Synergistic Response Mechanism and Gene Regulatory Network of Arundo donax Leaf Under Multiple Stresses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Observation of Leaf Phenotype
2.3. Determination of Energy Metabolism Substances
2.4. Determination of the Contents of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and ROS-Scavenging Enzyme Systems
2.5. Determination of Photosynthetic Pigment Content and Photosynthesis-Related Parameters
2.6. Determination of Cell Wall Components
2.7. Determination of Nitrogen in Plants
2.8. Obtaining and Processing of Transcriptome Data
2.9. Gene Expression Analysis and Functional Enrichment
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
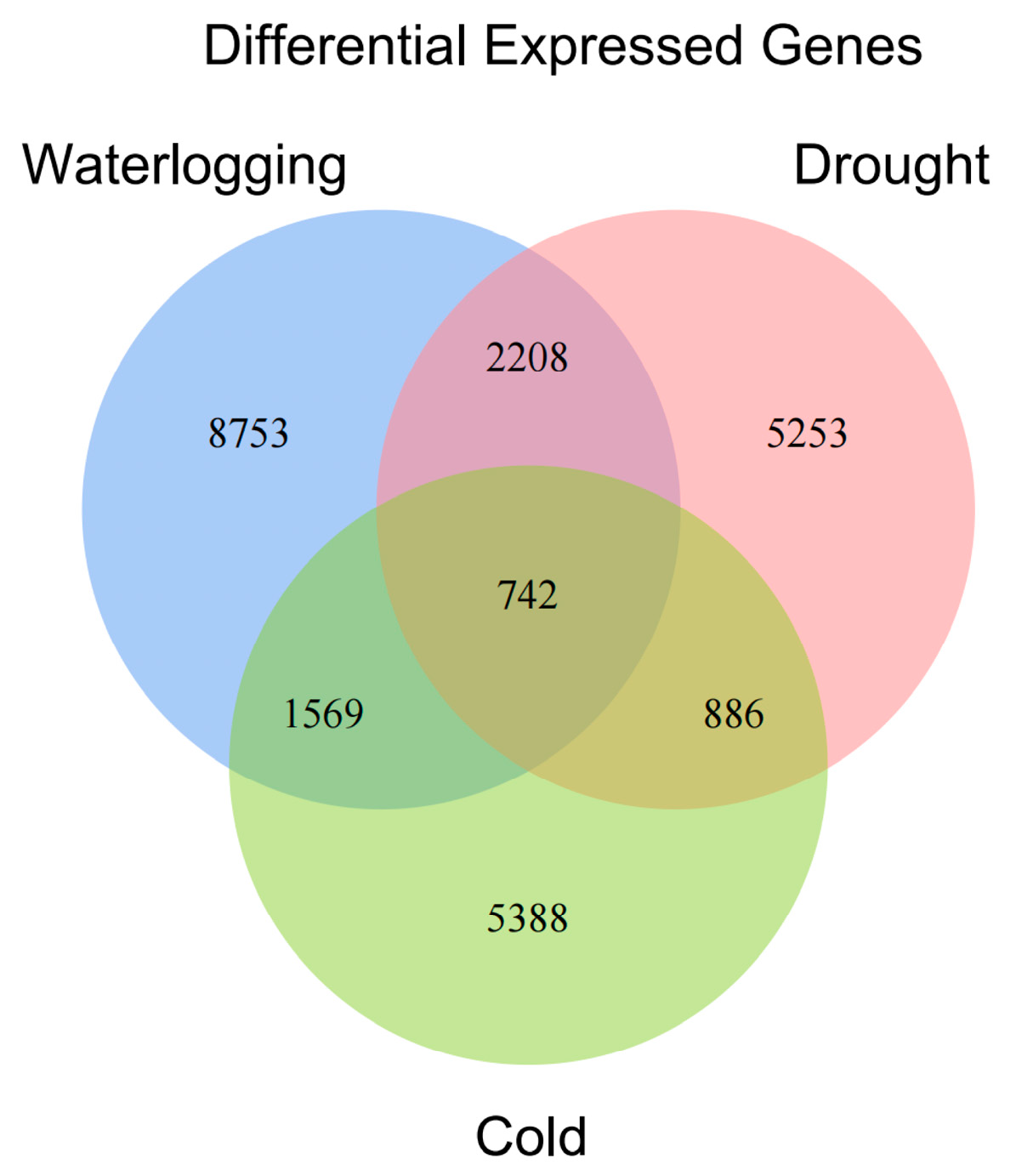
3.1. Identification of DEGs by RNA-Seq Under Three Different Stresses
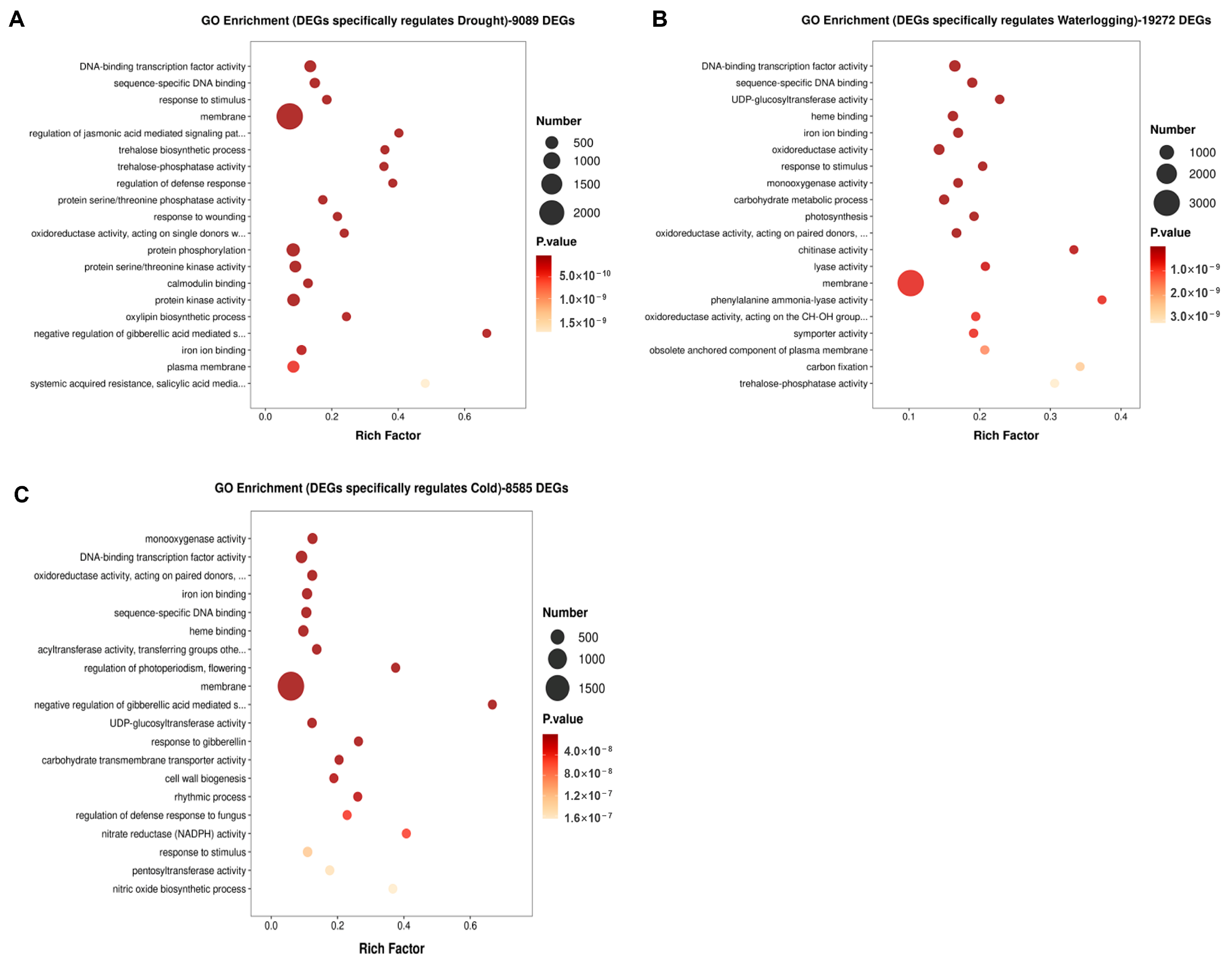
3.2. Analysis of DEGs Under Single Stress of Drought, Waterlogging and Cold in A. donax
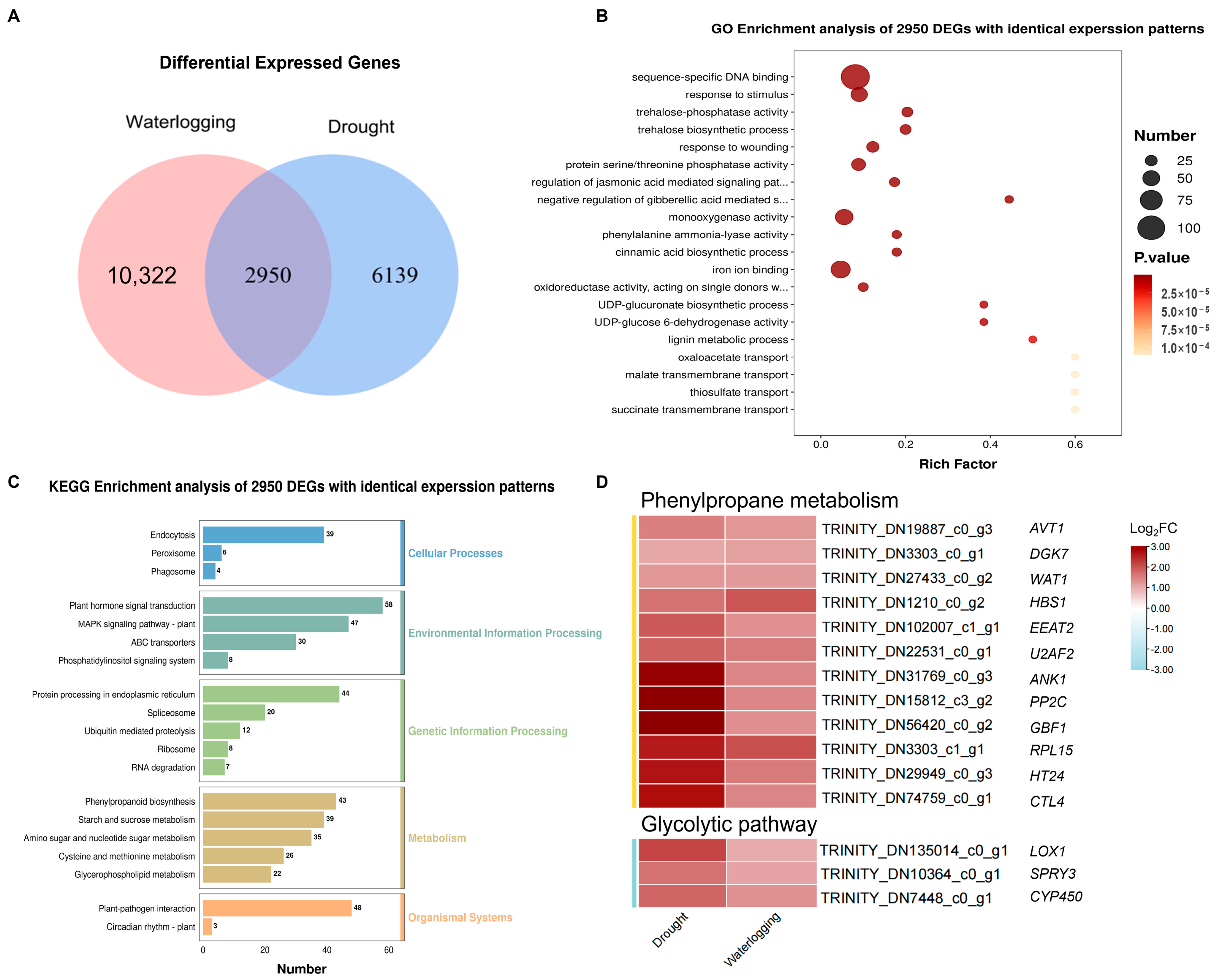
3.3. Coordinated Regulation Analysis of DEGs in Response to Drought and Waterlogging Stress in A. donax
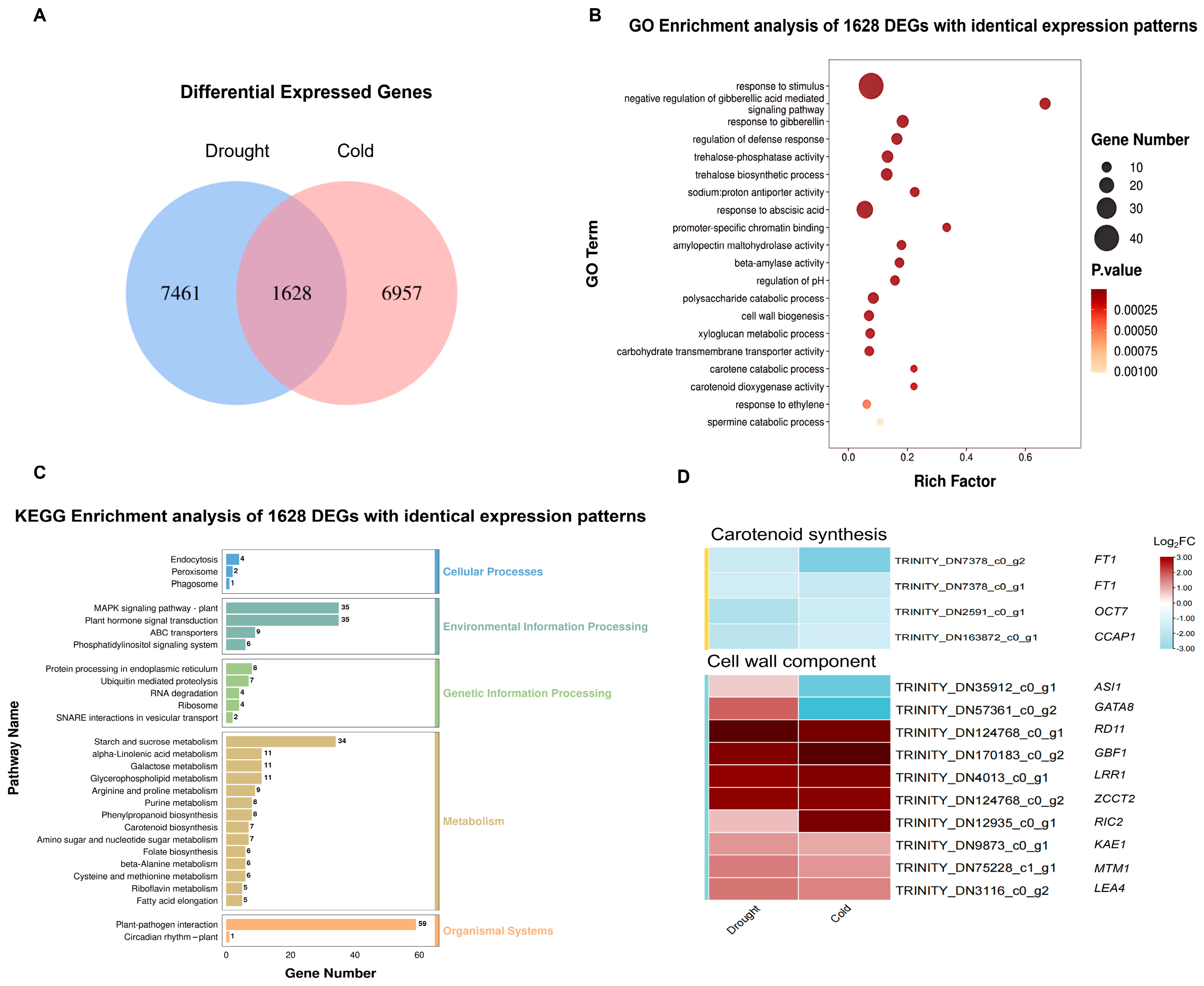
3.4. Coordinated Regulation Analysis of DEGs in Response to Drought and Cold Stress in A. donax
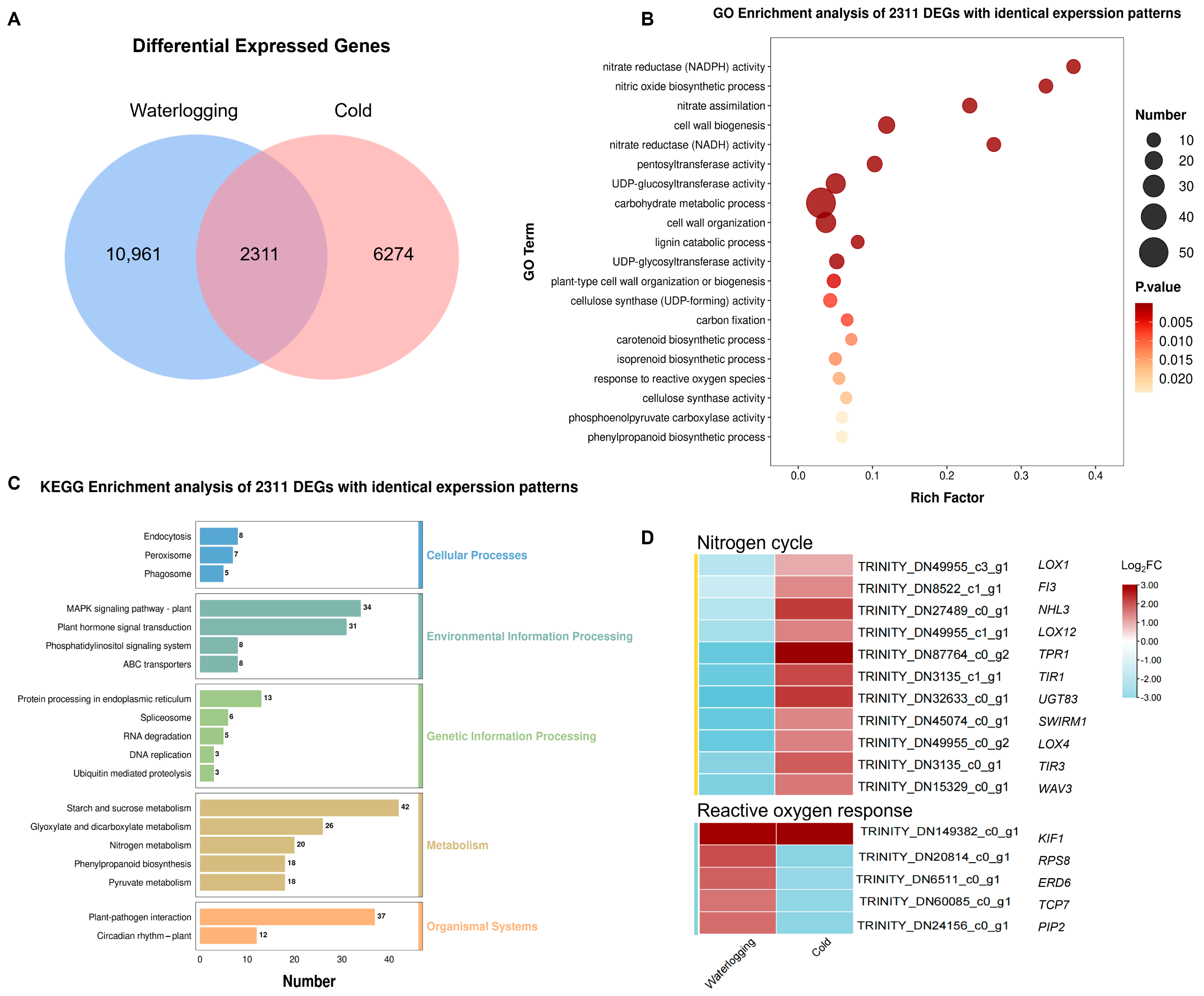
3.5. Coordinated Regulation Analysis of DEGs in Response to Waterlogging and Cold Stress in A. donax
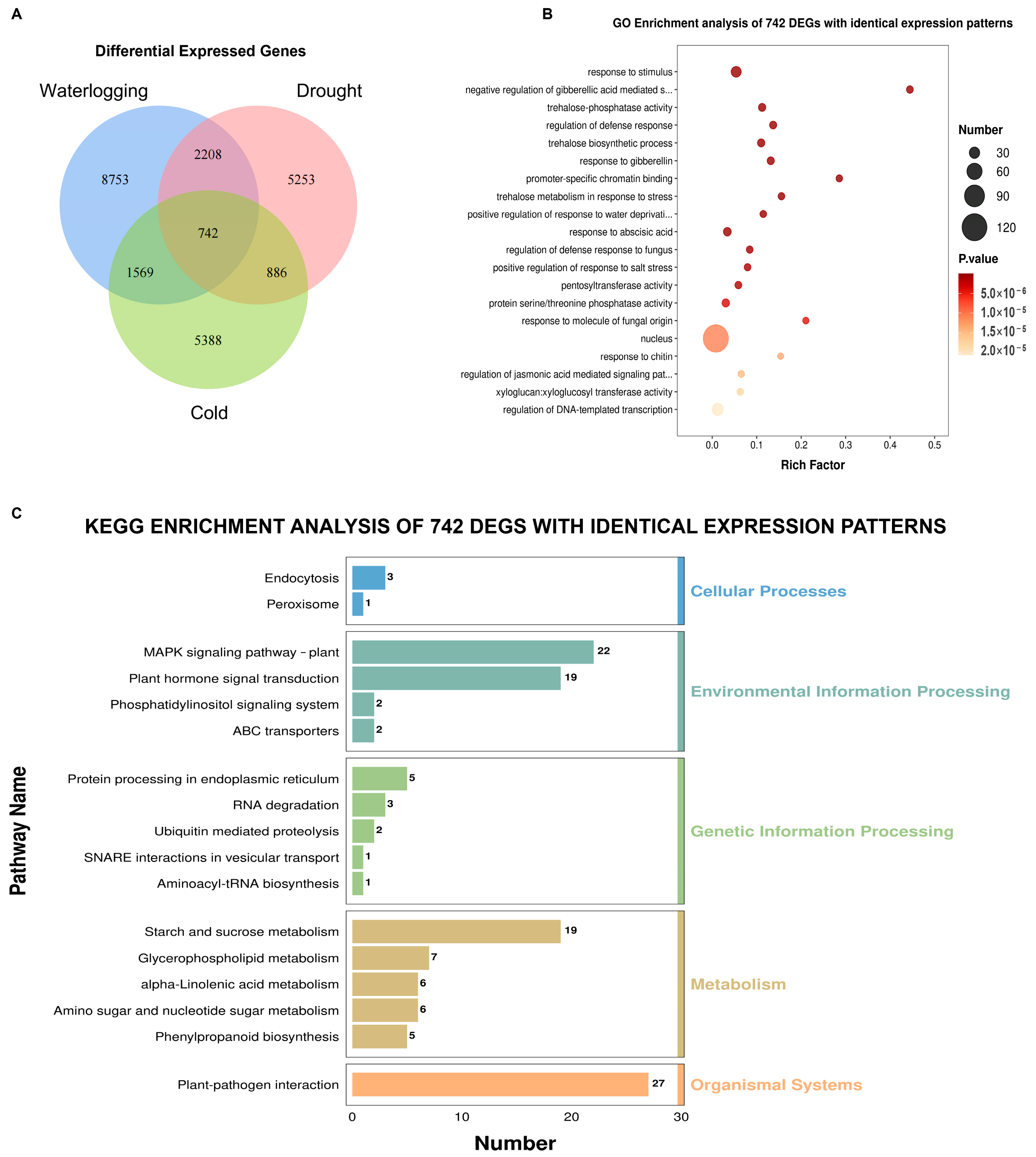
3.6. Coordinated Regulation Analysis of DEGs in Response to Three Stresses in A. donax
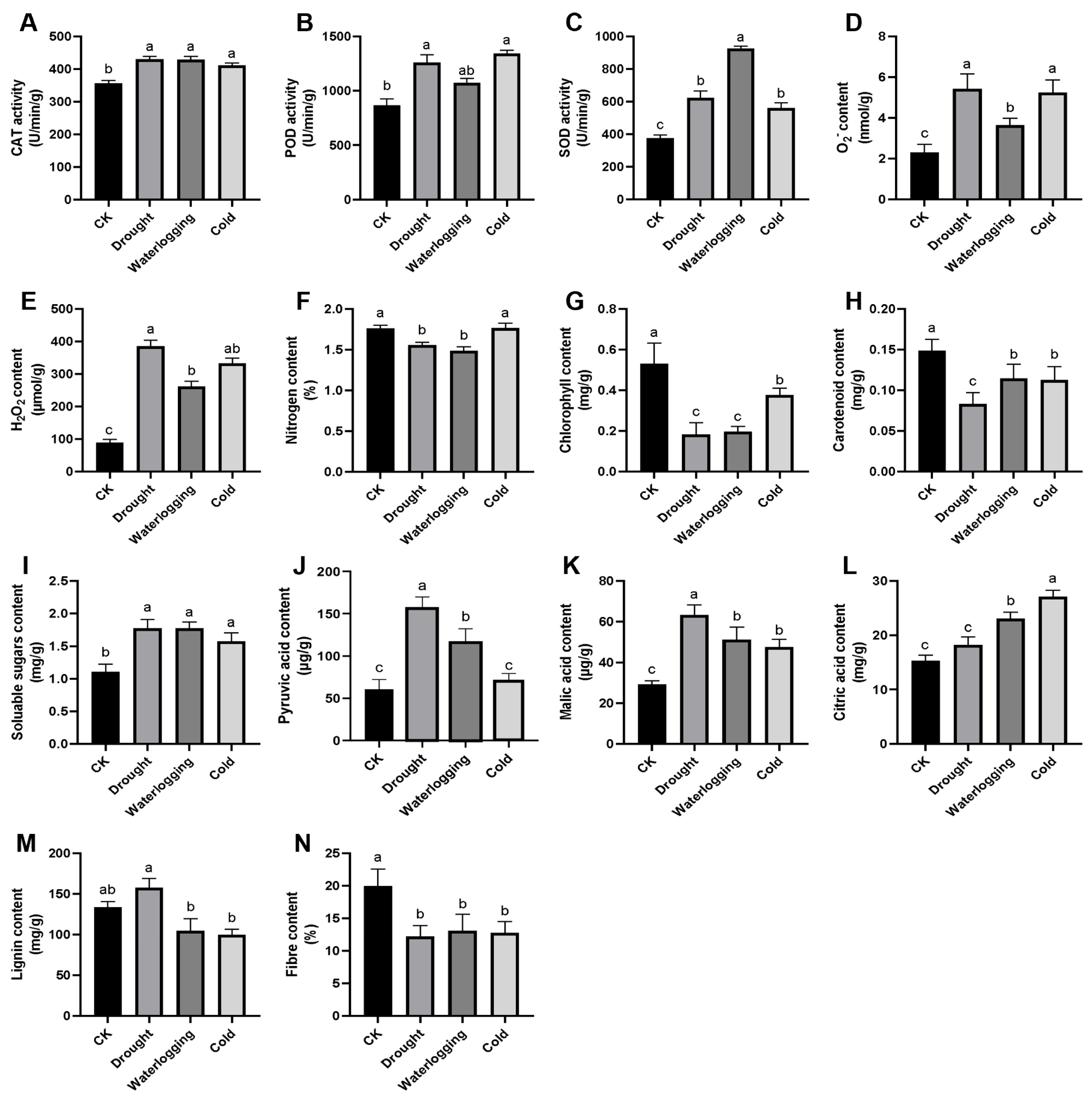
3.7. Scavenging of ROS and Adjustment of Cell Wall Components Are Involved in the Response of A. donax Leaves to the Three Stresses
4. Discussion
4.1. The Leaves of A. donax Tolerate Typical Abiotic Stresses by Activating the Scavenging of ROS
4.2. The Leaves of A. donax Tolerate Typical Abiotic Stresses by Changing the Composition of the Cell Wall
4.3. The Leaves of A. donax Tolerate Typical Abiotic Stresses by Accumulating Substances Involved in Energy Metabolism
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| CAT | catalase |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| POD | peroxidase |
References
- Lesk, C.; Rowhani, P.; Ramankutty, N. Influence of extreme weather disasters on global crop production. Nature 2016, 529, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandalinas, S.I.; Balfagón, D.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; Mittler, R.; Beckles, D. Plant responses to climate change: Metabolic changes under combined abiotic stresses. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 3339–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pan, T.; Chen, Q.; Qin, Y.; Ge, Q. Climate-associated major food crops production change under multi-scenario in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 151393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, A.; Ullah, S.; Dar, A.A.; Sardar, M.F.; Mehmood, T.; Tufail, M.A.; Shakoor, A.; Haris, M. Nexus on climate change: Agriculture and possible solution to cope future climate change stresses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 14211–14232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Certini, G.; Scalenghe, R. The crucial interactions between climate and soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egidi, G.; Bianchini, L.; Cividino, S.; Quaranta, G.; Salvia, R.; Cudlin, P.; Salvati, L. Toward a spatially explicit analysis of land vulnerability to degradation: A country-level approach supporting policy strategies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardion, L.; Verlaque, R.; Saltonstall, K.; Leriche, A.; Vila, B. Origin of the invasive Arundo donax (Poaceae): A trans-Asian expedition in herbaria. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Qu, Q.; Lin, H.; Chen, J.; Lin, Z.; Shao, E.; Lin, D. Exploring the Evolutionary History and Phylogenetic Relationships of Giant Reed (Arundo donax) through Comprehensive Analysis of Its Chloroplast Genome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, G. Arundo donax as a potential biomonitor of trace element contamination in water and sediment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 80, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, E.M.; Alrumman, S.A.; Ahmed, M.T.; Alshahrani, M.S.F.; Alshahrani, A.H.; Alhag, S.K. Population Ecology of Giant Reed (Arundo donax L.) Along the Environmental Gradient in Abha Valley, Asir Mountains, Saudi Arabia. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 25, 2590–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corno, L.; Pilu, R.; Adani, F. Arundo donax L.: A non-food crop for bioenergy and bio-compound production. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1535–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krička, T.; Matin, A.; Bilandžija, N.; Jurišić, V.; Antonović, A.; Voća, N.; Grubor, M. Biomass valorisation of Arundo donax L., Miscanthus × giganteus and Sida hermaphrodita for biofuel production. Int. Agrophys. 2017, 31, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Study on Preparation of Regenerated Cellulose Fiber from Biomass Based on Mixed Solvents. Materials 2024, 17, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarone, N.; Iovane, G.; Marranzini, D.; Sessa, R.; Guedes, M.C.; Faggiano, B. Arundo donax L. as sustainable building material. Sustain. Build. 2023, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduro Dias, C.S.A.M.; Nunes, H.; Vouzela, C.; Madruga, J.; Borba, A. In Vitro Rumen Fermentation Kinetics Determination and Nutritional Evaluation of Several Non-Conventional Plants with Potential for Ruminant Feeding. Fermentation 2023, 9, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Singh, J.; Kamboj, S.S.; Sexana, A.K.; Pandita, R.M.; Shamnugavel, M. Isolation of an N-acetyl-d-glucosamine specific lectin from the rhizomes of Arundo donax with antiproliferative activity. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Ruiz, J.; Ruiz Galea, M.; Amorós, M.C.; Alonso, J.; Mauri, P.V.; Lobo, M.C. Assessing Arundo donax L. in vitro-tolerance for phytoremediation purposes. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppa, E.; Astolfi, S.; Beni, C.; Carnevale, M.; Colarossi, D.; Gallucci, F.; Santangelo, E. Evaluating the potential use of Cu-contaminated soils for giant reed (Arundo donax, L.) cultivation as a biomass crop. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 8662–8672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Hong, Y.; Yao, Q.; Chang, X.; Shi, G.; Chen, W.; Tian, B.; Hegazy, A. Differences in the Microbial Composition and Function of the Arundo donax Rhizosphere Under Different Cultivation Conditions. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lino, G.; Espigul, P.; Nogués, S.; Serrat, X. Arundo donax L. growth potential under different abiotic stress. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompeiano, A.; Remorini, D.; Vita, F.; Guglielminetti, L.; Miele, S.; Morini, S. Growth and physiological response of Arundo donax L. to controlled drought stress and recovery. Plant Biosyst.-Int. J. Deal. All Asp. Plant Biol. 2017, 151, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, M.; Cosentino, S.L.; Marino, G.; Brunetti, C.; Scordia, D.; Testa, G.; Riggi, E.; Avola, G.; Loreto, F.; Centritto, M. Physiological responses of Arundo donax ecotypes to drought: A common garden study. GCB Bioenergy 2016, 9, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.; Scordia, D.; Lino, G.; Arias, C.; Cosentino, S.L.; Nogués, S. Salinity and Water Stress Effects on Biomass Production in Different Arundo donax L. Clones. BioEnergy Res. 2015, 8, 1461–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompeiano, A.; Huarancca Reyes, T.; Moles, T.M.; Guglielminetti, L.; Scartazza, A. Photosynthetic and Growth Responses of Arundo donax L. Plantlets Under Different Oxygen Deficiency Stresses and Reoxygenation. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompeiano, A.; Guglielminetti, L.; Bargiacchi, E.; Miele, S. Responses in chemical traits and biomass allocation of Arundo donax L. to deficit resources in the establishment year. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 73, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antal, G.; Kurucz, E.; Fari, M.G.; Popp, J. Tissue culture and agamic propagation of winter-frost tolerant ‘longicaulis’ Arundo donax L. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2014, 13, 2709–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompeiano, A.; Vita, F.; Miele, S.; Guglielminetti, L. Freeze tolerance and physiological changes during cold acclimation of giant reed [Arundo donax (L.)]. Grass Forage Sci. 2013, 70, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.; Gil, S.; Azcón-Bieto, J.; Nogués, S. The response of Arundo donax L. (C3) and Panicum virgatum (C4) to different stresses. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 85, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, J.M.; Virtue, J.G.; Williams, C.; Preston, C. Genetic diversity of giant reed (Arundo donax) in Australia. Weed Biol. Manag. 2017, 17, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huangfu, Y.; Chen, W.; Xie, Z.; Tian, B.; Wu, T.; Cao, G.; Guo, J.; Wei, F.; et al. The synergistic response of Arundo donax to multiple stressors: New insights from root genome-wide transcription analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 228, 120893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Tian, Z.; Guo, J.; Xie, Z.; Tian, B.; Liu, Z.; Chen, W.; Cao, G.; Zhang, L.; Yang, T.; et al. Physiological, Cellular, and Transcriptomic Analyses Provide Insights into the Tolerance Response of Arundo donax to Waterlogging Stress. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Liu, F.; Han, X.; Wu, D.; Peng, H. Chromosome-scale genome assembly of the autoalloenneaploid Arundo donax. Grassl. Res. 2024, 3, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Huang, M. Changes of Drought Stress onMain Osmotic Adjustment Substance in Leaves and Roots of Two Banana Plantlets. Genom. Appl. Biol. 2010, 29, 518–522. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, N.; González, C.; Molina, A.; Zirulnik, F.; Luna, C.M. Cadmium-induced early changes in O2 •−, H2O2 and antioxidative enzymes in soybean (Glycine max L.) leaves. Plant Growth Regul. 2008, 56, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, A.; Wu, T.; Guo, J.; Shi, G.; Tian, B.; Wei, F.; Cao, G. Integrated physiological and transcriptomic analysis reveals the involvement of photosynthesis and redox homeostasis in response of Arundo donax to low and high nitrogen supply. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 221, 119377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, N.B.; Aleem, S.; Khan, M.R.; Ashraf, S.; Busquets, R. Quantitative Estimation of Protein in Sprouts of Vigna radiate (Mung Beans), Lens culinaris (Lentils), and Cicer arietinum (Chickpeas) by Kjeldahl and Lowry Methods. Molecules 2022, 27, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Malik, L.; Sarkar, H.; Zakeri, M.; Almodaresi, F.; Soneson, C.; Love, M.I.; Kingsford, C.; Patro, R. Alignment and mapping methodology influence transcript abundance estimation. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrar, M.; Doneva, D.; Tattini, M.; Brunetti, C.; Gori, A.; Rodeghiero, M.; Wohlfahrt, G.; Biasioli, F.; Varotto, C.; Loreto, F.; et al. Phenotypic differences determine drought stress responses in ecotypes of Arundo donax adapted to different environments. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2439–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, L. Reactive Oxygen Species and Phytohormone Signaling Transduction Pathways. Subtrop. Plant Sci. 2008, 37, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sang, H.; Wang, H.; Shi, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Sun, K.; Zhang, J.; Feng, H. Research Progress of Plant Signaling in Systemic Responses to Abiotic Stresses. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2024, 59, 122–133. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, P.K.; Jayalakshmi, K.; Tilgam, J.; Gupta, A.; Nagaraju, Y.; Kumar, A.; Hamid, S.; Singh, H.V.; Minkina, T.; Rajput, V.D.; et al. ROS generated from biotic stress: Effects on plants and alleviation by endophytic microbes. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1042936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xue, X.; Lu, C.; Lin, J.; Wan, Y. Signal transduction and detection methods of reactive oxygen species in plants. J. Chin. Electron. Microsc. Soc. 2014, 33, 188–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Gong, Z.; Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Haensch, R.; Alfarraj, S.; Rennenberg, H. Strategies of plants to overcome abiotic and biotic stresses. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2024, 99, 1524–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, K.J.; Vogelsang, L. A general concept of quantitative abiotic stress sensing. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhou, W.; Guo, C. The Role of Plant Peroxisomes in ROS Signalling Network. Chin. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 33, 220–226. [Google Scholar]
- Waadt, R.; Seller, C.A.; Hsu, P.K.; Takahashi, Y.; Munemasa, S.; Schroeder, J.I. Plant hormone regulation of abiotic stress responses. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, N.; Rather, A.M.; John, R.; Chaturvedi, P.; Ghatak, A.; Weckwerth, W.; Zargar, S.M.; Mir, R.A.; Khan, M.A.; Mir, R.R. Proteomics for abiotic stresses in legumes: Present status and future directions. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2023, 43, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.-N. Epigenetic regulation of abiotic stress response in plants to improve the stress tolerance. Yi Chuan=Hereditas 2013, 35, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Xiao, Z.; Li, M.W.; Wong, F.L.; Yung, W.S.; Ku, Y.S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Xie, M.; Yim, A.K.; et al. Transcriptomic reprogramming in soybean seedlings under salt stress. Plant Cell Env. 2019, 42, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.L.; Cardoso, F.S.; Bohn, A.; Neves, A.R.; Santos, H. Engineering trehalose synthesis in Lactococcus lactis for improved stress tolerance. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4189–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorge, T.F.; António, C. Plant Metabolomics in a Changing World: Metabolite Responses to Abiotic Stress Combinations. In Plant, Abiotic Stress and Responses to Climate Change; InTech: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, J.; Wang, Z.; Ying, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, C.; Shi, R. Combined analysis of multi-omics reveals the potential mechanism of flower color and aroma formation in Macadamia integrifolia. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1095644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martino, M.; Rathmell, J.C.; Galluzzi, L.; Vanpouille-Box, C. Cancer cell metabolism and antitumour immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 654–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huangfu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, W.; Shi, G.; Tian, B.; Cao, G.; Zhang, L.; Guo, J.; Wei, F.; Xie, Z. Synergistic Response Mechanism and Gene Regulatory Network of Arundo donax Leaf Under Multiple Stresses. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080985
Huangfu Y, Sun Y, Chen W, Shi G, Tian B, Cao G, Zhang L, Guo J, Wei F, Xie Z. Synergistic Response Mechanism and Gene Regulatory Network of Arundo donax Leaf Under Multiple Stresses. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(8):985. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080985
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuangfu, Yixin, Yibo Sun, Weiwei Chen, Gongyao Shi, Baoming Tian, Gangqiang Cao, Luyue Zhang, Jialin Guo, Fang Wei, and Zhengqing Xie. 2025. "Synergistic Response Mechanism and Gene Regulatory Network of Arundo donax Leaf Under Multiple Stresses" Horticulturae 11, no. 8: 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080985
APA StyleHuangfu, Y., Sun, Y., Chen, W., Shi, G., Tian, B., Cao, G., Zhang, L., Guo, J., Wei, F., & Xie, Z. (2025). Synergistic Response Mechanism and Gene Regulatory Network of Arundo donax Leaf Under Multiple Stresses. Horticulturae, 11(8), 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080985










