Abstract
Humic acid (HA), as an important by-product, has been demonstrated to affect anaerobic digestion performance and subsequent land application of digestate via the batch anaerobic digestion process. However, the knowledge about the evolution of structure and function of HA during continuous anaerobic digestion (AD) is still unclear. Therefore, the current study examined the structural changes in HA produced during the continuous AD process and its metal-adsorption-reduction abilities. The results of three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy showed a general upsurge in humic-like components’ abundance (70–77%), with an increase in humification index (2.56–3.43). Likewise, the content of HA increased from 4.8 g L−1 to 6.9 g L−1 in the continuous AD process. The evolution of C-H, O-H, C=O, C=C, and C-O functional groups of HA was observed via the 2D COS FTIR analysis. Moreover, the concurrent dynamics of functional groups contributed to the higher adsorption (255.2 mg g−1) of Cr (VI) and reduction (60.3 mg g−1) of Cr (VI) to Cr (III) after 168 days of the continuous AD process. The findings of the current study not only advanced understanding of the evolution of HA during continuous anaerobic digestion and its metal remediation potential but also support further research toward developing an eco-friendly and innovative strategy for the remediation of heavy metals contaminated soils employing anaerobic digestate as an auxiliary agent.
1. Introduction
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is widely used as an economical, effective, and environmentally friendly way of disposing of organic waste [1,2]. During the AD process, organic waste is degraded and converted into various soluble macromolecules and followed by the production of biogas via the hydrolysis, acidogenesis and methanogenesis processes [3,4]. Likewise, humic acids (HA), as an organic macromolecule by-product, are formed during the degradation and transformation of organic waste [5]. The complexity of the structure and function of HA may affect the efficiency of the AD process and subsequent land application of the anaerobic digestate as fertilizer and remediation agents [6,7]. Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate the structural changes in HA generated during the AD process.
The effect of HA on the efficiency of the AD process has been investigated previously [8,9,10]. For example, Azman et al. (2017) found that the hydrolysis efficiency of crystalline cellulose was about 78% without HA, which remained 39% when the HA content reached 5 g L−1. The inhibitory effect of HA on the hydrolysis phase may be attributed to the complexation between the functional groups in HA (hydroxyl and phenolic hydroxyl groups) and key enzymes through covalent and electrostatic bonds. Moreover, the quinone groups in HA can serve as the electron transfer shuttle to participate in the acidogenesis and methanogenesis stages [8]. Yang et al. (2012) investigated the mechanism of HA in influencing the acidification stage by adding HA analogues (anthraquinone-2, 6-disulfonate, AQDS) to the AD system. They observed that the yield of volatile fatty acids increased by 0.9 times and 1.7 times with the addition of 0.066 g/gTS and 0.33 g/gTS AQDS, respectively. However, the presence of HA may interact with the key enzymes of the methanogenic stage (e.g., F420-reducing hydrogenase) in an electronically competitive manner, thus inhibiting the acetic acid-loving methanogenic pathway and leading to a decrease in methane production [9]. Moreover, Bai et al. (2019) showed that HA could act as a terminal electron acceptor to mediate the anaerobic oxidation of methane occurring in anaerobic methanotrophic archaea (e.g., ANME-2a and ANME-2c), thus driving the conversion of methane to CO2, which may also be a major reason for the reduced methane production by HA [10].
Furthermore, the characteristics of the structure and function of HA contributed to its soil fertilization and remediation potential [11]. As the major component of organic fertilizer, HA contains abundant active functional groups, including carboxyl, hydroxyl, and aromatic groups [6,12,13]. Moreover, the presence of these functional groups in HA not only contributed to various agronomic effects, including enhanced seed germination, plant growth, and water/nutrient-holding capacity, but also to the adsorption of various pollutants (e.g., heavy metals and organic pollutants) in soil [14]. It was also reported that HA immobilized pollutants by forming stable complexes through electrostatic adsorption and complexation reactions [15,16]. Likewise, the quinone functional groups in the HA serve as an electron transferring shuttle, providing electron donors continuously to mediate bio- or abiotic redox reactions, thus driving the degradation and conversion of pollutants [17]. Our already published study explored the dynamic evolution of HA from the batch AD process and the heavy metal removal potential of HA. We have observed that the content of oxygen-containing groups increased during the batch AD process, contributing to the variable capacity of HA to adsorb heavy metals [6]. Although previous studies have extensively explored the structural changes in HA produced during the batch AD process, the evolution of structural characteristics of HA during the practical biogas plant remains unclear, especially its pollution remediation capacity.
Therefore, to address this knowledge gap, this study performed in situ monitoring of HA formed from the practical biogas plant. The main objectives were to (i) explore the structural characteristics of HA via a combination of 2D-COS Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Excitation-Emission Matrix (EEM) Spectroscopy and (ii) evaluate the potential of HA to remediate soil contaminants through chromium adsorption and reduction experiment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Anaerobic Digestate Collection
The digestate was collected from a local biogas plant (Beijing, China), which used a continuous stirred tank reactor operated under the mesophilic condition (37 °C) with a hydraulic retention time of 28 days. Sewage sludge was used as the substrate for the reaction, feeding with 8–9% total solid (TS) content every day. The ratio of volatile solid content and total solid is 0.6–0.7. Likewise, the organic load rate of the reactor is 1.5 kgVS L−1 d−1. During the reaction process, the total chemical oxygen demand (TCOD) removal efficiency reached up to about 60% and the methane content in the biogas was a maximum of about 62%. Likewise, about 37% carbon dioxide and minor constituents (e.g., sulphuric components) were observed in the biogas. In addition, the pH ranged from 7.5 to 8.0 during the start-up periods. In this study, the digestate samples were collected after 28, 56, 84, 112, 140, and 168 days to explore the dynamic evolution of the structure and function of HA during the start-up periods of the AD process. The collected digestate was separated to reduce the impact of suspended solids and then kept at 4 °C until usage.
2.2. HA Component Analysis
The HA components of digestates were determined via a fluorescence spectrophotometer (Aqualog, HORIBA) following the method described in Wang et al. (2021) [2]. Briefly, around 50 mL digestate sample from the continuous AD process was diluted 20 times with distilled water. Likewise, the pH of digestate was adjusted to 7.0. Then, 2 mL of the diluted digestate was placed in the fluorescence spectrophotometer for analysis. The emission wavelengths and excitation ranges of 250–550 nm and 250–600 nm, with 0.5 nm and 5 nm increments, respectively, were set to obtain fluorescence excitation-emission spectra (EEMs). Finally, PARAFAC analysis was performed on the EEMs dataset using MATLAB R2018a (MathWorks, USA) with the DOM Fluor Toolbox [18]. The number of components was identified based on the split-half validation and compared with a library of PARAFAC models using the modified Turker’s Congruence Coefficient [19]. The relative contents of each PARAFAC component were estimated from the Fmax output from DOMFluor. Moreover, the humification index (HIX), biological index (BIX), and fluorescence index (FI) were calculated by the fluorescence spectroscopy according to previous studies [20,21,22].
2.3. HAs Extraction
This study used the alkaline–acid alternate chemical extraction method to obtain the HA from sampled digestates according to the method described by Wang et al. (2021) [6]. Briefly, about 50 mL digestate sample was first mixed and shaken with 100 mL of 0.1 M Na4P2O4/NaOH for 24 h, followed by centrifugation for 20 min. The supernatant, after centrifugation, was filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane to remove impurities. Subsequently, the pH of the supernatant was set to 1 with 6 M HCl solution and left to stand for 12 h. Finally, the HA fraction (the precipitate) was collected from the acidified solution by centrifugation. This process (re-suspended and precipitated) was performed three times to purify the HA fraction.
2.4. Characteristics of HAs
The elemental composition (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen) of HAs was determined by an elemental analyzer (Vario EL cube, Hanau, Germany). The functional groups of HAs were analyzed employing Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR, Nicolet IS10, Akron, OH, USA) combined with 2 D correlation spectroscopy following the method described by Gao et al. (2019) [23]. Briefly, the FTIR spectra of HA mixing with spectrometry-grade KBr were first measured using a Nicolet IS10 FTIR spectrophotometer to obtain a series of FTIR spectra. Then, the digestion time was used as an external perturbation to obtain 2D synchronous spectra and 2D asynchronous spectra via the 2D Shige version 1.3 software (Kwansei-Gakuin University, Kobe, Japan). Moreover, in order to quantitative the content of the main functional groups including total acidify group, carboxylic acid groups and phenolic-OH groups, which were correlated to the heavy metals adsorption, were determined via the Boehm titration methods according to the method described by Boehm (1994) [24].
2.5. Chromium Adsorption and Reduction Potential of HAs
The Chromium [Cr (VI)] was selected as the representative heavy metal to explore the adsorption and redox capacity of HA formed from the continuous anaerobic digestion process. The Cr (VI) adsorption and reduction experiments were conducted following the method described in Zou et al. (2021) [25]. Briefly, 100 mL Cr (VI) solution (30 mg L−1) was mixed with 0.1 g HA in a 200 mL conical flask at 25 °C. The pH was adjusted to 2 using the HCl or NaOH solution. Then, the mixtures were shaken at 200 rpm and equilibrated for 72 h. A similar set of experiments was conducted without HA addition, which serves as a control. To analyze the Cr adsorption and reduction efficiency, samples were taken after 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, and 72 h for measuring the contents of Cr (VI) and Cr (III), respectively. The samples were filtered through 0.22 µm nylon filter membranes (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) before determining the total concentrations of Cr and Cr (VI) in the solution. An inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, Agilent ICPMS 7800) and 1, 5-diphenylcarbazide colorimetric method were employed for measuring total Cr and Cr (VI), respectively. The concentrations of Cr (III) were obtained by subtraction. Finally, the pseudo-first-order kinetic (Equation (1)) and pseudo-second-order kinetic (Equation (2)) models were used to describe the adsorption behavior:
where, (mg g−1) represents the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent at time t, (mg g−1) the adsorption equilibrium of the adsorbent at time t; (h−1) is the kinetic adsorption constants for pseudo-first-order kinetic models, and (g mg−1 h−1) is the kinetic adsorption constants for pseudo-second-order kinetic models.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evolution of HA Component
The Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix (EEM) spectroscopy combined with PARAFAC analysis is often used to monitor the characteristics of organic matters [2,6,26]. The composition and evolution of the HA components were analyzed by EEM-PARAFAC analysis in this study. Five fluorescence components (C1–C5) were identified based on all EEMs data from the continuous AD process (Table S1). Based on the previous studies, the C1 and C3 were ascribed to HA fluorescence components, C2 was associated with fulvic acid fluorescence components, and C4 and C5 were ascribed to tyrosine and tryptophan fluorescence component, respectively.
The relative proportion of five fluorescence components in the continuous AD process was calculated and labelled as Fmax. The Fmax values of HA components increased from 70% to 77%, while the Fmax values of protein components decreased from 19% to 8% during the start-up periods of continuous AD process (Figure 1). The relative content of the fulvic acid component remained relatively stable. These results indicated an uplift in humic-like components’ abundance and a decrease in the abundance of protein-like components, consistent with the well-reported humification process. According to previous studies, protein-like substances are the major and easily biodegradable substrates for VFAs production compared to HA components. Likewise, Li et al. (2014) reported that tryptophan-like substances degraded gradually while degradation of tyrosine-like substances fluctuated over time during the AD process of dewatered sludge. They further observed that the average relative content of C1 increased from 37% to 48%, while the relative content of C3 decreased from 33% to 28% in the continuous AD process like the current study [27]. Previous studies demonstrated that components C1 and C3 were characterized as HA components with high molecular weight and low molecular weight, respectively [28,29,30,31]. These findings indicated that the HAs transformed from low to high molecular weight in start-up periods of the continuous AD process.
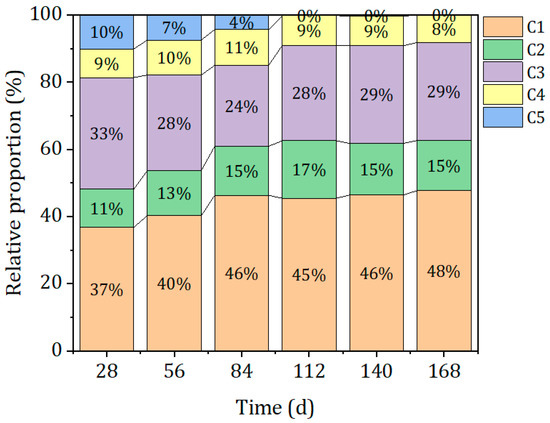
Figure 1.
Relative proportion of fluorescence components in the continuous anaerobic digestion process. (C1, C3: Humic-like substances; C2: Fulvic-like substance; C4: Tyrosine-like substance; C5: Tryptophan-like substance).
Moreover, an increasing trend in HA content was observed from 28 days to 168 days of the continuous AD process (Figure 2). The average content of HA increased from 4.8 g L−1 to 6.9 g L−1 during the formerly mentioned time span. However, it was noted that the increased rate of HA content decreased with the fermentation times. In the first 112 days of the AD process, the HA content increased relatively rapidly (13%), while from 112 to 168 days, the HA content increased more slowly (5%). These findings contradict the previously reported results, i.e., the content of HA first decreased and then increased steadily. According to our previous studies, the decomposition and re-polymerization process contribute to the change in HA content in the batch AD process [2,5]. For instance, the superficial labile aliphatics of HA were first degraded as the energy source for microorganisms’ growth due to insufficient substrate in batch AD process. Likewise, the exposed aromatic structures in HA were further degraded because of the low persistence of original aromatics, resulting in the decreased HA content during the first stage of the AD process [5]. However, with prolonged digestion, aliphatics and original aromatics degraded components (e.g., polyphenols and carboxylic acids) formed more unsaturated and stable HA via the re-polymerization process, resulting in increased HA content [2]. However, Liu et al. (2019) indicated that the change of HA content gradually increased by 48.3% in the liquid phase due to the degradation of total solid and volatile solid during the batch AD process with excess activated sludge [32]. Compared with the batch AD process, the regular feeding and discharging provided sufficient substrates for the microbial community in the continuous AD process, which may lead to lower degradation efficiency of HA, resulting in the accumulation of HA in the continuous AD process. In addition, some studies have shown that the evolution of HA content during AD process was generally positively correlated with the degree of humification [33], thus, we speculated that the HA formed from continuous AD process had a high degree of humification, resulting in HA being difficult to degrade and gradually accumulating in the AD process.
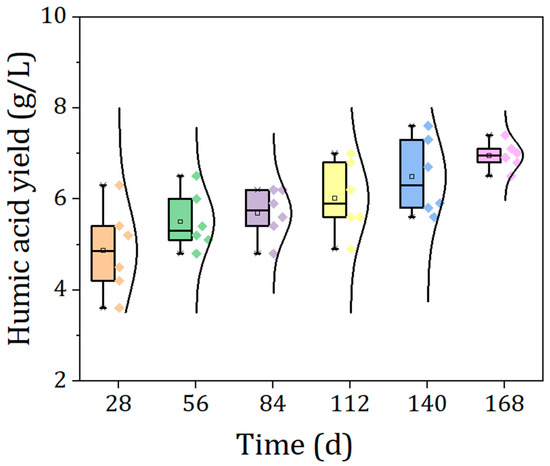
Figure 2.
The evolution of humic acid yield during the continuous anaerobic digestion process.
3.2. Characterization of the HA Component
The EEM data was further used to determine FI, HIX, and BIX indexes as indicators of source, biological activity, and degree of humification of HA, respectively [34] (Figure 3). It was found that the FI and BIX values of HA decreased (from 1.55 and 1.01 to 1.41 and 0.83, respectively) during the start-up periods of continuous AD process. According to the previous studies, the 1.2 < FI value < 1.8 represents HA formation from the terrestrial-derived and microbial-derived sources, and the BIX value > 0.6 means that the source of HA is mainly freshly produced [35]. Therefore, we can speculate that the degradation and re-polymerization of the original HA under the action of microorganisms might be responsible for the production of HA in the continuous AD process. Moreover, as an important indicator of the humification degree, the HIX value is usually positively correlated with the HA structure’s stability and maturity [2,36]. The HIX value of HA increased consistently from 2.56 to 3.43 during the start-up periods of continuous AD process, indicating that the structure stability and complexity of HA continued to increase during the degradation and re-polymerization process. A previous study confirmed that the HA formed from excess activated sludge batch AD process is more complex and with a low degree of humification via the SUVA254 and E4/E6 analysis [32]. These findings are in line with the outcomes of the current study.
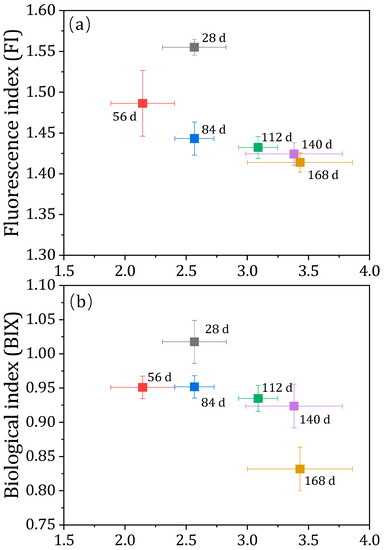
Figure 3.
Correlation between humification index (HIX) with fluorescence index (FI) (a) and biological index (BIX) (b) of humic acid during the continuous anaerobic digestion process.
Furthermore, the element composition analysis of HA is often used to predict its nature and structure [37]. As shown in Table 1, the C content increased from 38.06% to 41.28% (from 28 days to 168 days of AD process), and the nitrogen (N) content increased from 7.62% (after 28 days of AD process) to 8.56% (after 56 days of AD process). The nitrogen (N) content further increased to 8.85% after 168 days of the AD process. The increase in N might result from the condensation of lignin with protein [5]. Likewise, the condensation process might contribute to the evolution of C content in HA. Moreover, an increasing H content was observed (from 5.89% to 6.35%) herein, which may be because of the fusion of aliphatic chains with aromatic groups during the re-polymerization process [38]. The atomic ratios of H/C and C/N in HA were determined based on the results of elemental composition analysis for evaluating structural changes in the HA during the AD process, (Table 1). The H/C ratio for HA is negatively correlated with the aromaticity and positively related to the aliphaticity of the components [37]. The H/C ratio first decreased from 1.85 to 1.72 and then increased to 1.85 during the continuous AD process. The first decrease in the H/C ratio may be due to the increased maturity of HA, leading to an increase in the degree of aromatic condensation [5]. However, the H/C ratio reached a high level with the advancement of AD, which may ascribe to the increased aliphatic functional groups of HA through the degradation and re-polymerization process [37]. Moreover, the molar ratio of C/N decreased from 5.83 to 5.05 and then increased from 5.05 to 5.44 during the AD process. This changing trend can be described as carbon containing components (e.g., aliphatics) which are quickly degraded and utilized by microorganisms in the start-up periods of the AD process, resulting in a decrease in the C/N ratio, while with the extension of fermentation time, the re-polymerization of aromatic components (e.g., polyphenols and carboxylic acids) led to its ratio increasing [39].

Table 1.
The elemental composition of humic acid during the continuous anaerobic digestion process.
3.3. Dynamics of Functional Groups of HA
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is an effective tool for analyzing the functional groups of macromolecular organic compounds [23]. However, HA has complex structures and functional groups, and it might be not easy to accurately analyze the evolution of functional groups with a single FTIR spectrum. The 2D COS FTIR was employed to investigate the precise functional group alterations in HA caused by the AD process (Figure 4). It was perceived that the synchronous map of HA comprised of six auto-peaks at 3400, 1850, 1650, 1500, 1300, 1030 cm−1 and four positive cross-peaks at (1850, 3400), (1500, 1850), (1300, 1500), and (1030, 1300). The auto-peaks represented the evolution of these functional groups during the AD process, and the cross-peaks indicated a coupling interaction between these functional groups [2]. Therefore, the C-H (3400 cm−1, heteropolysaccharide-like or aliphatic-like compounds), O-H (1850 cm−1, aromatic compounds), C=O (1650 cm−1, ketones or carboxylic acid compounds), C=C (1500 cm−1, aromatic compounds), C-O (1300 cm−1 and 1030 cm−1, aryl ether or hydroxyl acid compounds), and functional groups of HA changed with the AD process.
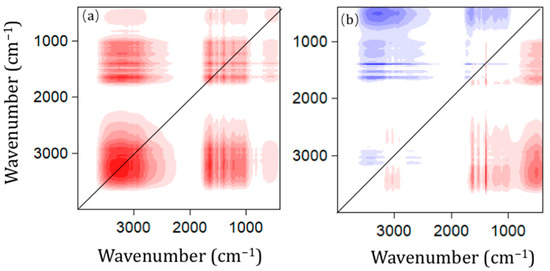
Figure 4.
2D COS FTIR correlation maps: (a) synchronous and (b) asynchronous generated from the 4000–400 cm−1 region of the spectra of humic acid formed during the continuous anaerobic digestion. Red and blue colors represent positive and negative correlations, respectively. A more intense color represents a stronger correlation.
Compared with the synchronous maps, only the occurrence of cross-peaks was observed in the asynchronous maps (Figure 4b). Eight positive cross-peaks at (1030, 3400), (1300, 3400), (1500, 3400), (1650, 3400), (1030, 1850), (1300, 1500), (1500, 1850), (1650, 1850), and three negative cross-peaks at (1030, 1300), (1500, 1850), and (1300, 1650). According to Noda’s rules, the reaction of the peaks observed during AD processes was in the following order: 3400 cm−1 > 1030 cm−1, 1300 cm−1 > 1650 cm−1 > 1500 cm−1, 1850 cm−1. Therefore, the functional groups of HA changed in the following sequence: heteropolysaccharide-like or aliphatic-like compounds > aryl ether or hydroxyl acid compounds > ketones or carboxylic acid compounds > aromatic compounds, aryl ethers. Furthermore, the content of main functional groups was further determined in this study (Table 2). An increasing trend of total acidic functional groups of HA during the AD process. A higher content of total acidic groups (9.01 ± 0.35 mmol g−1) was observed at AD 168 d. Moreover, the carboxylic acid groups (from 4.54 ± 0.48 to 5.38 ± 0.35 mmol g−1) and phenolic-OH groups (from 3.08 ± 0.24 to 3.63 ± 0.37 mmol g−1) showed a fluctuating upward trend during the continuous AD process. According to previous studies, the acidic functional groups, including carboxylic acid groups and phenolic-OH groups in HA structure, are the main functional groups contributing to the interaction between HA and heavy metals [40,41]. For instance, Wang et al. (2021) reported that the oxygen-containing functional groups (e.g., COOH and −OH) in HA were the main functional groups that contributed to its greater ability to bind heavy metals (Cu, Co, and Ni) [6]. Thus, we speculated that HA has a relatively high adsorption capacity for heavy metals based on the dynamic evolution of functional groups of HA.

Table 2.
The content of main functional groups in the humic acids extracted from different fermentation time of continuous anaerobic digestion.
3.4. Cr (VI) Adsorption and Reduction by HA
Adsorption experiments were performed to further investigate the efficient complexation of HA and Cr (VI). HA formed from the different fermentation times had a high adsorption performance (121.2 mg g−1, 135.4 mg g−1, 146.2 mg g−1, 155.1 mg g−1, 170.8 mg g−1, 179.7 mg g−1) for Cr (VI) in the initial stage (0–12 h) (Figure 5). Moreover, it was perceived that the Cr (VI) adsorption capacity of HA formed with different fermentation times was significantly different (p < 0.05). As the AD time increased from 28 days to 168 days, the overall adsorption of Cr (VI) by HA at 72 h increased from 152.1 mg g−1 to 234.9 mg g−1. Therefore, HA formed from the continuous AD process herein has a higher metal binding ability than already reported results. For example, Jang et al. (2020) employed chemically functionalized amorphous and mesoporous silica nanoparticles and observed maximum adsorption of Cr (VI), i.e., 34.0 and 42.2 mg g−1. Thus, it was concluded that the HA is an effective adsorbent for Cr (VI) [42]. The functional groups, such as oxygen-containing groups and aromatic groups in HA, may contribute to the rapid adsorption kinetics, consistent with the results of FTIR and functional groups content in the current study [25]. The kinetic data of Cr (VI) adsorption by HA was fitted using the Pseudo-first order and Pseudo-second order kinetic models, respectively (Figure 5b and Table 3). The results showed that the correlation coefficients (R2) of pseudo-first-order kinetic models were lower than pseudo-two order, indicating that the pseudo-second-order kinetic model could better interpret the Cr (VI) adsorption behavior on HA [43,44]. These findings indicated that the reaction between Cr (VI) and HA might involve multiple processes, i.e., physisorption and chemisorption [16].
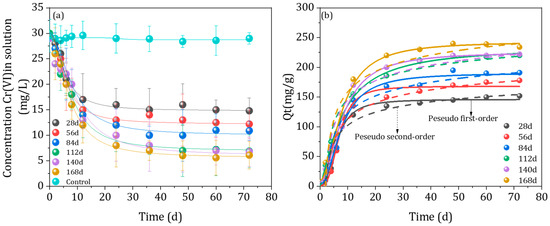
Figure 5.
Concentration variation of Cr (VI) adsorbed on humic acid formed at different times during continuous anaerobic digestion (a,b) fitted curves showing pseudo first and second order kinetics of humic acid formed at different times during continuous anaerobic digestion.

Table 3.
The Cr (VI) kinetic data and best-fit parameters of pseudo first- and second-order kinetic models.
Furthermore, to explore the Cr (VI) reduction by HA, the Cr speciation distribution in HA was determined by XPS analysis (Figure 6a). Four peaks were observed in the XPS Cr 2p peaks of HA at 585 eV, 583.5 eV, 581 eV, and 580 eV. The peaks at 583.5 eV, 581 eV, and 580 eV were ascribed to the Cr (VI), and the peak at 585 eV corresponded to Cr (III) [25,45], indicating that the Cr (VI) adsorbed onto the HA surface was reduced into Cr (III) [16]. In contrast, only the Cr (VI) peaks were observed in the XPS Cr 2p peaks of control group (Figure 6b). Moreover, the concentration of Cr (III) in HA was determined by the ICP-MS (Figure 6c). The result showed that the concentration of Cr (III) in HA formed with different fermentation times was significantly different (p < 0.05). As the time increased from 28 days to 168 days, Cr (III) concentration at 120 h increased from 49.5 mg g−1 to 60.3 mg g−1. The interaction between Cr (III) and HA followed an adsorption-reduction mechanism as reported previously [39,46]. Briefly, Cr (VI) was first bound to the surface of HA through a complexation/ion exchange pathway. The bound Cr (VI) was then reduced into Cr (III) via functional groups of the HA. Zhang et al. (2018) confirmed through the 2D COS analysis method that during the adsorption-reduction process, the phenol, hydroxyl, and carboxyl functional groups might be the primary groups participating in the reaction of HA with Cr (VI) [16]. In this study, the evolution of functional groups in HA showed that the relative content of aromatic functional groups and acidic functional groups in HA gradually increased with the incremented AD process, contributing to the adsorption-reduction interaction between HA and Cr (VI).
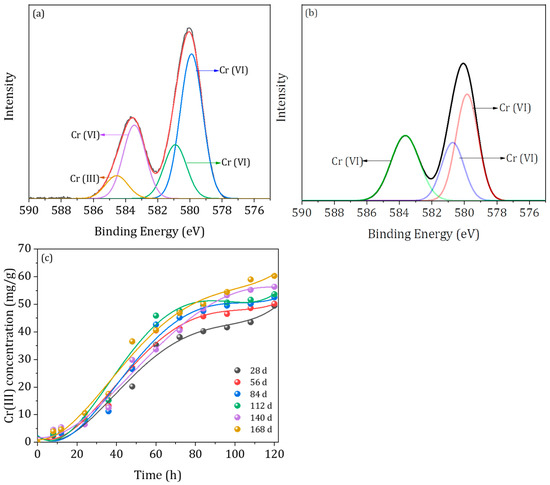
Figure 6.
(a) High-resolution XPS Cr 2p spectra of humic acid after Cr (VI) adsorption, (b) high-resolution XPS Cr 2p spectra without humic acid addition, and (c) the concentration of Cr (III) in humic acid.
4. Conclusions
The purpose of this work was to investigate the structural and functional changes in HA produced throughout the start-up periods of continuing AD process. The content of HA increased from 4.8 g L−1 to 6.9 g L−1 in the continuous AD process, with the humification index having increased. Likewise, the heteropolysaccharide-like or aliphatic-like compounds, aromatic compounds, ketones or carboxylic acid compounds, aromatic compounds), aryl ether, or hydroxyl acid compounds functional groups of HA changed following the sequence: heteropolysaccharide-like or aliphatic-like compounds > aryl ether or hydroxyl acid compounds > ketones or carboxylic acid compounds > aromatic compounds, aryl ethers. The structural evolution contributed to the high Cr (VI) adsorption and reduction by HA. The strategy of extracting HA from anaerobic digestate and its use as a metal adsorption and reduction agent will help mitigate metal contamination. However, more rigorous studies are required to explore the structure and function of HA generated during continuous anaerobic digestion and evaluate its potential of remediating contaminated soils.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation8070322/s1, Table S1: EEM location, contours and spectral loading of the five components identified by fluorescence-PARAFAC analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W. and R.D.; Methodology, A.M., X.W. and P.T.; Software, Y.S. and J.L.; Data curation, X.W., Q.Z. and Y.Z.; Writing-review and editing, A.M. and R.D.; Funding acquisition, P.T. and X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Foundation of Educational Commission of Hubei Province (Grant number: QDF2021011 and QDF2022007). The APC was found by Foundation of Educational Commission of Hubei Province (Grant number: QDF2022007).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support from the Foundation of Educational Commission of Hubei Province (QDF2021011 and QDF2022007).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Maynaud, G.; Druilhe, C.; Daumoin, M.; Jimenez, J.; Patureau, D.; Torrijos, M.; Pourcher, A.-M.; Wéry, N. Characterization of the biodegradability of post-treated digestates via the chemical accessibility and complexity of organic matter. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 231, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Muhmood, A.; Lyu, T.; Dong, R.; Liu, H.; Wu, S. Mechanisms of genuine humic acid evolution and its dynamic interaction with methane production in anaerobic digestion processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, N.; Zheng, X.; Li, M. Effect of humic acids with different characteristics on fermentative short-chain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4929–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hao, X.; Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Yu, J.; Liu, R. Adaptation of semi-continuous anaerobic sludge digestion to humic acids. Water Res. 2019, 161, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Dong, B.; Huang, J.; Wei, Y.; Dai, X.; Dai, L. Effect of aromatic repolymerization of humic acid-like fraction on digestate phytotoxicity reduction during high-solid anaerobic digestion for stabilization treatment of sewage sludge. Water Res. 2018, 143, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lyu, T.; Dong, R.; Liu, H.; Wu, S. Dynamic evolution of humic acids during anaerobic digestion: Exploring an effective auxiliary agent for heavy metal remediation. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hao, X.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Luo, Y.; Cao, D. Effect of humic acids on batch anaerobic digestion of excess sludge. Water Res. 2019, 155, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azman, S.; Khadem, A.F.; Plugge, C.M.; Stams, A.J.M.; Bec, S.; Zeeman, G. Effect of humic acid on anaerobic digestion of cellulose and xylan in completely stirred tank reactors: Inhibitory effect, mitigation of the inhibition and the dynamics of the microbial communities. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2017, 101, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Du, M.; Lee, D.J.; Wan, C.; Zheng, L.; Wan, F. Improved volatile fatty acids production from proteins of sewage sludge with anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate (AQDS) under anaerobic condition. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 103, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Lu, Y.; Fu, L.; Zhang, F.; Lau, T.; Zeng, R.J. Humic substances as electron acceptors for anaerobic oxidation of methane driven by ANME-2d. Water Res. 2018, 164, 114935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Tang, C.; Antonietti, M. Natural and artificial humic substances to manage minerals, ions, water, and soil microorganisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 6221–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canellas, L.P.; Olivares, F.L.; Aguiar, N.O.; Jones, D.L.; Nebbioso, A.; Mazzei, P.; Piccolo, A. Humic and fulvic acids as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, H.; Wu, S. Humic substances developed during organic waste composting: Formation mechanisms, structural properties, and agronomic functions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Hodson, M.E. Investigating the potential of synthetic humic-like acid to remove metal ions from contaminated water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wen, J.; Hu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xing, L.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, G. Humic substances from green waste compost: An effective washing agent for heavy metal (Cd, Ni) removal from contaminated sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Chen, H. The role of different functional groups in a novel adsorption- complexation-reduction multi-step kinetic model for hexavalent chromium retention by undissolved humic acid. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Dai, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, S.; Tian, H.; Zhu, K.; Jia, H. Mechanisms of Cr (VI) reduction by humin: Role of environmentally persistent free radicals and reactive oxygen species. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stedmon, C.A.; Bro, R. Characterizing dissolved organic matter fluorescence with parallel factor analysis: A tutorial. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2008, 6, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, T.B.; Ohno, T.; Cronan, C.S.; Simon, K.S. comPARAFAC: A Library and Tools for Rapid and Quantitative Comparison of Dissolved Organic Matter Components Resolved by Parallel Factor Analysis. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2014, 12, 114–125. Available online: http://digitalcommons.library.umaine.edu/mitchellcenter_pubs/78 (accessed on 5 June 2021). [CrossRef]
- Kamjunke, N.; Herzsprung, P.; Neu, T.R. Quality of dissolved organic matter affects planktonic but not biofilm bacterial production in streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506–507, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellerman, A.M.; Guillemette, F.; Podgorski, D.C.; Aiken, G.R.; Butler, K.D.; Spencer, R.G.M. Unifying concepts linking dissolved organic matter composition to persistence in aquatic ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2538–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.S.; Xi, B.D.; Gao, R.T.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Cui, D.Y.; Tan, W.B. Using fluorescence spectroscopy coupled with chemometric analysis to investigate the origin, composition, and dynamics of dissolved organic matter in leachate-polluted groundwater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8499–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Tan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J.; Sun, Q.; Qi, H.; Xie, X.; Wei, Z. Diversity in the mechanisms of humin formation during composting with different materials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3653–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, H.P. Some aspects of the surface chemistry of carbon blacks and other carbons. Carbon 1994, 32, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhao, J.; He, F.; Zhong, Z.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Y. Ball milling biochar iron oxide composites for the removal of chromium (Cr (VI)) from water: Performance and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Xi, B.D.; He, X.S.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, X.H. Hydrophobicity-dependent electron transfer capacities of dissolved organic matter derived from chicken manure compost. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zou, S.; Li, C. Recovery of sludge humic acids with alkaline pretreatment and its impact on subsequent anaerobic digestion. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclntyre, A.M.; Gueguen, C. Binding interactions of algal-derived dissolved organic matter with metal ions. Cheremosphere 2013, 90, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, S.K.; Boyer, T.H. Behavior of recoccurring PARAFAC components in fluorescent dissolved organic matter in natural and engineered systems: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2006–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santin, C.; Yamashita, Y.; Otero, X.L.; Alvarez, M.A.; Jaffe, R. Characterizing humic substances from estuarine soils and sediments by excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy and parallel factor analysis. Biogeochemistry 2009, 96, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Hao, X.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Zhou, P.; Li, J. Dynamics of humic substance composition during anaerobic digestion of excess activated sludge. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2019, 145, 104771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Evolution of humic substances during anaerobic sludge digestion. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2017, 16, 1577–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedetti, M.; Cuet, P.; Guigue, C.; Goutx, M. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in a coral reef ecosystem subjected to anthropogenic pressures using multi-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2198–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Qi, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, H. Revealing the impact of pyrolysis temperature on dissolved organic matter released from the biochar prepared from Typha orientalis. Chemosphere 2019, 228, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguest, A.; Vacher, L.; Relexans, S.; Saubusse, S.; Froidefond, J.M.; Parlanti, E. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.S.; Xi, B.D.; Jiang, Y.H.; Li, M.X.; Yu, H.B.; An, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.L. Elemental and spectroscopic methods with chemometric analysis for characterizing composition and transformation of dissolved organic matter during chicken manure composting. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 2033–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.F.; Wu, Q.T.; Wong, J.W.C.; Nagar, B.B. Transformation of organic matter during co-composting of pig manure with sawdust. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, L.; Samuel, B.; Chang, J.; Liu, F.; Chen, H. Molecular structure-reactivity correlations of humic acid and humin fractions from a typical black soil for hexavalent chromium reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2975–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Muhmood, A.; Dong, R.; Wu, S. Synthesis of humic-like acid from biomass pretreatment liquor: Quantitative appraisal of electron transferring capacity and metal-binding potential. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Li, X.; Zhao, T.; Li, Z.; Wu, C.; He, Z.; Luo, J. Analysis of dynamic changes of sugars in the solid fermentation of monascus. Food Res. Dev. 2018, 39, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, E.H.; Pack, S.P.; Kim, I.; Chung, S. A systematic study of hexavalent chromium adsorption and removal from aqueous environments using chemically functionalized amorphous and mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalhmunsiama; Tiwari, D.; Lee, S.-M. Surface-functionalized activated sericite for the simultaneous removal of cadmium and phenol from aqueous solutions: Mechanistic insights. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 1414–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Yin, H.; Jin, S.; Liu, F.; Chen, H. Mechanism study of humic acid functional groups for Cr (VI) retention: Two-dimensional FTIR and 13C CP /MAS NMR correlation spectroscopic. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera-díaz, C.E.; Lugo-lugo, V.; Bilyeu, B. A review of chemical, electrochemical and biological methods for aqueous Cr (VI) reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 223–224, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).