Production of Nattokinase from Hemp Seed Meal by Solid-State Fermentation and Improvement of Its Nutritional Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Microorganism and Culture
2.3. Determination of HSM Composition
2.4. Solid-State Fermentation of Nattokinase by HSM
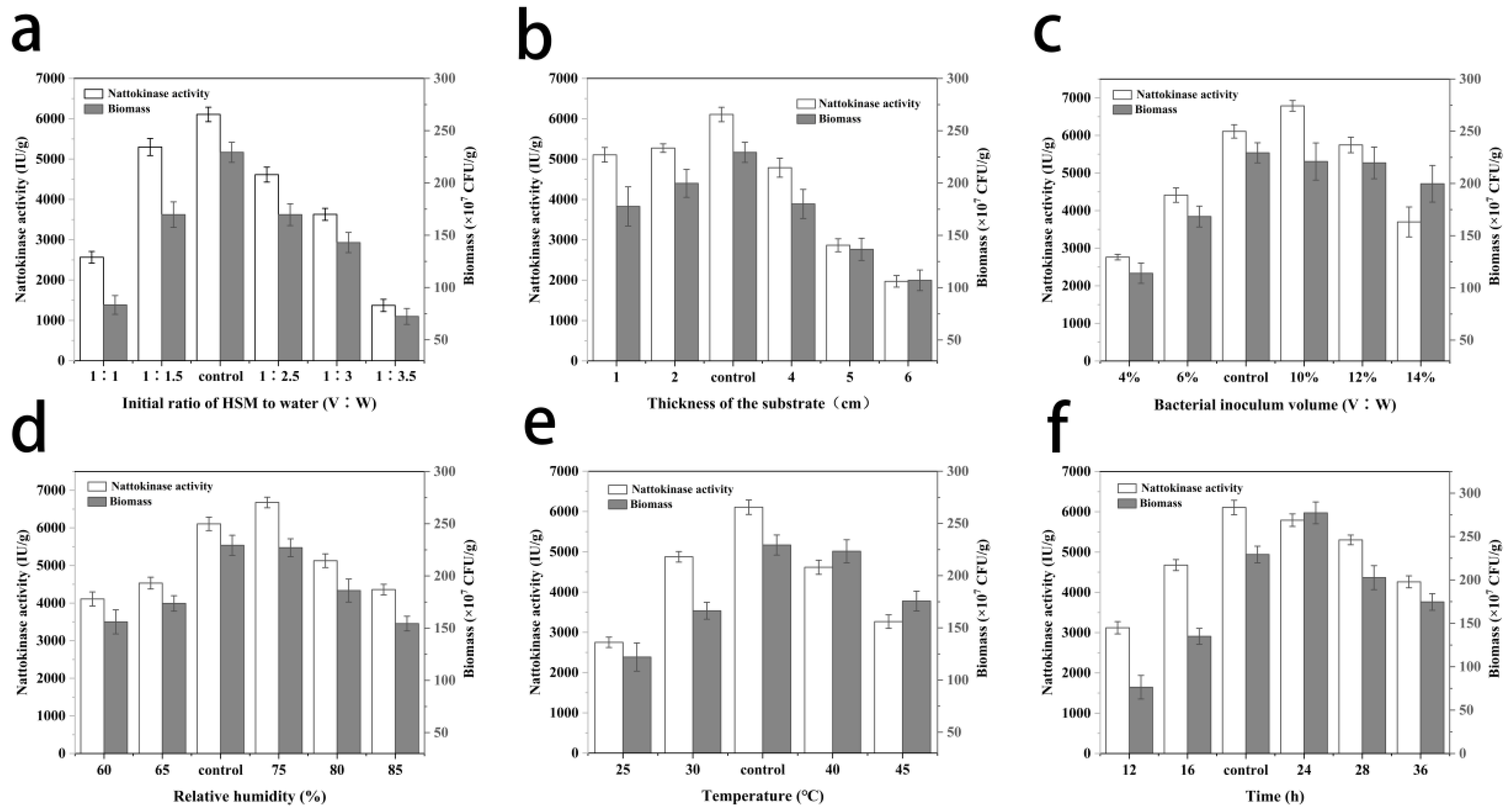
2.4.1. One-Factor-at-a-Time Experiments (OFAT)
2.4.2. Plackett–Burman Design (PB Design)
2.4.3. Box–Behnken Design (BBD)
2.5. Extraction of NK and Determination of Enzyme Activity
2.6. Determination of Soluble Peptide Content
2.7. Detection of Antioxidant Activity
2.8. Determination of Anti-Nutritional Factors
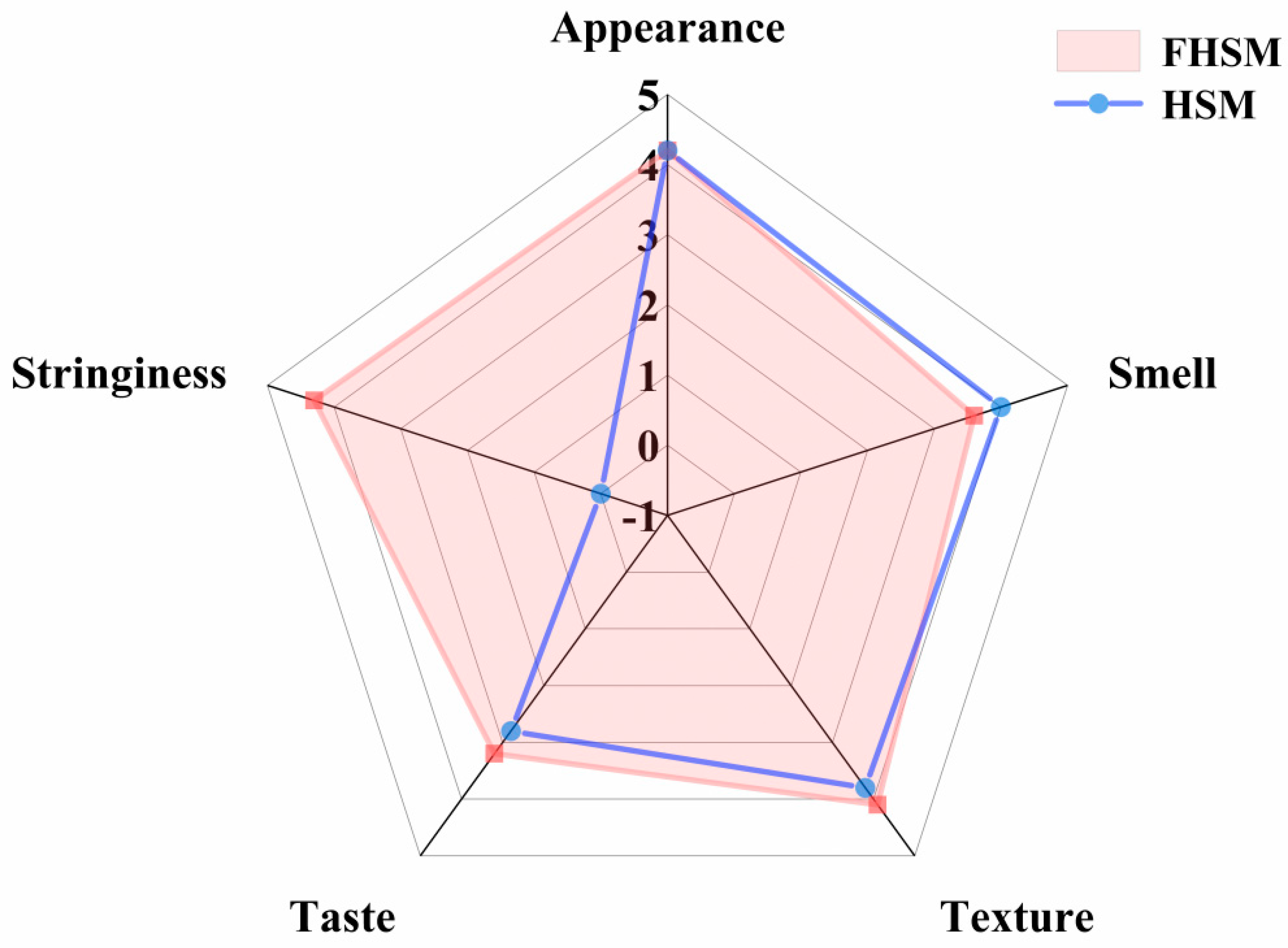
2.9. Sensory Characteristics
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Components of HSM
3.2. One-Factor-At-A-Time Experiments
3.3. PB Design
3.4. BBD
3.5. Contents of Soluble Polypeptides and Antioxidant Activities
3.6. Anti-Nutritional Factors in HSM
3.7. HSM Sensory Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hofmanová, T.; Švec, I.; Hrušková, M. Nutritional properties of non-traditional seeds. J. Life Med. 2014, 2, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, R.A.; Andres, M.; Cole, M.; Cowley, J.M.; Augustin, M.A. Industrial hemp seed: From the field to value-added food ingredients. J. Cannabis Res. 2022, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, J.D.; Neufeld, J.; Leson, G. Evaluating the quality of protein from hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) products through the use of the protein digestibility-corrected amino acid score method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11801–11807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-H.; Ten, Z.; Wang, X.-S.; Yang, X.-Q. Physicochemical and functional properties of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8945–8950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silversides, F.; Lefrancois, M. The effect of feeding hemp seed meal to laying hens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2005, 46, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radočaj, O.; Dimić, E.; Tsao, R. Effects of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed oil press-cake and decaffeinated green tea leaves (Camellia sinensis) on functional characteristics of gluten-free crackers. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, C318–C325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Norajit, K.; Kim, M.-H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Ryu, G.-H. Influence of extrusion condition and hemp addition on wheat dough and bread properties. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 22, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Singh, S.K.; Larroche, C.; Soccol, C.R.; Pandey, A. Oil cakes and their biotechnological applications—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2000–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, L.; Casciano, F.; Babini, E.; Gianotti, A. Prebiotic potential and bioactive volatiles of hemp byproduct fermented by lactobacilli. LWT 2021, 151, 112201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, H.; Hamada, H.; Tsushima, H.; Mihara, H.; Muraki, H. A novel fibrinolytic enzyme (nattokinase) in the vegetable cheese Natto; a typical and popular soybean food in the Japanese diet. Experientia 1987, 43, 1110–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Ohnishi, K.; Takaoka, S.; Ogasawara, K.; Fukuyama, R.; Nakamuta, H. Antihypertensive effects of continuous oral administration of nattokinase and its fragments in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hmood, S.A.; Aziz, G.M. Optimum conditions for fibrinolytic enzyme (Nattokinase) production by Bacillus sp. B24 using solid state fermentation. Iraqi J. Sci. 2016, 57, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, G.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, F.; Nie, Z.; Ye, Y.; Yue, W. Co-production of nattokinase and poly (γ-Glutamic Acid) under solid-state fermentation using soybean and rice husk. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2015, 58, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Luo, M.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Kong, P.; Liu, H. Production of fibrinolytic enzyme from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens by fermentation of chickpeas, with the evaluation of the anticoagulant and antioxidant properties of chickpeas. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3957–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-L.; Chen, H.-J.; Liang, T.-W.; Lin, Y.-D. A novel nattokinase produced by Pseudomonas sp. TKU015 using shrimp shells as substrate. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhan, C.; Guo, G.; Liu, Z.; Hao, N.; Ouyang, P. Tofu processing wastewater as a low-cost substrate for high activity nattokinase production using Bacillus subtilis. BMC Biotechnol. 2021, 21, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Jiang, Y.W.; Song, X.R.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.M.; Fu, Y.J. Effect of Bacillus natto solid-state fermentation on the functional constituents and properties of Ginkgo seeds. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.-Z.; An, J.-Y.; Wang, L.-T.; Fan, X.-H.; Lv, M.-J.; Zhu, Y.-W.; Fu, Y.-J. Development of fermented chestnut with Bacillus natto: Functional and sensory properties. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölker, U.; Lenz, J. Solid-state fermentation—Are there any biotechnological advantages? Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, C.R. Bacillus subtilis and its relatives: Molecular biological and industrial workhorses. Trends Biotechnol. 1992, 10, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Li, C.; Xi, T.; Ji, L. Biotechnology, bioengineering and applications of Bacillus nattokinase. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadnađev, M.; Dizdar, M.; Hadnađev-Dapčević, T.; Jovanov, P.; Mišan, A.; Sakač, M. Hydrolyzed hemp seed proteins as bioactive peptides. J. Process. Energy Agric. 2018, 22, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Morrissey, M.T. Protein hydrolysates from Pacific whiting solid wastes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3423–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Jin, S.; Luo, M.; Wang, W.; Xia, X.-X.; Zu, Y.-G., Fu. Optimization of production parameters for preparation of natto-pigeon pea with immobilized Bacillus natto and sensory evaluations of the product. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 31, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaszkiewicz, T. Nutritional value of soybean meal. Soybean Nutr. 2011, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- y Postigo, L.O.C.; Jacobo-Velázquez, D.A.; Guajardo-Flores, D.; Amezquita, L.E.G.; García-Cayuela, T. Solid-state fermentation for enhancing the nutraceutical content of agrifood by-products: Recent advances and its industrial feasibility. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 100926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilakamarry, C.R.; Sakinah, A.M.; Zularisam, A.; Sirohi, R.; Khilji, I.A.; Ahmad, N.; Pandey, A. Advances in solid-state fermentation for bioconversion of agricultural wastes to value-added products: Opportunities and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, C.V.; Nguyen, M.N.T.; Truong, M.H.T.; Bui, X.D. Screening for Optimal Parameters of Nattokinase Synthesis by Bacillus subtilis natto in Solid-State Fermentation. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2020, 10, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, P.; Sabu, A.; Pandey, A.; Szakacs, G.; Soccol, C.R. Extra-cellular L-glutaminase production by Zygosaccharomyces rouxii under solid-state fermentation. Process Biochem. 2002, 38, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Tian, Z.; Ma, X. Study on the mechanism of production of γ-PGA and nattokinase in Bacillus subtilis natto based on RNA-seq analysis. Microb. Cell Factories 2021, 20, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Li, W.; Shu, L.; Yi, J.; Chen, G.; Liang, Z. Non-sterilized fermentative co-production of poly (γ-glutamic acid) and fibrinolytic enzyme by a thermophilic Bacillus subtilis GXA-28. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, V.F.; Castilho, L.R.; Bon, E.P.; Freire, D.M. High-yield Bacillus subtilis protease production by solid-state fermentation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2005, 121, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, H.; Zhao, H.; Lu, F.; Zhang, C.; Bie, X.; Lu, Z. Improvement of the Nutritional Quality and Fibrinolytic Enzyme Activity of Soybean Meal by Fermentation of Bacillus subtilis. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2015, 39, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-H.; Wang, X.-S.; Yang, X.-Q. Enzymatic hydrolysis of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolate by various proteases and antioxidant properties of the resulting hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, W.; Zhang, P.; Ying, D.; Fang, Z. Hempseed in food industry: Nutritional value, health benefits, and industrial applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 282–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemede, H.F.; Ratta, N. Antinutritional factors in plant foods: Potential health benefits and adverse effects. Int. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 3, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, S.; Basman, A. Effects of infrared treatment on urease, trypsin inhibitor and lipoxygenase activities of soybean samples. Food Chem. 2015, 169, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbab Sakandar, H.; Chen, Y.; Peng, C.; Chen, X.; Imran, M.; Zhang, H. Impact of fermentation on antinutritional factors and protein degradation of legume seeds: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 39, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civille, G.V.; Oftedal, K.N. Sensory evaluation techniques—Make “good for you” taste “good”. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 107, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Yao, J.; Sparks, S.; Wang, K.Y. Nattokinase: An oral antithrombotic agent for the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Factor | Symbol | Level | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | ||
| Initial ratio of HSM to water (v:w) | A | 1:1.5 | 1:2.5 |
| Thickness of the substrate (cm) | B | 2 | 4 |
| Bacterial inoculum volume (v:w) | C | 8 | 12 |
| Relative humidity (%) | D | 70 | 80 |
| Temperature (°C) | E | 30 | 40 |
| Time (h) | F | 16 | 24 |
| Factor | Symbol | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | 0 | High | ||
| Initial ratio of HSM to water (v:w) | A | 1:1.5 | 1:2 | 1:2.5 |
| Thickness of the substrate (cm) | B | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Relative humidity (%) | D | 70 | 75 | 80 |
| Temperature (°C) | E | 30 | 35 | 40 |
| Component | Moisture | Protein | Fat | Amylum | Dietary Fiber |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (g/100 g) | 7.91 ± 0.08 | 31.9 ± 0.91 | 1.8 ± 0.02 | 56.4 ± 1.17 | 1.16 ± 0.05 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 7.317 × 105 | 6 | 1.219 × 105 | 10.06 | 0.0114 | significant |
| A | 1.296 × 105 | 1 | 1.296 × 105 | 10.69 | 0.0222 | * |
| B | 3.869 × 105 | 1 | 3.869 × 105 | 31.92 | 0.0024 | ** |
| C | 23,994.96 | 1 | 23,994.96 | 1.98 | 0.2184 | |
| D | 84,101.76 | 1 | 84,101.76 | 6.94 | 0.0463 | * |
| E | 1.054 × 105 | 1 | 1.054 × 105 | 8.70 | 0.0319 | * |
| F | 1756.92 | 1 | 1756.92 | 0.1450 | 0.7190 | |
| Residual | 60,591.01 | 5 | 12,118.20 | |||
| Cor Total | 7.923 × 105 | 11 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 1.668 × 106 | 14 | 1.191 × 105 | 19.61 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A | 13,240.16 | 1 | 13,240.16 | 2.18 | 0.1619 | |
| B | 62,107.24 | 1 | 62,107.24 | 10.23 | 0.0064 | * |
| D | 1297.92 | 1 | 1297.92 | 0.2137 | 0.6510 | |
| E | 821.71 | 1 | 821.71 | 0.1353 | 0.7185 | |
| AB | 4489.00 | 1 | 4489.00 | 0.7392 | 0.4044 | |
| AD | 13,665.61 | 1 | 13,665.61 | 2.25 | 0.1558 | |
| AE | 41,575.21 | 1 | 41,575.21 | 6.85 | 0.0203 | * |
| BD | 16,218.02 | 1 | 16,218.02 | 2.67 | 0.1245 | |
| BE | 29,790.76 | 1 | 29,790.76 | 4.91 | 0.0439 | * |
| DE | 229.52 | 1 | 229.52 | 0.0378 | 0.8487 | |
| A² | 1.130 × 106 | 1 | 1.130 × 106 | 186.01 | <0.0001 | ** |
| B² | 5.112 × 105 | 1 | 5.112 × 105 | 84.17 | <0.0001 | ** |
| D² | 2.770 × 105 | 1 | 2.770 × 105 | 45.61 | <0.0001 | ** |
| E² | 35,695.42 | 1 | 35,695.42 | 5.88 | 0.0295 | * |
| Residual | 85,024.08 | 14 | 6073.15 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 68,251.07 | 10 | 6825.11 | 1.63 | 0.3379 | not significant |
| Pure Error | 16,773.01 | 4 | 4193.25 | |||
| Cor Total | 1.753 × 106 | 28 | ||||
| R2 | 0.9515 |
| Substrates | Strains | NK Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| soybeans | Bacillus subtilis natto | 1388 U/g | [30] |
| soybean, rice husk | Bacillus subtilis | 2503.4 IU/gs | [13] |
| chickpeas | Bacillus subtilis LSSE-22 | 39.28 FU/g | [14] |
| soybean residue | Bacillus subtilis GXA-28 | 986 U/g | [31] |
| shrimp shell | Pseudomonas sp TKU015 | 2.3 FU/mL | [15] |
| ginkgo seeds | Bacillus natto (no. 1A752) | 3682 ± 43 IU/g | [17] |
| chestnut | Bacillus natto | 6479 IU/g | [18] |
| hemp seed meal | Bacillus subtilis 13,932 | 7067.12 IU/g | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Li, T.; Guo, G.; Liu, Z.; Hao, N. Production of Nattokinase from Hemp Seed Meal by Solid-State Fermentation and Improvement of Its Nutritional Quality. Fermentation 2023, 9, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050469
Zhang M, Li T, Guo G, Liu Z, Hao N. Production of Nattokinase from Hemp Seed Meal by Solid-State Fermentation and Improvement of Its Nutritional Quality. Fermentation. 2023; 9(5):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050469
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Min, Tao Li, Gege Guo, Zhaoxing Liu, and Ning Hao. 2023. "Production of Nattokinase from Hemp Seed Meal by Solid-State Fermentation and Improvement of Its Nutritional Quality" Fermentation 9, no. 5: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050469
APA StyleZhang, M., Li, T., Guo, G., Liu, Z., & Hao, N. (2023). Production of Nattokinase from Hemp Seed Meal by Solid-State Fermentation and Improvement of Its Nutritional Quality. Fermentation, 9(5), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050469





