Got Whey? Sustainability Endpoints for the Dairy Industry through Resource Biorecovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
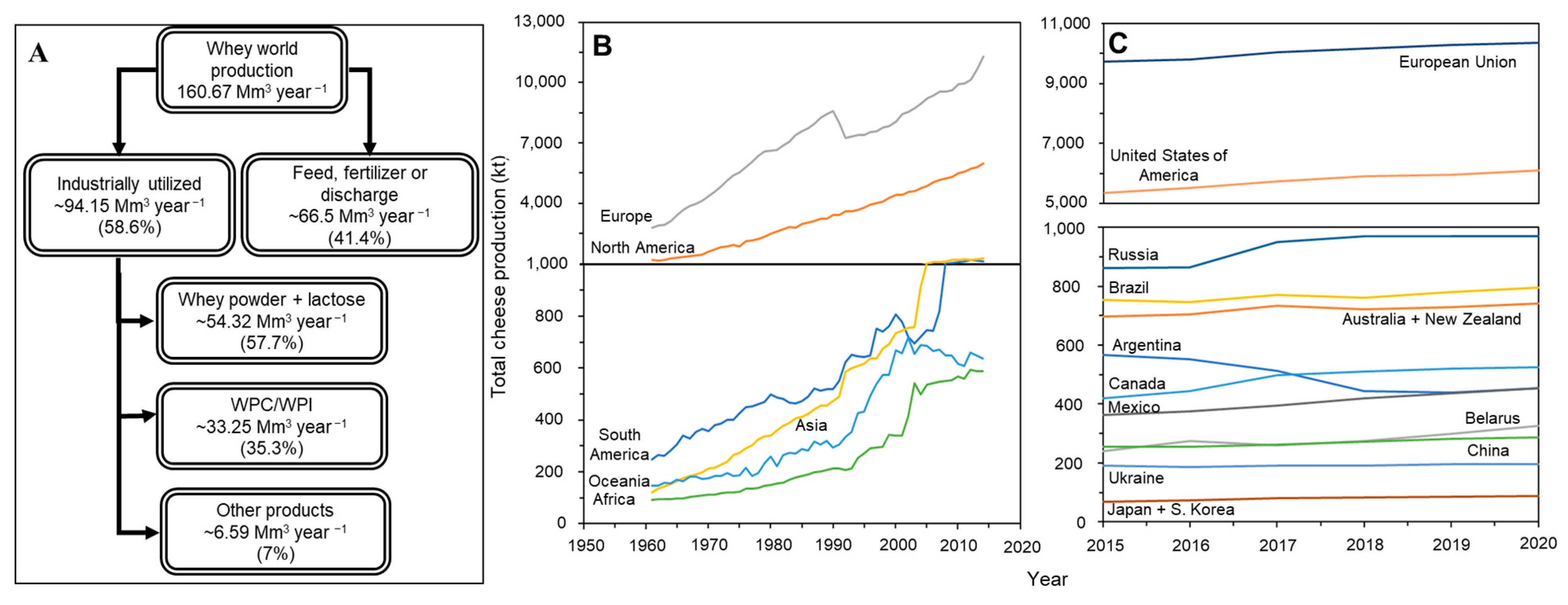
2. The Historical Significance and Contemporary Challenges of Dairying and Whey
2.1. From Dairy Discovery to the Role of Cheese and Whey
2.2. The Utilization and Environmental Impact of Whey
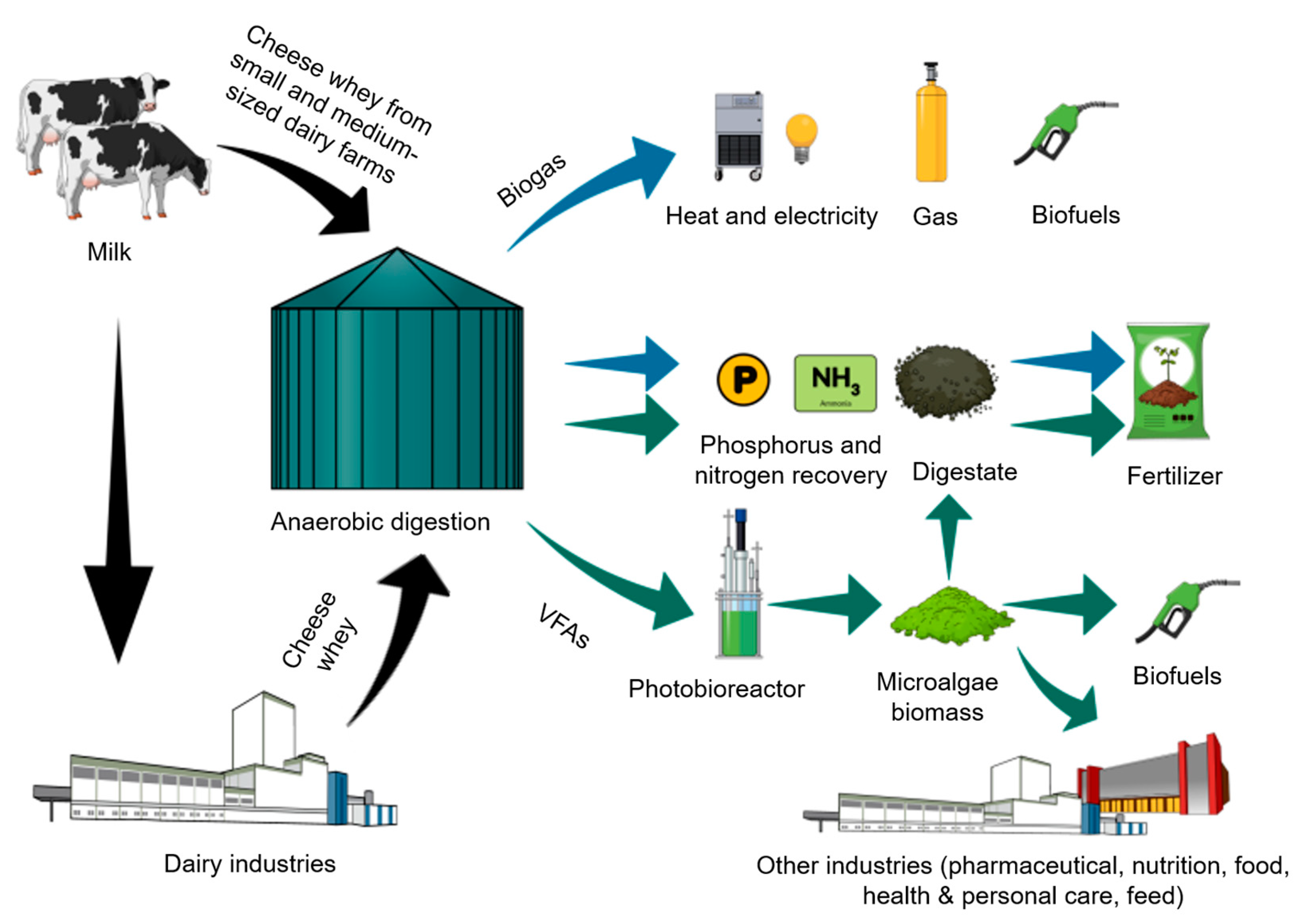
3. Environmental Impacts and Management of Cheese Whey Residues
3.1. Environmental Burden and Elevated Costs of Treatment of Whey Residues
3.2. Paving the Way for an Ecologically Balanced, Circular, and Participative Dairying Economy
| Country | Legislation | General Provisions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| AR | National constitution ART 121 civil code | Establishes that the provinces hold power that is not assigned to the Federal Government. | [89] |
| National constitution ART 124 civil code, 1994 | States that each province is the owner of the existing natural resources in their territory. | [90] | |
| Regime of Environmental Management of Waters (Law 25.6888), 2002 | Establishes the requirements for the preservation and use of water resources. | [91] | |
| AU | Environmental Protection Act, 1993 | Regulatory framework for land, air, and water protection. | [92] |
| The National Waste Policy, 2009 | National framework for waste and resource recovery in Australia. | [93] | |
| BY | Water Code of the Republic of Belarus, 2014 | Governs the public relations regarding the ownership, use, and order of waters and water objects in Belarus. | [94] |
| BR | Water code, 1934 | Allows the free use of any water for basic life necessities while complying with administrative regulations. | [95] |
| National Policy of Hydric Resources (Federal Law 9433), 1997 | Defines the objectives, principles, and instruments of the National Water Resources Policy and the National Water Resources Management System. | [96] | |
| National Solid Waste Policy, PNRS, 2010 | Sets the guideline to integrated management and solid waste management, generator’s responsibilities, and economic instruments. | [97] | |
| CA | Canada Water Act, 1985 | Framework for the conservation, development, and use of Canada’s water resources. | [98] |
| Wastewater Systems Effluent Regulations 2015 | Establishes a national baseline effluent quality standard in Canada. | [99] | |
| CN | The Water Law of the People’s Republic of China, 1988 | Allows for the development, use, and protection of water resources, as well as the prevention and control of water hazards. | [100] |
| EU | Waste Framework Directive (2006/12/EC) | Framework regarding waste management, waste disposal, and waste recovery. | [101] |
| Urban Wastewater Directive (91/271/EEC) | Framework regarding the collection, treatment, and discharge of urban waste water and the treatment and discharge of industrial waste water. | [102] | |
| JP | The Water pollution control law, 1970 | Framework for water pollution prevention (i.e., public waters and groundwater) by regulating effluent discharged by factories, businesses, and households. | [103] |
| KR | Water Quality and Ecosystem Conservation Act, 2009 | Establishes the regulation of the total water quality pollutants in an area. | [104] |
| MX | National Water Law | Regulates the use and exploitation of waters and their distribution, control, and preservation. | [105] |
| NZ | National Policy Statement for Freshwater Management under the Resource Management Act 1991 | Framework on the management of freshwater under the Resource Management Act 1991. | [106] |
| RU | Water Code of the Russian Federation, 2006 | Framework for water resources in the Russian Federation addressing the issues in the energy-water nexus. | [107] |
| UA | The Water Code of Ukraine, 1995 | Framework for the use of waters, pollution, contamination, and exhaustion prevention. | [108] |
| US | Clean Water Act, 1972 | Establishes the structure for regulating the discharges of pollutants in water bodies and the quality standards for surface waters. | [109] |
4. Clearing the Whey: Product, Resource, and Energy Recovery
4.1. Advancements in Whey Processing Technologies and Valued-Added Products
4.2. Anaerobic Digestion and Acidogenic Fermentation of Cheese Whey
4.3. Co-Digestion of Whey
4.4. Light-Based Valorization of Cheese Whey Using Photobioprocesses: Harnessing Eutrophication in Bioprocess Boundaries
4.5. Synergetic Interactions between Microalgal and Bacterial Processes to Valorize Whey
| Uses | Products | References |
|---|---|---|
| Fine chemicals | Fatty acids, carotenoids, antioxidants, vitamins, and other bioactive compounds | [193] |
| Industrial | Pharmaceutical, aquaculture, animal feed, biofertilizer | [194,195,196,197] |
| Drug screening | Antimicrobial agents, antiviral drugs, anticancer drugs | [194] |
| Environmental | Pollutants removal, wastewater co-digestion, CO2 mitigation | [198,199] |
| Commercial | Nutraceuticals, nutrition, cosmetics, pigments, recombinant proteins, stable isotopes, biochemicals | [200,201,202,203,204] |
| Biofuels | Biodiesel, bioethanol, biobutanol, bio syngas, biogas electricity, heat | [205,206,207] |
4.6. Phosphorus and Nitrogen Removal and Recovery from Cheese Whey
5. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gross, M. On the Origins of Cheese. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 1171–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD-FAO. Dairy and dairy products. In OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2020–2029; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2020; ISBN 9789264317673. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, N.; Jeon, J.; Elbert, J.; Kim, C.; Su, X. Redox-Mediated Electrochemical Desalination for Waste Valorization in Dairy Production. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božanić, R.; Barukčić, I.; Kl, J.; Tratnik, L. Possibilities of Whey Utilisation. Austin J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 2, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Smithers, G.W. Whey and Whey Proteins-From “Gutter-to-Gold”. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early, R. Technology of Dairy Products, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-0-7514-0344-2. [Google Scholar]
- Tsakali, E.; Petrotos, K.; D’Allessandro, A.; Goulas, P. A Review on whey composition and the methods used for its utilization for food and pharmaceutical products. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Simulation and Modelling in the Food and Bio-Industry, Braganca, Portugal, 24–26 June 2010; pp. 195–201. Available online: https://tarjomefa.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/7321-English-TarjomeFa.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2020).
- Hammam, A.; Tammam, A.; Elderwy, Y.; Hassan, A. Functional Peptides in Milk Whey: An Overview. Assiut J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 48, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, R.H. Whey Products; New Zealand Dairy Research Institute: Palmerston North, New Zealand, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Munien, I.; Telukdarie, A. COVID-19 Supply Chain Resilience Modelling for the Dairy Industry. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 180, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weersink, A.; von Massow, M.; McDougall, B.; Bannon, N. Re-Examining the Implications of COVID-19 on the Canadian Dairy and Poultry Sectors. Can. J. Agric. Econ. 2021, 69, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasian, M.; Sazvar, Z.; Mohammadisiahroudi, M. A Hybrid Optimization Method to Design a Sustainable Resilient Supply Chain in a Perishable Food Industry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 6080–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffstutter, P.J. U.S. Dairy Farmers Dump Milk as Pandemic Upends Food Markets. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-health-coronavirus-dairy-insight-idUSKBN21L1DW (accessed on 17 May 2021).
- Holden, L.A.; Goodling, R.C. Managing Milk Market Disruptions at the Dairy Farm Level in the USA. In Challenges in the Milk Market (Investments, Disruptions, Logistics, Competitiveness, Prices, and Policy); Bórawski, P., Parzonko, A., Żuchowski, I., Eds.; Wydawnictwo Ostrołęckiego Towarzystwa Naukowego im. Adama Chętnika: Ostrołęka, Poland, 2021; pp. 61–67. ISBN 9788362775453. [Google Scholar]
- Agustin, Y.; Kurniawan, M.; Astuti, R.; Rahman, M.A. Environmental Impact Evaluation of a Fresh Milk Production. Ind. J. Teknol. Dan Manaj. Agroindustri 2021, 10, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubík, H.; Lošťák, M.; Ketuama, C.T.; Procházka, P.; Soukupová, J.; Hakl, J.; Karlík, P.; Hejcman, M. Current Coronavirus Crisis and Past Pandemics—What Can Happen in Post-COVID-19 Agriculture? Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 30, 752–760. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, A.Y.; Bhojiya, A.A. Global Impact of Covid-19. J. Indian Res. 2021, 9, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Panghal, A.; Patidar, R.; Jaglan, S.; Chhikara, N.; Khatkar, S.K.; Gat, Y.; Sindhu, N. Whey Valorization: Current Options and Future Scenario—A Critical Review. Nutr. Food Sci. 2018, 48, 520–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvarova, I.; Atstaja, D.; Grinbergs, U.; Petersons, J.; Gegere-Zetterstroma, A.; Kraze, S. Transition to the Circular Economy and New Circular Business Models—An in-Depth Study of the Whey Recycling. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 578, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carus, M.; Dammer, L. The Circular Bioeconomy—Concepts, Opportunities, and Limitations. Ind. Biotechnol. 2018, 14, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.V.; Chiranjeevi, P.; Chandrasekhar, K.; Babu, P.S.; Sarkar, O. Acidogenic biohydrogen production from wastewater. In Biohydrogen; Pandey, A., Mohan, S.V., Chang, J.-S., Hallenbeck, P.C., Larroche, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 279–320. ISBN 9780444642035. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, B.; Pandey, A.; Kumar, L.R.; Tyagi, R.D. Bioconversion of Waste (Water)/Residues to Bioplastics—A Circular Bioeconomy Approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asunis, F.; De Gioannis, G.; Francini, G.; Lombardi, L.; Muntoni, A.; Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Rossi, A.; Spiga, D. Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of Polyhydroxyalkanoates Production from Cheese Whey. Waste Manag. 2021, 132, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetting, C. European commission circular economy action plan. In The European Green Deal; ESDN Office: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, J. Effective Governance of Circular Economies: An International Comparison. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 343, 130874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Lam, C.-Y. An Overview of Circular Economy in China: How the Current Challenges Shape the Plans for the Future. Chin. Econ. 2021, 54, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrador, M.; de Jong, W.; Nasu, K.; Granrath, L. Circular Economy and Zero-Carbon Strategies between Japan and South Korea: A Comparative Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Dairy: World Markets and Trade; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. FAOSTAT—Livestock Processed. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/?#data/QP (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- ISO 14044:2006; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Frameworks. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/37456.html (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Soares, B.B.; Alves, E.C.; de Almeida Neto, J.A.; Rodrigues, L.B. Environmental impact of cheese production. In Environmental Impact of Agro-Food Industry and Food Consumption; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 169–187. [Google Scholar]
- Mediboyina, M.K.; Holden, N.H.; O’Neill, S.; Routledge, K.; Morrissey, B.; Lawless, F.; Murphy, F. Upscale Fermenter Design for Lactic Acid Production from Cheese Permeate Focusing on Impeller Selection and Energy. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 2263–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalermthai, B.; Giwa, A.; Schmidt, J.E.; Taher, H.A.B. Life Cycle Assessment of Bioplastic Production from Whey Protein Obtained from Dairy Residues. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 15, 100695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacenetti, J.; Bava, L.; Schievano, A.; Zucali, M. Whey Protein Concentrate (WPC) Production: Environmental Impact Assessment. J. Food Eng. 2018, 224, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumati, B.; Atmani, M.; Benabderrahmane, A.; Benjelloun, M. Whey Valorization—Innovative Strategies for Sustainable Development and Value-Added Product Creation. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.L.; Langellotti, A.L.; Oliviero, M.; Baselice, M.; Sacchi, R.; Masi, P. Valorization of Second Cheese Whey through Cultivation of Extremophile Microalga Galdieria Sulphuraria. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2021, 8, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.L.; Langellotti, A.L.; Verardo, V.; Martín-García, B.; Oliviero, M.; Baselice, M.; Di Pierro, P.; Sorrentino, A.; Viscardi, S.; Marileo, L.; et al. Bioconversion of Cheese Whey and Food By-Products by Phaeodactylum Tricornutum into Fucoxanthin and n-3 Lc-PUFA through a Biorefinery Approach. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrapala, J. Whey Wastes and Powders. In Microstructure of Dairy Products; El-Barky, M.M.A.-R., Sanchez, A., Mehta, B.M., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 261–292. ISBN 9781118964224. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, A.F.; Marnotes, N.G.; Rubio, O.D.; Garcia, A.C.; Pereira, C.D. Dairy By-Products: A Review on the Valorization of Whey and Second Cheese Whey. Foods 2021, 10, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiouris, V.; Kontominas, M.G.; Filioussis, G.; Chalvatzi, S.; Giannenas, I.; Papadopoulos, G.; Koutoulis, K.; Fortomaris, P.; Georgopoulou, I. The Effect of Whey on Performance, Gut Health and Bone Morphology Parameters in Broiler Chicks. Foods 2020, 9, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketterings, Q.; Czymmek, K.; Gami, S.; Godwin, G.; Ganoe, K. Guidelines for Land Application of Acid Whey; Department of Animal Science, College of Agriculture & Life Sciences, Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- USDA. Dairy: World Markets and Trade; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Leonardi, M.; Gerbault, P.; Thomas, M.G.; Burger, J. The Evolution of Lactase Persistence in Europe. A Synthesis of Archaeological and Genetic Evidence. Int. Dairy. J. 2012, 22, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlekuž, D. Archaeological Culture, Please Meet Yoghurt Culture: Towards a Relational Archaeology of Milk. Doc. Praehist. 2015, 42, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dunne, J.; Evershed, R.P.; Salque, M.; Cramp, L.; Bruni, S.; Ryan, K.; Biagetti, S.; Di Lernia, S. First Dairying in Green Saharan Africa in the Fifth Millennium BC. Nature 2012, 486, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovski, D.; Živaljević, I.; Dimitrijević, V.; Dunne, J.; Evershed, R.P.; Balasse, M.; Dowle, A.; Hendy, J.; McGrath, K.; Fischer, R.; et al. Living off the Land: Terrestrial-Based Diet and Dairying in the Farming Communities of the Neolithic Balkans. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayless, T.M.; Brown, E.; Paige, D.M. Lactase Non-Persistence and Lactose Intolerance. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2017, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evershed, R.P.; Payne, S.; Sherratt, A.G.; Copley, M.S.; Coolidge, J.; Urem-Kotsu, D.; Kotsakis, K.; Özdoǧan, M.; Özdoǧan, A.E.; Nieuwenhuyse, O.; et al. Earliest Date for Milk Use in the Near East and Southeastern Europe Linked to Cattle Herding. Nature 2008, 455, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaway, E. Pottery Shards Put a Date on Africa’s Dairying. Nature 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunick, M.H. Whey Protein Production and Utilization: A Brief History. In Whey Processing, Functionality and Health Benefits; Onwulata, C.I., Huth, P.J., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; p. 400. ISBN 9780813809038. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, O.L.; Pereira, R.N.; Rodrigues, R.M.; Teixeira, J.A.; Vicente, A.A.; Malcata, F.X. Whey and Whey Powders: Production and Uses. Encycl. Food Health 2016, 5, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pien, J. Utilisation Des Sérum de Fromagerie et Des Lacto- Protéines Dans l’alimentation. Lait 1943, 227, 228. [Google Scholar]
- Ayto, J. The Diner’s Dictionary: Word Origins of Food and Drink, 2nd ed.; University of Michigan, Ed.; Oxford University Press by arrangement with Routledge: Oxford, UK, 1993; ISBN 0198661932/9780198661931. [Google Scholar]
- Grek, O.; Ovsiienko, K.; Tymchuk, A.; Onopriichuk, O.; Kumar, A. Influence of Wheat Food Fiber on the Structure Formation Process of Whey-Creamy Cheeses. Ukr. Food J. 2020, 9, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecchio, D.; Yuan, Y.; Malpei, F. Hydrogen Production Dynamic during Cheese Whey Dark Fermentation: New Insights from Modelization. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 17588–17601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithers, G.W. Whey-Ing up the Options—Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 48, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappa, I.; Papadaki, A.; Kachrimanidou, V.; Terpou, A.; Koulougliotis, D.; Eriotou, E.; Kopsahelis, N. Cheese Whey Processing: Integrated Biorefinery Concepts and Emerging Food Applications. Foods 2019, 8, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prazeres, A.R.; Carvalho, F.; Rivas, J. Cheese Whey Management: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 110, 48–68. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero, P.; Rodríguez-Morgado, B.; Sandra, M.; Manuel, T.; Juan, P. Obtaining Plant and Soil Biostimulants by Waste Whey Fermentation. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 3281–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, S.; Marescotti, F.; Sanmartin, C.; Macaluso, M.; Taglieri, I.; Venturi, F.; Zinnai, A.; Facioni, M.S. Lactose: Characteristics, Food and Drug-Related Applications, and Its Possible Substitutions in Meeting the Needs of People with Lactose Intolerance. Foods 2022, 11, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalermthai, B.; Ashraf, M.T.; Bastidas-Oyanedel, J.-R.; Olsen, B.D.; Schmidt, J.E.; Taher, H. Techno-Economic Assessment of Whey Protein-Based Plastic Production from a Co-Polymerization Process. Polymers 2020, 12, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloin, J.C. Milk and Dairy Products: Production and Processing Costs; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1988; ISBN 9251025037. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, P.; Risner, D.; Meunier-Goddik, L. Whey to Vodka. In Whey—Biological Properties and Alternative Uses; IntechOpen, Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lammifyad, C. Review on Impacts of COVID-19 Pandemic on Life Animals and Dairy Product Processing Industries of the World. Insights Vet. Sci. 2020, 4, 018–024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papademas, P.; Kotsaki, P. Technological Utilization of Whey towards Sustainable Exploitation. Adv. Dairy Res. 2019, 7, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.P.; Moreira, R.D.O.; Júnior, P.H.R.; Martins, M.C.D.F.; Ítalo Tuler Perrone, A.F.D.C. Whey: Technologies for Co-Products Production. Rev. Inst. Laticínios Cândido Tostes 2014, 69, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guo, M.; Wang, G. History of Whey Production and Whey Protein Manufacturing. In Whey Protein Production, Chemistry, Functionality, and Applications; Guo, M., Ed.; Wiley & Sons Ltd: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–12. ISBN 9781119256038. [Google Scholar]
- Lustrato, G.; Salimei, E.; Alfano, G.; Belli, C.; Fantuz, F.; Grazia, L.; Ranalli, G. Cheese Whey Recycling in Traditional Dairy Food Chain: Effects of Vinegar from Whey in Dairy Cow Nutrition. Acetic Acid Bact. 2013, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Kitsos, A.; Cannella, M.; Wang, S.; Han, L. Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Dairy Industry: Lessons from China and the United States and Policy Implications. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 2903–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, M.B.; Soares, B.C.V.; Scudino, H.; Guimarães, J.T.; Esmerino, E.A.; Freitas, M.Q.; Pimentel, T.C.; Silva, M.C.; Souza, S.L.Q.; Almada, R.B.; et al. Cheese Whey Exploitation in Brazil: A Questionnaire Survey. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 39, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellen MacArthur Foundation. Delivering the Circular Economy—A Toolkit for Policymakers; Ellen MacArthur Foundation: Isle of Wight, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Asunis, F.; De Gioannis, G.; Dessì, P.; Isipato, M.; Lens, P.N.L.; Muntoni, A.; Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Rossi, A.; Spiga, D. The Dairy Biorefinery: Integrating Treatment Processes for Cheese Whey Valorisation. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.S.S.; Yan, S.; Pilli, S.; Kumar, L.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Cheese Whey: A Potential Resource to Transform into Bioprotein, Functional/Nutritional Proteins and Bioactive Peptides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 756–774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gunningham, N. Environment Law, Regulation and Governance: Shifting Architectures. J. Environ. Law 2009, 21, 179–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Circular Economy Package (COM (2015) 614 Final; European Commision: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bruch, C.; Schang, S.; Pendergrass, J.; Fulton, S.; Moraga-Lewy, N.; Wright, M.; Swanson, G. Environmental Rule of Law—First Global Report; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Spence, D.B. The Shadow of the Rational Polluter: Rethinking the Role of Rational Actor Models in Environmental Law Recommended Citation. Calif. Law Rev. 2001, 89, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VALORLACT. Comprehensive Use of the Whey Generated by the Dairy Industry in the Basque Country VALORLACT—After Life Communication Plan; VALORLACT: Vitoria-Gasteiz, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- AgriChemWhey. AgriChemWhey. Available online: https://www.agrichemwhey.com/ (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Arla Food Ingredients Discovering the Wonders of Whey. Available online: https://www.arlafoodsingredients.com/ (accessed on 23 March 2022).
- Carbery Product Range. Available online: https://www.carbery.com/nutrition/product-range/ (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Clover Fonterra NZMP (Ingredients by Fonterra). Available online: https://www.cloverfonterra.com/ingredients_category/nzmp/ (accessed on 23 March 2022).
- FrieslandCampina Ingredients Nutrition Segments. Available online: https://www.frieslandcampinaingredients.com/ (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Glambia Specialised Nutrition. Available online: https://www.glanbiairelandingredients.com/applications/specialised-nutrition (accessed on 17 March 2022).
- Lactalis Global Lactalis Ingredients. Available online: https://www.lactalisingredients.com/ (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Milk Specialties Global Products. Available online: https://www.milkspecialties.com/ (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Saputo Functional Ingredients. Available online: https://uk.saputo.com/brands/functional-ingredients/demineralised-whey/ (accessed on 23 March 2022).
- Kemp-Benedict, E. 3 Key Steps to a More Sustainable Economy. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2015/09/3-key-steps-to-a-more-sustainable-economy/ (accessed on 3 April 2020).
- The Law Library of Congress; Rodriguez-Ferrand, G. National Constitution ART 121 Civil Code. Available online: https://www.loc.gov/law/help/water-law/argentina.php#Legal (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Republic of Argentine National Constitution of the Argentine Republic. Available online: http://www.biblioteca.jus.gov.ar/Argentina-Constitution.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Pochat, V.; Natenzon, C.E.; Murgida, A.M. Argentina Country Case Study on Domestic Policy Frameworks for Adaptation in the Water Sector. In Proceedings of the Annex I Expert Group Seminar in Conjunction with the OECD Global Forum on Sustainable Development; OECD: Paris, France, 2006. Available online: http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/29/2/36448827.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Government of South Australia South Australia Legislation. Available online: https://www.legislation.sa.gov.au/index.aspx (accessed on 24 April 2020).
- Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts. National Waste Policy: Less Waste, More Resources; Australian Government: Canberra, Australia, 2009. Available online: https://www.nepc.gov.au/projects/national-waste-policy-less-waste-more-resources (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Cis Legislation Water Code of the Republic of Belarus of April 30, 2014 No. 149-Z. Available online: https://cis-legislation.com/document.fwx?rgn=68800 (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Brazil.Water Code 1934 (Decree 24,643); Brasilia, Brazil. 1934. Available online: http://www.planalto.gov.br/ (accessed on 22 August 2020).
- National Congress of Brazil. National Policy of Hydric Resources (Federal Law 9433). Available online: https://www.braziliannr.com/brazilian-environmental-legislation/law-no-9433-brazilian-national-water-resources-policy/ (accessed on 24 September 2023).
- National Congress of Brazil. National Solid Waste Policy—PNRS (Federal Law 12305); Minitry of Environment: Brasilia, Brazil, 2010; p. 20. Available online: http://www.planalto.gov.br/ (accessed on 22 August 2020).
- Canada Water Act; Minister of Justice. 1985. Available online: https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/c-11/index.html (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- Canada The Wastewater Systems Effluent Regulations (the Regulations), Established Under the Fisheries Act 1985; Canada. 2015. Available online: https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/sor-2012-139/fulltext.html (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- Zhifang, X. China’s Water Law and Environment. Can. Water Resour. J. 1991, 16, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Journal of the European Union. Waste Framework Directive (2006/12/EC); European Commision: Brussels, Belgium, 2006; Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Official Journal of the European Union. Urban Wastewater Directive (91/271/ EEC); European Commision: Brussels, Belgium, 1991; Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Japan Ministry of The Environment Water Pollution Control Law Law No. 138 of 197. Available online: http://www.env.go.jp/en/laws/water/wlaw/index.html (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- Republic of Korea—Ministry of Environment. Water Quality and Ecosystem Conservation Act; Korea Legislation Research Institute: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mexican Official Standard NOM-001-ECOL-1996; Secretary of Environment Natural Resources and Fisheries: Mexico City, Mexico. Available online: https://dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=4863829&fecha=06/01/1997#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 22 August 2020).
- New Zealand Ministry for the Environment. The National Policy Statement for Freshwater Management (Freshwater NPS) Provides Direction on How Local Authorities Should Carry Out Their Responsibilities Under the Resource Management Act 1991 for Managing Fresh Water. Available online: http://www.mfe.govt.nz/fresh-water/regulations/national-policy-statement-freshwater-management (accessed on 24 April 2018).
- Cis Legislation. Water Code of the Russian Federation of June 3, 2006 No. 74-FZ. Available online: https://cis-legislation.com/document.fwx?rgn=13410 (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Legal Services Online. The Water Code of Ukraine. Available online: http://yurist-online.com/en/kodeks/009.php (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- United States of America. Clean Water Act. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/laws-regulations/summary-clean-water-act (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Onwulata, C.; Huth, P.J. Whey Processing, Functionality and Health Benefits; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. ISBN 978081380 9038.
- Tsitouras, A.; Basu, O.; Al-ghussain, N.; Delatolla, R. Kinetic Effects of Anaerobic Staging and Aeration Rates on Sequencing Batch Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors: Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Treatment of Cheese Production Wastewater. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marazzi, F.; Bellucci, M.; Fantasia, T.; Ficara, E.; Mezzanotte, V. Interactions between Microalgae and Bacteria in the Treatment of Wastewater from Milk Whey Processing. Water 2020, 12, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz-Ul-Islam, M.; Hong, L.; Langrish, T. CO2 Capture Using Whey Protein Isolate. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.S. Biotechnological approaches for valorization of whey. In Advances in Industrial Biotechnology; Singh, R.S., Pandey, A., Larroche, C., Eds.; IK International Publishing House Pvt. Ltd.: Bangalore, India, 2016; pp. 443–478. [Google Scholar]
- Dinika, I.; Utama, G.L. Cheese Whey as Potential Resource for Antimicrobial Edible Film and Active Packaging Production. Foods Raw Mater. 2019, 7, 229–239. [Google Scholar]
- Onwulata, C.I.; Konstance, R.P.; Tomasula, P.M. Minimizing Variations in Functionality of Whey Protein Concentrates from Different Sources. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, A.; Casanova, F.; Šimonis, P.; Stankevič, V.; Gomaa, M.A.E.; Stirkė, A. Pulsed Electric Field: Fundamentals and Effects on the Structural and Techno-Functional Properties of Dairy and Plant Proteins. Foods 2022, 11, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastani, S.; Bahmanyar, F.; Shojaee-Aliabadi, S.; Mirmoghtadaie, L.; Hosseini, S.M. Effect of Dual Physical Modifications on Structural and Functional Properties of Gluten and Whey Protein: Ultrasound and Microwave. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carullo, D.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V.; Ferrari, G. Changes of Structural and Techno-Functional Properties of High Hydrostatic Pressure (HHP) Treated Whey Protein Isolate over Refrigerated Storage. LWT 2021, 137, 110436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argenta, A.B.; Scheer, A.D.P. Membrane Separation Processes Applied to Whey: A Review. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 36, 499–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.; Kwak, H.-S. Bioactive components in whey products. In Bioactive Components in Milk and Dairy Products; Park, Y.W., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 263–285. ISBN 9780813819822. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Shen, X. Modifications of Whey Protein. In Whey Protein Production, Chemistry, Functionality, and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 205–225. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Mu, G.; Jiang, S.; Zhu, X.; Tuo, Y.; Qian, F. Evaluation of the Properties of Whey Protein Films with Modifications. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, O. A New Low Calorie Tagatose Sweetner D-Tagatose from Lactose in Cheese Whey as a Nutraceutical Value-Added Product. J. Food Health Technol. Innov. 2018, 1, 11–28. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, B.; Singha, P.; Rizvi, S.S.H. Supercritical Fluid Extrusion: Die Design and Physicochemical Properties of Milk Protein Extrudates. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 68, 102637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xie, J.; Liu, P.; Li, X.; Ouyang, J. Elegant and Efficient Biotransformation for Dual Production of d -Tagatose and Bioethanol from Cheese Whey Powder. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameiro, T.; Novais, R.M.; Correia, C.L.; Carvalheiras, J.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A.; Duarte, A.C.; Capela, I. Red Mud-Based Inorganic Polymer Spheres: Innovative and Environmentally Friendly Anaerobic Digestion Enhancers. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalambous, P.; Shin, J.; Shin, S.G.; Vyrides, I. Anaerobic Digestion of Industrial Dairy Wastewater and Cheese Whey: Performance of Internal Circulation Bioreactor and Laboratory Batch Test at PH 5-6. Renew Energy 2020, 147, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaspina, F.; Cellamare, C.M.; Stante, L.; Tilche, A. Anaerobic Treatment of Cheese Whey with a Downflow-Upflow Hybrid Reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 1996, 55, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, H.; Castro, L.; Amaya, M.P.; Jaimes, L.; Jaimes-Estévez, J. Anaerobic Digestion of Cheese Whey: Energetic and Nutritional Potential for the Dairy Sector in Developing Countries. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bella, K.; Venkateswara Rao, P. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cheese Whey and Septage: Effect of Substrate and Inoculum on Biogas Production. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 308, 114581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.; Lamb, J.J.; Hjelme, D.R.; Lien, K.M. A Review of the Role of Critical Parameters in the Design and Operation of Biogas Production Plants. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iona Capital Leeming Biogas. Available online: https://ionacapital.co.uk/investments/leeming-biogas/ (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- Kleerebezem, R.; Joosse, B.; Rozendal, R.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Anaerobic Digestion without Biogas? Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagoa-Costa, B.; Kennes, C.; Veiga, M.C. Cheese Whey Fermentation into Volatile Fatty Acids in an Anaerobic Sequencing Batch Reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 308, 123226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agler, M.T.; Wrenn, B.A.; Zinder, S.H.; Angenent, L.T. Waste to Bioproduct Conversion with Undefined Mixed Cultures: The Carboxylate Platform. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadavid-Rodríguez, L.S.; Horan, N.J. Production of Volatile Fatty Acids from Wastewater Screenings Using a Leach-Bed Reactor. Water Res. 2014, 60, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombouts, J.L.; Mos, G.; Weissbrodt, D.G.; Kleerebezem, R.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Diversity and Metabolism of Xylose and Glucose Fermenting Microbial Communities in Sequencing Batch or Continuous Culturing. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiy233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gioannis, G.; Friargiu, M.; Massi, E.; Muntoni, A.; Polettini, A. Biohydrogen Production from Dark Fermentation of Cheese Whey: Influence of PH. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 20930–20941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotto, F.; Lavagnolo, M.C.; Pivato, A.; Cossu, R. Acidogenic Fermentation of the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste and Cheese Whey for Bio-Plastic Precursors Recovery—Effects of Process Conditions during Batch Tests. Waste Manag. 2017, 70, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, M.; Mourti, C.; Tatoulis, T.; Akratos, C.S.; Tekerlekopoulou, G.; Vayenas, D. V Effect of Hydraulic Retention Time, Temperature, and Organic Load on a Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetland Treating Cheese Whey Wastewater. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 91, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venetsaneas, N.; Antonopoulou, G.; Stamatelatou, K.; Kornaros, M.; Lyberatos, G. Using Cheese Whey for Hydrogen and Methane Generation in a Two-Stage Continuous Process with Alternative PH Controlling Approaches. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3713–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, D. Improved Ethanol Production by Mixed Immobilized Cells of Kluyveromyces Marxianus and Saccharomyces Cerevisiae from Cheese Whey Powder Solution Fermentation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roukas, T.; Kotzekidou, P. Lactic Acid Production from Deproteinized Whey by Mixed Cultures of Free and Co-Immobilized Latobacillus Casei and Latococcus Lactis Cells Using Fedbatch Culture. Enzym. Microb. Technol 1998, 22, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angenent, L.T.; Richter, H.; Buckel, W.; Spirito, C.M.; Steinbusch, K.J.; Strik, D.P.B.T.B.; Grootscholten, T.I.M.; Buisman, C.J.N.; Hamelers, H.V.M. Chain Elongation with Reactor Microbiomes: Open- Culture Biotechnology to Produce Biochemicals—Extensive Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2796–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero, R.; Lagoa-Costa, B.C.; Kennes, C.; Fernandez-Feal, M.C.; Veiga, M.C. Volatile Fatty Acids Production from Cheese Whey: Influence of PH, Solid Retention Time and Organic Load Rate. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 1742–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pais-Chanfrau, J.M.; Núñez-Pérez, J.; Espin-Valladares, R.D.C.; Lara-Fiallos, M.V.; Trujillo-Toledo, L.E. Bioconversion of lactose from cheese whey to organic acids. In Lactose and Lactose Derivatives; Gutiérrez-Méndez, N., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; p. 22. ISBN 978-1-83962-605-0. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, B.; Sciarria, T.P.; Reis, M.; Scaglia, B.; Adani, F. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) Production from Fermented Cheese Whey by Using a Mixed Microbial Culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, D.; Pernicová, I.; Kovalcik, A.; Koller, M.; Mullerova, L.; Sedlacek, P.; Mravec, F.; Nebesarova, J.; Kalina, M.; Marova, I.; et al. Characterization of the Promising Poly (3-Hydroxybutyrate) Producing Halophilic Bacterium Halomonas Halophila. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulders, M.; Tamis, J.; Abbas, B.; Sousa, J.; Dijkman, H.; Rozendal, R.; Kleerebezem, R. Pilot-Scale Polyhydroxyalkanoate Production from Organic Waste: Process Characteristics at High PH and High Ammonium Concentration. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 146, 4020049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.P.; Walsh, G. The Biotechnological Potential of Whey. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila-vazquez, G.; De León-Rodríguez, A.; Alatriste-Mondragón, F.; Razo-Flores, E. The Buffer Composition Impacts the Hydrogen Production and the Microbial Community Composition in Non-Axenic Cultures. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 3174–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.D.; Kádár, Z.; Oleskowicz-Popiel, P.; Thomsen, M.H. Production of Bioethanol from Organic Whey Using Kluyveromyces Marxianus. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 38, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Hua, X.; Huang, L.; Xu, Y. Bio-Utilization of Cheese Manufacturing Wastes (Cheese Whey Powder) for Bioethanol and Specific Product (Galactonic Acid) Production via a Two-Step Bioprocess. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushwaha, D.; Srivastava, N.; Mishra, I.; Upadhyay, S.N.; Mishra, P.K. Recent Trends in Biobutanol Production. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2019, 35, 475–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganati, F.; Olivieri, G.; Procentese, A.; Russo, M.E.; Salatino, P.; Marzocchella, A. Butanol Production by Bioconversion of Cheese Whey in a Continuous Packed Bed Reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 138, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabaey, K.; Rozendal, R.A. Microbial Electrosynthesis—Revisiting the Electrical Route for Microbial Production. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagos, K.; Zong, J.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Lu, X. Anaerobic Co-Digestion Process for Biogas Production: Progress, Challenges and Perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 76, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, L.D.; Koch, K.; Bolzonella, D.; Drewes, J.E. Full Scale Co-Digestion of Wastewater Sludge and Food Waste: Bottlenecks and Possibilities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Molano, L.D.P.; Escalante-Hernández, H.; Lambis-Benítez, L.E.; Marín-Batista, J.D. Synergistic Effects in Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Chicken Manure with Industrial Wastes. DYNA 2018, 85, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maragkaki, A.E.; Vasileiadis, I.; Fountoulakis, M.; Kyriakou, A.; Lasaridi, K.; Manios, T. Improving Biogas Production from Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge with a Thermal Dried Mixture of Food Waste, Cheese Whey and Olive Mill Wastewater. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanchenko, A.; Yelatontsev, D.; Savenkov, A. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Agro-Industrial Waste with Cheese Whey: Impact of Centrifuge Comminution on Biogas Release and Digestate Agrochemical Properties. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 147, 106010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimes-Estévez, J.; Castro, L.; Escalante, H.; Carrillo, D.; Portillo, S.; Sotres, A.; Morán, A. Cheese Whey Co-Digestion Treatment in a Tubular System: Microbiological Behaviour along the Axial Axis. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2020, 12, 5719–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón-Pérez, J.; Celis, L.B.; Morales, M.; Alatriste-Mondragón, F.; Tapia-Rodríguez, A.; Razo-Flores, E. Improvement of Methane Production at Alkaline and Neutral PH from Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Microalgal Biomass and Cheese Whey. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 169, 107972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila-Vazquez, G.; Alatriste-Mondragón, F.; de León-Rodríguez, A.; Razo-Flores, E. Fermentative Hydrogen Production in Batch Experiments Using Lactose, Cheese Whey and Glucose: Influence of Initial Substrate Concentration and PH. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 4989–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Takahashi, P. Biophotolysis-Based Hydrogen Production by Cyanobacteria and Green Microalgae. In Communicating Current Research and Educational Topics and Trends in Applied Microbiology; Méndez-Vilas, A., Ed.; FORMATEX: Norriston, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Najafpour, G.D.; Shahavi, M.H.; Neshat, S.A. Assessment of Biological Hydrogen Production Processes: A Review. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 9–12 December 2015; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2016; Volume 36. [Google Scholar]
- Alfano, M.; Cavazza, C. The Biologically Mediated Water-Gas Shift Reaction: Structure, Function and Biosynthesis of Monofunctional [NiFe]-Carbon Monoxide Dehydrogenases. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2018, 2, 1653–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Srivastava, S.; Rai, P.; Duke, M. Cheese Whey to Biohydrogen and Useful Organic Acids: A Non-Pathogenic Microbial Treatment by L. Acidophilus. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeini, M.A.; Zandieh, M.; Najafi, S.E.; Sajadi, S.M. Analyzing the Development of the Third-Generation Biodiesel Production from Microalgae by a Novel Hybrid Decision-Making Method: The Case of Iran. Energy 2020, 195, 116895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Shah, S.Z.; Ahmad, H.; Abubshait, S.A.; Abubshait, H.A.; Laref, A.; Manikandan, A.; Kusuma, H.S.; Iqbal, M. Microalgae an Ecofriendly and Sustainable Wastewater Treatment Option: Biomass Application in Biofuel and Bio-Fertilizer Production. A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Farias Silva, C.E.; de Oliveira Cerqueira, R.B.; de Lima Neto, C.F.; de Andrade, F.P.; de Oliveira Carvalho, F.; Tonholo, J. Developing a Kinetic Model to Describe Wastewater Treatment by Microalgae Based on Simultaneous Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorous Removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gu, X.; Wang, Z.; Shatner, W.; Wang, Z. Progress, Challenges and Solutions of Research on Photosynthetic Carbon Sequestration Efficiency of Microalgae. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 110, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Guo, X.; Su, G.; Danquah, M.K.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lin, L. Bioprocess Considerations for Microalgal-Based Wastewater Treatment and Biomass Production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.; Acharya, A.; Gargey, I.A.; Aly, N.; Balasubramanian, P. Bioprocess Engineering Principles of Microalgal Cultivation for Sustainable Biofuel Production. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 5, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutanda, T.; Naidoo, D.; Bwapwa, J.K.; Anandraj, A. Biotechnological Applications of Microalgal Oleaginous Compounds: Current Trends on Microalgal Bioprocessing of Products. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 598803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.K.; Singhania, R.R.; Sim, S.J.; Dong, C. Di Recent Advancements in Mixotrophic Bioprocessing for Production of High Value Microalgal Products. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y. Revisiting Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Metabolisms in Microalgae for Wastewater Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 144590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, J.; Cho, Y.; Hwang, S. Growth Rate, Organic Carbon and Nutrient Removal Rates of Chlorella Sorokiniana in Autotrophic, Heterotrophic and Mixotrophic Conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, J.K.; Dean, A.P.; Osundeko, O. The Potential of Sustainable Algal Biofuel Production Using Wastewater Resources. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giulianetti de Almeida, M.P. Ecological Engineering of Acidogenic Fermentation and Microalgae Phototrophic Coupled Processes for Cheese Whey Valorization. Ph.D. thesis, University of Campinas-Unicamp, Campinas, Brazil, 7 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cheirsilp, B.; Torpee, S. Enhanced Growth and Lipid Production of Microalgae under Mixotrophic Culture Condition: Effect of Light Intensity, Glucose Concentration and Fed-Batch Cultivation. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Garcia, O.; Escalante, F.M.E.; De-Bashan, L.E.; Bashan, Y. Heterotrophic Cultures of Microalgae: Metabolism and Potential Products. Water Res. 2011, 45, 11–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, N.; Gu, X.; Kirchhoff, H.; Lei, H.; Roje, S. Exploiting Mixotrophic for Improving Productivities of Biomass and Co-Products of Microalgae. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 112, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Fernandez, C.; Sialve, B.; Molinuevo-Salces, B. Anaerobic Digestion of Microalgal Biomass: Challenges, Opportunities and Research Needs. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadas, E.; Bochon, S.; Coca, M.; García-González, M.; García-Encina, P.; Muñoz, R. Microalgae-Based Agro-Industrial Wastewater Treatment: A Preliminary Screening of Biodegradability. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnurr, P.J.; Espie, G.S.; Allen, D.G. Algae Biofilm Growth and the Potential to Stimulate Lipid Accumulation through Nutrient Starvation. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, G.-H.; Wu, G.-X.; Wang, X.-X.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Zhan, X.-M.; Hu, H.-Y. Enhanced Microalgae Growth through Stimulated Secretion of Indole Acetic Acid by Symbiotic Bacteria. Algal. Res. 2018, 33, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, R.; Kim, B.H.; Cho, D.H.; Oh, H.M.; Kim, H.S. Algae-Bacteria Interactions: Evolution, Ecology and Emerging Applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzuma, A.; Watanabe, K. Exploring the Potential of Algae/Bacteria Interactions. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jung, H.; Lee, C. Shifts in Bacterial and Archaeal Community Structures during the Batch Biomethanation of Ulva Biomass under Mesophilic Conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, W.; Cui, F.; Lens, P.N.L.; Tay, J.H. A Microalgal-Bacterial Consortia: From Interspecies Interactions to Biotechnological Applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 118, 109563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadim, S.R.; Mohanta, A.; Maurya, P.; Singh, P.; Asthana, R.K. Strategies for Increased Production of Lipids and Fine Chemicals from Commercially Important Microalgae. In Natural Bioactive Compounds; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 165–186. [Google Scholar]
- Khavari, F.; Saidijam, M.; Taheri, M.; Nouri, F. Microalgae: Therapeutic Potentials and Applications. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 4757–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.; Lu, Q.; Fan, L.; Zhou, W. A Review on the Use of Microalgae for Sustainable Aquaculture. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.F.; Ribeiro, D.M.; Costa, M.; Coelho, D.; Alfaia, C.M.; Lordelo, M.; Almeida, A.M.; Freire, J.P.B.; Prates, J.A.M. Using Microalgae as a Sustainable Feed Resource to Enhance Quality and Nutritional Value of Pork and Poultry Meat. Foods 2021, 10, 2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, E.E.; Aioub, A.A.A.; Elesawy, A.E.; Karkour, A.M.; Mouhamed, M.S.; Amer, A.A.; EL-Shershaby, N.A. Algae as Bio-Fertilizers: Between Current Situation and Future Prospective. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 3083–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molazadeh, M.; Ahmadzadeh, H.; Pourianfar, H.R.; Lyon, S.; Rampelotto, P.H. The Use of Microalgae for Coupling Wastewater Treatment with CO2 Biofixation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmayadi, A.; Huang, C.-Y.; Kit Leong, Y.; Lu, P.-H.; Yen, H.-W.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Integration of Microalgae Cultivation and Anaerobic Co-Digestion with Dairy Wastewater to Enhance Bioenergy and Biochemicals Production. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 376, 128858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grama, S.B.; Liu, Z.; Li, J. Emerging Trends in Genetic Engineering of Microalgae for Commercial Applications. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Ghosh, S.; Dubinsky, Z.; Verdelho, V.; Iluz, D. Unconventional High-Value Products from Microalgae: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 329, 124895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morocho-Jácome, A.L.; Ruscinc, N.; Martinez, R.M.; de Carvalho, J.C.M.; Santos de Almeida, T.; Rosado, C.; Costa, J.G.; Velasco, M.V.R.; Baby, A.R. (Bio)Technological Aspects of Microalgae Pigments for Cosmetics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 9513–9522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, H.; Yusoff, F.M.D.; Banerjee, S.; Khatoon, H.; Shariff, M. Availability and Utilization of Pigments from Microalgae. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2209–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.Y.; Low, S.S.; Manickam, S.; Ma, Z.; Banat, F.; Munawaroh, H.S.H.; Show, P.L. Prospects of Microalgae in Nutraceuticals Production with Nanotechnology Applications. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, R.K. Bio-Energy Production by Contribution of Effective and Suitable Microbial System. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.; Tripathi, S.; Poluri, K.M. Microalgal-Based Bioenergy: Strategies, Prospects, and Sustainability. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 14584–14612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Reyes, J.; Buitrón, G.; Arcila, J.S.; López-Gómez, M.O. Thermophilic Biogas Production from Microalgae-Bacteria Aggregates: Biogas Yield, Community Variation and Energy Balance. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 129898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaño, B.; Blanco, S.; Becares, E.; García-González, M.C. Bioremediation and Biomass Harvesting of Anaerobic Digested Cheese Whey in Microalgal-Based Systems for Lipid Production. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 97, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, G.; Georgakakis, D. Cultivation of Filamentous Cyanobacteria (Blue-Green Algae) in Agro-Industrial Wastes and Wastewaters: A Review. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3389–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolcha, O.N.; Tekerlekopoulou, A.G.; Akratos, C.S.; Bellou, S.; Aggelis, G.; Katsiapi, M.; Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Vayenas, D.V. Treatment of Second Cheese Whey Effluents Using a Choricystis-Based System with Simultaneous Lipid Production. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 2349–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Chua, A.S.M.; Yeoh, H.K.; Ngoh, G.C. A Review of the Production and Applications of Waste-Derived Volatile Fatty Acids. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 235, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.; Wanner, J. Activated Sludge—100 Years and Counting, 1st ed.; Jenkins, D., Wanner, J., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014; ISBN 9781780404936. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolella, C.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Heijnen, J.J. Wastewater Treatment with Particulate Biofilm Reactors. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 80, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaneeckhaute, C.; Lebuf, V.; Michels, E.; Belia, E.; Vanrolleghem, P.A. Nutrient Recovery from Digestate: Systematic Technology Review and Product Classification. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigger, G. Changing Paradigms: From Wastewater Treatment to Resource Recovery. Proc. Water Environ. Fed. 2011, 2011, 942–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, J.S.; Skerlos, S.J.; Barnard, J.L.; Beck, M.B.; Daigger, G.T.; Hilger, H.; Jackson, S.J.; Karvazy, K.; Kelly, L.; Macpherson, L.; et al. A New Planning and Design Paradigm to Achieve Sustainable Resource Recovery from Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6126–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissbrodt, D.G.; Winkler, M.K.H.; Wells, G.F. Responsible Science, Engineering and Education for Water Resource Recovery and Circularity. Environ. Sci. 2020, 6, 1952–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmidt, E.; Ghyselbrecht, K.; Zhang, Y.; Pinoy, L.; Van Der Bruggen, B.; Verstraete, W.; Rabaey, K.; Meesschaert, B. Global Phosphorus Scarcity and Full-Scale P-Recovery Techniques: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 336–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Hoek, J.P.; Duijff, R.; Reinstra, O. Nitrogen Recovery from Wastewater: Possibilities, Competition with Other Resources, and Adaptation Pathways. Sustainability 2018, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, S.A.; Smith, J.A. Phosphorus Removal and Recovery from Municipal Wastewaters. Elements 2008, 4, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckinghausen, A.; Odlare, M.; Thorin, E.; Schwede, S. From Removal to Recovery: An Evaluation of Nitrogen Recovery Techniques from Wastewater. Appl. Energy 2020, 263, 114616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilsenach, J.A.Ã.; Schuurbiers, C.A.H.; Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Van Phosphate and Potassium Recovery from Source Separated Urine through Struvite Precipitation. Water Res. 2007, 41, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numviyimana, C.; Warchoł, J.; Ligas, B.; Chojnacka, K. Nutrients Recovery from Dairy Wastewater by Struvite Precipitation Combined with Ammonium Sorption on Clinoptilolite. Materials 2021, 14, 5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prot, T.; Wijdeveld, W.; Eshun, L.E.; Dugulan, A.I.; Goubitz, K.; Korving, L.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Full-Scale Increased Iron Dosage to Stimulate the Formation of Vivianite and Its Recovery from Digested Sewage Sludge. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Aleem, M.; Fang, F.; Xue, Z.; Cao, J. Potentials and Challenges of Phosphorus Recovery as Vivianite from Wastewater: A Review. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alloul, A.; Cerruti, M.; Adamczyk, D.; Weissbrodt, D.G.; Vlaeminck, S.E. Control Tools to Selectively Produce Purple Bacteria for Microbial Protein in Raceway Reactors. bioRxiv 2020, 2020-01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerruti, M.; Stevens, B.; Ebrahimi, S.; Alloul, A.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Weissbrodt, D.G. Enrichment and Aggregation of Purple Non-Sulfur Bacteria in a Mixed-Culture Sequencing-Batch Photobioreactor for Biological Nutrient Removal from Wastewater. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 557234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarezadeh, S.; Moheimani, N.R.; Jenkins, S.N.; Hülsen, T.; Riahi, H.; Mickan, B.S. Microalgae and Phototrophic Purple Bacteria for Nutrient Recovery from Agri-Industrial Effluents: Influences on Plant Growth, Rhizosphere Bacteria, and Putative Carbon- and Nitrogen-Cycling Genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Process | Technique | Description | Products Obtained | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Separation | Membrane Separation | Broadly used in milk and whey processing to separate concentrated whey proteins and whole milk after the production of cheese so whey proteins can be fractionated into specific components. This process has evolved and can be subdivided into particulate filtration (PF), microfiltration (MF), ultrafiltration (UF), reverse osmosis (RO), and nanofiltration (NF). | Whey powder Dry whey powder (DWP) Whey powder concentrate (WPC) 35% Whey permeate α-, β-lactoalbumin Lactose Casein | [116,117,118,119,120,121] |
| High Hydrostatic Pressure | High pressure processing (HPP) was used to induce changes in milk proteins, and it does not influence the hydrolysis, the nutritional characteristics of milk, or the stability of vitamins significantly. However, it does affect the proteins, casein micelles, and whey proteins. | |||
| Pulsed Electric Field | Pulsed electric field (PEF) is a nonthermal process where pulsed electric fields of alternating currents (10–100 kV) are applied in circa 20 μs, creating high-voltage fields (up to 50 kV/cm), thus killing microorganisms and rupturing spores in the medium in the process. It is speculated that whey proteins that have undergone PEF are less denaturated, meaning that they could offer better immunological benefits. | |||
| Ultrasound | The applications of ultrasound and sonication in milk processing are diverse. The whey product depends on the effects of sonication on the proteins, and this process can be combined with high temperatures to produce products with new properties. | |||
| Microwave | The main issue of microwave processing for pasteurized milk products is inconsistent heating, which can be sorted through improving the tubular design and using focused microwave heaters. Microwave-processed milk or whey may present whey products with superior functionality and improved flavor. | |||
| Protein Modification | Enzymatic Modification | Whey proteins’ functions and values can be enhanced by enzymatic hydrolysis, generating hydrolysates with low-molecular-weight peptides. | Lactic acid, lactulose Bovine serum albumin (BSA) D-Tagatose Galactooligosacchatides (GOS) Other bioactive compounds (immunoglobulins, lactoferrins, glycomacropeptides, transferrins, lactoperoxidase, lysozymes, albutensin A, lactorphin, β-lactotensin, β-lactorphin, serorphin) | [116,122,123,124] |
| Chemical Modification | Milk can be modified chemically either via rennet–enzyme action or direct acidification. Primary structures are significantly changed in milk proteins through reactions involving the sulfide residues of the amino acids. | |||
| Protein separation | Extrusion Texturization | Short-time shear processing that modifies food structure, imparting texture. | Whey powder concentrate 80% Lactose pharma grade Whey protein blends (WPI + WPC) Pure whey isolate Minerals | [116,125] |
| Spray Drying | Conversion of liquid or slurry materials into dried powders or granules by atomizing the solution into fine droplets and drying them with hot air or gas, resulting in dried particles that can be easily stored, transported, and reconstituted when needed. | |||
| Carbon Dioxide Precipitation | Pressurized CO2 (27–55 bar, 54–64 °C) is used as an acid source, lowering whey’s protein pH, thus precipitating α-LA. Afterwards, solubilized CO2 is then released during the extraction and depressurization of the protein fractions, resulting in 55% α-La and 78% β-Lg. These ratios can be selectively enriched depending on the applications and functionality desired. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giulianetti de Almeida, M.P.; Mockaitis, G.; Weissbrodt, D.G. Got Whey? Sustainability Endpoints for the Dairy Industry through Resource Biorecovery. Fermentation 2023, 9, 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100897
Giulianetti de Almeida MP, Mockaitis G, Weissbrodt DG. Got Whey? Sustainability Endpoints for the Dairy Industry through Resource Biorecovery. Fermentation. 2023; 9(10):897. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100897
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiulianetti de Almeida, Maria Paula, Gustavo Mockaitis, and David G. Weissbrodt. 2023. "Got Whey? Sustainability Endpoints for the Dairy Industry through Resource Biorecovery" Fermentation 9, no. 10: 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100897
APA StyleGiulianetti de Almeida, M. P., Mockaitis, G., & Weissbrodt, D. G. (2023). Got Whey? Sustainability Endpoints for the Dairy Industry through Resource Biorecovery. Fermentation, 9(10), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100897






