Biostimulants Improve Bulb Yield, Concomitantly Affecting the Total Phenolics, Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Capacity of Onion (Allium cepa)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Experimental Site
2.3. Agricultural Practices
2.4. Laboratory Procedures
2.4.1. Total Phenolic Content
2.4.2. Total Flavonoid Content
2.4.3. Antioxidant Activity Tests (FRAP, DPPH, and ABTS)
2.5. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Yield of First-Class Onion Bulbs
3.2. Dry Matter Content
3.3. Total Phenolic Content
3.4. Flavonoid Content
3.5. Antioxidant Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sagar, A.N.; Pareek, S.; Benkeblia, N.; Xiao, J. Onion (Allium cepa L.) bioactives: Chemistry, pharmacotherapeutic functions, and industrial applications. Food Front. 2022, 3, 380–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojnović, Đ.; Maksimović, I.; Tepić Horecki, A.; Karadžić Banjac, M.; Kovačević, S.; Daničić, T.; Podunavac-Kuzmanović, S.; Ilin, Ž. Onion (Allium cepa L.) yield and quality depending on biostimulants and nitrogen fertilization-a chemometric perspective. Processes 2023, 11, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, L.J. Onions and Other Vegetable Alliums, 2nd ed.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2008; pp. 1–432. [Google Scholar]
- Vojnović, Đ.; Maksimović, I.; Tepić Horecki, A.; Žunić, D.; Adamović, B.; Milić, A.; Šumić, Z.; Sabadoš, V.; Ilin, Ž. Biostimulants affect differently biomass and antioxidant status of onion (Allium cepa) depending on production method. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Wohleb, H.C.; Waters, D.T. Yield, quality, and storage characteristics of onion cultivars in the Columbia Basin of Washington in 2012-14. HortTechnology 2016, 26, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojnović, Đ.; Adamović, B.; Ilin, Ž. Yields of new onion cultivars under two sowing methods. In Proceedings of the XIV International Scientific Agriculture Symposium “Agrosym 2023”, Jahorina, Bosnia and Hercegovina, 5–8 October 2023; pp. 507–512. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, G.; Conti, S.; Villari, G.; Borrelli, C.; Melchionna, G.; Minutolo, M.; Russo, G.; Amalfitano, C. Effects of transplanting time and plant density on yield, quality and antioxidant content of onion (Allium cepa L.) in southern Italy. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 166, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebretsadik, K.; Dechassa, N. Response of onion (Allium cepa L.) to nitrogen fertilizer rates and spacing under rain fed condition at Tahtay Koraro, Ethiopia. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golubkina, N.; Amalfitano, C.; Sekara, A.; Tallarita, A.; Pokluda, R.; Stoleru, V.; Cuciniello, A.; Agafonov, F.A.; Kalisz, A.; Brînduşa Hamburdă, S.; et al. Yield and bulb quality of storage onion cultivars as affected by farming system and nitrogen dose. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 293, 110751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafie, R.M.; Khoshgoftarmanesh, R.M.; Shariatmadari, H.; Darabi, A.; Dalir, N. Influence of foliar-applied zinc in the form of mineral and complexed with amino acids on yield and nutritional quality of onion under field conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 216, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, A.B.; Hsu, L.C.; Hoepting, A.C. Consequences of co-applying insecticides and fungicides for managing Thrips tabaci (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) on onion. Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 69, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degani, O.; Kalman, B. Assesment of commercial fungicides against onion (Allium cepa) basal rot disease caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cepae and Fusarium acutatum. J. Fungy 2021, 7, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piri, H.; Naserin, A. Effect of different levels of water, applied nitrogen and irrigation methods on yield, yield components and IWUE of onion. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 268, 109361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geries, M.S.L.; El-Shahawy, A.T.; Moursi, A.E. Cut-off irrigation as an effective tool to increase water-use efficiency, enhance productivity, quality and storability of some onion cultivars. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojnović, Đ. Unlocking the secrets of the onion genome: A path to sustainable onion production. AIDASCO Rev. 2024, 2, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.P.; Borza, T.; Critchley, T.A.; Hiltz, D.; Norrie, J.; Prithiviraj, B. Ascophyllum nodosum extract mitigates salinity stress in Arabidopsis thaliana by modulating the expression of miRNA involved in stress tolerance and nutrient acquisition. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jithesh, N.M.; Shukla, S.P.; Kant, P.; Joshi, J.; Critchley, T.A.; Prithiviraj, B. Physiological and transcriptomics analyses reveal that Ascophyllum nodosum extracts induce salinity tolerance in Arabidopsis by regulating the expression of stress responsive genes. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 38, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battacharyya, D.; Babgohari, M.Z.; Rathor, P.; Prithiviraj, B. Seaweed extracts as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canellas, L.P.; Olivares, F.L.; Aguiar, N.O.; Jones, D.L.; Nebbioso, A.; Mazzei, P.; Piccolo, A. Humic and fulvic acids as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bucio, J.; Pelagio-Flores, R.; Herrera-Estrella, A. Trichoderma as biostimulant: Exploiting the multilevel properties of a plant beneficial fungus. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; De Micco, V.; Arena, C.; Raimondi, G.; Colla, G.; De Pascale, S. Effect of Ecklonia maxima seaweed extract on yield, mineral composition, gas exchange, and leaf anatomy of zucchini squash grown under saline conditions. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mola, I.; Cozzolino, E.; Ottaiano, L.; Giordano, M.; Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G.; Mori, M. Effect of vegetal- and seaweed extract-based biostimulants on agronomical and leaf quality traits of plastic tunnel- grown baby lettuce under four regimes of nitrogen fertilization. Agronomy 2019, 9, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, O.; Ramsubhag, A.; Jayaraman, J. Biostimulatory activities of Ascophyllum nodosum extract in tomato and sweet pepper crops in a tropical environment. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francke, A.; Majkowska-Gadomska, J.; Kaliniewicz, Z.; Jadwisieńczak, K. No effect of biostimulants on the growth, yield and nutritional value of shallots grown for bunch harvest. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossak, K.; Dyki, B. Effects of biostimulators on cultivation of Aboney F1 greenhouse tomato. In Biostimulators in Modern Agriculture: Solanaceous Crops; Dąbrowski, Z.T., Ed.; Editorial House Wiés Jutra: Warsaw, Poland, 2008; pp. 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Colla, R.; Cardarelli, M.; Bonini, P.; Rouphael, Y. Foliar applications of protein hydrolysate, plant and seaweed extracts increase yield but differentially modulate fruit quality of greenhouse tomato. HortScience 2017, 52, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannin, L.; Arkoun, M.; Etienne, P.; Laîné, P.; Goux, D.; Garnica, M.; Fuentes, M.; Francisco, S.S.; Baigorri, R.; Cruz, F.; et al. Brassica napus growth is promoted by Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jol. seaweed extract: Microarray analysis and physiological characterization of N, C, and S Metabolisms. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 32, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzibra, A.; Aasfar, A.; El Arroussi, H.; Khouloud, M.; Dhiba, D.; Meftah Kadmiri, I.; Bamouh, A. Polysaccharides extracted from Moroccan seaweed: A promising source of tomato plant growth promoters. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2953–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akladious, A.S.; Mohamed, I.H. Ameliorative effects of calcium nitrate and humic acid on the growth, yield component and biochemical attribute of pepper (Capsicum annuum) plants grown under salt stress. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 236, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, H.; Shafie, F.; Aminifard, M.H.; Daghighi, S. Comparative effects of humic and fulvic acids as biostimulants on growth, antioxidant activity and nutrient content of yarrow (Achillea millefolium L.). Sci. Hortic. 2021, 279, 109912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, E.; Geries, L. Effect of nitrogen fertilization and biostimulative compounds on onion productivity. Certec. Agron. Mold. 2018, 1, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zandonadi, D.B.; Canellas, L.P.; Façanha, A.R. Indolacetic and humic acids induce lateral root development through a concentrated plasmalemma and tonoplast H+ pumps activation. Planta 2007, 225, 1583–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, M.; Pizzeghello, D.; Muscolo, A.; Vaccaro, S.; Francioso, O.; Nardi, S. High molecular size humic substances enhance phenylpropanoid metabolism in maize (Zea mays L.). J. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 36, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminifard, H.M.; Aroiee, H.; Azizi, M.; Nemati, H.; Hawa, Z.; Jaafar, E. Effect of humic acid on antioxidant activities and fruit quality of hot pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants 2021, 18, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visconti, D.; Fiorentino, N.; Cozzolino, E.; Woo, S.L.; Fagnano, M.; Rouphael, Y. Can Trichoderma-based biostimulants optimize N use efficiency and stimulate growth of leafy vegetables in greenhouse intensive cropping systems? Agronomy 2020, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carillo, P.; Woo, S.L.; Comite, E.; El-Nakhel, C.; Rouphael, Y.; Fusco, G.M.; Borzacchiello, A.; Lanzuise, S.; Vinale, F. Application of Trichoderma harzianum, 6-Pentyl-α-pyrone and plant biopolymer formulations modulate plant metabolism and fruit quality of plum tomatoes. Plants 2020, 9, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. The effect of Trichoderma biofertilizer on the quality of flowering Chinese cabbage and the soil environment. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 262, 109069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, N.; Ventorino, V.; Woo, S.L.; Pepe, O.; De Rosa, A.; Gioia, L.; Romano, I.; Lombardi, N.; Napolitano, M.; Colla, G.; et al. Trichoderma-based biostimulants modulate rhizosphere microbial populations and improve N uptake efficiency, yield, and nutritional quality of leafy vegetables. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukelić, D.I.; Prokić, T.L.; Racić, M.G.; Pešić, B.M.; Bojović, M.M.; Sierka, M.E.; Kalaji, M.H.; Panković, M.D. Effects of Trichoderma harzianum on photosynthetic characteristics and fruit quality of tomato plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Anwar, J.; Zafar-ul-Hye, M.; Iqbal Khan, R.; Saleem, M.; Rahi, A.A.; Danish, S.; Datta, R. Effect of seaweed extract on productivity and quality attributes of four onion cultivars. Horticulturae 2020, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, E.C.N.; Mógor, Á.F.; de Oliveira Amatussi, J.; Mógor, G.; de Lara, G.B.; Marques, H.M.C. Microalga biofertilizer triggers metabolic changes improving onion growth and yield. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettoni, M.M.; Mogor, F.A.; Pauletti, V.; Goicoechea, N. Growth and metabolism of onion seedlings as affected by the application of humic substances, mycorrhizal inoculation and elevated CO2. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 180, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dineshkumar, R.; Subramanian, J.; Arumugam, A.; Ahamed Rasheeq, A.; Sampathkumar, P. Exploring the microalgae biofertilizer effect on onion cultivation by field experiment. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Strik, A.W.; Plačková, L.; Kulkarni, G.M.; Doležal, K.; Van Staden, J. Interactive effects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and a seaweed extract on the growth and physiology of Allium cepa L. (onion). J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 262, 153437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, A.R. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Trichoderma viride cooperative effect on biochemical, mineral content, and protein pattern of onion plants. J. Basic Microbiol. 2020, 60, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, G.; Cesaro, P.; Bona, E.; Massa, N.; Gosetti, F.; Scarafoni, A.; Todeschini, V.; Berta, G.; Lingua, G.; Gamalero, E. The effects of plant growth-promoting bacteria with biostimulant features on the growth of a local onion cultivar and a commercial zucchini variety. Agronomy 2021, 11, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-García, G.J.; Montes-Belmont, R.; Rodríguez-Monroy, M.; Ramírez-Trujillo, A.J.; Suárez-Rodríguez, R.; Sepúlveda-Jiménez, G. Effect of Trichoderma asperellum applications and mineral fertilization on growth promotion and the content of phenolic compounds and flavonoids in onions. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 195, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidl—Quality Standards. Available online: https://www.lidl.com/quality-standards (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Maxi—Quality of Fruit & Vegetable. Available online: https://www.maxi.rs/sveze-voce-i-povrce-kontrolisanog-kvaliteta (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Faculty of Agriculture Novi Sad. Available online: http://polj.uns.ac.rs/en (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Faculty of Technology Novi Sad. Available online: https://www.tf.uns.ac.rs/en#lat (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Extension Service Sombor. Available online: https://www.psssombor.rs/o-nama.html (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Web of Science. Available online: https://mjl.clarivate.com/search-results (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Scopus. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/ (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Ubavić, M.; Bogdanović, D. Agrochemistry; Faculty of Agriculture, Institute of Field and Vegetable Crops: Novi Sad, Serbia, 2001; pp. 1–260. [Google Scholar]
- Manojlović, S.; Bogdanović, D. Practicum in Agrochemistry; Faculty of Agriculture, Institute of Field and Vegetable Crops: Novi Sad, Serbia, 1995; pp. 1–165. [Google Scholar]
- Žunić, D.; Sabadoš, V.; Vojnović, Đ.; Maksimović, I.; Ilin, D.; Tepić Horecki, A.; Ilin, Ž. Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) cultivar yield and quality affected by irrigation and fertilization-from field to chip bag. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Gazette SFRY 29/79,53/87. Available online: https://www.paragraf.rs/propisi/pravilnik-kvalitetu-voca-povrca-pecurki.html (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- EC No. 1508/2001. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/ALL/?uri=CELEX:02001R1508-20090701 (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harborne, J.B. Methods of Plant Analysis; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakula, A.; Tepić Horecki, A.; Pavlić, B.; Jokanović, M.; Ognjanov, V.; Milović, M.; Teslić, N.; Parpinello, G.; Decleer, M.; Šumić, Z. Application of different techniques on stone fruit (Prunus spp.) drying and assessment of physical, chemical and biological properties: Characterization of dried fruit properties. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 45, e15158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Tang, M.; Chan, S.P. A generalized Shapiro-Wilk W statistic for testing high-dimensional normality. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2009, 53, 3883–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazić, B.; Marković, V.; Đurovka, M.; Ilin, Ž. Vegetable; University of Novi Sad, Faculty of Agriculture: Novi Sad, Serbia, 2001; pp. 197–225. [Google Scholar]
- Kazimierczak, R.; Średnicka-Tober, D.; Barański, M.; Hallmann, E.; Góralska-Walczak, R.; Kopczyńska, K.; Rembiałkowska, E.; Górski, J.; Leifert, C.; Rempelos, L.; et al. The effect of different fertilization regimes on yield, selected nutrients, and bioactive compounds profiles of onion. Agronomy 2021, 11, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, S.; Rab, A. Response of Tomato to Nitrogen Levels with or without Humic Acid. Sarhad J. Agric. 2013, 29, 181–186. Available online: https://www.aup.edu.pk/sj_pdf/02%20281-2012%20RESPONSE%20OF%20TOMATO%20TO%20NITROGEN%20LEVELS%20WITH%20OR.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Vojnović, Đ. Effects of Biostimulants and Nitrogen on Yield and Quality of Onion. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Novi Sad, Faculty of Agriculture, Novi Sad, Serbia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna, A.; Ravishankar, A.G. Influence of abiotic stress signals on secondary metabolites in plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 1720–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietta, P.G. Flavonoids as antioxidants. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Z.; Li, B.; Nice, E.C.; Xu, J.; Huang, C. Antioxidant Therapy in Cancer: Rationale and Progress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocira, S.; Szparaga, A.; Hara, P.; Treder, K.; Findura, P.; Bartoš, P.; Filip, M. Biochemical and economical effect of application biostimulants containing seaweed extracts and amino acids as an element of agroecological management of bean cultivation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanek, M.; Pobereżny, J.; Wszelaczyńska, E.; Gościnna, K. Effect of biostimulants and storage on discoloration potential of carrot. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.B.; Malviya, D.; Singh, S.; Kumar, M.; Sahu, P.K.; Singh, H.V.; Kumar, S.; Roy, M.; Imran, M.; Rai, J.P.; et al. Trichoderma harzianum- and methyl jasmonate-induced resistance to bipolaris sorokiniana through enhanced phenylpropanoid activities in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şesan, T.E.; Oancea, A.O.; Ştefan, L.M.; Mănoiu, V.S.; Ghiurea, M.; Răut, I.; Constantinescu-Aruxandei, D.; Toma, A.; Savin, S.; Bira, A.F.; et al. Effects of foliar treatment with a Trichoderma plant biostimulant consortium on Passiflora caerulea L. yield and quality. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehiroglu, C.; Ozturk Sarikaya, S.B. The importance of antioxidants and place in today’s scientific and technological studies. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4757–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, A.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, T.M. Exploring the potential of antioxidants from fruits and vegetables and strategies for their recovery. Innov. Food Emerg. Technol. 2022, 77, 102974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
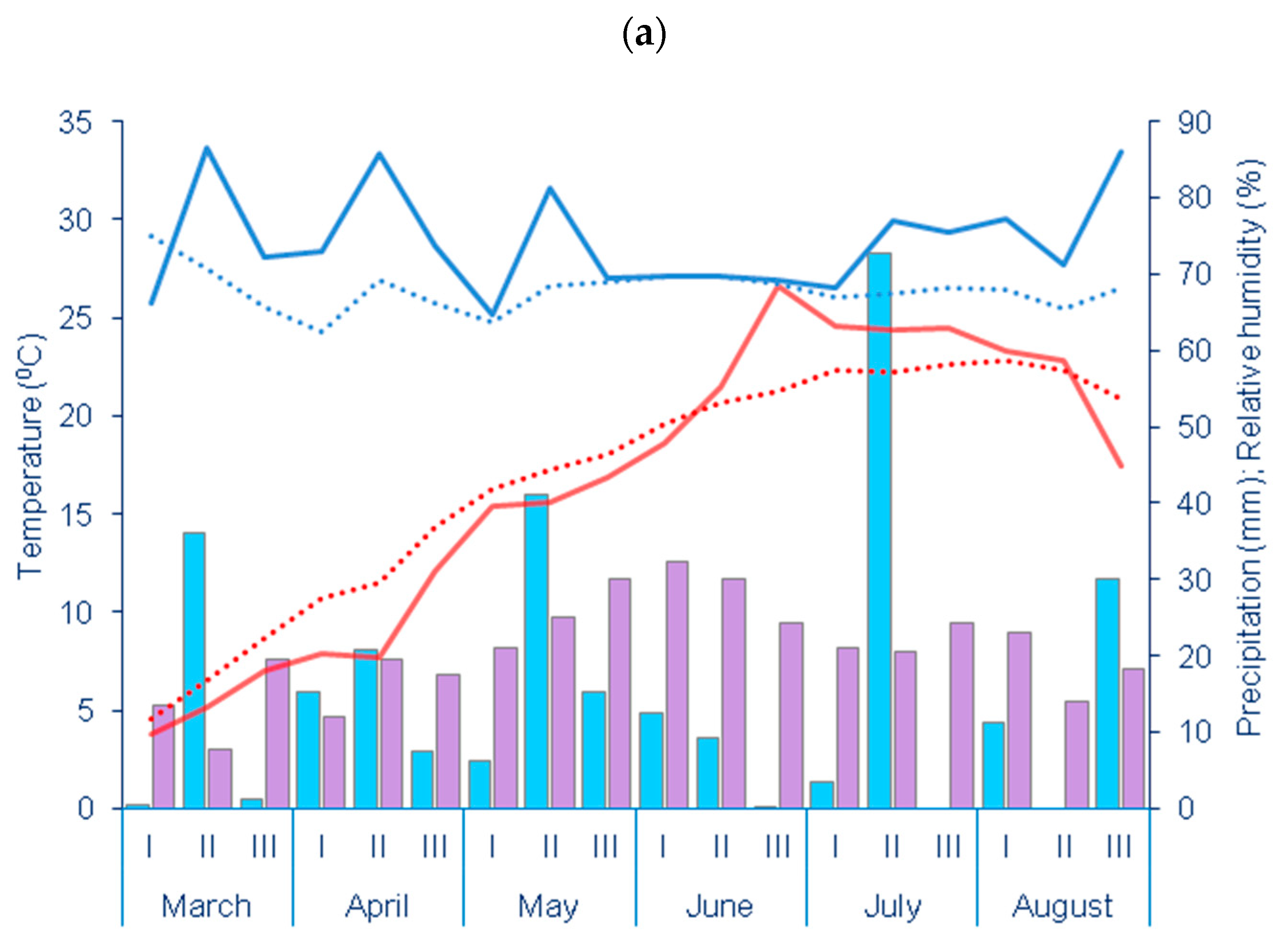
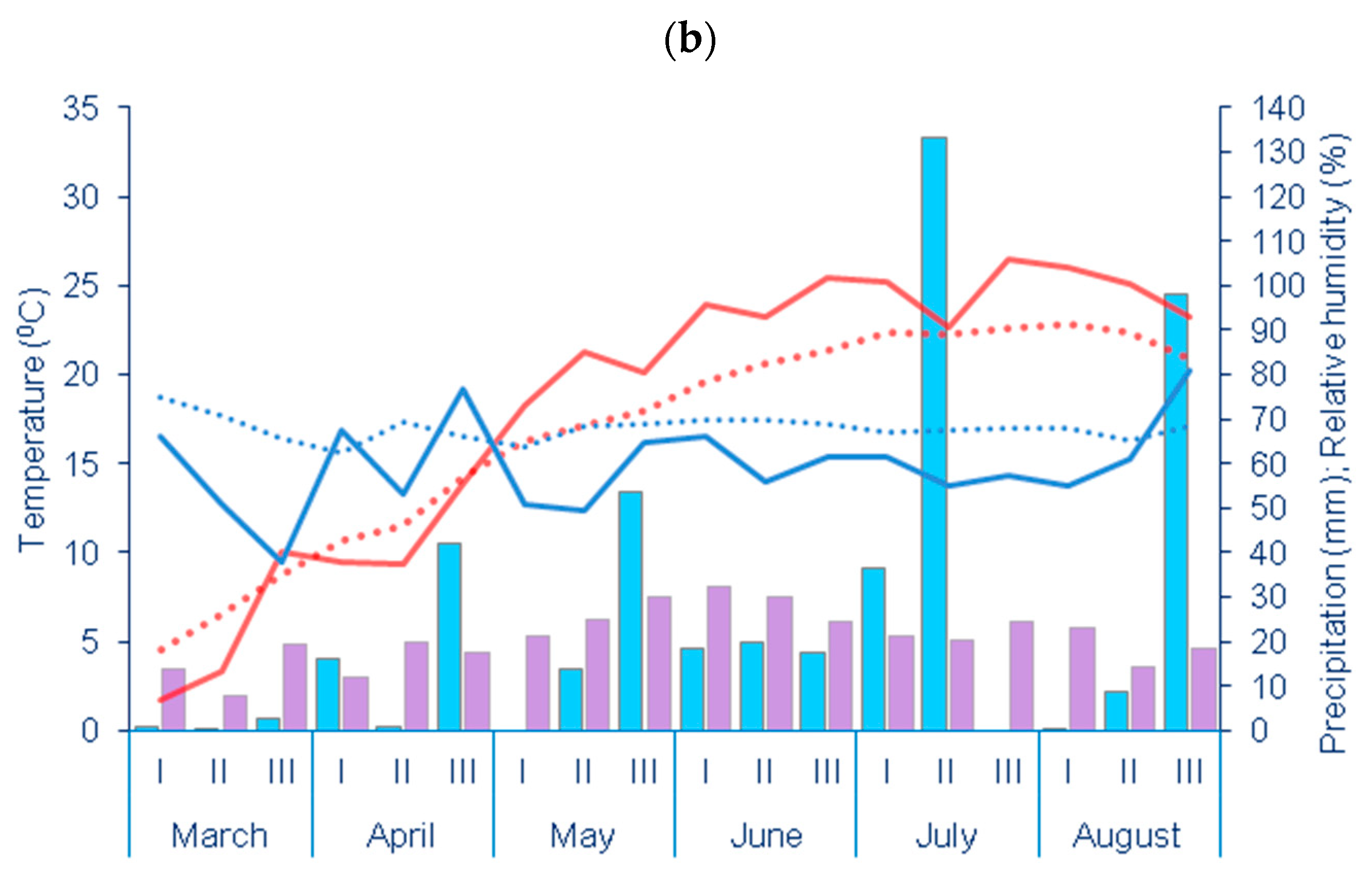
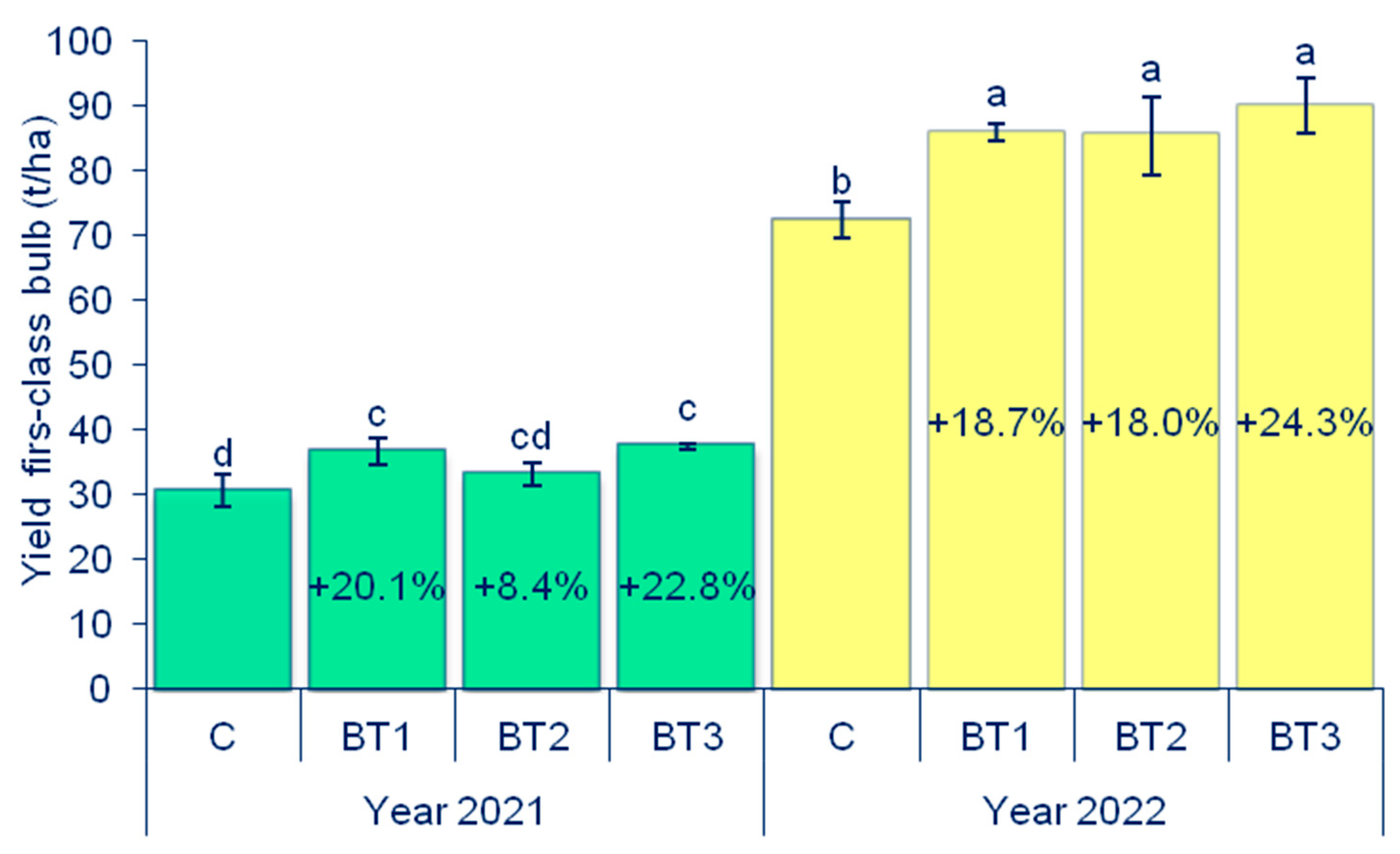

| Year | Depth | pH | CaCO3 | Humus | N | P | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O | (%) | (%) | (%) | mg/100 g Soil | |||
| 2021 | 30 cm | 8.1 | 6.2 | 1.7 | 0.08 | 4.6 | 39.8 |
| 2022 | 7.8 | 6.0 | 1.9 | 0.13 | 6.9 | 26.6 | |
| Biostimulants | Year 2021 | Relative Change (%) | Year 2022 | Relative Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 9.72 ± 0.12 a | / | 10.07 ± 0.03 c | / |
| BT1 | 9.56 ± 0.12 a | −1.64 | 9.73 ± 0.02 d | −3.37 |
| BT2 | 9.32 ± 0.00 b | −4.11 | 10.69 ± 0.08 a | +6.15 |
| BT3 | 8.94 ± 0.05 c | −8.02 | 10.55 ± 0.25 a | +4.76 |
| Biostimulants | Year 2021 | Relative Change (%) | Year 2022 | Relative Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 1066.06 ± 1.01 a | / | 795.28 ± 2.71 e | / |
| BT1 | 1047.08 ± 4.60 b | −1.78 | 744.47 ± 1.03 f | −6.38 |
| BT2 | 873.27 ± 2.15 c | −18.08 | 640.70 ± 2.00 h | −19.43 |
| BT3 | 960.88 ± 4.35 d | −9.86 | 731.93 ± 4.08 g | −7.96 |
| Biostimulants | Year 2021 | Relative Change (%) | Year 2022 | Relative Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 358.07 ± 2.61 b | / | 244.15 ± 1.12 e | / |
| BT1 | 418.53 ± 10.26 a | +16.88 | 265.71 ± 3.14 d | +8.83 |
| BT2 | 271.31 ± 10.18 d | −24.22 | 293.99 ± 4.04 c | +20.41 |
| BT3 | 417.97 ± 2.45 a | +16.72 | 238.24 ± 4.52 e | −2.42 |
| Year | Biostimulants | DPPH | Relative Change (%) | FRAP | Relative Change (%) | ABTS | Relative Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | C | 561.86 ± 1.75 b | / | 494.03 ± 0.97 b | / | 1489.22 ± 9.53 b | / |
| BT1 | 611.10 ± 4.33 a | +8.76 | 508.04 ± 1.51 a | +2.83 | 1508.9 ± 7.60 a | +1.32 | |
| BT2 | 419.54 ± 4.31 e | −25.33 | 327.65 ± 2.40 f | −33.67 | 1245.34 ± 5.42 f | −16.37 | |
| BT3 | 483.10 ± 2.77 c | −14.01 | 418.09 ± 2.80 c | −15.37 | 1333.43 ± 8.29 d | −10.46 | |
| 2022 | C | 486.93 ± 1.43 c | / | 344.90 ± 2.75 e | / | 1284.88 ± 2.67 e | / |
| BT1 | 430.74 ± 2.46 d | −11.53 | 377.54 ± 1.05 d | +9.46 | 1367.75 ± 6.54 c | +6.44 | |
| BT2 | 336.66 ± 3.57 g | −30.86 | 233.84 ± 1.80 h | −32.20 | 1010.10 ± 2.05 h | −21.33 | |
| BT3 | 361.84 ± 2.3 f | −25.68 | 290.71 ± 0.70 g | −15.71 | 1150.32 ± 2.98 g | −10.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vojnović, Đ.; Maksimović, I.; Tepić Horecki, A.; Milić, A.; Šumić, Z.; Žunić, D.; Adamović, B.; Ilin, Ž. Biostimulants Improve Bulb Yield, Concomitantly Affecting the Total Phenolics, Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Capacity of Onion (Allium cepa). Horticulturae 2024, 10, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10040391
Vojnović Đ, Maksimović I, Tepić Horecki A, Milić A, Šumić Z, Žunić D, Adamović B, Ilin Ž. Biostimulants Improve Bulb Yield, Concomitantly Affecting the Total Phenolics, Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Capacity of Onion (Allium cepa). Horticulturae. 2024; 10(4):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10040391
Chicago/Turabian StyleVojnović, Đorđe, Ivana Maksimović, Aleksandra Tepić Horecki, Anita Milić, Zdravko Šumić, Danijela Žunić, Boris Adamović, and Žarko Ilin. 2024. "Biostimulants Improve Bulb Yield, Concomitantly Affecting the Total Phenolics, Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Capacity of Onion (Allium cepa)" Horticulturae 10, no. 4: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10040391
APA StyleVojnović, Đ., Maksimović, I., Tepić Horecki, A., Milić, A., Šumić, Z., Žunić, D., Adamović, B., & Ilin, Ž. (2024). Biostimulants Improve Bulb Yield, Concomitantly Affecting the Total Phenolics, Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Capacity of Onion (Allium cepa). Horticulturae, 10(4), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10040391







