Aspergillus-Derived Cellulase Preparation Exhibits Prebiotic-like Effects on Gut Microbiota in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Diets
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene-Based Microbiome Analysis
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.5. Analyses of Cecal Organic Acids and pH
2.6. Data Analysis
2.7. Evaluation of the Risk of Bias in the Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Food Intake, Body Weight and Cecal Content Weight
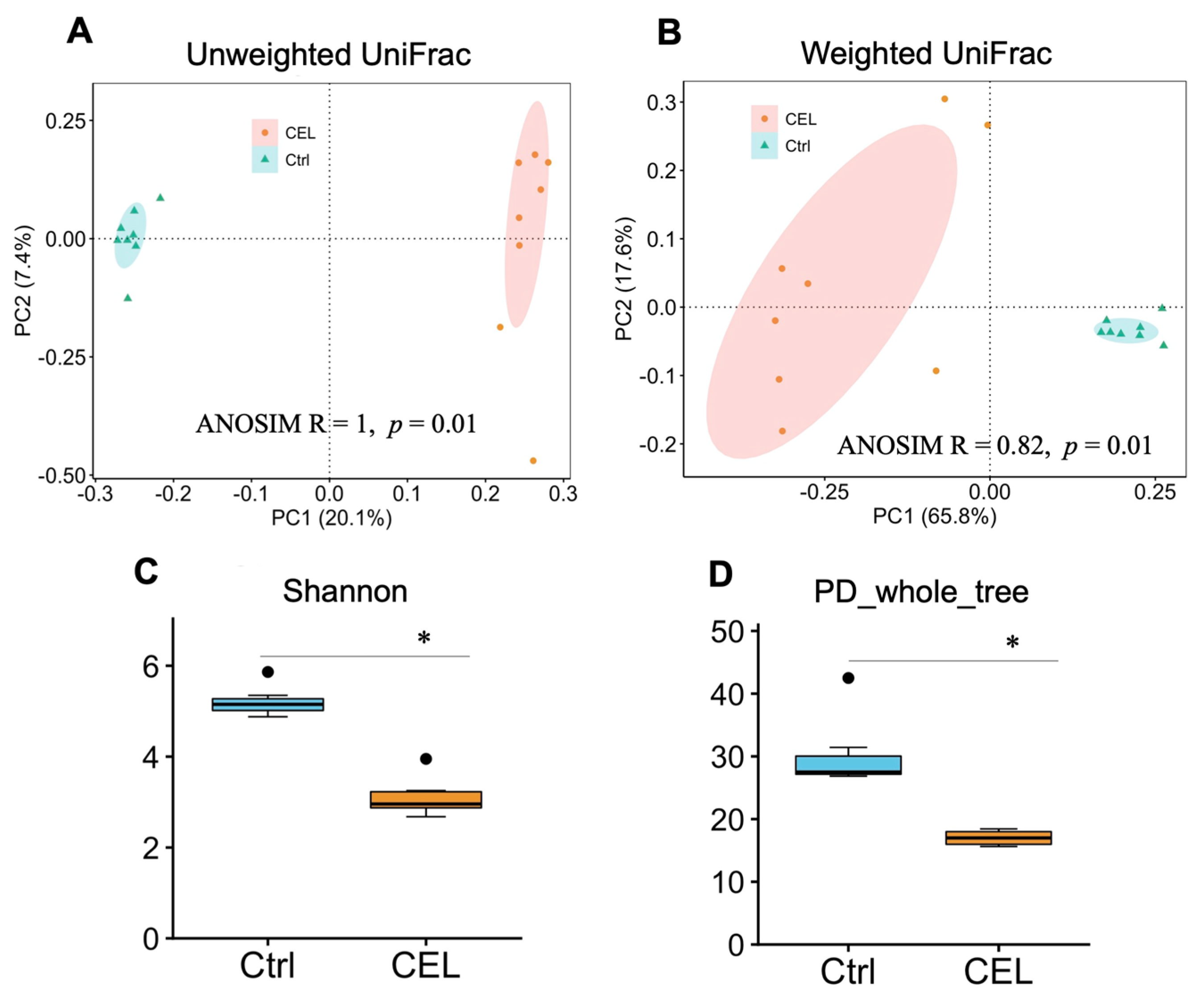
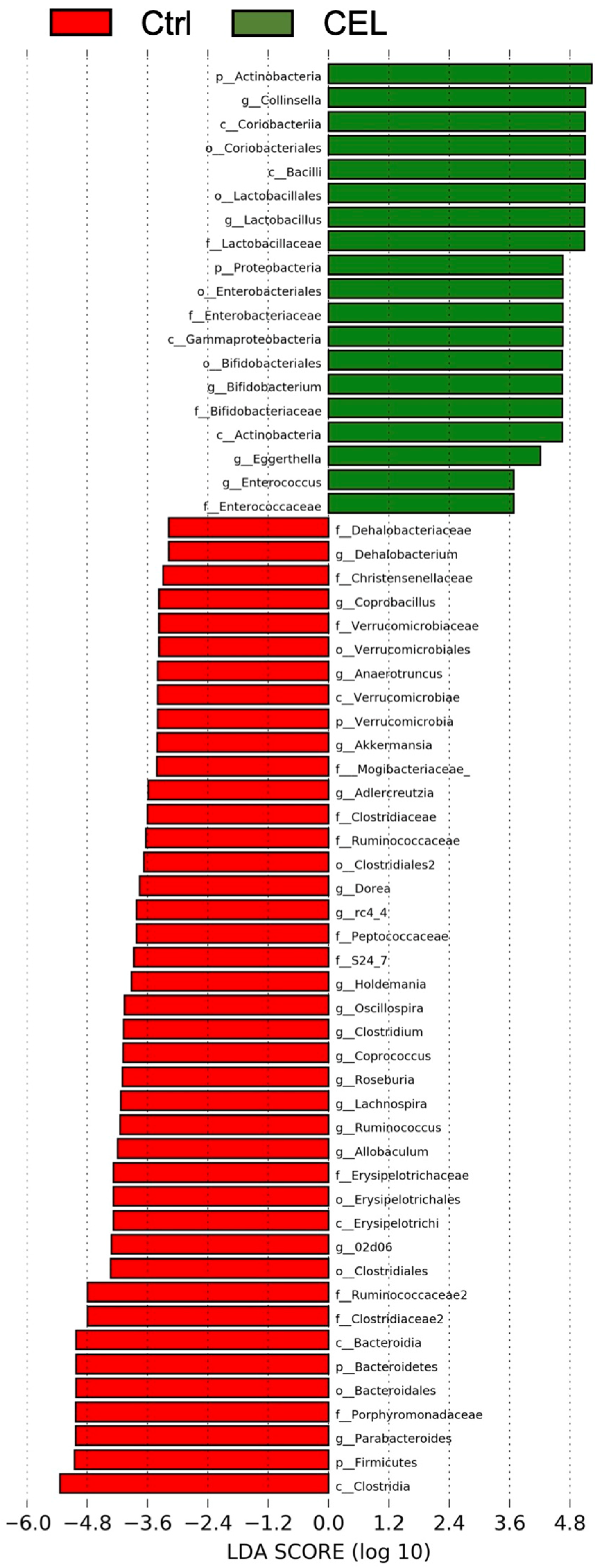
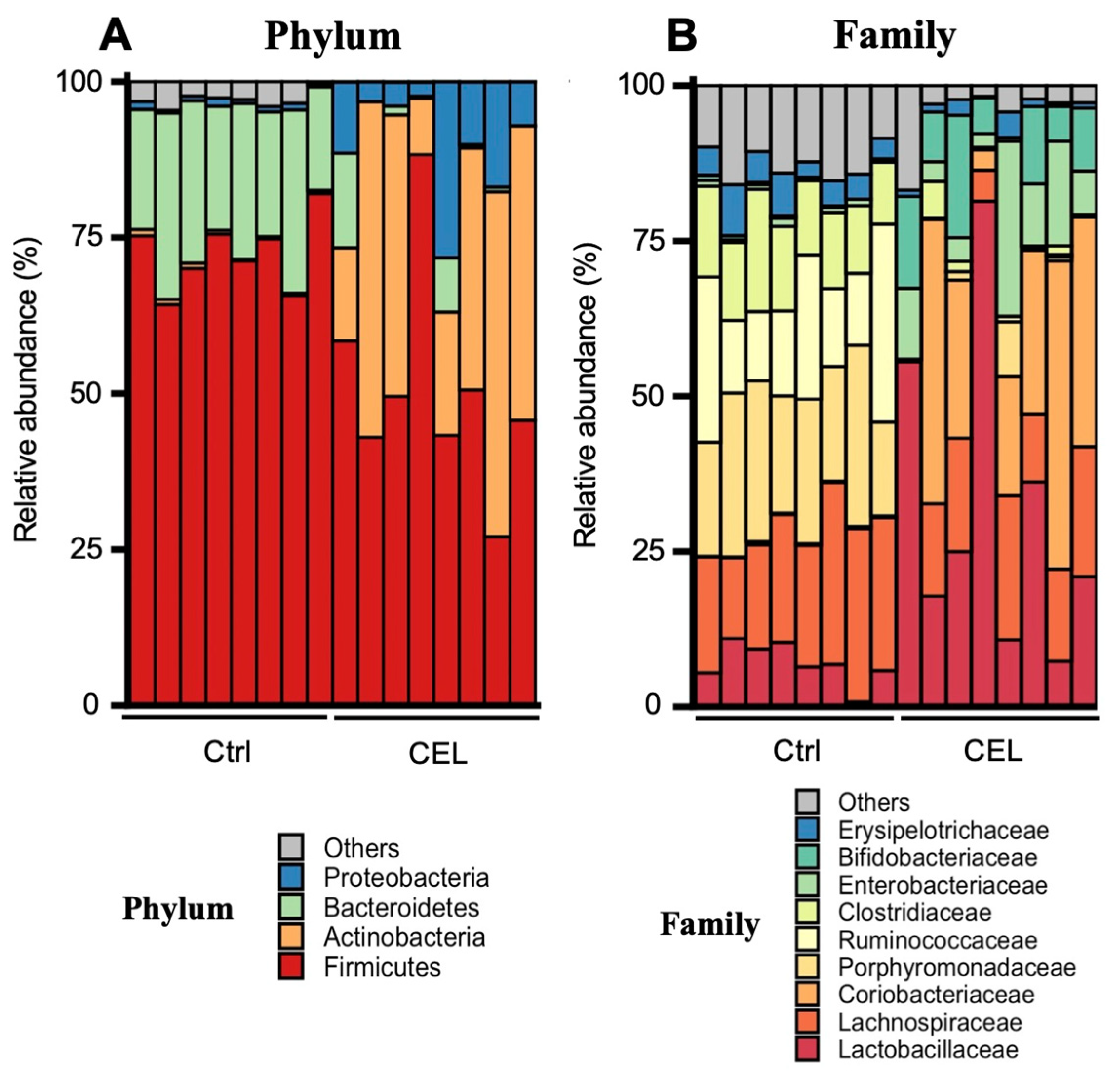
3.2. Cecal Microbiota
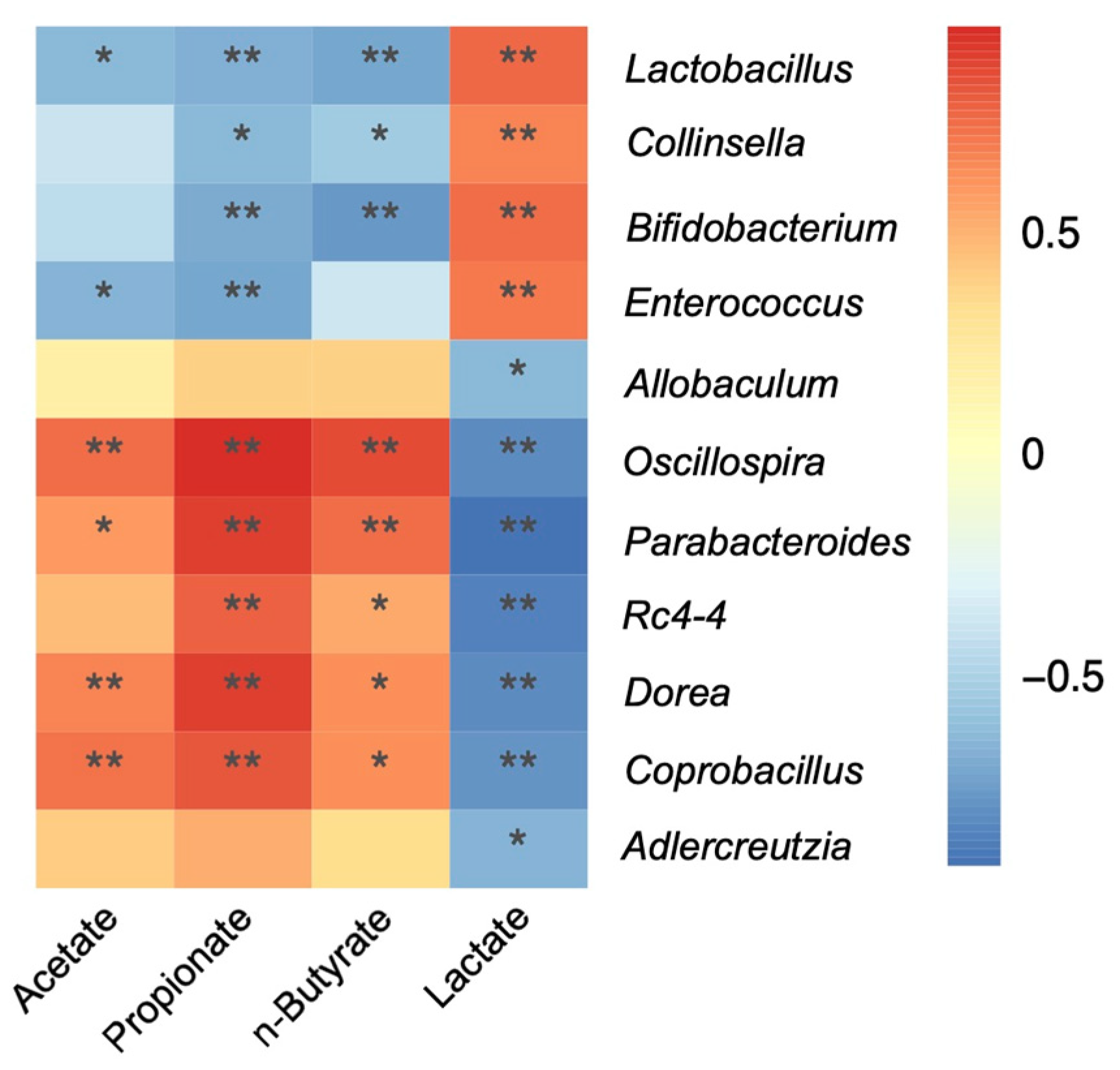
3.3. Cecal Organic Acids and pH
4. Discussion
4.1. Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus
4.2. Other Genera
4.3. Bacterial Diversity
4.4. Organic Acids
4.5. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board and Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ichishima, E. Enzymology of the national microorganisms of Japan in a historical context. J. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 2, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Sitanggang, N.V.; Kato, N.; Inoue, J.; Murakami, T.; Watanabe, T.; Iguchi, T.; Okazaki, Y. Beneficial effects of protease preparations derived from Aspergillus on the colonic luminal environment in rats consuming a high-fat diet. Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Iwamoto, A.; Kumrungsee, T.; Okazaki, Y.; Kuroda, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kato, N. Consumption of an acid protease derived from Aspergillus oryzae causes bifidogenic effect in rats. Nutr. Res. 2017, 44, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Kumrungsee, T.; Kuroda, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kato, N. Feeding Aspergillus protease preparation combined with adequate protein diet to rats increases levels of cecum gut-protective amino acids, partially linked to Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 2019, 83, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kumrungsee, T.; Kato, N.; Fukuda, F.; Kuroda, M.; Yamaguchi, S. Supplemental Aspergillus lipase and protease preparations display powerful bifidogenic effects and modulate the gut microbiota community of rats. Fermentation 2021, 7, 294. [Google Scholar]
- Jecu, L. Solid state fermentation of agricultural wastes for endoglucanase production. Ind. Crop Prod. 2000, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.A.; Kurup, R.S.C.; Snishamol, C.; Prabhu, G.N. Role of Cellulases in Food, Feed, and Beverage Industries. In Green Bio-processes. Energy, Environment, and Sustainability; Parameswaran, B., Varjani, S., Raveendran, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 323–343. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Tewari, R.; Rana, S.S.; Soni, R.; Soni, S.K. Cellulases: Classification, Methods of Determination and Industrial Applications. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 179, 1346–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, U.; Sohail, M.; Ghanemi, A. Cellulases: From Bioactivity to a Variety of Industrial Applications. Biomimetics 2021, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, Y.; Fukuda, H.; Mikami, S.; Kizaki, Y.; Wakabayasi, S. Properties of Cellulase Produced by Aspergillus oryzae and its Effect on Sake Moromi Fermentation. Nippon Jyozo Kyokaishi (J. Brew. Soc. Jap.) 2004, 99, 84–92. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Text Sison, G. Digestive Enzymes: Uses, Common Brands, and Safety Information. Available online: https://www.singlecare.com/blog/digestive-enzymes/ (accessed on 12 November 2021).
- Van Hul, M.; Karnik, K.; Canene-Adams, K.; De Souza, M.; Abbeele, P.V.D.; Marzorati, M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Everard, A.; Cani, P.D. Comparison of the effects of soluble corn fiber and fructooligosaccharides on metabolism, inflammation, and gut microbiome of high-fat diet-fed mice. Am J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 319, E779–E791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, C.; Nakanishi, Y.; Murakami, S.; Nozu, R.; Ueno, M.; Hioki, K.; Aw, W.; Hirayama, A.; Soga, T.; Ito, M.; et al. A metabologenomic approach reveals changes in the intestinal environment of mice fed on American diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhu, M. A sensitive GC/MS detection method for analyzing microbial metabolites short chain fatty acids in fecal and serum samples. Talanta 2019, 196, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Rovers, M.M.; BM de Vries, R.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Langendam, M.W. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med. Res. Meth. 2014, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-L.; Lin, T.-L.; Chang, C.-J.; Wu, T.-R.; Lai, W.-F.; Lu, C.-C.; Lai, H.-C. Probiotics, prebiotics and amelioration of diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.F.; Song, Z.H.; Ke, Y.L.; Xiao, K.; Hu, C.H.; Shi, B. Cello-oligosaccharide influences intestinal microflora, mucosal architecture and nutrient transport in weaned pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 195, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Ukowitz, C.; Domig, K.J.; Nidetzky, B. Short-Chain Cello-oligosaccharides: Intensification and Scale-up of Their Enzymatic Production and Selective Growth Promotion among Probiotic Bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 8557–8567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klancic, T.; Laforest-Lapointe, I.; Choo, A.; Nettleton, J.E.; Chleilat, F.; Tuplin, E.W.N.; Alukic, E.; Cho, N.A.; Nicolucci, A.C.; Arrieta, M.; et al. Prebiotic Oligofructose Prevents Antibiotic-Induced Obesity Risk and Improves Metabolic and Gut Microbiota Profiles in Rat Dams and Offspring. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, e2000288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewulf, E.M.; Cani, P.; Claus, S.; Fuentes, S.; Puylaert, P.G.B.; Neyrinck, A.; Bindels, L.B.; De Vos, W.M.; Gibson, G.R.; Thissen, J.-P.; et al. Insight into the prebiotic concept: Lessons from an exploratory, double blind intervention study with inulin-type fructans in obese women. Gut 2013, 62, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassinen, A.; Krogius-Kurikka, L.; Mäkivuokko, H.; Rinttilä, T.; Paulin, L.; Corander, J.; Malinen, E.; Apajalahti, J.; Palva, A. The Fecal Microbiota of Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients Differs Significantly From That of Healthy Subjects. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saalman, R.; Alderberth, I.; Wold, A.; Sjoberg, F. Use of Collinsella for Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. U.S. Patent 15/510,245, 1 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hanchi, H.; Mottawea, W.; Sebei, K.; Hammami, R. The Genus Enterococcus: Between Probiotic Potential and Safety Concerns–An Update. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugaban, J.I.F.; Holzapfel, W.H.; Todorov, S.D. Probiotic potential and safety assessment of bacteriocinogenic Enterococcus faecium strains with antibacterial activity against Listeria and vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2021, 2, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habermann, W.; Zimmermann, K.; Skarabis, H.; Kunze, R.; Rusch, V. The effect of a bacterial immunostimulant (human Enterococcus faecalis bacteria) on the occurrence of relapse in patients with chronic bronchtis. Arzneimittelforschung 2001, 51, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pieniz, S.; Andreazza, R.; Anghinoni, T.; Camargo, F.; Brandelli, A. Probiotic potential, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Enterococcus durans strain LAB18s. Food Control 2014, 37, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Li, D.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Gu, Z.; Chen, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Metagenomic insights into the effects of fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) on the composition of fecal microbiota in mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Yu, D.; Na, L.; Sun, T.; Zhang, D.; Shi, X.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, T.; et al. Effects of prebiotics on immunologic indicators and intestinal microbiota structure in perioperative colorectal cancer patients. Nutrition 2019, 61, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pan, M.; Li, D.; Yin, Y.; Jiang, T.; Fang, S.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Metagenomic insights into the effects of oligosaccharides on the microbial composition of cecal contents in constipated mice. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin, K.; Pamer, E.G. Enterococci and Their Interactions with the Intestinal Microbiome. Microbiol. Spectrum 2014, 5, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, D.; Xie, M.; Lan, S.; Wang, Z. Xylooligosaccharide Modulates Gut Microbiota and Alleviates Colonic Inflammation Caused by High Fat Diet Induced Obesity. Front. Physiol. 2020, 10, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Barcenas-Walls, J.R.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M. Molecular assessment of the fecal microbiota in healthy cats and dogs before and during supplementation with fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) and inulin using high-throughput 454-pyrosequencing. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, A.; Lazarevic, V.; Gaïa, N.; Johansson, M.; Ståhlman, M.; Bäckhed, F.; Delzenne, N.; Schrenzel, J.; Francois, P.; Cani, P. Microbiome of prebiotic-treated mice reveals novel targets involved in host response during obesity. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2116–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.; Cross, T.-W.L.; Devendran, S.; Neumer, F.; Theis, S.; Ridlon, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S.; de Godoy, M.R.C.; Swanson, K.S. Effects of prebiotic inulin-type fructans on blood metabolite and hormone concentrations and faecal microbiota and metabolites in overweight dogs. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audebert, C.; Even, G.; Cian, A.; Loywick, A.; Merlin, S.; Viscogliosi, E.; Chabe, M.; Blastocystis Investigation Group. Colonization with the Enteric Protozoa Blastocystis is Associated with Increased Diversity of Human Gut Bacterial Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöberg, F.; Barkman, C.; Nookaew, I.; Östman, S.; Adlerberth, I.; Saalman, R.; Wold, A.E. Low-complexity microbiota in the duodenum of children with newly diagnosed ulcerative colitis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186178. [Google Scholar]
- Shade, A. Diversity is the question, not the answer. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Duncan, S.H.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P. Links between diet, gut microbiota composition and gut metabolism. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2015, 74, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groussard, C.; Morel, I.; Chevanne, M.; Monnier, M.; Cillard, J.; Delamarche, A. Free radical scavenging and antioxidant effects of lactate ion: An in vitro study. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, I.; Prasad, P.D.; Thangaraju, M.; Manicassamy, S. Lactate-Dependent Regulation of Immune Responses by Dendritic Cells and Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 691134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Phylum | Family | Genus | Ctrl | CEL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (% of total bacteria) | ||||
| Firmicute | Lactobacillaceae | Lactobacillus | 0.698 ± 0.108 | 3.186 ± 0.833 * |
| Actinobacteria | Coriobacteriaceae | Collinsella | 0.005 ± 0.003 | 2.578 ± 0.601 ** |
| Actinobacteria | Bifidobacteriaceae | Bifidobacterium | 0.034 ± 0.010 | 0.965 ± 0.198 ** |
| Firmicute | Enterococaceae | Enterococcus | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.83 ± 0.15 ** |
| Firmicute | Ruminococacceae | Ruminococcus | 3.13 ± 1.38 | 0.01 ± 0.00 |
| Firmicute | Erysipelotrichaceae | Allobaculum | 3.03 ± 0.68 | 0.38 ± 0.20 ** |
| Firmicute | Lachnospiraceae | Roseburia | 2.60 ± 1.34 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Firmicute | Ruminococaceae | Oscillospira | 2.32 ± 0.31 | 0.18 ± 0.08 ** |
| Bacteroidetes | Porphyromonadaceae | Parabacteroides | 2.19 ± 0.16 | 0.15 ± 0.01 ** |
| Actinobacteria | Peptococcaceae | rc4-4 | 1.27 ± 0.16 | 0.00 ± 0.00 ** |
| Firmicute | Lachnospiraceae | Dorea | 1.12 ± 0.17 | 0.00 ± 0.00 ** |
| Firmicute | Erysipelotrichaceae | Coprobacillus | 0.35 ± 0.06 | 0.00 ± 0.00 ** |
| Actinobacteria | Eggerthellaceae | Adlercreutzia | 0.21 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 ** |
| Organic Acids | Ctrl | CEL |
|---|---|---|
| (μmol/g dry wt of cecal contents) | ||
| Acetate | 40.3 ± 5.9 | 10.8 ± 4.0 * |
| Propionate | 11.1 ± 0.0 | 1.1 ± 0.2 * |
| n-Butyrate | 7.8 ± 0.9 | 1.5 ± 1.2 * |
| Lactate | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 188.7 ± 13.1 * |
| Succinate | 13.9 ± 3.1 | 12.5 ± 3.3 |
| Total organic acids | 75.2 ± 8.8 | 213.9 ± 10.0 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Kumrungsee, T.; Kato, N.; Fukuda, S.; Kuroda, M.; Yamaguchi, S. Aspergillus-Derived Cellulase Preparation Exhibits Prebiotic-like Effects on Gut Microbiota in Rats. Fermentation 2022, 8, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8020071
Yang Y, Kumrungsee T, Kato N, Fukuda S, Kuroda M, Yamaguchi S. Aspergillus-Derived Cellulase Preparation Exhibits Prebiotic-like Effects on Gut Microbiota in Rats. Fermentation. 2022; 8(2):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8020071
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yongshou, Thanutchaporn Kumrungsee, Norihisa Kato, Shinji Fukuda, Manabu Kuroda, and Shotaro Yamaguchi. 2022. "Aspergillus-Derived Cellulase Preparation Exhibits Prebiotic-like Effects on Gut Microbiota in Rats" Fermentation 8, no. 2: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8020071
APA StyleYang, Y., Kumrungsee, T., Kato, N., Fukuda, S., Kuroda, M., & Yamaguchi, S. (2022). Aspergillus-Derived Cellulase Preparation Exhibits Prebiotic-like Effects on Gut Microbiota in Rats. Fermentation, 8(2), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8020071






