Occurrence and Distribution of Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Sweet Potato Fields in the Philippines and Their Implication in the Biological Control of Sweet Potato Weevil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Collection of Soil Samples
2.2. Rearing of Galleria mellonella
2.3. Nematode Extraction
2.4. Killing, Staining and Mounting of Nematodes
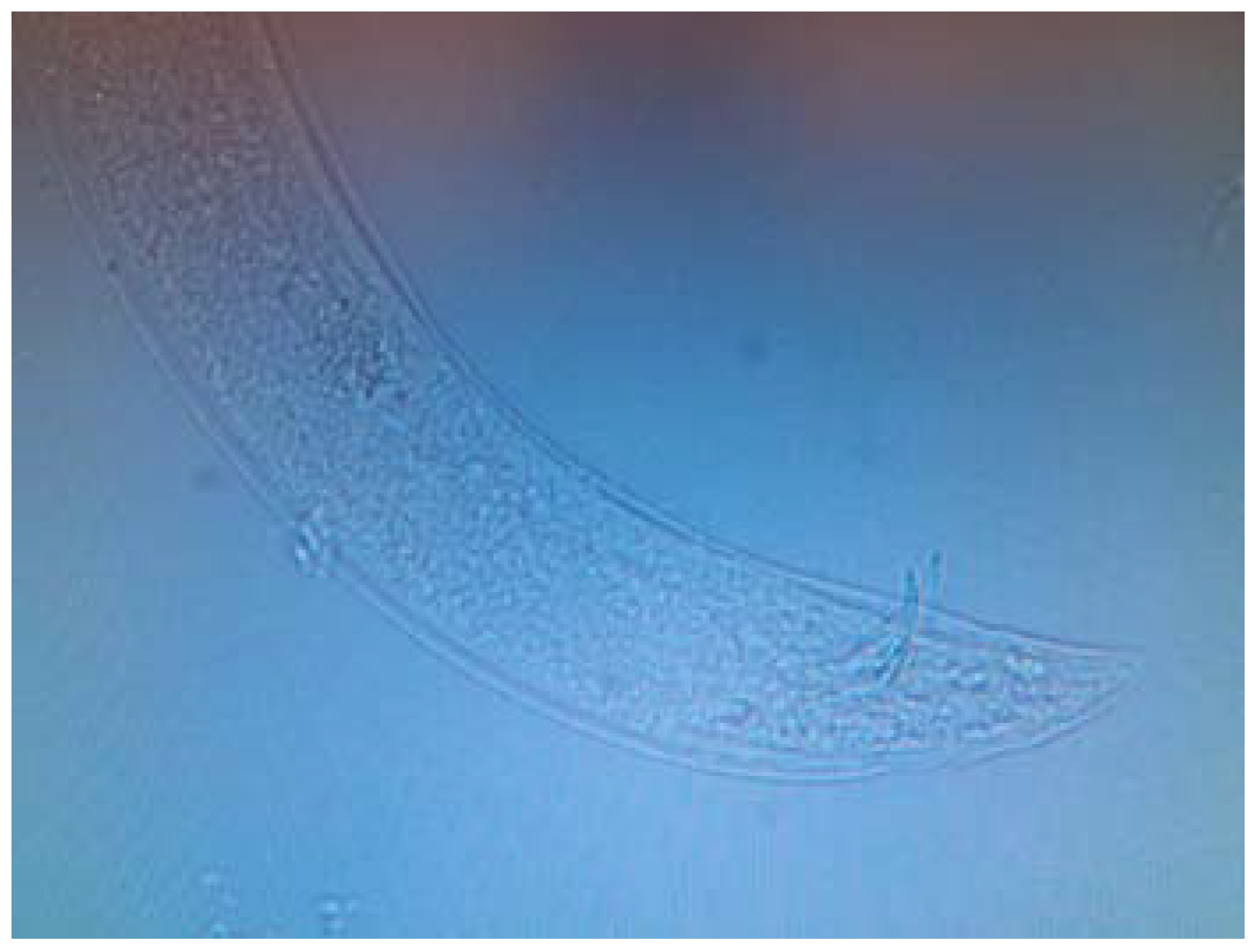
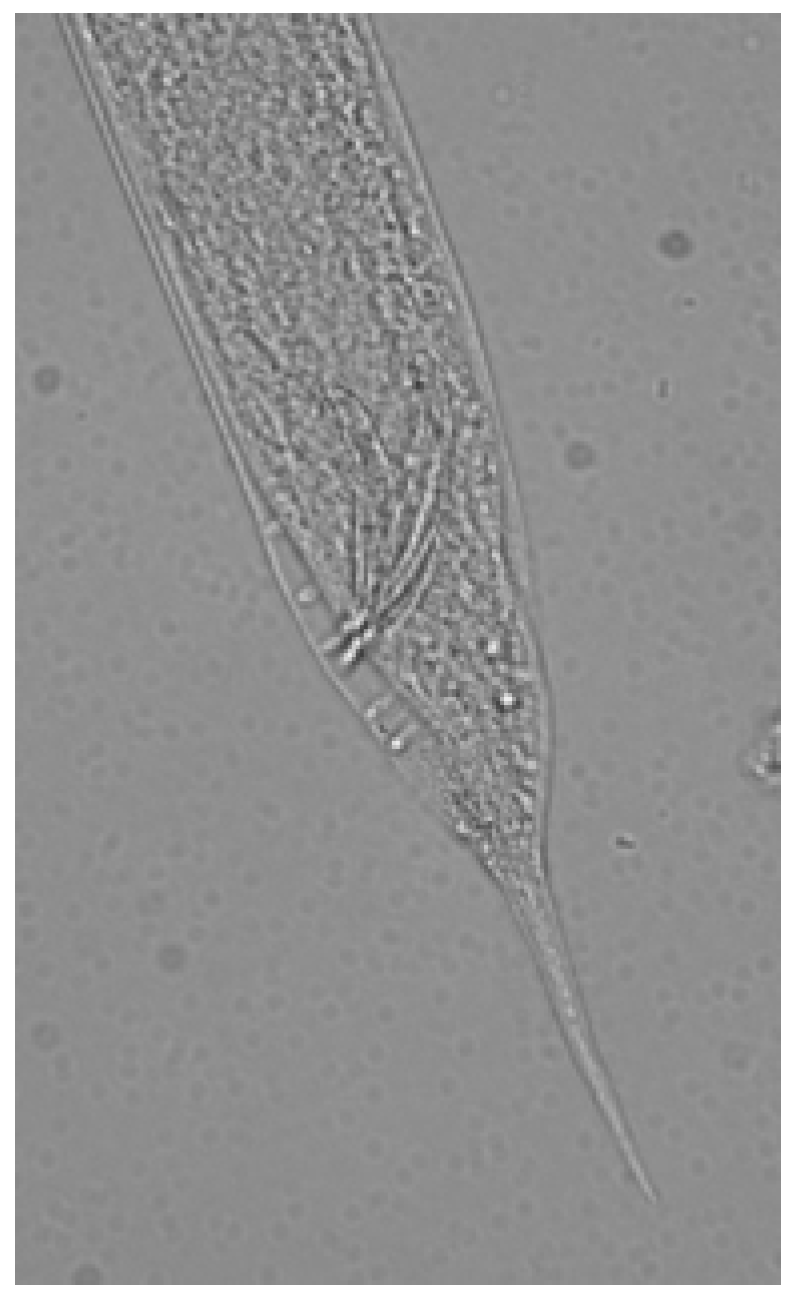
2.5. Identification of Nematodes
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Capinera, J.L. Sweet Potato Weevil, Cylas formicarius (Fabricius); Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rovesti, L.; Desco, K.V. Compatibility of chemical pesticides with the entomopathogenic nematodes, Steinernema carpocapsae Weiser and S. feltiae Feilipjev (Nematoda: Steinernematidae). Nematologica 1990, 36, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaugler, R. Biological control potential of neoaplectanid nematodes. J. Nematol. 1981, 13, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shanks, C.H.; Agudelo-Silva, F. Field pathogenicity and persistence of heterorhabditid and steinernematid nematodes (Nematoda) infecting black vine weevil larvae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in cranberry bogs. J. Econ. Entomol. 1990, 83, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner, A. Die Indduction der Immunabwehr eines Inaeks (Galleria mellonella, Lepidoptera) Durxh Arteigene Haemolymph Faltoren; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Goodey, J.B. Laboratory Methods for Work with Plant and Soil Nematodes; Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food: London, UK, 1957.
- Molyneux, A.S. Survival of infective juveniles of Heterorhabditis spp. and Steinernema spp. (Nematoda: Rhabditida) at various temperatures and their subsequent infectivity for insects. Rev. Nematol. 1985, 8, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Eivazian, K.N.; Niknam, G.; Griffin, C.T.; Mohammadi, S.A.; Moghaddam, S.A. A survey of entomopathogenic nematodes of the families Steinernematidae and Heterorhabditidae (Nematoda: Rhabditida) from north-west of Iran. Nematology 2009, 11, 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, G.C. Entomopathogenic nematode for the biological control of insects. Suppl. J. Nematol. 1995, 27, 529–534. [Google Scholar]
| Major Islands | Province | City/Barangay (Brgy)/Municipality | Occurrence of EPN z |
|---|---|---|---|
| Luzon | Benguet | Benguet State University (BSU) | + |
| Laguna | IPB, UP Los Banos | + | |
| Nueva Ecija | Central Luzon State University (CLSU) | - | |
| Tarlac | Tarlac College Of Agriculture | - | |
| Visayas | Biliran | DA, Naval | Steinernema |
| Provincial scion grove and nursery, Sitio San Roque, Brgy. Larrazabal | - | ||
| Sitio San Roque, Larrazabal, | + | ||
| Cebu | Dakit, Barili | Steinernema | |
| Cebu Technological University (CTU), Barili Campus | - | ||
| Cambinocot | + | ||
| Eastern Samar | Lawaan | + | |
| Brgy. Dos, Giporlos | - | ||
| Brgy. Cabong, Borongan | Steinernema | ||
| Balangiga | + | ||
| Brgy. San Pablo, Taft | + | ||
| Leyte | Brgy. San Esteban, Burauen | Steinernema | |
| Brgy. Maliwaliw, Dagami | - | ||
| Brgy. Tinocdugan, Leyte | Steinernema | ||
| DA, Babatngon (SP) | - | ||
| DA, Babatngon (Okra) | - | ||
| Del Pilar, Dulag | - | ||
| Fatima, Dulag | - | ||
| Gakat, Baybay | - | ||
| San Vicente, Dulag | Heterorhabditis | ||
| VSU, Agromet | - | ||
| Zone 11, Mayorga | Steinernema | ||
| Sitio Madocao, Brgy. Damos, Leyte | + | ||
| Visayas | Negros Oriental | Brgy. Apolong, Valencia | Heterorhabditis |
| Brgy. North Poblacion, Valencia | Heterorhabditis | ||
| Brgy. Lepayo, Dauin | + | ||
| Bacong | Heterorhabditis | ||
| Brgy. MaayongTubig, Dauin | - | ||
| Sito May-abo, Brgy. Maluwag, Zamboangita | - | ||
| Zamboangita | + | ||
| Western Samar | Brgy. Bachao, Basey | - | |
| Brgy. Mabuhay, Marabut | - | ||
| Brgy. Osmena, Hinabangan | - | ||
| Mindanao | Agusan del Sur | Sta. Josefa | + |
| Trento | - | ||
| Compostela Valley | Mabini | Steinernema | |
| New Bataan | - | ||
| Kapatagan, Laak | - | ||
| South Cotabato | Sulit, Polomolok | Steinernema | |
| Sarabia, Koronadal | - | ||
| Sitio Cabuling, Sarabia, Koronadal | - | ||
| Crossing, Polkan, Polomolok (Peanut) | + | ||
| Crossing, Polkan, Polomolok (SP) | - |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gapasin, R.M.; Lim, J.L.; Oclarit, E.L.; Ubaub, L.T.; Alde, M.C. Occurrence and Distribution of Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Sweet Potato Fields in the Philippines and Their Implication in the Biological Control of Sweet Potato Weevil. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae3010022
Gapasin RM, Lim JL, Oclarit EL, Ubaub LT, Alde MC. Occurrence and Distribution of Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Sweet Potato Fields in the Philippines and Their Implication in the Biological Control of Sweet Potato Weevil. Horticulturae. 2017; 3(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae3010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleGapasin, Ruben Madayag, Jesusito Laborina Lim, Elvira Lopez Oclarit, Leslie Toralba Ubaub, and Mannylen Coles Alde. 2017. "Occurrence and Distribution of Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Sweet Potato Fields in the Philippines and Their Implication in the Biological Control of Sweet Potato Weevil" Horticulturae 3, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae3010022
APA StyleGapasin, R. M., Lim, J. L., Oclarit, E. L., Ubaub, L. T., & Alde, M. C. (2017). Occurrence and Distribution of Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Sweet Potato Fields in the Philippines and Their Implication in the Biological Control of Sweet Potato Weevil. Horticulturae, 3(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae3010022





