Effects of Different Soybean and Maize Mixed Proportions in a Strip Intercropping System on Silage Fermentation Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
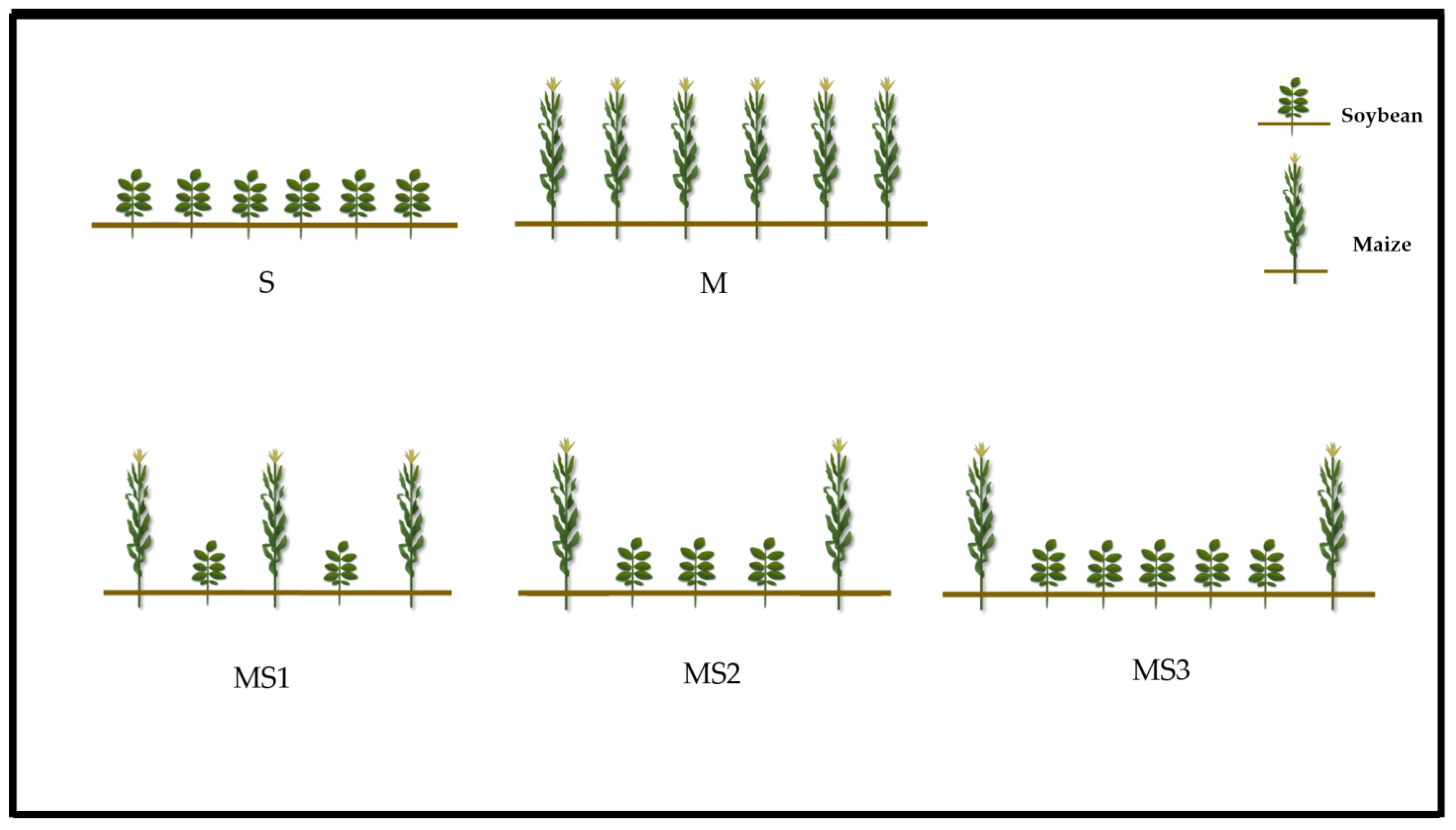
2.1. Materials and Experimental Design
2.2. Measuring Yield and Silage Materials Preparation
2.3. Silage Chemical Composition Analysis
2.3.1. Conventional Silage Quality Detection
2.3.2. Organic Acid and Ammonia-N
2.4. Silage Bacterial Community Analysis
2.4.1. Bacterial DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.4.2. Illumina Miseq Sequencing Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Intercropping on the Yield
3.2. Chemical Composition of Materials before Ensiling
3.3. Chemical Composition and Characteristics of Silage Fermentation
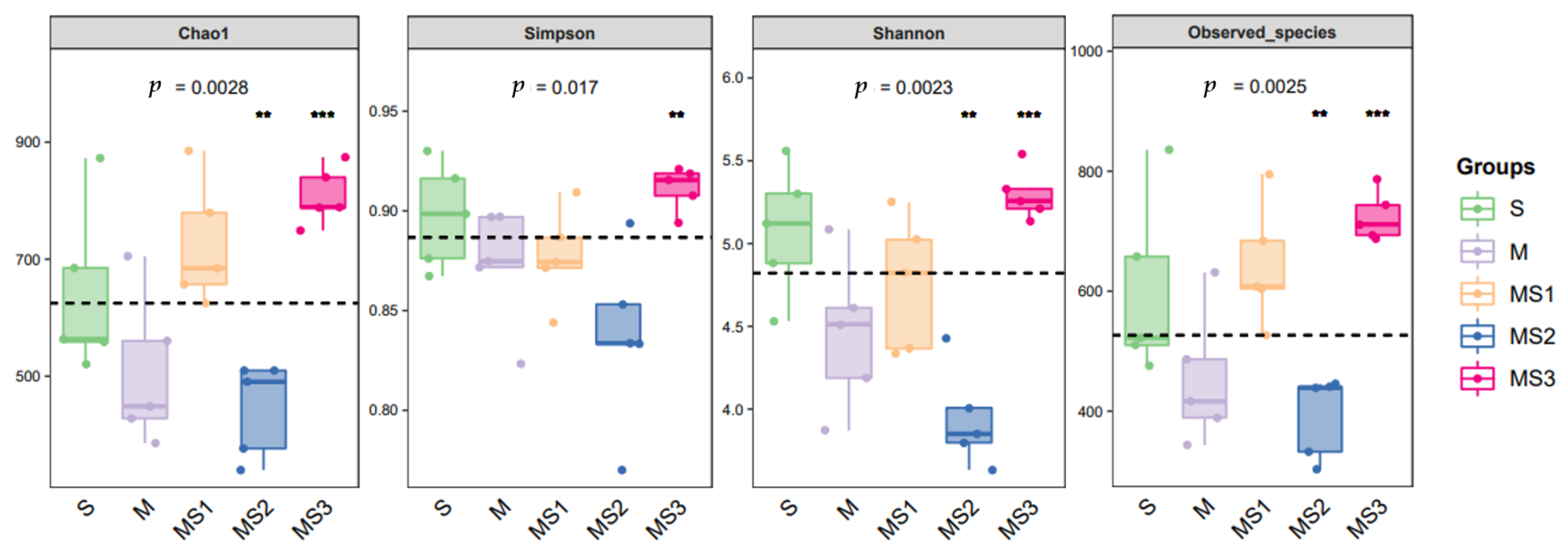
3.4. Microbial Community of the Silage
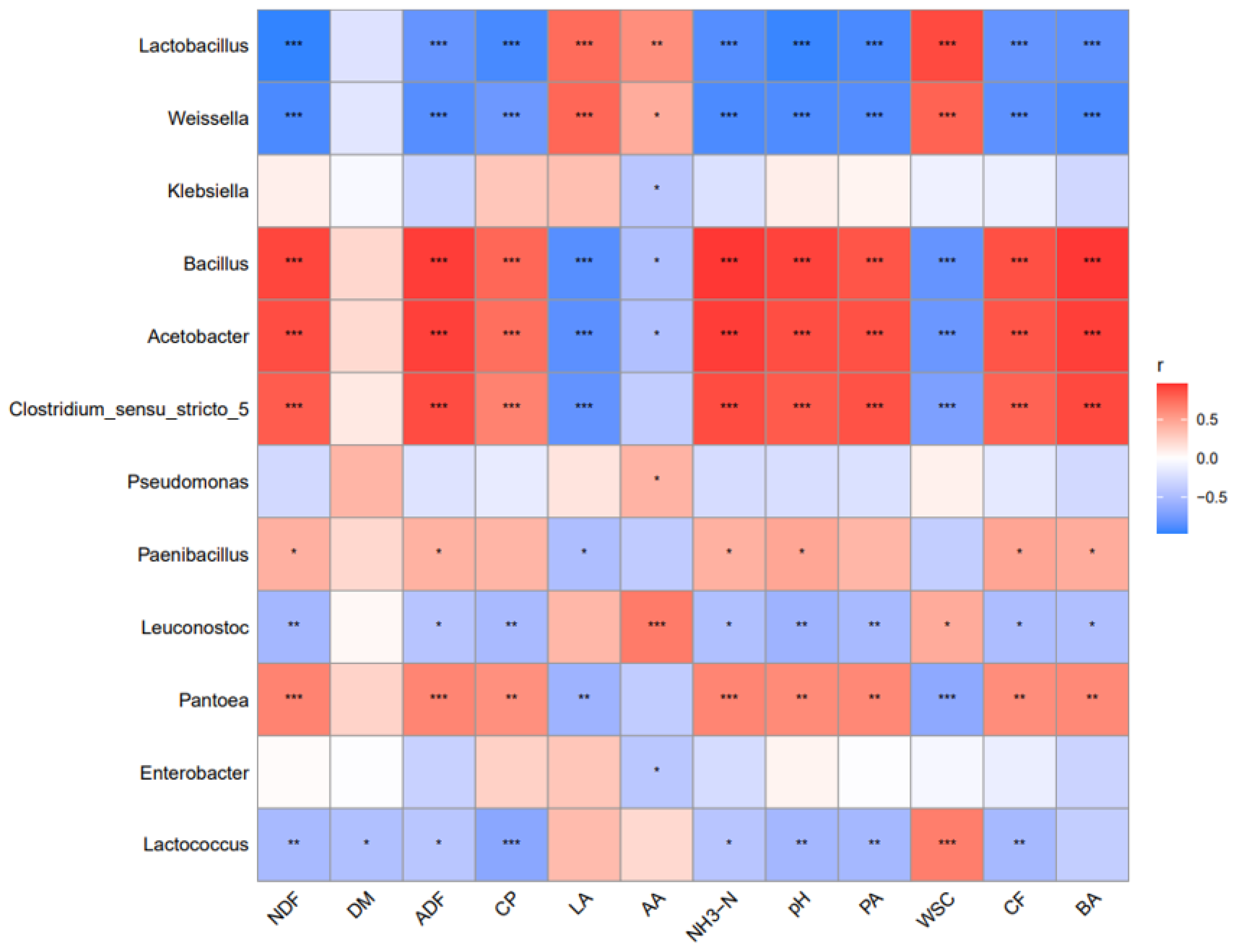
3.5. Correlations between Chemical Composition and Microbial Community
4. Discussion
4.1. Crop Yield and Chemical Composition of the Silage
4.2. Microbial Community and Bacterial Diversity of the Silage
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.; Bao, X.; Guo, G.; Huo, W.; Xu, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, Q. Effects of Hydrolysable Tannin with or without Condensed Tannin on Alfalfa Silage Fermentation Characteristics and In Vitro Ruminal Methane Production, Fermentation Patterns, and Microbiota. Animals 2021, 11, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Zhao, H.; Liu, G.; You, Y.; Ma, L.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Y. Effects of nitrogen and maize plant density on forage yield and nitrogen uptake in an alfalfa–silage maize relay intercropping system in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2021, 263, 108068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanzad, E.; Sadeghpour, A.; Hashemi, M.; Keshavarz Afshar, R.; Hosseini, M.B.; Barker, A.V. Silage fermentation profile, chemical composition and economic evaluation of millet and soya bean grown in monocultures and as intercrops. Grass Forage Sci. 2016, 71, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Yin, G.; Wei, C.; Bao, J. Effects of Feeding Corn-lablab Bean Mixture Silages on Nutrient Apparent Digestibility and Performance of Dairy Cows. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 26, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Muck, R.E.; Armstrong, K.L.; Albrecht, K.A. Nutritive value of corn silage in mixture with climbing beans. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2009, 150, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, H.; Banerjee, S.; Guan Yuan, G.T.; Haris, N.; Ikhwanuddin, M.; Ambak, M.A.; Endut, A. Biofloc as a potential natural feed for shrimp postlarvae. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 113, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatungimana, E.; Stahl, T.C.; Erickson, P.S. Growth performance and apparent total tract nutrient digestibility of limit-fed diets containing wet brewer’s grains to Holstein heifers. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2020, 4, txaa079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Wang, F.; Zhu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhou, G.; Pan, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhong, J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and molasses additives on the microbial community and fermentation quality of soybean silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.; Henderson, A.; Heron, S.J.E. The Biochemistry of Silage, 2nd ed.; Chalcombe Publications: Shedfield, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Carpici, E.B. Nutritive values of soybean silages ensiled with maize at different rates. Legume Res.-Int. J. 2016, 39, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, S.U.; Hjort-Gregersen, K.; Vazifehkhoran, A.H.; Triolo, J.M. Co-ensiling of straw with sugar beet leaves increases the methane yield from straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Dennehy, C.; Lawlor, P.G.; Hu, Z.; Zhan, X.; Gardiner, G.E. Inactivation of enteric indicator bacteria and system stability during dry co-digestion of food waste and pig manure. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muck, R.E. Microbiologia da silagem e seu controle com aditivos. Rev. Bras. De Zootec. 2010, 39, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, B.; Su, R.; Pan, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, G.; Tao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhong, J. Assessing the fermentation quality and microbial community of the mixed silage of forage soybean with crop corn or sorghum. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, M.S.; Cormican, P.; Keogh, K.; O’Connor, A.; O’Hara, E.; Palladino, R.A.; Kenny, D.A.; Waters, S.M. Illumina MiSeq Phylogenetic Amplicon Sequencing Shows a Large Reduction of an Uncharacterised Succinivibrionaceae and an Increase of the Methanobrevibacter gottschalkii Clade in Feed Restricted Cattle. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gao, R.; Franco, M.; Hannaway, D.B.; Ke, W.; Ding, Z.; Yu, Z.; Guo, X. Effect of Mixing Alfalfa with Whole-Plant Corn in Different Proportions on Fermentation Characteristics and Bacterial Community of Silage. Agriculture 2021, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Gong, W.; Yang, W.; Wan, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L. Seed Treatment with Uniconazole Powder Improves Soybean Seedling Growth under Shading by Corn in Relay Strip Intercropping System. Plant Prod. Sci. 2010, 13, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echarte, L.; Maggiora, A.D.; Cerrudo, D.; Gonzalez, V.H.; Abbate, P.; Cerrudo, A.; Sadras, V.O.; Calviño, P. Yield response to plant density of maize and sunflower intercropped with soybean. Field Crops Res. 2011, 121, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Li, X.; Guan, H.; Yang, W.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Du, Z.; Li, X.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, X.; et al. Dynamic microbial diversity and fermentation quality of the mixed silage of corn and soybean grown in strip intercropping system. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 313, 123655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, T.; Wu, Y.; Xin, Y.; Chen, C.; Du, Z.; Li, X.; Zhong, J.; Tahir, M.; Kang, B.; Jiang, D.; et al. Silage Quality and Output of Different Maize–Soybean Strip Intercropping Patterns. Fermentation 2022, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazli, M.H.; Halim, R.A.; Abdullah, A.M.; Hussin, G.; Samsudin, A.A. Potential of four corn varieties at different harvest stages for silage production in Malaysia. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, VA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for Dietary Fiber, Neutral Detergent Fiber, and Nonstarch Polysaccharides in Relation to Animal Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated Simultaneous Determination of Ammonia and Total Amino Acids in Ruminal Fluid and In Vitro Media1. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamang, J.P. Biochemical and modern identification techniques|Microfloras of Fermented Foods. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 250–258. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Rahman, T.; Song, C.; Yang, F.; Su, B.; Cui, L.; Bu, W.; Yang, W. Relationships among light distribution, radiation use efficiency and land equivalent ratio in maize-soybean strip intercropping. Field Crops Res. 2018, 224, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Yang, W.-y.; Huang, N.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.-l.; Wang, X.-h.; Liu, Y.; Yan, S. Effects of maize plant types on dry matter accumulation characteristics and yield of soybean in maize-soybean intercropping systems. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2015, 26, 2414–2420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riaz, M.Q.; Südekum, K.H.; Clauss, M.; Jayanegara, A. Voluntary feed intake and digestibility of four domestic ruminant species as influenced by dietary constituents: A meta-analysis. Livest. Sci. 2014, 162, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, L. Is Intestinal Bacterial Diversity Enhanced by Trans-Species Spread in the Mixed-Species Flock of Hooded Crane (Grus monacha) and Bean Goose (Anser fabalis) Wintering in the Lower and Middle Yangtze River Floodplain? Animals 2021, 11, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, P.; Ferrero, F. Testing selectivity of bacterial and fungal culture media compared to original silage samples using next generation sequencing. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 179, 106088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Ohmomo, S.; Kumai, S.; Nakase, T. Influence of Lactobacillus spp. from an Inoculant and of Weissella and Leuconostoc spp. from Forage Crops on Silage Fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2982–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimal, S.; Sang, J.; Poudel, S.; Thakur, D.; Montell, C.; Lee, Y. Mechanism of Acetic Acid Gustatory Repulsion in Drosophila. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 1432–1442.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-H.; Yun, K.E.; Kim, J.; Park, E.; Chang, Y.; Ryu, S.; Kim, H.-L.; Kim, H.-N. Gut microbiota and metabolic health among overweight and obese individuals. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGarvey, J.A.; Franco, R.B.; Palumbo, J.D.; Hnasko, R.; Stanker, L.; Mitloehner, F.M. Bacterial population dynamics during the ensiling of Medicago sativa (alfalfa) and subsequent exposure to air. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Guan, H.; Huang, L.; Ma, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Nie, G.; Zhou, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Microbial community and fermentation characteristic of Italian ryegrass silage prepared with corn stover and lactic acid bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, F. Effect of maize straw additives on the nutritional quality and bacterial communities of ensiled forage rape for animal feed. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2021, 81, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Treatment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | S | M | MS1 | MS2 | MS3 | SEM | p-Value |
| SFM(t/ha) | 23.86 a | 0 d | 16.36 c | 19.25 b | 20.24 b | 0.58 | <0.001 |
| MFM(t/ha) | 0 d | 75.19 b | 77.69 a | 75.36 b | 70.81 c | 0.45 | <0.001 |
| MSFM(t/ha) | 23.86 d | 75.19 c | 94.05 a | 94.61 a | 91.05 b | 0.47 | <0.001 |
| SDM(t/ha) | 7.25 a | 0 c | 5.89 b | 6.89 a | 7.24 a | 0.16 | <0.001 |
| MDM(t/ha) | 0 d | 26.04 c | 27.96 a | 27.00 b | 25.31 c | 0.24 | <0.001 |
| MSDM(t/ha) | 7.25 d | 26.04 c | 33.85 a | 33.90 a | 32.55 b | 0.17 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | S | M | MS1 | MS2 | MS3 | SEM | p-Value |
| NDF (g/kg DM) | 477.06 a | 419.72 e | 422.30 d | 425.91 c | 446.72 b | 0.69 | <0.001 |
| ADF (g/kg DM | 385.21 a | 275.06 d | 282.66 c | 289.33 b | 275.39 d | 1.15 | <0.001 |
| CF (g/kg DM) | 35.15 a | 25.00 c | 27.51 bc | 28.13 bc | 29.45 b | 0.85 | <0.001 |
| DM (g/kg FW) | 304.00 c | 346.35 b | 359.51 a | 358.31 a | 357.49 a | 1.04 | <0.001 |
| WSC (g/kg DM) | 41.55 e | 130.33 a | 94.03 b | 88.53 c | 80.08 d | 0.34 | <0.001 |
| CP (g/kg DM) | 183.55 a | 85.17 e | 125.10 c | 125.53 d | 150.03 b | 0.27 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | S | M | MS1 | MS2 | MS3 | SEM | p-Value |
| pH | 4.62 a | 3.63 e | 3.92 c | 3.83 d | 4.06 b | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| LA (g/kg DM) | 50.47 d | 85.00 a | 77.54 bc | 79.55 ab | 72.54 c | 1.28 | <0.001 |
| AA (g/kg DM) | 36.99 a | 18.66 d | 25.27 c | 23.75 c | 28.76 b | 0.77 | <0.001 |
| PA (g/kg DM) | 5.06 a | 2.55 c | 2.56 c | 2.78 c | 3.61 b | 0.11 | <0.001 |
| BA (g/kg DM) | 2.14 a | 0.00 b | 0.00 b | 0.00 b | 0.00 b | 0.09 | <0.001 |
| NDF (g/kg DM) | 476.50 a | 416.58 d | 419.50 d | 422.95 c | 443.15 b | 0.67 | <0.001 |
| ADF (g/kg DM) | 380.80 a | 272.06 d | 282.76 c | 288.05 b | 274.84 d | 0.95 | <0.001 |
| NH3-N (g/kg TN) | 84.98 a | 44.12 c | 44.63 c | 47.78 b | 48.93 b | 0.44 | <0.001 |
| CF (g/kg DM) | 36.65 a | 25.59 d | 28.71 c | 29.13 c | 30.45 b | 0.21 | <0.001 |
| DM (g/kg FW) | 305.98 d | 356.35 b | 369.03 a | 368.31 ab | 337.49 c | 2.69 | <0.001 |
| WSC (g/kg DM) | 19.40 e | 43.23 a | 33.03 b | 31.53 c | 30.08 d | 0.27 | <0.001 |
| CP (g/kg DM) | 173.55 a | 81.17 d | 121.10 c | 120.53 c | 147.03 b | 0.32 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Tong, X.; Wang, S. Effects of Different Soybean and Maize Mixed Proportions in a Strip Intercropping System on Silage Fermentation Quality. Fermentation 2022, 8, 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120696
Meng H, Jiang Y, Wang L, Wang S, Zhang Z, Tong X, Wang S. Effects of Different Soybean and Maize Mixed Proportions in a Strip Intercropping System on Silage Fermentation Quality. Fermentation. 2022; 8(12):696. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120696
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, He, Yan Jiang, Lin Wang, Sui Wang, Zicheng Zhang, Xiaohong Tong, and Shaodong Wang. 2022. "Effects of Different Soybean and Maize Mixed Proportions in a Strip Intercropping System on Silage Fermentation Quality" Fermentation 8, no. 12: 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120696
APA StyleMeng, H., Jiang, Y., Wang, L., Wang, S., Zhang, Z., Tong, X., & Wang, S. (2022). Effects of Different Soybean and Maize Mixed Proportions in a Strip Intercropping System on Silage Fermentation Quality. Fermentation, 8(12), 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120696





