The Effect of Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Inoculants on Silage Quality, Phenolic Acid Profiles, Bacterial Community and In Vitro Rumen Fermentation Characteristic of Whole Corn Silage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Preparation of Corn Silage
2.2. Sampling and Analytical Methods
2.3. Determination of Extracted Phenolic Acids
2.4. In Vitro Rumen Fermentation
2.5. Bacterial Community Analysis
2.6. Calculations
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
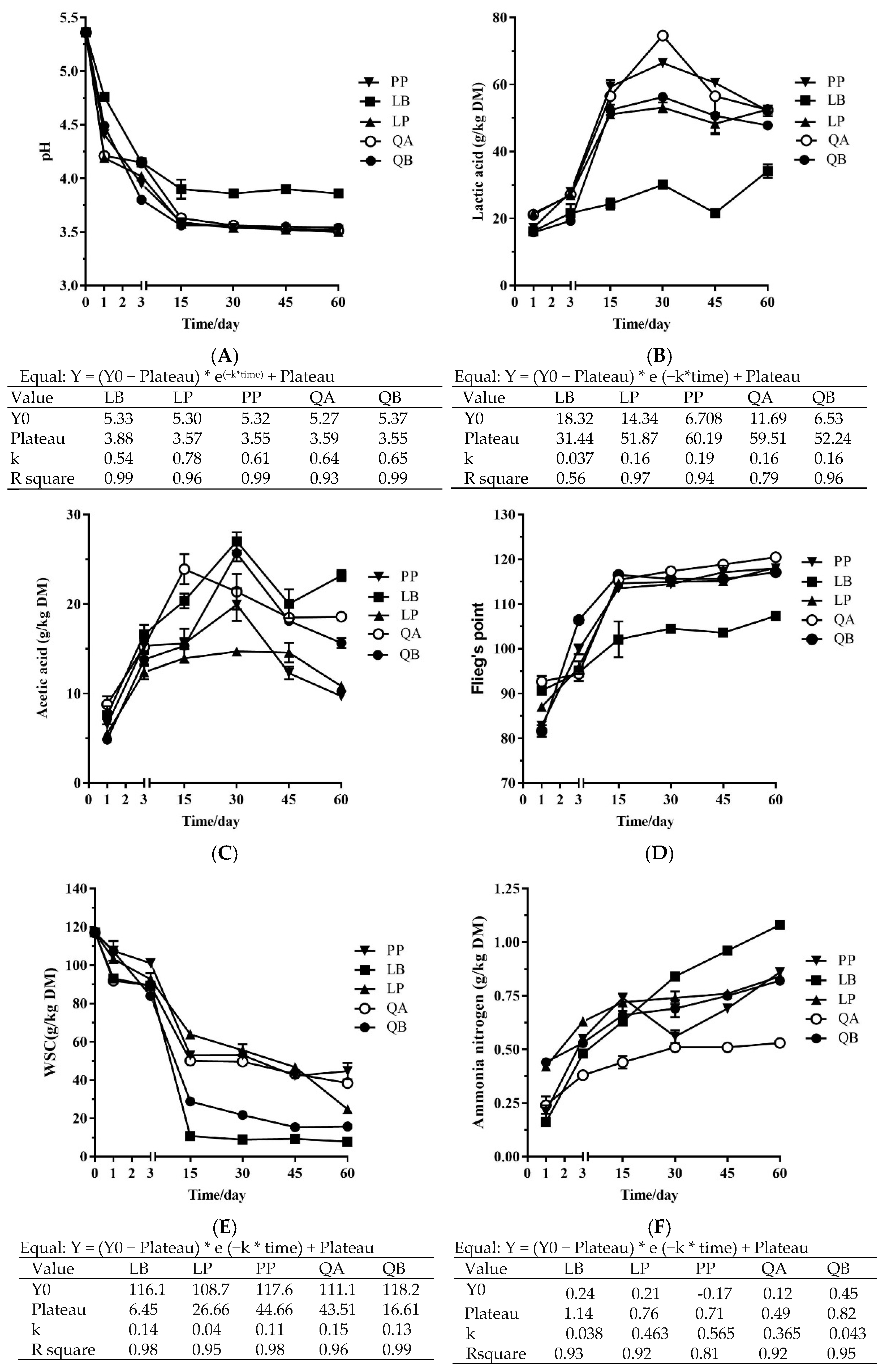
3.1. Fermentation Profile, Chemical Composition and Microbial Numbers of Silage during Fermentation
3.2. Structural Carbohydrate Compositions of Whole Corn Silages after 60 Days Ensiling
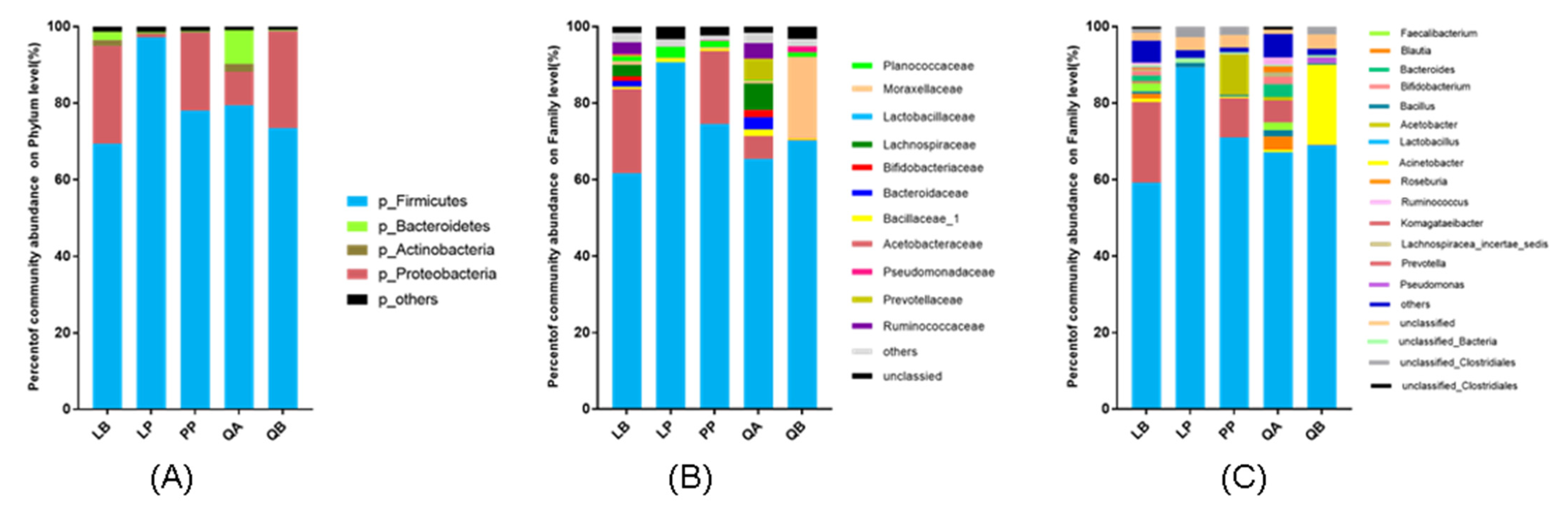
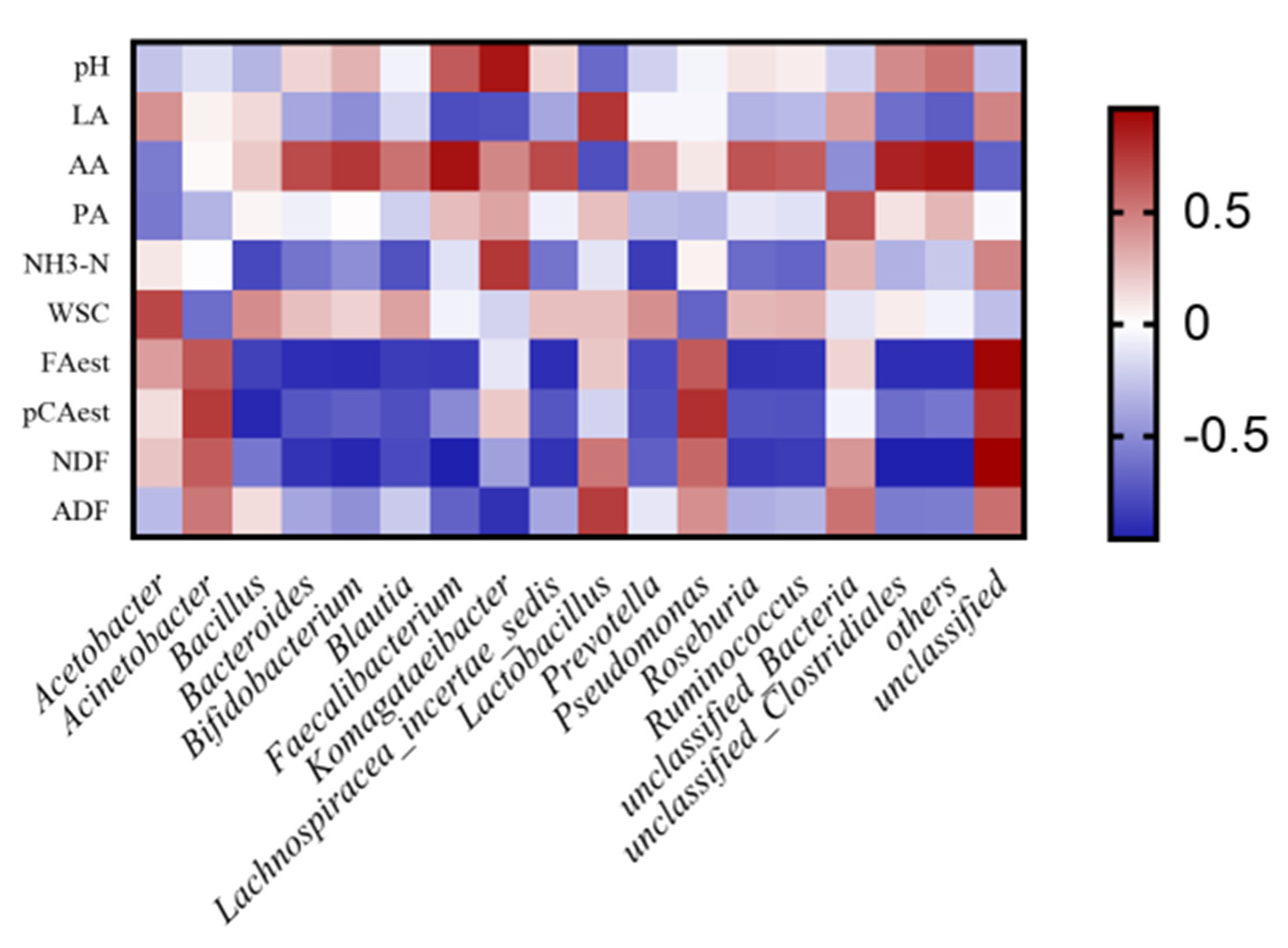
3.3. Bacterial Community of Silage after 60 Days Ensiling
3.4. In Vitro Degradability and Kinetic Gas Production of 60 Days Ensiling Whole Corn Silage
4. Discussion
4.1. Fermentation Profile, Chemical Composition and Microbial Profile of Whole Corn Silages during Fermentation
4.2. Chemical Composition of Whole Corn Silage in Response to Different LAB after 60 Days Ensiling
4.3. The Change of Ester-Linked Ferulic and P-Coumaric Acid of Whole Corn Silage during Ensiling in Response to Different LAB Inoculants
4.4. Bacterial Community of Silage after 60 Days Ensiling
4.5. In Vitro Rumen Fermentation Characteristic of Whole Corn Silage in Responses to Different LAB Inoculants
4.5.1. In Vitro Rumen Degradation in Different LAB Treated Whole Corn Silage
4.5.2. Kinetic Gas Production in Different LAB Treated Whole Corn Silage
4.5.3. In Vitro Rumen-Fermentation Characteristic Responses to LAB
4.5.4. Fermentation Gas Composition
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faulds, C.B. What can feruloyl esterases do for us? Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Gao, Y.; He, W.; Hu, H.; Tian, M.; Wang, K.; Pan, S. Production of nano bacterial cellulose from beverage industrial waste of citrus peel and pomace using Komagataeibacter xylinus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badhan, A.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y.; Han, S.; Kowalczys, K.; Brown, D.C.; Ayala, C.J.; Latoszek-Green, M.; Miki, B.; Tsang, A. Expression of a fungal ferulic acid esterase in alfalfa modifies cell wall digestibility. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2014, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casler, M.D.; Jung, H.-J.G. Relationships of fibre, lignin, and phenolics to in vitro fibre digestibility in three perennial grasses. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2006, 125, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casler, M.D.; Jung, H.-J.G. Selection and evaluation of smooth bromegrass clones with divergent lignin or etherified ferulic acid concentration. Crop Sci. 1999, 39, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, C.; Surget, A.; Rouau, X. Relative amounts of tissues in mature wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grain and their carbohydrate and phenolic acid composition. J. Cereal Sci. 2007, 45, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabber, J.H. How do lignin composition, structure, and cross-linking affect degradability? A review of cell wall model studies. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabber, J.H.; Hatfield, R.D.; Ralph, J.; Zon, J.; Amrhein, N. Ferulate Cross-Linking in Cell-Walls Isolated from Maize Cell-Suspensions. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besle, J.M.; Cornu, A.S.; Jouany, J.I. Roles of structural phenylpropanoids in forage cell wall digestion. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1994, 64, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabber, J.H.; Mertens, D.R.; Kim, H.; Funk, C.; Lu, F.; Ralph, J. Cell wall fermentation kinetics are impacted more by lignin content and ferulate cross-linking than by lignin composition. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blajman, J.E.; Vinderola, G.; Páez, R.B.; Signorini, M.L. The role of homofermentative and heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria for alfalfa silage: A meta-analysis. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 158, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Lei, L.; Wang, X.F.; Zeng, Z.H.; Hu, Y.G.; Cui, Z.J. Effects of Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus plantarum on fermentation, aerobic stability, bacteria diversity and ruminal degradability of alfalfa silage. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.B.; Jin, X.; Yang, H.J.; Li, S.L.; Jiang, L.S. Microbial release of ferulic and p-coumaric acids from forages and their digestibility in lactating cows fed total mixed rations with different forage combinations. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, I.M. Changes in the cell wall components of laboratory silages and the effect of various additives on these changes. J. Agric. Sci. 1979, 93, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ke, W.; Ding, Z.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D.; Li, Z.; Guo, X. Pretreatment of Pennisetum sinese silages with ferulic acid esterase-producing lactic acid bacteria and cellulase at two dry matter contents: Fermentation characteristics, carbohydrates composition and enzymatic saccharification. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 295, 122261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, D.G.; Yang, H.J.; Cao, B.B.; Wu, T.T.; Wang, J.Q. The beneficial effect of Enterococcus faecium on the in vitro ruminal fermentation rate and extent of three typical total mixed rations in northern China. Livest. Sci. 2014, 167, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisheries and Food: Ministry of Agriculture. The Analysis of Agricultural Materials, 3rd ed.; HM Stationery Office: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.-B.; Wang, R.; Bo, Y.-K.; Bai, S.; Yang, H.-J. In situ rumen digestibility of ester-linked ferulic and p-coumaric acids in crop stover or straws in comparison with alfalfa and Chinese wild ryegrass hays. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 212, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdouw, H.; Echteld, C.; Dekkers, E. Ammonia determination based on indophenol formation with sodium salicylate. Water Res. 1978, 12, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, H.; Sharma, O.; Dawra, R.; Negi, S. Simple determination of microbial protein in rumen liquor. J. Dairy Sci. 1982, 65, 2170–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, W.K.; Zhang, Z.W.; Yang, H.J. Beneficial effect of Rhodopseudomonas palustris on in vitro rumen digestion and fermentation. Benefic. Microbes 2019, 11, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Yu, Z. Fermentation dynamics and bacterial diversity of mixed lucerne and sweet corn stalk silage ensiled at six ratios. Grass Forage Sci. 2019, 74, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, T.; Sun, Z.; Gao, R.; Yu, Z. Lactic acid bacterial inoculant effects on the vitamin content of alfalfa and Chinese leymus silage. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, J.C.; Cone, J.W.; Williams, B.A.; Debersaques, F.M.; Lantinga, E.A. Multiphasic analysis of gas production kinetics for in vitro fermentation of ruminant feeds. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1996, 64, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ørskov, E. Manipulation of rumen fermentation for maximum food utilization. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 1975, 22, 152–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Wu, J.; Shao, T. Enhancement of lignocellulosic degradation in high-moisture alfalfa via anaerobic bioprocess of engineered Lactococcus lactis with the function of secreting cellulase. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 12, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ke, W.; Ding, W.; Ding, L.; Xu, D.; Wang, W.; Zhang, P.; Yang, F. Profiling of metabolome and bacterial community dynamics in ensiled Medicago sativa inoculated without or with Lactobacillus plantarum or Lactobacillus buchneri. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zobell, D.R.; Okine, E.K.; Olson, K.C.; Wiedmeier, R.D.; Stonecipher, C. The Feasibility of Feeding High Levels of Whey Silage and Effects on Production in Growing Cattle. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2004, 3, 804–809. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, V.R.N.; Oliveira-Tintino, C.C.D.M.; Santos, E.S.; Morais, L.S.P.; Tintino, S.R.; Freitas, T.S.; Geraldo, Y.S.; Pereira, R.L.S.; Cruz, R.P.; Menezes, I.R.A. Antimicrobial and enhancement of the antibiotic activity by phenolic compounds: Gallic acid, caffeic acid and pyrogallol. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 99, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.S.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Ogunade, I.M.; Cervantes, A.; Arriola, K.G.; Yun, J.; Kim, D.; Li, X.; Goncalves, M.C.M.; Vyas, D. Meta-analysis of effects of inoculation with homofermentative and facultative heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria on silage fermentation, aerobic stability, and the performance of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4587–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, D.R.; Muck, R.E.; Harrison, J.H. Silage Science and Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Ding, W.; Ke, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, P.; Guo, X. Modulation of metabolome and bacterial community in whole crop corn silage by inoculating homofermentative Lactobacillus plantarum and heterofermentative Lactobacillus buchneri. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.X.; Zhao, Q.X.; Zhang, M.Z. Lactic acid bacteria strains for enhancing the fermentation quality and aerobic stability of Leymus chinensis silage. Grass Forage Sci. 2016, 71, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addah, W. Effects of Silage Inoculants on Silage Fermentation, Aerobic Stability and Animal Performance; University of Alberta: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ambyejensen, M. Ensiling as Pretreatment of Grass for Lignocellulosic Biomass Conversion; Technical University of Denmark: Lyngby, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Gao, F.; Yu, Z.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Cai, Y. Fermentation quality and chemical composition of shrub silage treated with lactic acid bacteria inoculants and cellulase additives. Anim. Sci. J. 2012, 83, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunière, L.; Sindou, J.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Chevallier, I.; Thévenot-Sergentet, D. Silage processing and strategies to prevent persistence of undesirable microorganisms. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2013, 182, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Franco, M.; Cai, Y.; Yu, Z. Dynamics of fermentation profile and bacterial community of silage prepared with alfalfa, whole-plant corn and their mixture. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2020, 270, 114702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlow, G.; Muck, R.E.; Driehuis, F.; Elferink, S.J.O.; Spoelstra, S.F. Microbiology of ensiling. Silage Sci. Technol. 2003, 42, 31–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addah, W. Can inoculation of silage with a ferulic acid esterase-producing inoculant reduce enteric methane emissions in Ghana? Ghana J. Sci. Technol. Dev. 2015, 3, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Ávila, C.; Pinto, J.; Carvalho, B.; Dias, D.; Schwan, R. Fermentative profile and bacterial diversity of corn silages inoculated with new tropical lactic acid bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, W.; Wu, Z.; Yu, Z. Effects of ferulic acid esterase-producing lactic acid bacteria and storage temperature on the fermentation quality, in vitro digestibility and phenolic acid extraction yields of sorghum (sorghum bicolor L.) silage. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmit, D.H.; Kung, L., Jr. The Effects of Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 and Pediococcus pentosaceus R1094 on the Fermentation of Corn Silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 3999–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ding, Z.; Ke, W.; Xu, D.; Zhang, P.; Bai, J.; Mudassar, S.; Muhammad, I.; Guo, X. Ferulic acid esterase-producing lactic acid bacteria and cellulase pretreatments of corn stalk silage at two different temperatures: Ensiling characteristics, carbohydrates composition and enzymatic saccharification. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Bai, Y.; Jia, Y.; Shao, T. Ensiling as pretreatment of rice straw: The effect of hemicellulase and Lactobacillus plantarum on hemicellulose degradation and cellulose conversion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, G.; Shen, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, S.L.; Shao, T.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.X.; Xu, Q.F.; Huo, W.J. The effect of lactic acid bacteria inoculums on in vitro rumen fermentation, methane production, ruminal cellulolytic bacteria populations and cellulase activities of corn stover silage. J. Integr. Agr. 2020, 19, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.S.; Chan, V.J.; Liao, H.; Zidwick, M.J. Cloning of a novel feruloyl esterase gene from rumen microbial metagenome and enzyme characterization in synergism with endoxylanases. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giada, M. Food phenolic compounds: Main classes, sources and their antioxidant power. In Oxidative Stress and Chronic Degenerative Diseases: A Role for Antioxidants; Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2013; Volume 2013, pp. 87–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.S.; Chan, V.J.; Liao, H. Metagenomic discovery of feruloyl esterases from rumen microflora. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 8449–8457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spínola, J.E.L.; Reis, S.T.D.; Sales, E.C.J.D.; Monção, F.P.; Rigueira, J.P.S.; Delvaux, N.D.A. Phenolic acids and ruminal parameters of different varieties of sugarcane in natura or ensiled. Acta Sci. Anim. Sci. 2017, 39, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boudaoud, S.; Aouf, C.; Devillers, H.; Sicard, D.; Segond, D. Sourdough yeast-bacteria interactions can change ferulic acid metabolism during fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2021, 98, 103790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; He, H.; Zhang, S.; Guo, T.; Kong, J. Characterization of Feruloyl Esterases Produced by the Four Lactobacillus Species: L. amylovorus, L. acidophilus, L. farciminis and L. fermentum, Isolated from Ensiled Corn Stover. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.A.M.; Guedes, C.M.; Cone, J.W.; van Gelder, A.H.; Ferreira, L.M.M.; Sequeira, C.A. Effects of phenolic acid structures on meadow hay digestibility. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 136, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.G.; Allen, M.S. Characteristics of plant cell walls affecting intake and digestibility of forages by ruminants. J. Anim. Sci. 1995, 73, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, N.; Adesogan, A.; Staples, C.; Krueger, W.; Dean, D.; Littell, R. The potential to increase digestibility of tropical grasses with a fungal, ferulic acid esterase enzyme preparation. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2008, 145, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Shao, T. Dynamics of microbial community and fermentation quality during ensiling of sterile and nonsterile alfalfa with or without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Huan, H.; Gu, H.; Xu, N.; Shen, Q.; Ding, C. Dynamics of a microbial community during ensiling and upon aerobic exposure in lactic acid bacteria inoculation-treated and untreated barley silages. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikmeyer, F.G.; Köfinger, P.; Poschenel, A.; Jünemann, S.; Zakrzewski, M.; Heinl, S.; Mayrhuber, E.; Grabherr, R.; Pühler, A.; Schwab, H. Metagenome analyses reveal the influence of the inoculant Lactobacillus buchneri CD034 on the microbial community involved in grass ensiling. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 167, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgarvey, J.A.; Franco, R.B.; Palumbo, J.D.; Hnasko, R.; Stanker, L.; Mitloehner, F.M. Bacterial population dynamics during the ensiling of Medicago sativa (alfalfa) and subsequent exposure to air. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, B.; Su, R.; Pan, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, G.; Tao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhong, J. Assessing the fermentation quality and microbial community of the mixed silage of forage soybean with crop corn or sorghum. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Shuai, Y.; Feng, G.; Ran, Q.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Microbial communities and natural fermentation of corn silages prepared with farm bunker-silo in Southwest China. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominik, S.; Anna, D. Novel ferulic acid esterases from Bifidobacterium sp. produced on selected synthetic and natural carbon sources. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2010, 9, 563–567. [Google Scholar]
- Donaghy, J.; Kelly, P.F.; Mckay, A.M. Detection of ferulic acid esterase production by Bacillus spp. and lactobacilli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 50, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Xiong, T.; Wang, X.; Deng, H.; Bai, Y.; Fan, T.; Zheng, X.; Cai, Y. A novel feruloyl esterase with high rosmarinic acid hydrolysis activity from Bacillus pumilus W3. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSweeney, C.; Dulieu, A.; Katayama, Y.; Lowry, J. Solubilization of lignin by the ruminal anaerobic fungus Neocallimastix patriciarum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 2985–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semjonovs, P.; Ruklisha, M.; Paegle, L.; Saka, M.; Treimane, R.; Skute, M.; Rozenberga, L.; Vikele, L.; Sabovics, M.; Cleenwerck, I. Cellulose synthesis by Komagataeibacter rhaeticus strain P 1463 isolated from Kombucha. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksu, T.; Baytok, E.; Bolat, D. Effects of a bacterial silage inoculant on corn silage fermentation and nutrient digestibility. Small Rumin. Res. 2004, 55, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.; Soderlund, S.; Loney, K. Effect of inoculation rate of selected strains of lactic acid bacteria on fermentation and in vitro digestibility of grass-legume forage. J. Dairy Sci. 1989, 72, 2421–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsereko, V.L.; Smiley, B.K.; Rutherford, W.M.; Spielbauer, A.; Forrester, K.J.; Hettinger, G.H.; Harman, E.K.; Harman, B.R. Influence of inoculating forage with lactic acid bacterial strains that produce ferulate esterase on ensilage and ruminal degradation of fiber. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2008, 145, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addah, W.; Baah, J.; Groenewegen, P.; Okine, E.K.; Mcallister, T.A. Comparison of the fermentation characteristics, aerobic stability and nutritive value of barley and corn silages ensiled with or without a mixed bacterial inoculant. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 91, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandebvu, P.; West, J.W.; Hill, G.M.; Gates, R.N.; Hatfield, R.D.; Mullinix, B.G.; Parks, A.H.; Caudle, A.B. Comparison of Tifton 85 and Coastal bermudagrasses for yield, nutrient traits, intake, and digestion by growing beef steers. J. Anim. Sci. 1999, 77, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Torres, M.; Reverón, I.; Mancheño, J.M.; de Las Rivas, B.; Muñoz, R. Characterization of a feruloyl esterase from Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5130–5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.; Kroon, P.A.; Faulds, C.B. Hairy plant polysaccharides: A close shave with microbial esterases. Microbiology 1998, 144, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesogan, A.T.; Arriola, K.G.; Jiang, Y.; Oyebade, A.; Paula, E.M.; Pech-Cervantes, A.A.; Romero, J.J.; Ferraretto, L.F.; Vyas, D. Symposium review: Technologies for improving fiber utilization. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 5726–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffrenato, E.; Fievisohn, R.; Cotanch, K.W.; Grant, R.J.; Chase, L.E.; Van Amburgh, M.E. Effect of lignin linkages with other plant cell wall components on in vitro and in vivo neutral detergent fiber digestibility and rate of digestion of grass forages. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 8119–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Shao, T. Effects of lactic acid bacteria inoculants and fibrolytic enzymes on the fermentation quality, in vitro degradability, ruminal variables and microbial communities of high-moisture alfalfa silage. Grassl. Sci. 2019, 64, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Shao, T. Ensiling characteristics, in vitro rumen fermentation, microbial communities and aerobic stability of low-dry matter silages produced with sweet sorghum and alfalfa mixtures. J. Sci. Food. Argic. 2019, 99, 2140–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynal, S.M.; Ipharraguerre, I.R.; Liñeiro, M.; Brito, A.F.; Broderick, G.A.; Clark, J.H. Omasal flow of soluble proteins, peptides, and free amino acids in dairy cows fed diets supplemented with proteins of varying ruminal degradabilities. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1887–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jal, D.; Váradyová, Z.; Lauková, A.; Homolka, P.; Jan?Ík, F. Effect of inoculated corn silage on rumen fermentation and lipid metabolism in an artificial rumen (RUSITEC). Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 152, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khota, W.; Pholsen, S.; Higgs, D.; Yimin, C. Fermentation quality and in vitro methane production of sorghum silage prepared with cellulase and lactic acid bacteria. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.; Hindrichsen, I.; Klop, G.; Kinley, R.; Milora, N.; Bannink, A.; Dijkstra, J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria silage inoculation on methane emission and productivity of Holstein Friesian dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 7159–7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, S.E.; Wright, A.-D.G.; McBride, B.W. Methanogens: Methane producers of the rumen and mitigation strategies. Archaea 2010, 2010, 945785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.H. Influence of hydrogen on rumen methane formation and fermentation balances through microbial growth kinetics and fermentation thermodynamics. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2010, 160, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Item 1 | Value |
|---|---|
| DM | 283 g/kg FM |
| WSC | 117 g/kg DM |
| NDF | 373 g/kg DM |
| ADF | 214 g/kg DM |
| pCAest | 9.54 g/kg DM |
| FAest | 5.33 g/kg DM |
| Item 1 | Microbial Inoculant 2 | SEM 3 | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LB | LP | PP | QA | QB | |||
| pH | 3.85 a | 3.50 d | 3.52 c | 3.51 cd | 3.54 b | 0.019 | <0.01 |
| Lactate (g/kg DM) | 34.18 c | 52.52 a | 52.14 a | 47.26 b | 47.78 b | 1.161 | <0.01 |
| Acetate (g/kg DM) | 23.18 a | 10.84 d | 9.71 d | 18.58 b | 15.65 c | 0.503 | <0.01 |
| Propionate (g/kg DM) | 3.56 c | 3.56 c | 2.29 a | 2.52 b | 2.53 b | 0.191 | <0.01 |
| Butyrate (g/kg DM) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.004 | ns |
| Lactae:Acetate | 1.47 e | 4.86 b | 5.37 a | 2.54 d | 3.06 c | 0.091 | <0.01 |
| WSC (g/kg DM) | 7.86 e | 24.72c | 44.61 a | 38.42 b | 15.73 d | 0.787 | <0.01 |
| NH3-N (g/kg DM) | 1.04 a | 0.84 b | 0.87 b | 0.52 c | 0.81 b | 0.012 | <0.01 |
| Item 1 | Microbial Inoculant 2 | SEM 3 | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LB | LP | PP | QA | QB | |||
| DM (g/kg FW) | 283.08 a | 265.67 b | 268.44 b | 280.02 a | 269.27 b | 2.259 | 0.007 |
| Flieg’s point | 107.35 c | 118.13 b | 118.02 b | 120.47 a | 117.12 b | 0.472 | <0.001 |
| NDF (g/kg DM) | 347.28 b | 368.95 a | 368.97 a | 345.13 b | 378.33 a | 4.905 | 0.01 |
| ADF (g/kg DM) | 196.49 b | 215.83 a | 203.32 ab | 206.81 ab | 215.44 a | 4.104 | 0.001 |
| Hemicellullose (g/kg DM) | 150.78 ab | 153.12 ab | 165.64 a | 138.31 b | 162.88 a | 6.093 | 0.002 |
| Phenolic acid(g/kg DM) | |||||||
| FAest | 4.37 b | 4.32 b | 4.63 ab | 4.12 c | 4.75 a | 0.160 | 0.002 |
| pCA est | 8.38 b | 8.62 ab | 8.11c | 8.11 c | 8.76 a | 0.104 | 0.03 |
| Item 1 | Microbial Inoculant 2 | S.E.M 3 | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LB | LP | PP | QA | QB | |||
| Reads number | 58850 | 60847 | 48528 | 70558 | 46562 | 4133.1 | ns |
| OTU2 number | 275.00 b | 359.50 a | 391.50 a | 411.67 a | 398.00 a | 20.149 | 0.03 |
| Ace | 326.64 b | 415.74 a | 467.84 a | 429.32 a | 472.64 a | 17.067 | 0.01 |
| Shannon | 1.81 b | 0.61 d | 1.26 bc | 2.51 a | 0.82 cd | 0.078 | 0.01 |
| Simpson | 0.36 c | 0.78 a | 0.56 b | 0.20 c | 0.69 ab | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| Chao | 329.50 b | 429.87 a | 459.54 a | 434.39 a | 488.42 a | 16.87 | 0.03 |
| Coverage (%) | 99.86 | 99.85 | 99.83 | 99.95 | 99.83 | 0.052 | ns |
| Items 1 | Microbial Inoculant 2 | SEM 3 | p Value 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LB | LP | PP | QA | QB | |||
| Ruminal degradability | |||||||
| IVDMD48 | 77.84 ab | 75.73 c | 76.64 bc | 78.48 a | 76.04 c | 0.465 | 0.02 |
| IVNDFD48 | 47.93 a | 43.79 b | 44.17 b | 47.45 a | 43.14 b | 0.577 | 0.004 |
| IVADFD48 | 44.20 bc | 45.55 ab | 45.45 ab | 46.55 a | 42.42 c | 0.643 | <0.01 |
| IVDMD96 | 86.27 bc | 87.15 ab | 87.54 ab | 88.20 a | 85.23 c | 0.532 | <0.01 |
| GP48 | 79.35 abc | 79.92 abc | 71.30 c | 88.98 a | 75.46 bc | 2.683 | 0.03 |
| Gas production kinetics | |||||||
| A (mL/g DM) | 85.13 ab | 81.81 bc | 74.65 c | 91.65 a | 74.50 c | 1.376 | <0.01 |
| B | 1.93 bc | 1.76 c | 2.10 ab | 1.76 c | 2.17 a | 0.059 | 0.01 |
| C (h) | 4.63 c | 5.17 b | 4.34 d | 5.44 a | 4.85 c | 0.056 | <0.01 |
| AGPR | 9.82 a | 7.41 c | 8.17 bc | 8.19 bc | 8.09 bc | 0.262 | <0.01 |
| Ruminal fermentation profile | |||||||
| pH | 6.91 | 6.91 | 6.9 | 6.89 | 6.85 | 0.04 | Ns |
| NH3-N (mmol/L) | 14.33 a | 11.53 c | 13.40 ab | 12.65 bc | 13.28 ab | 0.34 | <0.01 |
| MCP (mg/mL) | 0.42 ab | 0.40 b | 0.37 b | 0.45 a | 0.28 c | 0.018 | 0.01 |
| tVFA (mmol/L) | 99.47 a | 92.89 b | 100.42 a | 103.48 a | 93.16 b | 1.403 | 0.04 |
| VFA pattern (%, molar) | |||||||
| Acetate | 48.42 | 48.55 | 48.93 | 48.60 | 47.95 | 0.337 | ns |
| Propionate | 36.73 b | 37.42 b | 36.40 b | 38.27 a | 36.56 b | 0.37 | 0.02 |
| Butyrate | 10.53 | 10.52 | 10.81 | 10.59 | 10.83 | 0.286 | ns |
| Iso-valerate acid | 1.99 | 1.67 | 1.67 | 1.84 | 1.84 | 0.096 | ns |
| Valerate | 2.22 | 2.11 | 2.17 | 2.15 | 2.25 | 0.045 | ns |
| Acetate:Propionate | 1.31 ab | 1.30 ab | 1.36 a | 1.25 b | 1.35 a | 0.024 | <0.01 |
| NGR | 1.77 b | 1.82 b | 1.84 b | 2.03 a | 1.72 b | 0.031 | <0.01 |
| Gas component (%, molar) | |||||||
| H2 | 0.06 a | 0.05 a | 0.03 bc | 0.01c | 0.04 ab | 0.006 | <0.01 |
| CH4 | 16.57 bc | 18.53 a | 17.37 b | 15.89 c | 17.24 b | 0.211 | 0.03 |
| CO2 | 83.35 ab | 80.59 c | 81.16 b | 84.09 a | 83.00 ab | 0.664 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-L.; Wang, W.-K.; Wu, Q.-C.; Zhang, F.; Li, W.-J.; Yang, Z.-M.; Bo, Y.-K.; Yang, H.-J. The Effect of Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Inoculants on Silage Quality, Phenolic Acid Profiles, Bacterial Community and In Vitro Rumen Fermentation Characteristic of Whole Corn Silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8060285
Wang Y-L, Wang W-K, Wu Q-C, Zhang F, Li W-J, Yang Z-M, Bo Y-K, Yang H-J. The Effect of Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Inoculants on Silage Quality, Phenolic Acid Profiles, Bacterial Community and In Vitro Rumen Fermentation Characteristic of Whole Corn Silage. Fermentation. 2022; 8(6):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8060285
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yan-Lu, Wei-Kang Wang, Qi-Chao Wu, Fan Zhang, Wen-Juan Li, Zhuo-Meng Yang, Yu-Kun Bo, and Hong-Jian Yang. 2022. "The Effect of Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Inoculants on Silage Quality, Phenolic Acid Profiles, Bacterial Community and In Vitro Rumen Fermentation Characteristic of Whole Corn Silage" Fermentation 8, no. 6: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8060285
APA StyleWang, Y.-L., Wang, W.-K., Wu, Q.-C., Zhang, F., Li, W.-J., Yang, Z.-M., Bo, Y.-K., & Yang, H.-J. (2022). The Effect of Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Inoculants on Silage Quality, Phenolic Acid Profiles, Bacterial Community and In Vitro Rumen Fermentation Characteristic of Whole Corn Silage. Fermentation, 8(6), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8060285







