Abstract
Konjac glucomannan flour, which mainly consists of glucomannan, is an indigestible dietary fiber. Therefore, it has been broadly used as low-calorie food ingredient in various kinds of foods, beverages, and pharmaceutical products. In this study, the production of dried konjac noodles was evaluated by studying the effects of alkalinity using limewater versus calcium hydroxide and the gelling agent sodium alginate on textural properties of konjac noodles. Drying and rehydration conditions were studied to evaluate the optimum conditions for producing dried konjac noodles. By considering the springiness and cohesiveness of the konjac noodles, the results indicated that using 3% konjac glucomannan flour with limewater and an incubation time of 30 min were the most suitable conditions. In addition, hot air drying at 80 °C for 55 min and soaking in hot water for 9 min were the optimum drying and rehydration conditions.
1. Introduction
Konjac glucomannan (KGM) flour is high in dietary fiber. KGM flour is a hydrocolloidal polysaccharide obtained from the tubers of various species of Amorphophallus. The proximate composition of konjac glucomannan flour obtained from Amorphophallus muelleri contains 86.8% glucomannan, 0.2% other carbohydrates, 3% protein, 0.1% lipids, 3.3% ash, and 6.6% moisture content [1]. The main component of KGM is a non-ionic, high molecular weight polysaccharide of mannose and glucose, with a small number of branched side chains, connected by β-1,4-glycosidic linkages with a mannose: glucose molar ratio of approximately 1.6 to 4:1. Acetyl groups along the glucomannan backbone contribute to solubility properties and are located every 9 to 19 sugar units [2]. The outstanding characteristics of KGM are its indigestible dietary fiber, water-absorbing ability, and high viscosity. Thus, KGM has been given much attention in food industries for centuries, being broadly used as a food, a food additive, and in traditional Chinese medicine. Studies on KGM applications have been presented in many fields, such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, fine chemicals, and other areas [3].
Functional uses of KGM as a food and a food additive have been approved for many purposes such as a carrier, emulsifier, stabilizer, thickener, gelling agent, glazing agent, and humectant in many kinds of foods and beverages [2]. For food applications, KGM is also used as a fat replacement in low-fat meat products [4]. It has recently been marketed in capsule form, as a drink mix, and in food products for the treatment of obesity and diabetes. The potential use of KGM as a prebiotic has also been suggested [5].
As for the health benefits of KGM, it is a soluble fiber which can increase transit time of food and prolong gastric emptying time, delay glucose diffusion in the intestinal lumen, reduce body weight, decrease the ingestion of foods that increase cholesterol and glucose concentrations, reduce the postprandial rise in plasma glucose, suppress hepatic cholesterol synthesis, and increase the fecal elimination of cholesterol containing bile acids [6].
Konjac glucomannan-based foods were originally developed in Japan and China over several decades. They are a popular health food in world markets since they are a great source of water-soluble dietary fiber and very low calories. A unique characteristic of KGM foods is that they are translucent and gelatinous, with no flavor of their own. KGM foods can be made into many different styles and shapes, with examples at http://www.konjacfoods.com. One of the most popular styles is as a noodle. In order to make KGM foods, KGM is first dissolved in water where it becomes a highly viscous pseudoplastic solution, even at low concentrations [7]. However, it does not form a gel in water. Gelation of KGM takes place when it loses its acetyl groups in the presence of alkaline coagulants (e.g., calcium hydroxide). Thermo-irreversible and heat-stable gels are created by the deacetylation reaction [8]. KGM can also become a gel by synergistic interactions with other plant/algal hydrocolloids such as starch, carrageenan, furcellaran, xanthan and gellan gum [9]. Sodium alginate is one of the hydrocolloids which can interact with KGM to form a strong gel network structure [10,11]. However, there are no scientific reports about noodles derived from KGM and sodium alginate.
Currently, konjac noodles are found in wet forms. In order to preserve the stability of konjac gel, it needs to be packaged in alkaline solution and stored at a low temperature (4–5 °C). The drawbacks of wet KGM noodles are their bitterness and astringent taste, unpleasant odor, high transportation cost, short shelf life, and the requirement for refrigeration even before opening. There is, however, no literature dealing with the use konjac glucomannan flour as a main ingredient in the noodle making process. Therefore, the aim of this research was to evaluate the effects of alkaline solution (limewater and calcium hydroxide) and a gelling agent (sodium alginate with calcium chloride) on textural and rehydration properties of KGM noodles for the possible reduction in use of alkaline solution and its replacement with a gelling agent. The drying temperature and rehydration conditions were also studied to evaluate the optimum conditions for producing dried KGM noodles.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Material
Commercial konjac glucomannan flour (>98% glucomannan) was purchased from Yunnan Lvyuan Bio-technology Co., Ltd. (Kunming, China). Limewater was prepared by dissolving traditional Thai red lime paste (a mixture of calcium hydroxide, turmeric, and salt) in distilled water until the solution was saturated (pH 12). Calcium hydroxide, sodium alginate, and calcium chloride (AR grade) were purchased from CTi & Science Co., Ltd. (Bangkok, Thailand).
2.2. Production of Konjac Noodles by Using Alkaline Solution
KGM flour was dissolved in alkaline solution to prepare a 3% (w/w) solution. The two alkaline solutions used in this study were limewater and 0.1 M calcium hydroxide. The final pH values of the alkaline solutions were 12.56 and 12.73 for limewater and calcium hydroxide, respectively. Based on preliminary work, the solution of KGM and limewater was incubated for 15, 20, 25, 30, and 35 min, while the KGM-calcium hydroxide solution was incubated for 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 and 2 h, all at room temperature (35 °C). Then, the KGM-alkaline solutions were extruded through a 2 mm diameter-opening of a syringe into boiling water and held for 1 min. After that, the konjac noodles were placed in 4 °C water for 1 min, and then placed in a sieve to drain the excess water.
2.3. Production of Konjac Noodles by Using Sodium Alginate and Calcium Chloride
KGM flour was dissolved in 0.25%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.25%, and 1.5% sodium alginate solution to prepare a 3% (w/w) solution. Then, KGM-sodium alginate solution was extruded through a 2 mm diameter-opening of a syringe into a 1% calcium chloride solution for a minute. The resulting KGM noodles were placed on sieve to drain the excess water.
2.4. Drying Experiments
The KGM noodles were analyzed for initial moisture content by using a hot air oven (Programmable Laboratory Oven, Fisher Scientific Worldwide, United States) at 105 ± 2 °C for 3 h [12]. For the drying experiment, 100 ± 0.5 g of konjac noodles were placed on a stainless tray and placed in the hot air oven. The air temperature of the dryer was set at 60, 70, or 80 °C. The weight of konjac noodles and tray were determined every 10 min until they reached a constant weight (the equilibrium moisture content). All drying experiments were performed in triplicate. The moisture content change of konjac noodles during the drying process was expressed as a moisture ratio, calculated by the following Equation (1) to describe the drying curve [13].
where M = moisture content (% dry weight basis (d.b.)) at each weighing time, M0 = initial moisture content (% d.b.), Me = equilibrium moisture content (% d.b.).
2.5. Rehydration Properties
The water uptake percentage of the dried konjac noodles was determined according to Zhou et al. [14] with some modifications. Dried konjac noodles (10 ± 0.5 g) were placed in a beaker containing 400 mL of ambient temperature water, hot water (98 °C), or boiling water for 3, 6, 9, or 12 min. The rehydrated konjac noodles were then drained on a sieve for 5 min before weighing. The water uptake percentage was calculated by following Equation (2) [15].
2.6. Texture Profile Analysis
Texture profile analyses (TPA) were performed by using a TA.XT Plus Stable Micro Systems Texture Analyser (Stable Micro Systems, model TA.XT. Plus, Surrey, UK) with the Texture Expert software. The TPA parameters were evaluated both on fresh and rehydrated konjac noodles. According to Jimenez-Colmenero et al. [9], Zhou et al. [14], and Kaur et al. [15] with some modifications, each strand of konjac noodles had a cross-sectional area of approximately 2 mm and length of 40 mm. A set of four strands was placed parallel on the flat metal plate. The samples were axially compressed twice to 50% of their original sample height. A 2 kg load cell with a cylinder P/36R probe was used at 2, 0.8, and 0.8 mm/s for pre-test, test, and post-test speeds, respectively. The trigger type is auto with a trigger force of 0.5 g. Ten replicate samples were tested. Some of the TPA parameters obtained from the force-time curves such as cohesiveness and springiness were determined. Tensile strength and % elongation were measured by using the A/SPR-Spaghetti/Noodle Rig following Stable Micro Systems guidelines at 2 mm/s with a 2 kg load cell.
2.7. Microstructure of Konjac Noodles
Cross-sections of each konjac noodle sample were examined by cutting the konjac noodles and mounting on a stub. The cross-sectional surface of all samples was observed from the top under a scanning electron microscope (JEOL, model JSM-6400LV, Tokyo, Japan) at an accelerating voltage of 15 kV in high vacuum mode. Magnifications of 30×, 5000× and 20,000× were used for observing the cross-sections.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Except for the TPA analyses which were replicated 10 times, all other analyses were replicated 3 times. The differences between treatment means were established using analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s New Multiple Range test at a confidence level of p = 0.05 using the SPSS Statistical Analysis Program for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Production of Konjac Noodles
In general, when KGM is dissolved in water, it become a viscous solution and cannot form a gel. However, KGM gel can be produced by deacetylation using alkaline solution or in synergistic interactions with other hydrocolloids such as sodium alginate, κ-carrageenan, or xanthan gum [4,5,7,8,10,11]. The texture of alkaline-KGM gel is stronger than with other hydrocolloid-KGM gels. In this study, the konjac noodles, which were produced by using 0.1 M limewater with 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 min of incubation time, 0.1 M calcium hydroxide with 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 and 2 h of incubation time, and 0.25%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.25%, and 1.5% sodium alginate solution/1% calcium chloride, were evaluated by considering the TPA of springiness and cohesiveness values (Table 1).

Table 1.
Some textural profile analysis (TPA) parameters of fresh konjac noodles.
Springiness is a measure of how well the product physically responds after it has been deformed during a first compression, while cohesiveness is how well the product withstands a second deformation relative to how it behaved after the first deformation, which is related to the strength of hydrogen bonding among KGM molecules. Noodles are considered good quality if they exhibit high springiness and cohesiveness values.
The springiness values of konjac noodles produced from all treatments showed no significant difference from the commercial product, although some variation among treatments was evident, while cohesiveness values from some treatments did differ from the commercial product. Also, 1.25% sodium alginate had the lowest cohesiveness. The results generally showed higher cohesiveness values when using alkaline solution compared with sodium alginate. This may due to the loss of acetyl groups from KGM chains by adding alkaline solution, called deacetylation [16,17,18,19,20,21]. The effects of eliminating acetyl groups produced junction zones through hydrogen bonding between calcium ions and deacetylated anions (R–CH2O–), between water molecules and hydroxyl groups (OH–) of deacetylated KGM, and by van der Waals, charge transfer and hydrophobic interactions, forming a strong, elastic, and thermally stable gel network structure [11,22,23] to provide high springiness and cohesiveness of samples. While KGM and alkaline solution are cross-linked by several bonds, the springiness and cohesiveness of konjac noodles from KGM and sodium alginate came from only gelation of divalent cations (like Ca2+) and polysaccharides to form an “egg box” model structure [24]. Thus, using alkaline solution showed better cohesiveness values than sodium alginate. It may be possible to use calcium ions (Ca2+) from calcium hydroxide to absorb CO2 and precipitate calcium carbonate (CaCO3) [25]. Thus, the strength of konjac noodle structure may result from Ca2+ from limewater or calcium hydroxide solution which reacted with CO2 in the environment of the samples to produce crystals of CaCO3 in the noodle matrix to make a strong and elastic gel. It can be concluded that the different types of alkaline solutions and incubation times significantly influenced the gel strength of KGM noodles as observed in springiness and cohesiveness values. The optimum conditions for producing the highest springiness and cohesiveness of KGM noodles was 3% KGM with limewater, incubated for 30 min.
Figure 1 shows that konjac noodles produced from 3% KGM and 1% sodium alginate were transparent, while noodles from the other methods were opaque as a result of using alkaline solution.
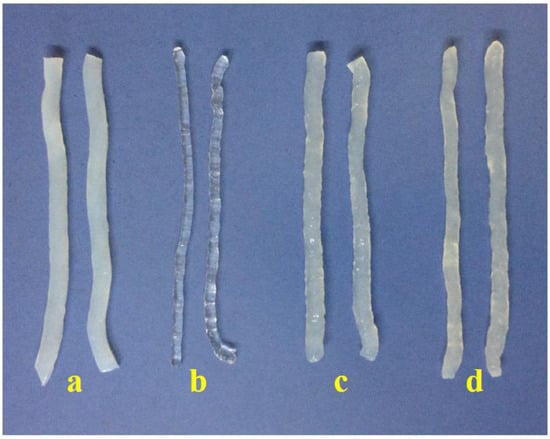
Figure 1.
Konjac noodles from (a) commercial product, or produced from (b) 3% KGM and 1% sodium alginate; (c) 3% KGM and Ca(OH)2 with 2 h incubation time; and (d) 3% KGM and limewater with 30 min incubation time.
Scanning electron micrographs of cross-sectioned konjac noodles revealed the inner structure of the noodles (Figure 2). The konjac noodles formed strong and elastic hydrogels when heated with alkali by deacetylation and disruption of the hydrogen bonding between the glucomannan chain and water molecules [26]. Thus, a reticular structure was formed. Only konjac noodle produced from 3% KGM and sodium alginate showed a different structure, a ionically cross-linked by divalent Ca2+ cations. The results also indicated that the structures of the noodles tended to be denser when increasing the concentration of sodium alginate.
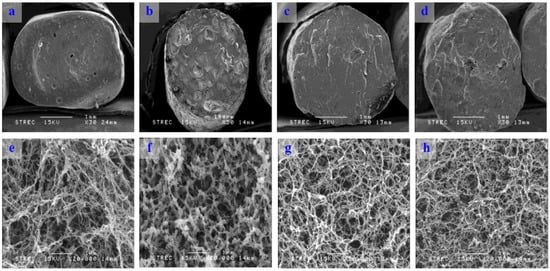
Figure 2.
Scanning electron micrographs (SEM) of konjac noodle from a commercial process (a,e); from 3% KGM and 1% sodium alginate (b,f); from 3% KGM and Ca(OH)2 with a 2 h incubation time (c,g); and from 3% KGM and limewater with 30 min incubation time (d,h). Magnifications of 30× (a–d) and 20,000× (e–h) were used.
3.2. Drying Experiments
In order to study the drying time to reduce moisture content of konjac noodles from the initial moisture content of 1.24% ± 22% d.b. (moisture ratio = 1) to the target moisture content 10%–12% d.b. (moisture ratio = 0.01), konjac noodles were dried by using hot air at 60, 70, or 80 °C. The drying patterns among the temperatures were determined from the mass loss of the samples. The drying progress of konjac noodles subjected to hot air drying treatments (60–80 °C) is shown in Figure 3.
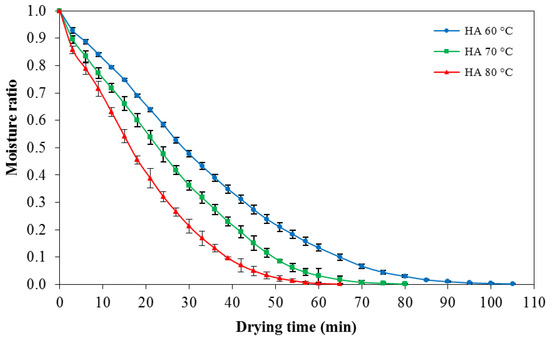
Figure 3.
Moisture ratio versus drying time of konjac noodles using hot air at 60, 70, or 80 °C.
The results indicated that drying of konjac noodles using hot air at 60, 70, and 80 °C required 85, 65, and 55 min, respectively, to reduce moisture content to 10%–12% d.b. Thus, drying at 80 °C was chosen for the following experiment since it had the shortest drying time.
3.3. Rehydration Properties, Texture Profile Analysis, and Microstructure Observation
The dried konjac noodles obtained from the previous experiment (3% KGM in limewater, incubation for 30 min, drying at 80 °C for 55 min) were used to study the water absorption properties of the samples by analyzing the water uptake percentage, the tensile strength, and the elongation percentage of rehydrated konjac noodles to determine the most suitable rehydration conditions. Tensile strength is the maximum amount of stress (force per unit area) that is required for pulling the noodle to the breaking point.
The water uptake percentage of the samples tended to increase with increasing the rehydration time and water temperature (Figure 4). In general, the dried noodle has a porous structure that is created during dehydration. The pores serve as channels for water to enter the noodles, leading to rehydration [27]. The higher the water temperature that was used, the more rapidly water was adsorbed.
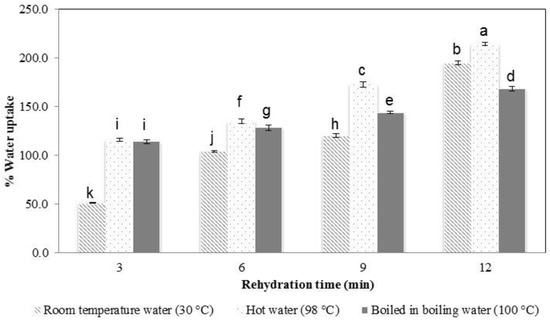
Figure 4.
Water uptake percentage as affected by duration and water temperature of rehydrated konjac noodles created from 3% KGM with limewater and incubation for 30 min. Means with different letters are significantly different (p ≤ 0.05).
Scanning electron micrographs showed that the drying process had a large impact on the reticular structure of konjac noodles (Figure 5). Moreover, the higher water temperature for rehydration also affected their reticular structure. When the reticular structure was destroyed, the rehydration properties decreased. Thus, these two factors were extremely important for the rehydration of the konjac noodle.
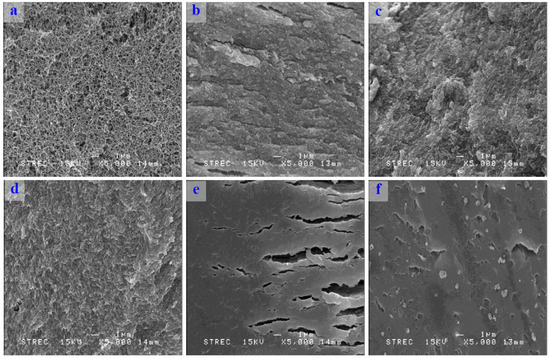
Figure 5.
Scanning electron micrographs (SEM) of (a) a konjac noodle from 3% KGM and limewater with 30 min incubation; (b) a dried konjac noodle; (c) a rehydrated konjac noodle in boiling water for 3 min; (d) 6 min; (e) 9 min; and (f) 12 min. Magnification was at 5000×.
When konjac noodles were boiled in hot water, the water migrated from the noodle surface toward the center, affecting the structure of the noodles (Figure 5). Therefore, the noodle textural traits of tensile strength and elongation changed, with the sample becoming softer on rehydration with a longer hydration time in hot water.
In the early stages of rehydration, the konjac noodles had absorbed less water (Figure 4) and were tough and showed a higher tensile strength (Figure 6 and Figure 7). By the latter stages of rehydration, the konjac noodles had absorbed more water and showed a softer texture and lower tensile strength. Thus, rehydration temperature and time affected the strength of the samples. Elongation percentage also tended to decrease with time (Figure 6 and Figure 7). The most suitable rehydration method was soaking in hot water for 9 min which provided the optimum values of tensile strength, elongation, and water uptake percentage.
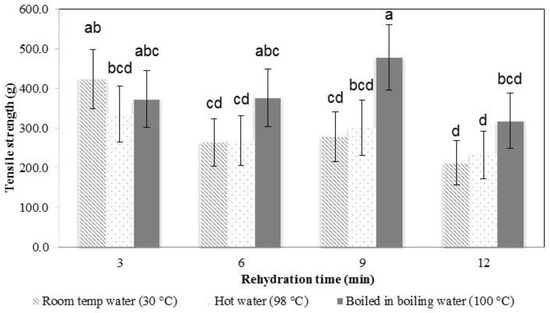
Figure 6.
Tensile strength of rehydrated konjac noodles from 3% KGM with limewater and incubation for 30 min. Means with different letter are significantly different (p ≤ 0.05).
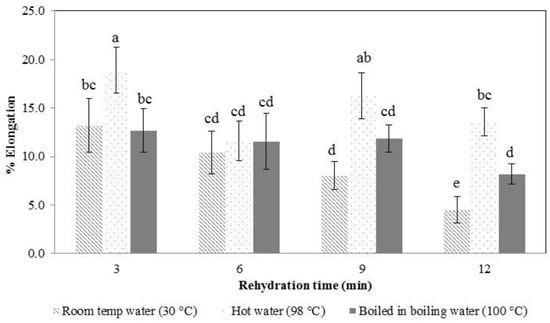
Figure 7.
Elongation percentage of rehydrated konjac noodles from 3% KGM with limewater and incubation for 30 min. Means with different letters are significantly different (p ≤ 0.05).
4. Conclusions
This study showed that springiness values of konjac noodles produced from all treatments showed some variation. Higher cohesiveness values resulted when using alkaline solution compared with sodium alginate. However, the springiness and cohesiveness values were comparable to a commercial product. The optimum method for producing the highest springiness and cohesiveness of KGM noodles was 3% KGM with limewater and incubation for 30 min. Hot air drying at 80 °C for 55 min was the optimum drying condition for producing dried konjac noodles since it resulted in the shortest drying time. The most suitable rehydration procedure was soaking in hot water for 9 min which provided optimum values of tensile strength, elongation, and water uptake percentage. The drying process and rehydration conditions had significant impacts on the structure and rehydration properties of konjac noodles.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thanks Department of Microbiology, King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi for the research facilities. This research is supported by Faculty of Science, King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi Grant No. SCI58-001.
Author Contributions
This work was a product of the combined effort of all authors. Sujika Piyarat, Natnicha Sophontanakij, and Nattiya Sakulnate jointly performed the experiments, gathered and analyzed the data. Rarisara Impaprasert designed the experiment and wrote the manuscript with the help of Suwit Paengkanya. Chaleeda Borompichaichartkul and George Srzednicki revised and improved the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Impaprasert, R.; Borompichaichartkul, C.; Srzednicki, G. A new drying approach to enhance quality of konjac glucomannan extracted from Amorph. Muelleri. Dry. Technol. Int. J. 2014, 32, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konjac Flour. Available online: http://www.fao.org/gsfaonline/additives/details.html?id=10 (accessed on 15 August 2015).
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Xie, B.J.; Gan, X. Advance in the applications of konjac glucomannan and its derivatives. Carbohyd. Polym. 2005, 60, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tye, R.J. Konjac flour: Properties and applications. Food Technol. 1991, 45, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, M.; Baldwin, T.C.; Hocking, T.J.; Chan, K. Traditional uses and potential health benefits of Amorphophallus konjac K Koch ex N.E.Br. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 128, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, B.R.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Wei, X.; Weiping, J.; Zhenshun, L. Health benefits of konjac glucomannan with special focus on diabetes. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fiber 2015, 5, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, V.; McCarthy, S.P. Review of Konjac Glucomannan. J. Environ. Polym. Degr. 1997, 5, 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- Nishinari, K.; Zhang, H. Recent advances in the understanding of heat set gelling polysaccharides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Colmenero, F.; Cofrades, S.; Herrero, A.M.; Solas, M.T.; Ruiz-Capillas, C. Konjac gel for use as potential fat analogue for healthier meat product development: Effect of chilled and frozen storage. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, S.E.; Smith, I.H.; Lawson, C.J.; Gahlerd, R.J.; Wood, S. Studies on macromolecular interactions in ternary mixtures of konjac glucomannan, xanthan gum and sodium alginate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Shuai, Y.; Cui, X.; Nie, L. Controlled release of anticancer drug using graphene oxide as a drug-binding effector in konjac glucomannan/sodium alginate hydrogels. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists International: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.Y.; Zhang, H.; Miao, Y. The effect of quantity of salt on the drying characteristics of fresh noodles. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia. 2014, 2, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cao, H.; Hou, M.; Nirasawa, S.; Tatsumi, E.; Foster, T.J.; Cheng, Y. Effect of konjac glucomannan on physical and sensory properties of noodles made from low-protein wheat flour. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Singh, N.; Kaur, S.; Katyal, M.; Virdi, A.S.; Kaur, D.; Ahlawat, A.K.; Singh, A.H. Relationship of various flour properties with noodle making characteristics among durum wheat varieties. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Takahashi, R.; Kobayashi, S.; Kawase, T.; Nishinari, K. Gelation behavior of native and acetylated konjac glucomannan. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekaji, K. Mechanism of gelation of konjac mannan. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1974, 38, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.A.; Foster, T.J.; Martin, D.R.; Norton, I.T.; Yoshimura, M.; Nishinari, K. A molecular description of the gelation mechanism of konjac mannan. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, M.; Nishinari, K. Dynamic viscoelastic study on the gelation of konjac glucomannan with different molecular weights. Food Hydrocoll. 1999, 13, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yoshimura, M.; Nishinari, K.; Williams, M.A.K.; Foster, T.J.; Norton, I.T. Gelation behaviour of konjac glucomannan with different molecular weights. Biopolymers 2001, 59, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solo-de-Zaldivar, B.; Herranz, B.; Borderias, J. First steps in using glucomannan to make thermostable gels for potential use in mince fish restructuration. Int. J. Food Eng. 2012, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapasin, R.; Pricl, S. Rheology of Industrial Polysaccharides: Theory and Applications; Aspen Publishers: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Herranz, B.; Tovar, C.A.; Solo-de-Zaldívar, B.; Borderias, A.J. Effect of alkalis on konjac glucomannan gels for use as potential gelling agents in restructured seafood products. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.T.; Morris, E.R.; Rees, D.A.; Smith, P.J.C.; Thom, D. Biological interactions between polysaccharides and divalent cations: The Egg-Box model. FEBS Lett. 1973, 32, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuajiw, W.; Nakano, M.; Takatori, K.; Kojima, T.; Wakimoto, Y.; Fukushima, Y. Effects of amine, amine salt and amide on the behaviour of carbon dioxide absorption into calcium hydroxide suspension to precipitate calcium carbonate. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 2507–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.G.; He, P.; Lin, X.Y. The mechanism of sodium hydroxide solution promoting the gelation of Konjac glucomannan (KGM). Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, A.; Kim, H.; Shim, J.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, S. Correlation of thermal conductivity of instant noodles with their textural property for rehydration study. J. Texture Stud. 2016, 47, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).