Characterization of a Metallic-Ions-Independent L-Arabinose Isomerase from Endophytic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for Production of D-Tagatose as a Functional Sweetener
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Endophytic Bacteria
2.2. Screening and Identification of L-Arabinose Isomerase-Producing Bacteria
2.3. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of L-Arabinose Isomerase Gene
2.4. Expression and Characterization of L-Arabinose Isomerase
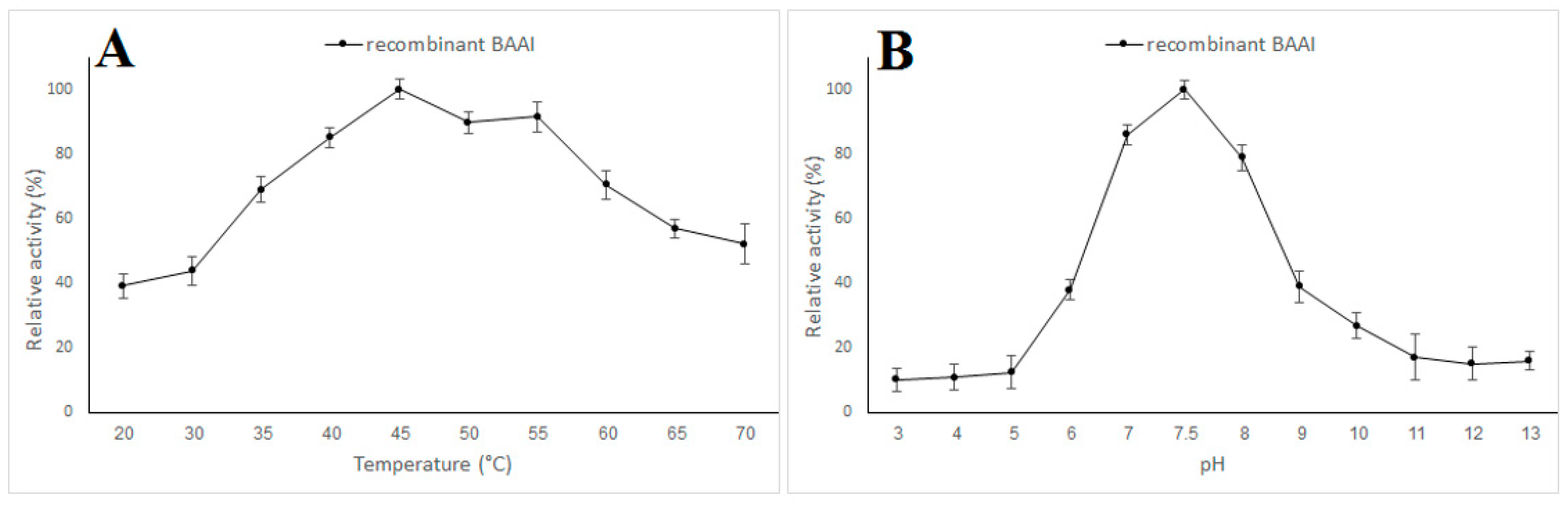
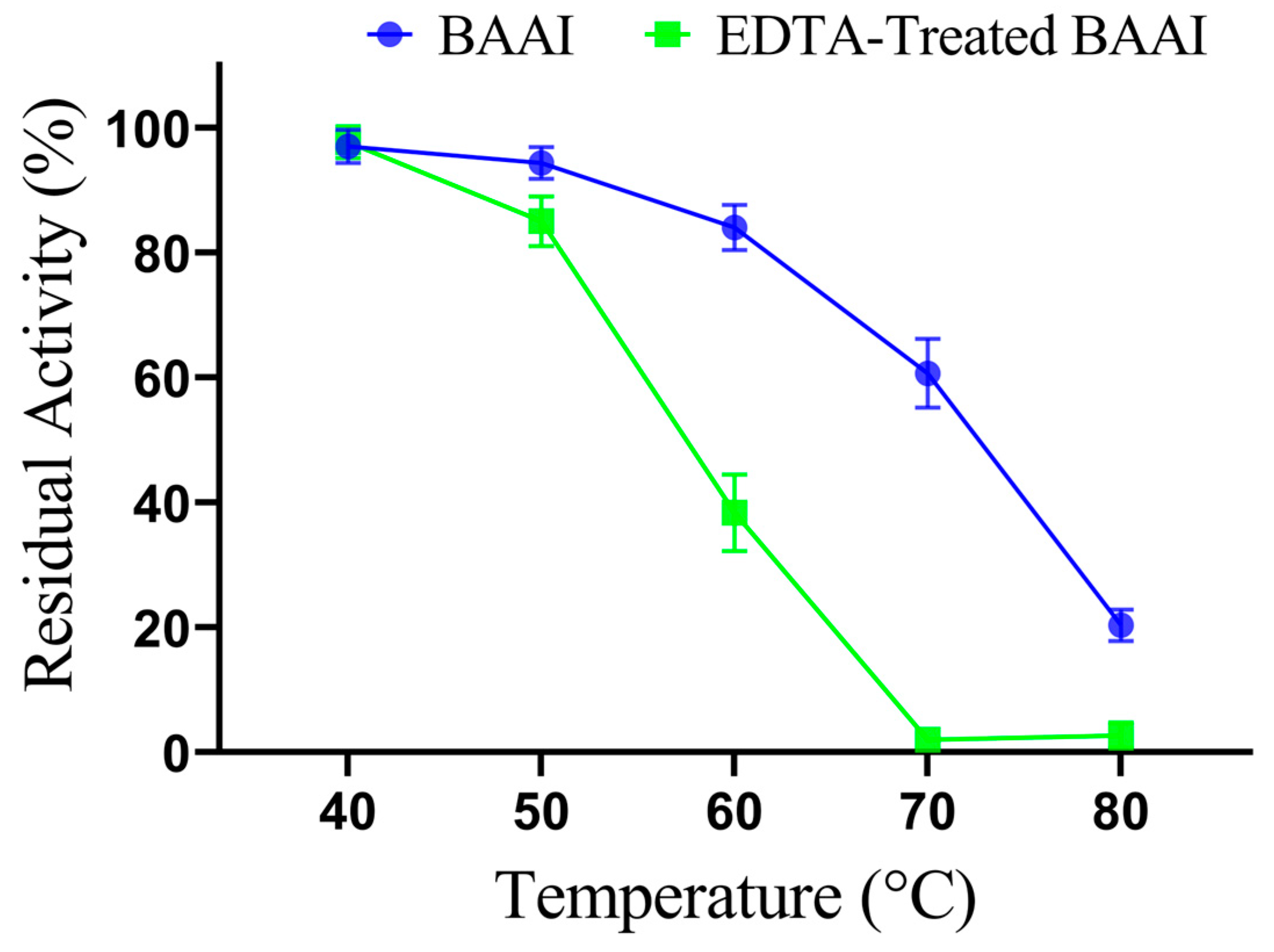
2.5. Characterization of BAAI
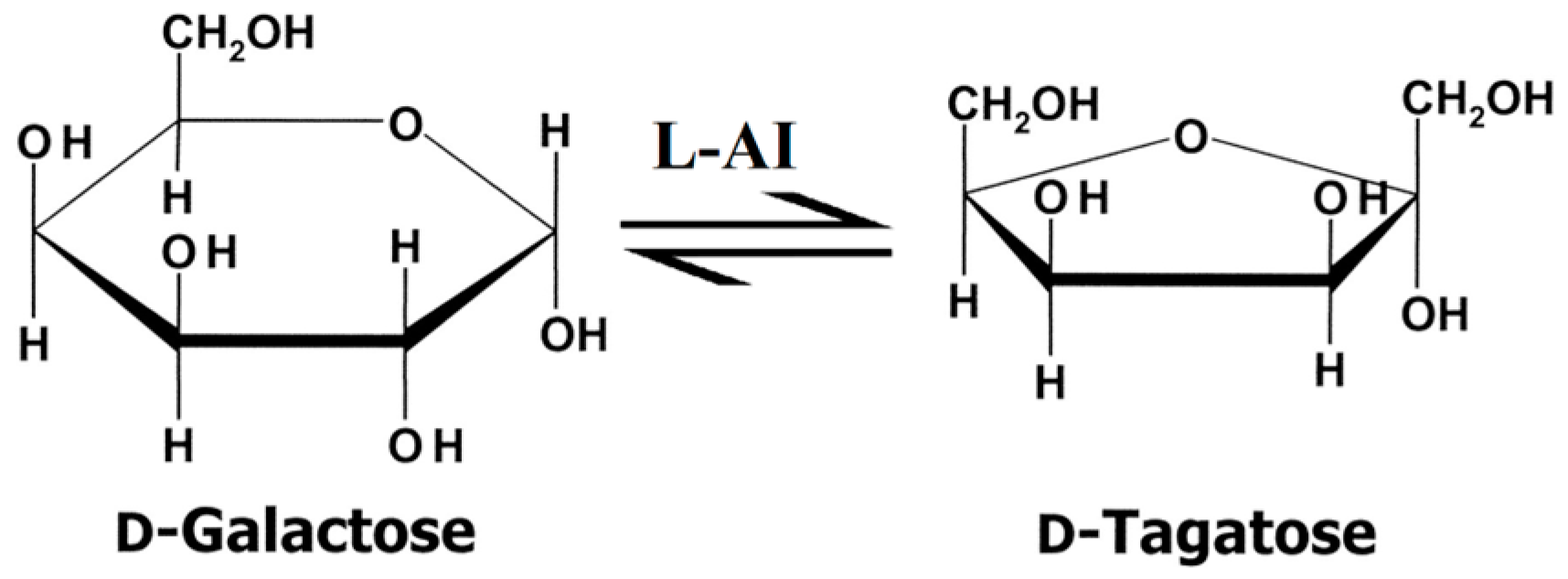
2.6. Bioconversion of D-Galactose into D-Tagatose by BAAI
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Identification of L-Arabinose Isomerase-Producing Bacteria
3.2. Cloning and Sequence Analysis
3.3. Expression and Characterization of L-AI
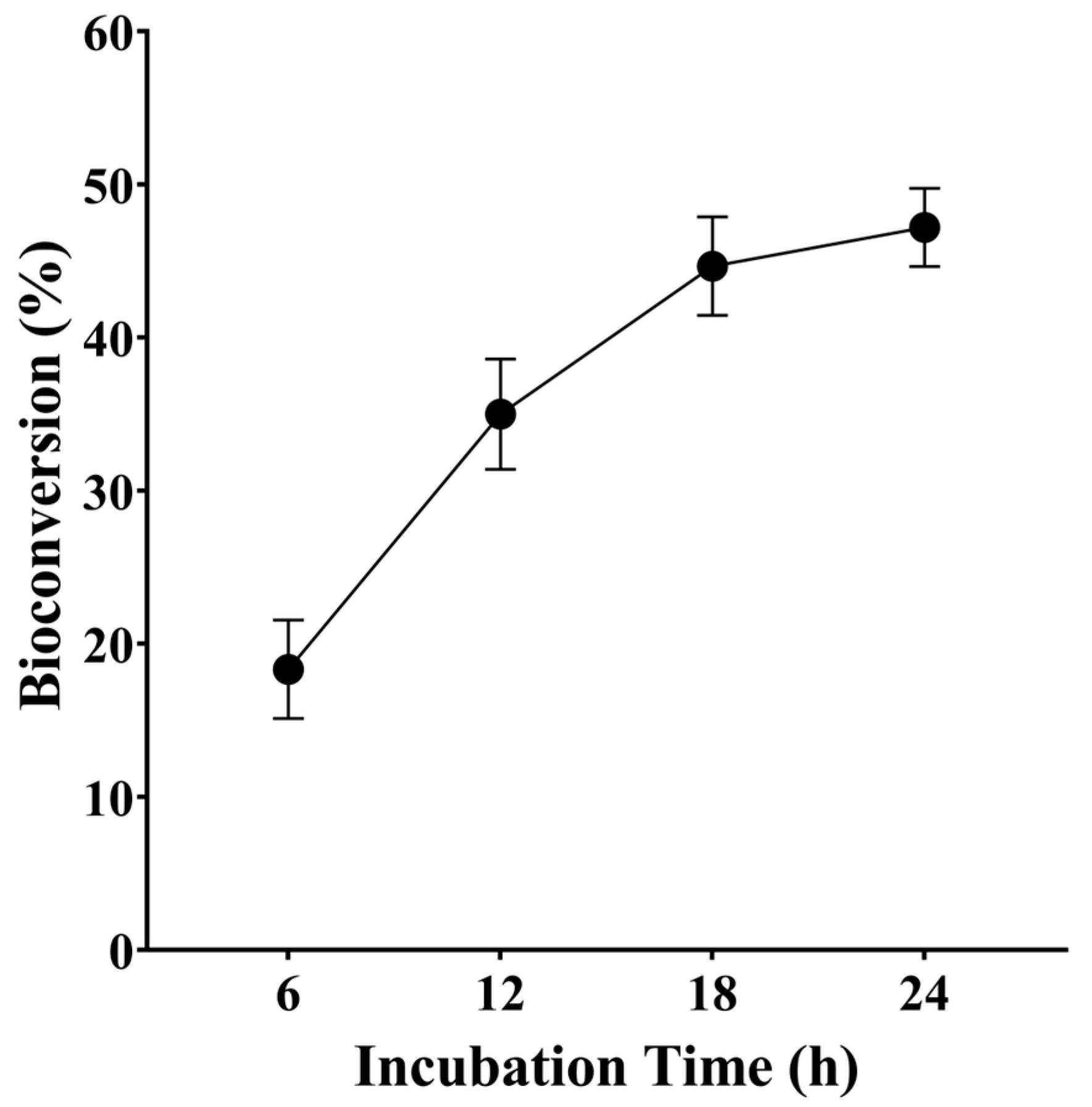
3.4. Bioconversion of D-Galactose into D-Tagatose by BAAI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levin, G.V. Tagatose, the New GRAS Sweetener and Health Product. J. Med. Food 2004, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Laar, A.D.E.; Grootaert, C.; Van Camp, J. Rare Mono- and Disaccharides as Healthy Alternative for Traditional Sugars and Sweeteners? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 61, 713–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravikumar, Y.; Ponpandian, L.N.; Zhang, G.; Yun, J.; Qi, X. Harnessing L-Arabinose Isomerase for Biological Production of d-Tagatose: Recent Advances and Its Applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 107, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Shi, T.; Shi, J. Synthesis of a Healthy Sweetener D-Tagatose from Starch Catalyzed by Semiartificial Cell Factories. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 3813–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donner, T.W.; Magder, L.S.; Zarbalian, K. Dietary Supplementation with D-Tagatose in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Leads to Weight Loss and Raises High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol. Nutr. Res. 2010, 30, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, M.C.; Lansang, M.C. Recent and Emerging Therapeutic Medications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Incretin-Based, Pramlintide, Colesevelam, SGLT2 Inhibitors, Tagatose, Succinobucol. Am. J. Ther. 2013, 20, 638–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Khan, T.A.; Ramdath, D.D.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; Ahmed, A.; Khan, T.A.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Sievenpiper, J.L. Rare Sugars and Their Health Effects in Humans: A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis of the Evidence from Human Trials. Nutr. Rev. 2022, 80, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Yang, Y.J.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, O.Y.; Lee, J.H. Beneficial Effect of Tagatose Consumption on Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Koreans: A Double-Blind Crossover Designed Study. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Police, S.B.; Harris, J.C.; Lodder, R.A.; Cassis, L.A. Effect of Diets Containing Sucrose vs. D-Tagatose in Hypercholesterolemic Mice. Obesity 2009, 17, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasibul, K.; Nakayama-Imaohji, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Yamasaki, H.; Ogawa, T.; Waki, J.; Tada, A.; Yoneda, S.; Tokuda, M.; Miyake, M.; et al. D-Tagatose Inhibits the Growth and Biofilm Formation of Streptococcus Mutans. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensor, M.; Banfield, A.B.; Smith, R.R.; Williams, J.; Lodder, R.A. Safety and Efficacy of D-Tagatose in Glycemic Control in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2014, 3, 1065. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Wyss, M.; Durán Agüero, S.; Angarita Dávila, L. D-Tagatose Is a Promising Sweetener to Control Glycaemia: A New Functional Food. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8718053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooradian, A.D.; Haas, M.J.; Onstead-Haas, L.; Tani, Y.; Iida, T.; Tokuda, M. Naturally Occurring Rare Sugars Are Free Radical Scavengers and Can Ameliorate Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2019, 90, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeri, F.; Boess, F.; Wolf, A.; Goldlin, C.; Boelsterli, U.A. Fructose and Tagatose Protect against Oxidative Cell Injury by Iron Chelation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 22, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterna, J.C.; Boess, F.; Staubli, A.; Boelsterli, U.A. Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Properties of D-Tagatose in Cultured Murine Hepatocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1998, 148, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo-Poveda, O.; Barbosa-Pereira, L.; Orden, D.; Stévigny, C.; Zeppa, G.; Bertolino, M. Physical Properties and Consumer Evaluation of Cocoa Bean Shell-Functionalized Biscuits Adapted for Diabetic Consumers by the Replacement of Sucrose with Tagatose. Foods 2020, 9, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayumi, S.; Kuboniwa, M.; Sakanaka, A.; Hashino, E.; Ishikawa, A.; Ijima, Y.; Amano, A. Potential of Prebiotic D-Tagatose for Prevention of Oral Disease. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 767944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, B.; Tao, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.; Gao, B.; Cheng, X.; et al. D-Tagatose Protects against Oleic Acid-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Rats by Activating PTEN/PI3K/AKT Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 928312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Chikkerur, J.; Roy, S.C.; Dhali, A.; Kolte, A.P.; Sridhar, M.; Samanta, A.K. Tagatose as a Potential Nutraceutical: Production, Properties, Biological Roles, and Applications. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 2699–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahed, A.; Nesler, A.; Aziz, A.; Barka, E.A.; Pertot, I.; Perazzolli, M. A Review of Knowledge on the Mechanisms of Action of the Rare Sugar D-Tagatose against Phytopathogenic Oomycetes. Plant Pathol. 2021, 70, 1979–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijailovic, N.; Richet, N.; Villaume, S.; Nesler, A.; Perazzolli, M.; Barka, E.A.; Aziz, A. D-Tagatose-Based Product Triggers Sweet Immunity and Resistance of Grapevine to Downy Mildew, but Not to Gray Mold Disease. Plants 2022, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahed, A.; Nesler, A.; Esmaeel, Q.; Barka, E.A.; Perazzolli, M. The Amount of the Rare Sugar Tagatose on Tomato Leaves Decreases after Spray Application under Greenhouse Conditions. Plants 2022, 11, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corneo, P.E.; Jermini, M.; Nadalini, S.; Giovannini, O.; Nesler, A.; Perazzolli, M.; Pertot, I. Foliar and Root Applications of the Rare Sugar Tagatose Control Powdery Mildew in Soilless Grown Cucumbers. Crop Prot. 2021, 149, 105753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, L.M.; Luecke, K.J.; Bell, L.N. Consumer Evaluation of Bakery Product Flavour as Affected by Incorporating the Prebiotic Tagatose. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijailovic, N.; Nesler, A.; Perazzolli, M.; Aït Barka, E.; Aziz, A. Rare Sugars: Recent Advances and Their Potential Role in Sustainable Crop Protection. Molecules 2021, 26, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, M.G.; Shehata, H.M.; Kamel, Z. Codon Optimization and Co-Expression of Thermostable β-Galactosidase and L-Arabinose Isomerase in Lactococcus Lactis for Single-Step Production of Food-Grade D-Tagatose. Biochem. Cell Arch. 2020, 20, 2545–2552. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; An, Y.; Yun, J.; Yang, M.; Magocha, T.A.; Zhu, J.; Xue, Y.; Qi, Y.; Hossain, Z.; Sun, W.; et al. Enhanced D-Tagatose Production by Spore Surface-Displayed l-Arabinose Isomerase from Isolated Lactobacillus Brevis PC16 and Biotransformation. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, S.; Feng, X.; Liang, J.; Xu, H. L-Arabinose Isomerase and Its Use for Biotechnological Production of Rare Sugars. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 8869–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Li, N.; Xu, H.; Xu, Z. Improved Thermostability and Robustness of L-Arabinose Isomerase by C-Terminal Elongation and Its Application in Rare Sugar Production. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 637, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, B.; Mu, W. L-Arabinose Isomerases: Characteristics, Modification, and Application. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Xia, W. Rational Design of L-Arabinose Isomerase from Lactobacillus Fermentum and Its Application in D-Tagatose Production. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Rai, S.K.; Yadav, S.K. Metal-Based Micro-Composite of L-Arabinose Isomerase and L-Ribose Isomerase for the Sustainable Synthesis of L-Ribose and D-Talose. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 217, 112637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, C.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, S.J.; Park, Y.-S.; Shin, K.-C.; Seo, M.-J.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Park, C.-S. Characterization of L-Arabinose Isomerase from Klebsiella Pneumoniae and Its Application in the Production of d-Tagatose from d-Galactose. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.; Ma, M.; Zhao, G.; Chang, R.; Si, H.; Dai, M. A Novel Lactococcus Lactis L-Arabinose Isomerase for d-Tagatose Production from Lactose. Food Biosci. 2022, 48, 101765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, S.L.; Romaní, A.; Oliveira, C.; Ferreira, S.; Rocha, C.M.R.; Domingues, L. Galactose to Tagatose Isomerization by the L-Arabinose Isomerase from Bacillus Subtilis: A Biorefinery Approach for Gelidium Sesquipedale Valorisation. LWT 2021, 151, 112199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, A.B.; Kandasamy, T.; Venkataraman, D.; Meenakshisundaram, S. Rational Design of Shewanella sp. L-Arabinose Isomerase for d-Galactose Isomerase Activity under Mesophilic Conditions. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2021, 147, 109796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, T.C.; Oliveira, R.C.; Bezerra, S.G.S.; Manzo, R.M.; Mammarella, E.J.; Hissa, D.C.; Gonçalves, L.R.B. Alternative Heterologous Expression of L-Arabinose Isomerase from Enterococcus faecium DBFIQ E36 by Residual Whey Lactose Induction. Mol. Biotechnol. 2021, 63, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Liu, K.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, L.; Xue, D.; Jiang, B.; Mu, W. Biochemical Characterization of a Thermostable L-Arabinose Isomerase from a Thermoacidophilic Bacterium, Alicyclobacillus Hesperidum URH17-3-68. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2014, 102, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, A.; Sun, Y. Identification and Characterization of a Novel L-Arabinose Isomerase from Anoxybacillus Flavithermus Useful in d-Tagatose Production. Extremophiles 2011, 15, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanarska, M.; Kur, J. A Method for the Production of D-Tagatose Using a Recombinant Pichia Pastoris Strain Secreting β-D-Galactosidase from Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus and a Recombinant L-Arabinose Isomerase from Arthrobacter sp. 22c. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.-J. Characterization of an L-Arabinose Isomerase from Bacillus Thermoglucosidasius for D-Tagatose Production. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laksmi, F.A.; Arai, S.; Tsurumaru, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Saksono, B.; Tokunaga, M.; Ishibashi, M. Mproved Substrate Specificity for D-Galactose of L-Arabinose Isomerase for Industrial Application. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2018, 1866, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zabed, H.M.; Yun, J.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qi, X. Two-Stage Biosynthesis of D-Tagatose from Milk Whey Powder by an Engineered Escherichia Coli Strain Expressing L-Arabinose Isomerase from Lactobacillus Plantarum. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 305, 123010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Kang, Z.; Izumori, K.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Y. Enzymatic Conversion of D-Galactose to d-Tagatose: Cloning, Overexpression and Characterization of l-Arabinose Isomerase from Pediococcus Pentosaceus PC-5. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Fan, C.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, B.; Mu, W. Cloning, Expression, and Characterization of a Novel l-Arabinose Isomerase from the Psychrotolerant Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas Haloplanktis. Mol. Biotechnol. 2016, 58, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.J.; Akhani, R.C.; Patel, A.T.; Dedania, S.R.; Patel, D.H. A Single and Two Step Isomerization Process for D-Tagatose and l-Ribose Bioproduction Using l-Arabinose Isomerase and d-Lyxose Isomerase. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2017, 97, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dische, Z.; Borenfreund, E. A New Spectrophotometric Method for the Detection and Determination of Keto Sugars and Trioses. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 192, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghany, M.N.A.; Hamdi, S.A.; Korany, S.M.; Elbaz, R.M.; Farahat, M.G. Biosynthesis of Novel Tellurium Nanorods by Gayadomonas sp. TNPM15 Isolated from Mangrove Sediments and Assessment of Their Impact on Spore Germination and Ultrastructure of Phytopathogenic Fungi. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevillon, E.; Silventoinen, V.; Pillai, S.; Harte, N.; Mulder, N.; Apweiler, R.; Lopez, R. InterProScan: Protein Domains Identifier. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W116–W120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Farahat, M.G.; Amr, D.; Galal, A. Molecular Cloning, Structural Modeling and Characterization of a Novel Glutaminase-Free L-Asparaginase from Cobetia Amphilecti AMI6. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Prabhu, P.; Lee, J.K. Immobilization of Bacillus Licheniformis L-Arabinose Isomerase for Semi-Continuous l-Ribulose Production. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 2234–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Mei, W.; Xia, M.; He, Q.; Ouyang, J. Rational Design of Bacillus Coagulans NL01 L-Arabinose Isomerase and Use of Its F279I Variant in D-Tagatose Production. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4715–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, W.; Wang, L.; Zang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Ouyang, J. Characterization of an L-Arabinose Isomerase from Bacillus Coagulans NL01 and Its Application for D-Tagatose Production. BMC Biotechnol. 2016, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; An, Y.; Parvez, A.; Zabed, H.M.; Yun, J.; Qi, X. Exploring a Highly D-Galactose Specific L-Arabinose Isomerase from Bifidobacterium Adolescentis for D-Tagatose Production. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, G.; Poonperm, W.; Rao, D.; Souda, A.; Nishizaki, T.; Morimoto, K.; Izumori, K. Cloning, Expression, and Transcription Analysis of L-Arabinose Isomerase Gene from Mycobacterium Smegmatis SMDU. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 2876–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Sharma, N.; Savitri; Bhalla, T.C. Comparative Analysis of Amino Acid Sequences from Mesophiles and Thermophiles in Respective of Carbon–Nitrogen Hydrolase Family. 3 Biotech 2013, 3, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DasSarma, S.; DasSarma, P. Halophiles and Their Enzymes: Negativity Put to Good Use. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 25, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvin, J.; Kennedy, J.; Lejon, D.P.H.; Kiran, G.S.; Dobson, A.D.W. Isolation Identification and Biochemical Characterization of a Novel Halo-Tolerant Lipase from the Metagenome of the Marine Sponge Haliclona Simulans. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolak, A.; Şişik, D.; Saglam, N.; Güner, S.; Çanakçi, S.; Beldüz, A.O. Characterization of a Thermoalkalophilic Esterase from a Novel Thermophilic Bacterium, Anoxybacillus Gonensis G2. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Zhao, D.; Cheng, S.; Sun, D.; Chen, M.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, C. Towards Efficient Enzymatic Conversion of D-Galactose to d-Tagatose: Purification and Characterization of L-Arabinose Isomerase from Lactobacillus Brevis. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 42, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.M.; Lee, Y.-J.; Cao, T.-P.; Shin, S.-M.; Park, M.-K.; Lee, H.-S.; di Luccio, E.; Kim, S.-B.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Structure of the Thermophilic L-Arabinose Isomerase from Geobacillus Kaustophilus Reveals Metal-Mediated Intersubunit Interactions for Activity and Thermostability. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 596, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, P.; Kumar Tiwari, M.; Jeya, M.; Gunasekaran, P.; Kim, I.W.; Lee, J.K. Cloning and Characterization of a Novel L-Arabinose Isomerase from Bacillus Licheniformis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 81, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.W.; Riaz, T.; Hassanin, H.A.M.; Ni, D.; Mahmood Khan, I.; Rehman, A.; Mahmood, S.; Adnan, M.; Mu, W. Characterization of a Novel D-Arabinose Isomerase from Thermanaeromonas Toyohensis and Its Application for the Production of D-Ribulose and L-Fuculose. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2019, 131, 109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranik, M.M.; Badawy, M.A.; Farahat, M.G. Fabrication of β-Glucosidase–Copper Phosphate Hybrid Nanoflowers for Bioconversion of Geniposide into Gardenia Blue. Int. J. Nanosci. 2023, 22, 2350040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qaysi, S.A.S.; Al-Haideri, H.; Al-Shimmary, S.M.; Abdulhameed, J.M.; Alajrawy, O.I.; Al-Halbosiy, M.M.; Moussa, T.A.A.; Farahat, M.G. Bioactive Levan-Type Exopolysaccharide Produced by Pantoea Agglomerans ZMR7: Characterization and Optimization for Enhanced Production. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghany, M.N.A.; Hamdi, S.A.; Elbaz, R.M.; Aloufi, A.S.; El Sayed, R.R.; Ghonaim, G.M.; Farahat, M.G. Development of a Microbial-Assisted Process for Enhanced Astaxanthin Recovery from Crab Exoskeleton Waste. Fermentation 2023, 9, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, N.; Nyyssölä, A.; Salonen, K.; Turunen, O. Bifidobacterium Longum L-Arabinose Isomerase Overexpression in Lactococcus Lactis, Purification, and Characterization. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 168, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.-S.; Kim, H.-J.; Oh, D.-K. Tagatose Production by Immobilized Recombinant Escherichia Coli Cells Containing Geobacillus Stearothermophilusl-Arabinose Isomerase Mutant in a Packed-Bed Bioreactor. Biotechnol. Prog. 2008, 21, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Chen, M.; Liu, X.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, X.W.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, M.; Wang, P. Bioconversion of D-Galactose to D-Tagatose: Continuous Packed Bed Reaction with an Immobilized Thermostable L-Arabinose Isomerase and Efficient Purification by Selective Microbial Degradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.C.; Kim, H.J.; Oh, D.K. High Production of D-Tagatose by the Addition of Boric Acid. Biotechnol. Prog. 2007, 23, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzo, R.M.; Antunes, A.S.L.M.; de Sousa Mendes, J.; Hissa, D.C.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; Mammarella, E.J. Biochemical Characterization of Heat-Tolerant Recombinant l-Arabinose Isomerase from Enterococcus Faecium DBFIQ E36 Strain with Feasible Applications in d-Tagatose Production. Mol. Biotechnol. 2019, 61, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, D.W.; Choe, E.A.; Hong, Y.H.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, B.C.; Pyun, Y.R. Characterization of a Thermoacidophilic L-Arabinose Isomerase from Alicyclobacillus Acidocaldarius: Role of Lys-269 in PH Optimum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 7888–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Huang, J.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Mu, W. Production of L-Ribose from L-Arabinose by Co-Expression of L-Arabinose Isomerase and D-Lyxose Isomerase in Escherichia Coli. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2020, 132, 109443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Choe, E.A.; Kim, S.B.; Eom, S.H.; Hong, Y.H.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, D.Y.; Pyun, Y.R. Distinct Metal Dependence for Catalytic and Structural Functions in the L-Arabinose Isomerases from the Mesophilic Bacillus Halodurans and the Thermophilic Geobacillus Stearothermophilus. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 434, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjasetty, B.A.; Chance, M.R. Crystal Structure of Escherichia Coli L-Arabinose Isomerase (ECAI), The Putative Target of Biological Tagatose Production. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 360, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouayekh, H.; Bejar, W.; Rhimi, M.; Jelleli, K.; Mseddi, M.; Bejar, S. Characterization of an L-Arabinose Isomerase from the Lactobacillus Plantarum NC8 Strain Showing Pronounced Stability at Acidic PH. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 277, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Jang, H.J.; Choe, E.A.; Kim, B.C.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.B.; Hong, Y.H.; Pyun, Y.R. Characterization of a Thermostable L-Arabinose (D-Galactose) Isomerase from the Hyperthermophilic Eubacterium Thermotoga Maritima. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Jeya, M.; Lee, J.K. Enhanced Activity and Stability of L-Arabinose Isomerase by Immobilization on Aminopropyl Glass. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, M.; Manzo, R.M.; García, J.L.; Mammarella, E.J.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; Pessela, B.C. Engineering the L-Arabinose Isomerase from Enterococcus Faecium for d-Tagatose Synthesis. Molecules 2017, 22, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, J.; Kim, S.B.; Park, S.W.; Han, J.K.; Kim, P. Characterization of L-Arabinose Isomerase in Bacillus Subtilis, a GRAS Host, for the Production of Edible Tagatose. Food Biotechnol. 2009, 23, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.K.; Kim, H.J.; Ryu, S.A.; Rho, H.J.; Kim, P. Development of an Immobilization Method of L-Arabinose Isomerase for Industrial Production of Tagatose. Biotechnol. Lett. 2001, 23, 1859–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Oh, D.K. Purification and Characterization of an L-Arabinose Isomerase from an Isolated Strain of Geobacillus Thermodenitrificans Producing d-Tagatose. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 120, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.K.; Hong, M.G.; Chang, P.S.; Lee, B.H.; Yoo, S.H. Biochemical Properties of L-Arabinose Isomerase from Clostridium Hylemonae to Produce D-Tagatose as a Functional Sweetener. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, K.S.; Ertan, H.; Poljak, A.; Bridge, W.J. Evaluating Enzymatic Productivity—The Missing Link to Enzyme Utility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staudigl, P.; Haltrich, D.; Peterbauer, C.K. L-Arabinose Isomerase and d-Xylose Isomerase from Lactobacillus Reuteri: Characterization, Coexpression in the Food Grade Host Lactobacillus Plantarum, and Application in the Conversion of d-Galactose and d-Glucose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, P.; Jeya, M.; Lee, J.K. Probing the Molecular Determinant for the Catalytic Efficiency of L-Arabinose Isomerase from Bacillus Licheniformis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guo, Z.; Long, L.; Ding, S. Characterization of an L-Arabinose Isomerase from Bacillus Velezensis and Its Application for L-Ribulose and L-Ribose Biosynthesis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 192, 935–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | BAAI |
|---|---|
| Number of amino acids | 499 |
| Molecular weight (kDa) | 56.41 |
| pI | 5.45 |
| Total number of negatively charged residues | 70 |
| Total number of positively charged residues | 52 |
| GRAVY | −0.337 |
| Instability index | 35.77 |
| Aliphatic index | 80.94 |
| Treatment | Relative Activity (%) |
|---|---|
| Control * | 100 d |
| EDTA-Treated L-AI ** | 94 e ± 2 |
| 1,10-phenanthroline-Treated L-AI *** | 96 e ± 1.2 |
| Pb2+ | 0 i |
| Cr2+ | 0 i |
| Cu2+ | 125 c ± 5 |
| Zn2+ | 46 g ± 2 |
| Ba2+ | 0 i |
| Sn2+ | 120 b ± 3 |
| Mg2+ | 160 a ± 5 |
| Ca2+ | 33 h ± 5 |
| Hg2+ | 0 i |
| Mn2+ | 165 a ± 3 |
| Co2+ | 74 f ± 4 |
| Organism | L-Arabinose | D-Galactose | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Km (mM) | Kcat (min−1) | Kcat/Km (mM–1 min–1) | Km (mM) | Kcat (min−1) | Kcat/Km (mM–1 min–1) | ||
| B. amyloliquefaciens | 92.84 | 4350 | 46.85 | 251.6 | 589.5 | 2.34 | This study |
| Geobacillus stearothermophilus | 77.0 | 4515 | 58.0 | 279.0 | 3185 | 11.4 | [82] |
| Lactobacillus reuteri | 633.0 | 57,540 | 90.0 | 647.0 | 3540 | 5.4 | [87] |
| Anoxybacillus flavithermus | 78.5 | 52.8 | 0.67 | 25.1 | 129.9 | 5.1 | [39] |
| Geobacillus thermodenitrificans | 142.0 | NR | 48 | 408.0 | NR | 0.5 | [84] |
| Bacillus licheniformis | 369.0 | 12,450 | 34.0 | NR | NR | NR | [88] |
| Lactobacillus sakai | 32.0 | 3516 | 109.2 | NR | NR | NR | [32] |
| Bifidobacterium adolescentis | 40.2 | NR | 8.6 | 22.4 | NR | 9.3 | [56] |
| Enterococcus faecium | NR | NR | NR | 225.0 | 151 | 0.68 | [37] |
| Bacillus coagulans | 269.8 | NR | 8.7 | 355.1 | NR | 1.0 | [55] |
| Bacillus velezensis | 194.6 | 2067.3 | 10.58 | NR | NR | NR | [89] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shehata, H.M.; Abd El-Ghany, M.N.; Hamdi, S.A.; Abomughaid, M.M.; Ghaleb, K.I.; Kamel, Z.; Farahat, M.G. Characterization of a Metallic-Ions-Independent L-Arabinose Isomerase from Endophytic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for Production of D-Tagatose as a Functional Sweetener. Fermentation 2023, 9, 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9080749
Shehata HM, Abd El-Ghany MN, Hamdi SA, Abomughaid MM, Ghaleb KI, Kamel Z, Farahat MG. Characterization of a Metallic-Ions-Independent L-Arabinose Isomerase from Endophytic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for Production of D-Tagatose as a Functional Sweetener. Fermentation. 2023; 9(8):749. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9080749
Chicago/Turabian StyleShehata, Hoda M., Mohamed N. Abd El-Ghany, Salwa A. Hamdi, Mosleh M. Abomughaid, Khaled I. Ghaleb, Zeinat Kamel, and Mohamed G. Farahat. 2023. "Characterization of a Metallic-Ions-Independent L-Arabinose Isomerase from Endophytic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for Production of D-Tagatose as a Functional Sweetener" Fermentation 9, no. 8: 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9080749
APA StyleShehata, H. M., Abd El-Ghany, M. N., Hamdi, S. A., Abomughaid, M. M., Ghaleb, K. I., Kamel, Z., & Farahat, M. G. (2023). Characterization of a Metallic-Ions-Independent L-Arabinose Isomerase from Endophytic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for Production of D-Tagatose as a Functional Sweetener. Fermentation, 9(8), 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9080749








