Abstract
Riboflavin or vitamin B2 is a water-soluble vitamin and a precursor of flavin coenzymes, flavin mononucleotide, and flavin adenine dinucleotide, which play a key role as enzyme cofactors in energy metabolism. Candida famata yeast is a promising producer of riboflavin, as it belongs to the group of so-called flavinogenic yeasts, capable of riboflavin oversynthesis under conditions of iron starvation. The role of the particular structural genes in the limitation of riboflavin oversynthesis is not known. To study the impact of overexpression of the structural genes of riboflavin synthesis on riboflavin production, a set of plasmids containing genes RIB1, RIB6, and RIB7 in different combinations was constructed. The transformants of the wild-type strain of C. famata, as well as riboflavin overproducer, were obtained, and the synthesis of riboflavin was studied. It was found that overexpression of RIB1 and RIB6 genes coding for enzymes GTP cyclohydrolase II and 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate synthase, which catalase the initial steps of riboflavin synthesis, elevated riboflavin production by 13–28% relative to the parental riboflavin-overproducing strains.
1. Introduction
Riboflavin was first documented in 1872 by British chemist Alexander Blyth as a yellow pigment found in milk. Riboflavin is also known as an essential and water-soluble vitamin B2 [1]. Riboflavin is a precursor of flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), which play a key role as cofactors in energy metabolism and are required for co-enzyme function in numerous oxidation and reduction reactions in all aerobic forms of life. Most microorganisms as well as all plants and fungi synthesize riboflavin, whereas it is not produced by animals and rare pro- and eukaryotic microorganisms. Thus, human and domestic animals must obtain a daily dose of 2 mg of riboflavin through nutrition or dietary supplements [1,2,3]. Vitamin B2 can be found in a wide variety of foods and natural sources, especially milk, organ meats (mostly in calf liver), egg, fish, nuts, certain fruits and legumes, wild rice, mushrooms, dark green leafy vegetables, yeast, beer, cheese, and dietary products [4,5]. Considering that it is heat-stable, cooking does not lower levels of riboflavin; however, exposure to light could destroy it. Riboflavin causes no known toxicity, since at higher intakes, it is excreted in the urine and not stored [5].
Riboflavin has been used in dietary supplements and for inflammatory disease treatments such as angulus infectious, cheilitis, glossitis, sepsis, cataracts, and migraine headaches [1]. Consequently, the development of riboflavin production at the industrial scale is of high importance. Currently, vitamin B2 is produced on a large scale by both chemical and biotechnological synthesis, with the latter gaining more significance because of the advantages of biotechnological processes such as cost effectiveness, reduction in waste and energy requirements, and the use of renewable resources—sugar or plant oil [6,7,8]. Over the past two decades, the microbial production of riboflavin by fermentation completely replaced the chemical synthesis [9]. The industrial production of riboflavin is achieved mainly through the use of constructed strains of the bacterium Bacillus subtilis and the filamentous fungus Ashbya gossypii [6,10,11]. Both accumulate large amounts of riboflavin (15–20 g riboflavin/L); however, each has its advantages and disadvantages [7]. Thus, B. subtilis accumulates riboflavin during exponential growth very rapidly; however, is susceptible to phage lysis and genetic instability. Contrary, A. gossypii accumulates riboflavin in the stationary phase so the growth phase is non-productive; however, strains are genetically very stable [3,6,7,9,10]. Some strains of C. famata also belong to the most known flavinogenic organisms and were used for industrial production of riboflavin for a long time in the USA [12]. However, it was stopped because of the low stability of the riboflavin-producing strain due to the high rate of its reversion to nonproducing variants [3]. Nonetheless, the flavinogenic potential of the yeast C. famata is still very high [3,6,7], and the use of yeasts has several benefits compared to more traditional fungi or bacteria. They are much easier to grow and maintain in culture, and separation and purification of riboflavin is less technologically challenging.
The biosynthesis of riboflavin starts from guanosine triphosphate and ribulose-5-phosphate and is completed in six enzymatic steps [13]. Methods of molecular genetics have been developed for the wild-type strain of C. famata NRRL Y-30292 [14,15]. The structural genes coding for enzymes of riboflavin synthesis has been cloned [15,16,17]. Specifically, the genes RIB1 (coding for GTP cyclohydrolase II), RIB2 (specific reductase), RIB5 (dimethylribityllumazine synthase), RIB6 (3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate synthase), and RIB7 (riboflavin synthase) were cloned via functional complementation of the corresponding mutations, leading to defects in riboflavin synthesis [12,15,16]. Insertion mutagenesis was used to identify genes involved in the regulation of riboflavin synthesis. Two genes, MET2, coding for homoserine O-acetyltransferase, and SEF1, coding for transcription activator, have been identified using the mentioned approach [18].
In the riboflavin pathway, guanosine triphosphate and ribulose-5-phosphate enter into the vitamin synthesis pathway by the action of GTP cyclohydrolase II (encoded by gene RIB1) and 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate synthase (encoded by gene RIB6), respectively. It is logical to assume that these enzymes catalyze the rate-limiting stages of the pathway; however, this assumption has not been investigated in yeast thus far. In the current work, we report on the construction of recombinant C. famata strains overexpressing RIB1 and RIB6 genes in riboflavin-overproducing strains, either isolated by conventional mutagenesis or constructed on its basis using metabolic engineering approaches.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Media, and Cultivation Conditions
The C. famata VKM Y-9 (All-Russian Collection of Microorganisms, Pushchino, Russia), L20105 (leu2) [14], AF-4 [2], AF-4/SEF1/RIB1/RIB7 (designated as BRP from the Best Riboflavin Producer) [19], and BRP/PRS3m/ADE4m (designated as BRPI from the Best Riboflavin Producer Improved) [20] strains were used throughout the described work and were grown at 30 °C on rich YPD (0.5% yeast extract, 1% peptone, and 2% glucose), or mineral YNB (0.67% yeast nitrogen base and 2% glucose) media. For selection of yeast transformants, 20 mg/L nourseothricin was added to the YPD. To estimate riboflavin synthesis, the yeast cells from a fresh plate were grown in 50 mL of liquid media in 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks during 120 h with initial biomass 2 mg/L. Cultivation of C. famata in liquid media was carried out in the shakers (220 rpm) at 30 °C.
Escherichia coli strain DH5α (Φ80dlacZΔM15, recA1, endA1, gyrA96, thi-1, hsdR17(r-K m+K), supE44, relA1, deoR, Δ(lacZYA-argF) U169) was used in experiments that required a bacterial host. DH5α was grown at 37 °C in LB medium as described [21]. Transformed E. coli cells were maintained in rich medium containing 100 mg/L of ampicillin.
2.2. Molecular Biology Techniques
Standard cloning techniques were used as described [21]. Genomic DNA of C. famata was isolated using the NucleoSpin® Tissue Kit (Macherey-Nagel, Duren, Germany). Restriction endonucleases and DNA ligase (Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, Vilnius, Lithuania) were used following the manufacturer’s specifications. Plasmid isolation from E. coli was performed with the ZyppyTM Plasmid Miniprep (Irvine, CA, USA). PCR amplification of the fragments of interest was performed using Phusion High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, Vilnius, Lithuania) according to the manufacturer’s specification. PCRs were performed in a GeneAmp PCR System 9700 thermocycler (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA).
2.3. Plasmid Construction
For overexpression of the structural genes of the riboflavin biosynthesis, a number of recombinant plasmids were constructed on the basis of the plasmid pTb [18]. The E. coli gene SAT-1 conferring resistance to nourseothricin was amplified by PCR from plasmid pG-SAT-1 [22] using the pair of primers OL86 (AAA GCG GCC GCA TAT GAG TCT TAT ATA TAT C)/OL87 (AAG CGG CCG CAT ATG TCA CAT AAC CAC AAG). The obtained fragment was cloned into the NdeI site of the basis plasmid, resulting in pTb/SAT-1. Restriction sites were introduced into the primers to simplify cloning (restriction sites are underlined in all primers). The C. famata RIB1, RIB6, and RIB7 genes [17] were PCR-amplified from genomic DNA of C. famata VKMY-9 using pairs of primers OL42 (ATA GCA TGC CTG CCT ATG CTT GAT GCA T)/OL43 (ATA GCA TGC GTC TCG TTT ACT CAT CCT T), OL44 (ATA CTG CAG GAA TTC CCC GGA TCC G)/OL45 (ATA CTG CAG AAG AGG TGT GTA GCG GA), and OL46 (ATA GGG CCC GCT TAA AGT CGG TAA GC)/OL47 (ATG GGC CCC GAC TCT AGA GGA TCA A), respectively. The RIB1 gene was cloned into the SphI site, RIB6—into the PstI site, and RIB7—into the ApaI restriction site of the pTb/SAT-1 plasmid. The constructed recombinant plasmids were designated as pTb/SAT-1/R1, pTb/SAT-1/R6, pTb/SAT-1/R7, pTb/SAT-1/R1/R6, pTb/SAT-1/R1/R7, pTb/SAT-1/R6/R7, and pTb/SAT-1/R1/R6/R7 (Figure 1). The accuracy of constructed plasmids was verified by restriction analysis and sequencing.
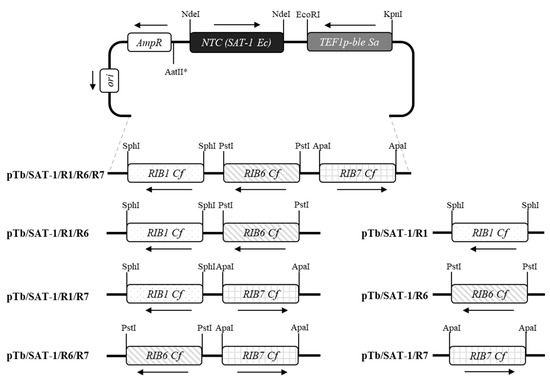
Figure 1.
Circular scheme of plasmids pTb/SAT-1/R1, pTb/SAT-1/R6, pTb/SAT-1/R7, pTb/SAT-1/R1/R6, pTb/SAT-1/R1/R7, pTb/SAT-1/R6/R7, and pTb/SAT-1/R1/R6/R7 for co-expression of C. famata RIB genes. All plasmids had the same plasmid backbone containing SAT-1 gene conferring resistance to nourseothricin and indicated as a black box, and gene ble under control of TEF1 promoter from C. famata conferring resistance to phleomycin and indicated as a dark grey box. The RIB1 gene is presented as a dotted box, RIB6—as a striped box, and RIB7—as a square grid box, * AatII—plasmid linearization enzyme.
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Expression of the RIB1 and RIB6 genes was confirmed by qRT-PCR. Total RNA was extracted from yeast cells using the GeneMATRIX Universal RNA Purification Kit with DNAseI (EURx Ltd., Gdansk, Poland). The qRT-PCR was performed by 7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System (The Applied Biosystems, USA) with a SG OneStep qRT-PCR kit (EURx Ltd., Gdansk, Poland) using corresponding pairs of primers RIB1f (GAG AAT GGG TCA TCT ATT AGA G)/RIB1r (AGT AAT CAA CAT CTG CTC TAT TTG), RIB6f (TTT GAT GAT GAG ATT GGA TGA TTG)/RIB6r (AAA TTA CTG GTA AAA GAA AGG CC), and ACT1f (TAA GTG TGA TGT CGA TGT CAG)/ACT1r (TTT GAG ATC CAC ATT TGT TGG AA); RNA as a template; and ROX reference passive dye following the manufacturer’s instructions as previously described [20].
2.5. Biochemical Analysis
The biomass was determined turbidimetrically with a Helios Gamma spectrophotometer (OD, 546 nm; cuvette, 10 mm) with gravimetric calibration. The riboflavin concentration was determined by measuring fluorescence (TurnerQuantechFM109510-33 fluorometer, maximum excitation = 440 nm, emission maximum = 535 nm) after cultivation in batch culture in flasks.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All the experimental data shown in this manuscript were collected from three independent samples to ensure reproducibility of the trends and relationships observed in the cultures. Each error bar indicates the standard deviation (SD) from the mean obtained from triplicate samples. The 5% significance level was used in the statistical analyses.
3. Results
3.1. Construction of Riboflavin-Producing Strains
Our long-term goal is to construct riboflavin overproducers on the basis of the flavinogenic yeast C. famata. In our previous study, it was shown that co-expression of the first RIB1 and last RIB7 genes of riboflavin synthesis coding for GTP cyclohydrolase II and riboflavin synthetase resulted in increase in riboflavin production [2]. However, the effect of each of these genes on riboflavin synthesis has not been studied. Furthermore, the impact of the RIB6 gene encoding 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate synthase, on riboflavin production alone or in combination with the aforementioned genes, has also not been studied. To fill this gap, homologous genes RIB1, RIB6, and RIB7 separately or in different combination were expressed in C. famata wild-type strain L20105. The plasmids pTb/SAT-1/R1, pTb/SAT-1/R6, pTb/SAT-1/R7, pTb/SAT-1/R1/R6, pTb/SAT-1/R1/R7, pTb/SAT-1/R6/R7, and pTb/SAT-1/R1/R6/R7 were linearized with the restriction endonuclease AatII and used for transformation of L20105. The transformants were selected on a solid mineral medium, containing nourseothricin at a concentration of 20 mg/L after three days of incubation. The selected transformants were stabilized by alternating cultivation on non-selective media followed by selective media. The transformation frequency was calculated at 50–100 colonies/µg of DNA.
In the same way, several types of transformants were obtained on the basis of riboflavin-overproducing strains such as AF-4, BRP, and BRPI selected or constructed previously. The strains AF-4, BRP, and BRPI were transformed with AatII-linearized plasmids pTb/SAT-1/R1, pTb/SAT-1/R1/R6, pTb/SAT-1/R6, and pTb/SAT-1/R1/R6, respectively.
The presence of the plasmids pTb/SAT-1/R1, pTb/SAT-1/R6, and pTb/SAT-1/R7 in the stabilized transformants was confirmed by diagnostic PCR, using primers OL40 (CCC TAT TTA CTG TTA CCA TCC) or OL39 (CCA AGC CTA CTC CCC AGT AAT A), homologous to the selective markers, with Ko73 (TGC TCT AGA TTC ATG TAT TGG TAA AGC G), OL67 (AAA TCT AGA ATT TTT TGA TAT CTA AGG GGT TCC TAA TT), and OL64 (AAA GAG CTC GCT TAA AGT CGG TAA GCA CTG) corresponding to the genes RIB1, RIB6, and RIB7 respectively. Similarly, the presence of plasmids pTb/SAT-1/R1/R6, pTb/SAT-1/R1/R7, pTb/SAT-1/R6/R7, and pTb/SAT-1/R1/R6/R7 in the transformants was supported by PCR, using primers Ko73/OL66 (AAA CAG CTG TCC TCG CAC CAA AAC CC) for the genes RIB1 and RIB6, OL67/OL65 (AAA TCT AGA GAT CTA CAG TCG ATG ATG GGG) for RIB6 and RIB7, and Ko73/OL65 for RIB1 and RIB7 (data not shown).
The expression of the RIB1 and RIB6 genes was analyzed by qRT-PCR in BRPI/RIB1-RIB6. It was found that the expression profiles of RIB1 and RIB6 were 2.1-fold and 1.6-fold increased as compared to that of the parental strain, respectively (Figure 2).
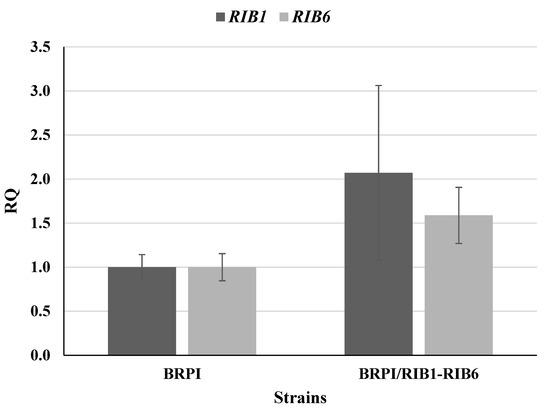
Figure 2.
Relative quantification (RQ) of RIB1 and RIB6 genes. Strains BRPI and BRPI/RIB1-RIB6 were cultivated on YNB medium supplemented with yeast extract at 28 °C, 220 rpm. The mRNA quantification was normalized to ACT1 mRNA.
3.2. Biochemical Characteristics of Strains Producing Riboflavin
Initial characterization of riboflavin production was performed in the C. famata strain L20105 and its derivatives L2/RIB1, L2/RIB6, L2/RIB7, L2/RIB1-RIB6, L2/RIB1-RIB7, L2/RIB6-RIB7, and L2/RIB1-RIB6-RIB7 on 72 h of cultivation in the YNB medium. The level of biomass accumulation by the constructed strains was similar to that observed in recipient strain L20105. The strains L2/RIB1, L2/RIB6, L2/RIB7, L2/RIB1-RIB6, L2/RIB1-RIB7, L2/RIB6-RIB7, and L2/RIB1-RIB6-RIB7 revealed 47%, 18%, 7%, 100%, 57%, 22%, and 47% increase in riboflavin yield (mg of riboflavin per g of CDW), respectively, as compared to that of the parental strain L20105 (Figure 3).
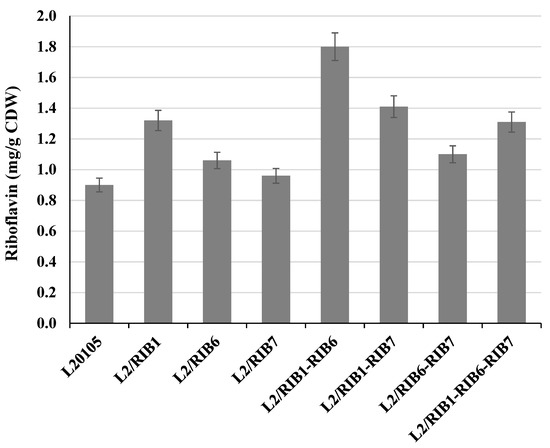
Figure 3.
Riboflavin yield (mg/g CDW) of C. famata strains expressing RIB1, RIB6, and RIB7 genes in different combinations derivative of strain L20105 in the YNB medium on the third day of cultivation.
The expression of single genes of riboflavin synthesis, various combinations of two genes, and co-expression of all three genes, led to an increase in riboflavin production to a lesser or greater extent. The highest impact on riboflavin yield was achieved by co-expression of RIB1 and RIB6 genes reaching a twofold increase. The obtained results encourage us to express the combination of RIB1 and RIB6 genes or RIB6 alone on the background of riboflavin-overproducing strains.
The riboflavin overproducing strain AF-4 was isolated from the wild-type strain of C. famata through several stages of mutagenesis and subsequent selection [2]. Its derivative strains AF-4/RIB6 and AF-4/RIB1-RIB6 accumulated slightly less biomass at 6% and 17%, respectively, when compared to parental strain (Table 1, Figure 4A). At the same time, riboflavin production or riboflavin yield of the AF-4/RIB6 and AF-4/RIB1-RIB6 strains revealed 4% and 13% or 11% and 35% increase as compared to the parental strain, respectively (Table 1, Figure 4B).

Table 1.
Cell biomass, riboflavin production, and riboflavin yield of C. famata strains AF-4, AF-4/RIB6, AF-4/RIB1-RIB6, BRP, BRP-RIB6, BRPI, and BRPI/RIB1-RIB6 in the YNB medium at the fifth day of cultivation.
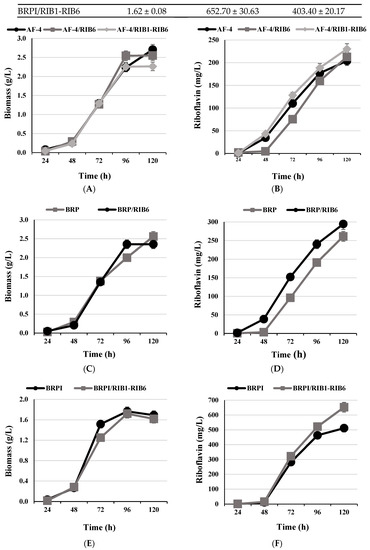
Figure 4.
Time profiles of biomass accumulation (A,C,E) and riboflavin production (B,D,F) concentration by C. famata AF-4, AF-4/RIB6, AF-4/RIB1-RIB6, BRP, BRP/RIB6, BRPI, and BRPI/RIB1-RIB6 on YNB medium in flasks.
BRP strain derivative of AF-4 harboring additional copies of RIB1, RIB7, and SEF1 genes [19] was transformed with a plasmid containing the gene RIB6. As the result, the BRP/RIB6 strain accumulated around 8% less biomass when compared to the parental strain (Table 1, Figure 4C), while riboflavin production and riboflavin yield were increased by 13% and 23%, respectively (Table 1, Figure 4D).
BRPI is a derivative of BRP that contains modified genes of purine nucleotide synthesis de novo [20]. BRPI co-expression of RIB1 and RIB6 genes was designated as BRPI/RIB1-RIB6. Such a strain accumulated nearly the same amount of biomass when compared to the parental strain with only 4% decrease (Table 1, Figure 4E). However, riboflavin production and riboflavin yield by the strain was 28% and 33% increased as compared to the parental strain, respectively (Table 1, Figure 4F). The riboflavin production and riboflavin yield by BRPI/RIB1-RIB6 amounted to 653 mg/L and 403 mg/g of CDW, respectively (Table 1).
4. Discussion
The application of methods of classical selection and metabolic engineering, including overexpression of structural and regulatory genes of riboflavin synthesis and excretion, genes involved in GTP synthesis, and deletion of the genes of negative regulators of vitamin B2 synthesis, resulted in the construction of highly effective riboflavin producers based on yeast C. famata [2,19,20,21,22,23,24]. Despite our success in the construction of stable riboflavin producers, in our opinion, the flavinogenic potential of this yeast remains only partially realized. This is because the strains of C. famata, such as dep8, are known, which are characterized by higher riboflavin accumulation relative to our strains [25,26]. However, the described strains are highly genetically unstable and are reverted to the strains that do not overproduce riboflavin [3]. Contrary, our riboflavin overproducers are genetically very stable [2,20]; still, further increase in riboflavin accumulation is necessary. This goal we plan to achieve in the future by combining in one genome all genetic changes identified by us, leading to an increase in riboflavin accumulation. We also plan to sequence the genome of C. famata wild-type strain and available riboflavin-overproducing strain AF-4 and use this information for further metabolic engineering. The complete genome sequence was recently published for other flavinogenic yeast Candida membranifaciens [27].
In this work, we explored the impact of RIB1, RIB6, and RIB7 genes on riboflavin production. It was shown that among strains expressing single genes, the highest increase in riboflavin yield was fixed for strain L2/RIB1, reaching 47% when compared to the parental strain (Figure 3). The constructed strains L2/RIB6 and L2/RIB7 revealed a less pronounced 18% and 7% increase in riboflavin yield as compared to that of L20105 (Figure 3).
It is of interest to note that co-expression of RIB1 and RIB6 genes revealed a more pronounced increase in riboflavin yield on the wild-type strain rather than on riboflavin overproducers. This fact can be explained by other limiting stages of riboflavin synthesis when the amount of produced vitamin increases significantly. For instance, a sufficient supply of precursors for vitamin B2 synthesis or efficient secretion of riboflavin from the cell are among them. Recently, we proved the essential role of purine nucleotide supply for riboflavin overproduction [20]; however, the role of the other precursor molecule, ribulose-5-phosphate, in riboflavin overproduction in C. famata remains unknown [3,12], and it has been planned to be elucidated in further studies. In the bacterial system of B. subtilis, genetic changes lead to an increase of ribulose-5-phosphate-activated riboflavin accumulation [28,29]. We suggest that activation of ribulose-5-phosphate supply together with overexpression of the RIB6 gene will substantially enhance riboflavin synthesis in already available riboflavin overproducers of C. famata.
The results of this work revealed that co-expression of RIB1 and RIB6 resulted in higher increase of riboflavin yield than co-expression of RIB1, RIB6, and RIB7 on the wild-type background. It is well known that riboflavin synthase generates 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino) uracil, which is the substrate of lumazine synthase Rib5. In other words, the substrate produced by riboflavin synthase may be recycled by lumazine synthase [30]. It can be speculated that the shift of the stoichiometry between Rib5 and Rib7 may have a negative impact on the overall synthesis of riboflavin. However, this assumption requires further experimental confirmation.
Overall obtained results led us to conclude that co-expression of RIB1 and RIB6 is more essential for riboflavin overproduction than other combinations. It was shown that overexpression of RIB1 and RIB6 genes elevates riboflavin yield by 33% relative to the parental riboflavin-overproducing strain, reaching 403 mg/g of CDW (Table 1), which is the highest riboflavin yield described in the scientific literature. The present work is also of greater importance in the context of genetic strategies to improve riboflavin production in yeast.
5. Conclusions
To study the impact of genes RIB1, RIB6, and RIB7 on riboflavin production in yeast, a set of plasmids containing these genes in different combinations was constructed. The transformants of the wild-type strain of C. famata were obtained, as well as on the background of the previously isolated riboflavin-overproducing strains, and riboflavin synthesis was studied. It was shown that overexpression of RIB1 and RIB6 genes of the initial steps of both branches of riboflavin biosynthesis elevated riboflavin yield by 33–35% relative to the parental riboflavin overproducing strains.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S., K.D.; methodology, Y.P., O.L., J.R., K.D.; investigation, Y.P., O.L., J.R., K.D.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S., K.D.; writing—review and editing, Y.P., O.L., J.R., K.D.; project administration, A.S.; funding acquisition, A.S., K.D., J.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grant of National Science Centre of Poland (NCN) Opus UMO-2018/29/B/NZ1/01-497, grant of National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine (0121U109268), and National Research Foundation of Ukraine grant 2020.01/0090.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Suwannasom, N.; Kao, I.; Pruß, A.; Georgieva, R.; Bäumler, H. Riboflavin: The Health Benefits of a Forgotten Natural Vitamin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmytruk, K.V.; Yatsyshyn, V.Y.; Sybirna, N.O.; Fedorovych, D.V.; Sibirny, A.A. Metabolic engineering and classic selection of the yeast Candida famata (Candida flareri) for construction of strains with enhanced riboflavin production. Metab. Eng. 2011, 13, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, C.A.; Sibirny, A.A. Genetic control of biosynthesis and transport of riboflavin and flavin nucleotides and construction of robust biotechnological producers. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 321–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, D.R.; Libardi, S.H.; Skibsted, L.H. Riboflavin as a photosensitizer. Effects on human health and food quality. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, B.A. Vitamin B2: Riboflavin. J. Evid.-Based Integr. Med. 2011, 16, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Choi, J.S.; Park, E.Y. Microbial production of riboflavin using riboflavin overproducers, Ashbya gossypii, Bacillus subtilis, and Candida famata: An overview. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2001, 6, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahmann, K.-P.; Revuelta, J.L.; Seulberger, H. Three biotechnical processes using Ashbya gossypii, Candida famata, or Bacillus subtilis compete with chemical riboflavin production. Appl. Microbiolol. Biotechnol. 2000, 53, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandamme, E.J. Production of vitamins, coenzymes and related biochemicals by biotechnological processes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1992, 53, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwechheimer, S.K.; Park, E.Y.; Revuelta, J.L.; Becker, J.; Wittmann, C. Biotechnology of riboflavin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2107–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, C.M.; Smid, E.J.; van Sinderen, D. Bacterial vitamin B2, B11 and B12 overproduction: An overview. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 133, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Ming, H.; Park, E.Y.; Choi, J.S. Improvement of riboflavin production using mineral support in the culture of Ashbya gossypii. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2003, 41, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Dmytruk, K.V.; Sibirny, A.A. Candida famata (Candida flareri). Yeast 2012, 29, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.; Bacher, A. Biosynthesis of flavocoenzymes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 324–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voronovsky, A.A.; Abbas, C.A.; Fayura, L.R.; Kshanovska, B.V.; Dmytruk, K.V.; Sybirna, K.A.; Sibirny, A.A. Development of a transformation system for the flavinogenic yeast Candida famata. FEMS Yeast Res. 2002, 2, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, C.A.; Voronovsky, A.Y.; Fayura, L.R.; Kshanovska, B.V.; Dmytruk, K.V.; Sibirna, K.A.; Sibirny, A.A. Transformation Systems for Flavinogenic Yeast. U.S. Patent 7,009,045B2, 7 March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dmytruk, K.V.; Abbas, C.A.; Voronovsky, A.Y.; Kshanovska, B.V.; Sybirna, K.A.; Sibirny, A.A. Cloning of structural genes involved in riboflavin synthesis of the yeast Candida famata. Ukr. Biokhim. Zh. 2004, 76, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Voronovsky, A.Y.; Abbas, C.A.; Dmytruk, K.V.; Ishchuk, O.P.; Kshanovska, B.V.; Sybirna, K.A.; Gaillardin, C.; Sibirny, A.A. Candida famata (Debaryomyces hansenii) DNA sequences containing genes involved in riboflavin synthesis. Yeast 2004, 21, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmytruk, K.V.; Voronovsky, A.Y.; Sibirny, A.A. Insertion mutagenesis of the yeast Candida famata (Debaryomyces hansenii) by random integration of linear DNA fragments. Curr. Genet. 2006, 50, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmytruk, K.; Lyzak, O.; Yatsyshyn, V.; Kluz, M.; Sibirny, V.; Puchalski, C.; Sibirny, A. Construction and fed-batch cultivation of Candida famata with enhanced riboflavin production. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmytruk, K.V.; Ruchala, J.; Fedorovych, D.V.; Ostapiv, R.D.; Sibirny, A.A. Modulation of the purine pathway for riboflavin production in flavinogenic recombinant strain of the yeast Candida famata. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, e1900468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsh, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Millerioux, Y.; Clastre, M.; Simkin, A.J.; Courdavault, V.; Marais, E.; Sibirny, A.A.; Papon, N. Drug-resistant cassettes for the efficient transformation of Candida guilliermondii wild-type strains. FEMS Yeast Res. 2011, 11, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsyrulnyk, A.O.; Fedorovych, D.V.; Dmytruk, K.V.; Sibirny, A.A. Overexpression of riboflavin excretase enhances riboflavin production in the yeast Candida famata. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2280, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreieva, Y.; Petrovska, Y.; Lyzak, O.; Liu, W.; Kang, Y.; Dmytruk, K.; Sibirny, A. Role of the regulatory genes SEF1, VMA1 and SFU1 in riboflavin synthesis in the flavinogenic yeast Candida famata (Candida flareri). Yeast 2020, 37, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heefner, D.L.; Boyts, A.; Burdzinski, L.; Yarus, M. Efficient Riboflavin Production with Yeast. U.S. Patent 5,231,007, 27 July 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Heefner, D.L.; Weaver, C.A.; Yarus, M.J.; Burdzinski, L.A. Method for Producing Riboflavin with Candida famata. U.S. Patent 5,164,303, 17 November 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Palma, M.; Mondo, S.; Pereira, M.; Vieira, E.; Grigoriev, I.V.; Sá-Correia, I. Genome Sequence and Analysis of the Flavinogenic Yeast Candida membranifaciens IST 626. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.X.; Chen, T.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X.M. Overexpression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enhances riboflavin production in Bacillus subtilis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Sun, Y.; Fu, S.; Xia, M.; Su, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, D. Improving the Production of Riboflavin by Introducing a Mutant Ribulose 5-Phosphate 3-Epimerase Gene in Bacillus subtilis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 704650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladenstein, R.; Fischer, M.; Bacher, A. The lumazine synthase/riboflavin synthase complex: Shapes and functions of a highly variable enzyme system. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 2537–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).