Structure Characteristics, Variation of Main Quantitative Traits, and Probability Grading of Chinese Olive (Canarium album) Seeds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
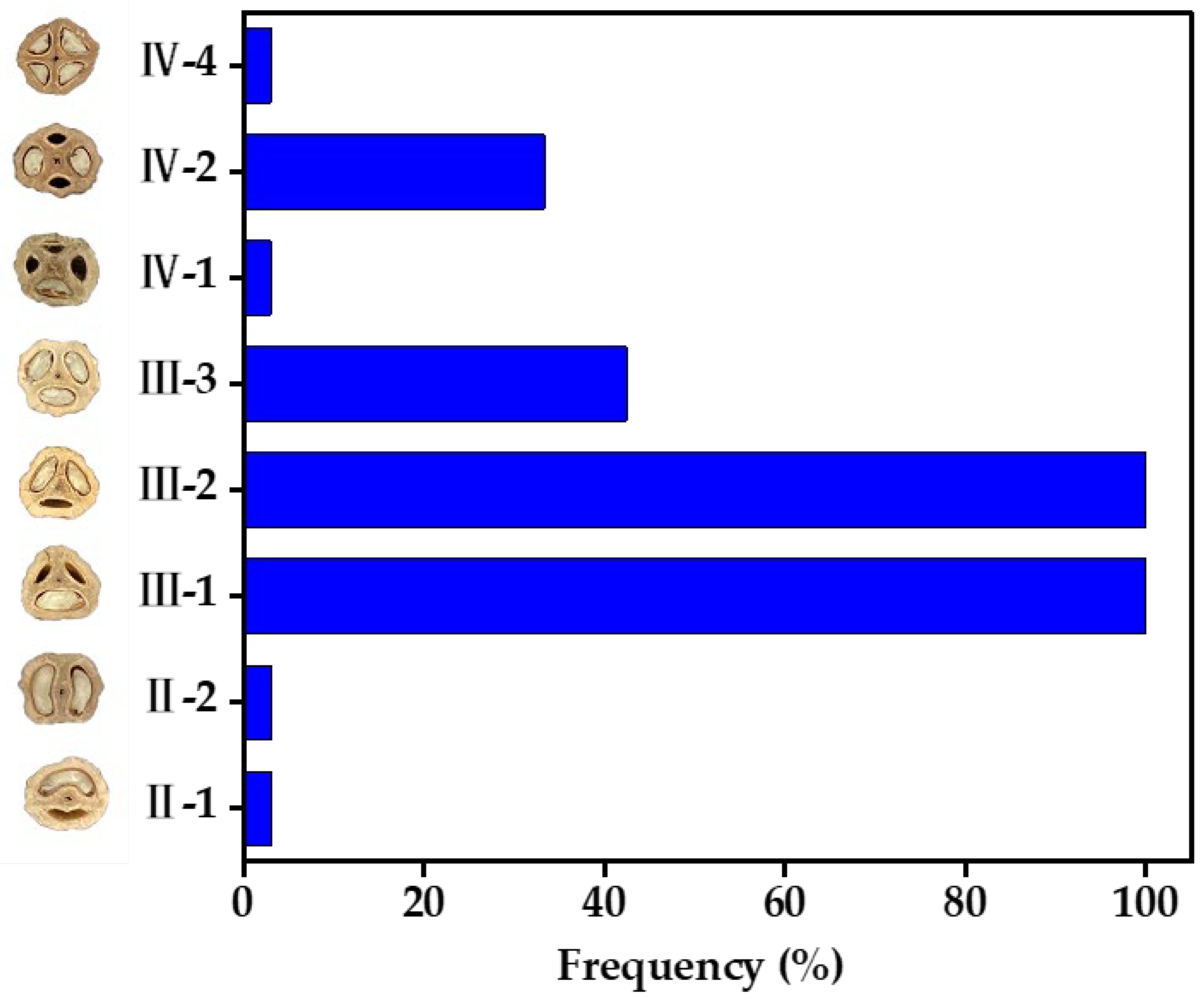
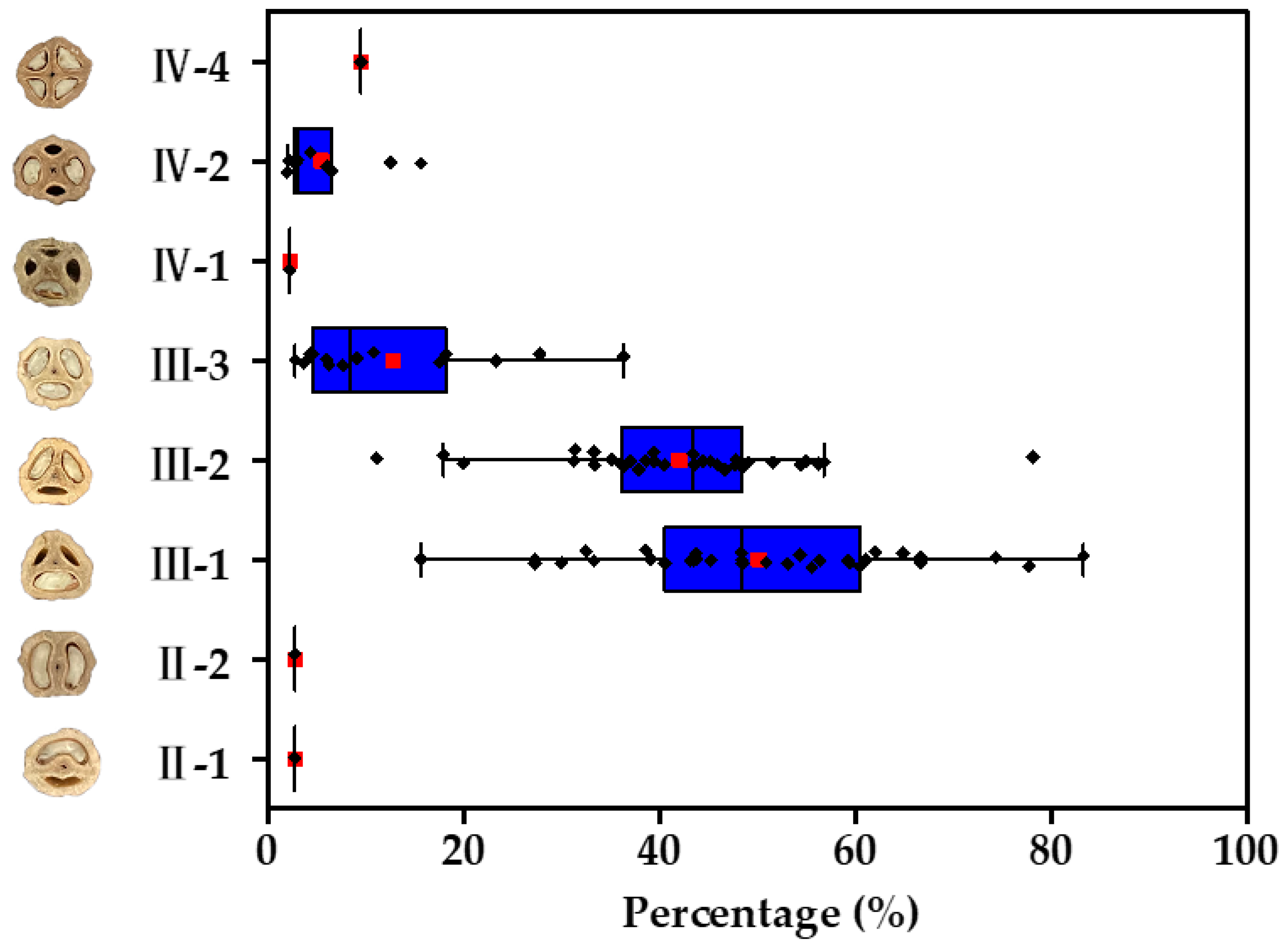
3.1. Structural Characteristics of Seeds and Statistical Analysis of the Locule and Embryo
3.2. Statistical Analysis and Probability Classification of Seed Quantitative Traits
3.2.1. Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Analysis of Quantitative Traits
3.2.2. Normality Test of Quantitative Traits
3.2.3. Probability Classification of Quantitative Traits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Editorial Committee of Flora of China; Chinese Academy of Sciences. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1997; Volume 43, pp. 17–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Xia, W. Nutritional composition of the kernels from Canarium Album L. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 808–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Q. Study on dormant and germination characteristics of Chinese Olive (Canarium album) seeds. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.B.; Xie, Q.; Chen, Q.X. Introduction to several fresh olive varieties (strains) and good breeding methods. South China Fruits 2016, 45, 154–156, 166. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Su, M.H.; Chen, Q.X.; Zeng, B.Y.; Li, H.H.; Wang, W. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant capacity of Chinese olive (Canarium album L.) Cultivars. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, N.; Liu, L.; Wang, W.; Xie, Q.; Chang, Q.; Chen, Q. Identification and characterization of glucosyltransferase that forms 1-galloyl-β-d-glucogallin in Canarium album L., a functional fruit rich in hydrolysable tannins. Molecules 2021, 26, 4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Q.; Su, M.; Chen, Q. The advance on the research of chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Chinese olive. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2013, 34, 1610–1616. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China: 2020 Ed.; The Medicine Science and Technology Press of China: Beijing, China, 2020; p. 206. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.H.; Liu, L.M.; Qiu, N.N.; Xie, Q.; Wang, W.; Chen, Q.X. Seed morphological structure and quantitative trait analysis of Canarium album. Plant Sci. J. 2019, 37, 413–421. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.J. Studies on the variations and grading standards of several economid charcters of peach. J. Beijing Univ. Agric. 1992, 2, 98–104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, L.; Li, L.; Sun, L.W.; Hao, B.C. Variation and probability grading of main quantitative characters of fruit in strawberry germplasm resource. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2007, 20, 1067–1069. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.H. Seed Science of Horticultural Crops; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 17–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, S. Botany, 2nd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 208–209. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bobrov, A.V.F.C.; Romanov, M.S. Morphogenesis of fruits and types of fruit of angiosperms. Bot. Lett. 2019, 166, 366–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropelewska, E.; Rutkowski, K.P. Differentiation of peach cultivars by image analysis based on the skin, flesh, stone and seed textures. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 2371–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oriani, A.; Scatena, V.L. Ovule, Fruit and seed development in Abolboda (xyridaceae, poales): Implications for taxonomy and phylogeny. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2014, 175, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenzadeh, S.; Sheidai, M.; Koohdar, F. Seed Morphology of some Plantago (plantaginaceae) species in Iran and Its systematic and phylogenetic implications. Turk. J. Bot. 2023, 47, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, K.M.A.; Arnold, R.J. Seed Source variation for growth and stem form in the exotic species Khaya senegalensis in Sri Lanka. New For. 2018, 49, 489–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Mummenhoff, K. Effective seedbank management to ensure food security and preserve biodiversity. Plant Syst. Evol. 2024, 310, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.N.; Huang, F.; Zhu, L.; Guo, M.W.; Li, Z.Y.; Xin, X. Phenotypic diversity analysis and comprehensive evaluation of 143 agropyron germplasm resources in Lnner Mongolia. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2024, 1–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.H.; Zhao, W.W.; Wang, L.T.; Zhao, L.L.; Wang, P.C. Genetic diversity analysis of 22 lotus corniculatus germplasm resources based on phenotypic quantitative traits. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2023, 31, 173–179. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, S.; Fan, L.; Yang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, G.; Liu, S.; et al. Natural allelic variation of GMST05 controlling seed size and quality in soybean. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigliucci, M.; Murren, C.J.; Schlichting, C.D. Phenotypic plasticity and evolution by genetic assimilation. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coomes, D.A.; Grubb, P.J. Colonization, tolerance, competition and seed-size variation within functional groups. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.F.; Deng, X.J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L.B.; Zhang, J.F.; Luo, Y.H. Effects of seed size and drought stress on the growth and physiological characteristics of Quercus wutaishanica seedlings. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 3331–3339. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.K.; Cao, B.; Li, G.S. Correlations of plant seed dispersal pattern with genome size and 1000-seed mass. Chin. J. Ecol. 2013, 32, 832–837. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Q.X. Classification of phenotypic traits, identification of volatile compounds and characteristic aroma analysis of Canarium album fruit. Food Sci. 2024, 45, 26–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.H.; Zhao, Q.F.; Dong, Z.G.; Tang, X.P.; Wang, M.; Ren, R. Variation and probability grading of main quantitative traits of table grape resources. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2013, 14, 1185–1189. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, G.L.; Xiao, Q.W.; Cai, L.J.; Luo, Y.F.; Zhou, X.M. Variation and probability grading of main quantitative traits of walnut (Juglansregia L.) Germplasm resources. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2015, 41, 647–650. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.J.; Liu, W.S.; Lui, N.; Zhang, Y.P.; Zhan, Q.P.; Liu, S. Variation and probability grading of main quantitative traits of apricot (Armeniaca vulgaris) germplasm. J. Fruit Sci. 2013, 30, 37–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
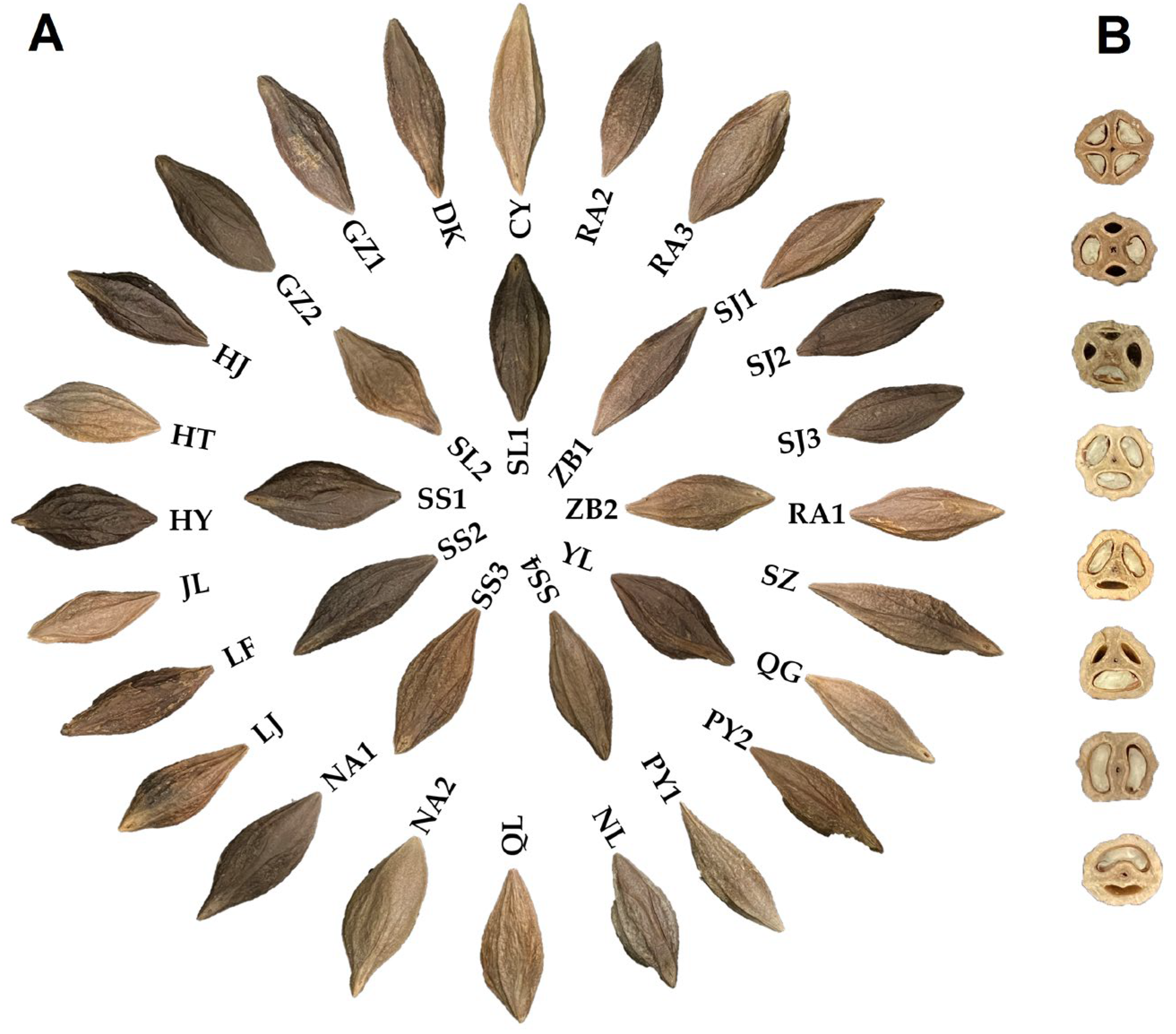


| Code | Name | Source | Code | Name | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CY | Wampee Changying | Fuzhou, Fujian, China | RA1 | Rui’an 1 | Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China |
| DK | Meixi 1 | Fuzhou, Fujian, China | RA2 | Rui’an 2 | Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China |
| GZ1 | Gaozhou 1 | Maoming, Guangdong, China | RA3 | Rui’an 3 | Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China |
| GZ2 | Gaozhou 2 | Maoming, Guangdong, China | SJ1 | Sijilan 1 | Ningde, Fujian, China |
| HJ | Hejiang Er‘’baiyuan | Luzhou, Sichuan, China | SJ2 | Sijilan 2 | Ningde, Fujian, China |
| HT | Yongding 1 | Longyan, Fujian, China | SJ3 | Sijilan 3 | Ningde, Fujian, China |
| HY | Huiyuan | Fuzhou, Fujian, China | SL1 | Suiganlan 1 | Zhangzhou, Fujian, China |
| JL | Jiexi Xianglan | Jieyang, Guangdong, China | SL2 | Suiganlan 2 | Zhangzhou, Fujian, China |
| LF | Lingfeng | Fuzhou, Fujian, China | SS1 | Shisheng 1 | Fuzhou, Fujian, China |
| LJ | Lengjian | Caozhou, Guangdong, China | SS2 | Shisheng 2 | Fuzhou, Fujian, China |
| NA1 | Nan’an 1 | Quanzhou, Fujian, China | SS3 | Shisheng 3 | Fuzhou, Fujian, China |
| NA2 | Nan’an 2 | Quanzhou, Fujian, China | SS4 | Shisheng 4 | Fuzhou, Fujian, China |
| NL | Niulan 1 | Qinzhou, Guangxi, China | SZ | Hejiang Dasuozi | Luzhou, Sichuan, China |
| PY1 | Pingyang 1 | Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China | YL | Zhuyaolan | Qinzhou, Guangxi, China |
| PY2 | Pingyang 2 | Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China | ZB1 | Zhuangbian 1 | Putian, Fujian, China |
| QG | Chinese White Olive 1 | Fuzhou, Fujian, China | ZB2 | Zhuangbian 2 | Putian, Fujian, China |
| QL | Green-Rind Chinese | Maoming, Guangdong, China |
| Code | Locule Type | Percentage (%) | Code | Locule Type | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CY | III-1 | 43.75 | GZ1 | III-1 | 59.46 |
| III-2 | 56.25 | III-2 | 40.54 | ||
| HJ | III-1 | 48.39 | HT | III-1 | 56.41 |
| III-2 | 51.61 | III-2 | 43.59 | ||
| JL | III-1 | 62.07 | PY2 | III-1 | 55.56 |
| III-2 | 37.93 | III-2 | 44.44 | ||
| QL | III-1 | 66.67 | RA1 | III-1 | 64.86 |
| III-2 | 33.33 | III-2 | 35.14 | ||
| SJ3 | III-1 | 50.91 | SS2 | III-1 | 60.53 |
| III-2 | 49.09 | III-2 | 39.47 | ||
| GZ2 | III-1 | 48.48 | LF | III-1 | 38.64 |
| III-2 | 48.48 | III-2 | 56.82 | ||
| IV-2 | 3.03 | III-3 | 4.55 | ||
| LJ | III-1 | 43.18 | NA2 | III-1 | 53.13 |
| III-2 | 47.73 | III-2 | 31.25 | ||
| III-3 | 9.09 | IV-2 | 15.63 | ||
| QG | III-1 | 43.86 | RA2 | III-1 | 74.36 |
| III-2 | 38.60 | III-2 | 17.95 | ||
| III-3 | 17.54 | III-3 | 7.69 | ||
| SJ1 | III-1 | 39.13 | SJ2 | III-1 | 32.50 |
| III-2 | 54.35 | III-2 | 55.00 | ||
| IV-2 | 6.52 | IV-2 | 12.50 | ||
| SL1 | III-1 | 54.35 | SL2 | III-1 | 27.27 |
| III-2 | 43.48 | III-2 | 36.36 | ||
| IV-2 | 2.17 | III-3 | 36.36 | ||
| SS1 | III-1 | 45.24 | SS3 | III-1 | 27.27 |
| III-2 | 45.24 | III-2 | 54.55 | ||
| IV-4 | 9.52 | III-3 | 18.18 | ||
| SS4 | III-1 | 77.78 | SZ | III-1 | 15.63 |
| III-2 | 20.00 | III-2 | 78.13 | ||
| IV-1 | 2.22 | III-3 | 6.25 | ||
| YL | III-1 | 59.26 | ZB1 | III-1 | 66.67 |
| III-2 | 37.04 | III-2 | 31.37 | ||
| III-3 | 3.70 | IV-2 | 1.96 | ||
| DK | II-1 | 2.78 | HY | II-2 | 2.78 |
| III-1 | 83.33 | III-1 | 33.33 | ||
| III-2 | 11.11 | III-2 | 36.11 | ||
| IV-2 | 2.78 | III-3 | 27.78 | ||
| NA1 | III-1 | 48.48 | NL | III-1 | 40.54 |
| III-2 | 39.39 | III-2 | 45.95 | ||
| III-3 | 6.06 | III-3 | 10.81 | ||
| IV-2 | 6.06 | IV-2 | 2.70 | ||
| PY1 | III-1 | 43.48 | RA3 | III-1 | 61.11 |
| III-2 | 47.83 | III-2 | 33.33 | ||
| III-3 | 4.35 | III-3 | 2.78 | ||
| IV-2 | 4.35 | IV-2 | 2.78 | ||
| ZB2 | III-1 | 30.00 | |||
| III-2 | 46.67 | ||||
| III-3 | 23.33 |
| Phenotypic Trait | Max | Min | Mean | SD | CV/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seed width (mm) | 12.85 | 8.69 | 10.89 | 1.04 | 9.55 |
| Seed length (mm) | 42.47 | 26.70 | 31.20 | 2.93 | 9.39 |
| Seed shape index | 3.94 | 2.19 | 2.89 | 0.41 | 14.19 |
| Single seed weight (g) | 2.26 | 0.99 | 1.55 | 0.30 | 19.35 |
| Phenotypic Trait | Extreme Differences | K-S Value | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute | Positive | Negative | |||
| Seed width (mm) | 0.097 | 0.097 | −0.065 | 0.097 | 0.200 |
| Seed length (mm) | 0.137 | 0.137 | −0.083 | 0.137 | 0.119 |
| Single seed weight (g) | 0.104 | 0.104 | −0.070 | 0.104 | 0.200 |
| Seed shape index | 0.162 | 0.162 | −0.090 | 0.162 | 0.028 |
| Phenotypic Trait | Grade | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Adjusting | After Adjusting | |||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Seed width (mm) | 9.56 | 10.34 | 11.44 | 12.22 | 9.6 | 10.3 | 11.5 | 12.2 |
| Seed length (mm) | 27.44 | 29.66 | 32.74 | 34.96 | 27.6 | 29.7 | 32.6 | 34.7 |
| Single seed weight (g) | 1.17 | 1.39 | 1.71 | 1.93 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.7 | 1.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Q.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Q. Structure Characteristics, Variation of Main Quantitative Traits, and Probability Grading of Chinese Olive (Canarium album) Seeds. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10070736
Xie Q, Jiang L, Zhao Q, Zheng Y, Yang Y, Chen Q. Structure Characteristics, Variation of Main Quantitative Traits, and Probability Grading of Chinese Olive (Canarium album) Seeds. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(7):736. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10070736
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Qian, Lai Jiang, Qingqing Zhao, Yanju Zheng, Yanfei Yang, and Qingxi Chen. 2024. "Structure Characteristics, Variation of Main Quantitative Traits, and Probability Grading of Chinese Olive (Canarium album) Seeds" Horticulturae 10, no. 7: 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10070736
APA StyleXie, Q., Jiang, L., Zhao, Q., Zheng, Y., Yang, Y., & Chen, Q. (2024). Structure Characteristics, Variation of Main Quantitative Traits, and Probability Grading of Chinese Olive (Canarium album) Seeds. Horticulturae, 10(7), 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10070736






