Evaluation of the Black Tea Taste Quality during Fermentation Process Using Image and Spectral Fusion Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
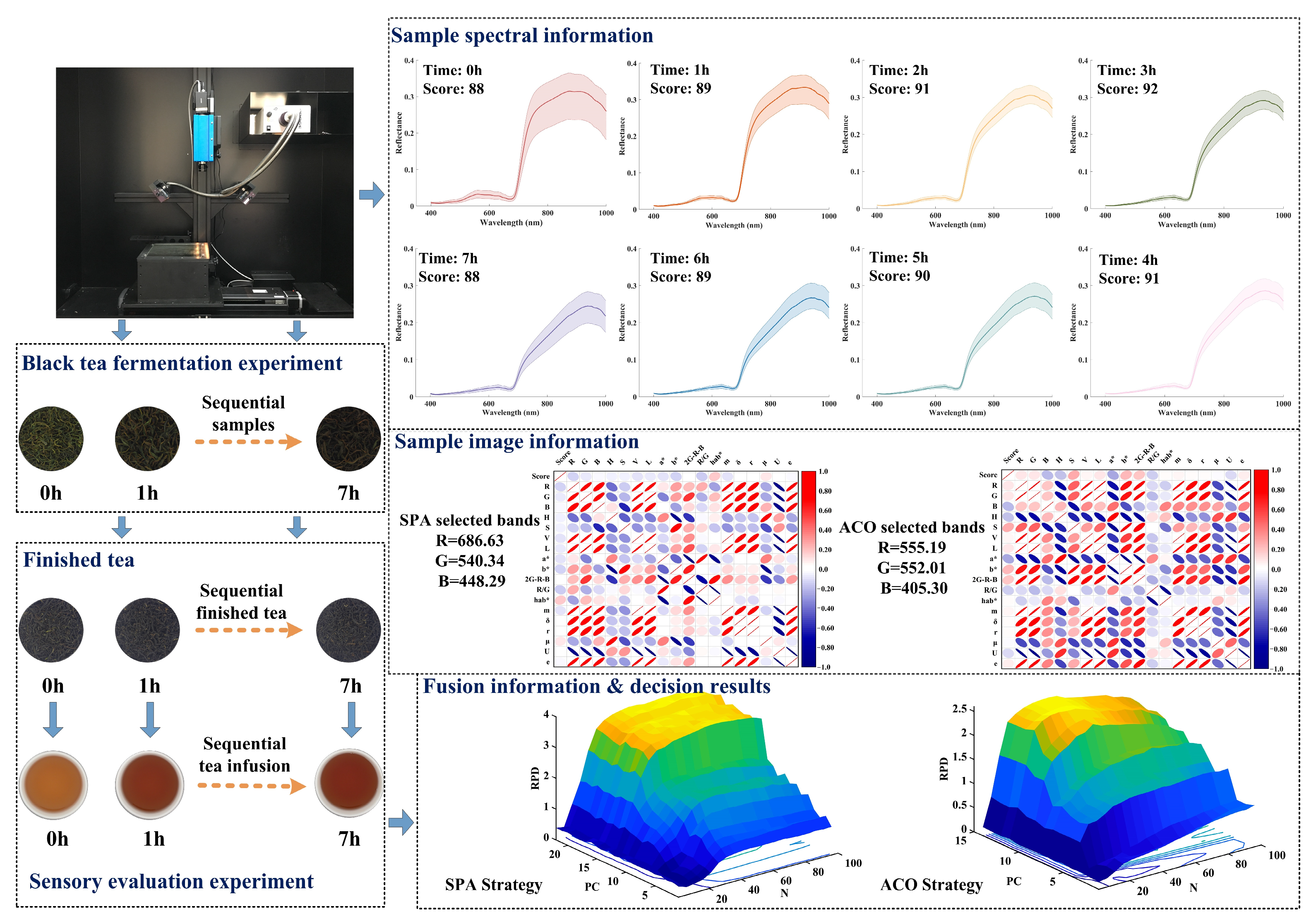
2.1. Samples
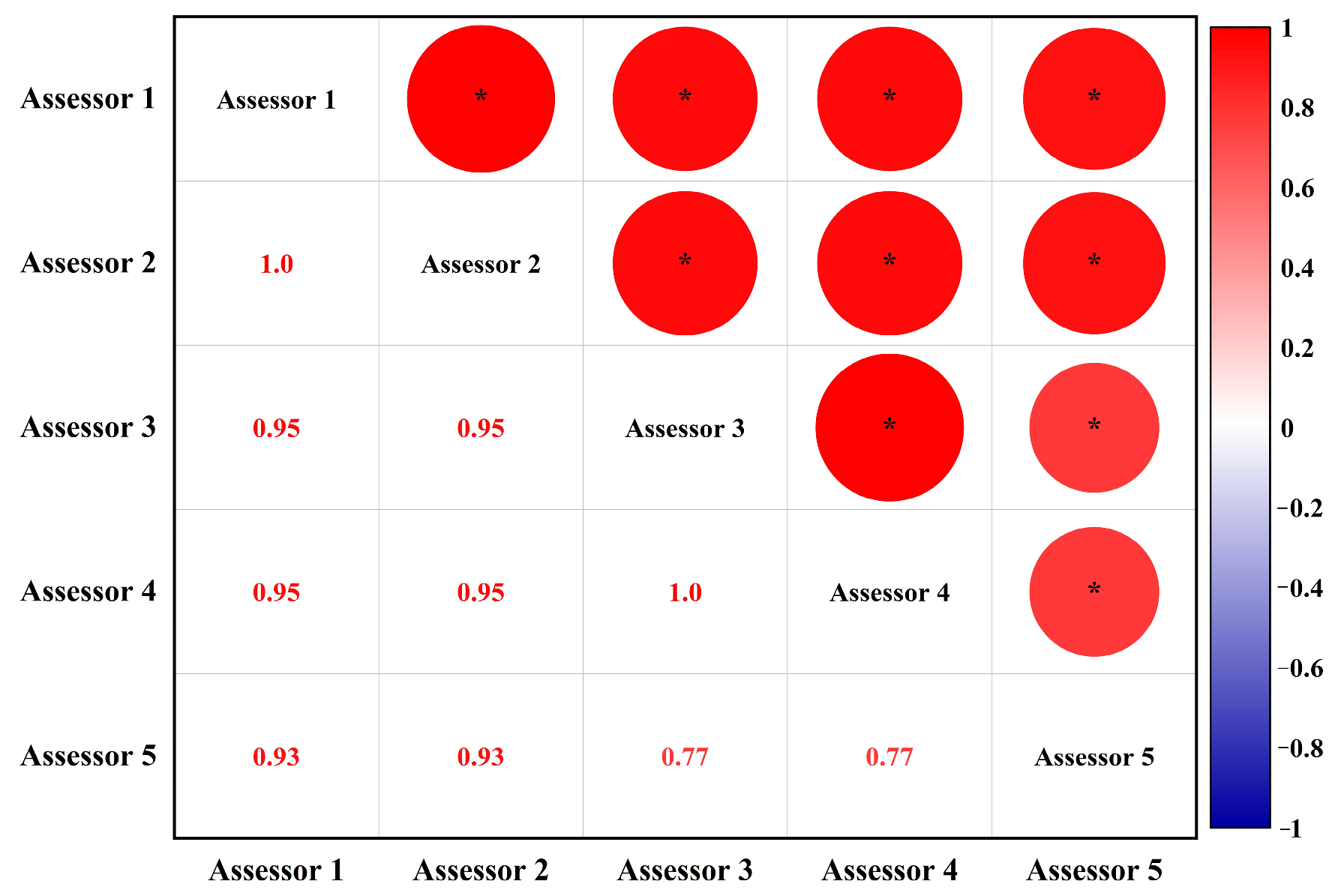
2.2. Sensory Evaluation of Black Tea Taste Quality
2.3. Acquisition of Hyperspectral Images
2.4. Data Processing
2.4.1. Extraction of Spectral Data
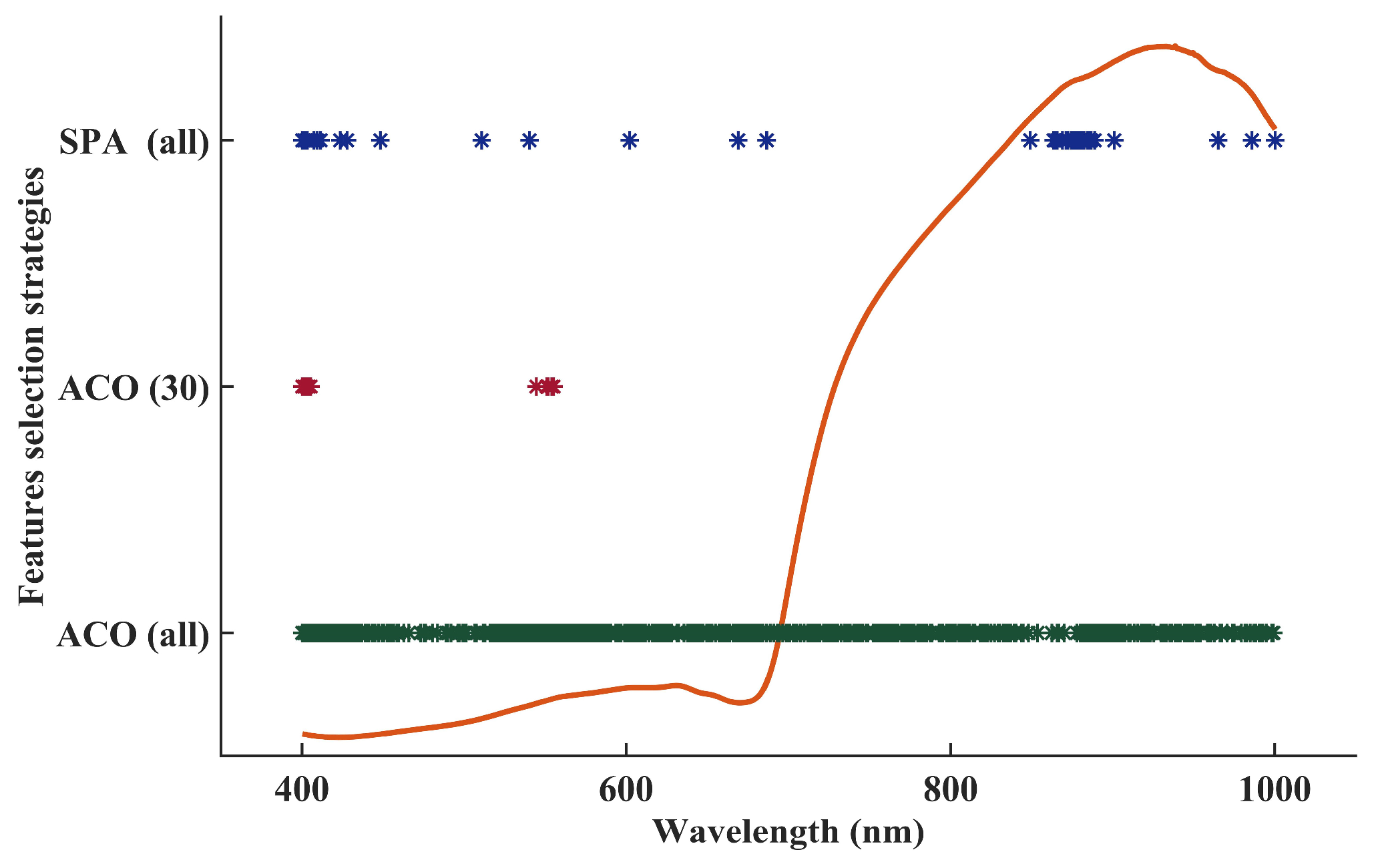
2.4.2. Selection of Characteristic Spectral Information
2.4.3. Image Acquisition and Feature Extraction
2.4.4. Data Fusion and Dimension Reduction
2.4.5. Regression Models
3. Results
3.1. Taste Evaluation Results
3.2. Response Spectra of Fermentation Samples
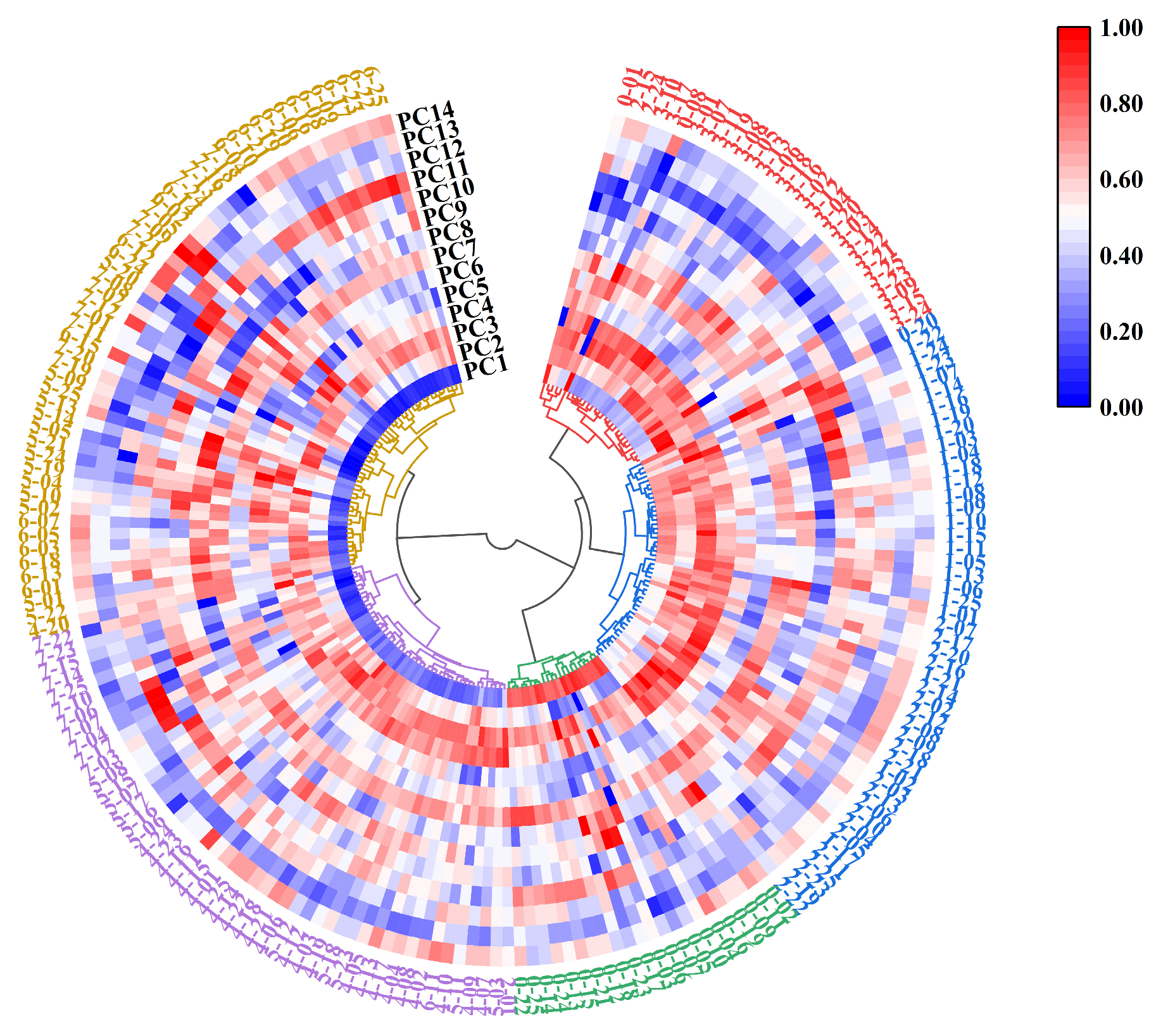
3.3. Hierarchical Clustering Analysis (HCA) of Sample Spectra
3.4. Quantitative Prediction Models with Single Data
3.4.1. Regression Model Based on Full Bands
3.4.2. Regression Model Based on Effective Bands
3.4.3. Regression Models Based on Image Features
3.5. Regression Models with Fusion Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, C.; Ye, Y.; Yang, C.S.; An, T.; Jiang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y. Rapid detection of catechins during black tea fermentation based on electrical properties and chemometrics. Food Biosci. 2021, 40, 100855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Zhao, Y.; An, T.; Liu, Z.Y.; Jiang, Y.W.; Li, Y.Q.; Dong, C.W. Quantitative prediction and visualization of key physical and chemical components in black tea fermentation using hyperspectral imaging. LWT.-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 141, 110975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Gao, M.J.; Hou, R.Y.; Hu, X.Y.; Zhang, L.; Wan, X.C.; Wei, S. Determination of quality constituents in the young leaves of albino tea cultivars. Food Chem. 2014, 155, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.L.; Yan, J.N.; Cui, J.L.; Mao, S.H.; Li, M.F.; Liao, X.L.; Tong, H.R. Dynamic changes in amino acids, catechins, caffeine and gallic acid in green tea during withering. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 66, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.S.; Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Chen, X.H. Application of FT-NIR spectroscopy for simultaneous estimation of taste quality and taste-related compounds content of black tea. J. Food Sci. Tech-Mys. 2018, 55, 4363–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.S.; Sun, C.C.; Ouyang, Q.; Wang, Y.X.; Liu, A.P.; Li, H.H.; Zhao, J.W. Classification of different varieties of Oolong tea using novel artificial sensing tools and data fusion. LWT.-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Wu, W.Q.; Wan, X.C.; Ning, J.M. Discriminating geographical origins of green tea based on amino acid, polyphenol, and caffeine content through high-performance liquid chromatography: Taking Lu’an guapian tea as an example. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F.; Ma, J.Q.; Huang, D.J.; Ma, C.L.; Jin, J.Q.; Yao, M.Z.; Chen, L. Comprehensive Dissection of Metabolic Changes in Albino and Green Tea Cultivars. J. Agri. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2040–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Hwang, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Choung, M.G. The characterization of caffeine and nine individual catechins in the leaves of green tea (Camellia sinensis L.) by near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Yu, S.Y.; Huang, W.Q.; Li, G.L.; Tian, X.; Fan, S.X.; Dong, C.W.; Zhao, C.J. Robustness and accuracy evaluation of moisture prediction model for black tea withering process using hyperspectral imaging. Spectrochim. Acta A 2022, 269, 120791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.J.; Huang, W.Q.; Wang, Z.L.; Liu, S.Q.; He, X.; Fan, S.X. Calibration transfer between developed portable Vis/NIR devices for detection of soluble solids contents in apple. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2022, 183, 111720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, N.; Bhol, C.S.; Das, B.S. Rapid assessment of black tea quality using diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. J. Food Eng. 2016, 190, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Tian, P.; Fan, G.Z.; Dong, W.T.; Zhang, H.L.; Liu, X.M. Non-destructive determination of four tea polyphenols in fresh tea using visible and near-infrared spectroscopy. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 123, 104037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.W.; Liang, G.Z.; Hu, B.; Yuan, H.B.; Jiang, Y.W.; Zhu, H.K.; Qi, J.T. Prediction of Congou Black Tea Fermentation Quality Indices from Color Features Using Non-Linear Regression Methods. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.W.; An, T.; Yang, M.; Yang, C.S.; Liu, Z.Y.; Li, Y.; Duan, D.D.; Fan, S.X. Quantitative prediction and visual detection of the moisture content of withering leaves in black tea (Camellia sinensis) with hyperspectral image. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 123, 104118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Huang, W.Q.; Tian, X.; Fan, S.X.; Duan, D.D.; Dong, C.W.; Zhao, C.J.; Li, G.L. Hyperspectral imaging technology coupled with human sensory information to evaluate the fermentation degree of black tea. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 366, 131994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Fan, S.X.; Duan, D.D.; Zhao, C.J.; Huang, W.Q.; Dong, C.W. Evaluation of aroma quality using multidimensional olfactory information during black tea fermentation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 371, 132518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.W.; Zhu, H.K.; Zhao, J.W.; Jiang, Y.W.; Yuan, H.B.; Chen, Q.S. Sensory quality evaluation for appearance of needle-shaped green tea based on computer vision and nonlinear tools. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2017, 18, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Li, T.H.; Li, L.Q.; Ning, J.M.; Zhang, Z.Z. Evaluating taste-related attributes of black tea by micro-NIRS. J. Food Eng. 2021, 290, 110181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvao, R.K.H.; Araujo, M.C.U.; Silva, E.C.; Jose, G.E.; Soares, S.F.C.; Paiva, H.M. Cross-validation for the selection of spectral variables using the successive projections algorithm. J. Brazil Chem. Soc. 2007, 18, 1580–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegrini, F.; Olivieri, A.C. A new and efficient variable selection algorithm based on ant colony optimization. Applications to near infrared spectroscopy/partial least-squares analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 699, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borras, E.; Ferre, J.; Boque, R.; Mestres, M.; Acena, L.; Busto, O. Data fusion methodologies for food and beverage authentication and quality assessment—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 891, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewers, F.L.; Ferreira, G.R.; De Arruda, H.F.; Silva, F.N.; Comin, C.H.; Amancio, D.R.; Costa, L.D. Principal Component Analysis: A Natural Approach to Data Exploration. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.l.; He, Y. Evaluation of Least Squares Support Vector Machine Regression and other Multivariate Calibrations in Determination of Internal Attributes of Tea Beverages. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2010, 3, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, S.B.; Fang, J.; Xu, Z.B. Is extreme learning machine feasible? A theoretical assessment (part I). IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. 2015, 26, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Chen, C.; Chen, S.N.; Wang, K.X.; Huang, H.T.; Wu, Y.Y.; He, P.M.; Tu, Y.Y.; Li, B. Dynamic changes and mechanisms of organic acids during black tea manufacturing process. Food Control 2022, 132, 108535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Wang, Q.G.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Q.B. Prediction of color and moisture content for vegetable soybean during drying using hyperspectral imaging technology. J. Food Eng. 2014, 128, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Q.; Li, M.H.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Q.Q.; Bi, K.Y.; Jin, S.S.; Wang, Y.J.; Ning, J.M.; Zhang, Z.Z. High-sensitivity hyperspectral coupled self-assembled nanoporphyrin sensor for monitoring black tea fermentation. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2021, 346, 130541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Jin, J.J.; Sun, C.J.; Ye, D.P.; Liu, Y.F. Simultaneous determination of six main types of lipid-soluble pigments in green tea by visible and near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Shen, S.; Wang, J.J.; Jiang, Y.W.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.Q.; Hua, J.J.; Yuan, H.B. Novel insight into the effect of fermentation time on quality of Yunnan Congou black tea. LWT.-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 155, 112939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.X.; Li, T.H.; Wei, Y.M.; Ning, J.M.; Zhang, Z.Z. Estimation of Congou black tea quality by an electronic tongue technology combined with multivariate analysis. Microchem. J. 2021, 163, 105899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.X.; Zhang, X.S.; Wu, R.; Yin, L.L.; Hu, W.Y.; Zhang, Z.Z. Rapid Characterization of Black Tea Taste Quality Using Miniature NIR Spectroscopy and Electronic Tongue Sensors. Biosensors 2023, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Data | Method | No.of Variables | Parameter | Calibration Set | Prediction Set | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVs | Rc | RMSEC | Rp | RMSEP | |||
| Spectra | none | 557 | 5 | 0.788 | 0.868 | 0.763 | 0.897 |
| Spectra | SNV | 557 | 5 | 0.854 | 0.731 | 0.827 | 0.778 |
| Spectra | SNV + SPA | 38 | 5 | 0.909 | 0.585 | 0.927 | 0.553 |
| Spectra | SNV + ACO (30) | 11 | 4 | 0.903 | 0.602 | 0.923 | 0.543 |
| Spectra | SNV + ACO (all) | 411 | 5 | 0.857 | 0.723 | 0.833 | 0.767 |
| Image | SPA | 18 | 10 | 0.643 | 1.055 | 0.452 | 1.279 |
| Image | ACO | 18 | 14 | 0.698 | 0.993 | 0.554 | 1.101 |
| Model | Methods | No. of Variables | Parameter | Calibration Set | Prediction Set | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rc | RMSEC | Rp | RMSEP | RPD | ||||
| PLSR | Fusion (SPA) | 56 | LV = 18 | 0.986 | 0.239 | 0.978 | 0.282 | 4.118 |
| Fusion (ACO) | 29 | LV = 15 | 0.947 | 0.448 | 0.910 | 0.538 | 2.267 | |
| SVR | Fusion (SPA) | 56 | LV = 13, c = 256, g = 256 | 0.993 | 0.174 | 0.969 | 0.324 | 3.748 |
| Fusion (ACO) | 29 | LV = 9, c = 256, g = 256 | 0.944 | 0.450 | 0.930 | 0.487 | 2.422 | |
| ELM | Fusion (SPA) | 56 | LV = 20, n = 75 | 0.992 | 0.174 | 0.969 | 0.317 | 3.748 |
| Fusion (ACO) | 29 | LV = 11, n = 35 | 0.949 | 0.441 | 0.928 | 0.481 | 2.547 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, T.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Fan, S.; Huang, W.; Qi, D.; Tian, X.; Yuan, C.; et al. Evaluation of the Black Tea Taste Quality during Fermentation Process Using Image and Spectral Fusion Features. Fermentation 2023, 9, 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100896
An T, Yang C, Zhang J, Wang Z, Fan Y, Fan S, Huang W, Qi D, Tian X, Yuan C, et al. Evaluation of the Black Tea Taste Quality during Fermentation Process Using Image and Spectral Fusion Features. Fermentation. 2023; 9(10):896. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100896
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Ting, Chongshan Yang, Jian Zhang, Zheli Wang, Yaoyao Fan, Shuxiang Fan, Wenqian Huang, Dandan Qi, Xi Tian, Changbo Yuan, and et al. 2023. "Evaluation of the Black Tea Taste Quality during Fermentation Process Using Image and Spectral Fusion Features" Fermentation 9, no. 10: 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100896
APA StyleAn, T., Yang, C., Zhang, J., Wang, Z., Fan, Y., Fan, S., Huang, W., Qi, D., Tian, X., Yuan, C., & Dong, C. (2023). Evaluation of the Black Tea Taste Quality during Fermentation Process Using Image and Spectral Fusion Features. Fermentation, 9(10), 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100896







