Ferrous-Iron-Activated Sulfite-Accelerated Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production from Waste-Activated Sludge Fermentation: Process Assessment and Underlying Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
2.3. DNA Extraction and Illumina Miseq Sequencing
2.4. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
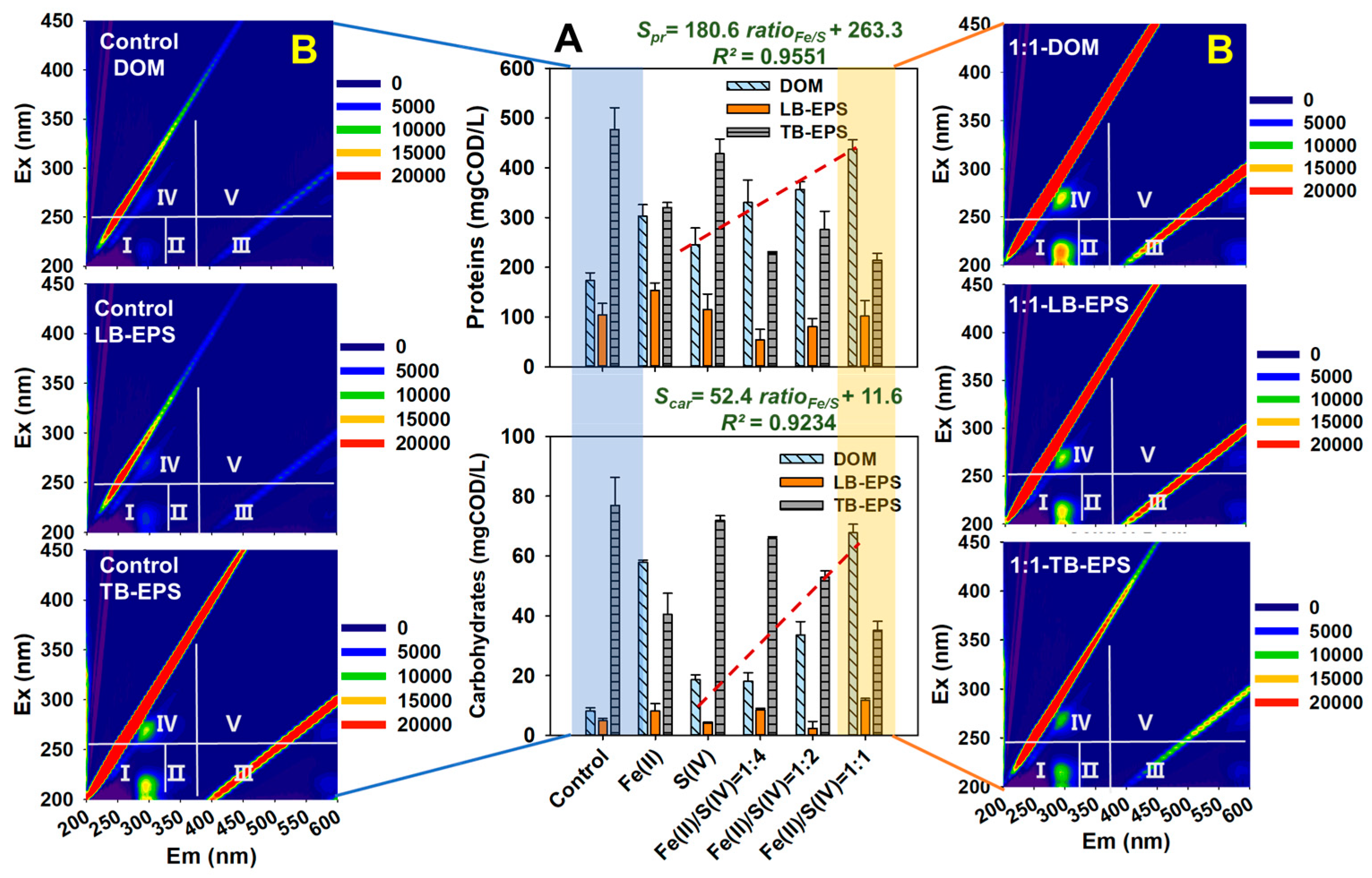
3.1. Exfoliation and Release of Extracellular Polymers in WAS Flocs
3.2. Changes in Soluble Organics during Fermentation
3.3. Influence of Fe(II)/S(IV) Dosages on Acidogenic Fermentation
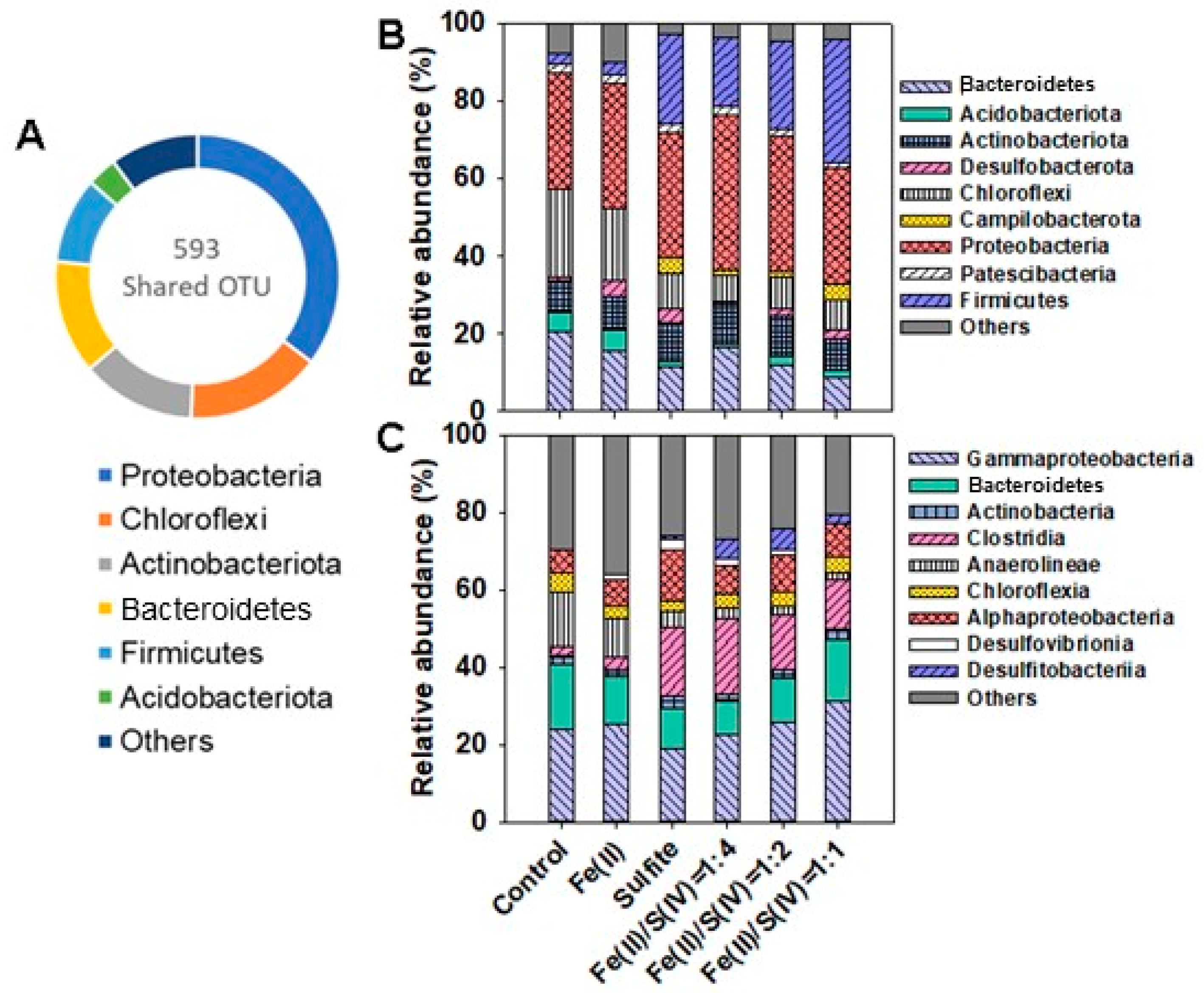
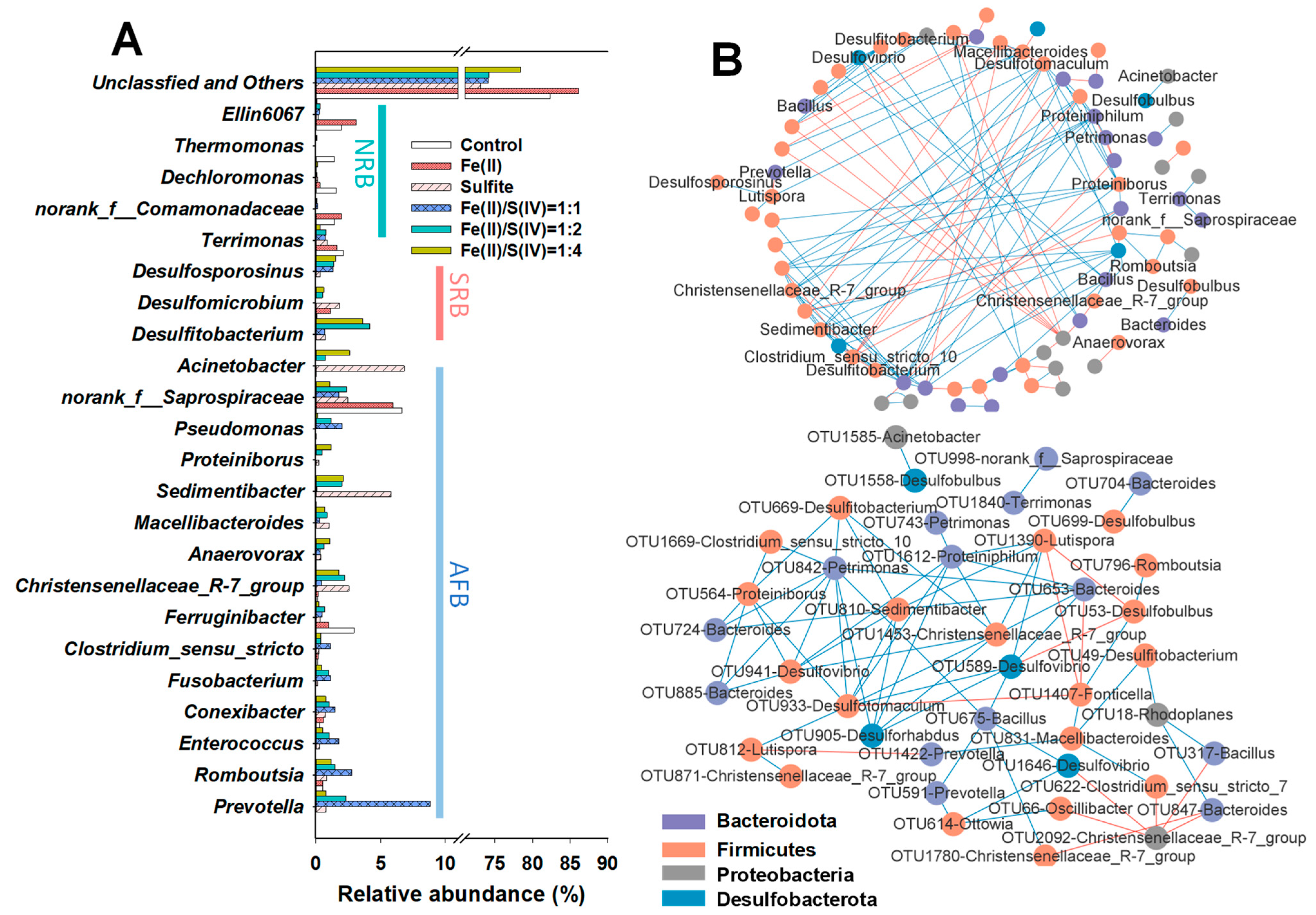
3.4. Microbial Community Diversity and MENs Analysis
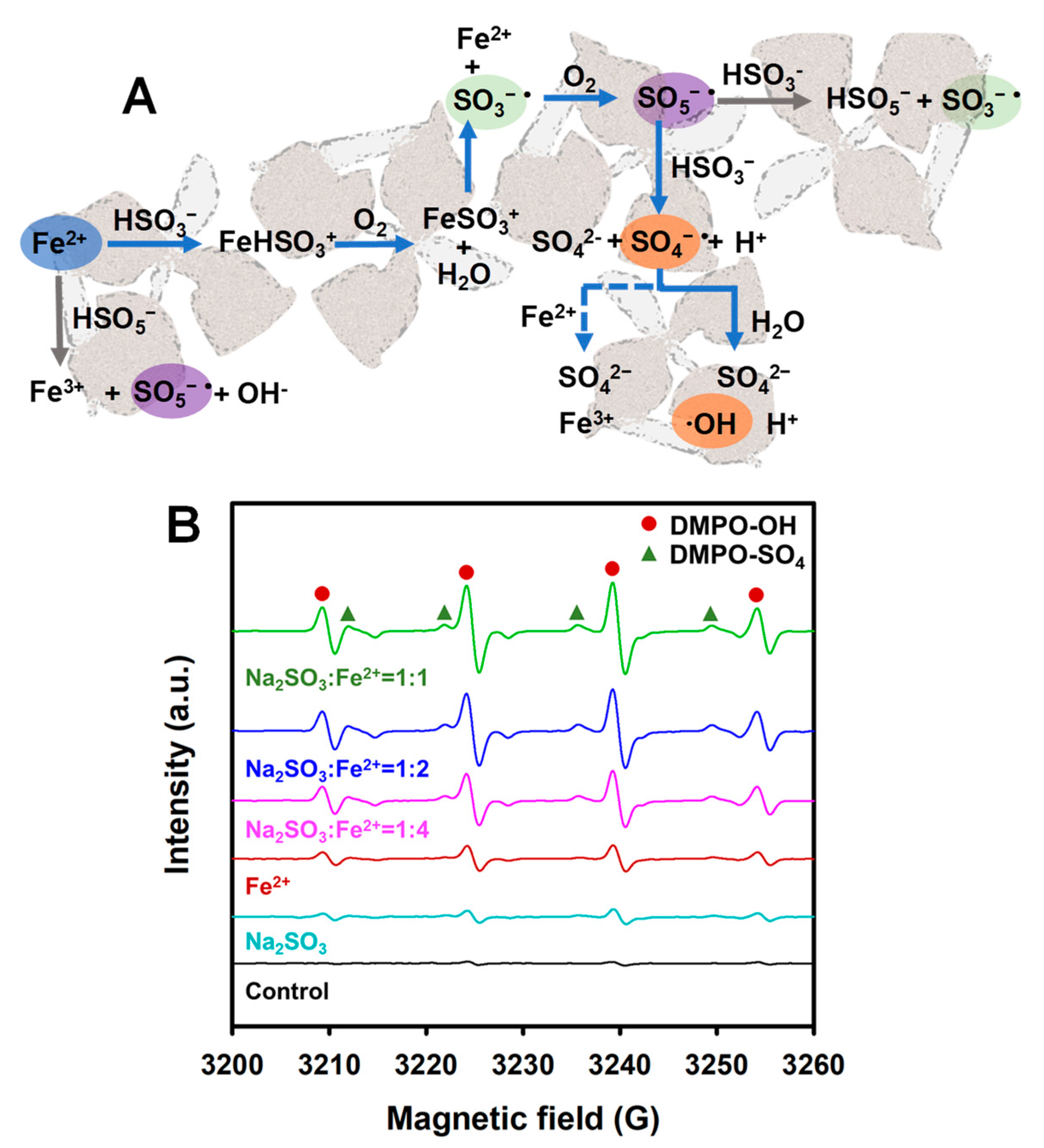
3.5. Potential Mechanism of Fe(II)-Activated Sulfite Pretreatment for Accelerating WAS Acidogenic Fermentation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Yang, X.; Tan, X.; Wan, C.; Liu, X. Sewage sludge treatment technology under the requirement of carbon neutrality: Recent progress and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Gong, H.; Dai, X. High-solid anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge: Achievements and perspectives. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Zhong, H.; Li, X.; Du, W.; Li, X.; Chen, R.; Zeng, G. A novel pretreatment process of mature landfill leachate with ultrasonic activated persulfate: Optimization using integrated Taguchi method and response surface methodology. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 98, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, R.; Zhao, Q. Distribution and removal of antibiotic resistance genes during anaerobic sludge digestion with alkaline, thermal hydrolysis and ultrasonic pretreatments. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appels, L.; Baeyens, J.; Degreve, J.; Dewil, R. Principles and potential of the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 755–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittmann, T.; Steinmetz, H. Potential for polyhydroxyalkanoate production on German or European municipal waste water treatment plants. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Chen, Y. Using Sludge Fermentation Liquid To Improve Wastewater Short-Cut Nitrification-Denitrification and Denitrifying Phosphorus Removal via Nitrite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8957–8963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Huang, S.; Zhou, A.; Zhou, G.; Ren, N.; Wang, A.; Zhuang, G. Hydrogen generation in microbial electrolysis cell feeding with fermentation liquid of waste activated sludge. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 13859–13864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, G.; Parker, W. Investigation of the impacts of thermal pretreatment on waste activated sludge and development of a pretreatment model. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5245–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, A.; Ortega-Martinez, E.; Pages-Diaz, J.; Montalvo, S.; Huilinir, C. Micro-Aerobic Pre-Treatment vs. Thermal Pre-Treatment of Waste Activated Sludge for Its Subsequent Anaerobic Digestion in Semi-Continuous Digesters: A Comparative Study. Fermentation 2022, 8, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, S.; Peng, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, L.; Zhao, M. Anaerobic digestion using ultrasound as pretreatment approach: Changes in waste activated sludge, anaerobic digestion performances and digestive microbial populations. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 139, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Shi, Z.; Chen, S.Y.; Luo, L. Feasibility of using lysozyme to reduce excess sludge in activated sludge process. J. Cent. South Univ. 2013, 20, 2472–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Jin, X.; Zhang, Y. Sequential pretreatment for cell disintegration of municipal sludge in a neutral Bio-electro-Fenton system. Water Res. 2018, 135, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.-W.; Liu, W.-Z.; Gao, Q.; Tang, C.-C.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.-C.; Zhou, A.-J.; Wang, A.-J. Potassium ferrate addition as an alternative pre-treatment to enhance shortchain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, G.-D.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Wang, Y.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Zhou, D.-M. Sulfate radical-based degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls: Effects of chloride ion and reaction kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 227, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Q.; Zeng, G.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Gong, J.; Ye, J.; et al. Mechanisms of peroxymonosulfate pretreatment enhancing production of short-chain fatty acids from waste activated sludge. Water Res. 2019, 148, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Yao, G.; Lai, B. The electrochemical advanced oxidation processes coupling of oxidants for organic pollutants degradation: A mini-review. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 2139–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zhu, F.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Wei, L.; Li, Q.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Q. A Review Study on Sulfate-Radical-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes for Domestic/Industrial Wastewater Treatment: Degradation, Efficiency, and Mechanism. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 592056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, D.; Chen, X.e.; Wu, B. Application of zero-valent iron/sulfite system for aerobically digested sludge conditioning. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Lee, K.-M.; Kim, H.-E.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, C.; Lee, C. Disintegration of Waste Activated Sludge by Thermally-Activated Persulfates for Enhanced Dewaterability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7106–7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Qiu, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Pang, S. Sulfite enhanced transformation of iopamidol by UV photolysis in the presence of oxygen: Role of oxysulfur radicals. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Wu, F. Transition metal catalyzed sulfite auto-oxidation systems for oxidative decontamination in waters: A state-of-the-art minireview. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Wang, Z.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Liu, M.; Deng, Y.; Tang, M.; Liao, G.; Hu, A.; Zhang, W. Understanding synergistic mechanisms of ferrous iron activated sulfite oxidation and organic polymer flocculation for enhancing wastewater sludge dewaterability. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, L.; Wu, F.; Ge, L. Enhanced Decolorization of Orange II Solutions by the Fe(II)-Sulfite System under Xenon Lamp Irradiation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 10089–10094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, F.; Zeng, Q.; Hao, T.; Ekama, G.A.; Hao, X.; Chen, G. Achieving methane production enhancement from waste activated sludge with sulfite pretreatment: Feasibility, kinetics and mechanism study. Water Res. 2019, 158, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.-L.; Ma, X.-d.; Hou, Y.-N.; Ren, N.-Q.; Wang, A.-J. Relationship between functional bacteria in a denitrification desulfurization system under autotrophic, heterotrophic, and mixotrophic conditions. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Cheng, R.; Chen, F.; Lin, X.-Q.; Yao, X.-J.; Liang, B.; Huang, C.; Sun, K.; Wang, A.-J. Selective stress of antibiotics on microbial denitrification: Inhibitory effects, dynamics of microbial community structure and function. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Wei, Y.; Fan, Y.; Shyryn, A.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Yuan, J.; Yue, X. Sulfate Reduction-Mediated Syntrophic Microbiomes Accelerated Waste-Activated Sludge Fermentation on the Basis of SO(4)(center dot-)Oxidation and Eliminated Superfluous Sulfate. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 9325–9334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, A.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, A.; Yue, X. Extracellular polymeric substance decomposition linked to hydrogen recovery from waste activated sludge: Role of peracetic acid and free nitrous acid co-pretreatment in a prefermentation-bioelectrolysis cascading system. Water Res. 2020, 176, 115724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Liu, H.; Varrone, C.; Shyryn, A.; Defemur, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Yue, X. New insight into waste activated sludge acetogenesis triggered by coupling sulfite/ferrate oxidation with sulfate reduction-mediated syntrophic consortia. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Karakashev, D.B.; Wang, J.; Angelidaki, I. Biological caproate production by Clostridium kluyveri from ethanol and acetate as carbon sources. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azman, S.; Khadem, A.F.; Van Lier, J.B.; Zeeman, G.; Plugge, C.M. Presence and Role of Anaerobic Hydrolytic Microbes in Conversion of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Biogas Production. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 2523–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q. Waste activated sludge hydrolysis and short-chain fatty acids accumulation under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions: Effect of pH. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3735–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Du, M.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, D.; Yang, Q.; Yang, G.; Li, X. Sulfite serving as a pretreatment method for alkaline fermentation to enhance short-chain fatty acid production from waste activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitamo, T.; Treu, L.; Boldrin, A.; Sartori, C.; Angelidaki, I.; Scheutz, C. Microbial population dynamics in urban organic waste anaerobic co-digestion with mixed sludge during a change in feedstock composition and different hydraulic retention times. Water Res. 2017, 118, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, H.; Liu, Z. Influence of zinc oxide nanoparticles on anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge and microbial communities. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 5580–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Fan, W. Long-term bioremediation of cadmium contaminated sediment using sulfate reducing bacteria: Perspective on different depths of the sediment profile. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyzer, G.; Stams, A.J. The ecology and biotechnology of sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.; Li, Q.; Cheng, C.; Shen, H.; Liu, S.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, S. Bio-competitive exclusion of sulfate-reducing bacteria and its anticorrosion property. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 194, 107480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Cai, Q.; Lin, W.; Chen, B. Towards sulfide removal and sulfate reducing bacteria inhibition: Function of biosurfactants produced by indigenous isolated nitrate reducing bacteria. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Ding, J.; Wan, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, A.; Ma, J. Enhanced degradation of organic contaminants by zero-valent iron/sulfite process under simulated sunlight irradiation. Water Res. 2019, 149, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Microbiome. | Similarity Threshold | Network Size | Links | Averaged Connectivity | Averaged Path Distance | Averaged Clustering Coefficient | Modularity (Fast Greedy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fermentation | 0.97 | 76 | 134 | 3.526 | 3.839 | 0.102 | 0.551 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, F.; Guo, X.; Yin, X.; Cui, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhou, A. Ferrous-Iron-Activated Sulfite-Accelerated Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production from Waste-Activated Sludge Fermentation: Process Assessment and Underlying Mechanism. Fermentation 2023, 9, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9010020
Cao F, Guo X, Yin X, Cui Z, Liu S, Zhou A. Ferrous-Iron-Activated Sulfite-Accelerated Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production from Waste-Activated Sludge Fermentation: Process Assessment and Underlying Mechanism. Fermentation. 2023; 9(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Fang, Xujiang Guo, Xiaoyun Yin, Zhixuan Cui, Shuli Liu, and Aijuan Zhou. 2023. "Ferrous-Iron-Activated Sulfite-Accelerated Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production from Waste-Activated Sludge Fermentation: Process Assessment and Underlying Mechanism" Fermentation 9, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9010020
APA StyleCao, F., Guo, X., Yin, X., Cui, Z., Liu, S., & Zhou, A. (2023). Ferrous-Iron-Activated Sulfite-Accelerated Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production from Waste-Activated Sludge Fermentation: Process Assessment and Underlying Mechanism. Fermentation, 9(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9010020







