, E. (2019). Effects of Rootstock/Scion Combination and Two Irrigation Water Qualities on Cherry Tomato Yield and Postharvest Fruit Quality. Horticulturae, 5(2), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae5020035





