Abstract
Bacillus accelerates lignocellulose degradation, promotes the stabilization and resource utilization of compost by secreting enzymes, and plays an important role in compost formation and quality control. This study evaluated enzyme activity, lignocellulosic degradation, and bacterial succession in composting inoculated with different microbial Bacillus agents. They were identified as B. licheniformis, B. subtilis, B. thermoamylovorans, B. thermoruber, and B. hisashii. Four treatments were established, including a CK (uninoculated microorganisms), A (B. licheniformis, B. subtilis, B. thermoamylovorans,and B. hisashii), B (B. subtilis, B. thermoamylovorans, B. thermoruber, and B. hisashii), and C (B. subtilis, B. thermoamylovorans, and B. hisashii), and the composting lasted 7–14 days. Lignin and cellulose degradation rates in B during composting were 17.1% and 36.7% at the cooling stage, respectively. Redundancy analysis showed that degradation of lignocellulose in the thermophilic stage was mainly related to the secretion of lignocellulose-degrading enzymes after microbial inoculation. 16S rRNA sequencing revealed that Bacillus (20.3%) and Thermobifida (20.2%) were the dominant genera. Inoculation with a combination including B. thermoruber was a feasible way to increase lignocellulose degradation and promote maturity in sewage sludge composting.
1. Introduction
With the development of natural resource recycling, many countries have established regulations to optimize solid waste recycling [1]. Composting can provide a useful way for transforming sewage sludge and straw into agricultural products to replace chemical fertilizers [2]. Aerobic composting is an effective and harmless means of stabilizing, recycling, and reducing solid waste [3]. Biomass resources can be used as composting conditioners due to their high moisture content, low porosity, and high sludge viscosity. Through the addition of an organic conditioner (straw, sawdust), the carbon to nitrogen (C/N) ratio can be adjusted, water is retained, and open space for microbial growth is created. Simultaneously, biological conditioners speed the decomposition of organic matter in compost, reducing composting time [4]. The lignocellulose treatment methods used in straw mainly include physical modification, chemical modification, and biodegradation. Biodegradation is a green, efficient, clean, and environmentally friendly way to achieve straw conversion [5,6].
Using solid waste straw for composting recycles natural biomass resources; it is also the basis for green, organic, and pollution-free agriculture, with multiple potential benefits [7]. However, due to the insufficient quantity and biodegradability of straw’s indigenous communities, a long time is required to obtain decomposed compost products. Straw’s internal structure is composed of cellulose, which serves as the cell wall skeleton; hemicellulose as the matrix material; and lignin, which is the hard solid material of the outer layer shell. Together, these components form a dense three-dimensional network structure that makes biodegradation difficult. Furthermore, during the initial stage of composting, the pH is low (<5.0), and organic acids accumulate quickly, leading to inhibition of aerobic microbial activity, which slows down the aerobic fermentation process of composting. Thus, lignin biodegradation is the rate-limiting step of humus formation in composting [7]. Currently, the role of microbial additives in the composting process to accelerate the composting process and improve the quality of composting has received increased attention [8]. Studies have shown that microbial inoculation can promote agricultural and domestic waste degradation and increase the quality of organic fertilizer [9]. The pH, moisture content, and temperature in the composting process are related to enzymatic activity at different stages of microbial succession and are the key to strengthening the biodegradation of lignocellulose and promoting heap decomposition [10,11].
Microorganisms have fast propagation, low pollution, and high metabolic intensity [4]. They can be used in composts for microbial preparation, accelerating the decrement of compost [12]. Moreover, complex microbial inoculants can contribute to lignocellulose breakdown. Microbes produce cellulase, which cleaves the β-1, 4-glycosidic bond and the free end of fibrinose, and then hydrolyzes it to obtain glucose [13]. Under aerobic conditions, microbial catalysis is very important; many microorganisms participate in cellulose degradation, including fungi, actinomycetes, bacteria (Bacillus, Pseudomonas, and Proteus) [14]. Adding lignin peroxidase- (Lip-) and manganese peroxidase -(Mnp-) secreting basidiomycetes to compost augments lignin degradation, and improves lignocellulose biodegradability and the quality of compost products [15]. The reported cellulose-degrading bacteria mainly include Bacillus, Fibromonas, and Bacteroidetes [16]. The bacterial genus Bacillus can also form endophytic spores. Geobacillus and Bacillus palladium, with 91% sequence similarity, have a wide range of physiological characteristics, including the degradation of animal and plant macromolecules, such as cellulose, starch, and protein [17]. Bacillus thermophilus showed the best cellulase (CMCase) and polyphenol oxidase activities at 70 °C and 40 °C [18]. Bacillus subtilis, which mainly exists as spores, can resist high temperatures and acidic and alkali conditions, and is very effective at degrading cellulose.
Microbial supplementation studies have shown that after B. subtilis is added to the composting pile, it quickly becomes the main bacterial strain, prolongs the high-temperature period, and accelerates the composting process. The composting time was reduced by 40–43% by a mixed inoculation of Bacillus (B. licheniformis, B. amylolitica, B. subtilis, and B. thermophilus) on straw, and the composting lasted 51–58 days [19]. Another study [20] showed that the addition of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SL-7 to straw compost increased the degradation rate of lignin and humus content after 41 days, reaching a lignin degradation rate of 63.84%. At the same time, the Bacillus-secreted laccase (Lac) has higher heat and alkali resistance than other bacteria’s Lac, which is conducive to the degradation and transformation of lignin. In our previous study [21], Bacillus thermophilus effectively degraded lignin, mainly by secreting Lip, Mnp, and Lac, and producing phenolic and quinone products, which are important precursors of humus formation.
This study aimed to determine the influence of microbial inoculation on enzyme activity, lignocellulose breakdown, and bacterial succession during maize straw composting, and analyzed the relationship between environmental factors, metabolic function, and the bacterial community. The degradation variables were identified using the physical and chemical features of the waste and the succession of the microbial community. The results provide a microbial basis for biomass breakdown and organic fertilizer production, and the effects of microbial inoculation on the metabolic function of microorganisms during maize straw composting.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Liquid Compounds of Microbial Agents
Microorganisms were screened as inoculants from the moderate and high-temperature stages of compost. The main screening process was as follows: In the mesophilic and thermophilic phases, five equal volumes of compost samples were obtained from the center and about 0–30 cm of the heap, combined, and screened through a 20 μm mesh. A 10-g sample of mixed compost was mixed with 90 mL of sterile water and shaken at 160 r/min at 37 °C and 55 °C for 1 h. Serial dilutions from 10−2 g/mL to 10−6 g/mL were prepared using sterilized water, and 100 μL of each dilution was inoculated on primary screening medium agar plates. The plates were incubated at 37 °C and 55 °C for aerobic culture for 24 h. The Congo Red agar overlay method was used to qualitatively screen cellulase-producing bacteria. Briefly, the bacteria plates were flooded with 1 mg/mL Congo Red for more than 60 min and then destained with a 1 mol/L NaCl solution until clear zones around the edge of colonies were visualized [22]. The ratio of the clear zone’s diameter to the bacterial colony was the standard for evaluating the initial screening strains. The colonies with larger diameters were selected and further isolated and purified on a new screening agar plate for 4–5 generations to obtain the purified microorganisms. Five microbial strains were obtained through this method, 2 from the 37 °C screening and 3 from the 55 °C screening. The microbes from the 37 °C screening were identified as Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis by 16S rRNA. The selected microorganisms at 55 °C were identified as Bacillus thermoamylovorans, Brevibacillus thermoruber, and Bacillus hisashii by 16S rRNA. The five purified strains were stored at −80 °C with glycerol.
The bacteria were activated and cultured in an LB Broth liquid medium containing NaCl (10.0 g/L), tryptone (10.0 g/L), and yeast extract (5.0 g/L). B. licheniformis and B. subtilis were cultured at 37 °C and 160 r/min; B. thermoamylovorans, B. thermoruber, and B. hisashii were cultured at 55 °C and 160 r/min. Strains were cultured in an LB liquid medium with 5% inoculum. When the OD600 = 1.0, the microorganisms (B. licheniformis, B. subtilis, B. thermoamylovorans, B. thermoruber, and B. hisashii) were mixed in equal proportions to form different combinations of microbial agents. To evaluate the lignocellulose-degrading effects of the bacterial agents, different combinations were inoculated in the reactor at 0.3% (w/w) of the reactor’s wet weight. Four groups of experiments were set up: CK (uninoculated microorganisms), A (B. licheniformis, B. subtilis, B. thermoamylovorans, and B. hisashii,), B (B. subtilis, B. thermoamylovorans, B. thermoruber, and B. hisashii), and C (B. subtilis, B. thermoamylovorans, and B. hisashii).
Sewage sludge from a food factory served as the raw material, and corn straw with a particle size of 2 mm(purchased from Zhengzhou, Henan Province) served as the conditioning agent. The sewage and corn straw were mixed at a 6:4 ratio, the water content was adjusted to 60–65% of the pile, and the C/N ratio was 25:1. Inoculation with different combinations of microbial agents was performed simultaneously. Fifteen kg of raw materials was mixed into the compost reactor and aerated daily for aerobic composting at the bottom of the pile. Details of the composting of raw materials are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Components of the composting materials.
2.2. Composting Experiment Setup and Physicochemical Index
The residual sludge and corn straw were mixed to compost, and 15 kg of the mixed samples were composted in a polypropylene plastic box (56 cm × 36 cm × 33 cm length × width × height) with a total volume of 65 L. A porous plate at 10 cm from the bottom of the box was used to achieve uniform oxygenation at the bottom. The aeration capacity was 0.3 L/(L·min), and the stack was turned over once a day. Compost samples were collected and mixed daily. The samples were divided into two parts: one was utilized to determine the compost’s physical and chemical properties, while the other was stored at −20 °C for additional investigations of microbial diversity. Microbial diversity, temperature, pH, CMCase activity, and Lip, Mnp, Lac, and lignocellulose content were determined.
2.3. Analytical Methods
Temperature measurement: the temperature was taken once every 12 h at the reactor’s center and at 4 points around the reactor’s periphery, and an average value was calculated. The sample was mixed 1:10 with water for 1 h, centrifuged at 10,000 r/min for 10 min to extract the supernatant, and the pH of the supernatant was evaluated using a pH meter. CMCase activity was determined using National Standard procedures [14]. The Lip, Lac, and Mnp determination methods were consistent with previous studies [21]. Hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin in the reactor were determined by an ANKOM A2000i automatic fiber analyzer (Beijing ANKOM Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China), and the lignocellulose contents were determined according to Zhang and Sun [23].
2.4. Microbiological Analysis
The microbial community’s structure was examined using 16S rRNA gene high-throughput sequencing to further investigate the potential effect of the microbial inoculum on lignocellulose breakdown in compost. Compost samples were taken from groups CK, A, B, and C. The mesophilic stage samples were labeled CK1, A1, B1, and C1; the thermophilic stage samples were labeled CK2, A2, B2, and C2; and the cooling stage samples were labeled CK3, A3, B3, and C3, accordingly. Following total DNA extraction, a microvolume spectrophotometer was used to measure the concentration and purity of DNA (NanoDrop 2000, New York, NY, USA). The V3–V4 hypervariable region gene fragment of 16S rRNA were amplified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using the primer pairs 338F (5’-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCA-3’) and 806R (5’-GGAC- TACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3’). Purification, quantification, and sequencing of the PCR products were performed at the Shanghai Magi Biomedical Technology Co., LTD, Shanghai, China, using the Illumina Miseq platform. For data processing on the Magi Biocloud platform, sequences were classified into various operational taxonomic units (OTUs) (www.majorbio.com, accessed on 25 November 2021).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Sequences that passed quality control were grouped into operational taxa (OTU) with 97% similarity. Diversity estimators, including the Sobs, Shannon, ACE, Chao, Coverage, and Simpson indices, were calculated. OTUs were classified according to the Silva database, and the similarity of bacterial community composition was compared by Venn diagrams, cluster analysis, and redundancy analysis. OTUs were uploaded into PICRUSt to predict the functional properties of bacterial communities based on the COG and KEGG databases.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Microbial Agents on the Physicochemical Properties of Compost
The compost’s initial temperature was about 20 °C, and the temperature of each group increased rapidly after 1 day. Figure 1a shows that the temperature of each group presented a trend of mesophilic, thermophilic, and cooling stages. The CK group reached the high-temperature stage (56 °C) after 72 h, which lasted for 1 day. In Group A, the temperature reached 55 °C at 48 h and lasted for 4 days. Group B reached 57 °C at 24 h and this lasted for 5 days. Group C entered the high-temperature stage at 36 h and the temperature reached 58 °C, which lasted for 2 days. The microbial biomass primarily affected the temperature of the compost and was related to the water content and microbial activity of the compost. After inoculation with exogenous microorganisms, the microbial community structure changed, resulting in enzymatic activity changes, which were key to the rapid temperature rise [24]. Compared with the CK group, the composts inoculated with exogenous microorganisms had a higher temperature and a longer duration of the high-temperature period, indicating that the microorganisms were active, remained viable for an extended period, and formed a symbiotic relationship with the indigenous microorganisms. As shown in Figure 1b, the pH of each reactor fluctuated between 5 and 9. Due to protein degradation and other easily degradable organic matter at the initial compost stage, NH3 was generated, making each group’s pH rise rapidly after 1 day.
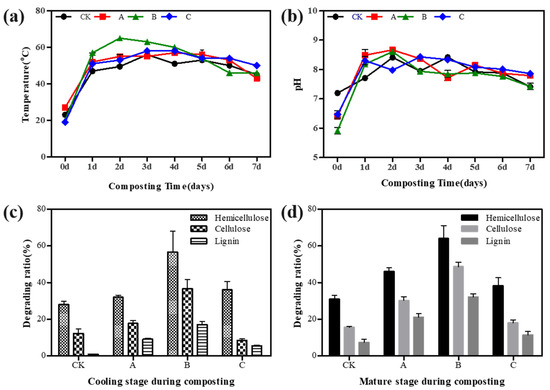
Figure 1.
Temperature (a) and pH (b) changes of composts with different treatments. Lignocellulose content changes in the cooling stage (c) and maturation stage (d) of composts with different treatments.
Each group’s hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin contents were detected on the 7th and 14th day of the cooling stage and maturity stage, respectively. As illustrated in Figure 1c,d, hemicellulose degraded at the fastest rate in all reactors, followed by cellulose and lignin. The rate of lignocellulose degradation was highest in Group B, followed by Groups A and C, and was lowest in Group CK. Bacterial agents mixed with B. thermoruber improved lignocellulose breakdown, extended the duration of the high-temperature period, and accelerated the composting process in Group B. The changes in CMCase, Lip, Mnp, and Lac for each group are shown in Figure 2. During the thermophilic period, the CMCase activity in B2 was 4.55 U/g, which was higher than CK2 (1.61 U/g), A2 (4.05 U/g), and C2 (4.09 U/g). Lip and Mnp increased rapidly at the thermophilic phase. The Lip activity in B2 was 1.93 U/g, which was higher than CK2 (1.68 U/g), A2 (1.77 U/g), and C2 (1.66 U/g). The Mnp activity in B2 was 0.94 U/g, which was higher than in CK2 (0.81 U/g), A2 (0.85 U/g), and C2 (0.81 U/g). The Lac activity in B2 was 0.20 U/g, which was higher than CK2 (0.16 U/g), A2 (0.11 U/g), and C2 (0.16 U/g). In summary, Group B showed the highest activity of CMCase, Lip, Mnp, and Lac, and inoculation with B. thermoruber promoted lignocellulose-related enzyme activity during composting.
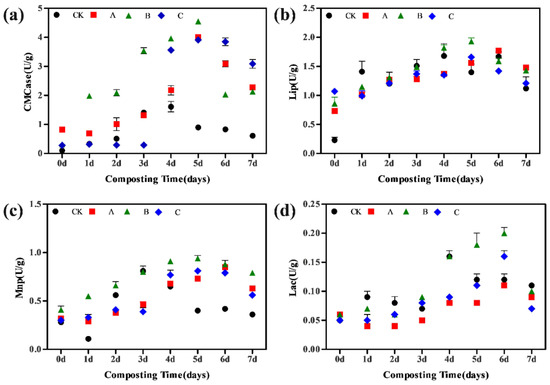
Figure 2.
Changes in CMCase (a), Lip (b), Mnp (c), and Lac (d) in composts with different treatments.
3.2. Diversity and Richness of Bacterial Communities during Composting
The bacterial alpha diversity indices at different composting stages are shown in Table 2. The coverage of all samples was no less than 99%, which proves their representativeness. Simpson’s and Shannon’s indices indicated the bacterial community’s diversity. In contrast, the ACE, Chao, and Sobs indices revealed the microbial community’s overall content and species richness, thus reflecting the microbial community’s overall state. Student’s T-test between the index groups of independent samples showed that the Sobs indices of A1 and C1 were significantly different from that of CK1 in the mesophilic phase. At the thermophilic stage, the Sobs, ACE, and Chao microbial richness indices of A2 and B2 were significantly different from those of CK2. In the cooling stage, the microbial community diversity and evenness (Simpson, Shannon) of B3 and CK3 were significantly different. Similar to earlier studies, inoculation with microorganisms considerably increased the diversity and richness of the bacterial community in the compost [25].

Table 2.
Bacterial alpha diversity indices at different composting stages.
There were 946 OTUs in the three periods of Group B, as shown in the Venn diagram, accounting for 22.91% of the total OTUs. Groups CK1, A1, B1, and C1 had 289 OTUs each during the thermophilic stage, indicating similar microbial composition during the mesophilic stage of compost. Thermobifida in Actinobacteriota was high, accounting for 6.91% of the total similarity ratio (Figure 3a). In the thermophilic composting stage, 150 OTUs were identified in the four composting groups, and 78 OTUs were identified in the inoculated groups A2, B2, and C2 (Figure 3b). Sphingobacterium in Bacteroidota accounted for 9.34% of the total similarity ratio of Groups A3, B3, and C3. In the cooling stage of composting, there were 117 OTUs in the four composting groups, among which Psychrobacillus in Firmicutes was predominant (Figure 3c), accounting for 18.66% of the total similarity ratio.
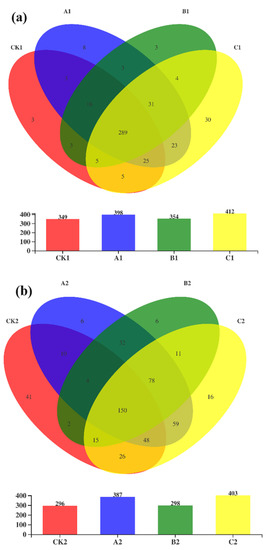
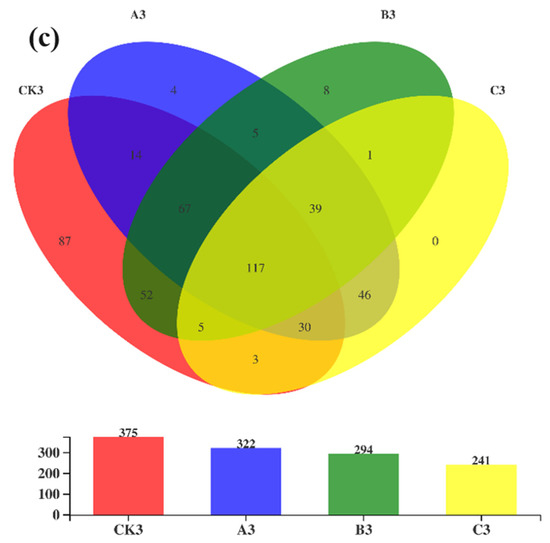
Figure 3.
Venn diagram of compost in the mesophilic phase (a), the thermophilic phase (b), and the cooling phase (c).
3.3. Changes in Bacterial Community Structure during Composting
The biochemical function of the bacterial community was explored by analyzing the distribution of bacterial sequences. As shown in Figure 4a, the dynamic distribution of phyla changed significantly throughout composting. Proteobacteria, Bacteroidota, Firmicutes, and Actinobacteriota were the dominant phyla and co-existed in all samples. Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, and Proteobacteria decomposed cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin during composting [25]. Firmicutes played an important role in cellulose degradation. The Proteobacteria, which have complex physiological functions, accounted for 30.7%, 23.2%, 20.2%, and 25.4% of the abundance in CK1 + CK2 + CK3, A1 + A2 + A3, B1 + B2 + B3, and C1 + C2 + C3, respectively. The Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes (F/B) ratio is a useful indicator of reaction stability [4]. The F/B in CK1 + CK2 + CK3, A1 + A2 + A3, B1 + B2 + B3, and C1 + C2 + C3 was 0.37, 0.59, 8.42, and 0.63, respectively. The F/B of Group B was much higher than that of Groups A1 + A2 + A3 and C1 + C2 + C3, especially at the thermophilic and cooling stages, indicating that the composting process of Group B was more efficient and stable, and confirmed that the straw had fully degraded in Group B. In addition, the abundance of actinomycetes in CK1 + CK2 + CK3, A1 + A2 + A3, B1 + B2 + B3, and C1 + C2 + C3 was 22%, 21.6%, 31.3%, and 24.2%, respectively. Patescibacteria, Acidobacteriota, and Chloroflexi phyla, which are essential and irreplaceable in the microbial system by ensuring a smooth composting process, were present at an abundance lower than 10%.
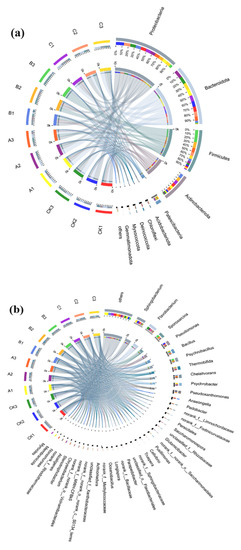
Figure 4.
Distribution of bacterial sequences at the phylum (a) and genus (b) levels.
Phylogenetic classification was carried out at the genus level to further analyze the microbial community’s structure. As shown in Figure 4b, 41 microbial genera were identified, 20 of which had a relative abundance of more than 1% in all samples. The dominant bacteria in the CK1 + CK2 + CK3 samples were Anseongella (13%), Sphingobacterium (15%), Pseudomonas (17%), and Flavobacterium (25%). The dominant species in the A1 + A2 + A3 samples were Thermobifida (7.1%), Flavobacterium (14%), Sphingobacterium (10%), and Sporosarcina (10%). The dominant species in the B1 + B2 + B3 samples were Bacillus (20.3%), Thermobifida (20.2%), Chelativorans (11%), Sporosarcina (24%), and Psychrobacillus (22%). The dominant species in the C1 + C2 + C3 samples were Flavobacterium (10%), Psychrobacter (12%), and Sphingobacterium (20%). Studies have shown that Flavobacteria and Sphingolbacter accelerate the degradation and transformation of organophosphorus [26], Pseudomonas can transform proteins and carbohydrates, and Flavobacteria can degrade polymers such as chitin and cellulose.
The composts inoculated with different microbial agents were further analyzed at the species level. Compared with CK, six strains of bacteria were differentially expressed in A and 15 strains were differentially expressed in B, as shown in Figure 5a,b. Compared with CK, microbial inoculation with Group A promoted the growth of Patescibacteria bacterium, candidate_division_WS5 bacterium, Conexibacter, Pseudomonas, and Solirubrobacteraceae, which accounted for 0.94% (p = 0.031), 0.78% (p = 0.045), 0.11% (p = 0.043), 0.06% (p = 0.024), 0.05% (p = 0.046), and 0.01% (p = 0.009), respectively.
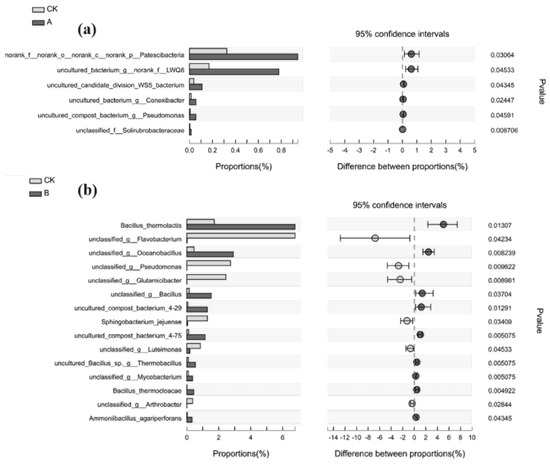
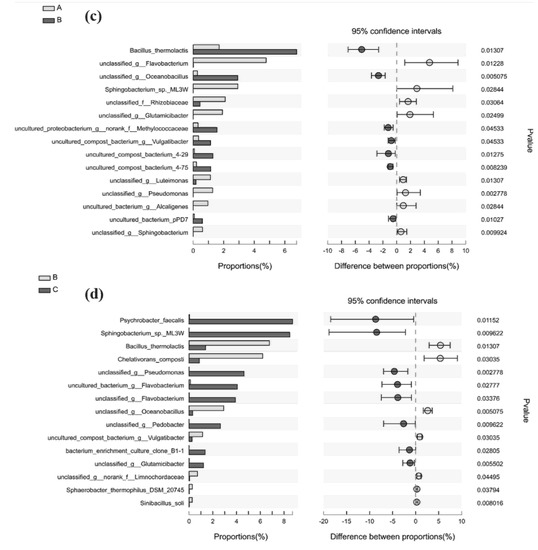
Figure 5.
Differences in bacteria at the species level: CK vs. A (a), CK vs. B (b), A vs. B (c), and B vs. C (d).
In Group B, microbial inoculation promoted the growth of Bacillus thermolactis, Oceanobacillus, Bacillus, compost_bacterium_4-29, compost_bacterium_4-75, Bacillus_sp._g_Thermobacillus, Bacillus_thermocloacae, Ammoniibacillus_agariperforans, and Paenibacillaceae, which were significantly higher than in CK, accounting for 6.78% (p = 0.013), 2.91% (p = 0.008), 1.53% (p = 0.037), 1.29% (p = 0.013), 1.15% (p = 0.005), 0.54% (p = 0.005), 0.44% (p = 0.005), 0.33% (p = 0.043), and 0.28% (p = 0.020), respectively. These bacteria are very common in compost. Bacillus belongs to the Firmicutes, which play an important role in cellulose degradation [27]. In CK, Flavobacterium, Pseudomonas, Glutamicibacter, Sphingobacterium jejuense, Luteimonas, and Arthrobacter were significantly higher than in Group B, accounting for 6.78% (p = 0.042), 2.74% (p = 0.010), 2.44% (p = 0.009), 1.29% (p = 0.034), 0.85% (p = 0.045), and 0.37% (p = 0.028), respectively. Flavobacterium and Sphingobacterium jejuense are related to the degradation and transformation of organophosphorus in compost [26].
Fifteen bacteria strains were identified as being differentially expressed in A and C compared with B, as shown in Figure 6c,d, with substantial differences. In Group A, microbial inoculation promoted the growth of Flavobacterium, Sphingobacterium_sp_ML3W, Rhizobiaceae, Glutamicibacter, Luteimonas, Pseudomonas, Alcaligenes, and Sphingobacterium to a significantly higher level than than B, accounting for 4.78% (p = 0.012), 2.92% (p = 0.028), 2.10% (p = 0.031), 1.92% (p = 0.025) 1.13% (p = 0.013), 1.28% (p = 0.003), and 0.96% (p = 0.028), 0.61% (p = 0.010), respectively. In Group B, Bacillus thermolactis, Oceanobacillus, Methylococcaceae, Vulgatibacter, uncultured_compost_bacterium_4-29, uncultured_compost_bacterium_4-75, and uncultured_bacterium_pPD7 were significantly higher than in Group A, accounting for 6.78% (p = 0.013), 2.91% (p = 0.005), 1.56% (p = 0.045), 1.14% (p = 0.045), 1.29% (p = 0.013), 1.15% (p = 0.008), and 0.6% (p = 0.010), respectively.
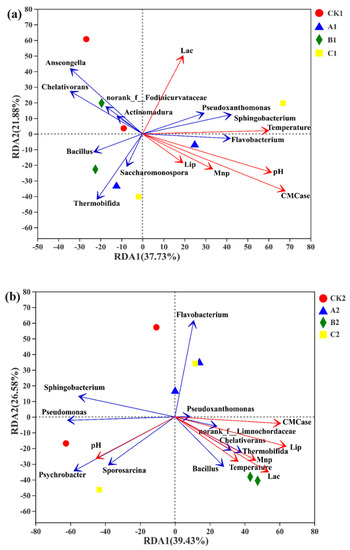
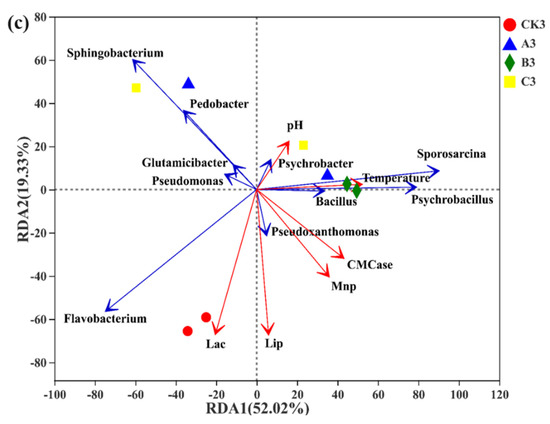
Figure 6.
RDA of environmental factors and the most abundant bacterial genera in compost groups inoculated with different microorganisms. Mesophilic phase (a); thermophilic phase (b); cooling phase (c).
In Group C, microbial inoculation promoted the growth of Psychrobacter faecalis, Sphingobacterium_sp._ML3W, Pseudomonas, Flavobacterium, g__Flavobacterium, Pedobacter, bacteriumB1-1, and Glutamicibacter, which were significantly higher than Group B, accounting for 8.72% (p = 0.012), 8.49% (p = 0.010), 4.64% (p = 0.003), 4.06% (p = 0.028), 3.9% (p = 0.034), 2.63% (p = 0.010), 1.35% (p = 0.028), and 1.21% (p = 0.006), respectively. In Group B, Bacillus thermolactis, Chelativorans composti, Oceanobacillus, Vulgatibacter, Limnochordaceae, Sphaerobacter_thermophilus_DSM_20745, and Sinibacillus soli were significantly higher than in Group C, accounting for 6.78% (p = 0.013), 6.20% (p = 0.030), 2.91% (p = 0.005), 1.14% (p = 0.030), 0.71% (p = 0.045), 0.28% (p = 0.038), and 0.26% (p = 0.008), respectively.
Bacillus was positively correlated with Thermobifida, indicating synergistic action in lignocellulose degradation. In addition, many Thermobifida can accelerate the lignocellulose decomposition and improve compost quality. The number of Thermobifida is positively correlated with organic matter content, and Proteobacteria play an important role in carbon and nitrogen metabolism. In addition, Actinomycetes degrade organic substrates that are difficult to break down rapidly [28].
Bacteroides can decompose cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin in the composting process [29]. Studies have shown that Firmicutes are the dominant bacteria in the thermophilic composting stage, mainly using cellulose that is difficult to degrade as the primary metabolic carbon source [30]. At the phylum level, Firmicutes hydrolyze sugars and nitrogenous compounds in compost to produce organic acids, alcohols, and lipids [31]. Bacillus, Sphingobacterium, and Pseudomonas were negatively correlated. This may be attributed to differences in the composting microenvironment and substrate competition. Psychrobacillus and Sporosarcina are facultative organisms with complex adaptive mechanisms that provide competitive ecological advantages, thus explaining their dominance in the early stages of composting.
3.4. Correlation between Microbial Species with Higher Abundance during Lignin Degradation and Environmental Factors
Composting is primarily a biological process in which microorganisms aid in organic matter decomposition, which is enhanced by supplementation with microbial agents [23]. Environmental conditions have a significant impact on microbial community succession during composting [12]. As a result, redundancy analysis (RDA) was utilized to decipher the relationship between lignocellulosic enzyme activity and environmental variables (pH, temperature). The top 10 microbial taxa with the highest abundance distribution following inoculation with various microbial combinations during the composting process are depicted in Figure 6.
RDA of bacterial species revealed significant correlations among environmental parameters (temperature and pH), enzyme activity (CMCase, Lip, Mnp, and Lac), and bacterial community makeup (p < 0.05). Temperature and pH were the primary determinants of the bacterial community in the mesophilic compost stage, as illustrated in Figure 6a. The abundance of Pseudoxanthomomonas, Sphingobacterium, Flavobacterium, and Saccharomonas was favorably linked with environmental parameters and the activity of lignocellulose-degrading enzymes. Environmental variables and enzyme activity were adversely linked with Actinomadura, Chelativorans, Bacillus, and Thermobifida. As illustrated in Figure 6b, CMCase and Lip were the primary bacterial population determinants during the thermophilic stage of compost, and the microbial community was relatively densely distributed. The quantity of Bacillus, Thermobifida, Chelativorans, Pseudoxanthomomonas, and Limnochordaceae was positively associated with the temperature and activity of lignocellulose-degrading enzymes during composting in the thermophilic phase of Group B with the most significant influence. Flavobacterium, Sphingobacterium, Pseudomonas, Psychrobacter, and Sporosarcina were negatively correlated with temperature and enzyme activity. As shown in Figure 6c, temperature and CMCase were the main influencing factors of the bacterial community in the cooling stage of compost. The abundance of Pseudoxanthomomonas, Bacillus, Psychrobacter, Sporosarcina, and Psychrobacillus was positively correlated with temperature and CMCase during composting. Flavobacterium, Sphingobacterium, Pseudomonas, Pedobacter, and Glutamicibacter were negatively correlated with temperature and CMCase activity.
3.5. The Relationships among Environmental Factors, Metabolic Function, and the Bacterial Community
A heat map of the activities of the top 20 enzymes (CMCase, Lip, Lac, and Mnp) and ambient composting parameters (pH and temperature) is shown in Figure 7a. This proved that CMCase, Lip, Mnp, and Lac were significantly positively correlated with Bacillus, Thermobifida, and Persicitalea, which influence lignocellulose degradation [22]. The temperature was significantly positively correlated with Sporosarcina (Firmicutes, r = 0.71, p = 0.0001) and Psychrobacillus (Firmicutes, r = 0.58, p = 0.003). The dominant species in Group B were Bacillus (20.3%), Thermobifida (20.2%), Sporosarcina (24%), and Psychrobacillus (22%). Therefore, the temperature rise in Group B and the degradation of lignocellulose were accelerated.
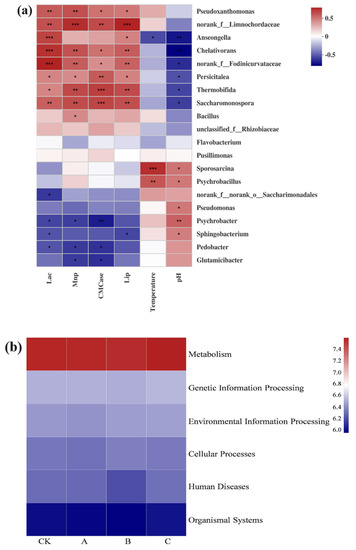
Figure 7.
Correlations among enzyme activity, environmental factors, and bacteria at the species level (a). The color of each square in the heat map represents the correlation coefficient from Spearman correlation; the right side of the legend is the color range of different r values. Red is positive and blue is negative. The value of p < 0.05 is marked with *, p < 0.01 is marked with **, and p < 0.001 is marked with ***. Analysis of microbial metabolism functions at Level 1 by PICRUSt (b).
The metabolic function of microorganisms was compared and analyzed by a heatmap. As illustrated in Figure 7b, there were four distinct groupings of compost samples. The functional genes were more abundant than those associated with metabolism and human illness [32,33], demonstrating that increased metabolic abundance promotes lignocellulose breakdown during composting. The presence of pathogens is indicated by the number of genes associated with human diseases [28]. Groups CK, A, B, and C were classified into the same category. The composting process was shown to have a higher concentration of genes involved in environmental information processing, genetic information processing, and cellular activities. In contrast, Group B had a lower concentration of human disease genes. The results indicated that the number of functional genes associated with human diseases was low in Group B following microbial agent inoculation, which accelerated the compost’s transition to the high-temperature stage, thereby killing many harmful bacteria. When the high-temperature stage reached 7 days, the compost hygiene requirements were met.
4. Conclusions
The microbial combination with B. thermoruber showed the best activity; the CMCase, Lip, Mnp, and Lac contents were the highest, and increased the degradation rate of lignocellulose during composting was increased. After inoculation with microorganisms, the abundance of human disease-related functional genes in Group B was lower, which accelerated lignocellulose degradation and improved the microbial community’s structure.
Author Contributions
The research was conceived and designed by J.N. and X.L.; compost experiments and microbial communities were analyzed by J.N.; the manuscript was written and revised by J.N. and X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was sponsored by the grant from the National Key Research and Development Program (No. 2016YFC0400707), as well as a grant from the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (No. KYCX18_1848).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Hao Sun’s support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- Fan, S.Y.; Li, A.; Heijne, A.T.; Buisman, C.J.N.; Chen, W.S. Heat potential, generation, recovery and utilization from composting: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 175, 105850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelsomino, A.; Abenavoli, M.R.; Princi, G.; Attinà, E.; Cacco, G.; Sorgonà, A. Compost from fresh orange waste: A suitable substrate for nursery and field crops? Compost Sci. Util. 2013, 18, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wei, Z.M.; Mohamed, T.A.; Zheng, G.R.; Qu, F.T.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Song, C.H. Lignocellulose biomass bioconversion during composting: Mechanism of action of lignocellulase, pretreatment methods and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2021, 286, 131635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Q.; Liu, Z.P.; Xia, J.S.; Chen, Y.P. Effects of microbial inoculation on physicochemical properties and bacterial community structure of citrus peel composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 291, 121843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.W.; Li, X.T.; Li, M.Q.; Zhu, Q.H.; Li, G.; Ma, C.F.; Li, Q.Y.; Meng, J.Z.; Liu, Y.Y.; Li, Q.L. Impacts of red mud on lignin depolymerization and humic substance formation mediated by laccase-producing bacterial community during composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 410, 124557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harindintwali, J.D.; Zhou, J.L.; Yu, X.B. Lignocellulosic crop residue composting by cellulolytic nitrogen-fixing bacteria: A novel tool for environmental sustainability. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, B.E.; Bals, B.D.; Kim, S.; Eranki, P. Biofuels Done Right: Land Efficient Animal Feeds Enable Large Environmental and Energy Benefits. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8385–8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, M.R.; Shi, M.Q.; Wang, Z.R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Gao, C.J.; Chai, L.Y.; Shi, Y. In-situ lignin bioconversion promotes complete carbohydrate conversion of rice straw by Cupriavidus basilensis B-8. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 6, 7969–7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, M.M.; Suárez-Estrella, F.; Vargas-García, M.C.; López, M.J.; López-González, J.A.; Moreno, J. Increasing native microbiota in lignocellulosic waste composting: Effects on process efficiency and final product maturity. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 1958–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, Ó.J.; Ospina, D.A.; Montoya, S. Compost supplementation with nutrients and microorganisms in composting process. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemati, A.; Aliasgharzad, N.; Khakvar, R.; Khoshmanzar, E.; Lajayer, B.A.; Hullebusch, E.D. Role of Lignin and Thermophilic Lignocellulolytic Bacteria in the evolution of humification indices and enzymatic activities during compost production. Waste Manag. 2021, 119, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.X.; Liu, H.T.; Wu, S.B. Humic substances developed during organic waste composting: Formation mechanisms, structural properties, and agronomic functions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wei, Y.Q.; Cui, H.Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.Q.; Shan, S.; Wei, Z.M. Effect of actinobacteria agent inoculation methods on cellulose degradation during composting based on redundancy analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-Líter, J.A.; Eugenio, L.D.; Nieto-Domínguez, M.; Prieto, A.; Martínez, M.J. Hemicellulases from Penicillium and Talaromyces for lignocellulosic biomass valorization: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 324, 124623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.F.; Xia, T.; Li, G.H.; Li, X.L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Wang, Y.M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Xie, G.S.; Bai, F.W.; et al. Overproduction of native endo-β-1,4-glucanases leads to largely enhanced biomass saccharification and bioethanol production by specific modification of cellulose features in transgenic rice. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choińska-Pulit, A.; Laba, W.; Rodziewicz, A. Enhancement of pig bristles waste bioconversion by inoculum of keratinolytic bacteria during composting. Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.M.; Awasthi, S.K.; Liu, T.; Verma, S.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.Y.; Ren, X.N.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Awasthi, M.K. Positive impact of biochar alone and combined with bacterial consortium amendment on improvement of bacterial community during cow manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 280, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohacz, J. Lignocellulose-degrading enzymes, free-radical transformations during composting of lignocellulosic waste and biothermal phases in small-scale reactors. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.Q.; Li, W.G.; Zhang, S.M.; Wu, C.D.; Lv, L.Y. Feasibility of co-composting of sewage sludge, spent mushroom substrate and wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 226, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhang, K.; Liu, P.; Han, H.W.; Zhao, S.; Kakade, A.; Khan, A.; Du, D.L.; Li, X.K. Lignin depolymerization and utilization by bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.F.; Shen, X.B.; Gang, L.P.; Xu, H.J.; Wu, F.F.; Sheng, L.Q. A novel lignin degradation bacteria—Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SL-7 used to degrade straw lignin efficiently. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.Y.; Li, X.F.; Qi, X.G.; Ren, Y.P. Pathway analysis of the biodegradation of lignin by Brevibacillus thermoruber. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.N.; Li, H.Y.; Yao, T.; Su, M.; Li, J.H.; Liu, Z.Y.; Xin, Y.Q.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.G.; Gun, S.B. Effects of microbial inoculation on enzyme activity, available nitrogen content, and bacterial succession during pig manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, X.Y. Changes in physical, chemical, and microbiological properties during the two-stage co-composting of green waste with spent mushroom compost and biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Y.; Xie, B.T.; Khan, R.; Dong, J.X.; Shen, G.M. The changes in macronutrients and microbial community structure during the co-composting of white wine distillers’ grains and potassium silicate. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Zhou, M.D.; Pan, X.F.; Li, C.X.; Lv, N.; Wang, T.; Cai, G.J.; Wang, R.M.; Zhu, G.F. Simultaneous biogas and biogas slurry production from co-digestion of pig manure and corn straw: Performance optimization and microbial community shift. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.Q.; Wu, D.; Wei, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J.Q.; Xie, X.Y.; Zhang, R.J.; Wei, Z.M. Improved lignocellulose-degrading performance during straw composting from diverse sources with actinomycetes inoculation by regulating the key enzyme activities. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Awasthi, S.K.; Wang, Q.; Awasthi, M.K.; Zhao, J.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Ren, X.N.; Wang, M.J.; Zhang, Z.Q. Role of Ca-bentonite to improve the humification, enzymatic activities, nutrient transformation and end product quality during sewage sludge composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 262, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.X.; Qiu, X.W.; Zhang, J.B.; Tao, C.Y. Effects of seaweed fertilizer on enzyme activities, metabolic characteristics, and bacterial communities during maize straw composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 286, 121375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, M.; Marilley, L.; Beffa, T.; Aragno, M. Thermophilic bacterial communities in hot composts as revealed by most probable number counts and molecular (16S rDNA) methods. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 28, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mao, H.; Lv, Z.Y.; Sun, H.D.; Li, R.H.; Zhai, B.N.; Wang, Z.H.; Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, L.N. Improvement of biochar and bacterial powder addition on gaseous emission and bacterial community in pig manure compost. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 258, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Hou, T.; Yin, H.J.; Han, L.J.; Huang, G.Q. Effects of amoxicillin on nitrogen transformation and bacterial community succession during aerobic composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, M.; Gutiérrez, M.C.; Siles, J.A.; García-Olmo, J.; Martín, M.A. Chemometric analysis and NIR spectroscopy to evaluate odorous impact during the composting of different raw materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).