Abstract
Industrial beer production generates brewer’s spent grains (BSG) as a primary solid waste. The disposal of industrial waste can cause negative environmental side effects, including greenhouse gas emissions. This study evaluated the dry anaerobic digestion (AD) of BSG for bioenergy recovery as a solution toward a more sustainable brewery. The laboratory-scale agitated tank batch reactor (6.8 L) was started up with BSG (25%), mesophilic inoculum (45%), and water (30%). The experimental results showed 82.12% solids biodegradation, 57.38% soluble chemical oxygen demand removal, and an accumulated methane yield of 10.53 L CH4 kg−1 TVS. The methane production efficiency was evaluated by the modified Gompertz, Cone, and first-order kinetic models. The Cone model fitted methane evolution better than the modified Gompertz and first-order kinetic models. The biogas produced from the dry AD of BSG could generate electricity (0.133 MWh ton−1) and heat (598.45 MJ ton−1), mitigating 0.0099 and 0.0335 tCO2eq ton−1 BSG, respectively, for electricity and heat. The implementation of dry AD could supply 7.38% of the electricity and 6.86% of the heat required for beer production. Finally, in a biorefinery concept, dry AD can be an alternative route for solid waste management and bioenergy recovery, contributing to reduce the environmental impact of breweries.
Keywords:
biomethane; circular economy; biogas; methane; electricity; energy; greenhouse gas emissions; biorefinery 1. Introduction
The Brazilian beer industry reached 1549 facilities in 2021, an increase of 12% compared to 2020. In addition, 14.3 billion liters of beer were produced in 2021, contributing to approximately 1.5% of the Brazilian gross domestic product [1]. The essential raw material for beer formulation is barley [2], and Brazil required approximately 1 million tons of barley in 2020 [3,4]. Nonetheless, widely associated with industrial production, wastewater and solid waste from the food industry are continually growing [5]. In the case of beer production, 20 kg of brewer’s spent grain (BSG) is generated per 100 L of beer produced [6,7,8]. Hence, considering Brazilian beer industry, the generation of BSG is estimated at 2.8 × 106 tons per year (wet basis) [9]. Without environmentally friendly management, industrial waste can cause several environmental side effects due to incorrect disposal [10,11]. Improper organic waste disposal increases greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, the proliferation of disease vectors, soil and groundwater contamination [12].
Waste management and biofuel policies could be trade-off alternatives to increase the use of bioenergy from the correct management of agri-food industry waste while contributing to energy efficiency and GHG mitigation [13,14]. Anaerobic digestion (AD) has been widely investigated as a promising technological route for waste management and bioenergy recovery in the food industry [15]. Despite the advantages of AD for treating liquid waste, the AD of solid waste (or dry AD) is still challenging for industrial implementation [16]. AD with a high solids content has received much attention in recent years [17]. Bi et al. [18] evaluated the digestion of chicken manure, finding that wet AD (0.35 m3 CH4 kg−1 solids) produced a higher content of methane compared to dry AD (0.18 m3 CH4 kg−1 solids). The same profile was obtained for sweet potato vine [19], municipal solid waste organic fractions [20], corn stover [21], and other industrial wastes. A high solid AD can be attractive to industry implementation since the digester can treat a high amount of solid waste with low water demand and energy consumption [22]. Additionally, some solid wastes generated by the food industry can present a composition rich in lignocellulose, which figures as an additional challenge to AD since lignin is a recalcitrant compound and can limit methane efficiency [23].
From an environmental perspective, the digestate obtained after AD can be upgraded into a biofertilizer for agricultural applications [24]. From the energy side, biogas has a high calorific content (35.59 MJ m−3), being highly suitable for electricity and heat combined generation [25,26]. Moreover, agro-industrial supply chains are increasingly required to lay on circular economy principles. For this, innovative industrial arrangements, including waste management systems to address technological parameters to subsidize future investments to adopt the AD of solid wastes, are required [27]. Industrial waste management systems can generate a sort of benefit [28]. However, few studies demonstrate the technical-economic-environmental parameters of the production of bioenergy and biofertilizer from dry AD [17]. The operational parameters of dry AD and energy recovery from biogas can support a breakthrough for industrial implementation [29].
The circular economy concept is based on four main pillars (reduction, reuse, recovery, and recycling) towards economic growth and resource consumption optimization, especially materials and energy [30,31]. Beyond, through the development of new processes, economically and environmentally viable, it is possible to flourish the circular economy transition by minimizing resource extraction, maximizing reuse, and developing new business models [32]. Notwithstanding, with the recovery of biofuels and value-added products, the biorefinery concept is fully fitted to circular economy development [33]. In a biorefinery, sustainable processes are integrated to convert biomass into value-added products and bioenergy [34,35]. Additionally, the biorefinery’s main objective is to optimize the use of resources and to minimize the final waste generated from the industrial process while maximizing environmental and economic amelioration [34,35]. A biorefinery for the beer industry could be proposed by using BSG to produce bioactive compounds, such as xylitol, lactic acid, activated carbon, and phenolic acids [36]. AD can be an additional technological route for BSG valorization in a circular economy concept, contributing to an industrial environmental burden relief.
Therefore, this study assessed the dry AD of BSG for bioenergy recovery to support a more sustainable brewery. For this, an AD reactor with a high solids content was started-up, and its operational performance was assessed. Methane production was evaluated according to the modified Gompertz, Cone, and first-order kinetic models. The potential for electricity, heat generation, and avoided GHG emissions were estimated from the AD reactor experimental dataset. Hence, this study fills in the research gap on the kinetics of methane production from the dry AD of BSG by proposing an integrated waste management system for electricity, heat, and biofertilizer production in a biorefinery concept, advocating the circular economy transition for the beer industry.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Solid Wastes and Inoculum
BSG (wet basis) was provided by Ambev Brewery (Jaguariúna, SP, Brazil). The BSG was oven-dried (105 °C, 8 h), packed, and stored (−18 °C) for later use. The granular mesophilic inoculum was obtained from the treatment of soft drink wastewater without pathogens in a full-scale up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor operated at 35 °C (Coca Cola Femsa Company, Jundiaí, SP, Brazil). Before the AD, the inoculum was acclimated at mesophilic temperature (35 °C) for 48 h and stirred at 50 rpm. Table 1 displays the characterization of the BSG and mesophilic inoculum used for dry AD.

Table 1.
Characterization of BSG and mesophilic inoculum.
2.2. Reactor Configuration for Dry AD
Figure 1 shows the laboratory reactor used for dry AD of BSG.
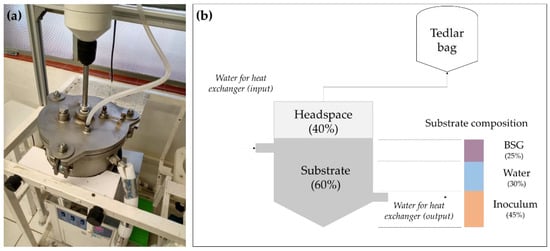
Figure 1.
Representation of the laboratory reactor for dry AD of BSG. (a) Laboratory reactor; (b) description of the reactor configuration. Adapted from Sganzerla et al. [29], with permission from Springer Nature.
The laboratory-scale agitated tank reactor (6.8 L) was operated in batch mode for 40 days. The reactor’s initial feed filled 60% of the volume for the substrate mixture (4.08 L), and 40% of the headspace was left for biogas production (2.72 L). The substrate mixture was composed of 25% BSG on a dry basis (192.35 g), 45% wet inoculum (1.83 L), and 30% water (1.22 L). The system was kept at a mesophilic temperature (35 °C) with a thermostatic water bath. Initially, the substrate pH was adjusted to approximately 6 with the addition of NaOH 6 mol L−1. During AD, the substrate pH was held between 7 and 8 to support methanogenic reactions [37]. The biogas was collected daily in a Tedlar bag (Supelco Analytical) coupled with the reactor. The digestate was analyzed to control the process efficiency.
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis
The digestate was analyzed according to the Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater [38]. The pH (method 4500-H+ B) and the solids (total, volatile, and fixed) (method 2540B) were directly determined from raw digestate. For the determination of alkalinity (method 2320 B), ammonia nitrogen (method 45000-NH3 C), and soluble chemical oxygen demand (COD) (method 5220 D), the digestate (5 g) was solubilized with deionized water (50 mL) under stirring (250 rpm) for 1 h. The solution was filtered on qualitative filter paper, and the liquid fraction was used for the analysis. The solids biodegradation and COD removal were calculated considering the initial (day 0 of AD) and final (day 40 of AD) values obtained.
2.4. Biogas Production, Composition, and Yield
The biogas volume was measured with a syringe. The accumulated biogas volume was determined by the sum of the daily biogas produced. The biogas composition was determined by gas chromatography equipped with a thermal conductivity detector. Biogas separation was conducted in a micropacked column (ShinCarbon, ST 50/80 mesh), and the chromatographic conditions were selected based on previous studies [39,40]. After the measurement of the biogas composition, the accumulated methane yield was calculated according to Equation (1).
where V is the biogas volume (mL); n is the number of days analyzed; is the percentage of methane in the biogas (%); and TVS is the content of volatile solids in the reactor.
2.5. Kinetic Analysis
The cumulative methane production from the dry AD of BSG was evaluated according to the modified Gompertz (Equation (2)), Cone (Equation (3)), and first-order kinetics (Equation (4)) models. The kinetic analysis was conducted using SigmaPlot® software (Systat Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA).
where M is the cumulative methane volume (mL); P is the methane production potential (mL); Rm is the maximum methane production rate (mL h−1); e = 2.718; λ is the lag phase time (h); t represents the fermentation time (h); kmethane is the hydrolysis rate constant (h−1); and n is the shape factor.
2.6. Bioenergy Recovery and Avoided GHG Emissions
Biogas burning in a combined heat and power unit produces electricity (Equation (5)) and heat (Equation (6)) [41]. For both estimations ( and ), on-site generation was assumed:
where is the estimated electricity generation from biogas (MWh ton−1 BSG); is the estimated heat produced from biogas (MJ ton−1 BSG); Qbiogas is the biogas volume (m3 ton−1 BSG); is the lower calorific value of methane (35.59 MJ m−3); Cm is the percentage of methane in the biogas (%); ηe is the engine efficiency (%), assumed as 40% for electric energy and 50% for thermal energy, considering commercial heat and power unit efficiencies [42]; and CF is the conversion factor from MJ to MWh (1 MWh = 3600 MJ).
The use of biogas for electricity and heat avoids GHG emissions (Equations (7) and (8)) [43].
where and were previously calculated in Equations (5) and (6), respectively; is the emission factor for 2019 (0.075 tCO2eq MWh−1), assuming the replacement of Brazilian electricity by electricity from biogas [44]; and is the emission factor (0.056 tCO2eq GJ−1), assuming the replacement of natural gas in a boiler by heat from biogas [45].
2.7. Industrial Design of AD for Bioenergy Recovery
Initially, an industrial system for BSG treatment using dry AD was proposed. Aiming to support a technological upscaling, a global industrial energy balance was assessed considering the generation of 1 ton of BSG, considering the experimental results obtained in this study.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Experiments were carried out in triplicate (n = 3), and the results are expressed as the average ± standard deviation (reported as error bars). The parameters evaluated in the AD experiment were statistically analyzed by one-way ANOVA, and the difference between the averages was verified by Tukey’s test (p < 0.05) using Statistica® software (StatSoft Inc., version 10.0, Tulsa, OK, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Operational Performance of the Dry AD Reactor
3.1.1. pH and Alkalinity
The pH is a determining parameter for microbiological growth [46]. The ideal range for methanogenic AD is from 6.5 to 8.5 [37]; however, it varies according to the substrate, the digestion technique, and the reactor configuration. Methanogenic reactions are inhibited at pH values below 6.5 and above 8.5, consequently decreasing methane production [47]. In the initial days of AD, the reactor was in an adaptation phase (Figure 2a). In the present study, the start-up was slower because of the raw material, predominantly composed of lignocellulose, requiring specific degradation conditions [26,48]. Based on the AD reactor’s operational performance, the pH remained within the methanogenic range during the first 16 days. After that, the pH increased to 8.35 until the final digestion time. The explanation for this fact is that the consortium of microorganisms (acidogenic and acetogenic bacteria and methanogenic archaea) digested the proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids from the substrate, and then, organic acids, ammonia, hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and other molecules were formed [49]. In addition, the pH remained high during the methanogenic phase, as expected, due to the formation of other molecules in the system [37]. Methanogenic microorganisms have a great affinity for a slightly alkaline pH [50].
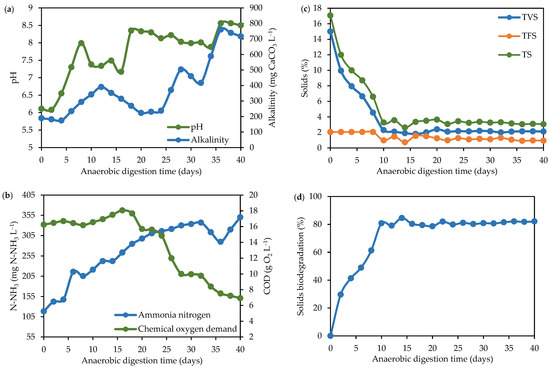
Figure 2.
Operational parameters evaluated in the dry AD of BSG. (a) pH and alkalinity; (b) ammonia nitrogen and chemical oxygen demand; (c) solids; and (d) solids biodegradation.
The pH is directly associated with alkalinity values. Alkalinity is an operational parameter related to weak acid neutralization, acting as a buffer system and an indicator to regulate the process pH [50]. As the pH increased during AD, the alkalinity exhibited the same behavior, increasing after day 24 (Figure 2a). In the initial days, between days 4 and 12, the alkalinity increased from 174 to 390 mg CaCO3 L−1. During this period, AD occurred with a methanogenic microbiota focused on hydrolyzing lignocellulosic organic matter [51]. This fact corroborates the decrease in the solids content on the same days (Figure 2c). Hence, in the hydrolytic phase of AD, complex molecules were hydrolyzed, and weak acids were generated [50,51,52], corroborating the pH evolution. From day 24 until day 40, the alkalinity increased from 250 to 760 mg CaCO3 L−1, indicating the complete biodegradation of the lignocellulose and organic matter present in the dry AD reactor.
3.1.2. Soluble Chemical Oxygen Demand
Figure 2b demonstrates the COD evolution during the dry AD of BSG, and Table 2 displays the general parameters recorded during the dry AD of BSG. In the first 16 days of digestion, the COD concentration remained high and constant (17,000 mg O2 L−1). Moreover, between days 8 and 16, it is possible to observe a slight increase in COD concentration caused by organic matter solubilization in the acidogenic and acetogenic phases [52]. From 18 days of AD, the process stabilized in the methanogenic phase, and the COD started to decrease. The COD concentration gradually declined until the end of the digestion process. After day 30, the COD concentration was below 10,000 mg O2 L−1, demonstrating positive organic matter degradation compared to the initial COD recorded (16,239.59 mg O2 L−1). Moreover, COD measures the amount of dissolved oxygen consumed in an environment due to organic matter degradation. In addition, COD reduction is directly associated with the efficiency of AD [47,53]. In the present study, COD degradation reached 57.38% compared to the beginning and the end of the AD process. Therefore, the high COD reduction in the AD of BSG can be associated with increased biogas production in the methanogenic phase. Hence, batch AD can be a promising alternative to manage the solid waste generated by the beer industry, since up to 50% of the organic matter could be degraded in this type of reactor.

Table 2.
General parameters recorded to the dry AD of BSG.
3.1.3. Ammonia Nitrogen
Ammonia nitrogen measures the ammonia content in the digestate during AD. The degradation of proteins and other nitrogen-rich organic materials results in ammonia after AD [51]. According to the results (Figure 2b), the ammonia nitrogen concentration gradually increased throughout the experimental period. At the beginning (day 0), the ammonia nitrogen was 118.36 mg N-NH3 L−1, and after day 40, the content reached 350.20 mg N-NH3 L−1. Such behavior can be associated with the degradation of protein present in the substrate. According to Castro and Colpini [54], BSG is a feedstock rich in cellulose (23.99%), hemicellulose (9.44%), and lignin (3.35%). However, the protein content of BSG can range from 18 to 30% [55], which is significant for AD [47,53]. Despite the high protein content, the methanogenic phase was not inhibited in the present study, a common fact for a protein-rich substrate [56]. During AD, the increase in ammonia nitrogen concentration can be associated with the conversion of the proteins present in the substrate into amino acids, which were digested and converted into ammonia [47].
3.1.4. Solids
AD can be classified as dry or wet AD. Although, it is not exactly possible to define a strict limit between them once the dry route is associated with high solids content (>15%) and wet digestion is related to low total solids content (<15%) [57,58]. In this study, the reactor was started with 17.06% solids (mixture of inoculum, substrate, and water), and on day 2 of AD, the total solids content was reduced to 12% (Figure 2c). After day 8, an expressive reduction in the solids content was observed, reaching 82.12% solids degradation (Figure 2d). Further, it remained stable until the end of the experimental digestion period. The results demonstrate that, at the beginning of the AD process, the methanogenic microbiota had high microbial activity, promoting organic matter reduction of smaller molecules and biogas [51,52]. Beyond this, while the solids content drastically decreased, the solids degradation increased and remained constant at approximately 80% during the AD, demonstrating the reactor’s efficiency in the degradation of BSG, and corroborating the COD results.
3.2. Biogas Production and Composition
Figure 3a displays the daily biogas and methane production and Figure 3b displays the accumulated biogas and methane production. The highest daily volume of methane was observed on the 18th day of AD, with 725 mL produced. On the same day, the accumulated methane volume reached 3.2 L. After the 18th day, methane production decreased daily until the 40th day of AD. In total, the batch reactor produced 11.92 L of biogas, which is equivalent to 6.47 L of methane. After the 30th day of digestion, the biogas and biomethane volumes stabilized since the daily production drastically decreased.
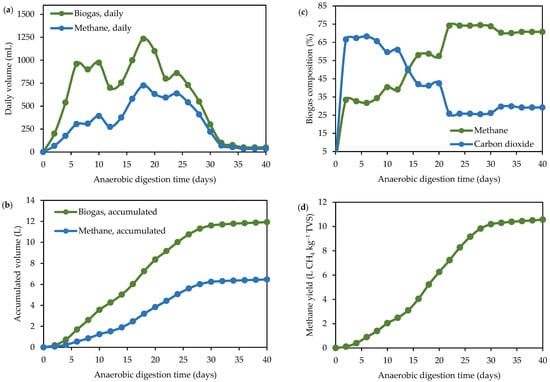
Figure 3.
Biogas and methane produced from dry AD of BSG. (a) Daily volume of biogas and methane; (b) accumulated volume of biogas and methane; (c) biogas composition; (d) methane yield.
The daily biogas production followed the pH behavior, especially regarding the accumulation of acid products [59]. Less acetate for the metabolism of bacteria producing organic acids in acidogenesis reduces pH to levels unfavorable to methanogenic microbiota [60]. Beyond this, in the start-up of the AD reactor, the COD reached 16,000 mg O2 L−1, and the daily methane production reached 725 mL. Otherwise, in the last days of AD, the digestate presented a COD lower than 10,000 mg O2 L−1, and the daily biogas productivity dropped to 35 mL. In AD, microorganisms oxidize organic substances due to the absence of oxygen, creating an oxidizing–reducing balance. Therefore, pH instability can result in poor adaptation of anaerobic microorganisms [49]. Otherwise, a significant COD and solids reduction indicated that the amount of substrate for biogas production decreased, affecting the reactor’s amount of methane.
Regarding the biogas composition (Figure 3c), the methane content gradually increased during AD. After 28 days of operation, the reactor reached the maximum methane composition (74.5%). A small decay in the methane content resulted in a stable behavior for 8 days, with a methane concentration close to 71%. After 30 days, the methane content was stable in the reactor, with an average value of 70%. The loss of methanogenic microorganism activity can be related to reducing the organic matter content and improving the biogas methane composition [52]. In this study, solids biodegradation reached values of approximately 85% after the 8th day of digestion. The COD decreased after the 18th day of digestion, which directly contributed to the methane-rich composition of the biogas. Notwithstanding, the accumulated methane yield was 10.53 L CH4 kg−1 TVS at the end of AD (Figure 3d). Compared with the literature, dry AD of agri-food by-products without pretreatment generated low methane yields, such as for the dry AD of apple pomace (2.75 mL CH4 g−1 TVS) [61], BSG (26.72 mL CH4 g−1 TVS) [62], açai seeds (19.82 mL CH4 g−1 TVS) [40], and poultry feathers (10.14 mL CH4 g−1 TVS) [40]. Otherwise, Rico et al. [58] obtained 470 mL CH4 g−1 TVS for the dry AD of food waste, with 90% solids reduction. Moreover, for the AD of corn stalks and cow dung (242 mL CH4 g−1 TVS) [63], cattle manure bedded with straw (146 mL CH4 g−1 TVS) [64], and corn silage (410 mL CH4 g−1 TVS) [65], high values of accumulated methane yield were obtained.
3.3. Kinetic Analysis
To evaluate the efficiency of methane production from the batch AD of BSG, the modified Gompertz model, Cone, and first-order kinetics models were applied (Table 3). The three models presented a good fit with the cumulative methane production, with R2 up to 0.94 and adjusted R2 up to 0.93 for all the kinetic models. The dry AD of BSG presented a cumulative methane production potential (P) adjusted to the modified Gompertz and first-order kinetics. The differences between the predicted and measured production from the kinetic models were lower than 30%. Otherwise, the first-order kinetic model did not explain the behavior of methane production by the AD of BSG since the difference was higher than 100%. Regarding lag time (λ) for the modified Gompertz kinetic model, the value of 0 h obtained represents that methane was produced before one day of incubation, corroborating the experimental data. A possible explanation for this is that the inoculum used was active, and biogas production was immediately started [66,67]. Therefore, the Cone model presented the lowest RMSE (216.92) and SEE (234.3) and can be suitable to predict methane production by batch AD of BSG.

Table 3.
Kinetic models applied to methane production from dry AD of BSG.
3.4. Recovery of Bioenergy from Biogas Potential and Avoided GHG Emissions
Biogas is a renewable energy source presenting potential GHG emissions avoidance [68,69]. According to Table 4, each ton of BSG submitted to AD can produce 0.133 MWh of electricity and 598.45 MJ of thermal energy. The thermal energy resulting from the AD process can be used in a combined cycle involving a heat exchanger, which heats the steam to be expanded with an electric generator [41]. The use of biogas as fuel connected to an electric generator can be an alternative use of thermal energy [70]. In addition, heat is widely used to increase steam production in boilers for several brewery processes, including bottling [71].

Table 4.
Potential of electric energy, heat, and avoided GHG emissions using dry anaerobic digestion of BSG.
Regarding GHG mitigation from electricity and heat, renewable energy is crucial to mitigate global warming. Combined with technologies that involve heat and energy from AD, electricity production could mitigate 0.0099 tCO2eq ton−1 BSG. In addition, the thermal energy could avoid 0.0335 tCO2eq ton−1 BSG (Table 4). In 2019, Brazil produced 400,000 tons of barley [3], and for each kilogram cultivated, 0.57 kg CO2eq was emitted [72]. Looking at the Brazilian barley cultivation, 228 × 103 tCO2eq year−1 are estimated, which, from a supply chain perspective, could be partially mitigated by biogas combustion (derived from the AD of BSG) electrical and thermal energies co-generation. Moreover, its contribution to the beer industry’s carbon footprint decrease could be appreciated as follows. In the beer industry, boilers consume approximately 16 kg CO2 for each hL of beer produced. In contrast, fermentation generates 3 kg CO2 hL−1 beer [73]. Other steps are GHG emitters, such as emissions from purchased electricity, combustion of company and rented vehicles for logistics processes, fugitive emissions from refrigeration units, fuel cell emissions, natural gas, and diesel oil [73]. This study shows a technological route from BSG valorization in anaerobic reactors with methane production and its energy application. The thermal and electric energy produced by AD contributes to the total amount of CO2 mitigated by boilers and fermentation emissions, reducing the beer industry’s carbon footprint [74].
The conversion of methane-rich biogas into heat and power can be a greener energy source for the beer industry. Nonetheless, biogas can be used in a range of different routes by other energy-demanding economic sectors. For instance, once converted into biomethane, it can be applied as a vehicular fuel or natural gas alternative for cooking [13]. Additionally, the digestate obtained from AD is a useful agricultural fertilizer to replace mineral fertilizers [24]. Therefore, batch reactors can be a positive management system for BSG treatment since they offer operational simplicity and low cost, do not consume a high volume of water and do not demand high active labor [75,76]. In addition, AD is an environmentally friendly technology that presents several benefits for treating food industry solid waste by reducing its organic material volume. Furthermore, it allows eco-friendly waste disposal reducing environmental side effects. Finally, energy recovery is prone to mitigate GHG emissions, contributing to industrial decarbonization [11,77,78].
Based on the experimental results and the theoretical calculation of electric and thermal energies, a global industrial balance was assessed to evaluate an industrial management system’s implementation to treat the BSG generated during beer production using dry AD (Figure 4). For this, two scenarios were studied considering the generation of 1 ton of BSG. Scenario 1 represents the energy demand of a conventional and well-managed brewery, which was estimated at 29.84 kWh of electricity and 154.05 MJ of heat per 100 L of beer produced [79,80], that is, 1.49 MWh electricity and 7702.5 MJ heat are required for the production of 5000 L beer and generation of 1 ton BSG (Figure 4a). Scenario 2 corresponds to the proposed management system with a dry AD of 1 ton of BSG generated by the brewery (Figure 4b). For the scale-up scheme proposed, the biogas produced (62 m3) in the anaerobic digester is collected by a pressurized gas pipe and destined for the “biogas holder” section. The biogas should be purified into biomethane to remove hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, and contaminants in the biogas purifier (BP). The purified biogas (33.63 m3) can be upgraded into electric (0.133 MWh) and thermal energies (598.45 MJ) in a heat and power unit.
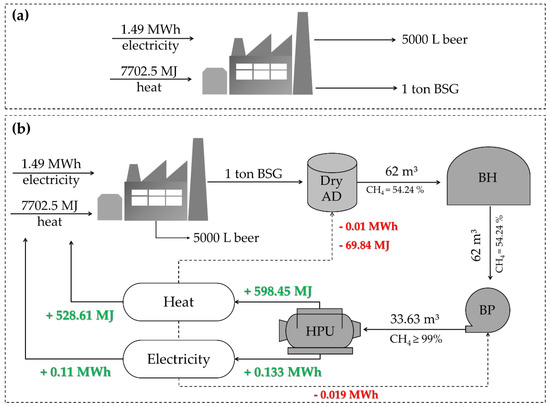
Figure 4.
Industrial mass and energy balance for bioenergy recovery from dry AD of BSG. (a) Demand of electricity and heat for beer production; (b) recovery of bioenergy with dry AD of BSG. Label: AD, anaerobic digester; BH, biogas holder; BP, biogas purificator; HPU, heat and power unit. Adapted from Sganzerla et al. [29], with permission from Springer Nature.
However, the energy consumption for biogas upgrading into biomethane is 0.301 kWh m−3 of biogas upgraded [81], which means that the current scenario demands 0.019 MWh of electricity for biogas purification. In addition, for the mesophilic treatment (1 ton) in a standard anaerobic reactor, there is a demand for approximately 10 kWh of electricity and 69.84 MJ of heat [82], and this energy can be used from the energy generated in the heat and power unit. Hence, the net electricity (0.11 MWh) and heat (528.61 MJ) generated from the dry AD of BSG are still insufficient to supply all of the energy demand to produce beer. From the scenario presented, 7.38% of the electricity and 6.86% of the heat required for beer production could be obtained from the dry AD of BSG. This approach represents a favorable strategy for the self-production and consumption of energy, by transitioning towards an energy-less dependency status [14]. Based on the industrial waste management system for BSG treatment, the proposed scheme would be an initial approach to promote the beer industry’s circular economy transition, since the industrial process designed can be a technological route to be applied in a biorefinery [83].
4. Conclusions
Methane-rich biogas was produced by the dry AD of BSG. Methanogenic reactions were demonstrated to be adaptable according to the increase in pH and alkalinity and a decrease in COD and solids during the dry AD. The reactor could operate with a high solids content, with degradation above 85% at the end of the process. The Cone model better-described methane production kinetics than the modified Gompertz and first-order kinetic models. Each ton of BSG could produce 0.133 MWh of electricity and 598.45 MJ of thermal energy by dry AD. When combined with technologies that involve heat and energy from AD, electricity production could mitigate 0.0099 tCO2eq ton−1 BSG, and thermal energy could avoid 0.0335 tCO2eq ton−1 BSG. From the industrial scenario proposed, 7.38% of the electricity and 6.86% of the heat required to produce beer could be obtained from the dry AD of BSG. This approach represents a positive strategy for the self-production and consumption of energy, therefore contributing to a lower carbon footprint of the beer industry. Furthermore, the BSG industrial management system based on dry AD, an eco-friendly biotechnological route, is presented as a valuable strategy for bioenergy recovery to support a more sustainable brewery peculiar to circular economy establishment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.G.S. and T.F.-C.; methodology, W.G.S. and J.M.C.; investigation, W.G.S., J.M.C. and M.T.-V.; writing—original draft preparation, W.G.S., J.M.C. and M.T.-V.; writing—review and editing, L.S.B., S.I.M. and T.F.-C.; supervision, S.I.M. and T.F.-C.; project administration, S.I.M. and T.F.-C.; funding acquisition, S.I.M. and T.F.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Brazilian Science and Research Foundation (CNPq) (productivity grant 302451/2021-8); Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES, Brazil) (Finance code 001); São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP, Brazil) (grant numbers 2018/14938-4, 2019/26925-7, 2020/10323-5, and 2021/03950-6); and Novo Nordisk Foundation (NNF, Denmark) (grant number NNF20SA0066233).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Brasil Anuário da Cerveja 2021—Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento. 2021. Available online: https://www.gov.br/agricultura/pt-br/assuntos/inspecao/produtos-vegetal/publicacoes/anuario-da-cerveja-2021.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Mussatto, S.I. Brewer’s Spent Grain: A Valuable Feedstock for Industrial Applications. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IBGE Anuário Estatístico do Brasil. Available online: https://biblioteca.ibge.gov.br/visualizacao/periodicos/20/aeb_2019.pdf (accessed on 11 September 2022).
- CONAB Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento—Importações e Exportações. Available online: www.portaldeinformacoes.conab.gov.br/comercio-exterior-por-pais (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Ricciardi, P.; Cillari, G.; Carnevale Miino, M.; Collivignarelli, M.C. Valorization of Agro-Industry Residues in the Building and Environmental Sector: A Review. Waste Manag. Res. 2020, 38, 487–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-García, S.; Morales, P.C.; Gullón, B. Estimating the Environmental Impacts of a Brewery Waste–Based Biorefinery: Bio-Ethanol and Xylooligosaccharides Joint Production Case Study. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 123, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Dragone, G.; Roberto, I.C. Brewers’ Spent Grain: Generation, Characteristics and Potential Applications. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Mayanga, P.C.; Azambuja, S.P.H.; Tyufekchiev, M.; Tompsett, G.A.; Timko, M.T.; Goldbeck, R.; Rostagno, M.A.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Subcritical Water Hydrolysis of Brewer’s Spent Grains: Selective Production of Hemicellulosic Sugars (C-5 Sugars). J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 145, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sganzerla, W.G.; Buller, L.S.; Mussatto, S.I.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Techno-Economic Assessment of Bioenergy and Fertilizer Production by Anaerobic Digestion of Brewer’s Spent Grains in a Biorefinery Concept. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margallo, M.; Ziegler-Rodriguez, K.; Vázquez-Rowe, I.; Aldaco, R.; Irabien, Á.; Kahhat, R. Enhancing Waste Management Strategies in Latin America under a Holistic Environmental Assessment Perspective: A Review for Policy Support. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 1255–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Castro, M.P.; Buller, L.S.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Bioenergy Production from Orange Industrial Waste: A Case Study. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2020, 14, 1239–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Lee, S.-H.; Kumar, P.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, S.S.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Solid Waste Management: Scope and the Challenge of Sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 658–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.F.; Buller, L.S.; Maciel-Silva, F.W.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Berni, M.D.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Waste Management and Bioenergy Recovery from Açaí Processing in the Brazilian Amazonian Region: A Perspective for a Circular Economy. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2021, 15, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sganzerla, W.G.; Ampese, L.C.; Mussatto, S.I.; Forster-Carneiro, T. A Bibliometric Analysis on Potential Uses of Brewer’s Spent Grains in a Biorefinery for the Circular Economy Transition of the Beer Industry. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2021, 15, bbb.2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Domenico Ziero, H.; Ampese, L.C.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Torres-Mayanga, P.C.; Timko, M.T.; Mussatto, S.I.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Subcritical Water Hydrolysis of Poultry Feathers for Amino Acids Production. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2022, 181, 105492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, S.R.; Banjara, S.P.; Choi, O.K.; Park, K.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, J.W. Pretreatment of Agricultural Biomass for Anaerobic Digestion: Current State and Challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocamora, I.; Wagland, S.T.; Villa, R.; Simpson, E.W.; Fernández, O.; Bajón-Fernández, Y. Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Waste: A Review of Operational Parameters and Their Impact on Process Performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Westerholm, M.; Qiao, W.; Xiong, L.; Mahdy, A.; Yin, D.; Song, Y.; Dong, R. Metabolic Performance of Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure under Wet, High Solid, and Dry Conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 296, 122342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Wang, F.; Yang, H.; Zhi, S.; Liu, G. Anaerobic Digestion Performance of Sweet Potato Vine and Animal Manure under Wet, Semi-Dry, and Dry Conditions. AMB Express 2018, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maria, F.; Barratta, M.; Bianconi, F.; Placidi, P.; Passeri, D. Solid Anaerobic Digestion Batch with Liquid Digestate Recirculation and Wet Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Waste: Comparison of System Performances and Identification of Microbial Guilds. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.; Shi, J.; Li, Y. Comparison of Solid-State to Liquid Anaerobic Digestion of Lignocellulosic Feedstocks for Biogas Production. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 124, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbassi-Guendouz, A.; Brockmann, D.; Trably, E.; Dumas, C.; Delgenès, J.-P.; Steyer, J.-P.; Escudié, R. Total Solids Content Drives High Solid Anaerobic Digestion via Mass Transfer Limitation. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Huang, C.; Chen, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xi, B.; Li, X. Performance of Dry Anaerobic Technology in the Co-Digestion of Rural Organic Solid Wastes in China. Energy 2015, 93, 2497–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buller, L.S.; da Silva Romero, C.W.; Lamparelli, R.A.C.; Ferreira, S.F.; Bortoleto, A.P.; Mussatto, S.I.; Forster-Carneiro, T. A Spatially Explicit Assessment of Sugarcane Vinasse as a Sustainable By-Product. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasapoor, M.; Young, B.; Brar, R.; Sarmah, A.; Zhuang, W.-Q.; Baroutian, S. Recognizing the Challenges of Anaerobic Digestion: Critical Steps toward Improving Biogas Generation. Fuel 2020, 261, 116497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainthola, J.; Kalamdhad, A.S.; Goud, V. V A Review on Enhanced Biogas Production from Anaerobic Digestion of Lignocellulosic Biomass by Different Enhancement Techniques. Process Biochem. 2019, 84, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rosa, R.G.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Barroso, T.L.C.T.; Castro, L.E.N.; Berni, M.D.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Sustainable Bioprocess Combining Subcritical Water Pretreatment Followed by Anaerobic Digestion for the Valorization of Jabuticaba (Myrciaria Cauliflora) Agro-Industrial by-Product in Bioenergy and Biofertilizer. Fuel 2023, 334, 126698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillero, L.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Carneiro, T.F.; Solera, R.; Perez, M. Techno-Economic Analysis of Single-Stage and Temperature-Phase Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge, Wine Vinasse, and Poultry Manure. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sganzerla, W.G.; Ampese, L.C.; Parisoto, T.A.C.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Process Intensification for the Recovery of Methane-Rich Biogas from Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Açaí Seeds. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijer, T.; Bakker, V.; Slootweg, J.C. Circular Chemistry to Enable a Circular Economy. Nat. Chem. 2019, 11, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Sarkis, J.; Bleischwitz, R. How to Globalize the Circular Economy. Nature 2019, 565, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hysa, E.; Kruja, A.; Rehman, N.U.; Laurenti, R. Circular Economy Innovation and Environmental Sustainability Impact on Economic Growth: An Integrated Model for Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.T.; Trierweiler, L.F.; Trierweiler, J.O. Food Waste Biorefinery Advocating Circular Economy: Bioethanol and Distilled Beverage from Sweet Potato. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragone, G.; Kerssemakers, A.A.J.; Driessen, J.L.S.P.; Yamakawa, C.K.; Brumano, L.P.; Mussatto, S.I. Innovation and Strategic Orientations for the Development of Advanced Biorefineries. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IEA Bioenergy—Task 42 Biorefining in a Circular Economy. Available online: http://task42.ieabioenergy.com/ (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Mussatto, S.I.; Moncada, J.; Roberto, I.C.; Cardona, C.A. Techno-Economic Analysis for Brewer’s Spent Grains Use on a Biorefinery Concept: The Brazilian Case. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 148, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G.; Yang, G. Process Performance and Methane Production Optimizing of Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Swine Manure and Corn Straw. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA—American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; Rice, E.W., Baird, R.B., Eaton, A.D., Eds.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-87553-287-5. [Google Scholar]
- Sillero, L.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Forster-Carneiro, T.; Solera, R.; Perez, M. A Bibliometric Analysis of the Hydrogen Production from Dark Fermentation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 27397–27420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sganzerla, W.G.; Tena-Villares, M.; Buller, L.S.; Mussatto, S.I.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Food Industry By-Products and Bioenergy Recovery: A Perspective to Promote the Circular Economy Transition. Waste Biomass Valorization 2022, 13, 2575–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campello, L.D.; Barros, R.M.; Tiago Filho, G.L.; dos Santos, I.F.S. Analysis of the Economic Viability of the Use of Biogas Produced in Wastewater Treatment Plants to Generate Electrical Energy. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 2614–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHP Brasil CHP Brasil. Available online: https://chpbrasil.com.br/en/solucoes/cogeracao-qualificada (accessed on 17 September 2022).
- dos Santos, I.F.S.; Braz Vieira, N.D.; de Nóbrega, L.G.B.; Barros, R.M.; Tiago Filho, G.L. Assessment of Potential Biogas Production from Multiple Organic Wastes in Brazil: Impact on Energy Generation, Use, and Emissions Abatement. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 131, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MCTIC Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia, Inovações e Comunicações. Available online: https://www.mctic.gov.br/mctic/opencms/ciencia/SEPED/clima/textogeral/emissao_corporativos.htm (accessed on 17 September 2022).
- IPCC. IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories—Volume 2: Energy. 2006. Available online: https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/vol2.html (accessed on 19 September 2022).
- Jin, Q.; Kirk, M.F. PH as a Primary Control in Environmental Microbiology: 1. Thermodynamic Perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Samadder, S.R. Performance Evaluation of Anaerobic Digestion Technology for Energy Recovery from Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste: A Review. Energy 2020, 197, 117253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawatdeenarunat, C.; Surendra, K.C.; Takara, D.; Oechsner, H.; Khanal, S.K. Anaerobic Digestion of Lignocellulosic Biomass: Challenges and Opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 178, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J. Enhancement of Methane Production in Anaerobic Digestion Process: A Review. Appl. Energy 2019, 240, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Náthia-Neves, G.; Berni, M.; Dragone, G.; Mussatto, S.I.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Anaerobic Digestion Process: Technological Aspects and Recent Developments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 2033–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Castro, M.P.; Buller, L.S.; Zoffreo, A.; Timko, M.T.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion of Orange Peel without Pre-Treatment: Experimental Evaluation and Application to São Paulo State. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel-Silva, F.W.; Mussatto, S.I.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Integration of Subcritical Water Pretreatment and Anaerobic Digestion Technologies for Valorization of Açai Processing Industries Residues. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atelge, M.R.; Atabani, A.E.; Banu, J.R.; Krisa, D.; Kaya, M.; Eskicioglu, C.; Kumar, G.; Lee, C.; Yildiz, Y.Ş.; Unalan, S.; et al. A Critical Review of Pretreatment Technologies to Enhance Anaerobic Digestion and Energy Recovery. Fuel 2020, 270, 117494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.E.N.; Colpini, L.M.S. All-around Characterization of Brewers’ Spent Grain. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 3013–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Johansen, A.Z.; Mussatto, S.I. Evaluation of Different Pretreatment Strategies for Protein Extraction from Brewer’s Spent Grains. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 125, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gabauer, W.; Li, Z.; Ortner, M.; Fuchs, W. Improving Exploitation of Chicken Manure via Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion with an Intermediate Membrane Contactor to Extract Ammonia. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, C.V.; von Sperling, M.; Fernandes, F. Sludge Treatment and Disposal. Water Intell. Online 2015, 6, 9781780402130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, C.; Montes, J.A.; Lobo, A. Dry Batch Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste in a Box-Type Reactor System: Inoculum Preparation and Reactor Performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Sheng, H.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Song, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; He, W.; et al. Water Free Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Vegetable Processing Waste with Cattle Slurry for Methane Production at High Total Solid Content. Energy 2014, 74, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, I.C.; Fonseca, A.; Morão, A.M.; Pinheiro, H.M.; Duarte, A.P.; Ferra, M.I.A. Evaluation of Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Spent Brewery Grains and an Azo Dye. Renew. Energy 2015, 74, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampese, L.C.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Di Domenico Ziero, H.; Costa, J.M.; Martins, G.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Valorization of Apple Pomace for Biogas Production: A Leading Anaerobic Biorefinery Approach for a Circular Bioeconomy. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buller, L.S.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Lima, M.N.; Muenchow, K.E.; Timko, M.T.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Ultrasonic Pretreatment of Brewers’ Spent Grains for Anaerobic Digestion: Biogas Production for a Sustainable Industrial Development. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 355, 131802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Li, Z.; Feng, J.; Zhao, L.; Yu, J. Effects of Digestate Recirculation Ratios on Biogas Production and Methane Yield of Continuous Dry Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patinvoh, R.J.; Kalantar Mehrjerdi, A.; Sárvári Horváth, I.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Dry Fermentation of Manure with Straw in Continuous Plug Flow Reactor: Reactor Development and Process Stability at Different Loading Rates. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veluchamy, C.; Gilroyed, B.H.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Process Performance and Biogas Production Optimizing of Mesophilic Plug Flow Anaerobic Digestion of Corn Silage. Fuel 2019, 253, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, M.; Luque, B.; Perez, M.; Solera, R. Enhanced Hydrogen Production from Sewage Sludge by Cofermentation with Wine Vinasse. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 15977–15984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, M.; Perez, M.; Solera, R. Effects of Several Inocula on the Biochemical Hydrogen Potential of Sludge-Vinasse Co-Digestion. Fuel 2019, 258, 116180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muench, S. Greenhouse Gas Mitigation Potential of Electricity from Biomass. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, V.; Dequiedt, B.; Le Cadre, E. Biomass for Electricity in the EU-27: Potential Demand, CO2 Abatements and Breakeven Prices for Co-Firing. Energy Policy 2014, 73, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loução, P.O.; Ribau, J.P.; Ferreira, A.F. Life Cycle and Decision Analysis of Electricity Production from Biomass—Portugal Case Study. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 108, 452–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olajire, A.A. The Brewing Industry and Environmental Challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 102817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaniemi, M.; Mikkola, H.; Ahokas, J. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Oats, Barley, Wheat and Rye Production. Agron. Res. 2011, 9, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Carr-Harris, H. Environmental Management in the Brewing Industry; United Nations Environment Programme, Industry and Environment: Paris, France, 1996; ISBN 9789280715231. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Garcia, G.; Rahimifard, S. Life-Cycle Environmental Impacts of Barley Straw Valorisation. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 149, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leme, R.M.; Seabra, J.E.A. Technical-Economic Assessment of Different Biogas Upgrading Routes from Vinasse Anaerobic Digestion in the Brazilian Bioethanol Industry. Energy 2017, 119, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudhoo, A.; Torres-Mayanga, P.C.; Forster-Carneiro, T.; Sivagurunathan, P.; Kumar, G.; Komilis, D.; Sánchez, A. A Review of Research Trends in the Enhancement of Biomass-to-Hydrogen Conversion. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, F.F.; De Souza, S.S.; Ferreira, L.R.A.; Otto, R.B.; Alessio, F.J.; De Souza, S.N.M.; Venturini, O.J.; Ando Junior, O.H. The Brazilian Market of Distributed Biogas Generation: Overview, Technological Development and Case Study. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 101, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, N.H.; Mattioli, A.; Gil, A.; Frison, N.; Battista, F.; Bolzonella, D. Evaluation of the Methane Potential of Different Agricultural and Food Processing Substrates for Improved Biogas Production in Rural Areas. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 112, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, D.; Carvalho, M.; Abrahão, R. Greenhouse Gas Accounting for the Energy Transition in a Brewery. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2021, 40, e13563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadare, D.A.; Nkpubre, D.O.; Oni, A.O.; Falana, A.; Waheed, M.A.; Bamiro, O.A. Energy and Exergy Analyses of Malt Drink Production in Nigeria. Energy 2010, 35, 5336–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, P.; Hélias, A.; Lardon, L.; Ras, M.; Goy, R.-A.; Steyer, J.-P. Life-Cycle Assessment of Microalgae Culture Coupled to Biogas Production. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstad, A.; la Cour Jansen, J. A Life Cycle Approach to the Management of Household Food Waste—A Swedish Full-Scale Case Study. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1879–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainaina, S.; Awasthi, M.K.; Sarsaiya, S.; Chen, H.; Singh, E.; Kumar, A.; Ravindran, B.; Awasthi, S.K.; Liu, T.; Duan, Y.; et al. Resource Recovery and Circular Economy from Organic Solid Waste Using Aerobic and Anaerobic Digestion Technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).