The Role and Significance of Bacillus and Lactobacillus Species in Thai Fermented Foods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Thai Fermented Foods (TFFs)
2.1. Sweet Alcoholic Rice Snack (Khao-mak)
2.2. Traditional Sato
2.3. Fermented Fish Product (Pla-ra)
2.4. Fermented Pork Sausage (Nham)
2.5. Fermented Soybean (Thua-nao or Thai Natto)
2.6. Traditional Fermented Tea (Miang)
2.7. Fermented Minced Fish Cake (Som-fug)
2.8. Fermented Rice Noodles (Khanom-jeen)
2.9. Fermented Shrimp Paste (Ka-pi)
2.10. Fermented Fish Paste (Ka-pi-plaa)
2.11. Thai Pickled Vegetables (Phak-dong)
3. Prevalence of Bacillus and Lactobacillus Species in Thai Fermented Foods
3.1. Bacillus Strains in Thai Fermented Foods
3.2. Lactobacillus Strains in Thai Fermented Foods
4. Enzymes and Bioactive Peptides of Bacillus and Lactobacillus Species in Thai Fermented Foods
4.1. Bioactive Peptides (Bacteriocin-like Substances)
4.2. Enzymes
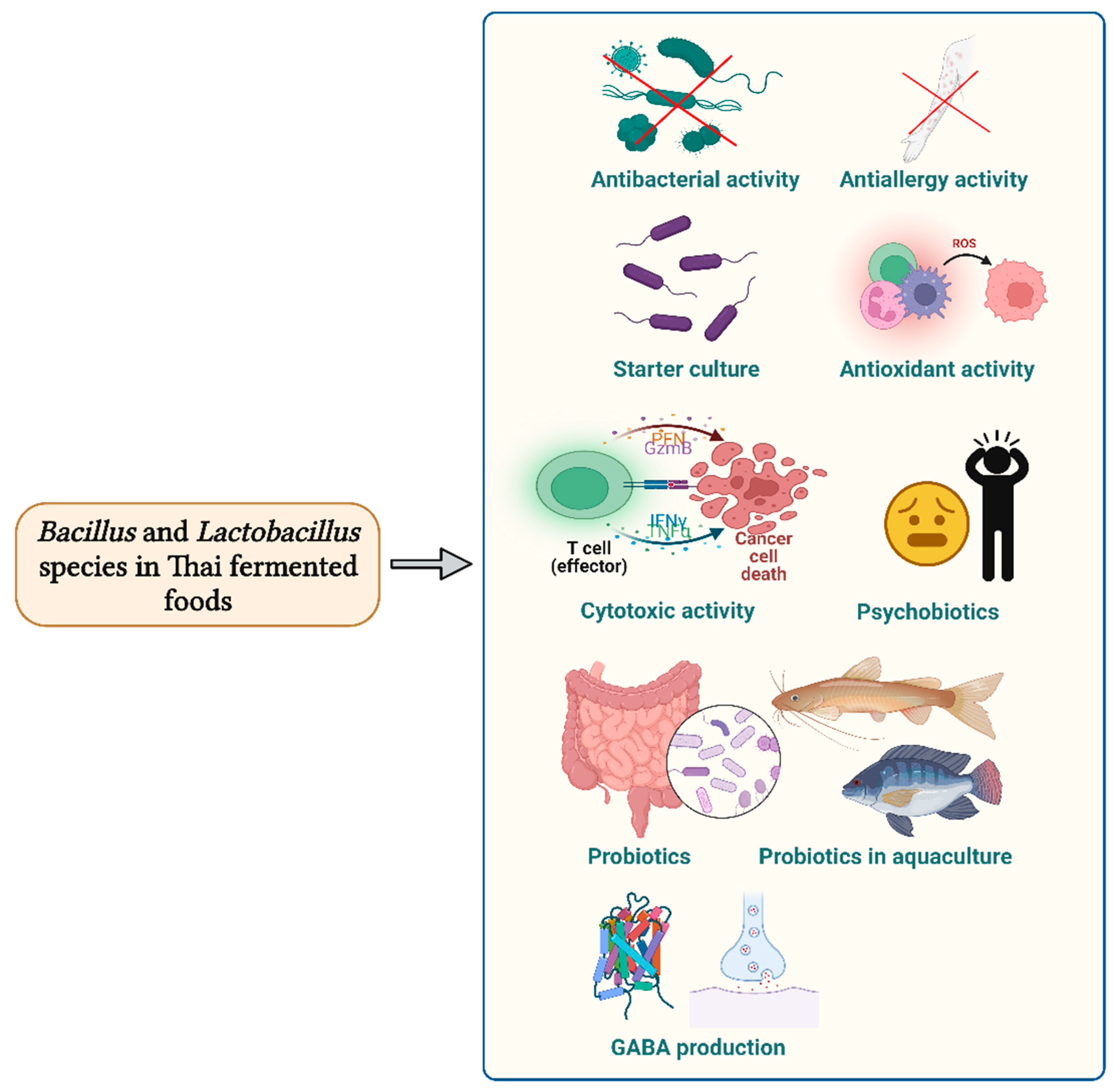
5. Bioactivities of Bacillus and Lactobacillus Strains Isolated from Thai Fermented Foods
5.1. Bioactivities of Bacillus Strains
5.2. Bioactivities of Lactobacillus Strains
5.2.1. Antimicrobial Activity
5.2.2. GABA-producing Strains
5.2.3. Starter Culture to Prepare Fermented Foods
5.2.4. Other Activities
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dimidi, E.; Cox, S.R.; Rossi, M.; Whelan, K. Fermented Foods: Definitions and Characteristics, Impact on the Gut Microbiota and Effects on Gastrointestinal Health and Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichońska, P.; Ziarno, M. Legumes and Legume-Based Beverages Fermented with Lactic Acid Bacteria as a Potential Carrier of Probiotics and Prebiotics. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Kesika, P.; Chaiyasut, C. Thai Fermented Foods as a Versatile Source of Bioactive Microorganisms—A Comprehensive Review. Sci. Pharm. 2018, 86, E37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voidarou, C.; Antoniadou, Μ.; Rozos, G.; Tzora, A.; Skoufos, I.; Varzakas, T.; Lagiou, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Fermentative Foods: Microbiology, Biochemistry, Potential Human Health Benefits and Public Health Issues. Foods 2021, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laureys, D.; Leroy, F.; Vandamme, P.; De Vuyst, L. Backslopping Time, Rinsing of the Grains During Backslopping, and Incubation Temperature Influence the Water Kefir Fermentation Process. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 871550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yann, D.; Pauline, G. Usefulness of Natural Starters in Food Industry: The Example of Cheeses and Bread. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5, 1679–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezac, S.; Kok, C.R.; Heermann, M.; Hutkins, R. Fermented Foods as a Dietary Source of Live Organisms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Kesika, P.; Chaiyasut, C. Impact of Fermented Foods on Human Cognitive Function-A Review of Outcome of Clinical Trials. Sci. Pharm. 2018, 86, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şanlier, N.; Gökcen, B.B.; Sezgin, A.C. Health benefits of fermented foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 506–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Paramithiotis, S.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Wijaya, C.H.; Suharta, S.; Sanlier, N.; Shin, H.S.; Patra, J.K. Traditional fermented foods with anti-aging effect: A concentric review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesika, P.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Chaiyasut, C. Health promoting effects of fermented foods against cancer: An updated concise review. Food Sci. Technol. Campinas. 2022, 42, e18220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeuwendaal, N.K.; Stanton, C.; O’Toole, P.W.; Beresford, T.P. Fermented Foods, Health and the Gut Microbiome. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petchkongkaew, A.; Taillandier, P.; Gasaluck, P.; Lebrihi, A. Isolation of Bacillus spp. from Thai fermented soybean (Thua-nao): Screening for aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin a detoxification. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daroonpunt, R.; Yiamsombut, S.; Sitdhipol, J.; Tanasupawat, S. Bacillus salacetis sp. Nov., a slightly halophilic bacterium from Thai shrimp paste (ka-pi). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phewpan, A.; Phuwaprisirisan, P.; Takahashi, H.; Ohshima, C.; Ngamchuachit, P.; Techaruvichit, P.; Dirndorfer, S.; Dawid, C.; Hofmann, T.; Keeratipibul, S. Investigation of Kokumi Substances and Bacteria in Thai Fermented Freshwater Fish (Pla-ra). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 10345–10351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luang-In, V.; Deeseenthum, S. Exopolysaccharide-producing isolates from Thai milk kefir and their antioxidant activities. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanganurat, W.; Quinquis, B.; Leelawatcharamas, V.; Bolotin, A. Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from Thai fermented fruits and vegetables. J. Basic Microbiol. 2009, 49, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaichumjai, P.; Valyasevi, R.; Assavanig, A.; Kurdi, P. Isolation and characterization of acid-sensitive Lactobacillus plantarum with application as starter culture for Nham production. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopermsub, P.; Yunchalard, S. Identification of lactic acid bacteria associated with the production of plaa-som, a traditional fermented fish product of Thailand. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 138, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powthong, P.; Suntornthiticharoen, P. Isolation, identification, and analysis of probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria from selective various traditional Thai fermented food and kefir. Pak. J. Nutr. 2015, 14, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannaphan, S. Isolation, identification and potential probiotic characterization of lactic acid bacteria from Thai traditional fermented food. AIMS Microbiol. 2021, 7, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangprapai, W.; Prasitpuriprecha, C.; Jantama, K.; Jantama, S.S. Probiotics isolated from Thai fermented foods for potential uses against foodborne pathogens. Asia Pac. J. Sci. Technol. 2022, 27, APST-27-01-13. [Google Scholar]
- Chukeatirote, E. Thua nao: Thai fermented soybean. J. Ethn. Foods 2015, 2, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanpamongkolchai, W. Ethnic Fermented Foods and Beverages of Thailand. In Ethnic Fermented Foods and Alcoholic Beverages of Asia, 1st ed.; Tamang, J.P., Ed.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 151–163. [Google Scholar]
- Mannaa, M.; Han, G.; Seo, Y.-S.; Park, I. Evolution of Food Fermentation Processes, and the Use of Multi-Omics in Deciphering the Roles of the Microbiota. Foods 2021, 10, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valyasevi, R.; Rolle, R.S. An overview of small-scale food fermentation technologies in developing countries with special reference to Thailand: Scope for their improvement. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 75, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karovicova, J.; Kohajdova, Z.; Greif, G. The use of PCA, CA, FA for evaluation of vegetable juices processed by lactic acid fermentation. Czech J. Food Sci. 2002, 20, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongkontanawat, N.; Lertnimitmongkol, W. Product Development of Sweet Fermented Rice (Khao-Mak) from Germinated Native Black Glutinous Rice. J. Agric. Technol. 2015, 11, 501–515. [Google Scholar]
- Wongsa, J.; Rungsardthong, V.; Yasutomo, T. Production and analysis of volatile flavor compounds in sweet fermented rice (Khao Mak). MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 192, 003044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangkhlaypho, A.; Pattaragulwanit, K.; Leepipatpiboon, N.; Yompakdee, C. Development of a defined starter culture mixture for the fermentation of sato, a Thai rice-based alcoholic beverage. Sci. Asia 2014, 40, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangjindavong, M.; Chuapoehuk, P.; Runglerdkriangkrai, J.; Klaypradit, W.; Vareevanich, D. Fermented Fish Product (Pla-ra) from Marine Fish and Preservation. Kasetsart J. Nat. Sci. 2008, 42, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Rodpai, R.; Sanpool, O.; Thanchomnang, T.; Wangwiwatsin, A.; Sadaow, L.; Phupiewkham, W.; Boonroumkaew, P.; Intapan, P.M.; Maleewong, W. Investigating the microbiota of fermented fish products (Pla-ra) from different communities of northeastern Thailand. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council (US) Panel on the Applications of Biotechnology to Traditional Fermented Foods. Using Mixed Starter Cultures for Thai Nham. In Applications of Biotechnology to Fermented Foods: Report of an Ad Hoc Panel of the Board on Science and Technology for International Development; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 1992; Chapter 17. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK234706/ (accessed on 11 October 2022).
- Chantawannakul, P.; Oncharoan, A.; Klanbut, K.; Chukeatirote, E.; Lumyong, S. Characterization of protease of Bacillus subtilis strain 38 isolated from traditionally fermented soybean in Northern Thailand. Sci. Asia 2002, 28, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inatsu, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Yuriko, Y.; Fushimi, T.; Watanasiritum, L.; Kawamoto, S. Characterization of Bacillus subtilis strains in Thua nao, a traditional fermented soybean food in northern Thailand. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukeatirote, E.; Chainun, C.; Siengsubchart, A.; Moukamnerd, C.; Chantawannakul, P.; Lumyong, S.; Boontim, N.; Thakang, P. Microbiological and biochemical changes in Thua Nao fermentation. Res. J. Microbiol. 2006, 1, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Leejeerajumnean, A. Thua nao: Alkali fermented soybean from Bacillus subtilis. Silpakorn Univ. Int. J. 2003, 3, 277–292. [Google Scholar]
- Khanongnuch, C.; Unban, K.; Kanpiengjai, A.; Saenjum, C. Recent research advances and ethno-botanical history of miang, a traditional fermented tea (Camellia sinensis var. assamica) of northern Thailand. J. Ethn. Foods 2017, 4, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, S.; Daengsubha, W.; Uchimura, T.; Ohara, N.; Kozaki, M. Flora of lactic acid bacteria in miang produced in northern Thailand. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 1986, 32, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukontasing, S.; Tanasupawat, S.; Moonmangmee, S.; Lee, J.S.; Suzuki, K.I. Enterococcus camelliae sp. nov., isolated from fermented tea leaves in Thailand. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2151–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasupawat, S.; Pakdeeto, A.; Thawai, C.; Yukphan, P.; Okada, S. Identification of lactic acid bacteria from fermented tea leaves (miang) in Thailand and proposals of Lactobacillus thailandensis sp. nov. Lactobacillus camelliae sp. nov., and Pediococcus siamensis sp. nov. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 53, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebroy, S.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Tanaka, M. Physical properties and microstructure of commercial Som-fug, a fermented fish sausage. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 220, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebroy, S.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Kijrongrojana, K.; Tanaka, M. Some characteristics of commercial Som-fug produced in Thailand. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebroy, S.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W. Properties and acceptability of Som-fug, a Thai fermented fish mince, inoculated with lactic acid bacteria starters. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasupawat, S.; Komagata, K. Lactic acid bacteria in fermented foods in Thailand. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1995, 11, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleekayai, T.; Saetae, D.; Wattanachaiyingyong, O.; Tachibana, S.; Yasuda, M.; Suntornsuk, W. Characterization and in vitro biological activities of Thai traditional fermented shrimp pastes. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 1839–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faithong, N.; Benjakul, S. Changes in antioxidant activities and physicochemical properties of Kapi, a fermented shrimp paste, during fermentation. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 2463–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongsetkul, J.; Benjakul, S.; Vongkamjan, K.; Sumpavapol, P.; Osako, K. Microbiological and chemical changes of shrimp Acetes vulgaris during Kapi production. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3473–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Yu, J.; Sun, J.; Lu, K.; Xie, W. Bacterial composition changes and volatile compounds during the fermentation of shrimp paste: Dynamic changes of microbial communities and flavor composition. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripokar, P.; Klomklao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hansen, E.B.; Maneerat, S.; Panyo, J. Thai traditional fermented fish paste Ka-pi-plaa: Chemical compositions and physical properties. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, E.M.; Hatate, H.; Kawabe, D.; Kuwahara, R.; Wakamatsu, S.; Yuki, T.; Murata, H. Improving antioxidant activity and nutritional components of Philippine salt-fermented shrimp paste through prolonged fermentation. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xia, W.; Gao, P.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Q. Proteolysis during fermentation of Suanyu as a traditional fermented fish product of China. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S166–S176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prihanto, A.A.; Nurdiani, R.; Jatmiko, Y.D.; Firdaus, M.; Kusuma, T.S. Physicochemical and sensory properties of terasi (an Indonesian fermented shrimp paste) produced using Lactobacillus plantarum and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 242, 126619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meidong, R.; Doolgindachbaporn, S.; Jamjan, W.; Sakai, K.; Tashiro, Y.; Okugawa, Y.; Tongpim, S. A novel probiotic Bacillus siamensis B44v isolated from Thai pickled vegetables (Phak-dong) for potential use as a feed supplement in aquaculture. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 63, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cagno, R.; Coda, R.; De Angelis, M.; Gobbetti, M. Exploitation of vegetables and fruits through lactic acid fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2013, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, A.; Kondo, A.; Takahashi, H.; Keeratipibul, S.; Kuda, T.; Kimura, B. Microbiological safety and microbiota of Kapi, Thai traditional fermented shrimp paste, from different sources. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakwan, C.; Chitov, T.; Chantawannakul, P.; Manasam, M.; Bovonsombut, S.; Disayathanoowat, T. Bacterial compositions of indigenous Lanna (Northern Thai) fermented foods and their potential functional properties. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inatsu, Y.; Chotiko, A.; Ananchaipattana, C. Contaminated Bacillus cereus in Lao and Thai fermented soybean “Tua Nao”. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2020, 54, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusporini, A.R.; Pasuwan, P. Microbiological evaluation of Thai fermented fish (Pla-ra) production contact surfaces. Asia Pac. J. Sci. Technol. 2020, 25, APST-25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khullar, G.; Det-udom, R.; Prombutar, P.; Prakitchaiwattana, C. Probiogenomic analysis and safety assessment of Bacillus isolates using Omics approach in combination with In-vitro. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 159, 113216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanaburee, A.; Kantachote, D.; Charernjiratrakul, W.; Sukhoom, A. Enhancement of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in Nham (Thai fermented pork sausage) using starter cultures of Lactobacillus namurensis NH2 and Pediococcus pentosaceus HN8. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 167, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phewpan, A.; Phuwaprisirisan, P.; Takahashi, H.; Ohshima, C.; Lopetcharat, K.; Techaruvichit, P.; Keeratipibul, S. Microbial diversity during processing of Thai traditional fermented shrimp paste, determined by next generation sequencing. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 122, 108989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanamool, V.; Hongsachart, P.; Soemphol, W. Screening and characterisation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) producing lactic acid bacteria isolated from Thai fermented fish (Plaa-som) in Nong Khai and its application in Thai fermented vegetables (Som-pak). Food Sci. Technol. Braz. 2020, 40, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumriw, S.; Luang-In, V.; Samappito, W. Screening of Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Fermented Pak-Sian for Use as a Starter Culture. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 2695–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saelao, S.; Maneerat, S.; Kaewsuwan, S.; Rabesona, H.; Choiset, Y.; Haertlé, T.; Chobert, J.M. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus in vitro by bacteriocinogenic Lactococcus lactis KTH0-1S isolated from Thai fermented shrimp (Kung-som) and safety evaluation. Arch. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noonpakdee, W.; Jumriangrit, P.; Wittayakom, K.; Zendo, J.; Nakayama, J.; Sonomoto, K.; Panyim, S. Two-peptide bacteriocin from Lactobacillus plantarum PMU 33 strain isolated from som-fak, a Thai low salt fermented fish product. Asia Pac. J. Mol. Biol. Biotechnol. 2009, 17, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Botthoulath, V.; Upaichit, A.; Thumarat, U. Identification and in vitro assessment of potential probiotic characteristics and antibacterial effects of Lactobacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum SKI19, a bacteriocinogenic strain isolated from Thai fermented pork sausage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2774–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Techo, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Vilaichone, R.K.; Tanasupawat, S. Characterization and Antibacterial Activity Against Helicobacter pylori of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Thai Fermented Rice Noodle. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showpanish, K.; Sonhom, N.; Janyaphisan, T.; Woraprayote, W.; Rumjuankiat, K. Isolation and optimization to enhance anti-Streptococcus suis bacteriocin production by Lactobacillus plantarum RB01-SO. Int. J. Agric. Technol. 2022, 18, 809–828. [Google Scholar]
- Phromraksa, P.; Nagano, H.; Boonmars, T.; Kamboonruang, C. Identification of proteolytic bacteria from Thai traditional fermented foods and their allergenic reducing potentials. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, M189–M195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoottosavako, M.; Keeratipibul, S.; Techo, S.; Tanasupawat, S. Identification and characterization of lipolytic bacteria from Thai fermented foods. Malays. J. Microbiol. 2015, 11, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woraharn, S.; Lailerd, N.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Wangcharoen, W.; Sirisattha, S.; Chaiyasut, C. Screening and kinetics of glutaminase and glutamate decarboxylase producing lactic acid bacteria from fermented Thai foods. Food Sci. Technol. Braz. 2014, 34, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woraharn, S.; Lailerd, N.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Wangcharoen, W.; Sirisattha, S.; Peerajan, S.; Chaiyasut, C. Evaluation of factors that influence the L-glutamic and γ-aminobutyric acid production during Hericium erinaceus fermentation by lactic acid bacteria. Cyta J. Food 2016, 14, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuengjayaem, S.; Booncharoen, A.; Tanasupawat, S. Characterization and comparative genomic analysis of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-producing lactic acid bacteria from Thai fermented foods. Biotechnol. Lett. 2021, 43, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakdeeto, A.; Phuengjayaem, S.; Arayakarn, T.; Phitchayaphon, C.; Tungkajiwangkoon, S.; Tanasupawat, S. Identification of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-producing lactic acid bacteria from plant-based Thai fermented foods and genome analysis of Lactobacillus brevis GPB7-4. ScienceAsia 2022, 48, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchart, C.; Rattanaporn, O.; Haltrich, D.; Phukpattaranont, P.; Maneerat, S. Technological and safety properties of newly isolated GABA-producing Lactobacillus futsaii strains. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchart, C.; Rattanaporn, O.; Haltrich, D.; Phukpattaranont, P.; Maneerat, S. Enhancement of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels using an autochthonous Lactobacillus futsaii CS3 as starter culture in Thai fermented shrimp (Kung-Som). World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanaburee, A.; Kantachote, D.; Charernjiratrakul, W.; Sukhoom, A. Selection of γ-aminobutyric acid-producing lactic acid bacteria and their potential as probiotics for use as starter cultures in Thai fermented sausages (Nham). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanklai, J.; Thongwai, N.; Rungsirivanich, P.; Tragoolpua, Y.; Pekkoh, J. Optimization of GABA production and partial gad gene identification of potential probiotic Levilactobacillus brevis F064A isolated from Thai fermented sausage. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2022, 49, 1013–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanaburee, A.; Kantachote, D.; Charernjiratrakul, W.; Penjamras, P.; Chaiyasut, C. Enhancement of γ-aminobutyric acid in a fermented red seaweed beverage by starter culture Lactobacillus plantarum DW12. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyokawa, Y.; Takahara, H.; Reungsang, A.; Fukuta, M.; Hachimine, Y.; Tachibana, S.; Yasuda, M. Purification and characterization of a halotolerant serine proteinase from thermotolerant Bacillus licheniformis RKK-04 isolated from Thai fish sauce. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 1867–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulprachakarn, K.; Chaipoot, S.; Phongphisutthinant, R.; Paradee, N.; Prommaban, A.; Ounjaijean, S.; Rerkasem, K.; Parklak, W.; Prakit, K.; Saengsitthisak, B.; et al. Antioxidant potential and cytotoxic effect of isoflavones extract from Thai fermented soybean (Thua-nao). Molecules 2021, 26, 7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajanta, K.; Janpum, P.; Leksing, W. Antioxidant capacities, total phenolics and flavonoids in black and yellow soybeans fermented by Bacillus subtilis: A comparative study of Thai fermented soybeans (thua nao). Int. Food Res. J. 2013, 20, 3125–3132. [Google Scholar]
- Chunhachart, O.; Itoh, T.; Sukchotiratana, M.; Tanimoto, H.; Tahara, Y. Characterization of γ-glutamyl hydrolase produced by Bacillus sp. isolated from Thai Thua-nao. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 2779–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woraharn, S.; Lailerd, N.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Wangcharoen, W.; Peerajan, S.; Sirisattha, S.; Chaiyasut, C. Development of fermented Hericium erinaceus juice with high content of L-glutamine and L-glutamic acid. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 2104–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchart, C.; Rattanaporn, O.; Haltrich, D.; Phukpattaranont, P.; Maneerat, S. Lactobacillus futsaii CS3, a New GABA-Producing Strain Isolated from Thai Fermented Shrimp (Kung-Som). Indian J. Microbiol. 2017, 57, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantachote, D.; Ratanaburee, A.; Sukhoom, A.; Sumpradit, T.; Asavaroungpipop, N. Use of γ-aminobutyric acid producing lactic acid bacteria as starters to reduce biogenic amines and cholesterol in Thai fermented pork sausage (Nham) and their distribution during fermentation. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 70, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanklai, J.; Somwong, T.C.; Rungsirivanich, P.; Thongwai, N. Screening of GABA-producing lactic acid bacteria from Thai fermented foods and probiotic potential of Levilactobacillus brevis f064a for GABA-fermented mulberry juice production. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limsuwan, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Kongkiattikajorn, J. The effects of starter cultures on biogenic amine and free amino acid contents in Nham during fermentation. Witthayasan Kasetsat 2007, 41, 363–372. [Google Scholar]
- Ngamsomchat, A.; Kaewkod, T.; Konkit, M.; Tragoolpua, Y.; Bovonsombut, S.; Chitov, T. Characterisation of Lactobacillus plantarum of Dairy-Product Origin for Probiotic Chèvre Cheese Production. Foods 2022, 11, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saithong, P.; Panthavee, W.; Boonyaratanakornkit, M.; Sikkhamondhol, C. Use of a starter culture of lactic acid bacteria in plaa-som, a Thai fermented fish. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 110, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luang-In, V.; Saengha, W.; Karirat, T.; Buranrat, B.; Nudmamud-Thanoi, S.; Ma, N.L.; Narbad, A. Cytotoxic effects of Saccharomyces cerevisiae TC6 and Lactobacillus brevis TBRC 3003 isolated from Thai fermented foods. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 2385–2393. [Google Scholar]
- Luang-In, V.; Katisart, T.; Konsue, A.; Nudmamud-Thanoi, S.; Narbad, A.; Saengha, W.; Wangkahart, E.; Pumriw, S.; Samappito, W.; Ma, N.L. Psychobiotic effects of multi-strain probiotics originated from Thai fermented foods in a rat model. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2020, 40, 1014–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luang-In, V.; Saengha, W.; Karirat, T.; Konsue, A.; Wangkahart, E.; Katisart, T. Probiotics from Thai fermented foods reduced anxiety and enhanced neuroplasticity in a Wistar rat model. Trop. J. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 6, 910–914. [Google Scholar]
- Meidong, R.; Nakao, M.; Sakai, K.; Tongpim, S. Lactobacillus paraplantarum L34b-2 derived from fermented food improves the growth, disease resistance and innate immunity in Pangasius bocourti. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meidong, R.; Doolgindachbaporn, S.; Sakai, K.; Tongpim, S. Isolation and selection of lactic acid bacteria from Thai indigenous fermented foods for use as probiotics in tilapia fish Oreochromis niloticus. AACL Bioflux 2017, 10, 455–463. [Google Scholar]
- Klayraung, S.; Viernstein, H.; Sirithunyalug, J.; Okonogi, S. Probiotic properties of lactobacilli isolated from Thai traditional food. Sci. Pharm. 2008, 76, 485–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Fermented foods | Isolates | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus species | |||
| Thai fermented soybean (Thua-nao) | B. licheniformis | Inhibits Aspergillus strains. Reduces AFB1 and OTA levels. | [13] |
| Thai fermented shrimp paste (Ka-pi) | B. salacetis sp. nov. | Novel isolate from Ka-pi, Gram+, aerobic, slightly halophilic, and endospore-forming bacterium. | [14] |
| Thai fermented foods (Milk kefir) | B. amyloliquefaciens SD-32, Bacillus sp. LB15, Bacillus sp. L_D12_A_P, Bacillus sp. C87, B. methylotrophicus 3B_1.1, and other 20 Bacillus spp. | EPS-producing strains. | [16] |
| Thai fermented shrimp paste (Ka-pi) | Bacillus species | - | [56] |
| Thai fermented freshwater fish (Pla-ra) | Bacillus spp. | Low abundance. Strain with aminopeptidase and protease genes. | [57] |
| Thua-nao | Bacillus spp. | Predominantly found in Thua-nao. | [58] |
| Thua-nao | B. cereus | Pathogenic strain. Toxin-coding gene was detected. | [59] |
| Pla-ra * | B. cereus | 20–30% of samples contain B. cereus. | [60] |
| Salt-fermented fish (Pla-ra) | B. velezensis, B. amyloliquefaciens, and B. infantis | Stress-resistant and acid-tolerant. Antimicrobial activity. Bacteriocin coding gene present. | [61] |
| Lactobacillus species | |||
| Pla-ra | Lactobacillus species | - | [15] |
| Fermented fruits and vegetables | L. plantarum | - | [17] |
| Thai fermented pork sausage (Nham) | L. plantarum BCC 9546 | Neomycin-resistant mutants. Acid-sensitive strain. | [18] |
| Thai traditional fermented fish product (Plaa-som) | L. plantarum, and L. fermentum. | - | [19] |
| Fermented sausage (Sai-krog-prieo), fermented beef (Mam), Nham, fermented shrimp (Pla-som) and fish with rice (Som-fak), Pla-ra, fermented crab (Phu-dong), fermented fish intestine (Sai-pra-mun; Tai-pra), fermented shellfish (Hoi-dong), fermented soybean (Toa-hu-yee; Toa jeaw), pickled green mustard (Phakgard-dong), fermented tea leaves (Bai-maeng), fermented mango (Mamuang-dong), and Kefir | L. plantarum, L. pentosus, L. brevis | Antimicrobial activity | [20] |
| Pla-ra, Thai fermented pork, Pha-gard-dorng, bamboo shoots and ginger pickles. | L. fermentum K4 | Probiotic strain | [21] |
| Pickled fish, kimchi, crab, minced fish, sausages and Nham. | L. plantarum P10 | Probiotic strain | [22] |
| Thai fermented pork sausage (Nham) | L. namurensis | GABA producer | [61] |
| Thai fermented fish (Plaa-som) | L. plantarum L10-11 | GABA producer | [63] |
| Thai fermented product (Pak-sian) | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, L. fermentum SK324. | Probiotic strains | [64] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Alagarsamy, K.; Suganthy, N.; Thangaleela, S.; Kesika, P.; Chaiyasut, C. The Role and Significance of Bacillus and Lactobacillus Species in Thai Fermented Foods. Fermentation 2022, 8, 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110635
Sivamaruthi BS, Alagarsamy K, Suganthy N, Thangaleela S, Kesika P, Chaiyasut C. The Role and Significance of Bacillus and Lactobacillus Species in Thai Fermented Foods. Fermentation. 2022; 8(11):635. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110635
Chicago/Turabian StyleSivamaruthi, Bhagavathi Sundaram, Karthikeyan Alagarsamy, Natarajan Suganthy, Subramanian Thangaleela, Periyanaina Kesika, and Chaiyavat Chaiyasut. 2022. "The Role and Significance of Bacillus and Lactobacillus Species in Thai Fermented Foods" Fermentation 8, no. 11: 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110635
APA StyleSivamaruthi, B. S., Alagarsamy, K., Suganthy, N., Thangaleela, S., Kesika, P., & Chaiyasut, C. (2022). The Role and Significance of Bacillus and Lactobacillus Species in Thai Fermented Foods. Fermentation, 8(11), 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110635









