Abstract
In this study, ultrasonication (US) (50 W, 30 kHz, 1–6 min) was used to increase the efficiency of Limosilactobacillus reuteri PTCC 1655 fermentation process (37 °C; 30 h) of Bakraei juice. Total sugars, pH, Brix, organic acids, vitamin C, polyphenols, antioxidant activity, α-amylase inhibition and anti-inflammatory properties were measured during the fermentation period. The results showed that by increasing the ultrasound time up to 5 min, pH, vitamin C, citric acid, and polyphenolic compounds decreased, while lactic acid, antioxidant capacity, α-amylase inhibition and anti-inflammatory properties were increased. When the ultrasound time was increased up to 6 min, compared to the non-ultrasound-treated sample, the efficiency of the fermentation process decreased and promoted a decrease in the microbial population, lactic acid levels, antioxidant activity, α-amylase inhibition, and anti-inflammatory properties of the juices. The initial anti-inflammatory activity (11.3%) of juice reached values of 33.4% and 19.5%, after US treatments of 5 and 6 min, respectively, compared to the non-sonicated juice (21.7%), after 30 h of fermentation. As a result, the use of ultrasound in the controlled fermentation process can increase the efficiency of fermentation process.
1. Introduction
Over the last few years, a consumer’s growing interest in fermented foods and beverages has been observed all over the world. The use of fermented products has a long history in human daily diet [1]. Fermentation was originally used as a way to improve taste, extend food shelf life, and eliminate food toxins, but nowadays, it is used because of the health benefits attributed to fermented foods [2]. Fermentation is a phenomenon caused by a set of biological activities in which organic compounds with large molecules are broken into compounds with smaller and simpler molecules. The fermentation process is carried out by microorganisms including bacteria, molds and yeasts, and can be used on many food products such as vegetables, fruits, grains, dairy products, meat, fish, seeds, etc. [1].
Different studies have shown that the application of non-conventional technologies in the food fermentation industry not only leads to saving time and energy, but also produces safer and higher quality products [3,4]. In the modern fermentation industry, it is tried to use sub-lethal methods to create stress conditions in order to stimulate microbial growth and improving their metabolic activities without affecting cell viability [1]. Several innovative processing technologies, such as ultrasonication (US), have been studied to increase the efficiency and productivity of the fermentation process [5]. Ultrasonic waves refer to those with a frequency of more than 18–20 kHz, which are not audible by humans [6]. These waves are classified in two ranges: waves with high frequency (low power) and waves with low frequency (high power). Low power US is in the frequency range of 1 to 10 MHz, which is also called diagnostic US. High-frequency and low-energy waves are used as an analytical technique to ensure the quality of food and control the process [7,8].
These waves are considered as a nondestructive and non-invasive inspection method and are used in the food industry, including homogenization process evaluation, container filling control, fluid flow control, and foreign bodies’ location [9]. In contrast, low frequency, and high energy US have frequencies between 20 and 100 kHz which is typically applied as a process intensification tool. These waves can create cavitation which can cause chemical and physical changes in materials. They are used in various processes in the food industry, including surface decontamination, degassing, improvement of mass transfer, enhancing fermentation rates, enzymatic and microbial inactivation, and foam destruction [10,11].
The use of US to accelerate fermentation, reducing fermentation time, improving microorganism-fermenting cell growth and increasing biomass yields due the cavitation phenomena has been shown in some previous studies [12,13]. For instance, Sulaiman et al. [14] reported that US increased the production of ethanol during fermentation by Kluyveromyces marxianus. Faster lactic acid production was observed by other authors as a result of applying US technology (frequency of 20 kHz) on milk samples inoculated with various Bifidobacterium strains [15]. In addition, an increase in biomass production rate (by 52%) and a decrease in ethanol content (by 0.55% (v/v)) were observed in US-assisted fermentation of Lebanese apple juice for production of cider [16].
Plants belonging to the genus Citrus are cultivated in different regions of the world due to their special characteristics, including the production of essential oils with a pleasant aroma and having edible fruits [17]. According to Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) data, in 2020, the amount of citrus fruit production in Iran was estimated approximately at 4 million tons [18]. Due to the properties and widespread cultivation of citrus fruits, various hybrids have been formed among Citrus species [19]. Bakraei (Citrus reticulata cv. Bakraei) is one of these hybrids that is obtained from mandarin and sweet lime (Citrus reticulata × Citrus limetta). This plant is native to North India, but it also exists in Iran, China, Indonesia, and Thailand. All parts of this plant (stem, peel, root, leaf, and fruit) have therapeutic effects and has a long history in traditional medicine [20]. Fruit pulp contains bioactive compounds such as carotenoids, phenols, alkaloids, coumarins, flavonoids, terpenes, and antioxidants [21]. It has been found that Bakraei juice has reduced serum glucose, triglyceride and cholesterol in diabetic rats [22].
Therefore, due to the demand of consumers for non-dairy beverages, especially for vegetarians and people with lactose intolerance, a lot of attention has been paid to fruit-based beverages. To the best of our knowledge, no study has been carried out before on Bakraei juice, so, it was decided to use this fruit in the present work. Hence, the current research aims are to investigate the impact of applying US on Bakraei juice at different time intervals in the fermentation process. The effects of US on viable cell count, physicochemical properties, contents of specific organic acids, antioxidant activity, polyphenols, and some enzyme inhibitory activity were evaluated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Strain
Limosilactobacillus reuteri PTCC 1655 was purchased from Iranian Research Organization for Science and Technology (Tehran, Iran). The strain was reactivated in the MRS broth (Oxoid, Hampshire, UK) at 37 °C for 24 h and the cell pellets were collected with centrifugation (Hettich, Westphalia, Germany) at 3500× g for 15 min at 4 °C. Low temperature was used to prevent cell damage.
2.2. Fermentation Process
About 12 kg of Backraei (Citrus reticulata cv. Bakraei) fruit were bought from a local fruit market in Shiraz (Fars province, Iran). Next, the fruits were washed with sterile water and peeled using a sterile knife. Peeled fruits were cut and after that, juiced using a juicer (Pars Khazar; JC-700P, Rasht, Iran). The seeds and pulps were separated using a cleaning cloth. Finally, the fruit juice was heated using a water bath (Memmert, WNE29, Schwabach, Germany) at 80 °C for 10 min. After cooling, in order to carry out the fermentation process, about 4.3 log CFU/mL of the strain was inoculated into the fruit juice and ultrasonicated 50 W, 30 kHz, 1–6 min) using a Hielscher UP50H equipment (Hattersheim am Main, Germany). The control sample was not sonicated. The fermentation process was performed in closed 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks at 37 °C for 30 h.
2.3. Determination of Viable Cell Count
MRS agar (Oxoid, Hampshire, UK) was used to count the colonies and peptone water was utilized to obtain proper dilutions. Colonies were counted after keeping the plates at 37 °C for 48 h.
2.4. Determination of pH, Total Soluble Solids Content (TSS) and Total Sugars Content
The pH was determined by a pH meter (Milwaukee, Padua, Italy) while the TSS were measured using a digital refractometer (Atago, Tokyo, Japan) and expressed as °Brix. Total sugars content was measured as glucose equivalents using the phenol sulfuric acid method [23].
2.5. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Determination of Lactic and Citric Acids
Quantitative determinations of lactic and citric acids were carried out using an HPLC (Knauer, Azura, Berlin, Germany) equipped with a K-2600UV-visible detector. The separation column was an Ultrasep ES-FS special (250 mm × 30 mm, 5µm, Knauer column). The ChromGate Software A1493 was utilized as software to measure targeted compounds [24].
2.6. Polyphenols
In order to determine total phenolics content, briefly, 0.5 mL of the diluted juice (1:16) were mixed with 2.5 mL of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent (10%). After 3 min, 2 mL of Na2CO3 (7.5% w/v) were added to the solution and after that it was placed in the dark for 1 h. Finally, the absorbance was read at 765 nm (Hitachi U-3000, Tokyo, Japan). The results were expressed as gallic acid equivalent (GAE) (mg GAE/L) [25].
For total flavonoids content, briefly, 4 mL of the diluted juice (1:5) were added to 0.5 mL of NaNO2 (50 g/L). After 5 min, 1 mL of AlCl3 (100 g/L) was added to the solution and kept for 5 min. Subsequently, 2 mL of NaOH (2 mol/L) were mixed with the solution and the absorbance was read at 510 nm following 10 min. The results were expressed as rutin equivalent (RE) (mg RE/L) [26].
2.7. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
In order to determine the DPPH radical scavenging activity, a DPPH solution (0.1 mmol/L) was prepared using methanol and 100 μL of juice sample were mixed with 200 μL of DPPH. After keeping the mixture at 37 °C for 30 min, the absorbance was determined at 517 nm. Distilled water was utilized as a control [27].
For ABTS radical scavenging activity, the ABTS radical cation was prepared with K2S2O8 (2.45 mmol/L) and after that the mixture was diluted using ethanol (80%). Subsequently, 400 μL of the diluted juice (1:50) were mixed with 3.6 mL of the mixture and kept in the dark for 6 min. Finally, the absorbance was read at 734 nm [28].
2.8. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Vitamin C Determination
The HPLC system (Knauer, Azura, Berlin, Germany) with a C18 column (15 cm × 4.6 mm, pore size 5 µm) was used for determination of vitamin C of juice samples. The mobile phase was KH2PO4 (0.025 M) with a flow rate of 1 mL/min. An ultraviolet visible detector (UVD2.1L) was set at 245 nm [29].
2.9. α-Amylase Inhibition
Juice sample (50 μL) was mixed with α-amylase (50 μL; 0.2 U/mL) and kept at 25 °C for 10 min in 96-well. Soluble starch solution (50 μL; 1%) was added and afterward it was kept at 25 °C for 10 min. After that, 100 μL dinitrosalicylic acid color reagent were added, and the reaction was stopped using boiling water bath. After dilution using distilled water, the absorbance of each well was measured at 540 nm and the distilled water was utilized as a control [30].
2.10. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
The activity of 5-LOX enzyme was measured in a 96-well plate containing phosphate buffer (150 μL), 20 μL of the juice solution, 60 μL of linoleic acid, and 20 μL of 5-LOX enzyme. Afterward, the mixture was kept at 25 °C for 15 min and the absorbance was determined at 234 nm [31].
2.11. Statistical Analysis
All tests were performed in triplicate. First, the results were subjected to one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), and then Duncan’s multiple range test was used at a confidence level of 95% to compare the means and check the significant difference between the treatments. Statistical analysis of data was carried out by SPSS version 20 software. The relevant graphs were drawn in EXCEL software version 2016 (Microsoft Office, Redmond, WA, USA, 2016).
3. Results
3.1. Viable Cell Counts
The effect of US on L. reuteri growth of in Bakraei juice during 30 h fermentation is depicted in Figure 1. As can be seen in the figure, the initial number of L. reuteri (4.3 CFU/mL) was significantly (p < 0.05) increased in both US-treated and control samples with the elapse of fermentation period. The highest cell counts were observed in the US-5 min treatment, followed by 4, 3, 2, and 1 min compared to the non-sonicated juice. In contrast, the US time increase up to 6 min negatively affected the bacterial growth and decreased the microbial population compared to the non-sonicated juice. The highest and lowest viable cell counts were observed in US-5 min (9.1 CFU/mL) and US-6 min (6.8 CFU/mL) treatments, respectively, compared to the control sample (7.3 CFU/mL). It is clear from the data that the bacterial population is mainly dependent on the duration of US treatment, in which short-term sonication (1-5 min) induced growth stimulation, while long-term treatment (6 min) induced growth inhibition compared to the control sample. These findings concur with the results of Hashemi et al. [5], who observed a growth intensification of Lactobacillus helveticus and Lactobacillus acidophilus after 10 and 20 min US treatment and a decreased cell viability after 30 min US treatment during date syrup fermentation. Growth stimulation under the influence of US can be attributed to the increase in the membrane permeability and the transfer rate of materials due to pore formation. For instance, US has the potential to create pores in the cell membrane and to form microcurrents inside the cell, promoting molecules transport from the boundary layers [3,32]. The effect of US on milk fermentation was previously investigated, observing the authors that some components were released from the ruptured cells that stimulated the growth of lactobacilli [33]. In contrast, the inhibition impact of US on microbial proliferation and cell viability has been reported by several studies [34,35,36]. Mechanical destruction of cells is the main reason for the inhibition impact of US on microbial cells. It is known that cavitation and mechanical impact caused by extreme pressure difference lead to the destruction of microbial cell wall [37]. In addition, the microbial inactivation by US is also related to the sonochemical effect. The very high temperature and pressure resulting from the collapse of microbubbles leads to the production of free radicals, causing oxidative damage [38].
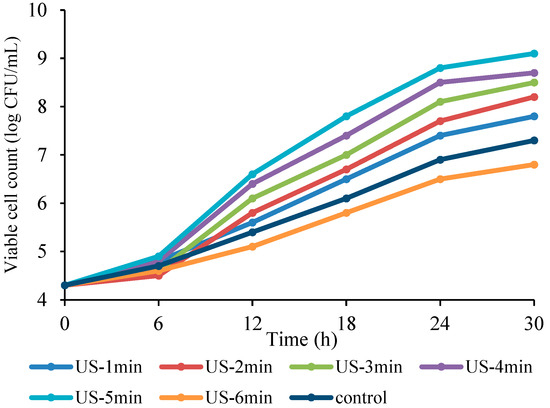
Figure 1.
Impact of US on viable cell count in Bakraei juice fermented with L. reuteri. Error bars reveal the standard deviation of viable count in Bakraei juice during 30 h of fermentation. US-1 min: ultrasound treatment for 1 min, Control: non-ultrasound treated juice.
3.2. pH, °Brix, and Total Sugars Content
The impact of US on pH, total soluble solids and total sugars of Bakraei juice during the fermentation process are presented in Figure 2. According to the Figure 2a, the content of total sugars notably (p < 0.05) decreased in all sonicated and unsonicated samples during 30 h of fermentation. The application of US in the fermentation process led to an increase in sugar consumption, while this increase was dependent on the duration of the US treatment. The initial amount of total sugars (144.4 g/L) reached 100.9 g/L and 115.4 g/L, in the treatments of US-5 min and US-6 min, respectively, compared to the unsonicated juice (112.7 g/L), at the end of the fermentation period. Generally, sugar is the main source of carbon and energy involved in the growth of microorganisms [39]. The greater reduction in total sugars in US-5 min treatment compared to the control sample indicates the greater growth of L. reuteri and the greater consumption of sugar during the fermentation process, which confirms the results of Figure 1. Similarly, US technology enhanced the carbohydrate metabolism in apple juice during fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum [3]. Furthermore, an increase in lactose hydrolysis as a result of increasing the duration of US treatment from 5 min to 15 min was observed in fermented milk containing L. plantarum [40].
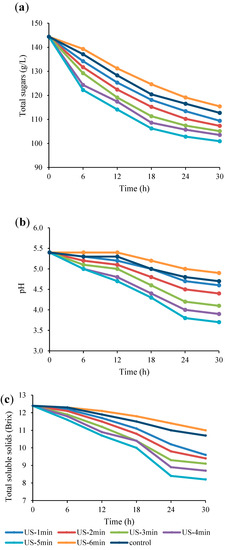
Figure 2.
Variations in total sugars (a), pH (b), and total soluble solids (c) in US-treated and non-US treated Bakraei juice during fermentation. Error bars reveal the standard deviation of each measurement in Bakraei juice during 30 h of fermentation. US-1 min: ultrasound treatment for 1 min, Control: non-ultrasound treated juice.
Changes in pH values of treated juices during fermentation are shown in Figure 2b. As can be seen, the pH value of the Bakraei juice samples markedly decreased after the fermentation period and altered by US processing (p < 0.05). US treatment for 1-5 min resulted in lower final pH, while US treatment for 6 min resulted in higher final pH values relative to the control sample. These changes are expected due to the impact of US treatment on the fermentation process. US treatment for 1-5 min, resulted in fermentation stimulation, promotion of microbial growth, production of lactic acid by lactobacilli, and thereby a decreased pH compared to the control juice. In contrast, the prolonged fermentation period (US-6 min), resulted in lower viable cells, decreased sugar consumption, lower lactic acid production and pH compared to control group. In this line, Nöbel et al. [41] reported that US treatment of raw skim milk during the fermentation period markedly reduced the pH compared to the unsonicated samples.
Total soluble solids (TSS) contents of the Bakraei juice samples under the influence of US during the fermentation period are illustrated in Figure 2c. Typically, TSS are related to the sugar contents in the fruit-based beverages [42]. Data revealed a significant decrease (p < 0.05) in TSS content for all treated samples, which is related to the consumption of sugars. The °Brix values were markedly decreased faster in US-treated (1–5 min) samples compared to the unsonicated samples. After 30 h of fermentation, the °Brix decreased by 51.22% and 12.73% for US-5 min and US-6 min treatments, respectively, compared to the control juice sample (15.89%). These results are consistent with the total sugars data, previously described (Figure 2b). This trend can be explained by the positive and negative effect of US on the microbial cell membrane. Short–term US may create temporary and reversible pores on the microbial cell membrane and improve the transport of substrates, leading to increased cell growth. In contrast, long-term US treatment may create irreversible pores leading to cell rupture and microbial death [32,43]. Our findings conform with the results of Al Daccache et al. [16], who indicated a faster °Brix depletion as well as glucose concentrations in US-treated samples compared to the control sample throughout the fermentation of apple juice.
3.3. Organic Acids
The impact of US on the concentration of organic acids (including lactic acid and citric acid) during the fermentation of Bakraei juice was analyzed by the HPLC method. Lactic acid was enhanced while citric acid decreased during the fermentation period (Figure 3). Moreover, as can be seen in Figure 3a, after 6 h of fermentation, no significant differences (p > 0.05) in the organic acids content were observed between the control, US-6 min, US-1 min, and US-2 min samples, while after 30 h, a significant difference (p < 0.05) for those compounds was noticed between the samples. Regarding lactic acid production, after 6 h of incubation, no significant differences (p > 0.05) were found between all treated samples, while at time 12, no significant differences were observed between the control, US-6 min, US-1 min, and US-2 min samples. However, after 30 h of incubation, there were observed significant differences (p < 0.05) between the samples.
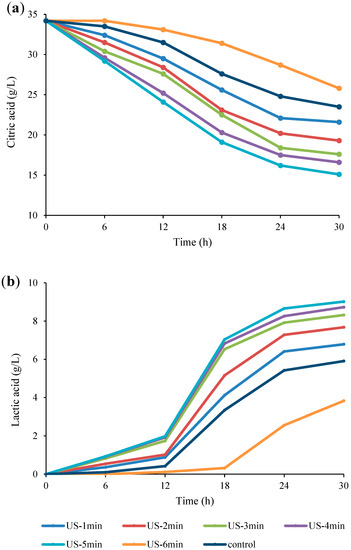
Figure 3.
Changes in the amount of citric acid (a) and lactic acid (b) in US-treated and non-US treated Bakraei juice during fermentation. Error bars reveal the standard deviation of each measurement in Bakraei juice during 30 h of fermentation. US-1 min: ultrasound treatment for 1 min, Control: non-ultrasound treated juice.
By increasing US duration treatment from 1 to 5 min, the concentrations of lactic acid significantly increased while the citric acid values decreased, compared to the control samples (p < 0.05). However, US treatment (6 min) markedly (p < 0.05) decreased the production of lactic acid and increased the citric acid values, compared to control samples. Regarding the citric acid (Figure 3a), the initial amount (34.2 g/L) reached 15.1 g/L, 25.8 g/L, and 23.5 g/L for US-5 min, US-6 min, and control samples, respectively, at the end of the fermentation period. The declining trend in the values of citric acid during fermentation can be attributed to lactic acid bacteria (LAB) metabolism [44]. In this line, some previous studies have shown that Lactobacillus species can use citric acid as an available carbon source to produce acetic acid, lactic acid, and diacetyl [34,35]. Similar results were reported for increased utilization of citric acid in US-treated apple juice compared to the unsonicated sample during fermentation [3]. After 30 h-fermentation with L. reuteri, the production of lactic acid reached 9.02 g/L and 3.83 g/L for US-5 min and US-6 min treatments, which were the highest and lowest levels of lactic acid production, respectively, compared to the unsonicated sample (5.91 g/L) (Figure 3b). The lower production of lactic acid and higher retention of citric acid can be related to the negative effect of long-term US treatment (6 min) on cell viability and microbial growth. In contrast, short treatments of US (1–5 min) increased the fermentation activity. These heterogeneous impact of US can be attributed to the role of electroporation on the cell membrane, in which short treatments increase the membrane permeability and metabolite exchange, while longer treatments compromise the cell structure and even cause cell rupture [45]. Similarly to our findings, Gholamhosseinpour and Hashemi [40] reported that increasing the duration of US treatment resulted in higher lactose hydrolysis and higher lactic acid production. In addition, it has been indicated that the application of 10 and 20 min US treatment during fermentation increased the lactic acid production from date syrup, while treatment of 30 min led to a decrease in lactic acid concentration [5].
3.4. Bioactive Compounds
The changes of bioactive compounds including total phenolics, total flavonoids, and vitamin C in US-treated juice samples during fermentation are presented in Figure 4. As can be seen in Figure 4a,b, both total phenolics and total flavonoids significantly (p < 0.05) decreased with the elapse of fermentation time, and the highest and lowest reductions were observed in US-5 min and US-6 min samples, respectively, compared to the controls. There was no significant difference (p > 0.05) between the total phenolics and total flavonoids levels of the control, US-6 min, US-1 min, and US-2 min samples after 6 h of fermentation, but a significant difference was observed between all samples at the end of the fermentation period (p < 0.05). After 30 h of fermentation, 19.75%, 7.35%, and 13.43% reductions of total phenolics and 24.42%, 8.55%, and 11.96% reductions of total flavonoids were noticed in US-5 min, US-6 min, and control samples, respectively. Our results are in agreement with Hashemi et al. [24], who reported that fermentation of sweet lemon juice by L. plantarum LS5 resulted in an 8.28% reduction of total phenolic compounds. A similar decrease in total phenolic compounds and total flavonoid compounds was reported in olives, beans, and Saccharina japonica during fermentation [46,47,48]. It is speculated that the reduction in phenolic compounds may be related to their metabolism by starter microorganisms [46]. In addition, Adebo et al. [49] reported that notable losses of flavonoids may be related to the decomposition of phenolic compounds during fermentation. According to the findings, the increment in the losses of total phenols and flavonoids as a result of the US process (1 to 5 min) could be related to the increase in the activity of L. reuteri and the increase in the metabolism of phenolic compounds, whereas long-term US treatment (6 min) reduced the metabolism of these bioactive compounds due to the negative impact on cell growth. Similar results were reported by Wang et al. [3].
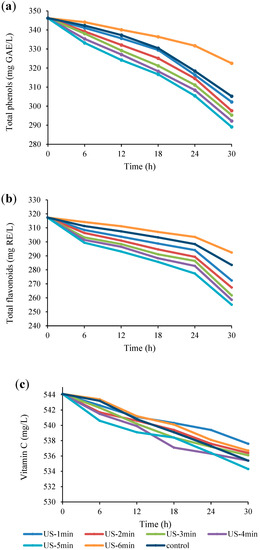
Figure 4.
Changes in total phenols (a), total flavonoids (b), and vitamin C (c) content in US-treated and non-US treated Bakraei juice during fermentation. Error bars reveal the standard deviation of each measurement in Bakraei juice during 30 h of fermentation. US-1 min: ultrasound treatment for 1 min, Control: non-ultrasound treated juice.
With respect to Figure 4c, there were insignificant (p > 0.05) differences in vitamin C content of US-treated samples and unsonicated juice, however it diminished markedly (p <0.05) throughout the fermentation time. These results are in good agreement with the findings of Hashemi and Jafarpour [11], who indicated a decline in vitamin C content of bergamot juice after 72 h fermentation with L. plantarum strains. This reduction may be related to the increase in the activity of ascorbate oxidase produced by the fermenting species [50]. Similarly, another research revealed that the oxidation process was the main cause of vitamin C loss [51].
3.5. Antioxidant Activity
The effect of US on the antioxidant activities of fermented Bakraei juice samples is shown in Figure 5. As can be seen, there was a notable enhancement in the inhibition percentage by ABTS and DPPH when the US time was increased from 1 to 5 min, while the 6-min US treatment led to a decrease in the inhibition percentage compared to the unsonicated juice (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference (p > 0.05) between the ABTS and DPPH levels of the control and US-6 min samples in the first 6 h of treatment, but from 12th h onwards, a significant difference was observed between all samples (p < 0.05). With respect to Figure 5a, b, the amount of DPPH increased from 56.4% to 92.3%, 75.4%, and 78.7%, and the initial level of ABTS (52.6%) enhanced to 88.2%, 71.3%, and 74.5% in US-5 min, US-6 min, and control samples, respectively, at the end of the fermentation time. The obtained results coincide with the findings of Wang et al. [3], who indicated that US treatment during apple juice fermentation led to a decrease in total phenolic compounds, while the ABTS radical scavenging activity of treated juices increased. Moreover, it has been demonstrated that fermentation of mulberry juice by Lactobacillus species for 36 h increased the antioxidant activity [26]. It has been found that the antiradical activities of fermented foods depends on various factors such as fermentation time, pH, microbial strains, dissolved oxygen, temperature, etc. [52]. Kim et al. [53] stated that certain metabolites produced by starter strains during fermentation may have a notable effect on enhancing the antioxidant activity of soybean paste. Meanwhile, some bioactive compounds produced during fermentation, such as peptides, xylooligosaccharides, etc. can play an important role in increasing the antioxidant properties of the final product [54]. Similarly, LAB has been shown to have antioxidant capacity [55]. Hence, in US-6 min treatment, lower number of viable cells resulted in less production of bioactive compounds and less antioxidant activity.
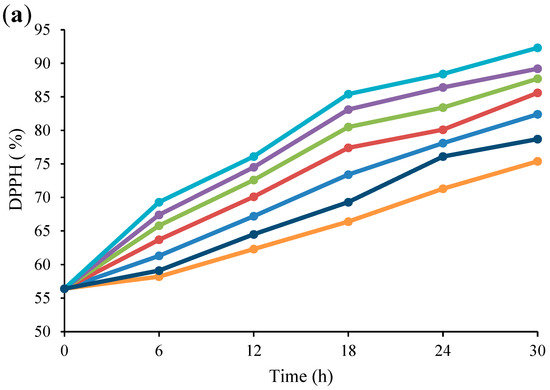
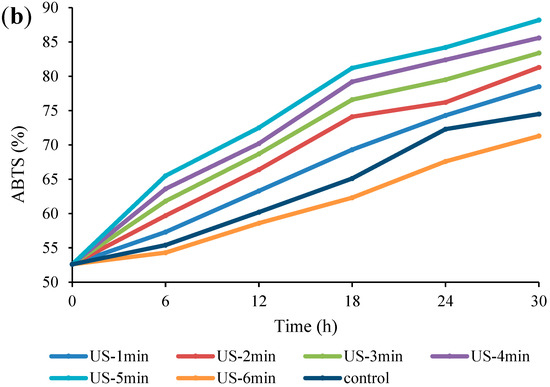
Figure 5.
Changes in antioxidant activity (DPPH (a), ABTS (b)) of US-treated and non-US treated Bakraei juice during fermentation. Error bars reveal the standard deviation of each measurement in Bakraei juice during 30 h of fermentation. US-1 min: ultrasound treatment for 1 min, Control: non-ultrasound treated juice.
3.6. Biological Properties
The influence of US process on some biological properties of fermented Bakraei juice samples including α-amylase inhibition and anti-inflammatory activity was also evaluated. Figure 6a, shows the variations in anti-hyperglycemic properties of juice samples throughout the fermentation period. Accordingly, the inhibition of α-amylase significantly (p < 0.05) increased during the fermentation time. In addition, US-5 min and US-6 min showed the highest and lowest inhibition rate of α-amylase, respectively. Similarly, Peláez-Acero et al. [56] showed that the highest inhibition of α-amylase was at 20 min, while as the US duration increased to 30 min, the enzyme inhibition significantly decreased in honey samples. This could be related to the positive effect of US on cell growth and production of functional compounds to inhibit α-amylase activity, whilst longer application of US possessed a negative effect on cell viability and growth due to the cavitation phenomenon [57]. Moreover, Gholamhosseinpour et al. [58] indicated that α-amylaseinhibition was higher in fermented milks treated with US and microwave compared to other processing including autoclave, microwave and US + autoclave. They also reported an increase in enzyme inhibition with fermentation time. Bioactive exopolysaccharides secreted by LAB and production of bioactive peptides during lactic acid fermentation have been considered as the main factors of α-amylase inhibition [59,60].
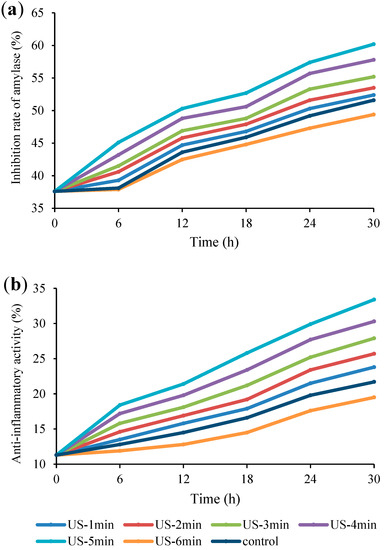
Figure 6.
Anti-hyperglycemic (a) and anti-inflammatory (b) activities of US-treated and non-US treated Bakraei juice during fermentation. Error bars reveal the standard deviation of each measurement in Bakraei juice during 30 h of fermentation. US-1 min: ultrasound treatment for 1 min, Control: non-ultrasound treated juice.
With respect to Figure 6b, data showed that the anti-inflammatory activity of juice samples significantly enhanced (p < 0.05) during the fermentation process. After 6 h of fermentation, insignificant difference (p > 0.05) was observed between the US-6 min, US-1 min, and control samples, while after 30 h of incubation, a significant difference (p < 0.05) was noticed between all the samples. The initial (11.3%) anti-inflammatory activity of Bakraei juices reached 33.4% and 19.5%, in the treatments of US-5 min and US-6 min, respectively, compared to the unsonicated juice (21.7%), after 30 h of fermentation. These findings are conform with the previous work, in which the fermentation of peach juice with L. fermentum and L. acidophilus resulted in increased anti-inflammatory activity [61]. This increase may be related to the production of some metabolites with anti-inflammatory potential, such as bacteriocins and natural acids, which are produced during fermentation with Lactobacillus species [62]. Furthermore, another study has shown that enhanced anti-inflammatory activity are associated with enhanced antioxidant activity in fermented pomegranate juice [63].
4. Conclusions
In this study, it was shown that the fermentation process can cause changes in the nutritional value and biological characteristics of Bakraei fruit juice. Ultrasound can increase the efficiency of the fermentation process and promote some of the biological characteristics of fruit juice including antioxidant capacity, α-amylase inhibition, and anti-inflammatory properties during this process. Of course, this process must be controlled since increasing the ultrasound treatment time can decrease the fermentation efficiency. In this research, increasing the ultrasound time to 6 min decreased the efficiency of the fermentation process. In future research, the effect of ultrasound power and other microorganisms can be investigated in this fruit juice and increase the scarce existing research related to this fruit.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M.B.H. and D.J.; methodology, S.M.B.H. and D.J.; formal analysis, S.M.B.H.; investigation, S.M.B.H.; resources, E.R.S. and F.J.B.; data curation, S.M.B.H. and D.J.; data curation, S.M.B.H., D.J., E.R.S. and F.J.B.; writing—original draft preparation, S.M.B.H., D.J., E.R.S. and F.J.B.; writing—review and editing, S.M.B.H., D.J., E.R.S. and F.J.B.; visualization, S.M.B.H., D.J., E.R.S. and F.J.B.; supervision, S.M.B.H., D.J., E.R.S. and F.J.B.; project administration, S.M.B.H. and D.J., funding acquisition, S.M.B.H. and D.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Research data are not shared.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ojha, K.S.; Mason, T.J.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Kerry, J.P.; Tiwari, B.K. Ultrasound Technology for Food Fermentation Applications. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Iborra, S.; Velty, A. Chemical Routes for the Transformation of Biomass into Chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2411–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Han, Y.; Manickam, S.; Show, P.L. Application of Ultrasonication at Different Microbial Growth Stages during Apple Juice Fermentation by Lactobacillus Plantarum: Investigation on the Metabolic Response. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 73, 105486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.N.; Vicente, A.A. Environmental Impact of Novel Thermal and Non-Thermal Technologies in Food Processing. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1936–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.M.B.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Saraiva, J.A.; Jambrak, A.R.; Barba, F.J.; Mota, M.J. Effect of Ultrasound on Lactic Acid Production by Lactobacillus Strains in Date (Phoenix Dactylifera Var. Kabkab) Syrup. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 2635–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butz, P.; Tauscher, B. Emerging Technologies: Chemical Aspects. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjha, M.M.A.N.; Irfan, S.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Shafique, B.; Kanwal, R.; Pateiro, M.; Arshad, R.N.; Wang, L.; Nayik, G.A.; Roobab, U. Sonication, a Potential Technique for Extraction of Phytoconstituents: A Systematic Review. Processes 2021, 9, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Kumar, S.; Bhat, H.F.; Aadil, R.M.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Jayawardena, S.R.; Brennan, C.S. Ultrasonication as an Emerging Technology for Processing of Animal Derived Foods: A Focus on in Vitro Protein Digestibility. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 124, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Khan, M.K. Applications of Ultrasound in Food Technology: Processing, Preservation and Extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 813–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, T.S.; Moharram, H.A.; Shaltout, O.E.; Asker, D.; Youssef, M.M. Applications of Ultrasound in Analysis, Processing and Quality Control of Food: A Review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 410–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.M.B.; Jafarpour, D. Fermentation of Bergamot Juice with Lactobacillus plantarum Strains in Pure and Mixed Fermentations: Chemical Composition, Antioxidant Activity and Sensorial Properties. LWT 2020, 131, 109803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarpour, D.; Hashemi, S.M.B.; Abedi, E.; Mousavifard, M.; Sayadi, M. Comparison between Response Surface Methodology and Genetic Algorithm Analysis to Optimize Lactic Acid Production by Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus acidophilus under Ultrasonic Pretreatment. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2021, 368, fnac005. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, C.; Xiong, F.; He, R.; Zhang, W.; Ma, H. Effects of Low-Intensity Ultrasound on the Growth, Cell Membrane Permeability and Ethanol Tolerance of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 36, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, A.Z.; Ajit, A.; Yunus, R.M.; Chisti, Y. Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation Enhances Bioethanol Productivity. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 54, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.P.; Lee, Y.K.; Zhou, W. Effect of High Intensity Ultrasound on Carbohydrate Metabolism of Bifidobacteria in Milk Fermentation. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Daccache, M.; Koubaa, M.; Salameh, D.; Maroun, R.G.; Louka, N.; Vorobiev, E. Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation for Cider Production from Lebanese Apples. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 63, 104952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golein, B.; Bigonah, M.; Azadvar, M.; Golmohammadi, M. Analysis of Genetic Relationship between ‘Bakraee’(Citrus Sp.) and Some Known Citrus Genotypes through SSR and PCR-RFLP Markers. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 148, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Barrett, H.C.; Rhodes, A.M. A Numerical Taxonomic Study of Affinity Relationships in Cultivated Citrus and Its Close Relatives. Syst. Bot. 1976, 1, 105–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patkar, A.N.; Desai, N.V.; Ranage, A.A.; Kalekar, K.S. A Review on Aegle Marmelos: A Potential Medicinal Tree. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2012, 3, 86–91. [Google Scholar]
- Charoensiddhi, S.; Anprung, P. Bioactive Compounds and Volatile Compounds of Thai Bael Fruit (Aegle marmelos (L.) Correa) as a Valuable Source for Functional Food Ingredients. Int. Food Res. J. 2008, 15, 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Razmi, N.; Jolodar, G.H.; Ebrahimi, H.; Baghshani, H. Effect of Aegle Marmelos Fruit Juice Concentrate on Serum Glucose and Lipid Level and ALT/AST Acivities in Diabetic Rats. J. Kerman Univ. Med. Sci. 2006, 13, 240–245. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Li, T.; Qi, J.; Jiang, T.; Xu, H.; Lei, H. Effects of Lactic Acid Fermentation-Based Biotransformation on Phenolic Profiles, Antioxidant Capacity and Flavor Volatiles of Apple Juice. LWT 2020, 122, 109064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.M.B.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Barba, F.J.; Nemati, Z.; Shokofti, S.S.; Alizadeh, F. Fermented Sweet Lemon Juice (Citrus limetta) Using Lactobacillus plantarum LS5: Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Teng, J.; Lyu, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M. Enhanced Antioxidant Activity for Apple Juice Fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum ATCC14917. Molecules 2018, 24, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwaw, E.; Ma, Y.; Tchabo, W.; Apaliya, M.T.; Wu, M.; Sackey, A.S.; Xiao, L.; Tahir, H.E. Effect of Lactobacillus Strains on Phenolic Profile, Color Attributes and Antioxidant Activities of Lactic-Acid-Fermented Mulberry Juice. Food Chem. 2018, 250, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Goyal, A. Antioxidant Activity and γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Producing Ability of Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum DM5 Isolated from Marcha of Sikkim. LWT-food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cagno, R.; Filannino, P.; Vincentini, O.; Cantatore, V.; Cavoski, I.; Gobbetti, M. Fermented Portulaca oleracea L. Juice: A Novel Functional Beverage with Potential Ameliorating Effects on the Intestinal Inflammation and Epithelial Injury. Nutrients 2019, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.M.B.; Roohi, R.; Mahmoudi, M.R.; Granato, D. Modeling Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes, Shigella sonnei, Byssochlamys fulva and Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Ascorbic Acid and β-Carotene Degradation Kinetics in Tangerine Juice by Pulsed-Thermosonication. LWT 2019, 111, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wei, Z.; Yin, B.; Man, C.; Jiang, Y. Enhancement of Functional Characteristics of Blueberry Juice Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum. LWT 2021, 139, 110590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-Soto, S.A.; Beaufort, S.; Bouajila, J.; Souchard, J.-P.; Renard, T.; Rollan, S.; Taillandier, P. Impact of Fermentation Conditions on the Production of Bioactive Compounds with Anticancer, Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties in Kombucha Tea Extracts. Process Biochem. 2019, 83, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, S.; Dai, C.; Sun, L.; Sun, W.; Tang, Y.; Xiong, F.; He, R.; Ma, H. Effects of Ultrasound on Microbial Growth and Enzyme Activity. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 37, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.M.P.; Lee, Y.K.; Zhou, W. Stimulating Fermentative Activities of Bifidobacteria in Milk by Highintensity Ultrasound. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mett, H.; Schacher, B.; Wegmann, L. Ultrasonic Disintegration of Bacteria May Lead to Irreversible Inactivation of β-Lactamase. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1988, 22, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abesinghe, A.; Islam, N.; Vidanarachchi, J.K.; Prakash, S.; Silva, K.; Karim, M.A. Effects of Ultrasound on the Fermentation Profile of Fermented Milk Products Incorporated with Lactic Acid Bacteria. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 90, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.M.B.; Jafarpour, D. Ultrasound and Malic Acid Treatment of Sweet Lemon Juice: Microbial Inactivation and Quality Changes. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyasena, P.; Mohareb, E.; McKellar, R.C. Inactivation of Microbes Using Ultrasound: A Review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 87, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sango, D.M.; Abela, D.; McElhatton, A.; Valdramidis, V.P. Assisted Ultrasound Applications for the Production of Safe Foods. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1067–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, Z.E.; Mousavi, S.M.; Razavi, S.H.; Hadinejad, M.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Mirzapour, M. Effect of Fermentation of Pomegranate Juice by Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus acidophilus on the Antioxidant Activity and Metabolism of Sugars, Organic Acids and Phenolic Compounds. Food Biotechnol. 2013, 27, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamhosseinpour, A.; Hashemi, S.M.B. Ultrasound Pretreatment of Fermented Milk Containing Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum AF1: Carbohydrate Metabolism and Antioxidant Activity. J. Food Process. Eng. 2019, 42, e12930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nöbel, S.; Ross, N.-L.; Protte, K.; Körzendörfer, A.; Hitzmann, B.; Hinrichs, J. Microgel Particle Formation in Yogurt as Influenced by Sonication during Fermentation. J. Food Eng. 2016, 180, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, K. Evaluating Ultrasound Pre-Treatment as a Tool for Improving the Process of a Fermented Beverage Made from Pineapple by-Products. Brazilian J. Food Technol. 2022, 25, e2021116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeredjian, R.; Bohris, C.; Hansen, A.; Katus, H.A.; Kuecherer, H.F.; Hardt, S.E. Impact of Microbubbles on Shock Wave-Mediated DNA Uptake in Cells in Vitro. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2007, 33, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezcan, F.; Gültekin-Özgüven, M.; Diken, T.; Özçelik, B.; Erim, F.B. Antioxidant Activity and Total Phenolic, Organic Acid and Sugar Content in Commercial Pomegranate Juices. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuanyun, D.; Bochu, W.; Chuanren, D.; Sakanishi, A. Low Ultrasonic Stimulates Fermentation of Riboflavin Producing Strain Ecemothecium Ashbyii. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2003, 30, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.B.; Roblain, D.; Chammen, N.; Thonart, P.; Hamdi, M. Antioxidant Phenolic Compounds Loss during the Fermentation of Chétoui Olives. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiquzzaman, S.M.; Kong, I.-S.; Kim, J.-M. Enhancement of Antioxidant Activity, Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Content of Saccharina japonica by Submerged Fermentation with Aspergillus Oryzae. KSBB J. 2015, 30, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Dun, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Ling, J. Effects on Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Content, Antioxidant Properties, and Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Activity of Beans by Solid-State Fermentation with Cordyceps Militaris. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebo, O.A.; Njobeh, P.B.; Kayitesi, E. Fermentation by Lactobacillus fermentum Strains (Singly and in Combination) Enhances the Properties of Ting from Two Whole Grain Sorghum Types. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 82, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, C.; Pan, S. Effect of Thermal Treatment on Carotenoids, Flavonoids and Ascorbic Acid in Juice of Orange Cv. Cara Cara. Food Chem. 2018, 265, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbienė, S.-A.; Mitkutė, D. Changes of Vitamin C during Milk Fermentation. Milchwissenschaft 2007, 62, 130–132. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, S.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, Y.-C.; Choi, I.; Kim, G.-B. Effect of Fermentation on the Antioxidant Activity in Plant-Based Foods. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Choi, J.N.; Kang, D.; Son, G.H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Choi, H.-K.; Kwon, D.Y.; Lee, C.H. Correlation between Antioxidative Activities and Metabolite Changes during Cheonggukjang Fermentation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veenashri, B.R.; Muralikrishna, G. In Vitro Anti-Oxidant Activity of Xylo-Oligosaccharides Derived from Cereal and Millet Brans–A Comparative Study. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyropoulos, B.G.; Misiakos, E.P.; Fotiadis, C.; Stoidis, C.N. Antioxidant Properties of Probiotics and Their Protective Effects in the Pathogenesis of Radiation-Induced Enteritis and Colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peláez-Acero, A.; Garrido-Islas, D.B.; Campos-Montiel, R.G.; González-Montiel, L.; Medina-Pérez, G.; Luna-Rodríguez, L.; González-Lemus, U.; Cenobio-Galindo, A.d.J. The Application of Ultrasound in Honey: Antioxidant Activity, Inhibitory Effect on α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase, and in Vitro Digestibility Assessment. Molecules 2022, 27, 5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.-Y.; Chu, Y.-L.; Sridhar, K.; Tsai, P.-J. Effect of Ultrasound, High-Pressure Processing, and Enzymatic Hydrolysis on Carbohydrate Hydrolyzing Enzymes and Antioxidant Activity of Lemon (Citrus limon) Flavedo. LWT 2021, 138, 110511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamhosseinpour, A.; Hashemi, S.M.B.; Jahromi, L.R.; Sourki, A.H. Conventional Heating, Ultrasound and Microwave Treatments of Milk: Fermentation Efficiency and Biological Activities. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 110, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.; Al-Nuaimi, A.K.; Al-Mahadin, S.; Liu, S.-Q. In Vitro Investigation of Anticancer and ACE-Inhibiting Activity, α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Inhibition, and Antioxidant Activity of Camel Milk Fermented with Camel Milk Probiotic: A Comparative Study with Fermented Bovine Milk. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dhaheri, A.S.; Al-Hemeiri, R.; Kizhakkayil, J.; Al-Nabulsi, A.; Abushelaibi, A.; Shah, N.P.; Ayyash, M. Health-Promoting Benefits of Low-Fat Akawi Cheese Made by Exopolysaccharide-Producing Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum Isolated from Camel Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7771–7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.M.B.; Jafarpour, D.; Jouki, M. Improving Bioactive Properties of Peach Juice Using Lactobacillus Strains Fermentation: Antagonistic and Anti-Adhesion Effects, Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties, and Maillard Reaction Inhibition. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.D.D.O.; do Carmo, F.L.R.; de Oliveira Junior, A.; Langella, P.; Chatel, J.-M.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Azevedo, V.; de Azevedo, M.S. Use of Wild Type or Recombinant Lactic Acid Bacteria as an Alternative Treatment for Gastrointestinal Inflammatory Diseases: A Focus on Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Mucositis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filannino, P.; Azzi, L.; Cavoski, I.; Vincentini, O.; Rizzello, C.G.; Gobbetti, M.; Di Cagno, R. Exploitation of the Health-Promoting and Sensory Properties of Organic Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Juice through Lactic Acid Fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 163, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).