Abstract
Probiotics retrieved from animal sources have substantial health benefits for both humans and animals. The present study was designed to identify lactic acid bacteria (LAB) isolated from domestic water buffalo milk (Bubalus bubalis) and to evaluate their potential as target-based probiotics. Forty-six LAB strains were isolated and, among them, five strains (NMCC-M2, NMCC-M4, NMCC-M5, NMCC-M6, and NMCC-M7) were regarded as possible probiotics on the basis of their phenotypic and biochemical properties. These isolates were molecularly identified as Weissella confusa (NMCC-M2), Leuconostoc pseudo-mesenteroides (NMCC-M4), Lactococcus lactis Subsp. hordniae (NMCC-M5), Enterococcus faecium NMCC-M6, and Enterococcus lactis NMCC-M7. The tested bacterial strains showed significant antimicrobial activity, susceptibility to antibiotics, acid and bile tolerance, sugar fermentation, enzymatic potential, and nonhemolytic characteristics. Interestingly, NMCC-M2 displayed the best probiotic features including survival at pH 3 and 0.5% (w/v) bile salts, complete susceptibility to the tested antibiotics, high enzymatic potential, and in vitro cholesterol reduction (48.0 µg/mL for NMCC-M2) with 0.3% bile salt supplementation. Therefore, the isolated strain NMCC-M2 could be considered as a potential target-based probiotic in cholesterol-lowering fermented food products.
1. Introduction
Probiotics are live microorganisms that provide health benefits to their host if consumed in an adequate amount. To be considered as a probiotic, a bacterium must fulfil the following criteria: survivability in the presence of bile salts and acids, production of compounds that antagonize the growth of other microbes, susceptibility to antibiotics, and ability to colonize the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) [1,2,3]. Commonly used probiotics include bifidobacteria, lactic acid bacteria (LAB), and yeasts isolated from sources such as human breast milk, parts of GIT, feces, and fermented food products [4,5,6]. In recent years, innumerable benefits have been ascribed to probiotic bacterial strains [7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. Probiotics are believed to play a pivotal role in promoting the growth of healthy microflora in the genital tract by preventing the attachment of pathogens to epithelial tissues, increasing the IgA antibody amount, reducing the effects of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), intestinal discomfort and cholesterol serum levels; as well as treating intestinal cancer and controlling oral infection [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21].
According to the WHO, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) have been considered the main cause of death globally with approximately 17.9 million affected people every year [22], and hypercholesterolemia (high blood cholesterol) is deemed as a risk factor for such diseases. In fact, the probability of a heart attack becomes three times higher in hypercholesterolemic individuals in contrast to those who have normal blood lipid profiles [23]. The increasing frequency of CVDs has created a huge push to find novel strategies to mitigate cardiovascular risk factors. Although high levels of serum cholesterol can be treated with medications, nonpharmacological cholesterol reduction methods are gaining popularity as they do not pose associated adverse effects. One such strategy is the use of probiotics to improve lipid metabolism. It has been proposed that people affected by hypercholesterolemia may consume probiotics and/or prebiotics as supplements and be on a diet in lieu of cholesterol-lowering drugs [24]. The consumption of L. acidophilus, a mixture of L. acidophilus and B. lactis, and L. plantarum significantly reduced the total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol when compared to the control [25,26]; more recent studies have also elucidated the hypocholesterolemic effect of probiotic strains. Furthermore, the probiotic bacterial bile salt hydrolase (BSH) enzyme has been proposed to produce the cholesterol-lowering effect by the deconjugation of bile salts [27]. Although it has been often proposed that probiotics for human consumption must have originated from humans, some bacterial strains with nonhuman origin, such as Bifidobacterium animalis, were proven to be immensely effective in inducing positive effects in humans (i.e., immune-enhancing effects) [28]. Scientific research on LAB from the current geographical region of Islamabad is scanty, and the current study reports the isolation of bacterial strains with cholesterol reduction potential from raw buffalo milk samples from local niches. The indigenous LAB isolates were then subjected to probiotic characterization, and the isolates with the best probiotic attributes were evaluated for in vitro hypocholesterolemic potential.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Milk Sampling
Twenty-five samples of buffalo raw milk (28 ± 1 months of age) from animals nourished with conventional feeding at the National Agriculture Research Center (NARC), Islamabad, were aseptically collected in sterile tubes and stored in a laboratory at 4 °C.
2.2. Bacterial Isolation and Phenotypic Characterization
Briefly, 1 mL of each sample was aseptically pipetted into 9 mL (1:10 dilution) of sterile phosphate buffer saline solution in a test tube and then homogenized for 1–2 min. The dilutions from 10−1 to10−5 were prepared and then poured and spread on De Man, Rogosa & Sharpe, and M17 agar (Oxoid Ltd., Basingstoke, Hampshire, UK) and incubated anaerobically at 37 °C for 24–48 h. Colonies with different morphological characteristics were picked and subcultured in triplicate on agar plates. Bergey’s manual was used for the morphological characterization of the bacterial isolates.
The morphological details were observed under a phase contrast microscope (Phase contrast 2, Nikon, Japan). Isolates were biochemically characterized by Gram’s stain test, catalase test, oxidase test, and carbohydrate fermentation test.
2.3. Bacterial Identification Based upon 16S rDNA Sequencing
Genomic DNA of pure bacterial isolates was extracted according to the method proposed by Naeem et al. [29]. The bacterial colony comprised of a single strain was suspended in 20 μL of TE buffer (Tris EDTA) and processed in a thermocycler at 95 °C for 10 min. The sample was centrifuged at 6000 rpm for (2–3 min), and the resulting supernatant was used as a DNA template. The 16S rDNA present in the extracted template DNA was then amplified. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was carried out by using Universal reverse and forward primers, namely, 1510R (5′-GGCTACCTTGTTACGA-3′) and 9F (5′-GAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′). Conditions for PCR were set as follows: Initial denaturation at 94 °C for 2 min followed by thirty cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 1 min. Annealing at 50 °C for 1 min, followed by extension at 72 °C for 1.5 min and the final extension at 72 °C for 5 min. After the completion of PCR, the amplified PCR products were sent for 16S rDNA sequencing through a commercial sequencing service of Macrogen Inc. (Seoul, Korea).
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
Following 16S rDNA sequencing, the sequence data of bacterial strains were aligned using ClustalW software. The sequence data were assembled via Bio Edit software. Identification of the bacterial strains at the species level was accomplished using BLAST search using Gene Bank internet service. The 16S rDNA sequence data were submitted to the GenBank database (https://submit.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 28 February 2022). For phylogenetic and molecular evolutionary analysis MEGA-X software was used.
2.5. Probiotic Characterization of Putative Probiotic Strains
2.5.1. Tolerance to Acid and Bile Salts
For screening the tolerance capacity, presumptive probiotic bacterial isolates were grown in MRS broth (Oxoid Ltd., Basingstoke, Hampshire, UK). Then 1 mL of the bacterial culture was centrifuged at 12,000× g rpm at 4 °C for 5 min, and the cell pellet was obtained. MRS broth in different test tubes was separately adjusted to pH 1, 2, and 3. Adjusted MRS broths were then inoculated with cell pellets earlier and then incubated at 37 °C for 3 h.
For control measurements, MRS broth with pH 7 was used. Using standard plate counting, viable cells were counted. Measurements were done in triplicate, and mean values were shown. Tolerance to bile salts was estimated by using two variants of MRS broth, containing 0.3% and 0.5% bile salts (Sigma-Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany). The fresh bacterial cultures (18 h growth) were centrifuged, harvested, and resuspended in 1 mL MRS broth enriched with 0.3% bile salt and incubated at 37 °C. After 3 and then 5 h incubation, the broth was poured onto MRS agar plates and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C; later colonies were counted.
The same procedure was performed for MRS broth variant enriched with 0.5% bile salts. All experiments were conducted in triplicate, and means were calculated [30].
2.5.2. Determination of Antimicrobial Potential
To analyze the antimicrobial potential of the putative probiotic isolates, well diffusion agar assay method was used. Four pathogenic bacterial strains from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) were selected as control, including Salmonella Typhimurium ATCC 14028, Escherichia coli (ATCC 8739), Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538), and Bacillus cereus (ATCC-11778). The probiotic isolates were added to the sterile MRS broth and anaerobically incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. Following incubation, the MRS broth culture (cell density 108 CFU mL−1) was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 20 min. To obtain cell-free supernatant (CFS), it was passed through a 0.22 mm syringe filter.
The pathogenic bacteria were lawned on Muller Hinton Agar media (MHA) (Oxoid Ltd., Basingstoke, Hampshire, UK), and 5 mm diameter wells were made in these agar plates; then filtered CFS of probiotic isolates (50 μL) were added to the wells, and then were set to diffuse in MHA plates at room temperature for 2 h. The MHA plates were then incubated for 24 h at 37 °C to measure the inhibition zone diameter in millimeters [31].
2.5.3. Antibiotic Resistance
The Kirby–Bauer disc diffusion method was used to procure the antibiotic resistance profiles of bacterial isolates [32]. The antibiotics (Oxoid Ltd., Basingstoke, Hampshire, UK) used in this study included Ampicillin, Bacitracin, Chloramphenicol, Gentamycin, Kanamycin, Metronidazole, and Penicillin. MHA plates were prepared and allowed to solidify at room temperature. Then freshly grown cultures of bacterial isolates were added to PBS buffer, and the turbidity of the buffer was matched with that of McFarland solution. Then with the help of cotton swab spreads of candidate probiotic isolates were made on MHA plates. Antibiotic discs were carefully placed on these plates and then incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. The zones of inhibition were observed, and diameters were measured. The results obtained were categorized as susceptible, intermediate resistance, or resistant. Zone diameters were interpreted by values given by performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests [33].
2.5.4. Screening of Proteolytic Activity
Skim milk agar plates were prepared by adding 10 g of skim milk powder (Oxoid Ltd., Basingstoke, Hampshire, UK) into 100 mL bacteriological agar media. Skim milk agar plates were then inoculated with fresh cultures of putative probiotic bacterial strains and incubated for 24–48 h at 37 °C. Translucent halos surrounding the colonies indicated proteolytic activity [34].
2.5.5. Screening of Lipolytic Activity
For evaluation of lipase activity, Tween 80 media (Oxoid Ltd., Basingstoke Hampshire, UK) was used [35]. It was separately autoclaved at 121 °C for 15 min. It was then added to TSA (Oxoid Ltd., Basingstoke, Hampshire, UK) in 1/100 mL ratio. Then phenol red (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) serving as an indicator was added into the media.
The resulting amalgam was plated, allowed to dry, streaked with presumptive probiotic isolates, and then incubated for 24–48 h at 37 °C. Change in color (red to yellow–orange) indicated positive results.
2.5.6. Screening of Amylolytic Activity
One g of starch and 2.5 g of nutrient agar (NA) (Serva Electrophoresis GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany) were added to 100 mL distilled water and autoclaved at 121 °C for 15 min. The starch agar plates were streaked with presumptive probiotic bacterial strains, incubated for 24 h at 37 °C, and flooded with 1% iodine solution (Serva Electrophoresis GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany). Clear zones around the streaked lines indicated the presence of amylase enzyme, while the absence of such zones indicated negative result [36].
2.5.7. Screening of Hemolytic Activity
LAB cultures were grown overnight, streaked on NA plates supplemented with 4% sheep blood agar base (HiMedia Laboratories, Mumbai, India), and incubated for 48 h at 37 °C. Presence or absence of zones of hydrolysis around the colonies were noted [29]. Results were reported as α-haemolysis (slight hydrolysis involving the appearance of green zones around the colonies), β-haemolysis (formation of clear zones of hydrolysis around the colonies), and γ-haemolysis (without any change in the media).
2.5.8. Cholesterol Reduction Assay
Putative probiotic bacterial strains were cultivated in MRS broth supplemented with 0.3% oxgall (HiMedia Laboratories, Mumbai, India) at 37 °C. Then filter-sterilized water-soluble cholesterol (polyoxyethanyl–cholesteryl sebacate) (Sigma-Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany) was added to the broth at a final concentration of 50–200 µg/mL. Each bacterial strain was inoculated at 1% level and incubated anaerobically at 37 °C for 24 h.
Following incubation, the mixture was centrifuged, and the supernatant was collected. Modified colorimetric method was used for the determination of cholesterol concentration present in the supernatant [37]. In brief, the supernatant was added with 1.5 mL of FeCl3 working solution; it was then thoroughly mixed and allowed to rest for 10 min; 1 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) was added to the sample solution and placed in the dark for 45 min. After 24 h incubation, optical density was observed at 560 nm (Spectro UV-VIS Double Beam PC Scanning Spectrophotometer, Labomed Inc., Los Angeles, CA, USA).
The cholesterol-reducing activity (µg/mL culture broth) was calculated as Equation (1):
where C1 and C2 represent the concentration of total cholesterol present in the uninoculated and inoculated medium, respectively. W1 and W2 represent the weight of the 1 mL bacterial culture before and after incubation [4]. The cholesterol binding of bacterial cells was examined by using a scanning electron microscope.
cholesterol assimilation (µg/mL) = ((C1 − C2))/((W2 − W1))
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All experiments were conducted in triplicate. Data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism8 software (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA), presented as the means ± standard deviation, and first checked for normality using the D’Agostino–Pearson normality test. A two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was used to compare differences between probiotic samples for their cholesterol-lowering activity. p < 0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
A total of 16 bacterial isolates exhibiting Gram-positive, catalase negative, and oxidase negative attributes were isolated. These bacterial isolates displayed optimum growth at 37 °C and were further short-listed based on their acid and bile salt tolerance profiles. Five isolates were selected, namely, NMCC-M2, NMCC-M4, NMCC-M5, NMCC-M6, and NMCC-M7. These bacterial isolates appeared as cocci under a simple microscope. Carbohydrate fermentation assays were also performed with 9 different substrates; the metabolic capacity to utilize dietary sugars for the production of acids differed significantly between the various bacterial strains. (Table 1).

Table 1.
Morphological and biochemical characteristics of selected bacterial isolates.
The neighbor-joining method was used for the construction of a phylogenetic tree with MEGA-X software (Figure 1). The tested bacterial isolates showed a mean low survival rate at pH 1, which significantly increased at pH 2 (from 25.72 ± 2.04 to 35.78 ± 3.13, p < 0.0001) after incubation of 3 h at 37 °C. However, at pH 3, the mean survival rate of bacterial strains significantly increased from 35.78 ± 3.13 to 72.38 ± 5.80 (p < 0.0001). Among all strains tested, NMCC-M2 was the most tolerant to acid at pH 3 (Table 2).
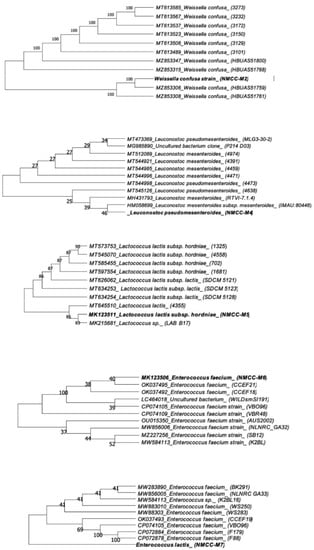
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of the bacterial isolates exhibiting the inter-relationship of most closely related type species inferred from 16S rRNA analysis.

Table 2.
Effects of different pH (1, 2, 3) on the survivability (log CFU mL−1) of candidate probiotics strains.
The results show that the potential to resist bile salts differed among the tested strains and decreased with the increased concentration of bile salts. Weissella confusa NMCC-M2 (6.44 log CFU mL−1) showed better resistance in terms of viable count (log CFU mL−1) with 0.3% (w/v) bile salt and 3 h incubation period (Table 3).

Table 3.
Different bile salt (0.3% and 0.5%) effects on survival of candidate probiotics strains.
Our present study reports the tolerance of Weissella confusa at 0.3% (w/v) bile salts upon 3 h incubation; our results are consistent with the recently reported study of Weissella sp. [38]. The CFS of putative probiotic strains exhibited different levels of antimicrobial activity against foodborne pathogens including Gram-negative (Salmonella Typhimurium and Escherichia coli) bacteria and Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus) bacteria. NMCC-M2 revealed the highest level of antimicrobial activity with no significant differences among pathogens. (Table 4). Further, NMCC-M5 showed a significant lower antimicrobial activity against Bacillus cereus with respect to the other pathogens (p < 0.05). As far as concerns NMCC-M7, significant differences of its antimicrobial activity against different pathogens were observed, with Bacillus cereus as the less inhibited (p < 0.001).

Table 4.
Antimicrobial activity spectrum of bacterial isolates against pathogens (n = 3) expressed in mm.
For the assessment of antibiotic resistance, bacterial isolates were tested according to the standard procedures [33]. The isolated bacterial strains revealed a varying degree of susceptibility toward most of the conventional antibiotics. However, Weissella confusa NMCC-2 showed complete susceptibility to the tested antibiotics (Table 5). The putative probiotic strains exhibited negative results for α-hemolysis as well as β-hemolysis, which make them probable candidates to be used as probiotics (Table 5).

Table 5.
Antibiotic susceptibility profiles and hemolysin activity of isolated bacterial strains.
The selected putative probiotic bacterial strains were tested for different in vitro enzymatic potential tests. In our study, all strains showed varying degrees of enzymatic potential, while NMCC-M2 showed maximum positive lipolytic, proteolytic, and amylolytic activities (Table 6).

Table 6.
Enzymatic potential of the presumptive probiotic bacterial isolates.
Our results indicate that the cholesterol reduction percentage changes with the variation of cholesterol concentration present in the media; thus, cholesterol concentration plays a pivotal role in cholesterol assimilation. Most tested strains showed higher cholesterol-reducing levels, within the range of 38.0 to 48.00 µg/mL when inoculated in bile salt supplemented MRS broth (p < 0.05) (Figure 2a); however, the cholesterol reduction decreased up to 15.0 to 23.0 µg/mL in media without bile salts (Figure 2b).
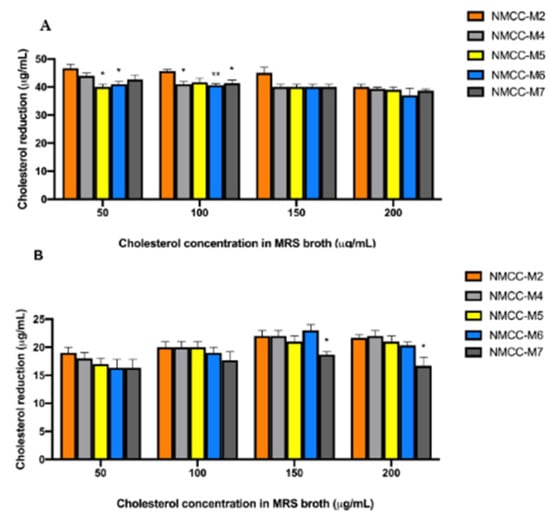
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of cholesterol-lowering activity of selected probiotic strains. (A) in vitro cholesterol reduction with 0.3% (w/v) bile salts upon 24 h incubation, (B) in vitro cholesterol reduction without 0.3% (w/v) bile salt upon 24 h incubation. (*) means p value is less than 0.05 and (**) means p value is less than 0.01.
NMCC-M2 (Weissella confusa) assimilated more cholesterol from the growth medium compared to the other tested strains. Many bacterial species (Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Enterococcus) present inside the GIT have this ability of deconjugating bile acids, therefore, resulting in hypocholesterolemia (low serum cholesterol level). Bile salt hydrolase (BSH) is reported to be responsible for the deconjugation of bile acids; once bile acids are deconjugated, they become less soluble, are absorbed by the intestine, and then excreted through the feces. The Environmental Scanning Electron microscopy analysis of the direct adhesion assay showed that cholesterol adhered to the outer cell surface of Weissella confusa (Figure 3).
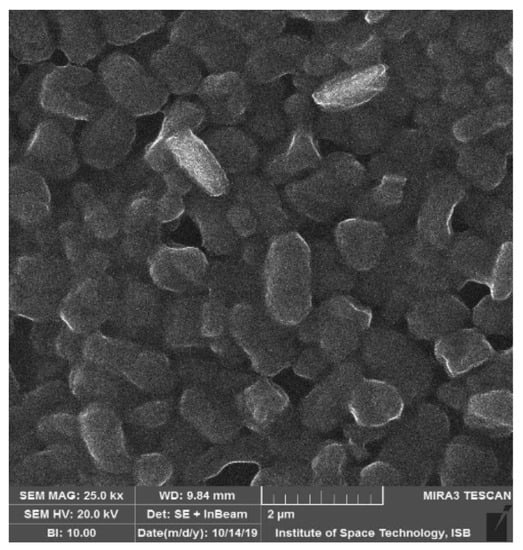
Figure 3.
Environmental Scanning Electron microscopy analysis of Weisella confusa (NMCC-M2) adhering to cholesterol at 37 °C upon 20 h incubation. The hypocholesterolemic effect of probiotic bacterial strains brought by deconjugation of bile salts is evident. Crystalline molecules of cholesterol (light in color) adhere onto the probiotic bacterial cells (dark in color).
4. Discussion
In total, twenty-five buffalo milk samples were processed for isolation of LAB on MRS selective medium. Initially, forty-six bacterial strains were isolated and went through further biochemical characterization. These isolates were regarded as Gram-positive when they had appeared purple–blue upon Gram staining. Furthermore, the bacterial cultures did not reproduce any gas bubbles when hydrogen peroxide was dropped on them, so they were pronounced as catalase negative.
The bacterial cultures were transferred onto disks soaked with N, N, N, N′-tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine, which did not produce dark-blue/brown color and were regarded as oxidase negative. The bacterial isolates were provisionally molecularly identified based on 16S rDNA sequencing and were categorized into four major groups of LAB: Weissella, Leuconostoc, Lactococci, and Enterococci. The sequence homologies detected through phylogenetic analysis showed that NMCC-M2 was provisionally similar to Weissella confusa; NMCC-M4 revealed 98.29% similarity to Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides, Lactococcus; NMCC-M5 revealed 99.90% similarity to Lactococcus lactis subsp. hordniae; NMCC-M6 revealed provisional similarity to Enterococcus faecium; and NMCC-M7 revealed 100% similarity to Enterococcus lactis.
To protect the cell membrane from harsh gastrointestinal acidic conditions, LAB release protons and lactic acid out of the cell [39]. Our findings are consistent with previous studies where Weissella confusa demonstrated its ability to survive in high acidic environments [40,41]. The bacterial isolates were subjected to 0.3% and 0.5% (w/v) bile salts concentrations.
The results show that the potential to resist bile salts differed among the tested strains and decreased with the increased concentration of bile salts. Weissella confusa NMCC-M2 (6.54 log CFU mL−1) showed better resistance in terms of viable count (log CFU/mL) with 0.3% (w/v) bile salt and 3 h incubation period.
Similar results were observed for 0.5% (w/v) bile salt tolerance, where again Weissella confusa NMCC-M2 (3.21 log CFU mL−1) showed better resistance than the rest of the tested strains. Probiotic strains must have the ability to resist bile salts that are present in the GIT to exert their positive effects in defense mechanisms [39]. Bile salts are injurious for bacterial cells as they solubilize cell surface proteins through detergent-like activity. Previous studies reported the bile tolerance of Weissella spp. at 0.3% (w/v) bile salts upon 2 h incubation [30].
Our present study reports the tolerance of Weissella confusa at 0.3% (w/v) bile salts upon 3 h incubation; our results are consistent with the recently reported study of Weissella spp. [40]. The CFS of putative probiotic strains exhibited different levels of antimicrobial activity against foodborne pathogens including Gram-negative (Salmonella Typhimurium and Escherichia coli) bacteria and Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus) bacteria. NMCC-M2 revealed the highest level of antimicrobial activity.
Interestingly, the adherence of probiotic bacteria to the cholesterol present in the small intestine has been linked to their hypocholesterolemic potential. This adherence has been reported to be growth and strain-specific [42]. Our findings concurred with the earlier study that also reported the in vitro cholesterol reduction potential of Weissella sp. [4]. The NMCC-M2 strain remained viable under simulated GIT conditions and showed outstanding antimicrobial activity against pathogens. Complete susceptibility to a wide range of antibiotics was also shown; hence, highlighting its safety to be used as a probiotic without being concerned about the transfer of resistance genes to the gut microflora.
Since many organisms are capable of synthesizing exotoxins that cause partial or whole lysis of human or animal cells, hemolysis analysis is a critical prerequisite for the selection of probiotic strains. All five putative probiotic strains displayed gamma hydrolysis, ergo no hydrolysis of blood cells was observed. The selected putative probiotic bacterial strains were tested for in vitro enzymatic potential tests. In our study, all strains showed varying degrees of enzymatic potential, while NMCC-M2 showed maximum positive lipolytic, proteolytic, and amylolytic activity. These functional enzymes possessed by probiotic bacteria participate in the bioavailability of nutrients and digestion.
Our findings concur with previous reports on the enzymatic potential of LAB [43,44,45,46,47]. Therefore, NMCC-M2 could be used as a target-based probiotic for the preparation of functional food. However, the beneficial effects of a probiotic depend on a myriad of factors. These factors are both strain-dependent as well as host-dependent. The survival and adaptability of a probiotic in the host GIT are most intricately related to the intrinsic probiotic potential of a strain, the host genetics, and diet as well as to the host gut microbiota.
The multiomics, i.e., metabolomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and microbiomics of host gut microbiota, play a fundamental role in the sustainability of a probiotic. Recent studies are focused on the development of probiotics that are indigenous to the host [48,49,50]. These have a better chance of accommodating the GIT as they are more compatible with the gut microbiota. Hence, the present study focused on the discovery of an indigenous probiotic strain endowed with a probiotic potential.
5. Conclusions
Among the tested bacterial isolates, Weissella confusa, NMCC-M2 was the most promising probiotic candidate with tremendous functional properties. Future studies will involve animal trials with NMCC-M2 to further validate its probiotic attributes, mechanisms, safety, and use as an addition to food or in combination with a biotherapeutic.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.H. and I.T.; methodology, A.H. and M.I.; software, M.M. and M.A.A.H.; validation, M.I., A.F. and C.O.A.; formal analysis, Y.H.; investigation, M.M., Y.N.A. and A.H.; resources, M.A.M. and A.J.A.; data curation, W.P.D. and Y.H.; writing—original draft preparation, A.H., I.T., M.I. and S.G.; writing—review and editing, A.F., M.I., C.C. and S.G.; visualization, A.F., A.A.A. and M.M.; supervision, S.G. and A.F.; project administration, S.G. and A.F.; funding acquisition, M.A.M. and A.J.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National Institute for Genomics Advanced Biotechnology (NIGAB) National Agricultural Research Centre, Islamabad, Pakistan, for providing financial support and lab facility for this research work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Division, N. Health and Nutritional Properties and Guidelines for Evaluation—Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Evaluation of Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria. FAO/WHO. 2006, p. 56. Available online: https://www.fao.org/publications/card/en/c/7c102d95-2fd5-5b22-8faf-f0b2e68dfbb6/ (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- Di Cerbo, A.; Palmieri, B.; Aponte, M.; Morales-Medina, J.C.; Iannitti, T. Mechanisms and therapeutic effectiveness of lactobacilli. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cerbo, A.; Canello, S.; Guidetti, G.; Laurino, C.; Palmieri, B. Unusual antibiotic presence in gym trained subjects with food intolerance; a case report. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 30, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandharaj, M.; Sivasankari, B.; Santhanakaruppu, R.; Manimaran, M.; Rani, R.P.; Sivakumar, S. Determining the probiotic potential of cholesterol-reducing Lactobacillus and Weissella strains isolated from gherkins (fermented cucumber) and south Indian fermented koozh. Res. Microbiol. 2015, 166, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cerbo, A.; Pezzuto, F.; Palmieri, L.; Rottigni, V.; Iannitti, T.; Palmieri, B. Clinical and experimental use of probiotic formulations for management of end-stage renal disease: An update. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2013, 45, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaiotta, G.; Murru, N.; Di Cerbo, A.; Succi, M.; Coppola, R.; Aponte, M. Commercially standardized process for probiotic “Italico” cheese production. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 79, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cerbo, A.; Pezzuto, F.; Palmieri, L.; Palmieri, B. The use of probiotics in the end-stage renal disease management. Minerva Biotecnol. 2012, 24, 155–170. [Google Scholar]
- Di Cerbo, A.; Palmieri, B. Lactobacillus Paracasei subsp. Paracasei F19; a farmacogenomic and clinical update. Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 28, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Blaiotta, G.; Di Cerbo, A.; Coppola, R.; Masi, P.; Aponte, M. Spray-dried chestnut extract containing Lactobacillus rhamnosus cells as novel ingredient for a probiotic chestnut mousse. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1632–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaiotta, G.; Murru, N.; Di Cerbo, A.; Romano, R.; Aponte, M. Production of probiotic bovine salami using Lactobacillus plantarum 299v as adjunct. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2285–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagawany, M.; Elnesr, S.S.; Farag, M.R.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Barkat, R.A.; Gabr, A.A.; Foda, M.A.; Noreldin, A.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; El-Sabrout, K.; et al. Potential role of important nutraceuticals in poultry performance and health—A comprehensive review. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 137, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, H.; Di Cerbo, A.; Zulfiqar, F.; Sabia, C.; Nawaz, A.; Siddiqui, F.M.; Aqeel, M.; Ghazanfar, S. Probiotic Characterization and Population Diversity Analysis of Gut-Associated Pediococcus acidilactici for Its Potential Use in the Dairy Industry. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiaterra, S.; Schmidt-Kuntzel, A.; Marker, L.; Di Cerbo, A.; Piccinini, R.; Guadagnini, D.; Turba, M.E.; Berardi, S.; Galosi, L.; Preziuso, S.; et al. Effect of a Probiotic Mixture in Captive Cheetahs (Acinonyx Jubatus) with Gastrointestinal Symptoms-A Pilot Study. Animals 2022, 12, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.L.; Lammers, K.; Brigidi, P.; Vitali, B.; Rizzello, F.; Gionchetti, P.; Campieri, M.; Kamm, M.A.; Knight, S.C.; Stagg, A.J. Modulation of human dendritic cell phenotype and function by probiotic bacteria. Gut 2004, 53, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdeano, C.M.; Perdigon, G. The probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus casei induces activation of the gut mucosal immune system through innate immunity. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saulnier, D.M.; Gibson, G.R.; Kolida, S. In vitro effects of selected synbiotics on the human faecal microbiota composition. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 66, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderpool, C.; Yan, F.; Polk, D.B. Mechanisms of probiotic action: Implications for therapeutic applications in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.S.; Pan, T.M. Beneficial effects of Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei NTU 101 and its fermented products. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Cerbo, A.; Palmieri, B. Review: The market of probiotics. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 28, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi, A.; Blaiotta, G.; Di Cerbo, A.; Succi, M.; Aponte, M. Behaviour of lactic acid bacteria populations in Pecorino di Carmasciano cheese samples submitted to environmental conditions prevailing in the gastrointestinal tract: Evaluation by means of a polyphasic approach. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 179, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cerbo, A.; Aponte, M.; Esposito, R.; Bondi, M.; Palmieri, B. Comparison of the effects of hyaluronidase and hyaluronic acid on probiotics growth. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Cardiovascular Diseases. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed on 31 July 2020).
- Ishimwe, N.; Daliri, E.B.; Lee, B.H.; Fang, F.; Du, G. The perspective on cholesterol-lowering mechanisms of probiotics. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 2003, 916, 1–149. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, W.; Lee, E.S.; Cho, H.T.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, S.M.; Kwon, H.T.; Yang, S.; Kim, Y.J. Lactobacillus plantarum LRCC 5273 isolated from Kimchi ameliorates diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in C57BL/6 mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 1964–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.A.; Kim, J. Effect of Probiotics on Blood Lipid Concentrations: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Medicine 2015, 94, e1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, G.; Öztürk, M.; Aslım, B.; Aslim, B. Identification of Lactobacillus strains from breast-fed infant and investigation of their cholesterol-reducing effects. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 2397–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E. Summary of probiotic activities of Bifidobacterium lactis HN019. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 40, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.; Ahmed, I.; Ahmed, S.; Ahmed, Z.; Riaz, M.N.; Ghazanfar, S. Screening of cattle gut associated Bacillus strains for their potential use as animal probiotic. Indian J. Anim. Res. 2018, B-948, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.; Park, J.Y.; Jeong, H.R.; Heo, H.J.; Han, N.S.; Kim, J.H. Probiotic properties of Weissella strains isolated from human faeces. Anaerobe 2012, 18, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristimuno Ficoseco, C.; Mansilla, F.I.; Maldonado, N.C.; Miranda, H.; Fatima Nader-Macias, M.E.; Vignolo, G.M. Safety and Growth Optimization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Feedlot Cattle for Probiotic Formula Design. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.W.; Kirby, W.M.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 29th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2019; Volume 39. [Google Scholar]
- Pailin, T.; Kang, D.H.; Schmidt, K.; Fung, D.Y. Detection of extracellular bound proteinase in EPS-producing lactic acid bacteria cultures on skim milk agar. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 33, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, G. A simple method for the detection of lipolytic activity of micro-organisms and some observations on the influence of the contact between cells and fatty substrates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1957, 23, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernfeld, P. Amylase α and β. Methods Enzymol. 1955, 1, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliland, S.E.; Nelson, C.R.; Maxwell, C. Assimilation of cholesterol by Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lakra, A.K.; Domdi, L.; Hanjon, G.; Tilwani, Y.M.; Arul, V. Some probiotic potential of Weissella confusa MD1 and Weissella cibaria MD2 isolated from fermented batter. LWT 2020, 125, 109261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, M.; Ilavenil, S.; Kim, D.H.; Arasu, M.V.; Priya, K.; Choi, K.C. In-vitro assessment of the probiotic potential of Lactobacillus plantarum KCC-24 isolated from Italian rye-grass (Lolium multiflorum) forage. Anaerobe 2015, 32, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Kandasamy, S.; Kavitake, D.; Shetty, P.H. Probiotic characterization and antioxidant properties of Weissella confusa KR780676, isolated from an Indian fermented food. LWT 2018, 97, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-S.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, N.-K.; Paik, H.-D. Evaluation of the probiotic characteristics and prophylactic potential of Weissella cibaria strains isolated from kimchi. LWT 2019, 112, 108229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto, H.; Ohmomo, S.; Okamoto, T. Cholesterol removal from media by lactococci. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 3182–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nami, Y.; Haghshenas, B.; Haghshenas, M.; Abdullah, N.; Yari Khosroushahi, A. The Prophylactic Effect of Probiotic Enterococcus lactis IW5 against Different Human Cancer Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assamoi, A.A.; Krabi, E.R.; Ehon, A.F.; N’guessan, G.A.; Niamké, L.S.; Thonart, P. Isolation and screening of Weissella strains for their potential use as starter during attiéké production. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2016, 20, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulini, F.L.; Hymery, N.; Haertle, T.; Le Blay, G.; De Martinis, E.C. Screening for antimicrobial and proteolytic activities of lactic acid bacteria isolated from cow, buffalo and goat milk and cheeses marketed in the southeast region of Brazil. J. Dairy Res. 2016, 83, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adel, M.; El-Sayed, A.M.; Yeganeh, S.; Dadar, M.; Giri, S.S. Effect of Potential Probiotic Lactococcus lactis Subsp. lactis on Growth Performance, Intestinal Microbiota, Digestive Enzyme Activities, and Disease Resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dincer, E.; Kivanc, M. Lipolytic Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Turkish Pastırma. Anadolu Univ. J. Sci. Technol. C-Life Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 7, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazanfar, S. Understanding the Mechanism of Action of Indigenous Target Probiotic Yeast: Linking the Manipulation of Gut Microbiota and Performance in Animals. In Saccharomyces; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazanfar, S.; Riaz, A.; Ali, G.M.; Naveed, S.; Arif, I.; Irshad, S.; Riaz, N.; Manzoor, K.N. Common Methods to Understand and Develop Indigenous Probiotics Yeast for Ruminant. In Yeasts in Biotechnology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazanfar, S.; Khalid, N.; Ahmed, I.; Imran, M. Probiotic yeast: Mode of action and its effects on ruminant nutrition. In Yeast—Industrial Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 179–202. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).