Perfluoroalkyl Substances Accumulation in Lettuce: Effects of Cultivar, Growth Stage, and Cultivation Conditions on Food Safety
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Plant Growth and Treatment in Hydroponics
2.3. Field Cultivation Trial
2.4. PFAS Sampling, Extraction, and Quantification by LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.5. Quality Control and Quality Assurance
2.6. Health Risk Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of PFAS Bioaccumulation in the Hydroponic Experiment
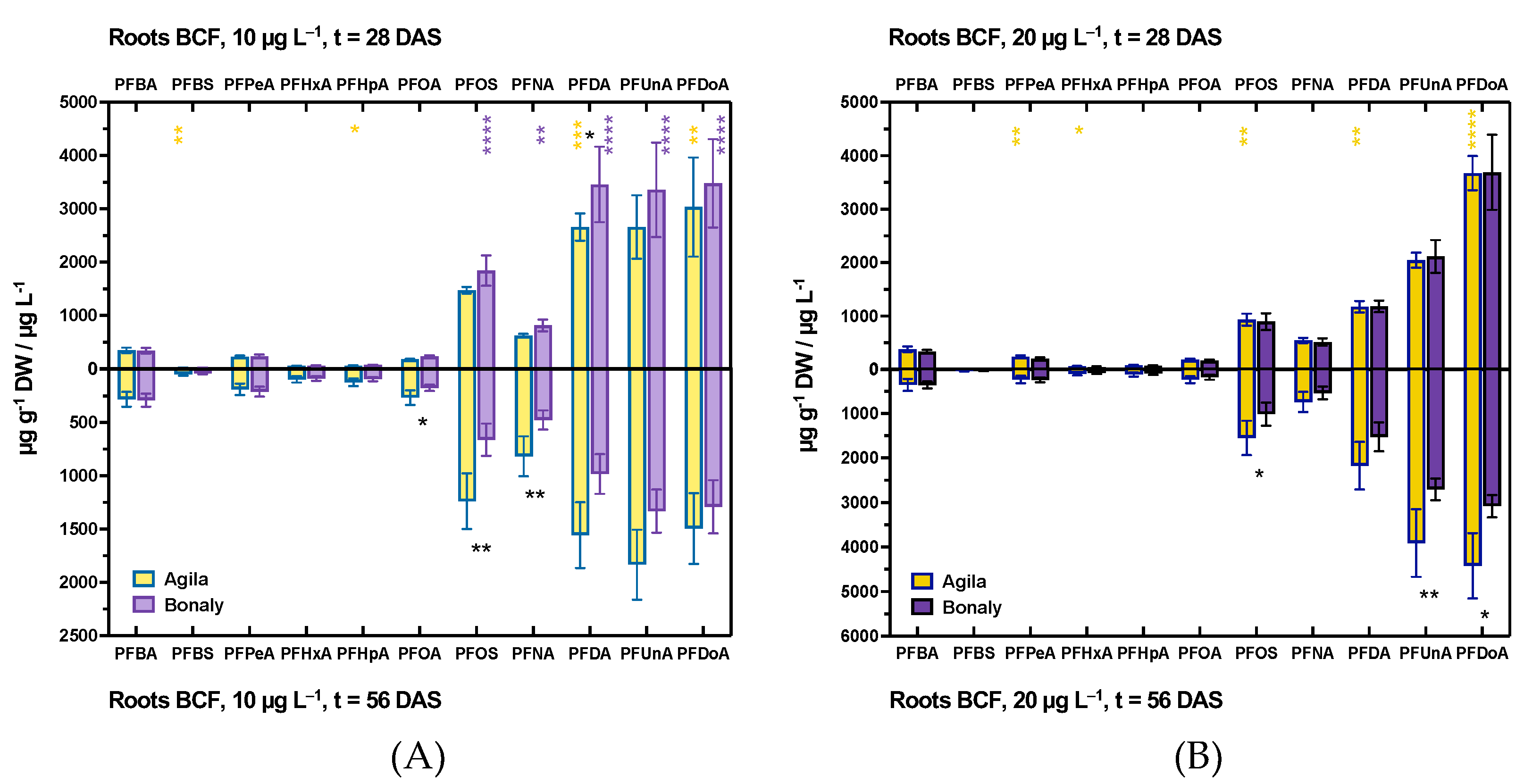
3.1.1. PFAS Accumulation in Root Tissues
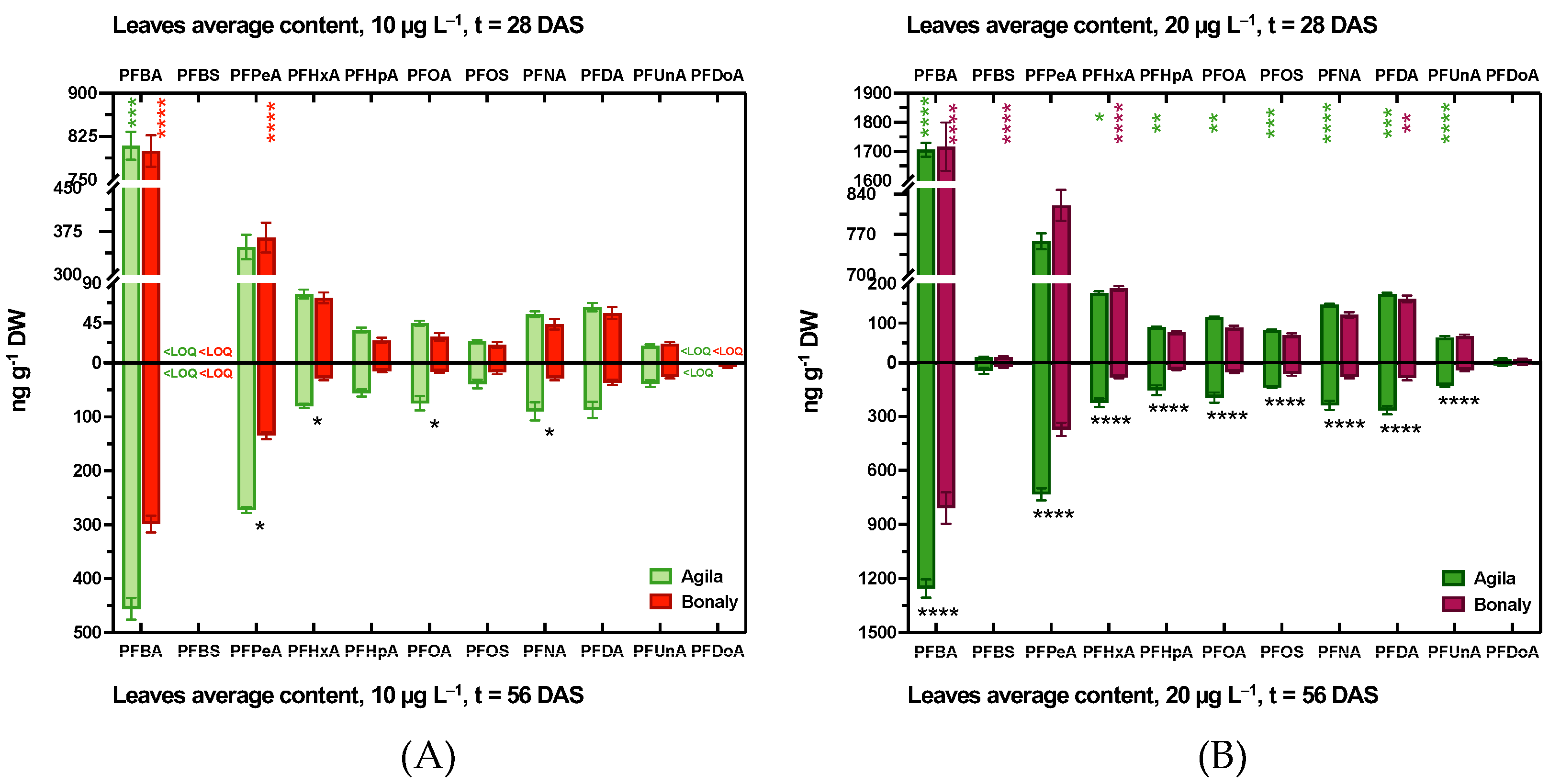
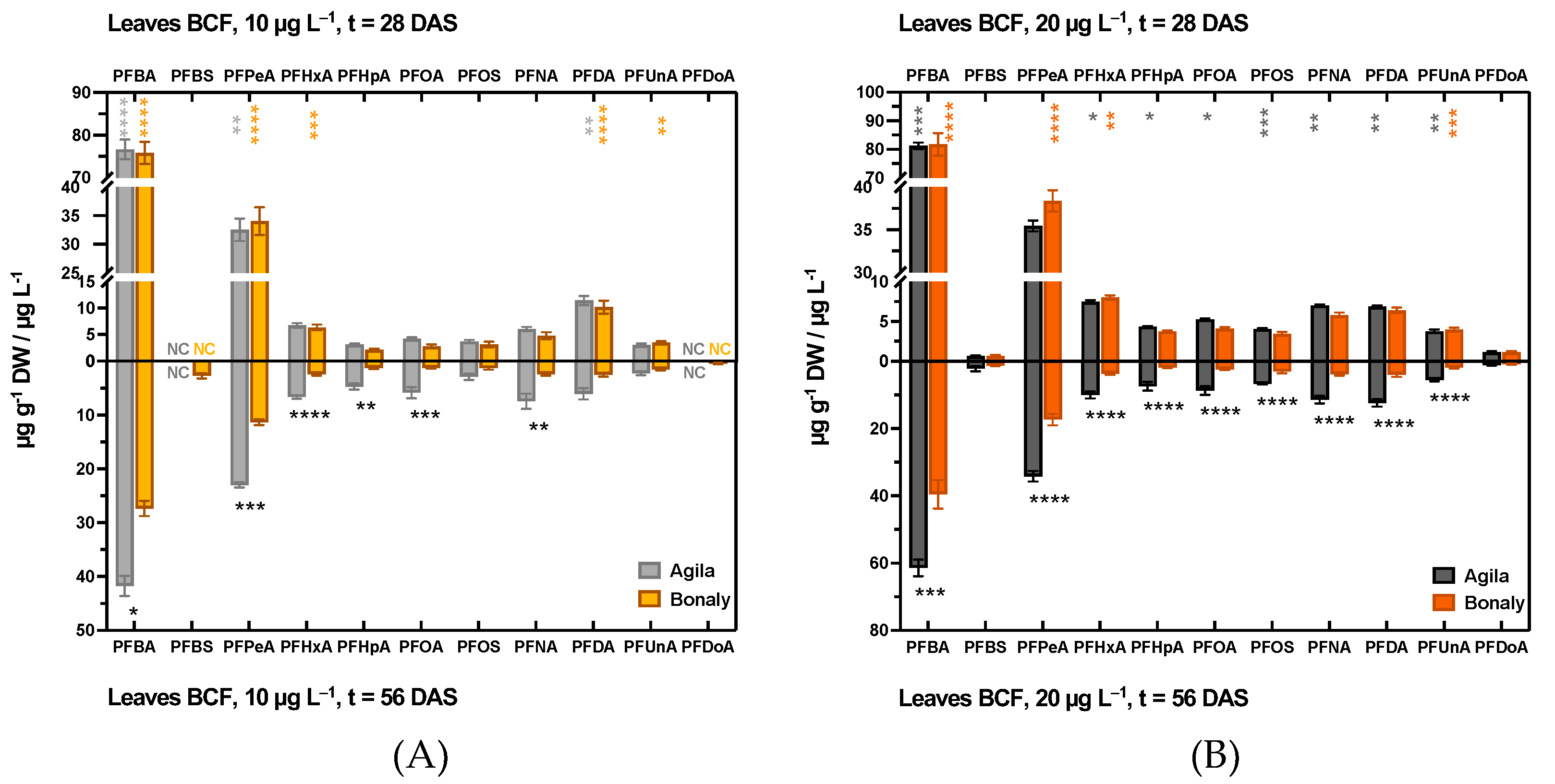
3.1.2. PFAS Accumulation in Leaf Tissues
3.2. PFAS Accumulation in Lettuce Cultivated in the Field
3.3. Dietary Exposure Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Influences of the Plant Age and Variety on PFAS Uptake and Accumulation
4.2. Accumulation in Lettuce Cultivated in the Field
4.3. Health Risk
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koch, A.; Aro, R.; Wang, T.; Yeung, L.W.Y. Towards a Comprehensive Analytical Workflow for the Chemical Characterisation of Organofluorine in Consumer Products and Environmental Samples. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 123, 115423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, D.C.; Meegoda, J.N. PFAS: The Journey from Wonder Chemicals to Environmental Nightmares and the Search for Solutions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.S.; Edirisinghe, D.; Seyedi, S.; Noteboom, H.; Blate, M.; Balci, D.D.; Abu-Orf, M.; Sharp, R.; Brown, J.; Aga, D.S. Burning Questions: Current Practices and Critical Gaps in Evaluating Removal of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) during Pyrolysis Treatments of Biosolids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 4, 100079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Dewitt, J.C.; Higgins, C.P.; Cousins, I.T. A Never-Ending Story of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghisi, R.; Vamerali, T.; Manzetti, S. Accumulation of perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) in agricultural plants: A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Death, C.; Bell, C.; Champness, D.; Milne, C.; Reichman, S.; Hagen, T. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in livestock and game species: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 144795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, S.E.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.S.; Roberts, S.M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Toxicity and Human Health Review: Current State of Knowledge and Strategies for Informing Future Research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allen, J.G. A review of the pathways of human exposure to poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and present understanding of health effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Zheng, S.; Sun, B. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Cancer: Detection Methodologies, Epidemiological Insights, Potential Carcinogenic Mechanisms, and Future Perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggeri, A. Valutazione Del Rischio Legato All’assunzione Di Sostanze per- e Polifluoroalchiliche per via Alimentare Da Parte Della Popolazione Veneta Residente Nella Zona Con Contaminazione Delle Acque. Aggiornamento Sulla Base Dei Limiti EFSA 2020. Campagna Di Sorveglianza degli alimenti 2016–2017. Epidemiol. Prev. 2024, 48, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARPAV, Agenzia Regionale per la Prevenzione e Protezione Ambientale del Veneto. Concentrazione di Sostanze Perfluoroalchiliche (PFAS) Nelle Acque Prelevate da ARPAV; Anni 2013–2024. Available online: https://www.arpa.veneto.it/dati-ambientali/open-data/idrosfera/concentrazione-di-sostanze-perfluoroalchiliche-pfas-nelle-acque-prelevate-da-arpav (accessed on 23 February 2025).
- ARPAV. Agenzia Regionale per la Prevenzione e Protezione Ambientale del Veneto. Monitoraggio delle Sostanze per- e Polifluoroalchiliche (PFAS) Nella Rete di Sorveglianza Delle Acque Sotterranee. 2024. Available online: https://www.arpa.veneto.it/temi-ambientali/acque-interne/acque-interne/pfas/20250102_monitoraggio_pfas_rete_sorveglianza.pdf/@@display-file/file (accessed on 23 February 2025).
- ARPAV. Agenzia Regionale per la Prevenzione e Protezione Ambientale del Veneto. Sostanze Perfluoro Alchiliche (PFAS). 2024. Available online: https://www.arpa.veneto.it/temi-ambientali/acque-interne/sostanze-perfluoro-alchiliche-pfas (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Adu, O.; Ma, X.; Sharma, V.K. Bioavailability, phytotoxicity and plant uptake of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 447, 130805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Qiu, W.; Du, J.; Wan, Z.; Zhou, J.L.; Chen, H.; Liu, R.; Magnuson, J.T.; Zheng, C. Translocation, bioaccumulation, and distribution of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in plants. iScience 2022, 25, 104061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, J.; Li, P. Exposure Routes, Bioaccumulation and Toxic Effects of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) on Plants: A Critical Review. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatilov, M.V.; Razin, A.F.; Ivanova, M.I. Analysis of the World Lettuce Market. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 395, 012053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damerum, A.; Chapman, M.A.; Taylor, G. Innovative Breeding Technologies in Lettuce for Improved Post-Harvest Quality. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 168, 111266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Ispizua, E.; Calatayud, Á.; Marsal, J.I.; Cannata, C.; Basile, F.; Abdelkhalik, A.; Soler, S.; Valcárcel, J.V.; Martínez-Cuenca, M.R. The Nutritional Quality Potential of Microgreens, Baby Leaves, and Adult Lettuce: An Underexploited Nutraceutical Source. Foods 2022, 11, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felizeter, S.; McLachlan, M.S.; De Voogt, P. Uptake of Perfluorinated Alkyl Acids by Hydroponically Grown Lettuce (Lactuca Sativa). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11735–11743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yuan, S.; Kwon, J.H. Insight into the Uptake and Translocation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Hydroponically Grown Lettuce. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 85454–85464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Ferro, N.; Pellizzaro, A.; Fant, M.; Zerlottin, M.; Borin, M. Uptake and Translocation of Perfluoroalkyl Acids by Hydroponically Grown Lettuce and Spinach Exposed to Spiked Solution and Treated Wastewaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, I.; Trentin, A.R.; Franzolin, E.; Nicoletto, C.; Masi, A.; Renella, G. Uptake and distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances by grafted tomato plants cultivated in a contaminated site in northern Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 170032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Barion, G.; Shrestha, I.; Ebinezer, L.B.; Trentin, A.R.; Vamerali, T.; Mezzalira, G.; Masi, A.; Ghisi, R. Accumulation and effects of perfluoroalkyl substances in three hydroponically grown Salix L. species. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, K.J.; Pratt, B.; Bose, N.; Dubois, L.G.; St John-Williams, L.; Perrott, K.M.; Ky, K.; Kapahi, P.; Sharma, V.; MacCoss, M.J.; et al. Alzheimer’s Disease Metabolomics Consortium. Skyline for Small Molecules: A Unifying Software Package for Quantitative Metabolomics. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1447–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battisti, I.; Zambonini, D.; Ebinezer, L.B.; Trentin, A.R.; Meggio, F.; Petit, G.; Masi, A. Perfluoroalkyl Substances Exposure Alters Stomatal Opening and Xylem Hydraulics in Willow Plants. Chemosphere 2023, 344, 140380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavcar, P.; Sofuoglu, A.; Sofuoglu, S.C. A health risk assessment for exposure to trace metals via drinking water ingestion pathway. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2009, 212, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Comprehensive European Food Consumption Database. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/data/datasets/the-efsa-comprehensive-european-food-consumption-database?locale=en (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- US EPA’s IRIS Toxicological Review for PFBA and Related Salts. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/iris (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- GraphPad Software. GraphPad Prism Version 10.0.0 for Mac. Boston, MA, 2025. Available online: www.graphpad.com (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio. PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Helsel, D.R. Statistics for Censored Environmental Data Using MINITAB® and R, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Q.; Wen, Y.; Wu, H.; Cui, X. Uptake and translocation of both legacy and emerging per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances in hydroponic vegetables. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 862, 160684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Cai, Y. Bioaccumulation of legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in hydroponic lettuce and risk assessment for human exposure. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 154, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, N. Role of Plant Nutrients in Plant Growth and Physiology. In Plant Nutrients and Abiotic Stress Tolerance; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 51–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiz, L.; Zeiger, E.; Moller, I.M.; Murphy, A. Plant Physiology and Development, 6th ed.; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, N.E.; Trontin, C.; Duan, L.; Dinneny, J.R. Beyond the Barrier: Communication in the Root through the Endodermis. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfson, K.N.; Esfandiari, M.; Bernards, M.A. Suberin Biosynthesis, Assembly, and Regulation. Plants 2022, 11, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Alder, A.C. Uptake Mechanisms of Perfluoroalkyl Acids with Different Carbon Chain Lengths (C2-C8) by Wheat (Triticum acstivnm L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.; Sun, H.; Song, M.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, W.; Ying, G.G.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in the Soil–Plant System: Sorption, Root Uptake, and Translocation. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Chen, L.; Yu, L.Y.; Yu, P.F.; Zhao, H.M.; Mo, C.H.; Li, Y.W.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.Y.; Zhou, D.M.; et al. Genotypic Variation and Mechanism in Uptake and Translocation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in Lettuce (Lactuca Sativa L.) cultivars Grown in PFOA-Polluted Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Yuan, J.; Kong, W.; Yang, Z. Genotype Variations in Cadmium and Lead Accumulations of Leafy Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) and Screening for Pollution-Safe Cultivars for Food Safety. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felizeter, S.; Jürling, H.; Kotthoff, M.; De Voogt, P.; McLachlan, M.S. Uptake of perfluorinated alkyl acids by crops: Results from a field study. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, 1158–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, S. The Roles of Protein and Lipid in the Accumulation and Distribution of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in Plants Grown in Biosolids-Amended Soils. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eun, H.; Yamazaki, E.; Taniyasu, S.; Miecznikowska, A.; Falandysz, J.; Yamashita, N. Evaluation of perfluoroalkyl substances in field-cultivated vegetables. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scearce, A.E.; Macrae, J.D.; Goossen, C.P.; Zhang, Y.J.; Holt, K.P.; Schattman, R.E. Uptake of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) into lettuce (Lactuca sativa), tall fescue (Schedonorus arundinaceus) and tomato (Solanum lycopersicum): A greenhouse experiment testing the effect of intercropping. Environ. Adv. 2025, 20, 100629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felizeter, S.; Jürling, H.; Kotthoff, M.; De Voogt, P.; McLachlan, M.S. Influence of Soil on the Uptake of Perfluoroalkyl Acids by Lettuce: A Comparison between a Hydroponic Study and a Field Study. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xiao, Z.; Sun, J.; Oyang, X.; Xie, X.; Li, Z.; Tian, X.; Li, J. Metabolic Regulations in Lettuce Root under Combined Exposure to Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate in Hydroponic Media. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, M.; Gong, T.; Zan, R.; Wang, W. Transport Behavior Difference and Transport Model of Long- and Short-Chain per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Underground Environmental Media: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Duan, J.; Tian, S.; Ji, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, D. Short-Chain per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Aquatic Systems: Occurrence, Impacts and Treatment. Chem. Engr. J. 2020, 380, 122506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solan, M.E.; Koperski, C.P.; Senthilkumar, S.; Lavado, R. Short-Chain per- and Polyfluoralkyl Substances (PFAS) Effects on Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Human Liver, Kidney, Muscle, and Microglia Cell Lines. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzolo, S.; Caligiuri, I.; Sfriso, A.A.; Mauceri, M.; Rotondo, R.; Campagnol, D.; Canzonieri, V.; Rizzolio, F. Early Warnings by Liver Organoids on Short-and Long-Chain PFAS Toxicity. Toxics 2022, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodlief, T.; Vance, S.; Hu, Q.; Dewitt, J. Immunotoxicity of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Insights into Short-Chain PFAS Exposure. Toxics 2021, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasters, R.; Groffen, T.; Eens, M.; Bervoets, L. Dynamic spatiotemporal changes of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in soil and eggs of private gardens at different distances from a fluorochemical plant. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 123613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling Costello, M.C.; Lee, L.S. Sources, Fate, and Plant Uptake in Agricultural Systems of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2020, 10, 799–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaseger, G.; Chan, K.L.; Yee Tan, K.; Ramasamy, S.; Khin, M.C.; Amaladoss, A.; Kadamb Haribhai, P. Hydroponics: Current trends in sustainable crop production. Bioinformation 2023, 19, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variety | Age | Treatment | HI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agila | 28 DAS | 10 µg L−1 | 1029 |
| 20 µg L−1 | 740 | ||
| 56 DAS | 10 µg L−1 | 1699 | |
| 20 µg L−1 | 4585 | ||
| Bonaly | 28 DAS | 10 µg L−1 | 3022 |
| 20 µg L−1 | 2389 | ||
| 56 DAS | 10 µg L−1 | 545 | |
| 20 µg L−1 | 1674 | ||
| Agila | / | Open field | 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sabia, A.; Battisti, I.; Trentin, A.R.; Wei, X.; Nicoletto, C.; Renella, G.; Masi, A. Perfluoroalkyl Substances Accumulation in Lettuce: Effects of Cultivar, Growth Stage, and Cultivation Conditions on Food Safety. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070775
Sabia A, Battisti I, Trentin AR, Wei X, Nicoletto C, Renella G, Masi A. Perfluoroalkyl Substances Accumulation in Lettuce: Effects of Cultivar, Growth Stage, and Cultivation Conditions on Food Safety. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(7):775. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070775
Chicago/Turabian StyleSabia, Andrea, Ilaria Battisti, Anna Rita Trentin, Xudong Wei, Carlo Nicoletto, Giancarlo Renella, and Antonio Masi. 2025. "Perfluoroalkyl Substances Accumulation in Lettuce: Effects of Cultivar, Growth Stage, and Cultivation Conditions on Food Safety" Horticulturae 11, no. 7: 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070775
APA StyleSabia, A., Battisti, I., Trentin, A. R., Wei, X., Nicoletto, C., Renella, G., & Masi, A. (2025). Perfluoroalkyl Substances Accumulation in Lettuce: Effects of Cultivar, Growth Stage, and Cultivation Conditions on Food Safety. Horticulturae, 11(7), 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070775











