Attributes of Lactobacillus acidophilus as Effected by Carao (Cassia grandis) Pulp Powder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analytical Method
2.3.1. Bacterial Viability
2.3.2. Bile Tolerance
2.3.3. Acid Tolerance
2.3.4. Protease Activity for Probiotics
2.3.5. Tolerance to Simulated Gastric Juice
2.3.6. Lysozyme Tolerance
2.3.7. Enumeration of L. acidophilus
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
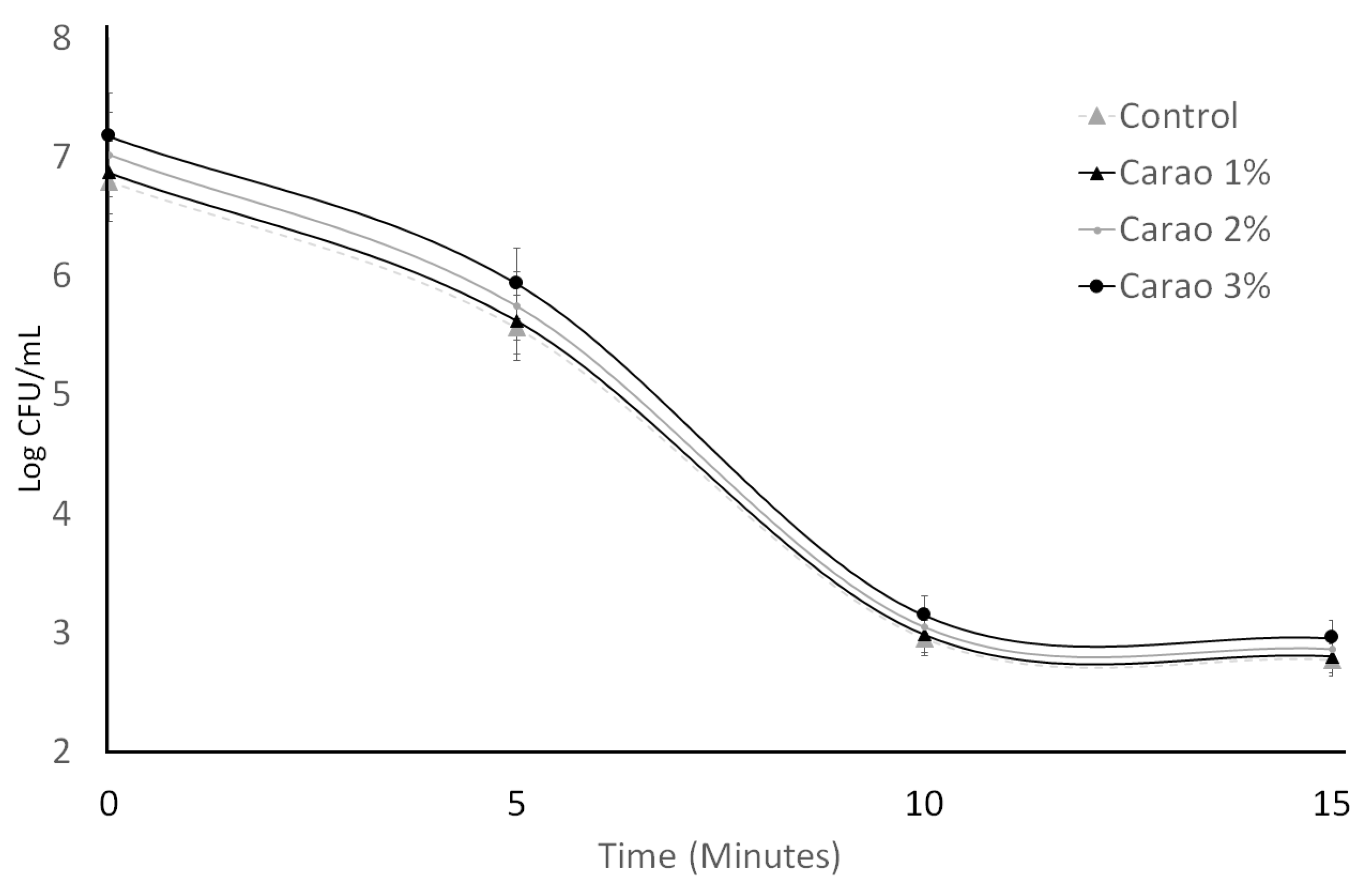
3.1. Bacterial Viability
3.2. Bile Tolerance
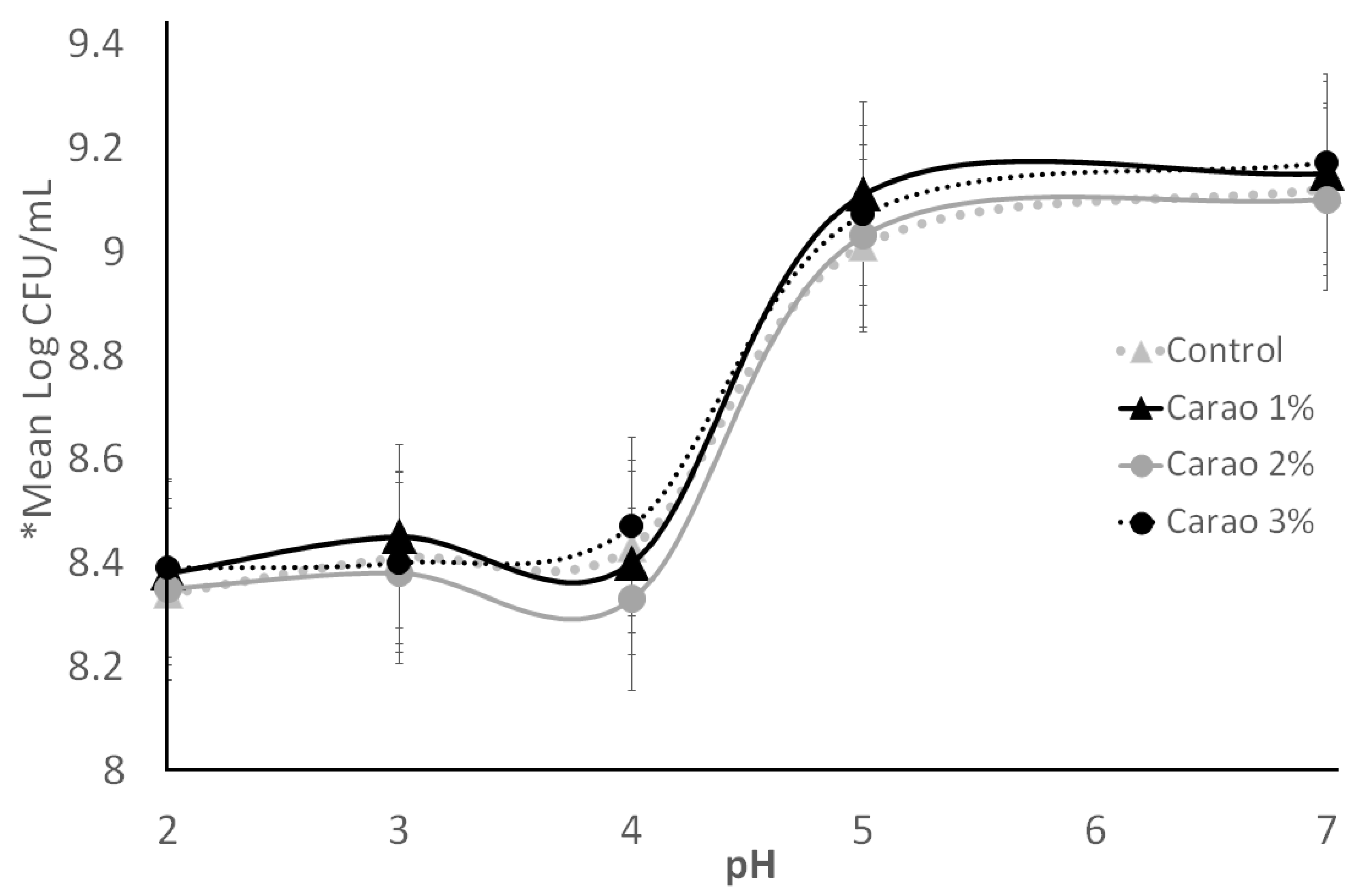
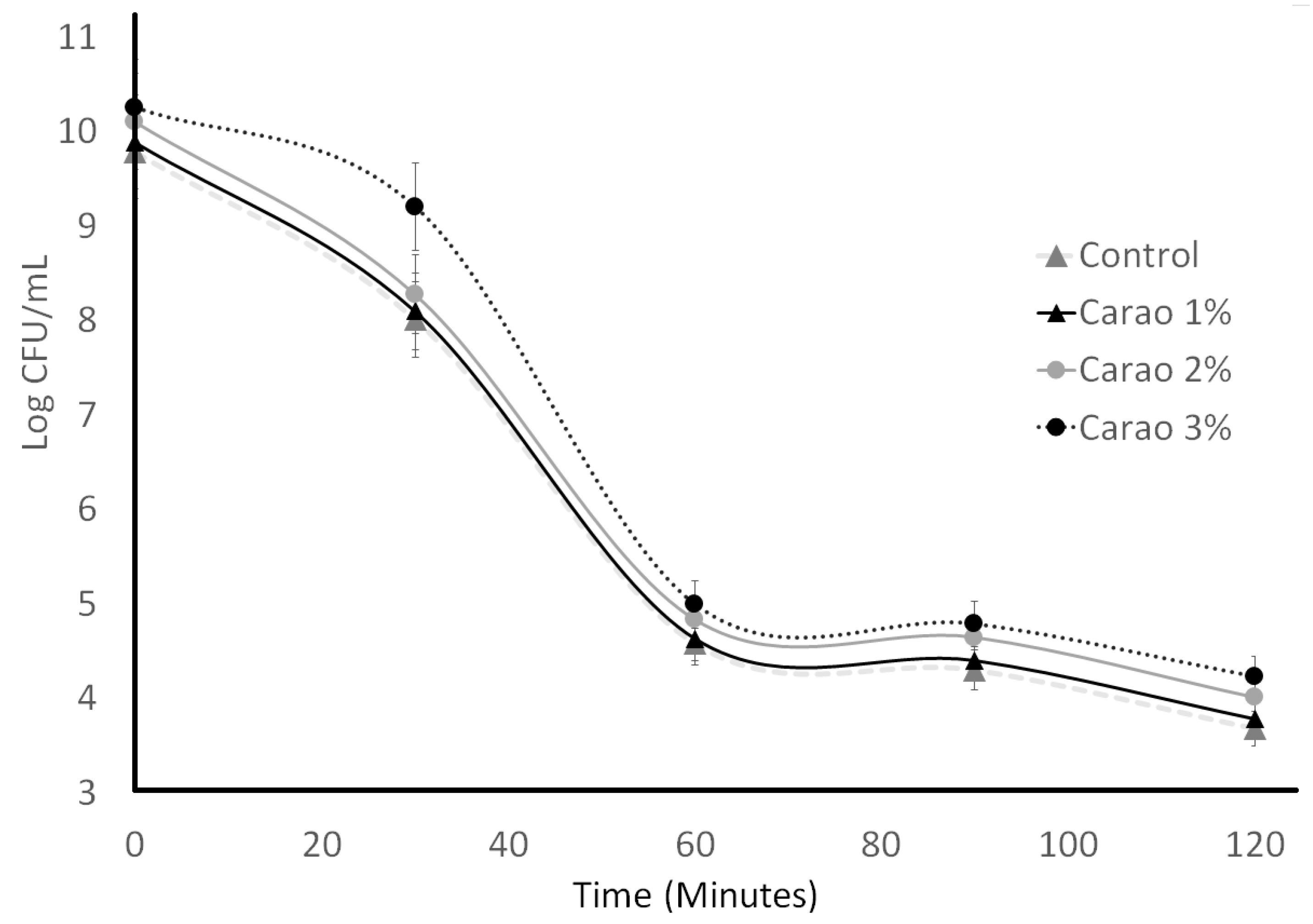
3.3. Acid Tolerance and Resistance to Gastric Juices
3.4. Protease Activity
3.5. Lysozyme Resistance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Troche, J.; Coss-Adame, E.; Ángel Valdovinos-Díaz, M.; Gómez-Escudero, O.; Eugenia Icaza-Chávez, M.; Antonio Chávez-Barrera, J.; Zárate-Mondragón, F.; Velarde-Ruíz Velasco, J.; Aceves-Tavares, R.G.; Lira-Pedrín, A.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus LB: A useful pharmabiotic for the treatment of digestive disorders. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820971201. [Google Scholar]
- Szajewska, H.; Ruszcynski, M.; Kolacek, S. Meta-analysis shows limited evidence for using Lactobacillus acidophilus LB to treat acuted gastroenteritis in children. Acta Paediatr. 2014, 103, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, K.R.; Naik, S.R.; Vakil, B.V. Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics-a reviw. J. Food Sci. Techonol. 2015, 52, 7577–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isazadeh, A.; Hajazimian, S.; Shadman, B.; Safaei, S.; Bedoustani, A.B.; Chavoshi, R.; Baradaran, B. Anti-cancer effects of probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus for colorectal cancer cell line caco-2 through apoptosis induction. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 27, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, Y.; Nakanishi, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Nuijima, Y.; Kato, T.; Umehara, M.; Kikuchi, J. In vitro evaluation method for screening of candidate prebiotic foods. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindels, L.B.; Delzenne, N.M.; Cani, P.D.; Walter, J. Towards a more comprehensive concept for prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schell, K.R.; Fernandes, K.E.; Shanahan, E.; Wilson, I.; Blair, S.E.; Carter, D.A.; Cokcetin, N.N. The potential of honey as a prebiotic food to re-engineer the gut microbiome toward a healthy state. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 957932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Câmara, A.K.F.I.; de Souza Paglarini, C.; Vidal, V.A.S.; Dos Santos, M.; Pollonio, M.A.R. Meat products as prebiotic food carrier. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 94, pp. 223–265. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Ren, Z.; Ye, J.; Fan, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Li, J. Fermented soybean dregs by neurospora crassa: A traditional prebiotic food. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 189, 608–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehinde, B.A.; Panghal, A.; Garg, M.K.; Sharma, P.; Chhikara, N. Vegetable milk as probiotic and prebiotic foods. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 94, pp. 115–160. [Google Scholar]
- Tuohy, K.M.; Brown, D.T.; Klinder, A.; Costabile, A.; Fava, F. Shaping the human microbiome with prebiotic foods–current perspectives for continued development. In Diet-Microbe Interactions in the Gut: Effects on Human Health and Disease; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 53–71. [Google Scholar]
- Montero-Fernández, I.; Marcía-Fuentes, J.A.; Cascos, G.; Saravia-Maldonado, S.A.; Lozano, J.; Martín-Vertedor, D. Masking effect of Cassia grandis sensory defect with flavoured stuffed olives. Foods 2022, 11, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotipalli, H.; Battu-Ganga, R.; Devarakonda, R. Qualitative physicochemical, phytochemical analysis and quantitative estimation of total phenols, flavonoids and alkaloids of Cassia grandis. J. Glob. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2017, 8, 3860–3867. [Google Scholar]
- Hegazi, N.M.; Hashim, A.N. Grandisin, 2-methoxy 6, 7, 2′, 6′-tetrahydroxy flavanone 6-O-glucoside, from Cassia grandis leaves—Antioxidant and cytotoxic activities. Pharmacology 2016, 71, 544–547. [Google Scholar]
- Prada, A.L.; Achod, L.D.; Keita, H.; Carvalho, J.C.; de Souza, T.P.; Amado, J. Development, pharmacological and toxicological evaluation of a new tablet formulation based on Cassia grandis fruit extract. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 16, 100244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, D.; Aleman, R.S.; Cedillos, R.; Olson, D.W.; Aryana, K.; Marcia, J.; Boeneke, C. Probiotic Characteristics of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus as Influenced by Carao (Cassia grandis). Fermentation 2022, 8, 499. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.Y.; Young, C.M. Biosynthesis of folates by Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbruekii ssp. bulgaricus. J. Food Drug Anal. 2000, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.I.A.; Gibson, G.R. Cholesterol assimilation by lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria isolated from the human gut. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4689–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberg, C.J.; Weimer, B.C.; Moyes, L.V.; Brown, R.J.; Richardson, G.H. Proteolytic Characterization of Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus Strains by the o-Phthaldialdehyde Test and Amino Acid Analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihata, A.; Shah, N.P. Proteolytic profiles of yogurt and probiotic bacteria. Int. Dairy J. 2000, 10, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, A.; González de Llano, D.; Esteban-Fernández, A.; Requena, T.; Bartolomé, B.; Moreno-Arribas, M.B. Assessment of probiotic properties in lactic acid bacteria isolated from wine. Food Microbiol. 2014, 44, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleman, R.S.; Paz, D.; Cedillos, R.; Tabora, M.; Douglas, W.; Kayanush, A. Attributes of Culture Bacteria as Influenced by Ingredients That Help Treat Leaky Gut. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, N.; Luo, B.; Gao, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, Y.; Tian, F. Oligosaccharides as co-encapsulating agents: Effect on oral Lactobacillus fermentum survival in a simulated gastrointestinal tract. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Talaverano, M.I.; Pérez-Nevado, F.; Boselli, E.; Cordeiro, A.M.; Martillanes, S.; Martín-Vertedor, D. Evaluation of phenolics and acrylamide and their bioavailability in high hydrostatic pressure treated and fried table olives. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 44, e14384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zago, M.; Fornasari, M.E.; Carminati, D.; Burns, P.; Suàrez, V.; Vinderola, G.; Reinheimer, J.; Giraffa, G. Characterization and probiotic potential of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from cheeses. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, L.A.; Olson, D.W.; Aryana, K.J. Whey protein isolate improves acid and bile tolerances of Streptococcus thermophilus ST-M5 and Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp: Bulgaricus LB-12. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2215–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, R.I.; Shah, N.P. Evaluation of Media for Selective Enumeration of Streptococcus thermophilus, Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus, Lactobacillus acidophilus, and Bifidobacteria. J. Dairy Sci. 1996, 79, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muramalla, T.; Aryana, K.J. Some low homogenization pressures improve certain probiotic characteristics of yogurt culture bacteria and Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-K. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 3725–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, V.A.; Nakata, H.M. Plantas medicinales: Efecto antibacteriano in vitro de Plantago major L., Erythroxylum novogranatense, Plowman var truxillense y Camellia sinensis sobre bacterias de importancia estomatológica. Odontol. Sanmarquina 2010, 13, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel-Ramirez, E.; Castillo, D.; Del Solar, Q.; Maurtua, D.; Villegas, L.; Díaz, C. Efecto antibacteriano de extractos etanólicos de plantas utilizadas en la tradiciones culinarias andinas sobre microorganismos de la cavidad bucal. Rev. Estomatol. Hered. 2015, 25, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, J.A.M.; Fernandez, I.M.; Aleman, R.S.; Maldonado, S.A.S.; Roger, L.F.; Funez, N.H.; Chavarría, L.A.; Kayanush, A. Chemical characterization of the essential oil of Syzygium aromaticum and its antimicrobial activity against a probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus. Eur. Sci. J. 2020, 16, 1857–7881. [Google Scholar]
- Theegala, M.; Arévalo, R.A.C.; Viana, V.; Olson, D.; Aryana, K. Effect of Flaxseed on Bile Tolerances of Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus bulgaricus, and Streptococcus thermophilus. Food Nutr. Sci. 2021, 12, 670–680. [Google Scholar]
- Urdaneta, V.; Casadesús, T.J. Interactions between bacteria and bile salts in the gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary tracts. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iltar, R.; Asci, A.; Kücükcetin, A. Viability and in Vitro Properties of Lactobacillus acidophilus Used in Yoghurt as Influenced by Inulin Addition. Milchwissenschaft 2012, 67, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.E.; Li, Z.H.; Li, D.T.; Xu, M.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Tang, Z.X. Encapsulation of Probiotic Lactobacillus bulgaricus in Alginate-Milk Microspheres and Evaluation of the Survival in Simulated Gastrointestinal Conditions. J. Food Eng. 2013, 117, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, D.H.; Darwish, M.S.; El-Awady, A.A.; Mohamed, A.H.; Zaki, A.A.; Taher, M.A. Chemical characterization of Cassia fistula polysaccharide (CFP) and its potential application as a prebiotic in synbiotic preparation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 13329–13340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfarlane, S.; Dillon, J.F. Microbial biofilms in the human gastrointestinal tract. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.S.; Pintado, J.; Stevens, W.F.; Guyot, J.P. Kinetic growth parameters of different amylolytic and non-amylolytic Lactobacillus strains under various salt and pH conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 94, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulachev, V.P. Bacterial energetics at high pH: What happens to the H+ cycle when the extracellular H+ concentration decreases? In Novartis Foundation Symposium 221—Bacterial Responses to pH: Bacterial Responses to pH: Novartis Foundation Symposium 221; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2007; pp. 200–217. [Google Scholar]
- Serra, M.; Trujillo, A.J.; Guamis, B.; Ferragut, V. Proteolysis of yogurts made from ultra-high-pressure homogenized milk during cold storage. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, G.; Smit, B.A.; Engels, W.J. Flavour formation by lactic acid bacteria and biochemical flavour profiling of cheese products. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 591–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.; Haandrikman, A. Proteolytic enzymes of lactic acid bacteria. Int. Dairy J. 1997, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidian, N.; Khanniri, E.; Koushki, M.R.; Sohrabvandi, S.; Yousefi, M. An overview of antimicrobial activity of lysozyme and its functionality in cheese. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 833618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, J.A.M.; López-Salas, L.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Navarro-Alarcón, M.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Lozano-Sánchez, J. Development of an innovative pressurized liquid extraction procedure by response surface methodology to recover bioactive compounds from Carao Tree Seeds. Foods 2021, 10, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Effect | L. acidophilus LA-K |
|---|---|
| Viability | |
| Carao concentration | 0.0770 |
| Time (Hours) | <0.0001 |
| Carao concentration × time | 0.4756 |
| Bile tolerance | |
| Carao concentration | 0.0057 |
| Time (Hours) | <0.0001 |
| Carao concentration × time | 0.0045 |
| Acid Tolerance | |
| Carao concentration | 0.095 |
| Time (Minutes) | <0.0001 |
| Carao concentration × time | 0.5867 |
| Resistance to gastric juices | |
| Carao concentration | 0.0786 |
| pH | <0.0001 |
| Carao concentration × pH | 0.7845 |
| Protease activity | |
| Carao concentration | 0.0155 |
| Time (Hours) | <0.0001 |
| Carao concentration × time | 0.4021 |
| Lysozyme resistance | |
| Carao concentration | 0.0085 |
| Time (Minutes) | <0.0001 |
| Carao concentration × time | 0.3945 |
| Test | L. acidophilus LA-K |
|---|---|
| Bacterial Viabiliy | |
| Carao 0% (Control) | NS |
| Carao 1% | NS |
| Carao 2% | NS |
| Carao 3% | NS |
| Bile tolerance | |
| Carao 0% (Control) | 10.20 A |
| Carao 1% | 10.17 A |
| Carao 2% | 10.24 B |
| Carao 3% | 10.33 C |
| Acid Tolerance | |
| Carao 0% (Control) | NS |
| Carao 1% | NS |
| Carao 2% | NS |
| Carao 3% | NS |
| Resistance to gastric juices | |
| Carao 0% (Control) | NS |
| Carao 1% | NS |
| Carao 2% | NS |
| Carao 3% | NS |
| Protease activity | |
| Carao 0% (Control) | 0.300 A |
| Carao 1% | 0.321 A |
| Carao 2% | 0.339 B |
| Carao 3% | 0.355 B |
| Lysozyme resistance | |
| Carao 0% (Control) | 6.06 A |
| Carao 1% | 6.15 A |
| Carao 2% | 6.36 B |
| Carao 3% | 6.68 B |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marcia, J.; Aleman, R.S.; Montero-Fernández, I.; Martín-Vertedor, D.; Manrique-Fernández, V.; Moncada, M.; Kayanush, A. Attributes of Lactobacillus acidophilus as Effected by Carao (Cassia grandis) Pulp Powder. Fermentation 2023, 9, 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050408
Marcia J, Aleman RS, Montero-Fernández I, Martín-Vertedor D, Manrique-Fernández V, Moncada M, Kayanush A. Attributes of Lactobacillus acidophilus as Effected by Carao (Cassia grandis) Pulp Powder. Fermentation. 2023; 9(5):408. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050408
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarcia, Jhunior, Ricardo Santos Aleman, Ismael Montero-Fernández, Daniel Martín-Vertedor, Víctor Manrique-Fernández, Marvin Moncada, and Aryana Kayanush. 2023. "Attributes of Lactobacillus acidophilus as Effected by Carao (Cassia grandis) Pulp Powder" Fermentation 9, no. 5: 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050408
APA StyleMarcia, J., Aleman, R. S., Montero-Fernández, I., Martín-Vertedor, D., Manrique-Fernández, V., Moncada, M., & Kayanush, A. (2023). Attributes of Lactobacillus acidophilus as Effected by Carao (Cassia grandis) Pulp Powder. Fermentation, 9(5), 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050408







