Antimicrobial Activity of Zymomonas mobilis Is Related to Its Aerobic Catabolism and Acid Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Media and Cultivation
2.2. Fractionation and Concentration of Culture Medium
2.3. Quantification of the Antimicrobial Activity
2.3.1. Inhibition Zone
2.3.2. Optical Density Measurements and Quantification of Growth in Liquid Media
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
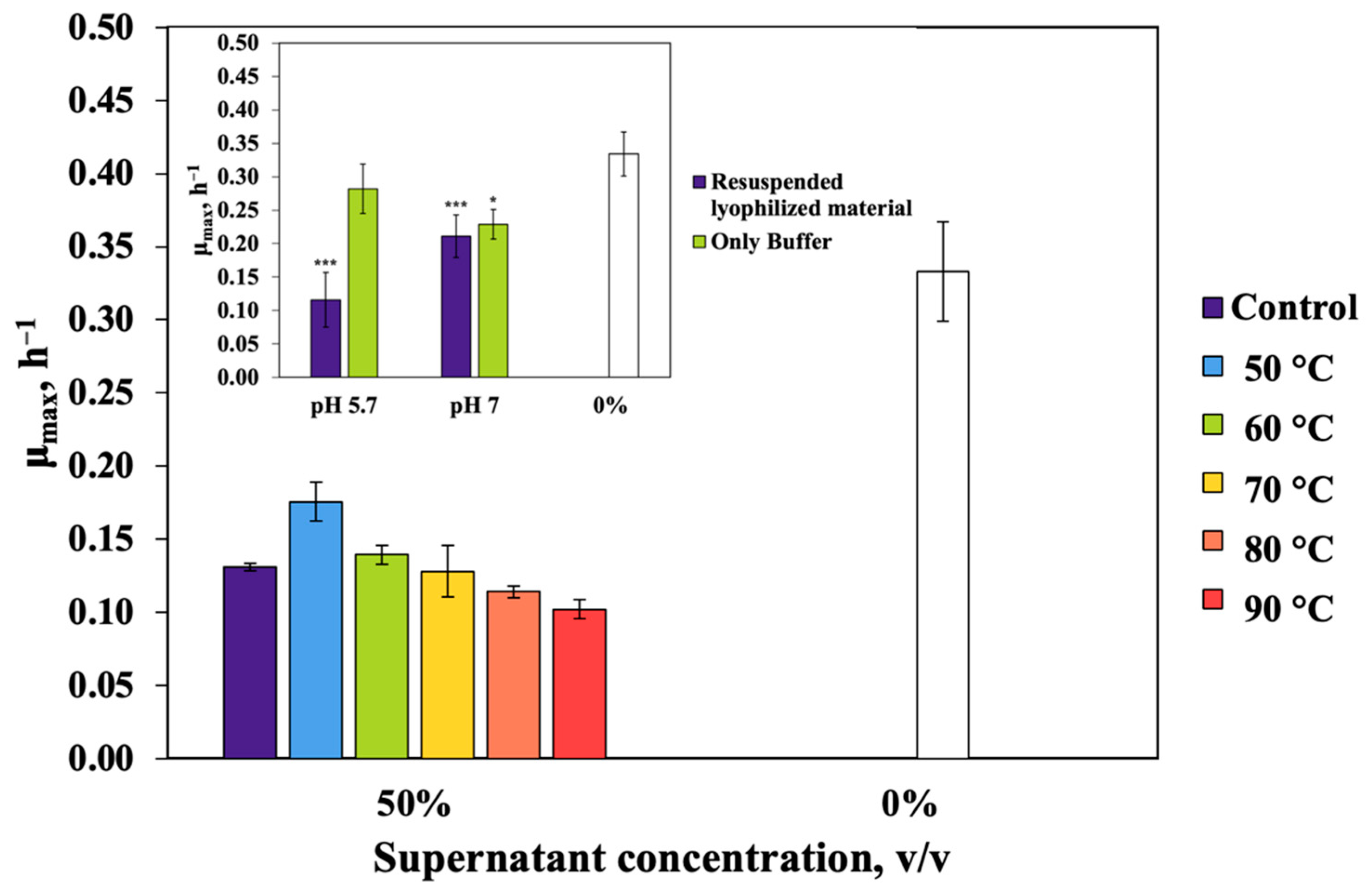
3.1. Z. mobilis Strains and Culture Conditions Producing Maximum AM Effect
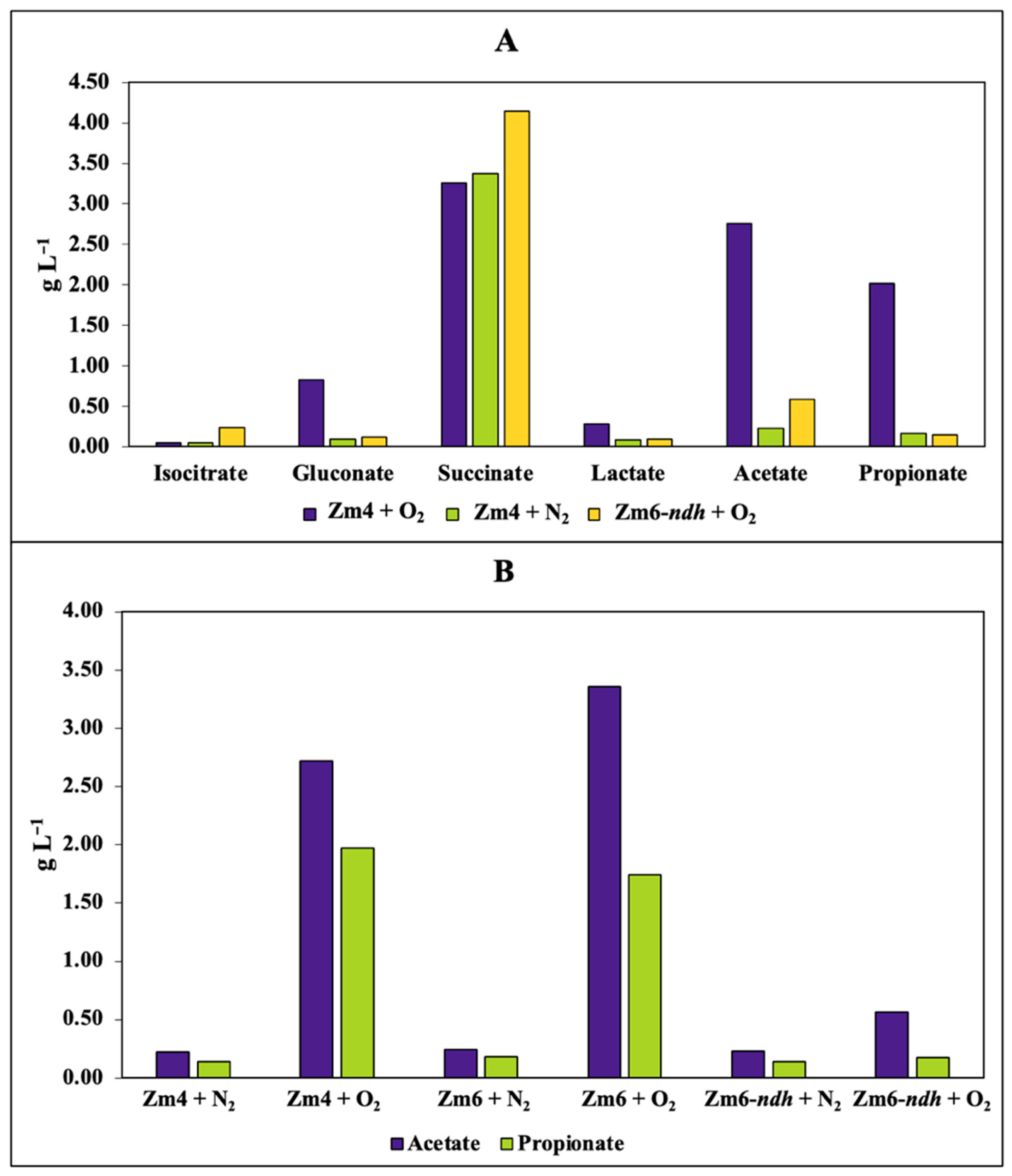
3.2. Properties of the Putative Antimicrobial Compound(s)
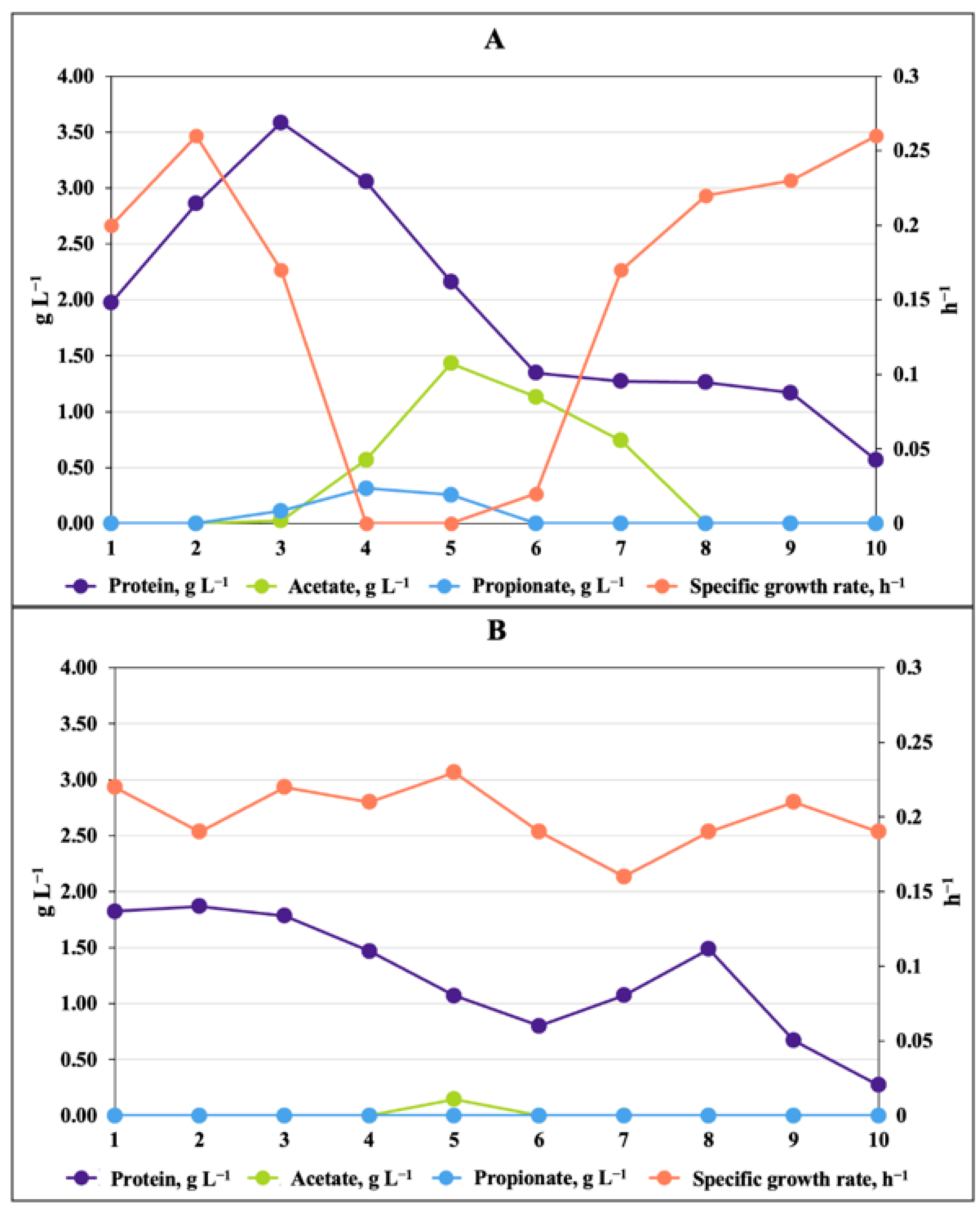
3.3. Evidence That Acetic and Propionic Acids Determine the Z. mobilis Antimicrobial Activity
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rogers, P.L.; Lee, K.J.; Skotnicki, M.L.; Tribe, D.E. Ethanol production by Zymomonas mobilis. In Microbial Reactions. Advances in Biochemical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982; Volume 23, pp. 37–84. [Google Scholar]
- Sprenger, G. Carbohydrate metabolism in Zymomonas mobilis: A catabolic highway with some scenic routes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1996, 145, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, A.A.; Striegel, K.; Wittig, R.M.; Laufer, B.; Schmitz, G.; Wiechert, W. Metabolic state of Zymomonas mobilis in glucose-, fructose-, and xylose-fed continuous cultures as analysed by 13C- and 31P-NMR spectroscopy. Arch. Microbiol. 1999, 171, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, T.B.; Adamczyk, P.A.; Stevenson, D.M.; Regner, M.; Ralph, J.; Reed, J.L.; Amador-Noguez, D. 2H and 13C metabolic flux analysis elucidates in vivo thermodynamics of the ED pathway in Zymomonas mobilis. Metabol. Eng. 2019, 54, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalnenieks, U.; de Graaf, A.A.; Bringer-Meyer, S.; Sahm, H. Oxidative phosphorylation in Zymomonas mobilis. Arch. Microbiol. 1993, 160, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnenieks, U.; Balodite, E.; Rutkis, R. Metabolic engineering of bacterial respiration: High vs. low P/O and the case of Zymomonas mobilis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkis, R.; Galinina, N.; Strazdina, I.; Kalnenieks, U. The inefficient aerobic energetics of Zymomonas mobilis: Identifying the bottleneck. J. Basic Microbiol. 2014, 54, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentjuss, A.; Odzina, I.; Kostromins, A.; Fell, D.A.; Stalidzans, E.; Kalnenieks, U. Biotechnological potential of respiring Zymomonas mobilis: A stoichiometric analysis of its central metabolism. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 165, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Haning, K.; Hu, Y.; Wu, B.; He, M.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, J.; et al. Advances and prospects in metabolic engineering of Zymomonas mobilis. Metab. Eng. 2018, 50, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnenieks, U.; Pappas, K.M.; Bettenbrock, K. Zymomonas mobilis metabolism: Novel tools and targets for its rational engineering. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2020, 77, 37–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weir, P.M. The ecology of Zymomonas: A review. Folia Microbiol. 2016, 61, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffie, T.L.; Louie, P.W.; Khachatourians, G.G. Isolation of noninhibitory strains of Zymomonas mobilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 1007–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, C.; Souza, L.A.G. Colpites and vulvovaginitis treatment using Zymomonas mobilis var. recifensis. Rev. Inst. Antibiot. 1973, 13, 85–87. [Google Scholar]
- Swings, J.; De Ley, J. The biology of Zymomonas. Bacteriol. Rev. 1977, 41, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.F.M.; Vasconcelos, J.; Souza, J.R.; Coutinho, E.M.; Montenegro, S.M.L.; Azevedo-Ximenes, E. The effect of Zymomonas mobilis culture on experimental Shistosoma mansoni infection. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2004, 37, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Campos, I.A.; Ximenes, E.A.; Carvalho Júnior, C.H.R.; de Mesquita, A.R.C.; Silva, J.B.N.F.; Maia, M.B.S. Zymomonas mobilis culture protects against sepsis by modulating the inflammatory response, alleviating bacterial burden and suppressing splenocyte apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weuster-Botz, D.; Aivasidis, A.; Wandrey, C. Continuous ethanol production by Zymomonas mobilis in a fluidized bed reactor. Part II: Process development for the fermentation of hydrolysed B-starch without sterilization. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1993, 39, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, N.; Peiris, P.; Markham, J.; Bavor, J. A novel co-culture process with Zymomonas mobilis and Pichia stipitis for efficient ethanol production on glucose/ xylose mixtures. Enz. Microb. Technol. 2009, 45, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, G.M.S.; Souza, L.I.O.; Rosato, Y.B.; Araújo, J.M. Detection of bacteriocins in Zymomonas mobilis and RAPD fingerprinting of the producer strains. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 2132–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franden, M.A.; Pilath, H.M.; Mohagheghi, A.; Pienkos, P.T.; Zhang, M. Inhibition of growth of Zymomonas mobilis by model compounds found in lignocellulosic hydrolysates. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Franden, M.A.; Brown, S.D.; Chou, Y.C.; Pienkos, P.T.; Zhang, M. Insights into acetate toxicity in Zymomonas mobilis 8b using different substrates. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2014, 7, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kalnenieks, U.; Galinina, N.; Strazdina, I.; Kravale, Z.; Pickford, J.L.; Rutkis, R. NADH dehydrogenase deficiency results in low respiration rate and improved aerobic growth of Zymomonas mobilis. Microbiology 2008, 154, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strazdina, I.; Kravale, Z.; Galinina, N.; Rutkis, R.; Poole, R.K.; Kalnenieks, U. Electron transport and oxidative stress in Zymomonas mobilis respiratory mutants. Arch. Microbiol. 2012, 194, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalnenieks, U.; Galinina, N.; Toma, M.M.; Pickford, J.L.; Rutkis, R.; Poole, R.K. Respiratory behaviour of a Zymomonas mobilis adhB::kanr mutant supports the hypothesis of two alcohol dehydrogenase isoenzymes catalysing opposite reactions. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 5084–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markwell, M.A.; Haas, S.M.; Bieber, L.L.; Tolbert, N.E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 87, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnenieks, U.; Balodite, E.; Strähler, S.; Strazdina, I.; Rex, J.; Pentjuss, A. Improvement of acetaldehyde production in Zymomonas mobilis by engineering of its aerobic metabolism. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wecker, M.S.; Zall, R.R. Production of acetaldehyde by Zymomonas mobilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 2815–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.C.; Lin, C.H.; Sung, C.T.; Fang, J.Y. Antibacterial activities of bacteriocins: Application in foods and pharmaceuticals. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Tschaplinski, T.J.; Engle, N.L.; Carroll, S.L.; Martin, S.L.; Davison, B.H. Transcriptomic and metabolomic profiling of Zymomonas mobilis during aerobic and anaerobic fermentations. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cray, J.A.; Stevenson, A.; Ball, P.; Bankar, S.B.; Eleutherio, E.C.A.; Ezeji, T.C. Chaotropicity: A key factor in product tolerance of biofuel-producing microorganisms. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 228–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cray, J.A.; Bell, A.N.W.; Bhaganna, P.; Mswaka, A.Y.; Timson, D.J.; Hallsworth, J.E. The biology of habitat dominance; can microbes behave as weeds? Microb. Biotechnol. 2013, 6, 453–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushell, F.M.L.; Tonner, P.D.; Jabbari, S.; Schmid, A.K.; Lund, P.A. Synergistic Impacts of Organic Acids and pH on Growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Comparison of Parametric and Bayesian Non-parametric Methods to Model Growth. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, A.J.; O’Byrne, C.; McLaggan, D.; Booth, I.R. Inhibition of Escherichia coli growth by acetic acid: A problem with methionine biosynthesis and homocysteine toxicity. Microbiology 2002, 148, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, V.C.; Sadykov, M.R.; Chaudhari, S.S.; Jones, J.; Endres, J.L.; Widhelm, T.J. A Central Role for Carbon-Overflow Pathways in the Modulation of Bacterial Cell Death. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joachimsthal, E.; Haggett, K.D.; Jang, J.H.; Rogers, P.L. A mutant of Zymomonas mobilis ZM4 capable of ethanol production from glucose in the presence of high acetate concentrations. Biotechnol. Lett. 1998, 20, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasko, D.R.; Zamboni, N.; Sauer, U. Bacterial response to acetate challenge: A comparison of tolerance among species. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 54, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Garcia, R.A.; McCubbin, T.; Navone, L.; Stowers, C.; Nielsen, L.K.; Marcellin, E. Microbial propionic acid production. Fermentation 2017, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
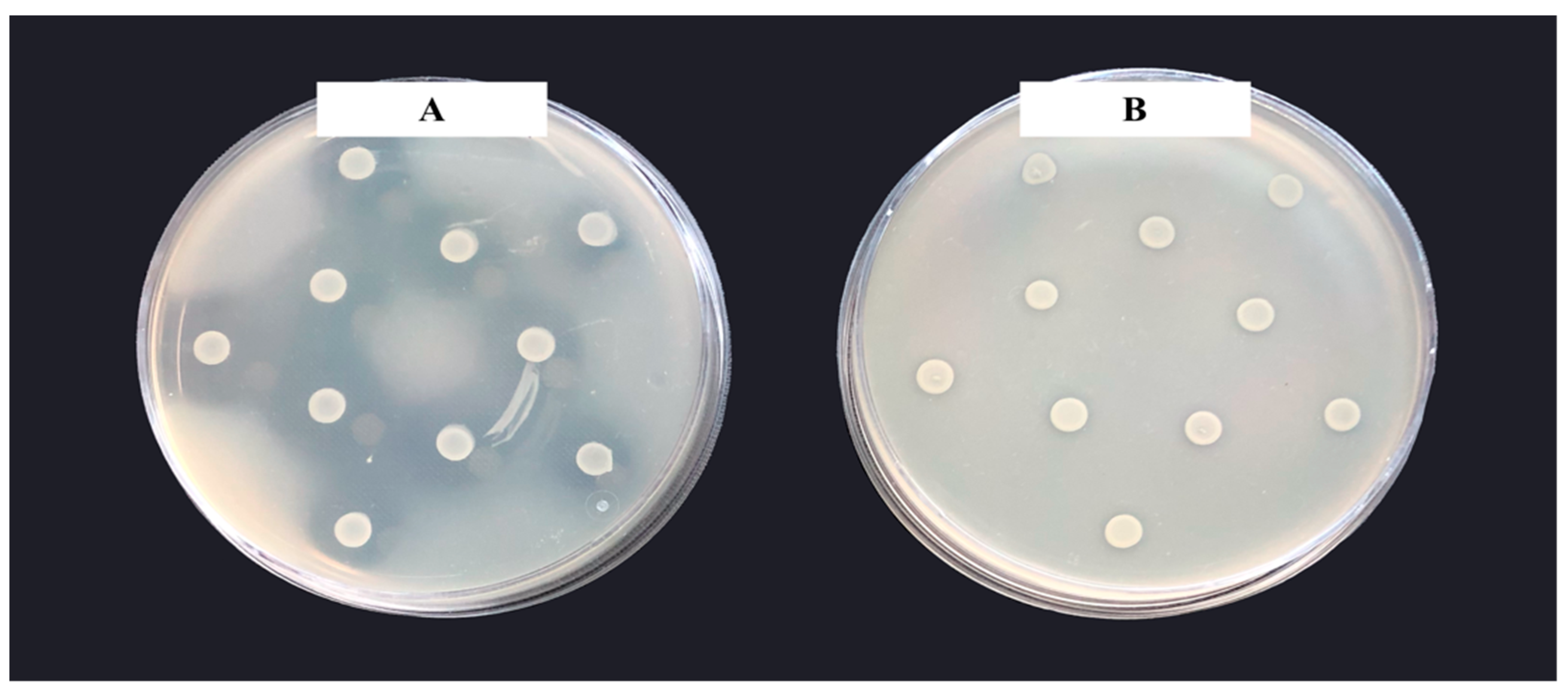
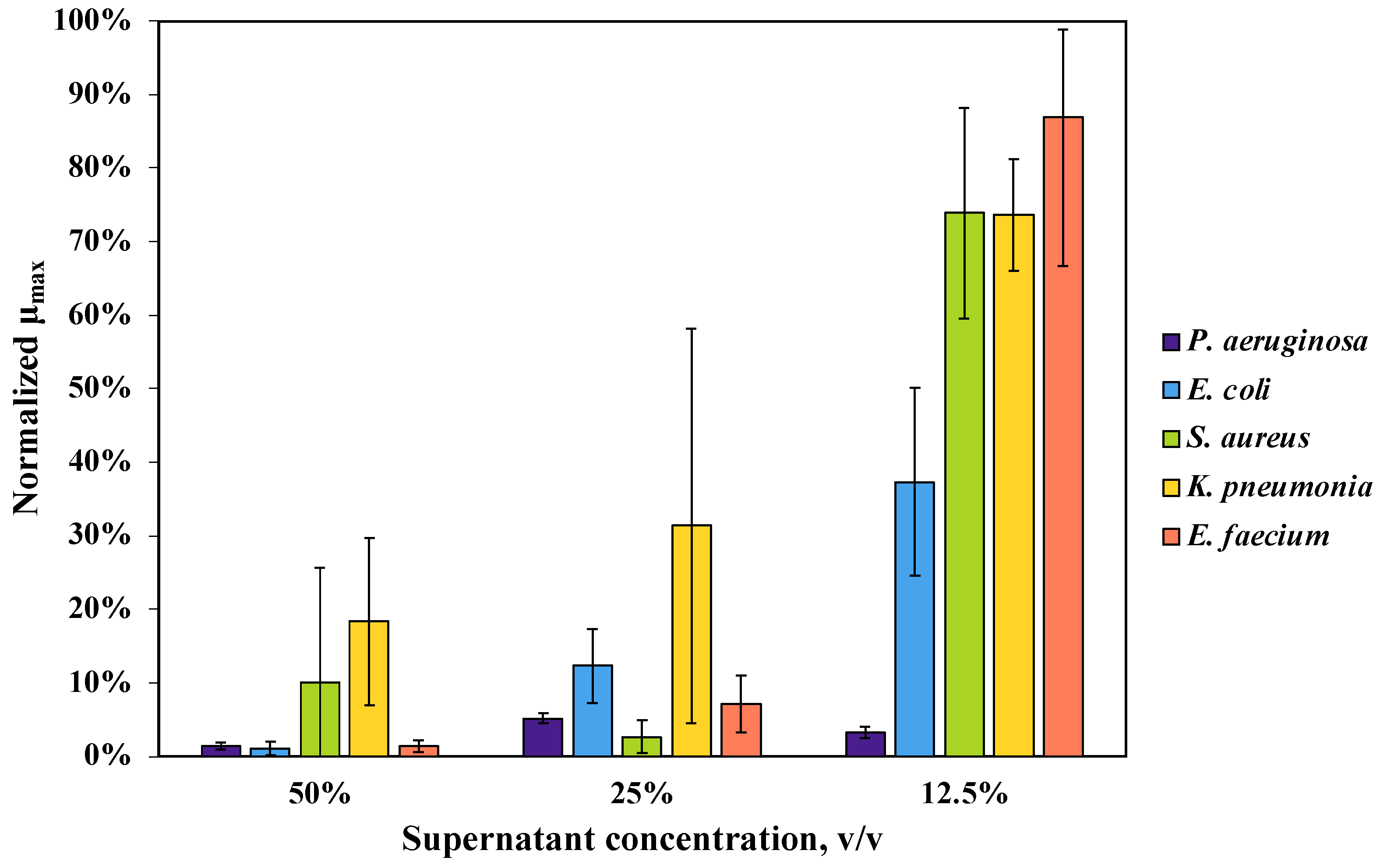
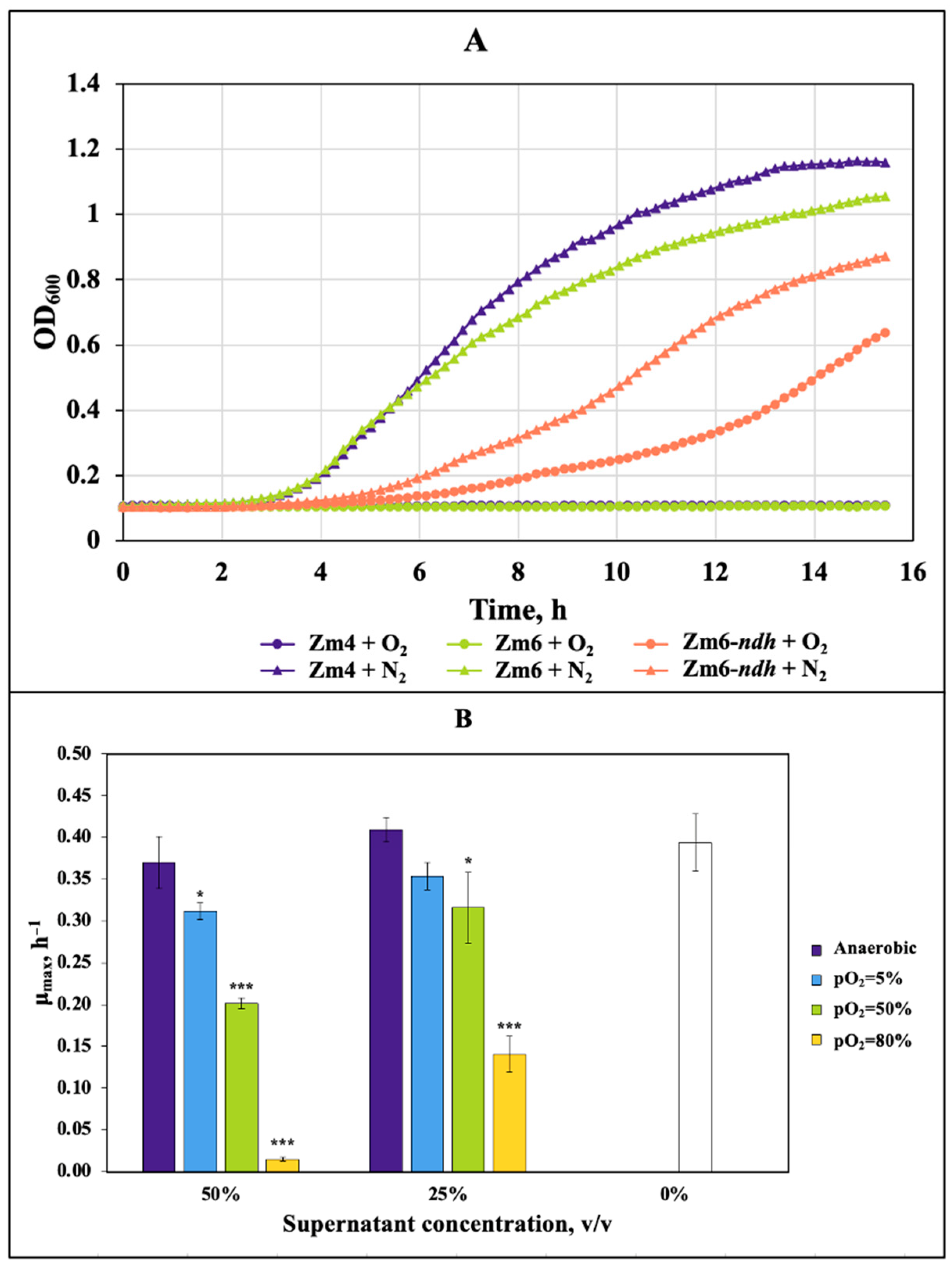
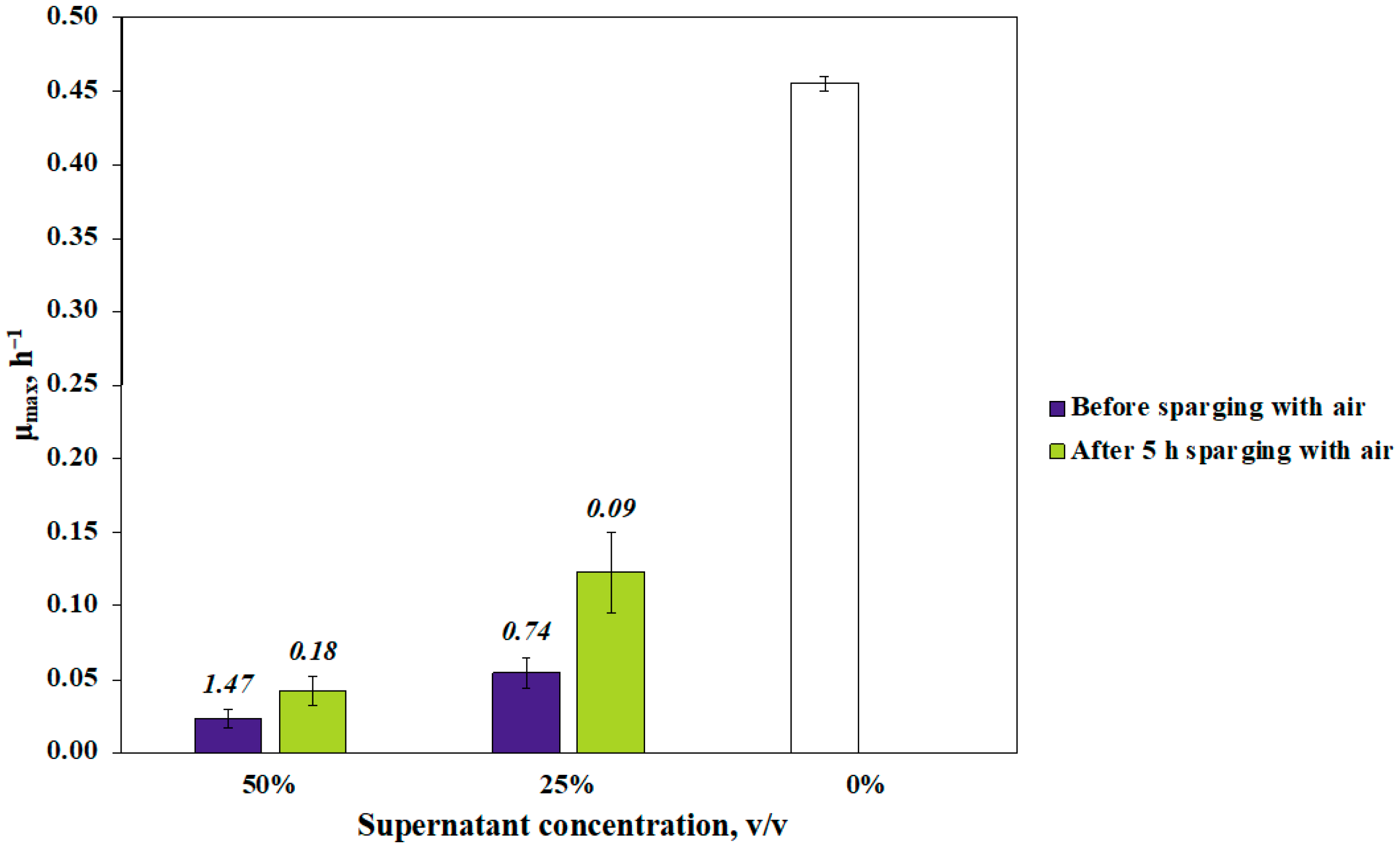
| Strain | Inhibition Zone Radius, mm |
|---|---|
| Zm4 | 8.75 ± 0.50 |
| Zm6 | 8.00 ± 0.82 |
| Zm6-adhB | 8.25 ± 0.50 |
| Zm6-cat | 7.50 ± 0.58 |
| Zm6-ndh | 3.25 ± 0.50 |
| Incubation Time (min) | Strain | Acetate (g·L−1) | Propionate (g·L−1) | E. coli μ (h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zm4 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.51 |
| Zm4 + cm | 0.99 | 0.00 | 0.38 | |
| Zm6-ndh | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.50 | |
| Zm6-ndh + cm | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.51 | |
| 10 | Zm4 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.58 |
| Zm4 + cm | 1.11 | 0.00 | 0.39 | |
| Zm6-ndh | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.51 | |
| Zm6-ndh + cm | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.51 | |
| 30 | Zm4 | 0.49 | 0.10 | 0.58 |
| Zm4 + cm | 1.62 | 0.00 | 0.05 | |
| Zm6-ndh | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.53 | |
| Zm6-ndh + cm | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.54 | |
| 120 | Zm4 | 1.81 | 0.22 | 0.01 |
| Zm4 + cm | 3.72 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Zm6-ndh | 0.57 | 0.11 | 0.39 | |
| Zm6-ndh + cm | 0.57 | 0.00 | 0.31 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rutkis, R.; Ļaša, Z.; Rubina, M.; Ščerbaka, R.; Kalniņš, G.; Bogans, J.; Kalnenieks, U. Antimicrobial Activity of Zymomonas mobilis Is Related to Its Aerobic Catabolism and Acid Resistance. Fermentation 2022, 8, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8020077
Rutkis R, Ļaša Z, Rubina M, Ščerbaka R, Kalniņš G, Bogans J, Kalnenieks U. Antimicrobial Activity of Zymomonas mobilis Is Related to Its Aerobic Catabolism and Acid Resistance. Fermentation. 2022; 8(2):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8020077
Chicago/Turabian StyleRutkis, Reinis, Zane Ļaša, Marta Rubina, Rita Ščerbaka, Gints Kalniņš, Jānis Bogans, and Uldis Kalnenieks. 2022. "Antimicrobial Activity of Zymomonas mobilis Is Related to Its Aerobic Catabolism and Acid Resistance" Fermentation 8, no. 2: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8020077
APA StyleRutkis, R., Ļaša, Z., Rubina, M., Ščerbaka, R., Kalniņš, G., Bogans, J., & Kalnenieks, U. (2022). Antimicrobial Activity of Zymomonas mobilis Is Related to Its Aerobic Catabolism and Acid Resistance. Fermentation, 8(2), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8020077





